
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2): 304-318.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0044
王光鹏, 刘同坤, 徐新凤, 李竹帛, 高瞻远, 侯喜林( )
)
收稿日期:2021-04-06
修回日期:2021-10-14
出版日期:2022-02-25
发布日期:2022-02-28
通讯作者:
侯喜林
E-mail:hxl@njau.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Guangpeng, LIU Tongkun, XU Xinfeng, LI Zhubo, GAO Zhanyuan, HOU Xilin( )
)
Received:2021-04-06
Revised:2021-10-14
Online:2022-02-25
Published:2022-02-28
Contact:
HOU Xilin
E-mail:hxl@njau.edu.cn
摘要:
基于大白菜全基因组数据对LEA家族基因进行全基因组鉴定与生物信息学分析,研究其序列特征、基因结构、启动子顺式作用元件、染色体定位、进化关系以及在不同组织中和低温胁迫下的表达模式。从大白菜基因组中总共鉴定出65个LEA家族基因成员,根据系统发育与保守基序分析,其可分为8个组;内含子较少,且不均匀地分布在10条染色体上,另有3个成员位于Scaffold上。启动子顺式作用元件分析显示,有29个(44.6%)成员拥有低温响应元件,除此之外,光响应元件和激素响应元件占比较高。共线性分析显示,大白菜BrLEA与拟南芥AtLEA同源性较高,并在进化中较为保守。大白菜不同组织转录组数据表明,BrLEA基因在大白菜不同组织中的表达存在组织特异性。对筛选出的13个家族成员进行低温胁迫表达分析表明,受低温胁迫表达量都有所升高。
中图分类号:
王光鹏, 刘同坤, 徐新凤, 李竹帛, 高瞻远, 侯喜林. 大白菜LEA家族基因的鉴定及其部分成员在低温胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 304-318.
WANG Guangpeng, LIU Tongkun, XU Xinfeng, LI Zhubo, GAO Zhanyuan, HOU Xilin. Identification of LEA Family and Expression Analysis of Some Members Under Low-temperature Stress in Chinese Cabbage[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 304-318.
| 基因 ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Bra008242 | BrDehydrin2 | F:GGAATCATCAGCGGAGGTCA;R:CCTCGTGTTTAACCTCAGGCA |
| Bra025819 | BrDehydrin4 | F:TTCCGGTGAAGGAGGAAACG;R:CCGTGTCGACCACTTGAGAA |
| Bra012230 | BrDehydrin5 | F:TTCACCGATCCAACAGCTCC;R:CCTCCGTGTTGACGACTTGA |
| Bra015779 | BrDehydrin6 | F:AGGAATCATCAACGGCCACC;R:CACCGGCTCTGAGATGTGAA |
| Bra003732 | BrDehydrin7 | F:AGGACACGGAAAGAAACCCG;R:CCTCAACGGTCTTTGAGTGG |
| Bra013992 | BrDehydrin8 | F:TGCAGCTTCCAAAGGTTGTG;R:CGTCGCGTCAGTCACATAGA |
| Bra035491 | BrLEA_1-3 | F:GGGCACGGACTAAAGAGGAG;R:TCACAGGTGTGTGATGAGGC |
| Bra000414 | BrLEA_2-2 | F:AAGGACGATAGCGTCGGGTA;R:CCGCTATGCTATAGGCCACC |
| Bra026541 | BrLEA_4-3 | F:GAATGCGACCATTACACCGC;R:CCACTTCACTCCCCATGTCC |
| Bra000263 | BrLEA_4-6 | F:GGCCTTGAAAAATGGCGAGA;R:TTTGTGGCGTCCTTAGCCTC |
| Bra000265 | BrLEA_4-7 | F:CTCAGGAGCTGTTCTCAGTGG;R:ATCAACGACTTCTTGCGCTG |
| Bra000173 | BrLEA_5-1 | F:GCCGAGGAGGGAATACAAGG;R:TGGGTTCGTCCATCTCCTCT |
| Bra022950 | BrLEA_6-1 | F:GCCACTAGAAACGAGTCCGTA;R:GGCCATGCTTAACCTGTTGG |
| Actin | F:AGGCTACACGTTCGGACAAG;R:TGGGGCACTAAACACAGTCA |
表1 本研究中所用引物
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 基因 ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Bra008242 | BrDehydrin2 | F:GGAATCATCAGCGGAGGTCA;R:CCTCGTGTTTAACCTCAGGCA |
| Bra025819 | BrDehydrin4 | F:TTCCGGTGAAGGAGGAAACG;R:CCGTGTCGACCACTTGAGAA |
| Bra012230 | BrDehydrin5 | F:TTCACCGATCCAACAGCTCC;R:CCTCCGTGTTGACGACTTGA |
| Bra015779 | BrDehydrin6 | F:AGGAATCATCAACGGCCACC;R:CACCGGCTCTGAGATGTGAA |
| Bra003732 | BrDehydrin7 | F:AGGACACGGAAAGAAACCCG;R:CCTCAACGGTCTTTGAGTGG |
| Bra013992 | BrDehydrin8 | F:TGCAGCTTCCAAAGGTTGTG;R:CGTCGCGTCAGTCACATAGA |
| Bra035491 | BrLEA_1-3 | F:GGGCACGGACTAAAGAGGAG;R:TCACAGGTGTGTGATGAGGC |
| Bra000414 | BrLEA_2-2 | F:AAGGACGATAGCGTCGGGTA;R:CCGCTATGCTATAGGCCACC |
| Bra026541 | BrLEA_4-3 | F:GAATGCGACCATTACACCGC;R:CCACTTCACTCCCCATGTCC |
| Bra000263 | BrLEA_4-6 | F:GGCCTTGAAAAATGGCGAGA;R:TTTGTGGCGTCCTTAGCCTC |
| Bra000265 | BrLEA_4-7 | F:CTCAGGAGCTGTTCTCAGTGG;R:ATCAACGACTTCTTGCGCTG |
| Bra000173 | BrLEA_5-1 | F:GCCGAGGAGGGAATACAAGG;R:TGGGTTCGTCCATCTCCTCT |
| Bra022950 | BrLEA_6-1 | F:GCCACTAGAAACGAGTCCGTA;R:GGCCATGCTTAACCTGTTGG |
| Actin | F:AGGCTACACGTTCGGACAAG;R:TGGGGCACTAAACACAGTCA |
