
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 2491-2506.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0546
陈丹*, 魏仪*, 张乐慧, 郭飞, 王璞, 王明乐, 王郁, 赵华**( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-16
修回日期:2025-06-23
出版日期:2025-09-25
发布日期:2025-09-24
通讯作者:
作者简介:* 共同第一作者
基金资助:
CHEN Dan, WEI Yi, ZHANG Lehui, GUO Fei, WANG Pu, WANG Mingle, WANG Yu, ZHAO Hua**( )
)
Received:2025-05-16
Revised:2025-06-23
Published:2025-09-25
Online:2025-09-24
摘要:
以一年生‘鄂茶10号’茶树(Camellia sinensis)盆栽苗为研究对象,设置单作与间作高硒积累型植物壶瓶碎米荠(Cardamine hupingshanensis)、结合喷硒与不喷硒处理,系统分析不同处理对茶树生长、茶叶品质和茶树根际土壤酶活性的影响。结果显示,间作壶瓶碎米荠联合喷硒处理,不仅显著促进了茶树主茎的增粗,增加了茶树根系的生物量,提高了茶鲜叶中游离氨基酸含量,同时降低了咖啡碱、儿茶素和黄酮类等多酚物质的含量。茶叶中的有机硒主要以硒代蛋氨酸和硒代半胱氨酸等生物有效态形式存在,其中硒代蛋氨酸占据主导地位。此外,间作联合喷硒处理显著增强了茶树根际土壤中β-葡萄糖苷酶、亮氨酸氨肽酶和N-乙酰-β-氨基葡萄糖苷酶的活性,而对芳基硫酸酯酶的活性和间作对酸性磷酸酶活性则表现出显著抑制效应。综上,间作壶瓶碎米荠联合喷硒处理不仅能够提升茶鲜叶的品质,促进富硒茶的生产,还能显著提高根际一些土壤酶的活性。
陈丹, 魏仪, 张乐慧, 郭飞, 王璞, 王明乐, 王郁, 赵华. 间作喷硒对盆栽茶苗生长、茶叶品质及根际土壤酶活的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2491-2506.
