
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 2410-2424.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0858
杜丽君, 刘英材, 史妍妍, 汪洋, 李春晖, 何银涛, 王旭, 边传杰, 张满让*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-24
修回日期:2025-03-15
出版日期:2025-09-25
发布日期:2025-09-24
通讯作者:
基金资助:
DU Lijun, LIU Yingcai, SHI Yanyan, WANG Yang, LI Chunhui, HE Yintao, WANG Xu, BIAN Chuanjie, ZHANG Manrang*( )
)
Received:2025-01-24
Revised:2025-03-15
Published:2025-09-25
Online:2025-09-24
摘要:
为探究接种丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)对盐碱胁迫下苹果嫁接苗生长的影响及其作用机理,以1年生‘秦脆’和‘瑞雪’嫁接盆苗(砧木M26)为试材,设置对照(清水灌溉)、盐碱胁迫(0.2 mol · L-1 NaHCO3︰NaCl = 1︰1,SA)、接种AMF(接种根内球囊霉,AMF)和SA + AMF(提前60 d接种AMF,再浇灌SA)处理。SA处理显著降低了‘秦脆’和‘瑞雪’的株高、茎粗、新梢生长量、根面积、根长、根体积以及叶绿素含量和光合速率,而接种AMF缓解了盐碱胁迫对苹果幼苗造成的伤害;与SA处理相比,SA + AMF处理‘秦脆’和‘瑞雪’的抗氧化酶活性显著升高,‘秦脆’叶片的POD、SOD和CAT活性分别升高了28.27%、48.72%和37.01%,而‘瑞雪’叶片POD、SOD和CAT活性分别升高了12.75%、23.37%和16.10%,并且叶片和根系的MDA含量均显著下降;‘秦脆’和‘瑞雪’的TTC还原强度分别升高71.40%和34.29%,根系柠檬酸含量分别增长了105.26%和122.22%,AMF通过促进柠檬酸的分泌来降低根系pH,增强了‘秦脆’和‘瑞雪’的耐盐碱性。盐碱条件下AMF共生降低了叶片中Na+含量,根系和叶片中的K+含量进一步上升,Na+/K+比值显著下降,其中‘秦脆’根系的Na+/K+比值恢复到了对照水平。可见,接种AMF能够促进苗木树势的恢复,增加根系活力、叶绿素含量和光合速率,调节Na+/K+比率来维持离子平衡,减少盐碱胁迫对植株造成的离子毒害,通过增强植株的SOD、POD和CAT活性来减少活性氧的积累,减少植株所受到的氧化损伤。此外,盐碱胁迫下AMF通过增加柠檬酸分泌来平衡根系pH,减少根系受到的pH胁迫,以此来缓解盐碱胁迫对植株造成的生长抑制。
杜丽君, 刘英材, 史妍妍, 汪洋, 李春晖, 何银涛, 王旭, 边传杰, 张满让. 丛枝菌根真菌对苹果品种耐盐碱的影响及缓解机理[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2410-2424.
DU Lijun, LIU Yingcai, SHI Yanyan, WANG Yang, LI Chunhui, HE Yintao, WANG Xu, BIAN Chuanjie, ZHANG Manrang. Effect of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on the Growth and Mechanism of Different Apple Cultivar Under Salt-Alkali Stress[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(9): 2410-2424.
