
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 984-996.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0191
孔佳涛1,2,*, 付彩霞3,*, 吴雅诺1,2, 刘园1,2, 胡哲辉1,2, 徐娟1,2, 黄皓4, 赵曌4, 陈磊4,**( ), 陈嘉景1,2,**(
), 陈嘉景1,2,**( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-24
修回日期:2025-01-31
出版日期:2025-05-08
发布日期:2025-04-25
通讯作者:
作者简介:*共同第一作者
基金资助:
KONG Jiatao1,2, FU Caixia3, WU Yanuo1,2, LIU Yuan1,2, HU Zhehui1,2, XU Juan1,2, HUANG Hao4, ZHAO Zhao4, CHEN Lei4,**( ), CHEN Jiajing1,2,**(
), CHEN Jiajing1,2,**( )
)
Received:2024-10-24
Revised:2025-01-31
Published:2025-05-08
Online:2025-04-25
摘要:
对湖南洪江和云南新平两个产区4份商业成熟期冰糖橙果实的理化指标及挥发性物质、可溶性糖、有机酸等风味物质进行测定,并与消费者偏好、风味强度等感官评价结果进行关联分析,旨在明确两个产区冰糖橙风味品质差异,解析与消费者偏好所关联的关键风味物质。结果表明:两份云南冰糖橙的化渣性、香气及整体品质较优,而湖南冰糖橙的有机酸含量高、可溶性糖含量较低,滋味更加浓郁;两地样品果皮挥发性物质种类相同,但绝大部分挥发性物质含量在云南冰糖橙中更高,导致其果实香味更加浓郁,而湖南冰糖橙香味则更加柔和。利用正交偏最小二乘法(OPLS-DA)分析,筛选出35种可用于区分两地冰糖橙风味品质的差异风味物质,其中D-柠檬烯、β-月桂烯、α-蒎烯、瓦伦烯、γ-氨基丁酸等含量高的主要风味物质均在云南地区冰糖橙中占优,仅L-脯氨酸和(E)-2-己烯醛在湖南冰糖橙中含量更高,以上风味物质可作为区分两地冰糖橙感官差异的代谢标志物。相关性分析表明苹果酸、柠檬酸和辛醛、(E)-2-己烯醛分别与滋味和香味高度相关,是影响消费者偏好的主要驱动因子。
孔佳涛, 付彩霞, 吴雅诺, 刘园, 胡哲辉, 徐娟, 黄皓, 赵曌, 陈磊, 陈嘉景. 冰糖橙风味组学解析及风味品质差异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 984-996.
KONG Jiatao, FU Caixia, WU Yanuo, LIU Yuan, HU Zhehui, XU Juan, HUANG Hao, ZHAO Zhao, CHEN Lei, CHEN Jiajing. Flavoromics Analysis and Flavor Quality Difference Analysis in Bingtang Oranges[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 984-996.
| 分组 Group | 样品 Sample | 色泽更好 Better color | 更甜 Sweeter taste | 更酸 More sour taste | 化渣更好 Better mastication | 香气更令人愉悦 More pleasant aroma | 整体品质更优 Better overall quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 3 | 26* | 7 | 24* | 13 | 15 |
| 新平-2 Xinping-2 | 29* | 6 | 25* | 8 | 19 | 17 | |
| 2 | 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 3 | 32* | 0 | 28* | 22* | 30* |
| 洪江-1 Hongjiang-1 | 29* | 0 | 32* | 4 | 10 | 2 | |
| 3 | 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 10 | 25* | 7 | 27* | 22* | 27* |
| 洪江-2 Hongjiang-2 | 22* | 7 | 25* | 5 | 10 | 5 |
表1 冰糖橙各属性的差别检验结果
Table 1 The results of the difference test of the attributes of the Bingtang Orange
| 分组 Group | 样品 Sample | 色泽更好 Better color | 更甜 Sweeter taste | 更酸 More sour taste | 化渣更好 Better mastication | 香气更令人愉悦 More pleasant aroma | 整体品质更优 Better overall quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 3 | 26* | 7 | 24* | 13 | 15 |
| 新平-2 Xinping-2 | 29* | 6 | 25* | 8 | 19 | 17 | |
| 2 | 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 3 | 32* | 0 | 28* | 22* | 30* |
| 洪江-1 Hongjiang-1 | 29* | 0 | 32* | 4 | 10 | 2 | |