| 基因号 Gene number | 基因名称 Gene name | 氨基酸长度 Amino acid length | 等电点 pI | 分子量/D MW | 不稳定性 指数 Instability index | 脂肪族指数 Aliphatic index | 亲水性 GRAVY | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bra011874 | BrDehydrin-1 | 149 | 5.65 | 15 928.40 | 23.71 | 58.93 | -0.863 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra036843 | BrDehydrin-10 | 134 | 9.19 | 13 834.22 | 42.98 | 49.55 | -0.887 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra037177 | BrDehydrin-11 | 144 | 8.81 | 15 139.46 | 45.61 | 33.26 | -1.360 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra008242 | BrDehydrin-2 | 194 | 5.52 | 21 840.38 | 62.43 | 53.71 | -1.352 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra031809 | BrDehydrin-3 | 192 | 7.14 | 18 844.17 | 33.09 | 32.14 | -1.021 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra025819 | BrDehydrin-4 | 271 | 5.00 | 31 018.16 | 61.44 | 47.49 | -1.508 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra012230 | BrDehydrin-5 | 220 | 5.11 | 24 837.39 | 62.24 | 55.41 | -1.399 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra015779 | BrDehydrin-6 | 195 | 5.45 | 22 044.52 | 63.15 | 50.41 | -1.455 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra003732 | BrDehydrin-7 | 194 | 5.47 | 21 755.35 | 56.38 | 53.25 | -1.308 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra013992 | BrDehydrin-8 | 257 | 6.17 | 28 978.00 | 34.53 | 35.33 | -1.645 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra031192 | BrDehydrin-9 | 183 | 6.49 | 19 183.88 | 36.64 | 49.18 | -1.016 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra005911 | BrLEA_1-1 | 159 | 9.22 | 16 286.99 | 17.53 | 43.71 | -0.789 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra005353 | BrLEA_1-2 | 98 | 9.22 | 10 666.89 | 42.18 | 49.18 | -1.115 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra035491 | BrLEA_1-3 | 132 | 9.68 | 14 933.95 | 56.61 | 51.89 | -1.109 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra023278 | BrLEA_1-4 | 133 | 9.24 | 14 507.53 | 59.47 | 48.65 | -0.878 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra009225 | BrLEA_1-5 | 159 | 8.93 | 16 180.83 | 16.45 | 38.81 | -0.818 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra000339 | BrLEA_2-1 | 777 | 9.02 | 84 314.53 | 32.33 | 96.22 | -0.135 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra000414 | BrLEA_2-2 | 166 | 4.81 | 17 823.38 | 17.04 | 96.81 | 0.030 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Bra039288 | BrLEA_2-3 | 166 | 4.50 | 18 119.88 | 16.96 | 100.36 | 0.013 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra037669 | BrLEA_2-4 | 506 | 8.85 | 55 465.06 | 27.06 | 85.89 | -0.399 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra004565 | BrLEA_2-5 | 166 | 4.81 | 17 725.34 | 20.39 | 106.20 | 0.093 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra030494 | BrLEA_2-6 | 151 | 4.72 | 16 404.92 | 10.57 | 106.42 | 0.075 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra033520 | BrLEA_3-1 | 99 | 9.72 | 10 582.01 | 50.01 | 70.10 | -0.400 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra000884 | BrLEA_3-2 | 94 | 9.85 | 10 095.53 | 39.42 | 78.94 | -0.349 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra014864 | BrLEA_3-3 | 122 | 9.20 | 14 152.16 | 50.98 | 63.20 | -0.598 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra018556 | BrLEA_3-4 | 93 | 9.99 | 10 112.56 | 52.38 | 72.47 | -0.482 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra038061 | BrLEA_3-5 | 57 | 4.94 | 6 614.40 | 49.22 | 56.67 | -0.912 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra036272 | BrLEA_3-6 | 94 | 9.99 | 10 088.55 | 43.90 | 72.77 | -0.299 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra033350 | BrLEA_3-7 | 98 | 8.03 | 10 298.59 | 40.91 | 76.84 | -0.229 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra021126 | BrLEA_4-1 | 226 | 9.02 | 24 598.55 | 28.79 | 22.79 | -1.475 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra022221 | BrLEA_4-10 | 298 | 5.45 | 32 431.59 | 30.10 | 54.50 | -1.126 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Bra027219 | BrLEA_4-11 | 229 | 8.83 | 24 810.86 | 27.04 | 22.97 | -1.414 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra005256 | BrLEA_4-12 | 399 | 5.74 | 43 565.34 | 20.90 | 52.93 | -0.970 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra019628 | BrLEA_4-13 | 451 | 5.20 | 48 554.47 | 12.26 | 47.98 | -1.141 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra025130 | BrLEA_4-14 | 201 | 5.40 | 22 054.03 | 38.33 | 77.21 | -0.429 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra039616 | BrLEA_4-15 | 480 | 6.47 | 52 652.67 | 18.82 | 47.04 | -0.921 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra010561 | BrLEA_4-16 | 487 | 5.63 | 52 431.94 | 23.72 | 46.65 | -0.923 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra020879 | BrLEA_4-17 | 218 | 5.12 | 24 376.73 | 15.32 | 38.72 | -1.441 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra027542 | BrLEA_4-18 | 311 | 7.60 | 35 005.70 | 23.66 | 43.79 | -1.371 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra037225 | BrLEA_4-19 | 722 | 8.58 | 80 928.05 | 43.18 | 68.66 | -0.722 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra013489 | BrLEA_4-2 | 253 | 8.55 | 27 837.93 | 20.67 | 47.31 | -1.202 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra036021 | BrLEA_4-20 | 253 | 5.72 | 28 430.30 | 32.23 | 43.72 | -1.355 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra041061 | BrLEA_4-21 | 241 | 6.17 | 26 330.13 | 20.46 | 50.83 | -1.111 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra026541 | BrLEA_4-3 | 192 | 8.57 | 20 399.00 | 33.96 | 62.55 | -0.669 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra008006 | BrLEA_4-4 | 462 | 9.03 | 50 701.68 | 32.68 | 78.53 | -0.390 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Bra001666 | BrLEA_4-5 | 276 | 5.54 | 30 311.37 | 25.62 | 53.22 | -1.093 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra000263 | BrLEA_4-6 | 142 | 8.65 | 14 760.62 | 19.57 | 77.75 | -0.430 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra000265 | BrLEA_4-7 | 129 | 5.31 | 13 894.51 | 22.81 | 71.86 | -0.692 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra017229 | BrLEA_4-8 | 398 | 6.02 | 43 386.25 | 20.77 | 55.63 | -1.065 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra016868 | BrLEA_4-9 | 679 | 5.98 | 72 972.61 | 33.88 | 45.77 | -1.088 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra000173 | BrLEA_5-1 | 88 | 5.88 | 9 630.38 | 37.14 | 25.57 | -1.659 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra004981 | BrLEA_5-2 | 84 | 6.74 | 9 264.98 | 49.89 | 27.96 | -1.704 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra040894 | BrLEA_5-3 | 172 | 6.17 | 18 997.70 | 42.85 | 30.64 | -1.635 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra022950 | BrLEA_6-1 | 71 | 6.03 | 7 581.23 | 52.98 | 40.00 | -1.238 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra021869 | BrLEA_6-2 | 72 | 5.21 | 7 627.30 | 58.73 | 40.83 | -1.174 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra039946 | BrLEA_6-3 | 82 | 4.72 | 8 433.11 | 44.84 | 37.07 | -1.055 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra022642 | BrSMP-1 | 173 | 5.88 | 18 379.46 | 40.43 | 86.36 | -0.357 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra020604 | BrSMP-2 | 181 | 4.76 | 18 366.26 | 31.03 | 71.44 | -0.481 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra001869 | BrSMP-3 | 239 | 5.70 | 25 385.45 | 46.14 | 76.78 | -0.380 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra029085 | BrSMP-4 | 177 | 5.43 | 18 691.81 | 41.22 | 82.20 | -0.351 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra039956 | BrSMP-5 | 262 | 4.71 | 26 692.50 | 34.19 | 77.21 | -0.239 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra009983 | BrSMP-6 | 192 | 4.76 | 19 473.41 | 23.22 | 69.32 | -0.515 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra036112 | BrSMP-7 | 191 | 4.99 | 19 600.77 | 26.99 | 75.81 | -0.414 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra033375 | BrSMP-8 | 177 | 4.53 | 18 185.98 | 30.21 | 71.24 | -0.540 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra033377 | BrSMP-9 | 283 | 8.89 | 32 586.25 | 52.20 | 75.72 | -0.543 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
表2 理化性质分析
Table 2 Physical and chemical properties analysis
