
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1463-1476.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0160
收稿日期:2025-03-19
修回日期:2025-05-20
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-06-20
通讯作者:
基金资助:
LI Meiqing, LUO Sifei, JIA Yaohao, WANG Weigui, and SUN Jin*( )
)
Received:2025-03-19
Revised:2025-05-20
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-06-20
摘要:
本研究以‘中农12号’黄瓜(Cucumis sativus L.)为材料,分析黄瓜CsMDC的表达情况,进一步验证其在叶绿素降解过程中的作用。对CsMDC蛋白的理化性质进行分析预测,发现其与同科同属植物甜瓜(Cucumis melo L.)相似度最高,其次是同科异属植物冬瓜(Benincasa hispida Cogn.)、南瓜(Cucurbita moschata Duch.)、笋瓜(Cucurbita maxima Duch.)等,与其他科植物的相似度较低,表明MDC具有明显的种属特征;qRT-PCR分析不同外源生长调节剂处理与非生物胁迫下CsMDC的表达模式,其具有不同的应答特征,该基因在衰老组织中相对表达量最高;构建CsMDC过表达烟草进行功能验证,过表达烟草叶绿素含量、干鲜比、净光合速率等均显著低于野生型,活性氧含量显著高于野生型,qRT-PCR结果显示过表达烟草在受到黑暗胁迫后光系统蛋白基因表达量显著下降,叶绿素降解相关基因表达量显著提高。以上说明黄瓜CsMDC与叶绿素降解密切相关,受不同激素和非生物胁迫诱导,正向调控叶绿素降解及植物衰老。
李媚晴, 罗思菲, 贾曜豪, 王维贵, 孙锦. 黄瓜脱镁螯合酶基因CsMDC表达分析及其调控叶绿素降解的功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1463-1476.
LI Meiqing, LUO Sifei, JIA Yaohao, WANG Weigui, and SUN Jin. Expression Analysis of the Cucumber Mg-Dechelatase Gene CsMDC and Functional Verification of Its Role in Regulating Chlorlorophyll Degradation[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1463-1476.