CHEN Dan, WEI Yi, ZHANG Lehui, GUO Fei, WANG Pu, WANG Mingle, WANG Yu, ZHAO Hua. Effect of Intercropping and Selenium-Foliar Application on the Growth of Potted Tea Seedlings,Tea Quality,and Rhizosphere Soil Enzyme Activities[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(9): 2491-2506.
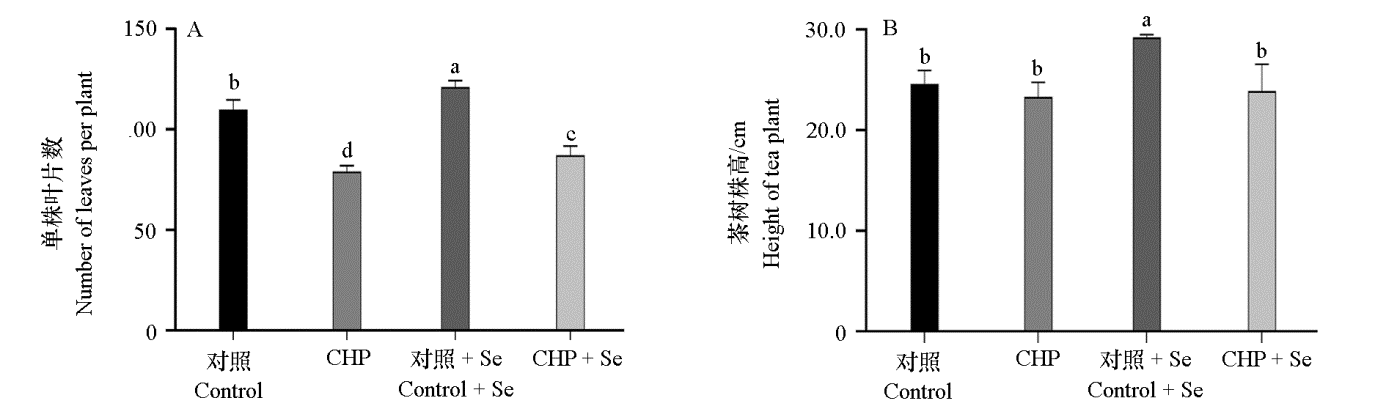
图2 间作壶瓶碎米荠(CHP)联合硒处理对茶树叶片数(A)和株高(B)的影响 对照:单作;CHP:间作壶瓶碎米荠;对照 + Se:单作喷硒(10 mg · L-1硒酸钠);CHP + Se:间作壶瓶碎米荠喷硒。 不同小写字母代表处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同
Fig. 2 The effect of intercropping with Cardamine hupingshanensis(CHP)and Se treatment on the number of leaves(A)and height(B)of tea plants Control:Monoculture;CHP:Tea plants-Cardamine hupingshanensis intercropping;Control + Se:Monoculture and spray Se(10 mg · L-1 Na2SeO4);CHP + Se:Tea plants-Cardamine hupingshanensis intercropping and spray Se(10 mg · L-1 Na2SeO4). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments(P < 0.05). The same below