| 基因号 Gene number | 基因名称 Gene name | 氨基酸长度 Amino acid length | 等电点 pI | 分子量/D MW | 不稳定性 指数 Instability index | 脂肪族指数 Aliphatic index | 亲水性 GRAVY | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bra011874 | BrDehydrin-1 | 149 | 5.65 | 15 928.40 | 23.71 | 58.93 | -0.863 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra036843 | BrDehydrin-10 | 134 | 9.19 | 13 834.22 | 42.98 | 49.55 | -0.887 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra037177 | BrDehydrin-11 | 144 | 8.81 | 15 139.46 | 45.61 | 33.26 | -1.360 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra008242 | BrDehydrin-2 | 194 | 5.52 | 21 840.38 | 62.43 | 53.71 | -1.352 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra031809 | BrDehydrin-3 | 192 | 7.14 | 18 844.17 | 33.09 | 32.14 | -1.021 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra025819 | BrDehydrin-4 | 271 | 5.00 | 31 018.16 | 61.44 | 47.49 | -1.508 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra012230 | BrDehydrin-5 | 220 | 5.11 | 24 837.39 | 62.24 | 55.41 | -1.399 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra015779 | BrDehydrin-6 | 195 | 5.45 | 22 044.52 | 63.15 | 50.41 | -1.455 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra003732 | BrDehydrin-7 | 194 | 5.47 | 21 755.35 | 56.38 | 53.25 | -1.308 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra013992 | BrDehydrin-8 | 257 | 6.17 | 28 978.00 | 34.53 | 35.33 | -1.645 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra031192 | BrDehydrin-9 | 183 | 6.49 | 19 183.88 | 36.64 | 49.18 | -1.016 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra005911 | BrLEA_1-1 | 159 | 9.22 | 16 286.99 | 17.53 | 43.71 | -0.789 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra005353 | BrLEA_1-2 | 98 | 9.22 | 10 666.89 | 42.18 | 49.18 | -1.115 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra035491 | BrLEA_1-3 | 132 | 9.68 | 14 933.95 | 56.61 | 51.89 | -1.109 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra023278 | BrLEA_1-4 | 133 | 9.24 | 14 507.53 | 59.47 | 48.65 | -0.878 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra009225 | BrLEA_1-5 | 159 | 8.93 | 16 180.83 | 16.45 | 38.81 | -0.818 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra000339 | BrLEA_2-1 | 777 | 9.02 | 84 314.53 | 32.33 | 96.22 | -0.135 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra000414 | BrLEA_2-2 | 166 | 4.81 | 17 823.38 | 17.04 | 96.81 | 0.030 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Bra039288 | BrLEA_2-3 | 166 | 4.50 | 18 119.88 | 16.96 | 100.36 | 0.013 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra037669 | BrLEA_2-4 | 506 | 8.85 | 55 465.06 | 27.06 | 85.89 | -0.399 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra004565 | BrLEA_2-5 | 166 | 4.81 | 17 725.34 | 20.39 | 106.20 | 0.093 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra030494 | BrLEA_2-6 | 151 | 4.72 | 16 404.92 | 10.57 | 106.42 | 0.075 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra033520 | BrLEA_3-1 | 99 | 9.72 | 10 582.01 | 50.01 | 70.10 | -0.400 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra000884 | BrLEA_3-2 | 94 | 9.85 | 10 095.53 | 39.42 | 78.94 | -0.349 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra014864 | BrLEA_3-3 | 122 | 9.20 | 14 152.16 | 50.98 | 63.20 | -0.598 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra018556 | BrLEA_3-4 | 93 | 9.99 | 10 112.56 | 52.38 | 72.47 | -0.482 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra038061 | BrLEA_3-5 | 57 | 4.94 | 6 614.40 | 49.22 | 56.67 | -0.912 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra036272 | BrLEA_3-6 | 94 | 9.99 | 10 088.55 | 43.90 | 72.77 | -0.299 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra033350 | BrLEA_3-7 | 98 | 8.03 | 10 298.59 | 40.91 | 76.84 | -0.229 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra021126 | BrLEA_4-1 | 226 | 9.02 | 24 598.55 | 28.79 | 22.79 | -1.475 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra022221 | BrLEA_4-10 | 298 | 5.45 | 32 431.59 | 30.10 | 54.50 | -1.126 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Bra027219 | BrLEA_4-11 | 229 | 8.83 | 24 810.86 | 27.04 | 22.97 | -1.414 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra005256 | BrLEA_4-12 | 399 | 5.74 | 43 565.34 | 20.90 | 52.93 | -0.970 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra019628 | BrLEA_4-13 | 451 | 5.20 | 48 554.47 | 12.26 | 47.98 | -1.141 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra025130 | BrLEA_4-14 | 201 | 5.40 | 22 054.03 | 38.33 | 77.21 | -0.429 