| 用途Application | 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CsMDC全长PCR PCR of CsMDC full length | CsMDC-F | TTAAACCGATCACAAACC |
| CsMDC-R | AGGGCAGTCAATAAAATG | |
| CsMDC实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR of CsMDC | qPCR-CsMDC-F | CGCAAAGAACTCCCTGTGGT |
| qPCR-CsMDC-R | AATGCAAGTAATTTGCTGATAGTGT | |
| CsAction实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR of CsActin | CsActin-F | CAGGAATCCACGAAACTACT |
| CsActin-R | AGACCCTCCAATCCAAACAC |
表1 CsMDC基因PCR及qRT-PCR引物
Table 1 The primers of CsMDC gene of PCR or qRT-PCR
| 用途Application | 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CsMDC全长PCR PCR of CsMDC full length | CsMDC-F | TTAAACCGATCACAAACC |
| CsMDC-R | AGGGCAGTCAATAAAATG | |
| CsMDC实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR of CsMDC | qPCR-CsMDC-F | CGCAAAGAACTCCCTGTGGT |
| qPCR-CsMDC-R | AATGCAAGTAATTTGCTGATAGTGT | |
| CsAction实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR of CsActin | CsActin-F | CAGGAATCCACGAAACTACT |
| CsActin-R | AGACCCTCCAATCCAAACAC |