图3 间作壶瓶碎米荠联合喷硒处理对茶树根系干质量(A)和主茎直径(B)的影响
Fig. 3 The effect of Cardamine hupingshanensis-intercropping and Se treatment on the root dry weight(A)and main stem diameter(B)of tea trees
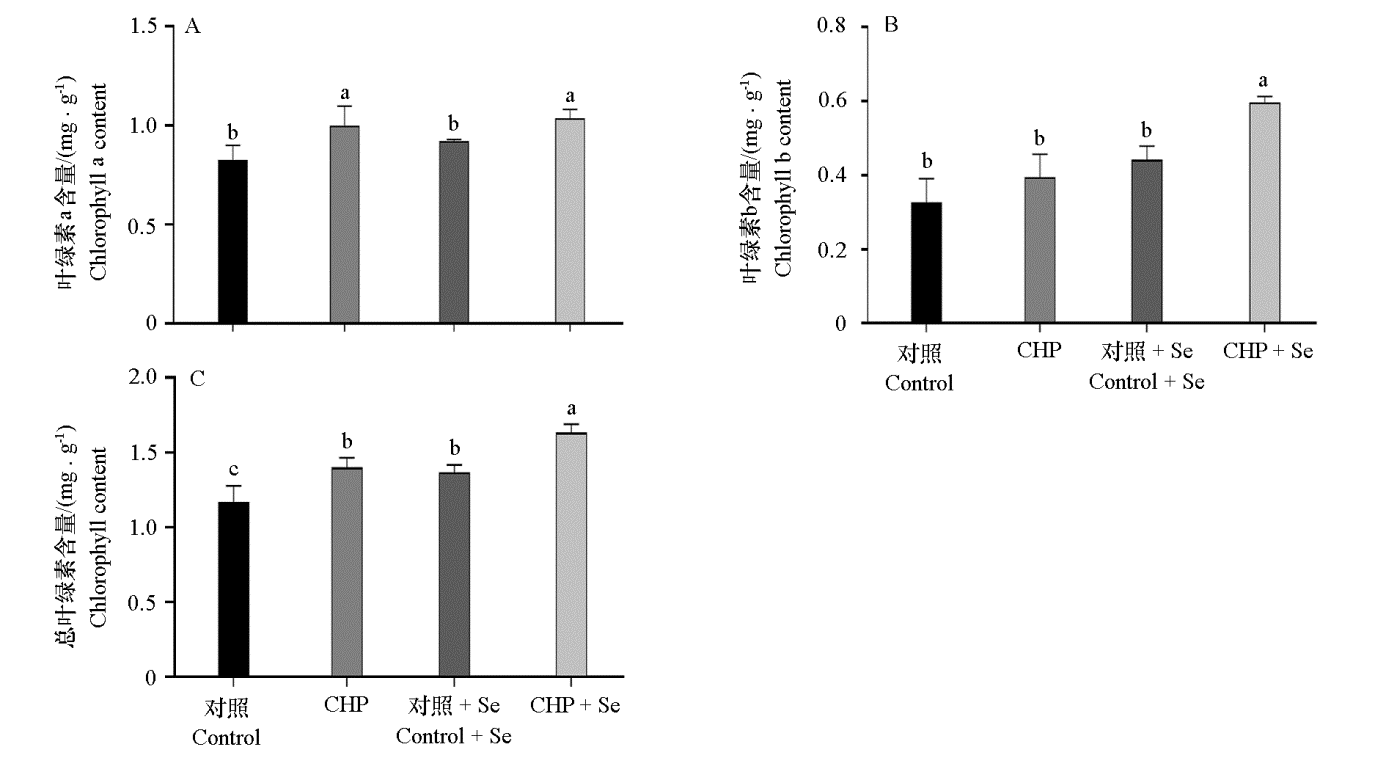
图4 间作壶瓶碎米荠联合喷硒处理对茶树叶片叶绿素含量的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of intercropping with Cardamine hupingshanensis and Se treatment on chlorophyll content of tea tree leaves
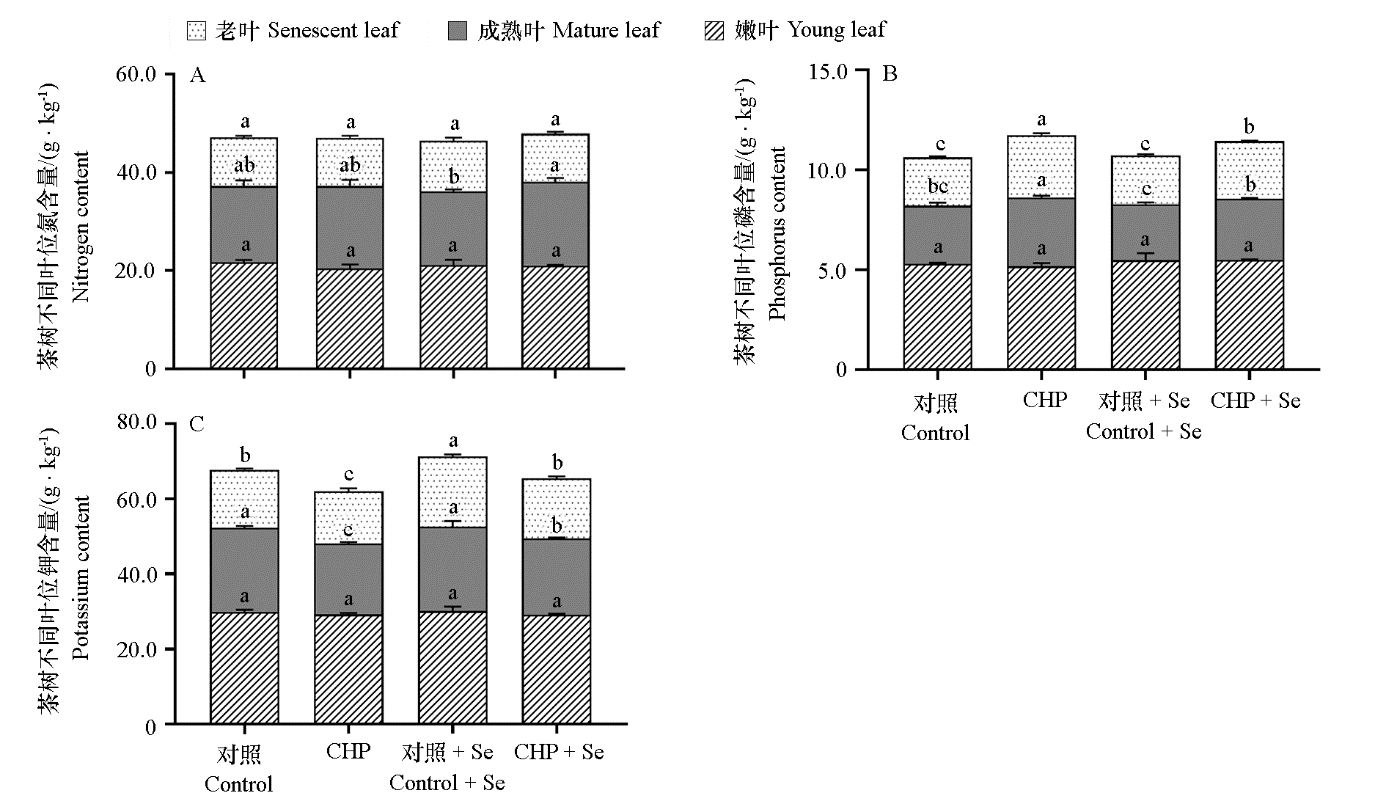
图5 间作壶瓶碎米荠联合喷硒处理对茶树不同成熟度叶片氮、磷、钾含量的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of intercropping with Cardamine hupingshanensis and Se treatment on nitrogen,phosphorus and potassium content in the tea leaves of gradient maturity
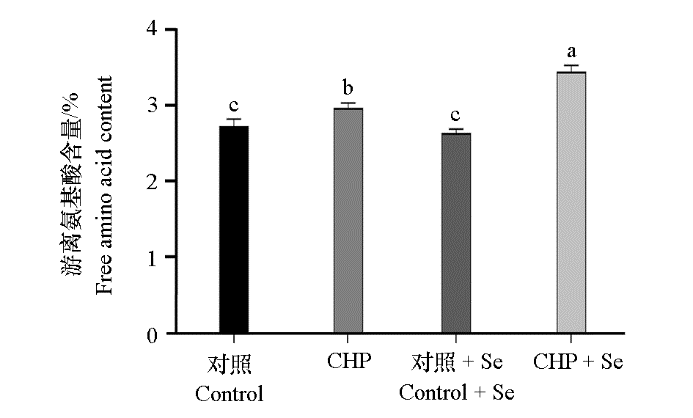
图6 间作壶瓶碎米荠联合喷硒处理对茶鲜叶游离氨基酸的含量的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of intercropping with Cardamine hupingshanensis and Se treatment on the content of free amino acids in tea fresh leaves