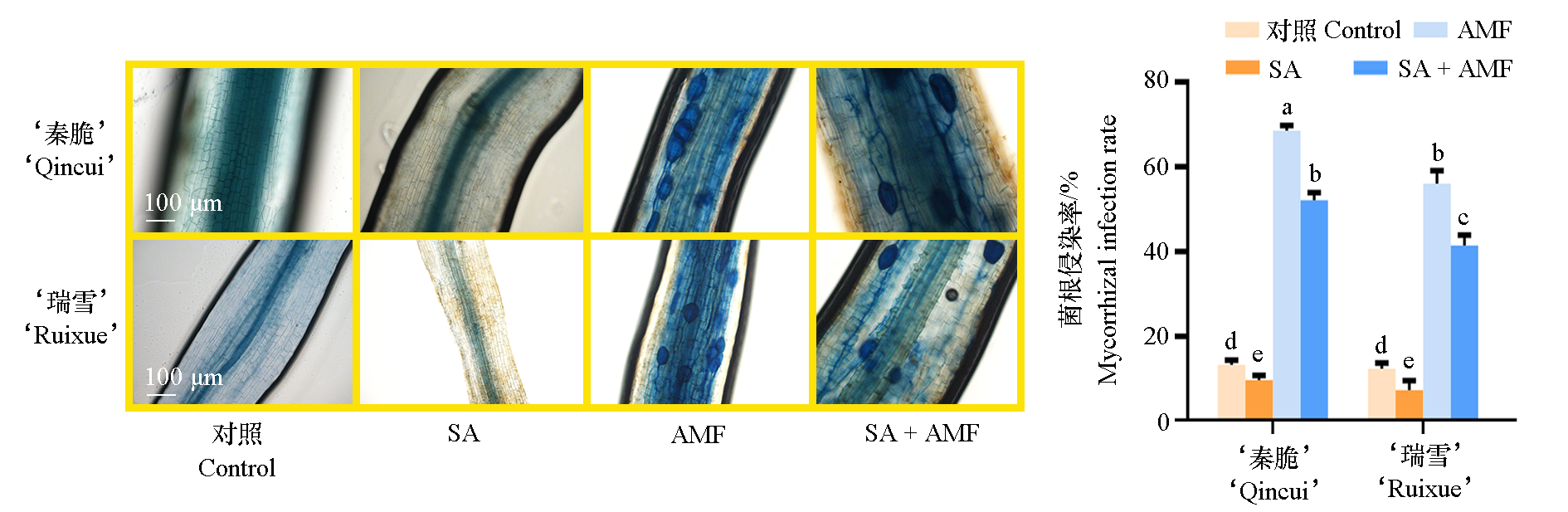
图1 盐碱胁迫下AMF对‘秦脆’和‘瑞雪’苹果嫁接苗根系的侵染情况 SA:0.2 mol · L-1 NaHCO3 + NaCl;AMF:接种根内球囊霉;SA + AMF:AMF接种60 d后再进行SA处理。不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著。下同
Fig. 1 The Phenotype and mycorrhizal infection rate of‘Qincui’and‘Ruixue’apples SA:0.2 mol · L-1 NaHCO3 + NaCl;AMF:Inoculation with Rhizophagus intraradices;SA + AMF:SA treatment applied 60 days after AMF inoculation. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 probability level. The same below
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 株高/cm Height | 茎粗/mm Stem diameter | 新梢生长量/cm Shoot growth | 根面积/cm2 Root area | 根长/cm Root length | 根体积/cm3 Root volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘秦脆’ ‘Qincui’ | 对照Control | 106.0 ± 2.6 b | 7.3 ± 0.3 b | 82.3 ± 2.5 b | 96.1 ± 3.5 b | 3 294.6 ± 74.8 b | 2 630.6 ± 187.5 b |
| SA | 83.0 ± 4.4 d | 6.4 ± 0.2 c | 71.3 ± 2.3 c | 77.1 ± 1.3 d | 2 672.1 ± 180.5 d | 1 924.0 ± 155.8 c | |
| AMF | 120.7 ± 5.6 a | 8.1 ± 0.5 a | 100.7 ± 2.1 a | 117.1 ± 5.3 a | 3 509.4 ± 110.3 a | 3 061.3 ± 161.4 a | |
| SA + AMF | 97.0 ± 5.2 c | 7.2 ± 0.3 b | 80.3 ± 2.5 b | 83.6 ± 2.5 c | 3 056.6 ± 19.1 c | 2 437.3 ± 231.1 b | |