| 3 | 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 10 | 25* | 7 | 27* | 22* | 27* |
| 洪江-2 Hongjiang-2 | 22* | 7 | 25* | 5 | 10 | 5 |
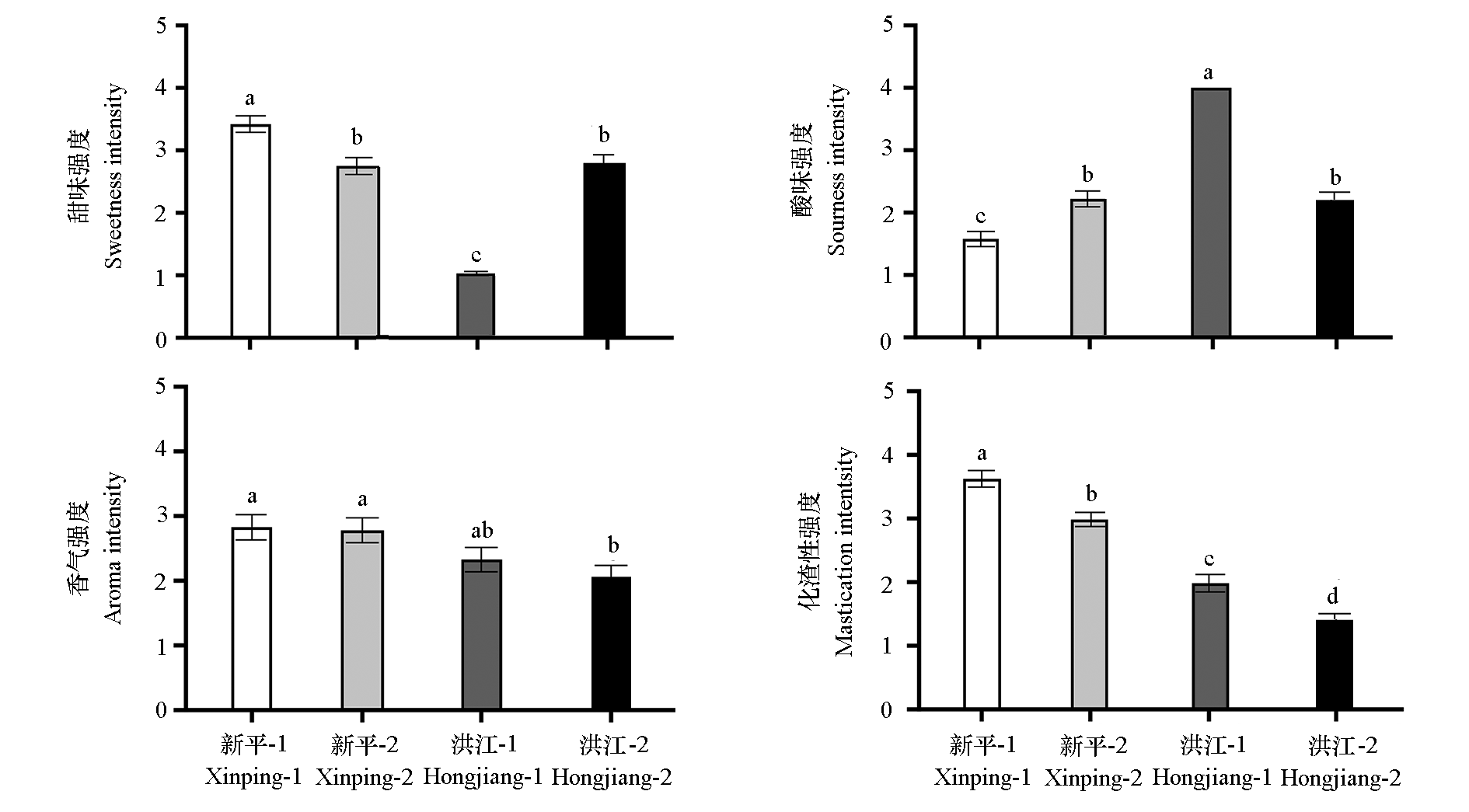
图2 冰糖橙感官属性强度评价 不同小写字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)
Fig. 2 Evaluation of sensory attribute intensity of Bingtang Orange Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences(P < 0.05)
| 样品 Sample | 外观喜好度 Appearance preference | 化渣性喜好度 Mastication preference | 滋味喜好度 Taste preference | 香气喜好度 Aroma preference | 整体喜好度 Overall quality preference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 6.81 ± 1.53 a | 7.63 ± 1.27 a | 7.56 ± 1.41 a | 6.81 ± 1.61 ab | 7.47 ± 1.32 a |
| 新平-2 Xinping-2 | 7.09 ± 1.40 a | 7.03 ± 1.21 a | 6.81 ± 1.47 b | 7.09 ± 1.49 a | 6.84 ± 1.28 a |
| 洪江-1 Hongjiang-1 | 6.66 ± 1.57 a | 5.84 ± 1.39 b | 4.06 ± 1.50 c | 6.13 ± 1.52 b | 4.56 ± 1.52 c |
| 洪江-2 Hongjiang-2 | 6.78 ± 1.90 a | 4.94 ± 1.66 c | 6.53 ± 1.39 b | 6.13 ± 1.27 b | 6.09 ± 1.47 b |
表2 冰糖橙样品不同感官属性9点喜好标度感官得分
Table 2 Sensory scores of different sensory attributes of Bingtang Orange samples on a 9 point preference scale
| 样品 Sample | 外观喜好度 Appearance preference | 化渣性喜好度 Mastication preference | 滋味喜好度 Taste preference | 香气喜好度 Aroma preference | 整体喜好度 Overall quality preference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 6.81 ± 1.53 a | 7.63 ± 1.27 a | 7.56 ± 1.41 a | 6.81 ± 1.61 ab | 7.47 ± 1.32 a |
| 新平-2 Xinping-2 | 7.09 ± 1.40 a | 7.03 ± 1.21 a | 6.81 ± 1.47 b | 7.09 ± 1.49 a | 6.84 ± 1.28 a |
| 洪江-1 Hongjiang-1 | 6.66 ± 1.57 a | 5.84 ± 1.39 b | 4.06 ± 1.50 c | 6.13 ± 1.52 b | 4.56 ± 1.52 c |
| 洪江-2 Hongjiang-2 | 6.78 ± 1.90 a | 4.94 ± 1.66 c | 6.53 ± 1.39 b | 6.13 ± 1.27 b | 6.09 ± 1.47 b |
| 样品 Sample | 可溶性固形物/% Total soluble solids | 可滴定酸/% Titratable acid | 固酸比 TSS/TA | 果肉硬度/g Pulp firmness | 最大剪切力/g Maximum shear force |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 13.40 ± 0.62 b | 0.70 ± 0.16 b | 19.91 ± 3.88 b | 135.71 ± 14.66 b | 7 406.93 ± 1 880.29 b |
| 新平-2 Xinping-2 | 12.57 ± 0.74 b | 0.59 ± 0.01 b | 21.29 ± 1.04 b | 146.96 ± 56.01 b | 6 257.65 ± 1 198.12 b |
| 洪江-1 Hongjiang-1 | 13.50 ± 0.67 b | 0.95 ± 0.05 a | 14.17 ± 0.16 c | 235.62 ± 40.73 a | 13 346.89 ± 2 990.99 a |
| 洪江-2 Hongjiang-2 | 15.63 ± 0.26 a | 0.55 ± 0.04 b | 28.38 ± 1.76 a | 270.34 ± 107.27 a | 8 404.20 ± 1 758.19 b |
表3 冰糖橙果实常规品质
Table 3 Regular quality of Bingtang Orange samples
| 样品 Sample | 可溶性固形物/% Total soluble solids | 可滴定酸/% Titratable acid | 固酸比 TSS/TA | 果肉硬度/g Pulp firmness | 最大剪切力/g Maximum shear force |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 13.40 ± 0.62 b | 0.70 ± 0.16 b | 19.91 ± 3.88 b | 135.71 ± 14.66 b | 7 406.93 ± 1 880.29 b |