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra039616 | BrLEA_4-15 | 480 | 6.47 | 52 652.67 | 18.82 | 47.04 | -0.921 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra010561 | BrLEA_4-16 | 487 | 5.63 | 52 431.94 | 23.72 | 46.65 | -0.923 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra020879 | BrLEA_4-17 | 218 | 5.12 | 24 376.73 | 15.32 | 38.72 | -1.441 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra027542 | BrLEA_4-18 | 311 | 7.60 | 35 005.70 | 23.66 | 43.79 | -1.371 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra037225 | BrLEA_4-19 | 722 | 8.58 | 80 928.05 | 43.18 | 68.66 | -0.722 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra013489 | BrLEA_4-2 | 253 | 8.55 | 27 837.93 | 20.67 | 47.31 | -1.202 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra036021 | BrLEA_4-20 | 253 | 5.72 | 28 430.30 | 32.23 | 43.72 | -1.355 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra041061 | BrLEA_4-21 | 241 | 6.17 | 26 330.13 | 20.46 | 50.83 | -1.111 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra026541 | BrLEA_4-3 | 192 | 8.57 | 20 399.00 | 33.96 | 62.55 | -0.669 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra008006 | BrLEA_4-4 | 462 | 9.03 | 50 701.68 | 32.68 | 78.53 | -0.390 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Bra001666 | BrLEA_4-5 | 276 | 5.54 | 30 311.37 | 25.62 | 53.22 | -1.093 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra000263 | BrLEA_4-6 | 142 | 8.65 | 14 760.62 | 19.57 | 77.75 | -0.430 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra000265 | BrLEA_4-7 | 129 | 5.31 | 13 894.51 | 22.81 | 71.86 | -0.692 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra017229 | BrLEA_4-8 | 398 | 6.02 | 43 386.25 | 20.77 | 55.63 | -1.065 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra016868 | BrLEA_4-9 | 679 | 5.98 | 72 972.61 | 33.88 | 45.77 | -1.088 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra000173 | BrLEA_5-1 | 88 | 5.88 | 9 630.38 | 37.14 | 25.57 | -1.659 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra004981 | BrLEA_5-2 | 84 | 6.74 | 9 264.98 | 49.89 | 27.96 | -1.704 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra040894 | BrLEA_5-3 | 172 | 6.17 | 18 997.70 | 42.85 | 30.64 | -1.635 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra022950 | BrLEA_6-1 | 71 | 6.03 | 7 581.23 | 52.98 | 40.00 | -1.238 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra021869 | BrLEA_6-2 | 72 | 5.21 | 7 627.30 | 58.73 | 40.83 | -1.174 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra039946 | BrLEA_6-3 | 82 | 4.72 | 8 433.11 | 44.84 | 37.07 | -1.055 | 线粒体 Mitochondrion |
| Bra022642 | BrSMP-1 | 173 | 5.88 | 18 379.46 | 40.43 | 86.36 | -0.357 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra020604 | BrSMP-2 | 181 | 4.76 | 18 366.26 | 31.03 | 71.44 | -0.481 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra001869 | BrSMP-3 | 239 | 5.70 | 25 385.45 | 46.14 | 76.78 | -0.380 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra029085 | BrSMP-4 | 177 | 5.43 | 18 691.81 | 41.22 | 82.20 | -0.351 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra039956 | BrSMP-5 | 262 | 4.71 | 26 692.50 | 34.19 | 77.21 | -0.239 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra009983 | BrSMP-6 | 192 | 4.76 | 19 473.41 | 23.22 | 69.32 | -0.515 | 细胞膜 Cell membrane |
| Bra036112 | BrSMP-7 | 191 | 4.99 | 19 600.77 | 26.99 | 75.81 | -0.414 | 细胞核 Nucleus |
| Bra033375 | BrSMP-8 | 177 | 4.53 | 18 185.98 | 30.21 | 71.24 | -0.540 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| Bra033377 | BrSMP-9 | 283 | 8.89 | 32 586.25 | 52.20 | 75.72 | -0.543 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
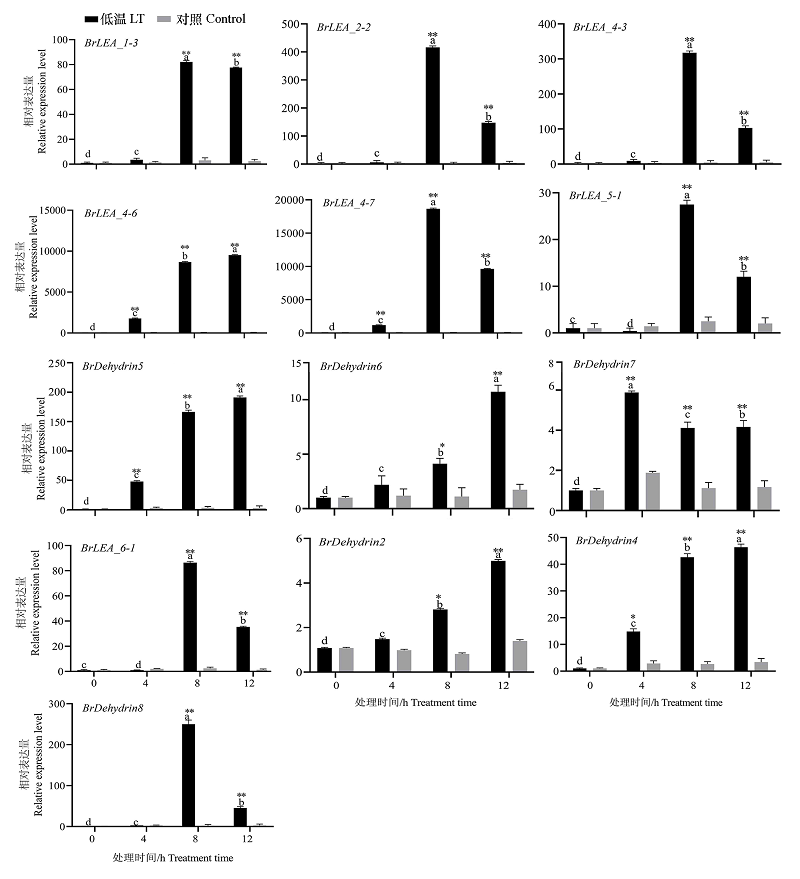
图6 低温处理下13个BrLEA基因的表达分析 不同小写字母表示低温处理不同时间在0.05水平上差异显著。*、**表示处理与对照在0.05和0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 Expression analysis of 13 BrLEA genes under low-temperature treatment Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in low temperature treatment at 0.05 level at different times. *,** indicated significant difference between treatment and control at 0.05 and 0.01 levels.