| ‘瑞雪’ ‘Ruixue’ | 对照Control | 81.0 ± 1.7 b | 7.1 ± 0.2 c | 73.9 ± 2.0 b | 91.4 ± 0.6 b | 3 060.0 ± 122.6 b | 2 592.3 ± 133.2 b |
| SA | 70.0 ± 1.7 d | 6.3 ± 0.2 d | 66.6 ± 1.4 c | 72.7 ± 2.2 c | 2 551.1 ± 174.8 d | 1 914.3 ± 124.1 c | |
| AMF | 89.0 ± 3.6 a | 8.1 ± 0.2 a | 98.2 ± 0.2 a | 102.9 ± 3.0 a | 3 441.2 ± 136.5 a | 3 030.0 ± 123.1 a | |
| SA + AMF | 77.7 ± 1.5 c | 7.6 ± 0.2 b | 71.3 ± 0.6 b | 91.7 ± 8.2 b | 2 706.4 ± 272.3 c | 2 347.7 ± 186.9 b |
表1 盐碱胁迫20 d后‘秦脆’和‘瑞雪’苹果嫁接苗的生理指标
Table 1 Physiological indexes of‘Qincui’and‘Ruixue’apple grafted seedings after 20 days under salt-alkali treatment
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 株高/cm Height | 茎粗/mm Stem diameter | 新梢生长量/cm Shoot growth | 根面积/cm2 Root area | 根长/cm Root length | 根体积/cm3 Root volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘秦脆’ ‘Qincui’ | 对照Control | 106.0 ± 2.6 b | 7.3 ± 0.3 b | 82.3 ± 2.5 b | 96.1 ± 3.5 b | 3 294.6 ± 74.8 b | 2 630.6 ± 187.5 b |
| SA | 83.0 ± 4.4 d | 6.4 ± 0.2 c | 71.3 ± 2.3 c | 77.1 ± 1.3 d | 2 672.1 ± 180.5 d | 1 924.0 ± 155.8 c | |
| AMF | 120.7 ± 5.6 a | 8.1 ± 0.5 a | 100.7 ± 2.1 a | 117.1 ± 5.3 a | 3 509.4 ± 110.3 a | 3 061.3 ± 161.4 a | |
