
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 655-670.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0378
收稿日期:2024-07-09
修回日期:2025-01-12
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
DENG Shuqin, GAO Yingrui, LI Yutong, WANG Ying, GONG Chunmei, BAI Juan*( )
)
Received:2024-07-09
Revised:2025-01-12
Published:2025-03-25
Online:2025-03-25
摘要:
以‘陕茶1号’茶树品种为材料,克隆得到U-box家族泛素E3连接酶基因CsPUB21并进行功能分析。序列分析发现CsPUB21编码区长度为1 242 bp,共编码413个氨基酸,在N端含有U-box保守结构域、C端含有ARM结构域,为不稳定的亲水性蛋白。启动子区含有多个响应干旱、高盐、低温胁迫的顺式作用元件。亚细胞定位结果表明,CsPUB21定位于细胞膜和细胞质。基因表达模式分析显示,在5个供试茶树品种中,CsPUB21受干旱和盐胁迫诱导表达上调,而在低温胁迫下降低。在拟南芥中过表达CsPUB21,显著增强了植株对干旱和盐胁迫的抗性。qRT-PCR结果显示,CsPUB21过表达拟南芥在干旱和盐胁迫后CsPUB21表达量上调。与野生型相比,CsPUB21过表达拟南芥在干旱、盐胁迫处理条件下叶绿素含量、可溶性糖含量较高,抗氧化酶SOD、POD、CAT活性增强,相对电导率和MDA含量降低。研究结果说明CsPUB21在茶树应对干旱和盐胁迫时发挥正向调节作用。
邓淑琴, 高莹瑞, 李雨桐, 王瑛, 龚春梅, 白娟. 茶树泛素连接酶基因CsPUB21对非生物胁迫的响应[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 655-670.
DENG Shuqin, GAO Yingrui, LI Yutong, WANG Ying, GONG Chunmei, BAI Juan. Response of Ubiquitin-ligase Gene CsPUB21 to Different Abiotic Stress in Camellia sinensis[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 655-670.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 用途 Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 1300-CsPUB21-F | GAGAACACGGGGGAC GAGCTCATGATTTCGTCTTGGCGGAG | 植物过表达 Plant overexpression |
| 1300-CsPUB21-R | CGCATAGCTAATCTG GGATCCTCAATTTTGAAGAGCTTCAACAAGA | |