| [1] |
Amara I, Odena A, Oliveira E, Moreno A, Masmoudi K, Pagès M, Goday A. 2012. Insights into maize LEA proteins:from proteomics to functional approaches. Plant Cell Physiol, 53 (2):312-329.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcr183 pmid: 22199372 |
| [2] |
Baker J, Van Dennsteele C, Dure L. 1988. Sequence and characterization of 6 LEA proteins and their genes from cotton. Plant Mol Biol, 11 (3):277-291.
doi: 10.1007/BF00027385 pmid: 24272341 |
| [3] |
Battaglia M, Olvera-Carrillo Y, Garciarrubio A, Campos F, Covarrubias A A. 2008. The enigmatic LEA proteins and other hydrophilins. Plant Physiol, 148 (1):6-24.
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.120725 pmid: 18772351 |
| [4] |
Bies-Ethève N, Gaubier-Comella P, Debures A, Lasserre E, Jobet E, Raynal M, Cooke R, Delseny M. 2008. Inventory,evolution and expression profiling diversity of the LEA(late embryogenesis abundant)protein gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol, 67 (1-2):107-124.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9304-x pmid: 18265943 |
| [5] |
Candat A, Paszkiewicz G, Neveu M, Gautier R, Logan D C, Avelange-Macherel M H, Macherel D. 2014. The ubiquitous distribution of late embryogenesis abundant proteins across cell compartments in Arabidopsis offers tailored protection against abiotic stress. Plant Cell, 26 (7):3148-3166.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.127316 URL |
| [6] |
Cao J, Li X. 2015. Identification and phylogenetic analysis of late embryogenesis abundant proteins family in tomato(Solanum lycopersicum). Planta, 241 (3):757-772.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2215-y URL |
| [7] |
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas H R, Frank M H, He Y, Xia R. 2020. TBtools:an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant, 13 (8):1194-1202.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009 URL |
| [8] | Chen Fang, Gu Xiaoping, Liang Ping, Yu Fei. 2017. Effects of low temperature freezing injury on morphological changes of Chinese cabbage. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 40 (2):55-59. (in Chinese) |
| 陈芳, 谷晓平, 梁平, 于飞. 2017. 低温冻害对大白菜形态变化的影响. 气象与环境科学, 40 (2):55-59. | |
| [9] | Chen Yiyin. 2007. Study on cold resistance of tobacco and transgenic plants induced by low temperature gene transformation of Amongillus amurensis[M. D. Dissertation]. BeiJing: Beijing Forestry University. (in Chinese) |
| 陈奕吟. 2007. 沙冬青低温诱导基因转化烟草及转基因植物的抗寒性研究[硕士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学. | |
| [10] |
Daniel C J, Christopher J P, Jürg B. 2008. Rapidly regulated genes are intron poor. Trends Genet, 24 (8):375-378.
doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2008.05.006 URL |
| [11] | Du Yongting, Wang Tiejuan, Du Junrui, Chen Jing. 2018. Expression and sequence analysis of LEA gene of Artemisia argyi under drought stress. Biotechnology, 28 (4):318-322,371. (in Chinese) |
| 杜永婷, 王铁娟, 杜俊瑞, 陈静. 2018. 干旱胁迫下白沙蒿LEA基因的表达及序列分析. 生物技术, 28 (4):318-322,371. | |
| [12] |
Dure L Ⅲ. 1993. A repeating 11-mer amino acid motif and plant desiccation. Plant J, 3 (3):363-369.
pmid: 8220448 |
| [13] |
Dure L Ⅲ, Crouch M, Harada J, Ho T H, Mundy J, Quatrano R, Thomas T, Sung Z R. 1989. Common amino acid sequence domains among the LEA proteins of higher plants. Plant Mol Biol, 12 (5):475-486.
doi: 10.1007/BF00036962 pmid: 24271064 |
| [14] |
Dure L Ⅲ, Greenway S C, Galau G A. 1981. Developmental biochemistry of cottonseed embryogenesis and germination:changing messenger ribonucleic acid populations as shown by in vitro and in vivo protein synthesis. Biochemistry, 20 (14):4162-4168.
pmid: 7284317 |
| [15] |
Espelund M, Saebøe-Larssen S, Hughes D W, Galau G A, Larsen F, Jakobsen K S. 1992. Late embryogenesis-abundant genes encoding proteins with different numbers of hydrophilic repeats are regulated differentially by abscisic acid and osmotic stress. Plant J, 2 (2):241-252.