| 基因Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′)Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′)Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| NtRbcL | GTCCCCTGTTGGGATGTACTATT | TGTGAGTTCACGTTCTCATCATC |
| NtRbcS | TCATTGGATTCGACAACGTG | CACAACCCCTAAAGACAAGACA |
| NtLhcb1 | GCTGCTACAATGGCTCTTT | TGGCGACAGTCTTTCTCA |
| NtLhcb2 | TCCGAGCAAACTCCATCT | CAGTGTCCCATCCGTAA |
| NtLhcb4 | GAGATGGGCTATGTTGGC | TGGAGAATGGGAGTGGTT |
| NtNYC | TAAACAACGCTGGGACAA | TAAACAACGCTGGGACAA |
| NtRCCR | CTGTGGAGAATCGGCTTGG | ACCTGGGAAGAGGAGTGGC |
| NtActin | CATTGGCGCTGAGAGATTCC | GCAGCTTCCATTCCGATCA |
表2 叶绿素降解相关基因qPCR引物
Table 2 qPCR primers for the Chl. degredation genes of tobacco
| 基因Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′)Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′)Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| NtRbcL | GTCCCCTGTTGGGATGTACTATT | TGTGAGTTCACGTTCTCATCATC |
| NtRbcS | TCATTGGATTCGACAACGTG | CACAACCCCTAAAGACAAGACA |
| NtLhcb1 | GCTGCTACAATGGCTCTTT | TGGCGACAGTCTTTCTCA |
| NtLhcb2 | TCCGAGCAAACTCCATCT | CAGTGTCCCATCCGTAA |
| NtLhcb4 | GAGATGGGCTATGTTGGC | TGGAGAATGGGAGTGGTT |
| NtNYC | TAAACAACGCTGGGACAA | TAAACAACGCTGGGACAA |
| NtRCCR | CTGTGGAGAATCGGCTTGG | ACCTGGGAAGAGGAGTGGC |
| NtActin | CATTGGCGCTGAGAGATTCC | GCAGCTTCCATTCCGATCA |