| 新平-2 Xinping-2 | 12.57 ± 0.74 b | 0.59 ± 0.01 b | 21.29 ± 1.04 b | 146.96 ± 56.01 b | 6 257.65 ± 1 198.12 b |
| 洪江-1 Hongjiang-1 | 13.50 ± 0.67 b | 0.95 ± 0.05 a | 14.17 ± 0.16 c | 235.62 ± 40.73 a | 13 346.89 ± 2 990.99 a |
| 洪江-2 Hongjiang-2 | 15.63 ± 0.26 a | 0.55 ± 0.04 b | 28.38 ± 1.76 a | 270.34 ± 107.27 a | 8 404.20 ± 1 758.19 b |
| 初生代谢物 Primary metabolites | 含量(mg · g-1 FW) Content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 新平-2 Xinping-2 | 洪江-1 Hongjiang-1 | 洪江-2 Hongjiang-2 | |
| 氨基酸类总计 Total amino acids | 2.70 ± 0.14 b | 3.39 ± 0.37 b | 8.80 ± 0.27 a | 8.48 ± 1.57 a |
| L-丙氨酸 L-Alanine | 0.21 ± 0 b | 0.26 ± 0 a | 0.26 ± 0. a | 0.26 ± 0 a |
| L-脯氨酸 L-Proline | 1.25 ± 0.08 b | 1.92 ± 0.25 b | 7.50 ± 0.28 a | 7.13 ± 1.52 a |
| L-甘氨酸 L-Glycine | 0.17 ± 0 a | 0.16 ± 0 b | 0.17 ± 0 a | 0.17 ± 0 a |
| L-焦谷氨酸 L-Pyroglutamic acid | 0.22 ± 0 b | 0.22 ± 0.01 b | 0.26 ± 0.01 b | 0.33 ± 0.05 a |
| γ-氨基丁酸 γ-Aminobutyric acid | 0.84 ± 0.08 a | 0.83 ± 0.12 a | 0.60 ± 0.03 b | 0.57 ± 0.03 b |
| 有机酸类总计 Total organic acids | 4.25 ± 0.42 c | 5.28 ± 0.45 bc | 11.76 ± 0.28 a | 6.43 ± 0.85 b |
| 草酸 Oxalic acid | 0.07 ± 0.01 ab | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0 b | 0.04 ± 0 c |
| 琥珀酸 Butanedioic acid | 0.31 ± 0.02 a | 0.25 ± 0.02 b | 0.31 ± 0.01 a | 0.33 ± 0.03 a |
| 苹果酸 Malic acid | 1.19 ± 0.06 a | 1.14 ± 0.12 a | 0.63 ± 0.05 b | 1.09 ± 0.08 a |
| 柠檬酸 Citric acid | 2.68 ± 0.38 c | 3.80 ± 0.58 bc | 10.76 ± 0.31 a | 4.97 ± 0.93 b |
| 可溶性糖类总计 Total soluble sugar | 67.43 ± 1.25 a | 69.36 ± 3.40 a | 66.76 ± 2.24 a | 72.18 ± 3.06 a |
| D-(+)-木糖 D-(+)-Xylose | 0.25 ± 0.01 a | 0.25 ± 0.01 a | 0.16 ± 0 c | 0.21 ± 0.01 b |
| L-山梨糖 L-Sorbose | 0.09 ± 0.02 | — | — | — |
| D-果糖 D-Fructose | 21.18 ± 0.69 c | 23.26 ± 0.77 b | 21.87 ± 0.64 bc | 26.82 ± 1.02 a |
| D-(+)-葡萄糖 D-(+)-Glucose | 21.14 ± 0.85 b | 22.59 ± 0.90 b | 21.85 ± 0.83 b | 27.00 ± 1.23 a |
| 蔗糖 Sucrose | 24.77 ± 0.59 a | 23.26 ± 1.75 a | 22.88 ± 0.84 a | 18.15 ± 0.83 b |
表4 冰糖橙果肉初生代谢物的GC-MS分析结果
Table 4 GC-MS analysis results of primary metabolites in Bingtang orange pulp
| 初生代谢物 Primary metabolites | 含量(mg · g-1 FW) Content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 新平-2 Xinping-2 | 洪江-1 Hongjiang-1 | 洪江-2 Hongjiang-2 | |
| 氨基酸类总计 Total amino acids | 2.70 ± 0.14 b | 3.39 ± 0.37 b | 8.80 ± 0.27 a | 8.48 ± 1.57 a |
| L-丙氨酸 L-Alanine | 0.21 ± 0 b | 0.26 ± 0 a | 0.26 ± 0. a | 0.26 ± 0 a |