| qRT-CsPUB21-F | GAAGGGTTTGGCGAAGGAGA | 荧光定量PCR Quantitative real time PCR |
| qRT-CsPUB21-R | AGCCCTCTCGCATATGCTTC | |
| qRT-Csβ-actin-F | GGTAACATTGTGCTCAGTGGTGG | |
| qRT-Csβ-actin-R | AACGACCTTAATCTTCATGCTGC |
表1 本研究中所用的引物序列信息
Table 1 Primers sequence information used in this study
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 用途 Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 1300-CsPUB21-F | GAGAACACGGGGGAC GAGCTCATGATTTCGTCTTGGCGGAG | 植物过表达 Plant overexpression |
| 1300-CsPUB21-R | CGCATAGCTAATCTG GGATCCTCAATTTTGAAGAGCTTCAACAAGA | |
| qRT-CsPUB21-F | GAAGGGTTTGGCGAAGGAGA | 荧光定量PCR Quantitative real time PCR |
| qRT-CsPUB21-R | AGCCCTCTCGCATATGCTTC | |
| qRT-Csβ-actin-F | GGTAACATTGTGCTCAGTGGTGG | |
| qRT-Csβ-actin-R | AACGACCTTAATCTTCATGCTGC |
| 顺式作用元件 cis-Acting element | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Amount | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| MYB | CAACCA CAACTG | 6 1 | 干旱、高盐、低温响应元件Drought,high salt,low temperature response element |
| MBS | CAACTG | 1 | 干旱响应元件Drought response element |
| STRE | AGGGG | 2 | 胁迫响应元件Stress response element |
| WUN-motif | AAATTACT | 2 | 损伤诱导元件Damage inductive element |
| WRE3 | CCACCT | 1 | 损伤诱导元件Damage inductive element |
| W box | TTGACC | 1 | 损伤与病原响应元件Damage and pathogen response element |
| ARE | AAACCA | 1 | 厌氧诱导调控元件Anaerobic inducible regulatory element |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 5 | 光响应元件Photoresponsive element |