图7 间作壶瓶碎米荠联合喷硒处理对茶鲜叶关键氨基酸含量的影响
Fig. 7 Effect of the intercropping with Cardamine hupingshanensis and Se treatment on the content of main amino acid components in tea fresh leaves

图8 间作壶瓶碎米荠联合喷硒处理对茶鲜叶咖啡碱含量的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of intercropping with Cardamine hupingshanensis and Se treatment on the content of caffeine in tea fresh leaves
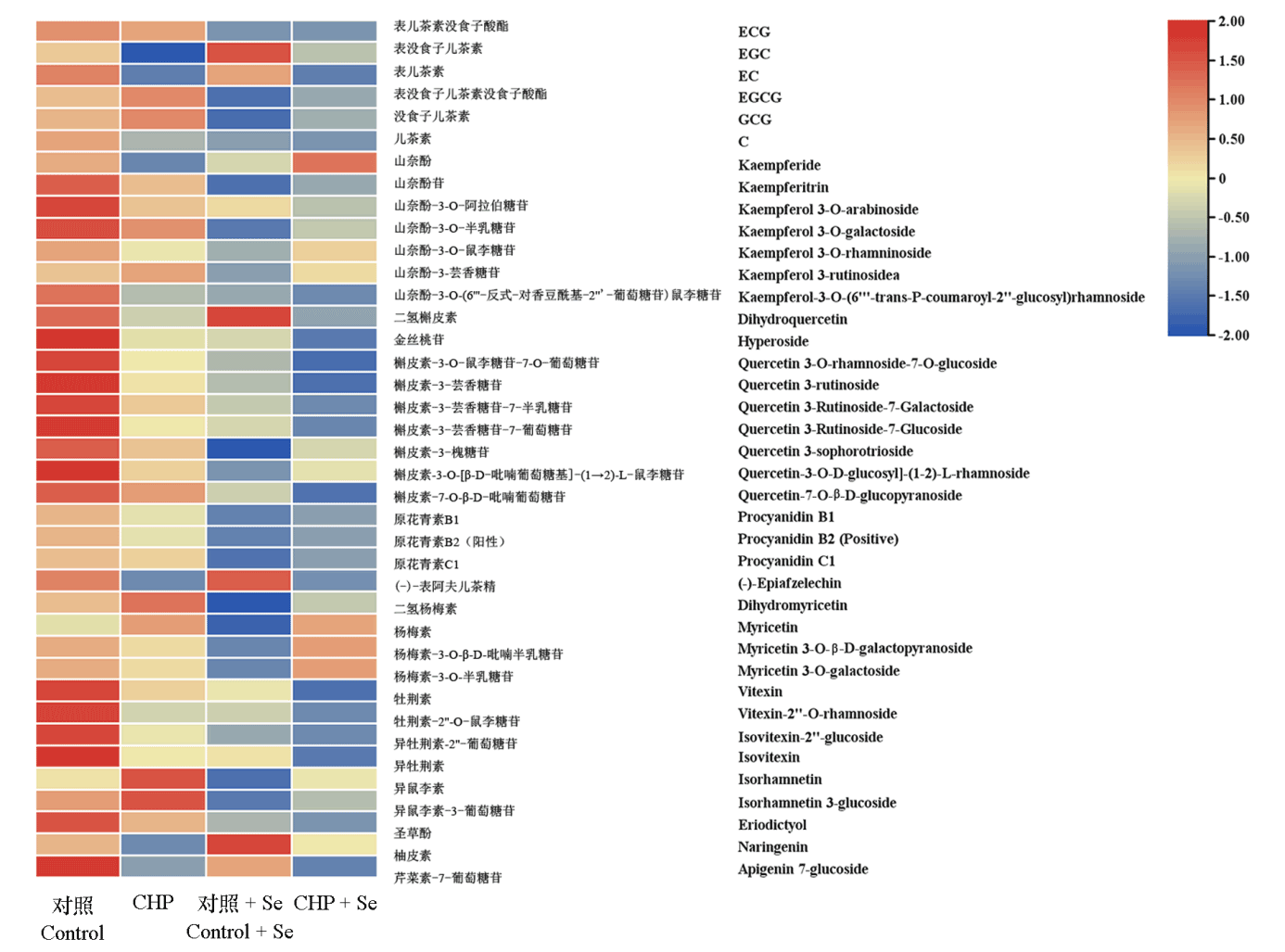
图9 间作壶瓶碎米荠联合喷硒处理对茶鲜叶类黄酮含量的影响
Fig. 9 Effect of intercropping with Cardamine hupingshanensis and Se treatment on the content of flavonoid content in tea fresh leaves
| 材料 Material | 处理 Treatment | SeMet | MeSeCys | SeCys2 | SeCys | SeO42- | SeO32- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 壶瓶碎米荠 Cardamine hupingshanensis | 硒 + Se | 46.6 ± 0.99 | 4.74 ± 0.18 | 2.64 ± 0.06 | nd | nd | nd |
| 茶树 Tea plant | 单作 + 硒 对照 + Se | 3.27 ± 0.11 a | nd | nd | 0.65 ± 0.04 a | nd | 0.05 ± 0.01 a |
