
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 591-602.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0274
王瑞1,2, 吴红霏1,3, 张长远1, 曹海顺1, 谭德龙1, 郭金菊1, 王云龙1, 王茹芳1, 袁余1, 吴廷全1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-30
修回日期:2025-02-13
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
WANG Rui1,2, WU Hongfei1,3, ZHANG Changyuan1, CAO Haishun1, TAN Delong1, GUO Jinju1, WANG Yunlong1, WANG Rufang1, YUAN Yu1, WU Tingquan1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-30
Revised:2025-02-13
Published:2025-03-25
Online:2025-03-25
摘要:
以高感疫病的黄瓜B80和瓜类疫霉菌(Phytophthora melonis)为材料,从B80黄瓜中克隆了1个含有U-box功能域的PUB蛋白家族基因CsPUB54,从P. melonis中克隆到1个RXLR效应蛋白基因,命名为PmRXLR1。B80接种P. melonis 24 h的转录组和qRT-PCR的试验结果均显示,P. melonis对B80黄瓜的侵染能够诱导CsPUB54和PmRXLR1表达量的快速提升。通过基因瞬时沉默方法将CsPUB54进行沉默,能够增加黄瓜子叶对P. melonis的抗性。另外,酵母双杂交和Pull-down的试验结果证实CsPUB54与PmRXLR1在体内和体外均可互作。利用碱基突变的方法将PmRXLR1的W和Y功能域分别进行突变,产生7个突变体。这些突变体分别与CsPUB54的互作检测显示,PmRXLR1中的W和Y功能域是PmRXLR1和CsPUB54互作所必需的,而W功能域中的异亮氨酸(I)是互作必需的关键氨基酸。CsPUB54与已发表的植物免疫负调控PUB蛋白进行遗传进化分析显示,CsPUB54与拟南芥AtPUB22、AtPUB23的遗传变异率较小,亲缘关系最近。这些研究数据表明CsPUB54能够通过与PmRXLR1互作负向调控黄瓜对瓜类疫霉的抗性。
王瑞, 吴红霏, 张长远, 曹海顺, 谭德龙, 郭金菊, 王云龙, 王茹芳, 袁余, 吴廷全. CsPUB54与PmRXLR1互作负向调控黄瓜对疫病的抗性[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 591-602.
WANG Rui, WU Hongfei, ZHANG Changyuan, CAO Haishun, TAN Delong, GUO Jinju, WANG Yunlong, WANG Rufang, YUAN Yu, WU Tingquan. CsPUB54 Negatively Regulates Cucumber Resistance to Phytophthora Melonis by Interacting with PmRXLR1 Effector[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 591-602.
| 名称Name | 编码序列Coding sequence | 蛋白序列Protein sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CsPUB54 | ATGGATGAACAAATCGAAGTCCCCCACTATTTCCTCTGCCCCATCTCCCTCCAAATCATGAAAGACCCTGTAACTCTTCCCTCCGGCATCACCTACGATCGCCACTCCATTGAAACTTGG CTCTTCTCCGGCAAAAACTCCTCCTGCCCCGTCACTAAACTCCCAGTCTCCGACTCCGATTCCGATCTCCTCACCCCCAACCACACCCTCCGCCGTCTCATCCAAGCTTGGTGTACTTTGA ACTCCTCCCATGGCGTCGAACGTTTCCCCACTCCTAAACCCCCCATTCATAAATCCCAAATCCTTCACATTATTTCCACTTCCAACACTTCCCCTTCTTCCCAAATCTCCTCCATTCGCCG TCTCCGCTCCATTTCCGCCGAGTCTGAAACTAATCGCCGATGCGTTGAATTCGCCGGTGCGCCGGAGTTTTTAGTCTCTGTTATTGTGGGTTCTGATTCCTCGGCTTCTCATGAAGCCCTCT CCACTCTTCATAACCTCCGTCTCTCTGATTCAACGTTTAAATCATTGGCTACCCGCCCTGAATTCCTCGAGTCCTTGACCGATTTCATGAAATTACAACAGGGTACTCATGAATCGTCCAGA ACGTACGCGGTGTTGATTTTGAAATCAATTATTGAAGTCGCTGAACCAATTCAACTAAGCTTCTTGAAACCCGAATTGTTTGTGCAAATCGTTGAGATTTTGAAAGATCGATCATCCTCTCAA CAGATTTTCAAAGCGGCATTGGGTATTTTGATTGCGGTGAGTCCATTGGGGAGAAACA GACTGAAGGCAGTAGAAGCAGGTGGAGTTAGGGCTTTGGTTGAGATTTTACTGTCGTCGCCGGAAAAAAGAGTATGTGAAATGACATTGACGGCGATGGATATACTGTGTGGGTGTGCGGAT GGAAGAGCGGCGCTGTTGGCACACGGCGGAGGGATGGCAGTGGTTTCGAAGAAGATATTGAGAGTGTCGCAATTGGGGAGTGAAAGGGCGGTGAGAATATTGTATTCGGTGGCTAAATTCTCA