| ATC-motif | AGTAATCT | 1 | 光响应元件Photoresponsive element |
| AAGAA-motif | GAAAGAA | 1 | 脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid response element |
| ABRE | TACGGTC | 1 | 脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid response element |
| MYC | CATGTG | 4 | 抗脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid resistant response element |
| F-box | CTATTCTCATT | 1 | 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin response element |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | 4 | 茉莉酸响应元件Jasmonic acid response element |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 4 | 茉莉酸响应元件Jasmonic acid response element |
| ERE | ATTTTAAA | 2 | 乙烯响应元件Ethylene responsive element |
| as-1 | TGACG | 4 | 根特异表达顺式作用调控元件Root specific expression of cis-acting regulatory elements |
表2 CsPUB21基因启动子区顺式作用元件预测
Table 2 Prediction of cis-acting elements in the promoter region of CsPUB21
| 顺式作用元件 cis-Acting element | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Amount | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| MYB | CAACCA CAACTG | 6 1 | 干旱、高盐、低温响应元件Drought,high salt,low temperature response element |
| MBS | CAACTG | 1 | 干旱响应元件Drought response element |
| STRE | AGGGG | 2 | 胁迫响应元件Stress response element |
| WUN-motif | AAATTACT | 2 | 损伤诱导元件Damage inductive element |
| WRE3 | CCACCT | 1 | 损伤诱导元件Damage inductive element |