| 间作 + 硒 CHP + Se | 1.38 ± 0.08 b | nd | nd | 0.21 ± 0.01 b | nd | 0.03 ± 0.01 a |
表1 硒处理条件下间作壶瓶碎米荠叶片与茶树一芽二叶中硒组分的含量(mg · kg-1 DW)
Table 1 The content of Se species in the leaves of Cardamine hupingshanensis and one bud with two leaves of tea plants intercropped with CHP-tea plants treated with Se(mg · kg-1 DW)
| 材料 Material | 处理 Treatment | SeMet | MeSeCys | SeCys2 | SeCys | SeO42- | SeO32- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 壶瓶碎米荠 Cardamine hupingshanensis | 硒 + Se | 46.6 ± 0.99 | 4.74 ± 0.18 | 2.64 ± 0.06 | nd | nd | nd |
| 茶树 Tea plant | 单作 + 硒 对照 + Se | 3.27 ± 0.11 a | nd | nd | 0.65 ± 0.04 a | nd | 0.05 ± 0.01 a |
| 间作 + 硒 CHP + Se | 1.38 ± 0.08 b | nd | nd | 0.21 ± 0.01 b | nd | 0.03 ± 0.01 a |
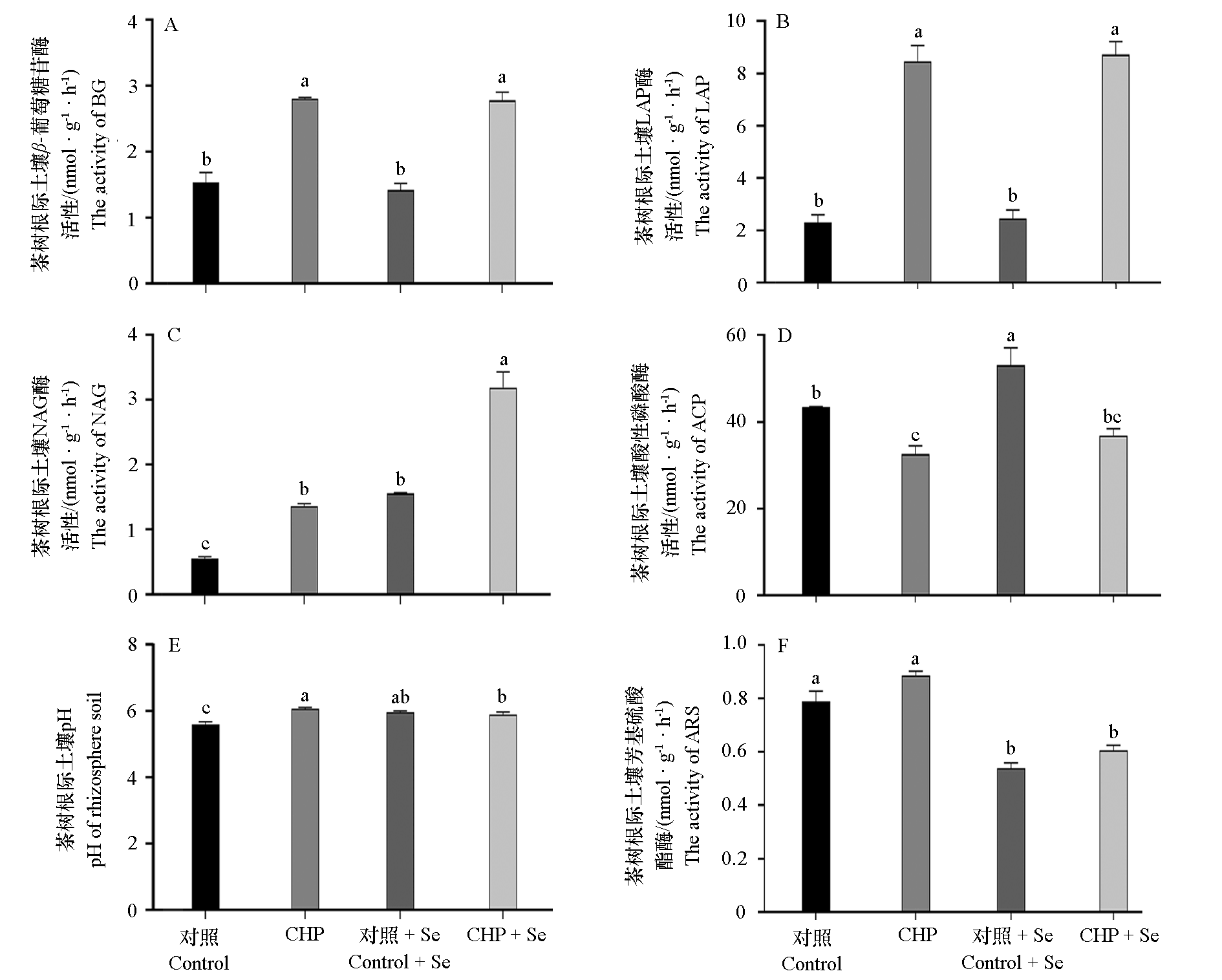
图10 间作壶瓶碎米荠联合喷硒处理对茶树根际土壤酶活的影响
Fig. 10 Effect of intercropping with Cardamine hupingshanensis and Se treatment on the enzyme activity of in the rhizosphere soil of tea trees