| L-脯氨酸 L-Proline | 1.25 ± 0.08 b | 1.92 ± 0.25 b | 7.50 ± 0.28 a | 7.13 ± 1.52 a |
| L-甘氨酸 L-Glycine | 0.17 ± 0 a | 0.16 ± 0 b | 0.17 ± 0 a | 0.17 ± 0 a |
| L-焦谷氨酸 L-Pyroglutamic acid | 0.22 ± 0 b | 0.22 ± 0.01 b | 0.26 ± 0.01 b | 0.33 ± 0.05 a |
| γ-氨基丁酸 γ-Aminobutyric acid | 0.84 ± 0.08 a | 0.83 ± 0.12 a | 0.60 ± 0.03 b | 0.57 ± 0.03 b |
| 有机酸类总计 Total organic acids | 4.25 ± 0.42 c | 5.28 ± 0.45 bc | 11.76 ± 0.28 a | 6.43 ± 0.85 b |
| 草酸 Oxalic acid | 0.07 ± 0.01 ab | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0 b | 0.04 ± 0 c |
| 琥珀酸 Butanedioic acid | 0.31 ± 0.02 a | 0.25 ± 0.02 b | 0.31 ± 0.01 a | 0.33 ± 0.03 a |
| 苹果酸 Malic acid | 1.19 ± 0.06 a | 1.14 ± 0.12 a | 0.63 ± 0.05 b | 1.09 ± 0.08 a |
| 柠檬酸 Citric acid | 2.68 ± 0.38 c | 3.80 ± 0.58 bc | 10.76 ± 0.31 a | 4.97 ± 0.93 b |
| 可溶性糖类总计 Total soluble sugar | 67.43 ± 1.25 a | 69.36 ± 3.40 a | 66.76 ± 2.24 a | 72.18 ± 3.06 a |
| D-(+)-木糖 D-(+)-Xylose | 0.25 ± 0.01 a | 0.25 ± 0.01 a | 0.16 ± 0 c | 0.21 ± 0.01 b |
| L-山梨糖 L-Sorbose | 0.09 ± 0.02 | — | — | — |
| D-果糖 D-Fructose | 21.18 ± 0.69 c | 23.26 ± 0.77 b | 21.87 ± 0.64 bc | 26.82 ± 1.02 a |
| D-(+)-葡萄糖 D-(+)-Glucose | 21.14 ± 0.85 b | 22.59 ± 0.90 b | 21.85 ± 0.83 b | 27.00 ± 1.23 a |
| 蔗糖 Sucrose | 24.77 ± 0.59 a | 23.26 ± 1.75 a | 22.88 ± 0.84 a | 18.15 ± 0.83 b |
| 挥发性物质 Volatiles | 含量/(μg · g-1 FW) Content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 新平-2 Xinping-2 | 洪江-1 Hongjiang-1 | 洪江-2 Hongjiang-2 | |
| α-侧柏烯 α-Thujene | 2.02 ± 0.29 a | 2.03 ± 0.24 a | 0.94 ± 0.12 b | 0.81 ± 0.09 b |
| α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | 249.85 ± 20.42 a | 197.29 ± 38.75 b | 64.75 ± 3.59 c | 75.47 ± 10.90 c |
| 莰烯 Camphene | 1.96 ± 0.05 a | 1.62 ± 0.26 b | 0.72 ± 0.03 c | 0.70 ± 0.08 c |
| 香桧烯 Sabinene | 103.87 ± 8.34 b | 136.77 ± 9.10 a | 56.39 ± 10.87 c | 39.66 ± 8.42 c |
| β-蒎烯 β-Pinene | 6.81 ± 0.19 a | 7.55 ± 0.97 a | 3.03 ± 0.72 b | 2.51 ± 0.27 b |
| β-月桂烯 β-Myrcene | 600.87 ± 51.30 a | 473.78 ± 89.65 b | 149.97 ± 8.88 c | 182.33 ± 25.53 c |
| α-水芹烯 α-Phellandrene | 29.67 ± 5.20 a | 18.62 ± 3.16 b | 5.96 ± 0.39 c | 7.74 ± 1.36 c |
| 3-蒈烯 3-Carene | 150.93 ± 41.73 a | 80.93 ± 15.26 b | 17.33 ± 1.23 c | 31.87 ± 8.15 bc |
| α-松油烯 α-Terpinene | 3.53 ± 0.86 a | 2.12 ± 0.36 b | 0.73 ± 0.10 c | 1.11 ± 0.06 bc |
| D-柠檬烯D-Limonene | 32 587.65 ± 2 307.47 a | 28 029.64 ± 4 536.10 a | 9 723.42 ± 503.76 b | 11 851.88 ± 1 456.73 b |
| 顺式-β-罗勒烯 cis-β-Ocimene | 1.92 ± 0.13 a | 1.37 ± 0.13 b | 0.61 ± 0.04 c | 0.69 ± 0.10 c |
| 反式-β-罗勒烯 trans-β-Ocimene | 11.44 ± 2.33 a | 10.52 ± 2.59 a | 3.38 ± 0.62 b | 4.46 ± 0.28 b |