| W box | TTGACC | 1 | 损伤与病原响应元件Damage and pathogen response element |
| ARE | AAACCA | 1 | 厌氧诱导调控元件Anaerobic inducible regulatory element |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 5 | 光响应元件Photoresponsive element |
| ATC-motif | AGTAATCT | 1 | 光响应元件Photoresponsive element |
| AAGAA-motif | GAAAGAA | 1 | 脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid response element |
| ABRE | TACGGTC | 1 | 脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid response element |
| MYC | CATGTG | 4 | 抗脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid resistant response element |
| F-box | CTATTCTCATT | 1 | 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin response element |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | 4 | 茉莉酸响应元件Jasmonic acid response element |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 4 | 茉莉酸响应元件Jasmonic acid response element |
| ERE | ATTTTAAA | 2 | 乙烯响应元件Ethylene responsive element |
| as-1 | TGACG | 4 | 根特异表达顺式作用调控元件Root specific expression of cis-acting regulatory elements |

图4 CsPUB21在茶树原生质体(A)和烟草叶表皮(B)中的亚细胞定位
Fig. 4 Subcellular localization of CsPUB21 in tea leaf mesophyll protoplasts(A)and leaf epidermis of Nicotiana benthamiana(B)
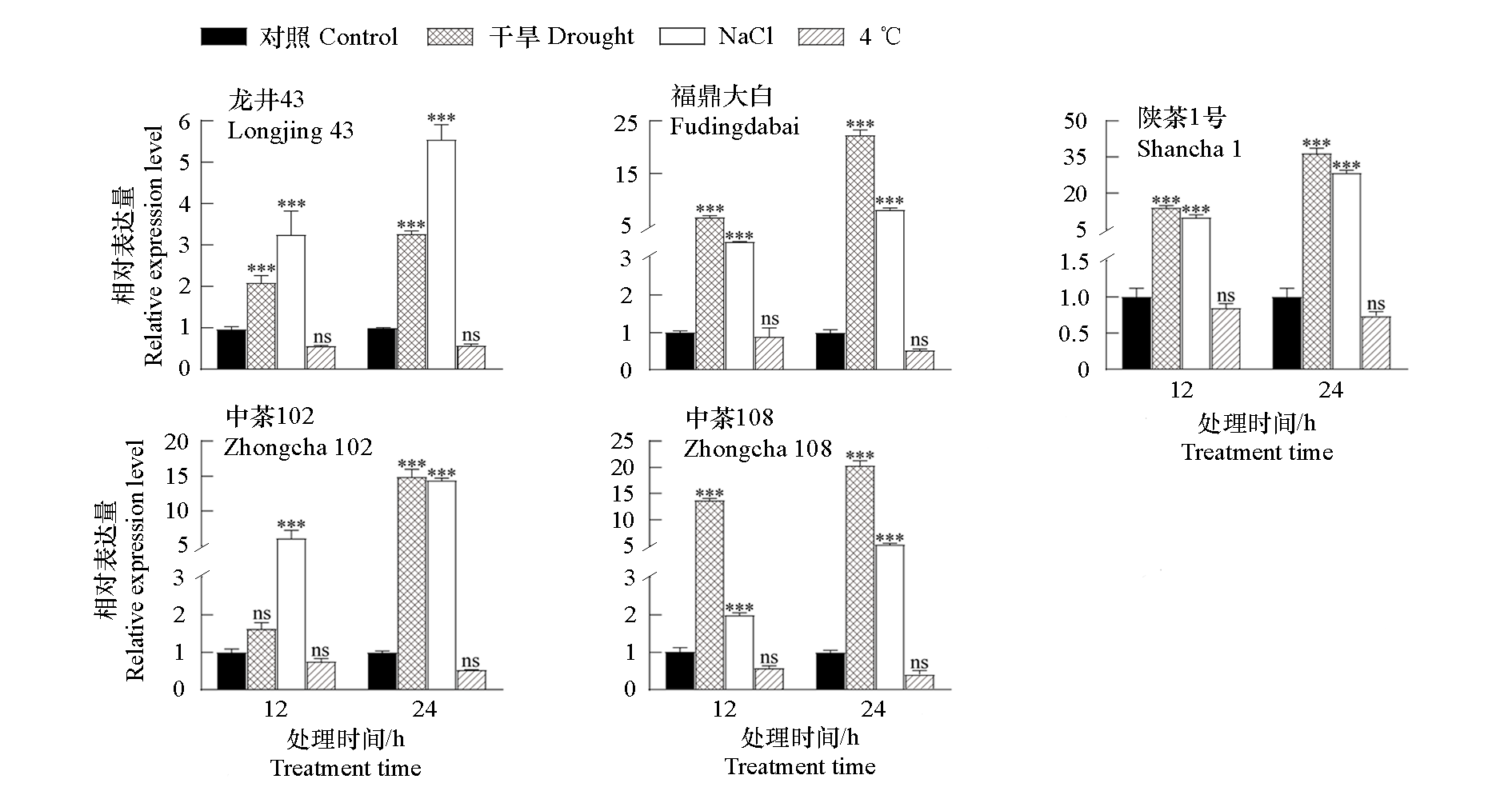
图5 不同茶树品种在干旱、盐(NaCl)、低温(4 ℃)胁迫处理下CsPUB21的表达模式 *、**、***分别表示在P < 0.05、P < 0.01、P < 0.001下的显著差异;ns:非显著差异。下同