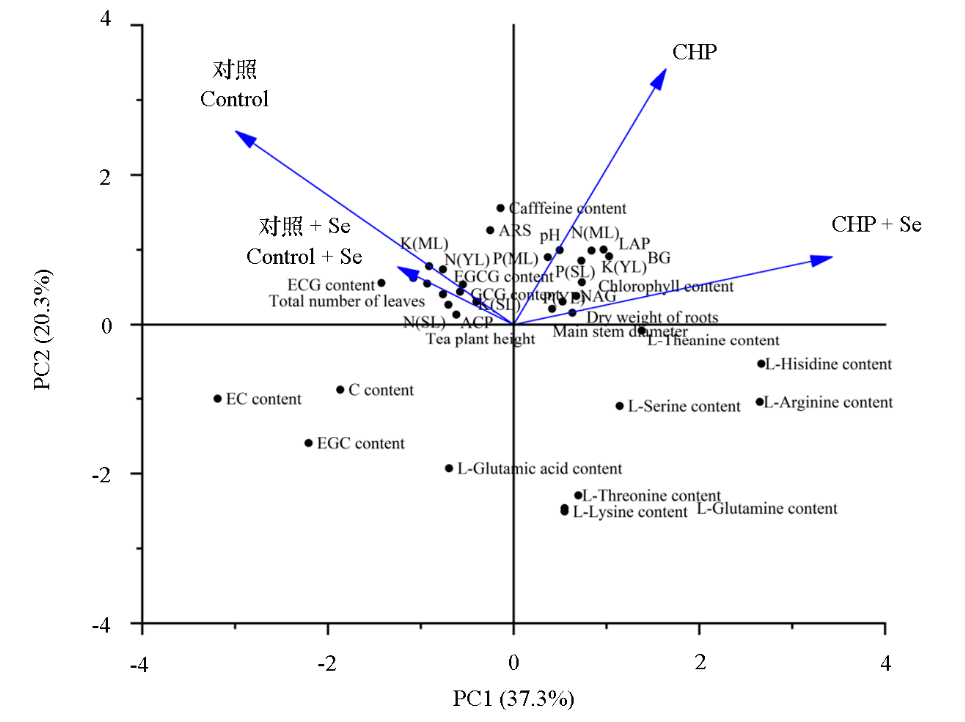
图11 茶树生长势、茶叶品质、茶树不同叶片养分含量和茶树根际土壤酶活性的PCA分析 各指标详见图2 ~ 图10。YL:嫩叶;ML:成熟叶;SL:衰老叶。指标与处理的夹角 < 90°则表示正相关,且夹角越小正相关性越强,夹角 > 90°则表示负相关,且夹角越大负相关性越强
Fig. 11 PCA analysis of tea tree growth,tea quality and nutrient concentration in different leaves and enzymatic activity of rhizosphere soil The details of each indicator are shown in Figures 2-10. YL:Young leaf;ML:Mature leaf;SL:Senescent leaf. When the angle between an indicator and a treatment is < 90°,it indicates a positive correlation,and the smaller the angle,the stronger the positive correlation. When the angle is > 90°,it indicates a negative correlation,and the larger the angle,the stronger the negative correlation
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [1] |
|
|
部金凤, 邹敬东, 张心昱, 徐丽丽, 杨风亭, 孙晓敏. 2014. 不同荧光校正方法对土壤水解酶活性测定结果影响的比较研究. 土壤通报, 45 (3):660-665.
|