| SA + AMF | 97.0 ± 5.2 c | 7.2 ± 0.3 b | 80.3 ± 2.5 b | 83.6 ± 2.5 c | 3 056.6 ± 19.1 c | 2 437.3 ± 231.1 b | |
| ‘瑞雪’ ‘Ruixue’ | 对照Control | 81.0 ± 1.7 b | 7.1 ± 0.2 c | 73.9 ± 2.0 b | 91.4 ± 0.6 b | 3 060.0 ± 122.6 b | 2 592.3 ± 133.2 b |
| SA | 70.0 ± 1.7 d | 6.3 ± 0.2 d | 66.6 ± 1.4 c | 72.7 ± 2.2 c | 2 551.1 ± 174.8 d | 1 914.3 ± 124.1 c | |
| AMF | 89.0 ± 3.6 a | 8.1 ± 0.2 a | 98.2 ± 0.2 a | 102.9 ± 3.0 a | 3 441.2 ± 136.5 a | 3 030.0 ± 123.1 a | |
| SA + AMF | 77.7 ± 1.5 c | 7.6 ± 0.2 b | 71.3 ± 0.6 b | 91.7 ± 8.2 b | 2 706.4 ± 272.3 c | 2 347.7 ± 186.9 b |
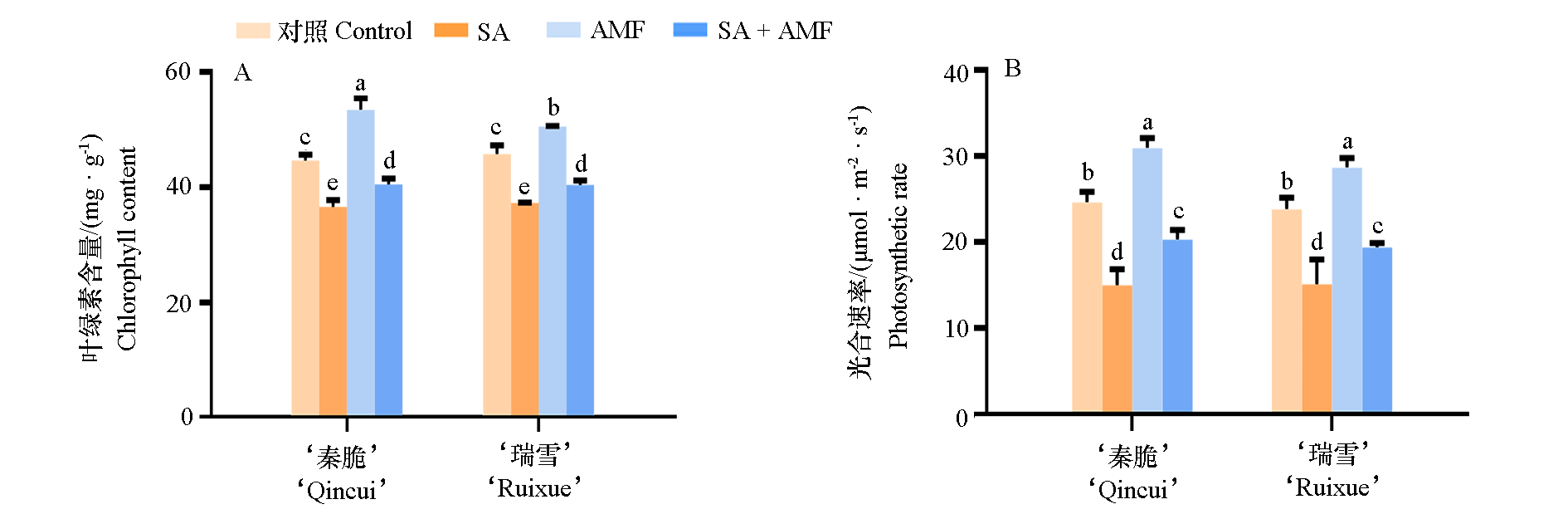
图3 盐碱胁迫20 d后‘秦脆’和‘瑞雪’苹果的叶片叶绿素相对含量(A)和光合速率(B)
Fig. 3 Chlorophyll content(A)and photosynthetic rate(B)of‘Qincui’and‘Ruixue’apple after 20 days under salt-alkali treatment
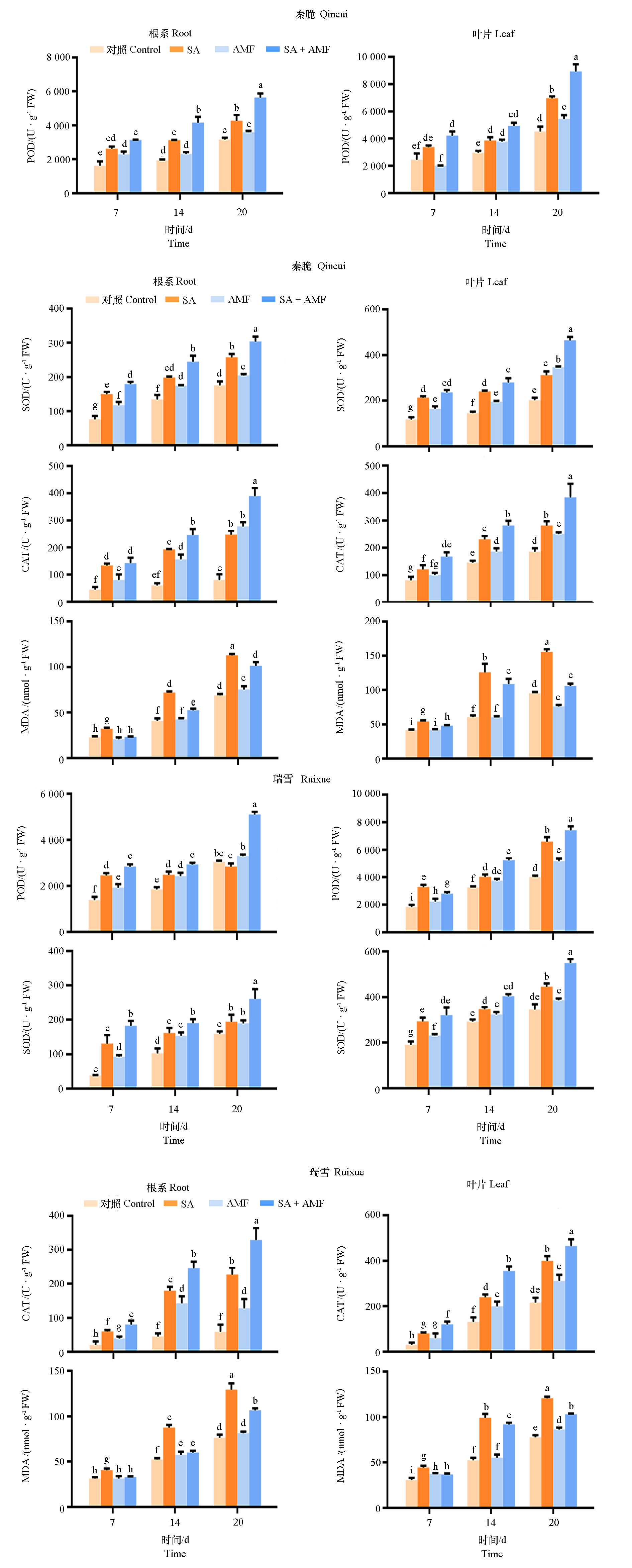
图6 盐碱处理20 d后‘秦脆’和‘瑞雪’苹果POD、SOD、CAT活性和MDA含量
Fig. 6 POD,SOD,CAT activities and MDA content in‘Qincui’and‘Ruixue’after 20 days under salt-alkali treatment

图7 盐碱胁迫后苹果嫁接苗根系TTC染色 根尖颜色越红表示根系越有活力
Fig. 7 TTC staining of apple seedlings under saline-alkali stress The redder the root tip color indicates the more active of root

图10 盐碱胁迫下AMF对‘秦脆’和‘瑞雪’苹果Na+含量、K+含量、Na+︰K+比率的影响