Fig. 5 Analysis of CsPUB21 gene expression patterns in different tea cultivars under drought,salt and low temperature stress treatments *,**,*** indicate significant difference as determined via two-way ANOVA at P < 0.05,P < 0.01,P < 0.001,respectively;ns:No significant difference. The same below
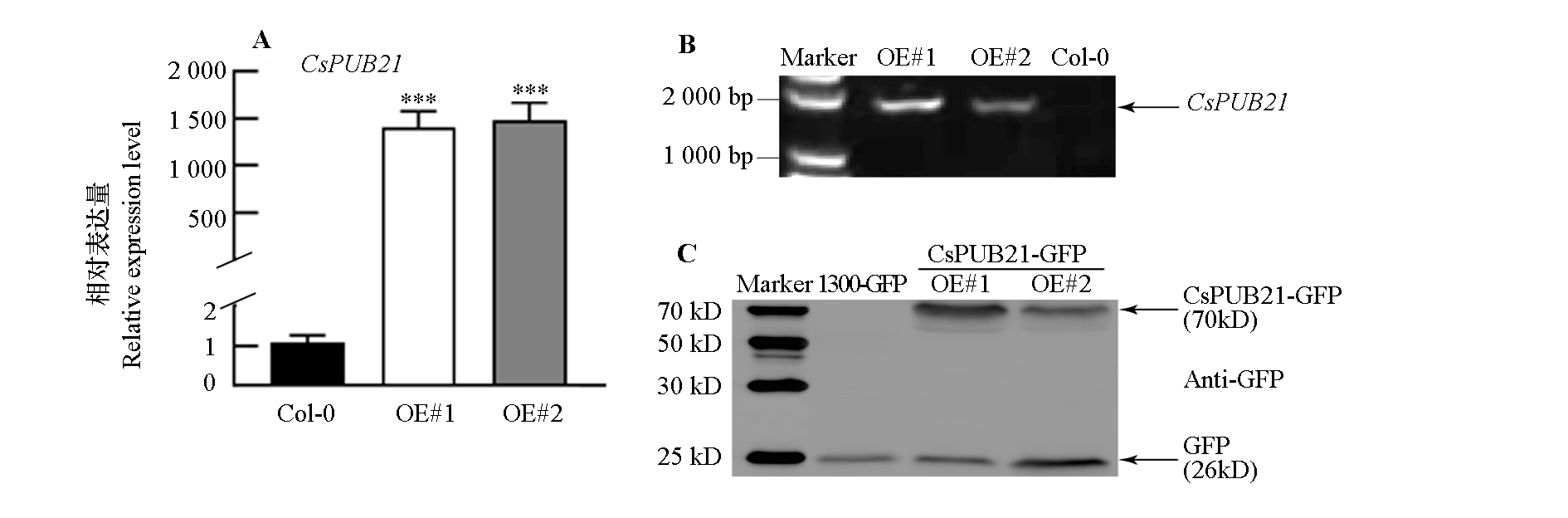
图6 拟南芥过表达CsPUB21株系(OE#1和OE#2)及其野生型(Col-0)的鉴定
Fig. 6 Identification of overexpressed CsPUB21 line(OE#1 and OE#2)and wild type(Col-0)in Arabidopsis thaliana

图7 非生物胁迫下拟南芥野生型(Col-0)和过表达CsPUB21株系(OE#1和OE#2)的表型
Fig. 7 Phenotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana widetype(Col-0)and CsPUB21 overexpressing line(OE#1和OE#2)under abiotic stress
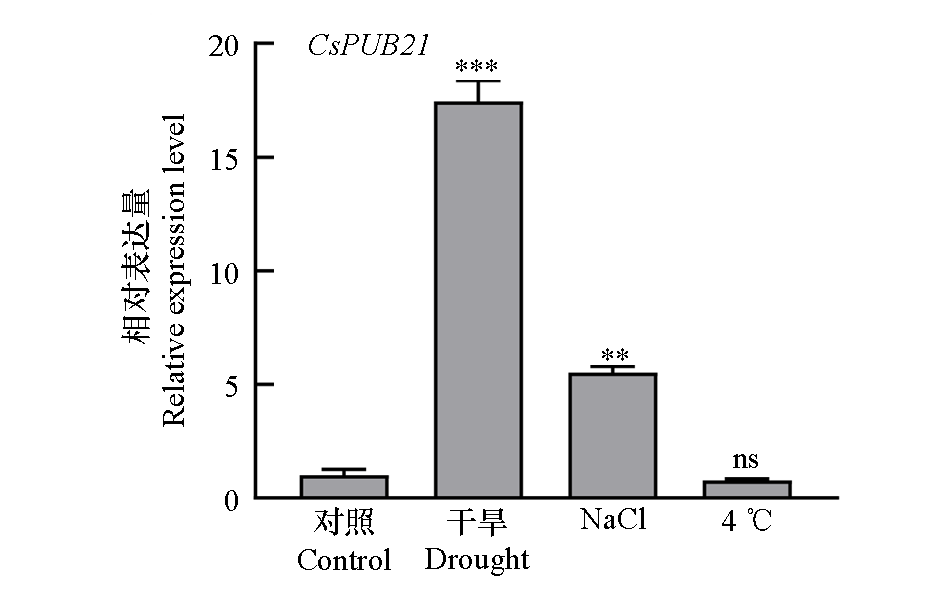
图8 非生物胁迫下拟南芥过表达CsPUB21植株中基因的表达量
Fig. 8 Relative expression of CsPUB21 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana with overexpression lines under different abiotic stress
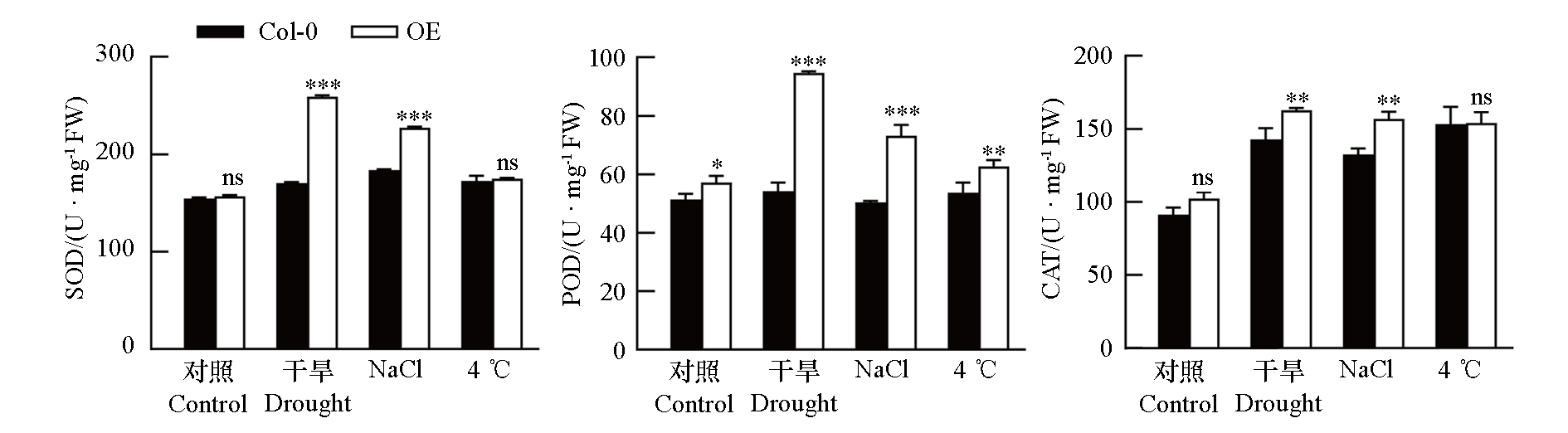
图9 非生物胁迫下拟南芥野生型(Col-0)和过表达CsPUB21株系(OE)中SOD、POD、CAT酶活性
Fig. 9 Activity of SOD,POD and CAT enzyme in Arabidopsis thaliana wild type(Col-0)and CsPUB21 overexpressing lines(OE)under abiotic stress
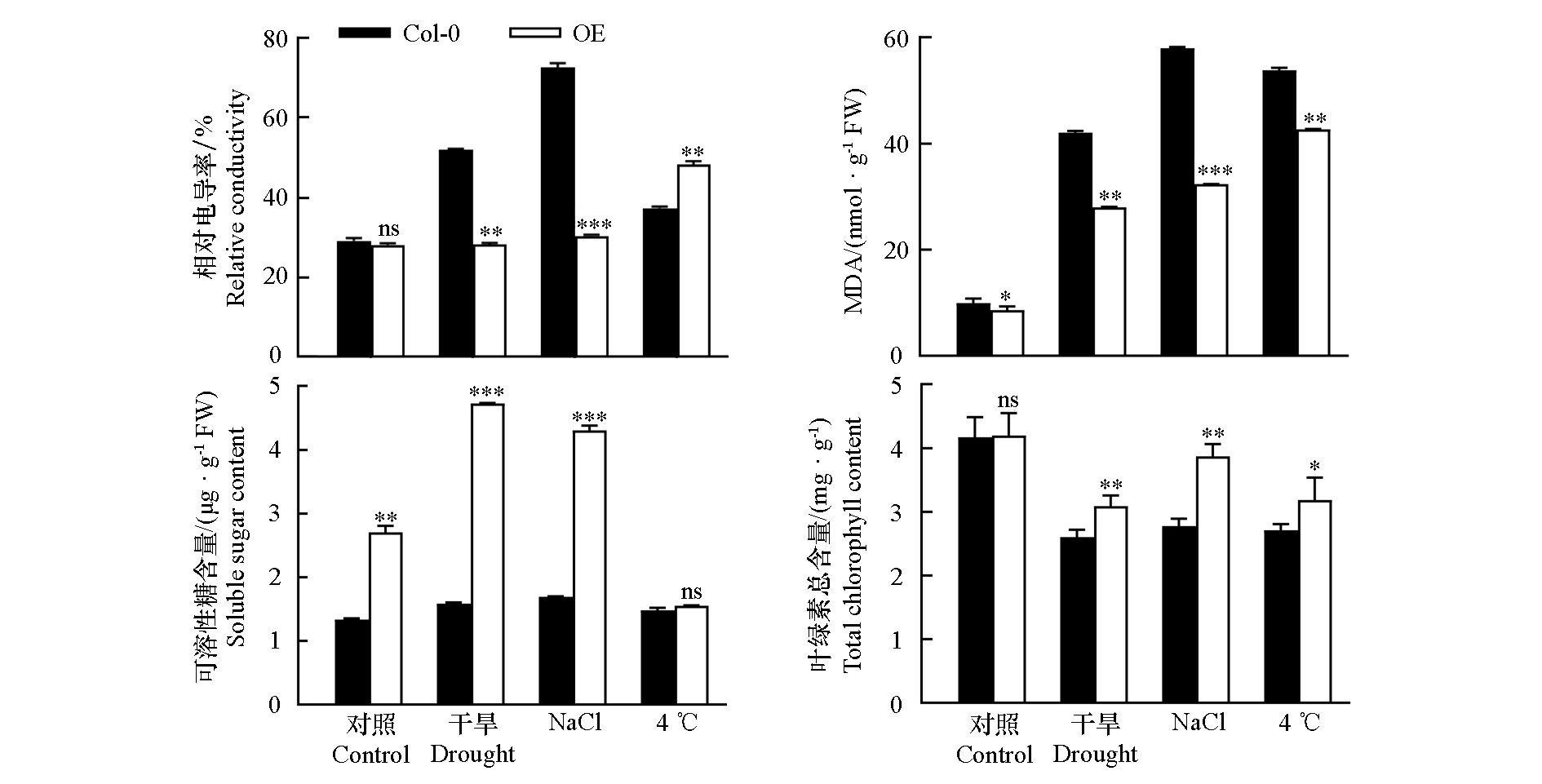
图10 非生物胁迫下拟南芥野生型(Col-0)和过表达CsPUB21株系(OE)的生理指标
Fig. 10 Physiological indices analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana wild type(Col-0)and CsPUB21 overexpressing lines(OE)under abiotic stress
| [1] |
doi: S0168-9452(18)30805-7 pmid: 30348322 |
| [2] |