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03258-1 pmid: 34686144 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
韦叶娜, 杨国涛, 范永义, 张杰, 蒋芬, 李亚男, 陈敬, 张圣豪, 胡运高. 2017. 外源硒处理对优质地方水稻品种产量及稻米硒氮磷钾含量的影响. 中国农学通报, 33 (36):14-19.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb17010116 |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
|
肖利杰, 刘春梅, 李梅, 尚海波, 马建辉, 高亚军. 2015. 施硒对水稻硒·氮·磷·钾含量及产量的影响. 安徽农业科学, 43 (34):59-61.
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
GB/T 8312-2013. Tea-determination of caffeine content. (in Chinese)
|
|
GB/T 8312-2013. 茶咖啡碱测定.
|
|
| [12] |
GB/T 8314-2013. Tea-determination of free amino acids content. (in Chinese)
|
|
GB/T 8314-2013. 茶游离氨基酸总量的测定.
|
|
| [13] |
GH/T 1135-2024. Selenium-enriched agricultural products. (in Chinese)
|
|
GH/T 1135-2024. 富硒农产品.
|
|
| [14] |
GH/T 1090-2014. Rich-selenium tea. (in Chinese)
|
|
GH/T 1090-2014. 富硒茶.
|
|
| [15] |
|
| [38] |
谢克孝, 薛志慧, 陈志丹. 2021. 茶园间作不同植物对茶叶产量和品质及茶园土壤的影响. 茶叶通讯, 48 (3):422-429.