Fig. 10 Effects of saline-alkali stress and AMF on the Na+ content,K+ content and Na+︰K+ ratio of‘Qincui’and‘Ruixue’
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
高华, 赵政阳. 2016. 苹果新品种——瑞雪. 中国果业信息, 33 (4):57.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0348 |
|
李敖, 郑旭, 吴承勖, 聂瑞宁, 姬新颖, 唐佳莉, 张俊佩. 2025. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下核桃幼苗生长及生理的影响. 园艺学报, 52 (2):423-438.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0348 |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1036 |
|
梁圣敏, 张菲, 吴强盛. 2023. 丛枝菌根真菌通过调节枳根系多胺提高抗旱性. 园艺学报, 50 (12):2680-2688.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1036 |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
刘燕湘, 杨海萌, 赖燕芬, 郑杰娜, 张福平. 2013. 杨桃果实过氧化氢酶活性研究. 南方农业学报, 44 (2):304-307.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
陆建增, 周丽颜, 黄馨仪, 吴凤芝, 高丹美. 2024. 番茄碳库强度对其与伴生分蘖洋葱和AMF的关系及钾吸收的影响. 园艺学报, 51 (11):1-13.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03234-7 pmid: 38764051 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
孙志娟, 刘文杰, 郑晓东, 袭祥利, 马长青, 刘晓丽, 王彩虹, 田义轲. 2023. 褪黑素对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及其机制. 园艺学报, 50 (8):1697-1710.