| γ-松油烯 γ-Terpinene | 3.00 ± 0.47 a | 2.01 ± 0.39 b | 1.13 ± 0.14 c | 1.28 ± 0.02 c |
| 异-吲哚烯 Isoterpinolene | 5.18 ± 1.38 a | 2.82 ± 0.50 b | 0.88 ± 0.17 c | 1.40 ± 0.25 bc |
| 异松油烯 Terpinolene | 28.51 ± 7.18 a | 15.43 ± 2.81 b | 3.83 ± 0.39 c | 6.43 ± 1.45 bc |
| 顺式-香桧烯水合物 cis-Sabinene hydrate | 6.35 ± 0.66 a | 4.73 ± 0.31 b | 1.84 ± 0.30 c | 2.07 ± 0.42 c |
| 芳樟醇 Linalool | 35.91 ± 1.51 a | 33.14 ± 0.99 a | 17.22 ± 1.27 b | 16.12 ± 3.24 b |
| α-松油醇 α-Terpineol | 20.14 ± 0.92 a | 16.20 ± 1.55 b | 5.42 ± 0.36 d | 8.12 ± 1.34 c |
| 香茅醇 Citronellol | 2.89 ± 0.27 a | 1.70 ± 0.28 b | 1.77 ± 0.30 b | 1.64 ± 0.19 b |
| 香叶醇 Geraniol | 3.46 ± 0.16 a | 3.90 ± 0.68 a | 1.79 ± 0.14 b | 2.18 ± 0.38 b |
| 香茅醛 Citronellal | 10.88 ± 0.53 a | 6.39 ± 0.75 b | 5.37 ± 0.39 b | 5.72 ± 0.79 b |
| β-柠檬醛 β-Citral | 25.93 ± 0.48 a | 19.72 ± 2.92 b | 7.71 ± 0.59 c | 9.91 ± 1.59 c |
| α-柠檬醛 α-Citral | 40.92 ± 0.33 a | 29.71 ± 4.52 b | 11.73 ± 0.54 c | 16.15 ± 3.28 c |
| 反式-柠檬烯氧化物 trans-Limonene oxide | 6.25 ± 0.69 a | 5.00 ± 0.58 ab | 3.74 ± 0.31 b | 5.03 ± 0.62 ab |
| α-胡椒烯α-Copaene | 8.26 ± 0.45 a | 7.20 ± 0.79 a | 3.07 ± 0.48 b | 4.03 ± 0.45 b |
| β-荜澄茄油烯 β-Cubebene | 5.69 ± 0.50 a | 4.56 ± 0.66 b | 2.24 ± 0.35 c | 2.94 ± 0.25 c |
| (-)-β-榄香烯 (-)-β-Elemen | 3.43 ± 0.65 a | 3.60 ± 0.59 a | 1.05 ± 0.23 b | 1.64 ± 0.17 b |
| 石竹烯 Caryophyllene | 15.84 ± 2.06 a | 12.99 ± 2.63 a | 3.98 ± 0.26 b | 5.27 ± 0.45 b |
| β-胡椒烯 β-Copaene | 6.29 ± 0.50 a | 5.85 ± 0.62 a | 2.20 ± 0.06 b | 2.99 ± 0.33 b |
| 吉马烯D Germacrene D | 4.62 ± 0.27 a | 3.59 ± 0.47 b | 2.22 ± 0.26 c | 2.45 ± 0.35 c |
| β-芹子烯 β-Selinene | 4.76 ± 0.68 a | 4.41 ± 0.69 a | 1.03 ± 0.25 b | 1.74 ± 0.28 b |
| 瓦伦烯 Valencene | 110.78 ± 16.58 a | 93.60 ± 14.39 a | 16.39 ± 0.34 b | 31.84 ± 4.18 b |
| δ-杜松烯 δ-Cadinene | 8.60 ± 0.89 a | 7.31 ± 0.98 a | 3.13 ± 0.24 b | 4.19 ± 0.67 b |
| 法尼醇 Farnesol | 5.64 ± 0.69 a | 2.05 ± 1.32 b | 1.16 ± 0.07 b | 1.25 ± 0.08 b |
| 石竹烯氧化物 Caryophyllene oxide | 6.52 ± 1.49 a | 5.18 ± 1.13 a | 1.65 ± 0.14 b | 1.46 ± 0.05 b |
| (E)-2-己烯醛 (E)-2-Hexenal | 1.12 ± 0.23 c | 1.14 ± 0.26 c | 3.27 ± 0.26 a | 1.96 ± 0.13 b |
| 辛醛 Octanal | 27.65 ± 3.83 b | 39.80 ± 2.87 a | 8.01 ± 1.15 c | 8.89 ± 1.76 c |
| 壬醛 Nonanal | 5.85 ± 0.35 b | 6.84 ± 0.52 a | 2.02 ± 0.40 c | 1.74 ± 0.29 c |
| 正癸醛 Decanal | 33.99 ± 1.80 b | 45.57 ± 0.91 a | 9.45 ± 0.79 c | 10.96 ± 1.56 c |
| 十一醛 Undecanal | 1.89 ± 0.23 a | 1.93 ± 0.17 a | 0.63 ± 0.12 b | 0.79 ± 0.08 b |
| 十二醛 Dodecanal | 6.12 ± 0.20 b | 7.73 ± 0.14 a | 2.29 ± 0.28 c | 2.11 ± 0.21 c |
| 正十六烷酸 n-Hexadecanoic acid | 7.34 ± 1.18 a | 7.87 ± 1.29 a | 4.51 ± 0.94 b | 4.06 ± 0.71 b |