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-00897-y pmid: 33833418 |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
|
赵茜, 施龙清, 何海芳, 李天璞, 李亚勍, 张力文, 杨广. 2021. 间作不同绿肥植物组合对茶园土壤改良的效果. 福建农业学报, 36 (5):602-609.
|
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.15302/J-FASE-2022451 |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
李增强, 王建红, 张贤. 2017. 绿肥腐解及养分释放过程研究进展. 中国土壤与肥料,(4):8-16.
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [1] | 邓淑琴, 高莹瑞, 李雨桐, 王瑛, 龚春梅, 白娟. 茶树泛素连接酶基因CsPUB21对非生物胁迫的响应[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 655-670. |
| [2] | 张芷苓, 张媛媛, 林晓蓉, 李斌, 陈忠正. 茶儿茶素合成关键酶基因CsANS和CsLAR的功能鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 804-814. |
| [3] | 袁青云, 韩昱, 贺巍, 苏会, 班秋艳, 吴春来, 周琼琼, 徐文静, 王丽鸳, 张芬. 茶树CsNPF6.1/6.3基因克隆及ABA转运功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2817-2828. |
| [4] | 胡锦瑜, 刘桂芝, 陈兰, 黄梦迪, 苏芹, 谭月萍, 刘硕谦, 田娜. 烟草脆裂病毒介导的茶树VIGS体系的构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2710-2724. |
| [5] | 陈鑫, 邬晓龙, 刘升锐, 胡贤春, 刘春艳. 干旱胁迫下AMF对茶树光合特性及其基因表达的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2358-2370. |
| [6] | 张力岚, 杨军, 王让剑. 茶树苯乙醇樱草糖苷含量相关遗传位点的挖掘[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 77-90. |
| [7] | 叶玙璠, 王誉洁, 傅前媛, 王璐, 郝心愿, 丁长庆, 王新超, 曹红利, 李娜娜. 茶树镁离子螯合酶H亚基基因CsChlH的克隆及其表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 91-102. |
| [8] | 彭 华, 王治会, 岳翠男, 杨普香 , 李文金 , 童忠飞, 郭 金. 茶树新品种‘赣茶 5 号’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 199-200. |
| [9] | 郑新强 , 李泽宇 , 李 凯 , 陆建良 , 赵 东 , 叶俭慧 , 叶晶晶 , 李寸羽 , 梁月荣 , . 早生优质茶树新品种‘浙农 301’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 201-202. |
| [10] | 王雷刚, 焦小雨, 刘丹丹, 阮 旭, 吴 琼, 王文杰. 黄化茶树新品种‘霍黄 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 203-204. |
| [11] | 刘丹丹, 阮 旭, 焦小雨, 王雷刚, 吴 琼, 王文杰. 茶树新品种‘金鸡 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 205-206. |
| [12] | 李宇腾, 陈瑶, 任恒泽, 李聪聪, 王浩乾, 曹红利, 岳川, 郝心愿, 王新超. 茶树CsIDM的鉴定、表达分析及互作验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1679-1696. |
| [13] | 侯炳豪, 高婷, 魏月德, 高水练, 蔡银笔, 陈志明, 金珊, 张兴坦, 王鹏杰, 叶乃兴. 基于高深度基因组重测序的‘铁观音’茶树无性繁殖后代遗传变异研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1505-1517. |
| [14] | 王泽涵, 于文涛, 王鹏杰, 刘财国, 樊晓静, 谷梦雅, 蔡春平, 王攀, 叶乃兴. 茶树秃房与茸房种质花器官差异表达基因的WGCNA分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 620-634. |
| [15] | 程庆华, 张志鹏, 吴艳萍, 万宇鹤, 陈应娟. 苦参碱对茶树炭疽菌的抑菌作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 432-440. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司