|
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
|
翟书林, 刘晓琳, 姚璐莹, 詹文晶, 高文俊. 2023. 混合盐碱下接种丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)对紫花苜蓿根系构型的影响. 饲料研究, 46 (21):90-94.
|
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0499 |
|
郑晓东, 袭祥利, 李玉琪, 孙志娟, 马长青, 韩明三, 李少旋, 田义轲, 王彩虹. 2022. 油菜素内酯对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及调控机理研究. 园艺学报, 49 (7):1401-1414.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0499 |
|
| [49] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0368 |
|
邹养军, 马锋旺, 符轩畅, 李翠英, 安贵阳, 李明军, 李超, 党志明. 2019. 晚熟苹果新品种‘秦脆’. 园艺学报, 46 (5):1011-1012.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0368 |
| [1] | 张宗营, 王 平, 王 楠, 马明德, 刘文军, 邹 琦, 徐月华, 陈晓流, 毛志泉, 陈学森. 苹果紫红色芽变新品种‘八仙新富’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 1-2. |
| [2] | 朱 钰, 刘肖烽, 周 佳, 李 静, 王 强. 苹果新品种‘华优宝丰’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 3-4. |
| [3] | 徐功勋, 闫帅, 何美琦, 马怀宇, 吕德国, 秦嗣军, 程存刚, 赵德英. 苹果抗寒性研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2021-2045. |
| [4] | 赵玉璞, 白一涵, 侯赛赛, 蒲子天, 乜兰春, 李青云, 王鑫鑫. 丛枝菌根真菌缓解设施蔬菜土壤连作障碍研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2166-2186. |
| [5] | 陈学森, 王楠, 张宗营, 张淑辉, 刘文军, 邹琦, 于蕾, 张静, 姜远茂, 胡大刚, 李媛媛, 毛志泉. 富营养强风味轻简化宜机化苹果育种研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1661-1676. |
| [6] | 田玉凤, 马松亚, 杨安, 韩晓蕾, 张彩霞. 苹果砧木B9再生体系的建立与优化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 947-958. |
| [7] | 段青青, 韩梅梅, 王友平, 常培培, 谭月强, 张自坤. 外源褪黑素影响盐碱复合胁迫下西瓜种子萌发的综合评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 1020-1036. |
| [8] | 程小改, 万源, 林琭, 谢鹏, 李志强, 李谧, 王鹏鹏, 牛自勉. 苹果开心树形树干高度对不同冠层部位叶片光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 671-692. |
| [9] | 李敖, 郑旭, 吴承勖, 聂瑞宁, 姬新颖, 唐佳莉, 张俊佩. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下核桃幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 423-438. |
| [10] | 李超楠, 李璐, 高丹蕾, 乔红雍, 袁涛. 原产地与引种地大花黄牡丹根系和根际土壤的AMF群落差异[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 467-480. |
| [11] | 史兴秀, 冯贝贝, 闫鹏, 耿文娟, 朱玛孜拉·沙尔山木汗. ‘王林’苹果早期水心病发生过程中的相关生理变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 171-184. |
| [12] | 邱辉, 朱德娟, 张永乐, 高玉洁, 李柳, 王国平, 洪霓. ACLSV外壳蛋白与梨两种E3泛素连接酶互作及亚细胞定位[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1715-1727. |
| [13] | 刘英浩, 李允, 吕伟静, 陈冉, 姜伟涛, 尹承苗, 毛志泉, 王艳芳. 不同温度烧制的生物炭对苹果连作土壤真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1853-1867. |
| [14] | 李旭娇, 吕齐, 姚东东, 赵丰云, 王小非, 于坤. ‘烟富3’苹果不同砧木嫁接对其15N–尿素吸收利用的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1868-1880. |
| [15] | 田雯, 李子琛, 王霖, 王大江, 王昆, 孙思邈, 王广艺, 刘昭, 路翔, 冯建荣, 高源. 苹果重要性状全基因组关联分析研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1565-1579. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司