| 香柏酮 Nootkatone | 8.40 ± 0.94 a | 6.51 ± 0.59 b | 1.37 ± 0.21 c | 2.40 ± 0.21 c |
| 2,2′-亚甲基双[6-(1,1-二甲基 乙基)-4-甲基—苯酚 2,2′-methylenebis[6-(1,1- Dimethylethyl)-4-methyl-Phenol | 64.68 ± 8.00 ab | 87.47 ± 2.31 a | 67.47 ± 16.97 ab | 47.57 ± 4.01 b |
表5 冰糖橙果皮挥发性物质的GC-MS分析结果
Table 5 GC-MS analysis results of volatile substances in Bingtang orange peel
| 挥发性物质 Volatiles | 含量/(μg · g-1 FW) Content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新平-1 Xinping-1 | 新平-2 Xinping-2 | 洪江-1 Hongjiang-1 | 洪江-2 Hongjiang-2 | |
| α-侧柏烯 α-Thujene | 2.02 ± 0.29 a | 2.03 ± 0.24 a | 0.94 ± 0.12 b | 0.81 ± 0.09 b |
| α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | 249.85 ± 20.42 a | 197.29 ± 38.75 b | 64.75 ± 3.59 c | 75.47 ± 10.90 c |
| 莰烯 Camphene | 1.96 ± 0.05 a | 1.62 ± 0.26 b | 0.72 ± 0.03 c | 0.70 ± 0.08 c |
| 香桧烯 Sabinene | 103.87 ± 8.34 b | 136.77 ± 9.10 a | 56.39 ± 10.87 c | 39.66 ± 8.42 c |
| β-蒎烯 β-Pinene | 6.81 ± 0.19 a | 7.55 ± 0.97 a | 3.03 ± 0.72 b | 2.51 ± 0.27 b |
| β-月桂烯 β-Myrcene | 600.87 ± 51.30 a | 473.78 ± 89.65 b | 149.97 ± 8.88 c | 182.33 ± 25.53 c |
| α-水芹烯 α-Phellandrene | 29.67 ± 5.20 a | 18.62 ± 3.16 b | 5.96 ± 0.39 c | 7.74 ± 1.36 c |
| 3-蒈烯 3-Carene | 150.93 ± 41.73 a | 80.93 ± 15.26 b | 17.33 ± 1.23 c | 31.87 ± 8.15 bc |
| α-松油烯 α-Terpinene | 3.53 ± 0.86 a | 2.12 ± 0.36 b | 0.73 ± 0.10 c | 1.11 ± 0.06 bc |
| D-柠檬烯D-Limonene | 32 587.65 ± 2 307.47 a | 28 029.64 ± 4 536.10 a | 9 723.42 ± 503.76 b | 11 851.88 ± 1 456.73 b |
| 顺式-β-罗勒烯 cis-β-Ocimene | 1.92 ± 0.13 a | 1.37 ± 0.13 b | 0.61 ± 0.04 c | 0.69 ± 0.10 c |
| 反式-β-罗勒烯 trans-β-Ocimene | 11.44 ± 2.33 a | 10.52 ± 2.59 a | 3.38 ± 0.62 b | 4.46 ± 0.28 b |
| γ-松油烯 γ-Terpinene | 3.00 ± 0.47 a | 2.01 ± 0.39 b | 1.13 ± 0.14 c | 1.28 ± 0.02 c |
| 异-吲哚烯 Isoterpinolene | 5.18 ± 1.38 a | 2.82 ± 0.50 b | 0.88 ± 0.17 c | 1.40 ± 0.25 bc |
| 异松油烯 Terpinolene | 28.51 ± 7.18 a | 15.43 ± 2.81 b | 3.83 ± 0.39 c | 6.43 ± 1.45 bc |
| 顺式-香桧烯水合物 cis-Sabinene hydrate | 6.35 ± 0.66 a | 4.73 ± 0.31 b | 1.84 ± 0.30 c | 2.07 ± 0.42 c |
| 芳樟醇 Linalool | 35.91 ± 1.51 a | 33.14 ± 0.99 a | 17.22 ± 1.27 b | 16.12 ± 3.24 b |
| α-松油醇 α-Terpineol | 20.14 ± 0.92 a | 16.20 ± 1.55 b | 5.42 ± 0.36 d | 8.12 ± 1.34 c |
| 香茅醇 Citronellol | 2.89 ± 0.27 a | 1.70 ± 0.28 b | 1.77 ± 0.30 b | 1.64 ± 0.19 b |
| 香叶醇 Geraniol | 3.46 ± 0.16 a | 3.90 ± 0.68 a | 1.79 ± 0.14 b | 2.18 ± 0.38 b |
| 香茅醛 Citronellal | 10.88 ± 0.53 a | 6.39 ± 0.75 b | 5.37 ± 0.39 b | 5.72 ± 0.79 b |
| β-柠檬醛 β-Citral | 25.93 ± 0.48 a | 19.72 ± 2.92 b | 7.71 ± 0.59 c | 9.91 ± 1.59 c |