pmid: 1302052 |
| [16] | Finn R D, Mistry J, Tate J, Coggill P, Heger A, Pollington J E, Gavin O L, Gunasekaran P, Ceric G, Forslund K, Holm L, Sonnhammer E L, Eddy R, Bateman A. 2000. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res, 38 (Database issue):D211-D222. |
| [17] |
Gao T, Mo Y X, Huang H Y, Yu J M, Wang Y, Wang W D. 2021. Heterologous expression of Camellia sinensis late embryogenesis abundant protein gene 1(CsLEA1)confers cold stress tolerance in Escherichia coli and yeast. Horticultural Plant Journal, 7 (1):89-96.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.09.005 URL |
| [18] |
Garay-Arroyo A, Colmener-Flores J M, Garciarrubio A, Covarrubias A A. 2000. Highly hydrophilic proteins in prokaryotes and eukaryotes are common during conditions of water deficit. J Biol Chem, 275 (8):5668-5674.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.8.5668 pmid: 10681550 |
| [19] |
Hand S C, Menze M A, Toner M, Boswell L, Moore D. 1996. LEA proteins during water stress:not just for plants anymore. Annu Rev Physiol, 73:115-134.
doi: 10.1146/physiol.2011.73.issue-1 URL |
| [20] |
Hundertmark M, Hincha D K. 2008. LEA(late embryogenesis abundant)proteins and their encoding genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genomics, 9 (1):118.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-118 URL |
| [21] |
Imai R, Chang L, Ohta A, Bray E A, Takagi M. 1996. A lea-class gene of tomato confers salt and freezing tolerance when expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene, 170 (2):243-248.
pmid: 8666253 |
| [22] |
Jeffares D C, Penkett C J, Bähler J. 2008. Rapidly regulated genes are intron poor. Trends Genet, 24 (8):375-378.
doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2008.05.006 pmid: 18586348 |
| [23] |
Kosová K, Vítámvás Prášil, Prasil I. 2007. The role of dehydrins in plant response to cold. Biol Plant, 51 (4):601-617.
doi: 10.1007/s10535-007-0133-6 URL |
| [24] |
Lysak M A, Koch M A, Pecinka A, Schubert I. 2005. Chromosome triplication found across the tribe Brassiceae. Genome Res, 15 (4):516-525.
doi: 10.1101/gr.3531105 URL |
| [25] |
Liu Y, Xie L, Liang X, Zhang S. 2015. pLEA5,the Late Embryogenesis Abundant Protein Gene from Chimonanthus praecox,possesses low temperature and osmotic resistances in prokaryote and eukaryotes. Int J Mol Sci, 16 (11):26978-26990.
doi: 10.3390/ijms161126006 URL |
| [26] |
Morran S, Eini O, Pyvovarenko T, Parent B, Singh R, Ismagul A, Eliby S, Shirley N, Langridge P, Lopato S. 2011. Improvement of stress tolerance of wheat and barley by modulation of expression of DREB/CBF factors. Plant Biotechnol J, 9 (2):230-249.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00547.x pmid: 20642740 |
| [27] |
Mowla S B, Cuypers A, Driscoll S P, Kiddle G, Thomson J, Foyer C H, Theodoulou F L. 2006. Yeast complementation reveals a role for an Arabidopsis thaliana late embryogenesis abundant(LEA)-like protein in oxidative stress tolerance. Plant J, 48 (5):743-756.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2006.48.issue-5 URL |
| [28] |
Nagaraju M, Kumar S A, Reddy P S, Kumar A, Rao D M, Kavi Kishor P B. 2019. Genome-scale identification,classification,and tissue specific expression analysis of late embryogenesis abundant(LEA)genes under abiotic stress conditions in Sorghum bicolor L. PLoS ONE, 14 (1):e0209980.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209980 URL |
| [29] |
Olvera-Carrillo Y, Luis Reyes J, Covarrubias A A. 2011. Late embryogenesis abundant proteins:versatile players in the plant adaptation to water limiting environments. Plant Signal Behav, 6 (4):586-589.
doi: 10.4161/psb.6.4.15042 pmid: 21447997 |
| [30] |
Park S C, Kim Y H, Jeong J C, Kim C Y, Lee H S, Bang J W, Kwak S S. 2011. Sweetpotato late embryogenesis abundant 14(IbLEA14)gene influences lignification and increases osmotic- and salt stress-tolerance of transgenic calli. Planta, 233 (3):621-634.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-010-1326-3 URL |
| [31] |
Tong C, Wang X, Yu J, Wu J, Li W, Huang J, Dong C, Hua W, Liu S. 2013. Comprehensive analysis of RNA-seq data reveals the complexity of the transcriptome in Brassica rapa. BMC Genomics, 14:689.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-689 URL |
| [32] |
Tunnacliffe A, Wise M J. 2007. The continuing conundrum of the LEA proteins. Naturwissenschaften, 94 (10):791-812.