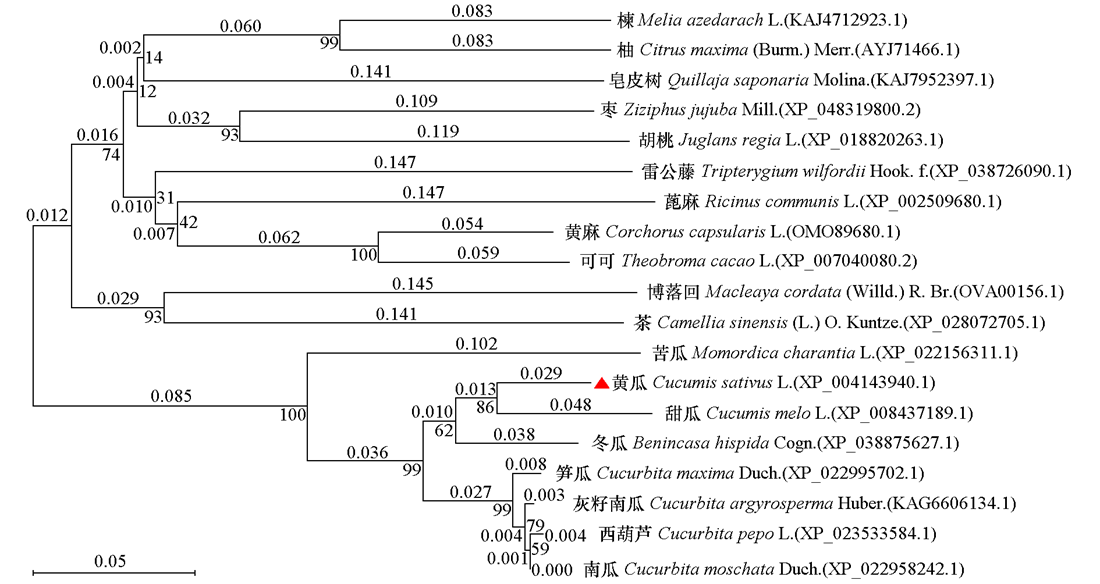
图2 19个物种MDC氨基酸序列系统进化关系 位于横线上方的小数代表进化分支长度,节点附近的整数为自展值
Fig. 2 Evolutionary relationships of MDC amino acid sequences of 19 species The decimal above the horizontal line represents the length of the evolutionary branch,and the integer near the node is the bootstrap value
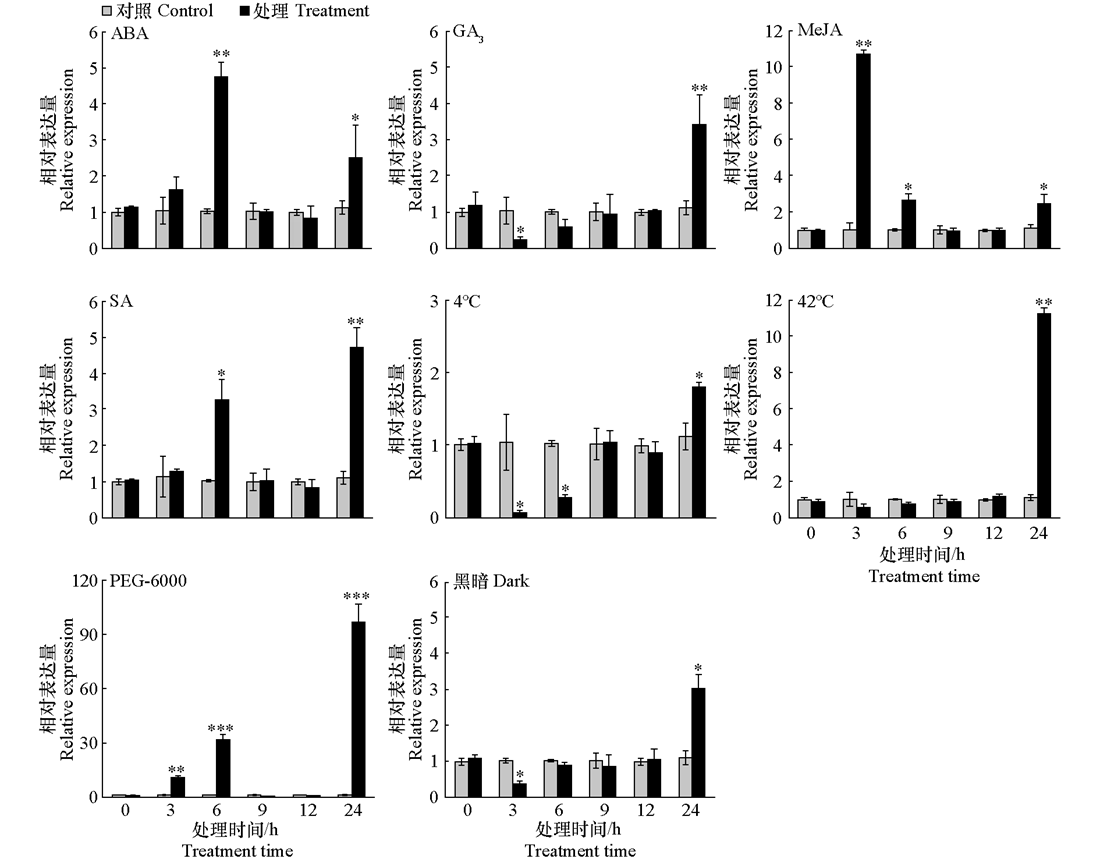
图3 黄瓜叶片CsMDC在不同外源植物生长调节剂处理与非生物胁迫下的qRT-PCR分析 对照:叶面喷施蒸馏水;外源ABA、GA3、SA和MeJA处理:分别在叶面喷施100 μmoL · L-1的ABA、GA3、SA和MeJA;干旱处理:20 %(w/v)聚乙二醇(PEG-6000);高温处理:42 ℃;低温处理:4 ℃;黑暗处理:光照强度0 μmoL · m-2 · s-1。使用2-ΔΔCT方法计算基因的相对表达量(Livak & Schmittgen,2001),经正态性检验证明数据符合正态性,采用独立样本t检验进行显著性分析,* P < 0.05,** P < 0.01,*** P < 0.001
Fig. 3 qRT-PCR analysis of CSMDC in cucumber leaves under different exogenous plant growth regulator treatments and abiotic stresses Control group:foliar spray with distilled water;Exogenous ABA,GA3,SA,and MeJA treatments:foliar spray with 100 μmoL · L⁻¹ ABA,GA3,SA,and MeJA,respectively;Drought treatment:20%(w/v)polyethylene glycol(PEG-6000);High temperature treatment:42 ℃;Low temperature treatment:4 ℃;Darkness treatment:Light intensity 0 μmoL · m-2 · s-1. Relative expression was calculated using the 2-∆∆CTmethod(Livak et al.,2001). Independent samples t-test was applied for significance analysis after confirming normality of the data through normality tests. * P < 0.05,** P < 0.01,*** P < 0.001