pmid: 11495788 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
曹佳佳, 熊涛, 潘亚楠, 严嘉麟, 叶凡, 陈佳慧, 赵紫薇, 罗天, 张在宝. 2024. 茶树CRKs基因家族的鉴定与表达分析. 宁夏大学学报(自然科学版),1-11.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
常笑君, 郭玉琼, 王仲, 赵姗姗, 朱晨, 林玉玲, 赖钟雄. 2016. 铁观音茶树RING型E3泛素连接酶基因克隆及其干旱胁迫下的表达分析. 福建农业学报, 31 (8):826-832.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
陈曙, 张彧, 陈卓, 金辉. 2022. 玉米泛素连接酶U-box基因家族的全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 西南农业学报, 35 (3):481-490.
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22455-y pmid: 33846350 |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00245-6 pmid: 12646216 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
姬新颖, 冯启科, 刘志月, 刘凯, 张俊佩, 王红霞. 2022. 核桃JrPUBs(U-box)基因家族鉴定与响应冷温胁迫基因筛选. 河北农业大学学报, 45 (6):68-80.
doi: 10.13320/j.cnki.jauh.2022.0096 |
|
| [15] |
|
|
焦小雨, 吴琼, 刘丹丹, 孙明慧, 王文杰. 2023. 茶树细胞壁关联蛋白激酶基因家族的鉴定与表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 31 (9):1816-1831.
|
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
|
李菲, 何小红, 龚记熠, 乙引. 2018. 番茄基因组中U-box基因家族的鉴定与分析. 分子植物育种, 16 (11):3468-3476.
|
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
李时雨. 2022. 茶树U-box基因家族的鉴定与功能分析[硕士论文]. 贵州: 贵州大学.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
李燕丽, 艾安涛, 胡腾, 吕立堂. 2022. 茶树F-box基因家族的鉴定和表达模式分析. 分子植物育种,1-25.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
莫晓丽, 黄亚辉. 2021. 茶树主要逆境胁迫反应及其适应逆境的生理机制. 茶叶学报, 62 (4):185-190.