doi: 10.1007/s00114-007-0254-y URL |
| [33] | Wang Ying, Zhang Changwei, Lv Shanwu, Hou Xilin. 2018. Genome identification and expression analysis BrCNGC Chinese cabbage. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 41 (6):994-1002. (in Chinese) |
| 汪影, 张昌伟, 吕善武, 侯喜林. 2018. 大白菜BrCNGC全基因组鉴定及其表达分析. 南京农业大学学报, 41 (6):994-1002. | |
| [34] |
Wang X S, Zhu H B, Jin G L, Liu H L, Wu W R, Zhu J. 2006. Genome-scale identification and analysis of LEA genes in rice ( Oryza sativa L.). Plant Science, 172 (2):414-420.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2006.10.004 URL |
| [35] |
Wang Y D, Chen G J, Lei J J, Cao B H, Chen C M. 2020. Identification and characterization of a LEA-like gene,CaMF5,specifically expressed in the anthers of male-fertile Capsicum annuum. Horticultural Plant Journal, 6 (1):39-48.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2019.07.004 URL |
| [36] |
Wise M J, Tunnacliffe A. 2004. POPP the question:what do LEA proteins do? Trends Plant Sci, 9 (1):13-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2003.10.012 URL |
| [37] |
Yu J, Lai Y, Wu X, Wu G, Guo C. 2016. Overexpression of OsEm1 encoding a group I LEA protein confers enhanced drought tolerance in rice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 478 (2):703-709.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.010 URL |
| [38] | Yu J N, Zhang J S, Shan L, Chen S Y. 2005. Two new group 3 LEA genes of wheat and their functional analysis in yeast. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology Formerly Aacta Botanica Sinica, 47 (11):1372-1381. |
| [39] | Zhang L, Cai X, Wu J, Liu M, Grob S, Cheng F, Liang J, Cai C, Liu Z, Liu B, Wang F, Li S, Li X, Cheng L, Yang W, Li M H, Grossniklaus U, Zheng H, Wang X. 2019. Improved Brassica rapa reference genome by single-molecule sequencing and chromosome conformation capture technologies. Hortic Res, 13 (6):124. |
| [40] | Zhang L S, Zhao W M. 2003. LEA protein functions to tolerance drought of the plant. Plant Physiol Comm, 39:61-66. |
| [41] | Zhang Mei, Zhang Hui. 2017. Research progress in late embryogenesis abundant protein(LEA protein)and plant stress resistance. Biotic Resources, 39 (3):155-161. (in Chinese) |
| 张美, 张会. 2017. 胚胎发育晚期丰富蛋白(LEA蛋白)与植物抗逆性研究进展. 生物资源, 39 (3):155-161. | |
| [42] | Zong Mei, Cai Yongping. 2005. Correlation between seed dehydration tolerance and protective system. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (2):342-347. (in Chinese) |
| 宗梅, 蔡永萍. 2005. 种子脱水耐性与保护系统的相关性. 园艺学报, 46 (2):342-347. |
| [1] | 任 菲, 卢苗苗, 刘吉祥, 陈信立, 刘道凤, 眭顺照, 马 婧. 蜡梅胚胎晚期丰富蛋白基因CpLEA的表达及抗性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 359-370. |
| [2] | 蔺海娇, 梁雨晨, 李玲, 马军, 张璐, 兰振颖, 苑泽宁. 薰衣草CBF途径相关耐寒基因挖掘与调控网络分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 131-144. |
| [3] | 韩书辉, 韩彩锋, 韩书荣, 韩彩梅, 韩 旭. 秋大白菜新品种‘胶研秋宝’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 83-84. |
| [4] | 汪维红, 张凤兰, 余阳俊, 张德双, 赵岫云, 于拴仓, 苏同兵, 李佩荣, 辛晓云. 秋大白菜新品种‘京秋1518’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 85-86. |
| [5] | 余阳俊, 汪维红, 苏同兵, 张凤兰, 张德双, 赵岫云, 于拴仓, 李佩荣, 辛晓云, 王 姣. 抗根肿病耐抽薹大白菜新品种‘京春CR3’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 87-88. |
| [6] | 王丽丽, 王 鑫, 吴海东, 温 蔷, 杨晓飞. 抗根肿病大白菜新品种‘辽白28’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 89-90. |
| [7] | 余阳俊, 苏同兵, 张凤兰, 张德双, 赵岫云, 于拴仓, 汪维红, 李佩荣, 辛晓云, 王 姣, 武长见. 紫色苗用型大白菜新品种‘京研紫快菜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 91-92. |
| [8] | 徐立功, 韩太利, 孙继峰, 杨晓东, 谭金霞. 苗用大白菜新品种‘锦绿2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 67-68. |
| [9] | 王钰, 张雪, 张学颖, 张思雨, 闻婷婷, 王迎君, 甘彩霞, 庞文星. 抗毒素Camalexin对大白菜抗根肿病的作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1689-1698. |
| [10] | 钱婕妤, 蒋玲莉, 郑钢, 陈佳红, 赖吴浩, 许梦晗, 付建新, 张超. 百日草花青素苷合成相关MYB转录因子筛选及ZeMYB9功能研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1505-1518. |
| [11] | 张鲁刚, 卢倩倩, 何琼, 薛一花, 马晓敏, 马帅, 聂姗姗, 杨文静. 紫橙色大白菜新种质的创制[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1582-1588. |
| [12] | 李琼, 李丽丽, 侯娟, 罗忍忍, 王瑞丹, 胡建斌, 黄松. 瓜类作物响应低温胁迫机制的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1382-1394. |
| [13] | 姜翠翠, 方智振, 周丹蓉, 林炎娟, 叶新福. ‘芙蓉李’糖转运蛋白家族基因鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 252-264. |
| [14] | 王荣花, 王树彬, 刘栓桃, 李巧云, 张志刚, 王立华, 赵智中. 大白菜花茎蜡粉近等基因系转录组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 62-72. |
| [15] | 徐立功, 韩太利, 孙继峰, 杨晓东, 谭金霞, 宋银行, 李 萌, 周陆红, 孙莎莎. 春大白菜新品种‘潍春22号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(S2): 2825-2826. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司