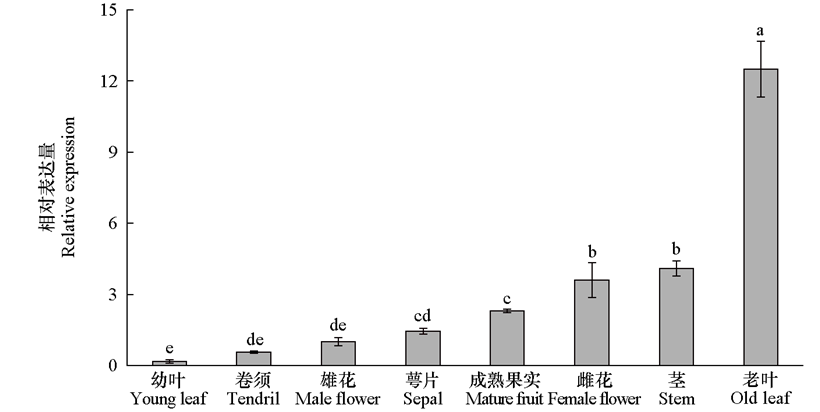
图4 黄瓜不同组织中CsMDC的相对表达量 使用2-∆∆CT方法计算基因的相对表达量(Livak & Schmittgen,2001),经正态性检验证明数据符合正态性,采用单因素ANOVA和Duncan’s检验进行显著性分析,不同小写字母表示有显著差异,P < 0.05,下同
Fig. 4 Tissue-specific expression of CsMDC in cucumber Relative expression was calculated using the 2-∆∆CT method. Normality tests confirmed that the data met the normality assumption. Statistical significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple range test and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences,P < 0.05,the same below
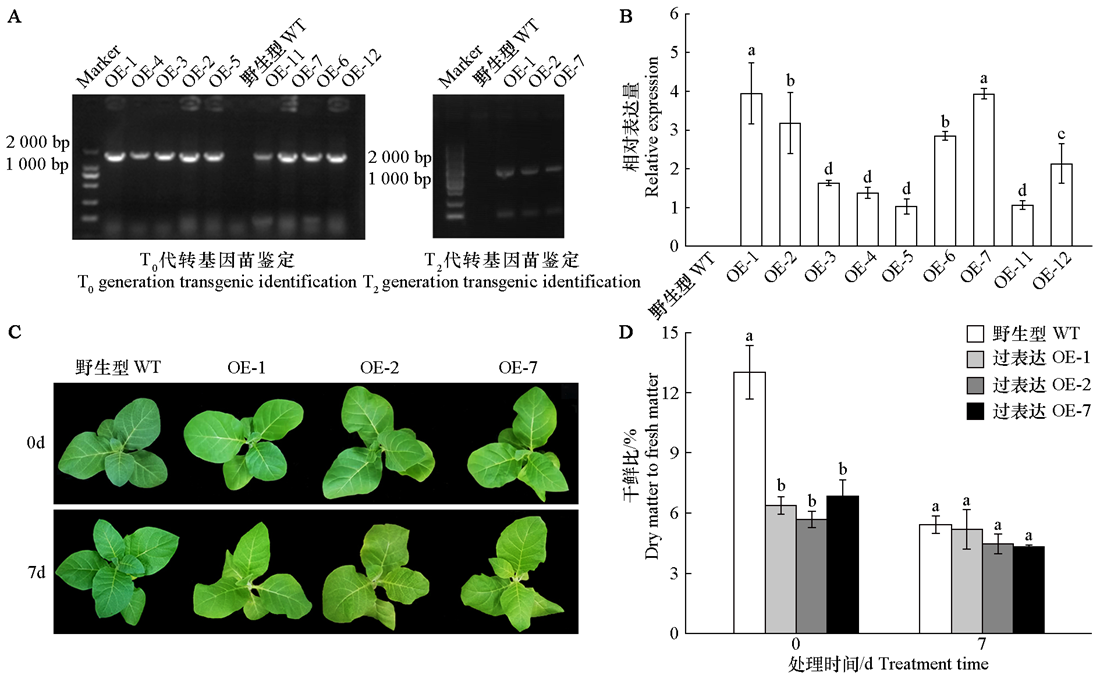
图5 黄瓜CsMDC转基因烟草的PCR鉴定(A)、qRT-PCR鉴定(B)、黑暗处理前后的烟草表型图(C)和干鲜比(D)
Fig. 5 The PCR analysis(A),qRT-PCR analysis(B),phenotype images of tobacco before and after dark treatment(C),and dry weight to fresh weight ratio(D)of cucumber CsMDC transgenic tobacco
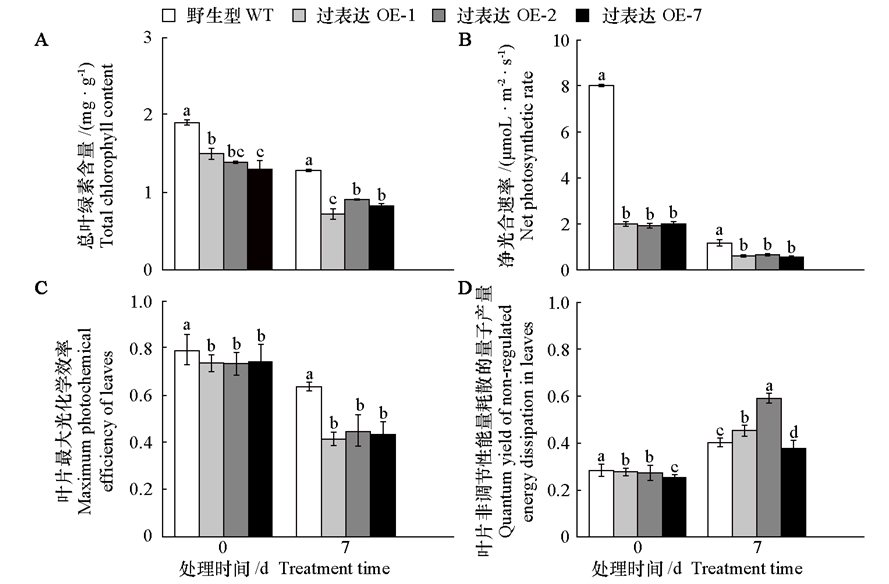
图6 黑暗处理前后黄瓜CsMDC转基因烟草植株的叶绿素含量、净光合速率、叶片最大光化学效率[Fv/Fm]和非调节性能量耗散的量子产量[Y(NO)]
Fig. 6 Chlorophyll content,net photosynthetic rate,maximum photochemical efficiency of leaves,and quantum yield of non-regulated energy dissipationin cucumber CsMDC transgenic tobacco plants before and after dark treatment