|
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00037 pmid: 24600457 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
|
王新超, 王璐, 郝心愿, 李娜娜, 丁长庆, 黄建燕, 杨亚军. 2022. 茶树抗寒机制研究进展与展望. 茶叶通讯, 49 (2):139-148.
|
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0835 URL |
|
王亦栖, 颜爽爽, 余炳伟, 甘雨薇, 邱正坤, 朱张生, 陈长明, 曹必好. 2023. 茄子青枯病抗性相关的E3泛素连接酶基因的筛选及鉴定. 园艺学报, 50 (10):2271-2287.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0835 URL |
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1042/BJ20071568 pmid: 18393940 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
|
岳川, 曹红利, 王赞, 林宏政, 叶乃兴. 2018. 茶树RING-finger型E3泛素连接酶基因CsSDIR的克隆与表达. 应用与环境生物学报, 24 (6):1375-1381.
|
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [1] | 汪芸芸, 周晖, 邱可立, 潘海发, 盛玉, 石佩, 谢庆梅, 陈红莉, 张金云, 李大辉. 桃JMJ组蛋白去甲基化酶家族基因鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 575-590. |
| [2] | 孙廷珍, 疏琴, 马玮, 史玉滋, 张蒙, 向成钢, 薄凯亮, 段颖, 王长林. 印度南瓜GAox家族基因鉴定及其在不同蔓长种质中的表达[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 603-622. |
| [3] | 仝宗军, 韩星, 段昕莲, 刘媛媛, 林俊彬, 甘颖, 陈杰, 谢宝贵, 甘炳成, 严俊杰. 金针菇PRX家族基因鉴定及其在子实体发育过程中的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 337-348. |
| [4] | 贺丹丹, 何宏泰, 王文庭, 周文美, 刘燕敏, 刘骕骦. 甜瓜GolS家族基因鉴定及其响应低温胁迫的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 136-148. |
| [5] | 刘宇香, 韩风庆, 赵鑫雨, 刘玉梅, 李占省, $\boxed{\hbox{方智远}}$. 青花菜侧枝调控基因BoBRC1的克隆及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 1997-2007. |
| [6] | 郭昌权, 李丹琪, 惠馨冉, 郑婧雅, 侯梦璐, 朱永兴. 姜DUF966基因家族成员鉴定与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2031-2047. |
| [7] | 赵佳莹, 曾周婷, 岑欣颖, 施姣淇, 李效贤, 沈晓霞, 俞振明. 铁皮石斛CCO基因家族鉴定及其在花发育中的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2075-2088. |
| [8] | 李娅娣, 王瀚祥, 胡柏耿, 杨辉, 胡新喜, 熊兴耀, 王万兴. 植物根际促生菌缓解园艺作物非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1964-1976. |
| [9] | 王佩云, 李子昂, 白杨, 杨萍, 尹承芃, 李传荣, 张馨文, 宋秀华. ‘海黄’牡丹芳樟醇合酶基因PsTPS14的克隆及功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1273-1283. |
| [10] | 张芷苓, 张媛媛, 林晓蓉, 李斌, 陈忠正. 茶儿茶素合成关键酶基因CsANS和CsLAR的功能鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 804-814. |
| [11] | 刘艳艳, 丁颖, 刘兴华, 郑佳秋, 刘志钦. 辣椒CaSYT1的鉴定及其在疫霉侵染过程中的功能初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 533-544. |
| [12] | 罗新锐, 张晓旭, 王玉萍, 王智, 马媛媛, 周丙月. 普通菜豆Trihelix基因家族鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2775-2790. |
| [13] | 袁青云, 韩昱, 贺巍, 苏会, 班秋艳, 吴春来, 周琼琼, 徐文静, 王丽鸳, 张芬. 茶树CsNPF6.1/6.3基因克隆及ABA转运功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2817-2828. |
| [14] | 杨娟博, 郭丽丽, 卢世雄, 苟惠敏, 王帅珽, 曾宝珍, 毛娟. 草莓FaGH3.17基因的克隆及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2483-2494. |
| [15] | 胡锦瑜, 刘桂芝, 陈兰, 黄梦迪, 苏芹, 谭月萍, 刘硕谦, 田娜. 烟草脆裂病毒介导的茶树VIGS体系的构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2710-2724. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司