| α-柠檬醛 α-Citral | 40.92 ± 0.33 a | 29.71 ± 4.52 b | 11.73 ± 0.54 c | 16.15 ± 3.28 c |
| 反式-柠檬烯氧化物 trans-Limonene oxide | 6.25 ± 0.69 a | 5.00 ± 0.58 ab | 3.74 ± 0.31 b | 5.03 ± 0.62 ab |
| α-胡椒烯α-Copaene | 8.26 ± 0.45 a | 7.20 ± 0.79 a | 3.07 ± 0.48 b | 4.03 ± 0.45 b |
| β-荜澄茄油烯 β-Cubebene | 5.69 ± 0.50 a | 4.56 ± 0.66 b | 2.24 ± 0.35 c | 2.94 ± 0.25 c |
| (-)-β-榄香烯 (-)-β-Elemen | 3.43 ± 0.65 a | 3.60 ± 0.59 a | 1.05 ± 0.23 b | 1.64 ± 0.17 b |
| 石竹烯 Caryophyllene | 15.84 ± 2.06 a | 12.99 ± 2.63 a | 3.98 ± 0.26 b | 5.27 ± 0.45 b |
| β-胡椒烯 β-Copaene | 6.29 ± 0.50 a | 5.85 ± 0.62 a | 2.20 ± 0.06 b | 2.99 ± 0.33 b |
| 吉马烯D Germacrene D | 4.62 ± 0.27 a | 3.59 ± 0.47 b | 2.22 ± 0.26 c | 2.45 ± 0.35 c |
| β-芹子烯 β-Selinene | 4.76 ± 0.68 a | 4.41 ± 0.69 a | 1.03 ± 0.25 b | 1.74 ± 0.28 b |
| 瓦伦烯 Valencene | 110.78 ± 16.58 a | 93.60 ± 14.39 a | 16.39 ± 0.34 b | 31.84 ± 4.18 b |
| δ-杜松烯 δ-Cadinene | 8.60 ± 0.89 a | 7.31 ± 0.98 a | 3.13 ± 0.24 b | 4.19 ± 0.67 b |
| 法尼醇 Farnesol | 5.64 ± 0.69 a | 2.05 ± 1.32 b | 1.16 ± 0.07 b | 1.25 ± 0.08 b |
| 石竹烯氧化物 Caryophyllene oxide | 6.52 ± 1.49 a | 5.18 ± 1.13 a | 1.65 ± 0.14 b | 1.46 ± 0.05 b |
| (E)-2-己烯醛 (E)-2-Hexenal | 1.12 ± 0.23 c | 1.14 ± 0.26 c | 3.27 ± 0.26 a | 1.96 ± 0.13 b |
| 辛醛 Octanal | 27.65 ± 3.83 b | 39.80 ± 2.87 a | 8.01 ± 1.15 c | 8.89 ± 1.76 c |
| 壬醛 Nonanal | 5.85 ± 0.35 b | 6.84 ± 0.52 a | 2.02 ± 0.40 c | 1.74 ± 0.29 c |
| 正癸醛 Decanal | 33.99 ± 1.80 b | 45.57 ± 0.91 a | 9.45 ± 0.79 c | 10.96 ± 1.56 c |
| 十一醛 Undecanal | 1.89 ± 0.23 a | 1.93 ± 0.17 a | 0.63 ± 0.12 b | 0.79 ± 0.08 b |
| 十二醛 Dodecanal | 6.12 ± 0.20 b | 7.73 ± 0.14 a | 2.29 ± 0.28 c | 2.11 ± 0.21 c |
| 正十六烷酸 n-Hexadecanoic acid | 7.34 ± 1.18 a | 7.87 ± 1.29 a | 4.51 ± 0.94 b | 4.06 ± 0.71 b |
| 香柏酮 Nootkatone | 8.40 ± 0.94 a | 6.51 ± 0.59 b | 1.37 ± 0.21 c | 2.40 ± 0.21 c |
| 2,2′-亚甲基双[6-(1,1-二甲基 乙基)-4-甲基—苯酚 2,2′-methylenebis[6-(1,1- Dimethylethyl)-4-methyl-Phenol | 64.68 ± 8.00 ab | 87.47 ± 2.31 a | 67.47 ± 16.97 ab | 47.57 ± 4.01 b |
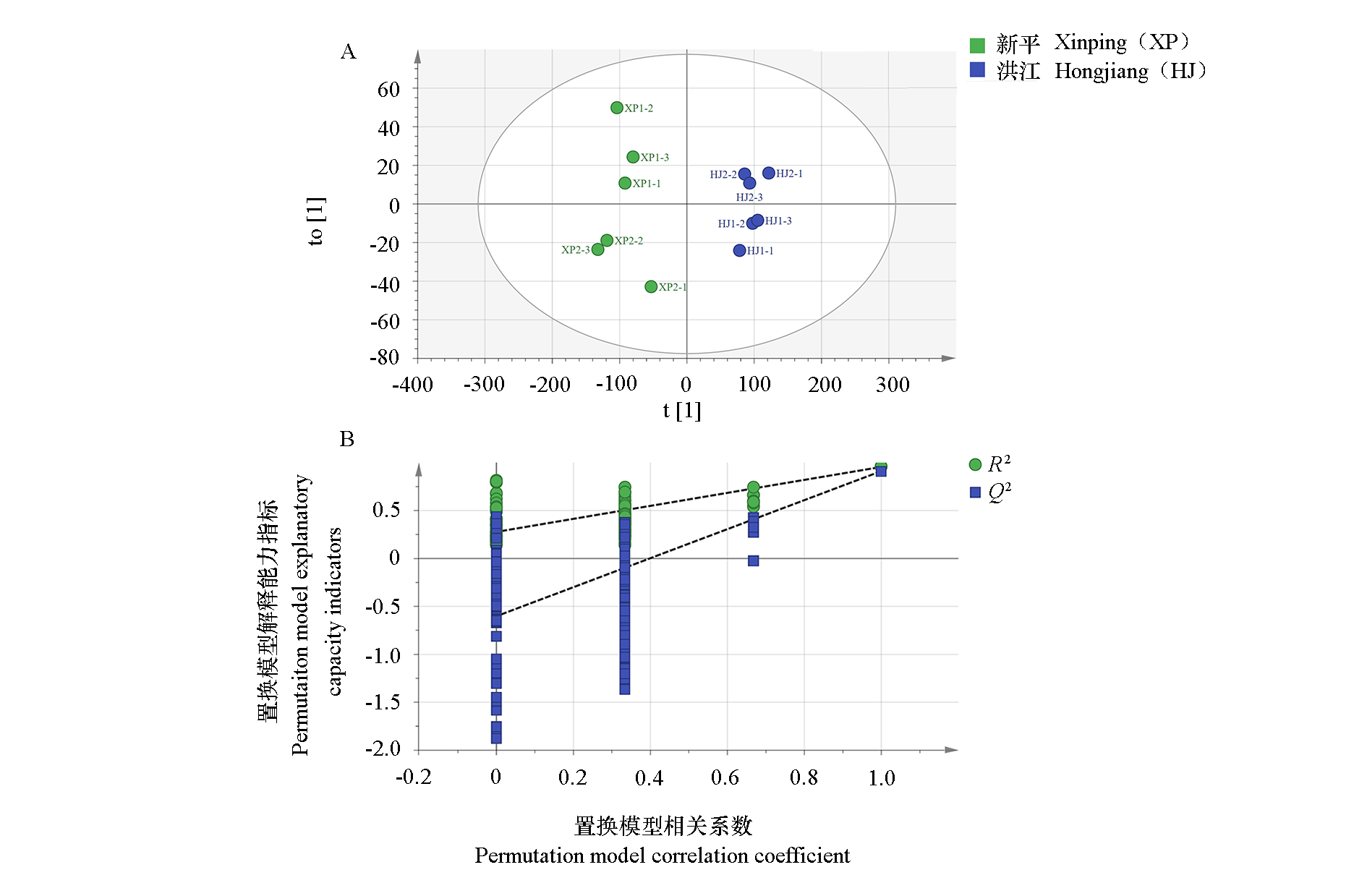
图3 正交偏最小二乘判别分析(A)和模型交叉验证结果(B) R2:因变量拟合指数,Q2:模型预测指数
Fig. 3 Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis(A)and permutation test(B)of Bingtang Orange from different origins R2:Goodness of fit index,Q2:Predictive index
| [1] |
|
|
安琪. 2022. 基于QDA法和CATA法的黄大茶的香气感官特性分析[硕士论文]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学.
|
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
鲍江峰. 2005. 纽荷尔脐橙和湖北省主要柑橘品种果实品质的研究与区划[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
|
陈梦昕, 蒋正品, 王振宇, 张朝春, 董治浩. 2024. 云南省新平县冰糖橙优质丰产影响因素分析. 热带农业科学, 44 (4):33-42.