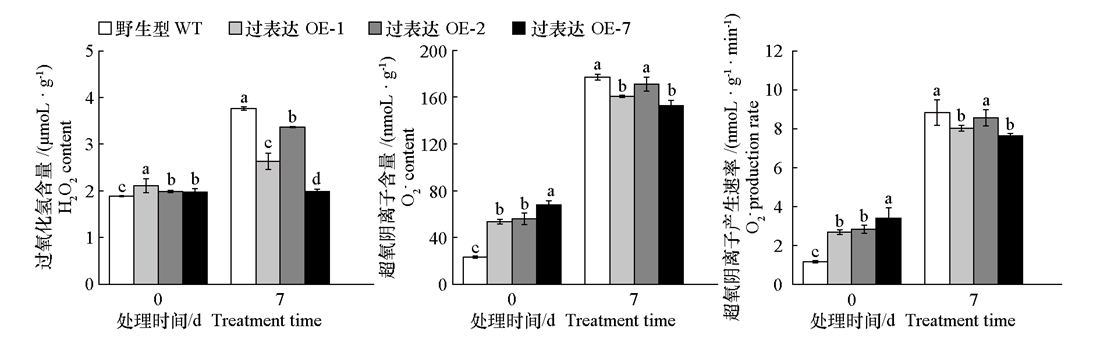
图7 黑暗处理前后黄瓜CsMDC转基因烟草的过氧化氢含量、超氧阴离子含量和超氧阴离子产生速率
Fig. 7 H2O2 content,O2- content,and O2- production rate in cucumber CsMDC transgenic tobacco before and after dark treatment
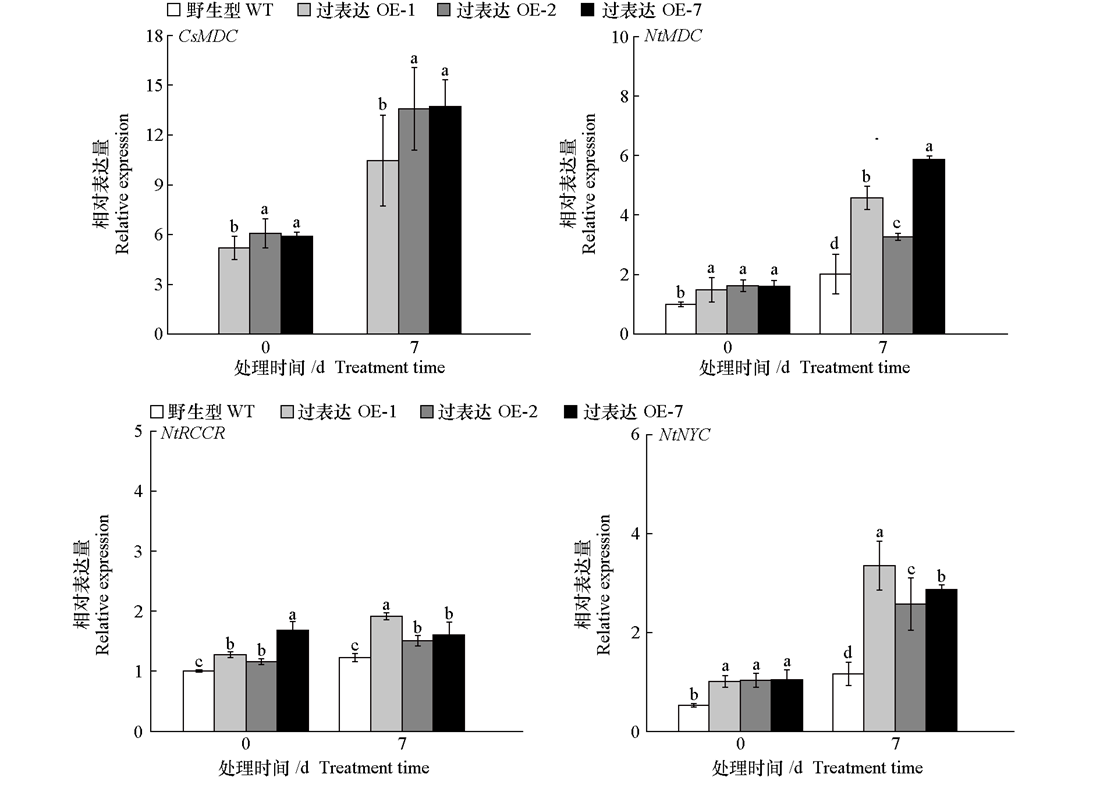
图8 黑暗处理前后黄瓜CsMDC转基因烟草叶绿素降解相关基因的相对表达量 野生型烟草不含CsMDC基因,因此图中不显示
Fig. 8 Relative expression of chlorophyll degradation-related genes in cucumber CsMDC transgenic tobacco before and after dark treatment Wild type tobacco lacks the CsMDC gene,resulting in no detectable signal in this figure
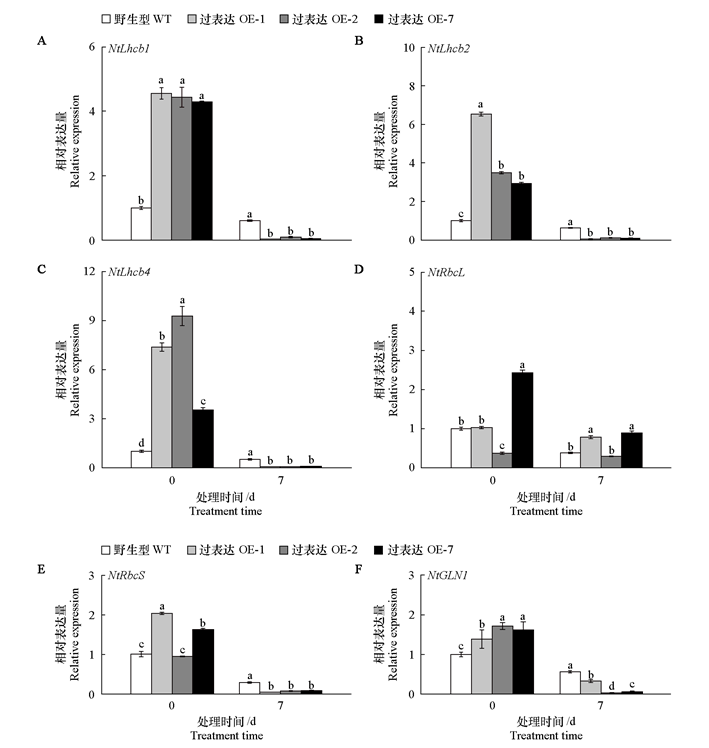
图9 黑暗处理前后黄瓜CsMDC转基因烟草光系统相关基因的相对表达量 Lhcb1、Lhcb2、Lhcb4、RbcL和RbcS:光系统蛋白基因;GLN1:谷氨酰胺合成酶基因,该基因编码蛋白通过氮同化和光呼吸调控间接支持光合作用(Ji et al.,2019)
Fig. 9 Relative expression of photosystem-related genes in cucumber CsMDC transgenic tobacco before and after dark treatment Lhcb1、Lhcb2、Lhcb4、RbcL and RbcS:Photosystem protein genes;GLN1:Glutamine synthetase gene,which encodes a protein that indirectly supports photosynthesis through nitrogen assimilation and photorespiration regulation
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.118430 pmid: 18359841 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1007/s00122-008-0768-5 pmid: 18427769 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2010.07.011 pmid: 20727617 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2016.11.001 |
|
丁跃, 吴刚, 郭长奎. 2016. 植物叶绿素降解机制研究进展. 生物技术通报, 32 (11):1-9.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2016.11.001 |
|
| [6] |
|
|
高亚新, 刘益克, 李恭峰, 李宁, 李青云. 2023. 新型稀土转光膜对塑料大棚早春茬黄瓜生长的影响. 现代农业科技,10:38-42.
|
|
| [7] |
|
|
顾兴芳, 方秀娟, 张天明, 张圣平, 李竹梅, 徐彩青. 2003. 黄瓜新品种中农12号的选育. 中国蔬菜,(5):30-31.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
关锦毅, 郝再彬, 张达, 王秀丽. 2009. 叶绿素提取与检测及生物学功效的研究进展. 东北农业大学学报, 40 (12):130-134.
|
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
|
李中海, 郭永峰, 任国栋, 张可伟, 缪颖, 郭红卫. 2023. 叶片衰老研究进展. 植物生理学报, 59 (9):1627-1656.
|
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [15] |
|
|
骆亮仲, 李卓蔚, 周浓, 夏李, 付旭娟, 黄梅, 郭冬琴. 2023. 滇重楼叶片和花萼的SPAD值与叶绿素含量的相关性分析. 南方农业, 17 (3):155-161,166.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
马林. 2007. 植物衰老期间生理生化变化的研究进展. 生物学杂志, 24 (3):12-15.
|
|
| [17] |
pmid: 11557069 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
戎红, 李美茹, 陈雅平, 吴国江, 姜华斌. 2011. 水稻永绿色基因超表达和突变对其叶片氮碳代谢若干指标的影响. 热带亚热带植物学报, 19 (5):407-411.