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
刘潇然, 石金瑞, 刘翠华, 李瑞, 周彬. 2018. 陕西不同产区苹果香气物质差异分析. 西北农业学报, 27 (8):1173-1183.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
刘园, 向思敏, 王江波, 吴翠云, 唐章虎, 龚涵, 张雪, 徐娟. 2020. 库尔勒香梨挥发性物质及初生代谢物的GC-MS分析. 华中农业大学学报, 39 (1):44-52.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
毛羽扬. 2000. 论味觉科学和味觉变化在烹饪中的应用. 食品科学,(12):124-126.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
沈衡, 王琳, 李骞, 袁守娟, 郑伟, 王涛涛, 叶志彪, 杨长宪. 2024. 番茄风味和功能性成分研究进展. 园艺学报, 51 (2):423-438.
|
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
|
孙系巍, 汤丹, 李峰, 龙桂友, 邓子牛, 李娜. 2015. 主要气象因子对冰糖橙果实品质的影响. 湖南农业科学,(5):77-80.
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
|
吴孔杰, 胡承孝, 谭启玲, 孙学成, 赵小虎, 武松伟. 2022. 柑橘果实糖积累特征及蔗糖转运机制研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (12):2543-2558.
|
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
张海朋, 刘翠华, 刘园, 温欢, 施要强, 张红艳, 徐娟. 2020. 柑橘中挥发性萜类物质代谢研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (8):1610-1624.
|
|
| [33] |
|
|
张海朋, 彭昭欣, 石梅艳, 温欢, 张红艳, 徐娟. 2021. 柑橘果实风味组学研究进展. 华中农业大学学报, 40 (1):32-39.
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
张涵, 鲁周民, 王锦涛, 郭旭. 2017. 4种主要柑橘类香气成分比较. 食品科学, 38 (4):192-196.
|
|
| [35] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
|
江东, 普金安, 朱延松, 陈磊. 2022. 锦红冰糖橙芽变优系——云锦1号的鉴定与评价. 中国南方果树, 51 (4):1-5.
|
|
| [14] |
|
| [35] |
赵婉彤, 普金安, 张翠英, 杨兆贵, 江东. 2023. 早熟甜橙新品种‘新冰30’. 园艺学报, 50 (S1):33-34.
|
| [1] | 孟璐, 马涛, 岳新丽, 王慧, 李小玉, 王力. 植物生长延缓剂延迟黄花菜花期及对代谢产物的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 997-1006. |
| [2] | 胡亚伟, 马金龙, 钟八莲, 姚锋先, 刘桂东. 脐橙幼树夏施15N-尿素的利用与土壤残留初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 705-713. |
| [3] | 张书凝, 郑舒琪, 王新胜, 柯甫志, 张岚岚, 孙学鹏, 宫金礼. 柑橘果皮生理性病害与细胞壁代谢的关系研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 513-525. |
| [4] | 杨金磊, 吕壁纹, 陈岳文, 金燕, 杨俊枫, 周铁, 唐俊, 常媛媛, 杨长耀, 卢晓鹏. 湖南柑橘产区镉污染状况及镉对柑橘发育影响分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 200-212. |
| [5] | 董丽婷, 屈荣荣, 庞淑炜, 莫凯琴, 陈爽, 商兰月, 邹修平. 柑橘CsMEKK1-1响应黄龙病菌侵染的表达特征与功能探究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2168-2182. |
| [6] | 张文龙, 万润楚, 郑妮, 陈焱, 赖恒鑫, 余歆, 钱春, 曹立. 柑橘不育系新品种‘阳光1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2221-2222. |
| [7] | 杜美霞, 庞淑玮, 董丽婷, 莫凯琴, 候梦圆, 王帅, 邹修平. 柑橘黄龙病菌与寄主互作的分子机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1623-1638. |
| [8] | 曹惠祥, 罗鑫, 刘婉荣, 管书萍, 王婷婷, 伍小萌, 郭文武, 解凯东. 柑橘2个三倍体果实囊衣发育与化渣性评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1179-1188. |
| [9] | 周慧珍, 张嘉, 胡军华, 李白雪, 曹立, 余歆, 王福生, 邹修平, 周彦. 柑橘感染褐斑病过程中BAG1的作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 956-970. |
| [10] | 彭爱红, 张婧芸, 陈志毅, 苏娟, 何永睿, 姚利晓. CsEXPA8过表达对‘晚锦橙’生长及溃疡病抗性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 971-981. |
| [11] | 王青, 胡燕, 陈姗, 陆景伟, 郑阳, 陶伟林, 孙现超, 周娜, 陈国康. 绛红褐链霉菌CC2-6抑制大白菜根肿病的效果及机制分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1137-1150. |
| [12] | 游平, 杨进, 周俊, 黄爱军, 鲍敏丽, 易龙. 柑橘黄龙病菌原噬菌体的遗传多样性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 727-736. |
| [13] | 熊志伟, 李智龙, 尹晖, 高玉霞. 柑橘黄龙病菌亚洲种的泛基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 737-747. |
| [14] | 易倩, 张曼曼, 汪小利, 冯继鹏, 朱世平, 王福生, 赵晓春. CclSAUR49对柑橘生长及类柠檬苦素代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 479-494. |
| [15] | 孙权, 何政辰, 叶俊丽, 魏冉冉, 尹映紫, 柴利军, 谢宗周, 徐强, 徐娟, 郭文武, 程运江, 邓秀新. 与呼吸跃变型果实共贮藏改善柑橘果实色泽和品质[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 601-615. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司