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
滕珂. 2020. 日本结缕草滞绿基因(ZjSGR)的功能研究[博士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学.
|
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru037 pmid: 24600017 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0799 |
|
王峰, 闫家榕, 陈雪玉, 姜程浩, 孟思达, 刘玉凤, 许涛, 齐明芳, 李天来. 2019. 光调控植物叶绿素生物合成的研究进展. 园艺学报, 46 (5):975-994.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0799 |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0128 |
|
叶玙璠, 王誉洁, 傅前媛, 王璐, 郝心愿, 丁长庆, 王新超, 曹红利, 李娜娜. 2024. 茶树镁离子螯合酶H亚基基因CsChlH的克隆及其表达分析. 园艺学报, 51 (1):91-102.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0128 |
|
| [30] |
|
|
郑赟, 尹艺臻, 温宏伟, 王鹏, 李贵全. 2020. 大豆滞绿(stay-green)突变体诱变后代生理指标及品质分析. 中国农业大学学报, 25 (9):27-35.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
朱金龙, 吕勇, 叶坤国. 2021. 设施栽培黄瓜生理性病害诊断与防治. 现代农业科技,(9):115-117.
|
| [1] | 胡继军, 邰连赛, 王天宇, 周 琦, 金海军. 黄瓜新品种‘短把申青’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 125-126. |
| [2] | 李强, 顾丽嫱, 窦雅静, 高永利, 赵玉倩, 陆亚茹, 宋小明. 黄瓜新品种‘多喜一号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1681-1682. |
| [3] | 马豫皖, 刘澳, 刘向东, 张雅婧, 董炫克, 李玉帆, 陈己任. 月季‘月月红’RcRAP2.7的克隆及其在非生物胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 921-932. |
| [4] | 王瑞, 吴红霏, 张长远, 曹海顺, 谭德龙, 郭金菊, 王云龙, 王茹芳, 袁余, 吴廷全. CsPUB54与PmRXLR1互作负向调控黄瓜对疫病的抗性[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 591-602. |
| [5] | 汪芸芸, 周晖, 邱可立, 潘海发, 盛玉, 石佩, 谢庆梅, 陈红莉, 张金云, 李大辉. 桃JMJ组蛋白去甲基化酶家族基因鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 575-590. |
| [6] | 邓淑琴, 高莹瑞, 李雨桐, 王瑛, 龚春梅, 白娟. 茶树泛素连接酶基因CsPUB21对非生物胁迫的响应[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 655-670. |
| [7] | 张圣平, 董邵云, 官健涛, 苗晗, 刘小萍, 顾兴芳. 黄瓜抗病分子育种研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 773-791. |
| [8] | 温正阳, 孙靖博, 张梦夏, 张锋, 董春娟. 黄瓜CsCuAO家族基因鉴定及其在不定根形成中的作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 309-321. |
| [9] | 毛欣, 元文飞, 郭雨润, 徐欣欣, 李艺, 张毅, 苗妍秀, 白龙强, 李衍素. 日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培中有机物料腐解及根区和叶片养分含量的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 439-452. |
| [10] | 王珊珊, 郭瑞, 何棱, 吴春红, 陈禅友, 万何平, 赵慧霞. 长豇豆Lhc家族基因鉴定及其在盐胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 111-122. |
| [11] | 王艳红, 席克勇, 田野, 刘德麒, 周克贵, 尹军良, 刘奕清, 朱永兴. 姜GST基因家族成员鉴定与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1803-1822. |
| [12] | 李娅娣, 王瀚祥, 胡柏耿, 杨辉, 胡新喜, 熊兴耀, 王万兴. 植物根际促生菌缓解园艺作物非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1964-1976. |
| [13] | 李欣, 柴应芳, 田真, 王鹏蔚, 程运江. 线粒体分离纯化及其在果实成熟衰老研究中的应用进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1516-1528. |
| [14] | 袁泉, 卢威, 王君, 陈茹, 李衍素, 于贤昌, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 闫妍. 日光温室不同土质灌水下限对早春黄瓜生长、产量和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1377-1385. |
| [15] | 王文娇, 邢军杰, 申成丞, 李斌. 黄瓜蜡质基因CsCER1调控因子CsCOL5的筛选及其功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1005-1016. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司