GGAAGTCCTGCGGTGTTGATGGAAATGGCGCAACTGGGGATTGTGGCAAAGCTATGTTTGGTTCTGCAAATTGAAAATGGAGGCAAGACGAAGGAGAAAGCTAAAGAGATTTTGAAAATGCAT TCTCGTCTTTGGAAGAACTCACCTTGTATTCCTTCTAAATTGGCTTCTTCATATCCTACAAATTAA | MDEQIEVPHYFLCPISLQIMKDPVTLPSGITYDRHSIETWLFSGKNSSCPVTKLPVSDSDSDLLTPNHTLRRLIQAWCTLNSSHGVERFPTPKPPIHKSQILHIISTSNTSPSSQISSIRRLRS ISAESETNRRCVEFAGAPEFLVSVIVGSDSSASHEALSTLHNLRLSDSTFKSLATRPEFLESLTDFMKLQQGTHESSRTYAVLILKSIIEVAEPIQLSFLKPELFVQIVEILKDRSSSQQIFKAA LGILIAVSPLGRNRLKAVEAGGVRALVEILLSSPEKRVCEMTLTAMDILCGCADGRAALLAHGGGMAVVSKKILRVSQLGSERAVRILYSVAKFSGSPAVLMEMAQLGIVAKLCLVLQIENGGKTK EKAKEILKMHSRLWKNSPCIPSKLASSYPTN* |
| PmRXLR1 | ATGCGTCTGTCTTTCATGCTTTCTGTTGCTGTGGTCATCGGCCACCTCGTGGCCTGCAACGCGACTGC GGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCG CTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAG ATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCG CATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA | MRLSFMLSVAVVIGHLVACNATADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKE AYEAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 (无信号肽 No signal peptide) | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGG AGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTA CACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATC TACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEA WAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
表1 CsPUB54、PmRXLR1的基因序列与蛋白序列
Table 1 Gene and protein sequences of CsPUB54 and PmRXLR1
| 名称Name | 编码序列Coding sequence | 蛋白序列Protein sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CsPUB54 | ATGGATGAACAAATCGAAGTCCCCCACTATTTCCTCTGCCCCATCTCCCTCCAAATCATGAAAGACCCTGTAACTCTTCCCTCCGGCATCACCTACGATCGCCACTCCATTGAAACTTGG CTCTTCTCCGGCAAAAACTCCTCCTGCCCCGTCACTAAACTCCCAGTCTCCGACTCCGATTCCGATCTCCTCACCCCCAACCACACCCTCCGCCGTCTCATCCAAGCTTGGTGTACTTTGA ACTCCTCCCATGGCGTCGAACGTTTCCCCACTCCTAAACCCCCCATTCATAAATCCCAAATCCTTCACATTATTTCCACTTCCAACACTTCCCCTTCTTCCCAAATCTCCTCCATTCGCCG TCTCCGCTCCATTTCCGCCGAGTCTGAAACTAATCGCCGATGCGTTGAATTCGCCGGTGCGCCGGAGTTTTTAGTCTCTGTTATTGTGGGTTCTGATTCCTCGGCTTCTCATGAAGCCCTCT CCACTCTTCATAACCTCCGTCTCTCTGATTCAACGTTTAAATCATTGGCTACCCGCCCTGAATTCCTCGAGTCCTTGACCGATTTCATGAAATTACAACAGGGTACTCATGAATCGTCCAGA ACGTACGCGGTGTTGATTTTGAAATCAATTATTGAAGTCGCTGAACCAATTCAACTAAGCTTCTTGAAACCCGAATTGTTTGTGCAAATCGTTGAGATTTTGAAAGATCGATCATCCTCTCAA CAGATTTTCAAAGCGGCATTGGGTATTTTGATTGCGGTGAGTCCATTGGGGAGAAACA GACTGAAGGCAGTAGAAGCAGGTGGAGTTAGGGCTTTGGTTGAGATTTTACTGTCGTCGCCGGAAAAAAGAGTATGTGAAATGACATTGACGGCGATGGATATACTGTGTGGGTGTGCGGAT GGAAGAGCGGCGCTGTTGGCACACGGCGGAGGGATGGCAGTGGTTTCGAAGAAGATATTGAGAGTGTCGCAATTGGGGAGTGAAAGGGCGGTGAGAATATTGTATTCGGTGGCTAAATTCTCA GGAAGTCCTGCGGTGTTGATGGAAATGGCGCAACTGGGGATTGTGGCAAAGCTATGTTTGGTTCTGCAAATTGAAAATGGAGGCAAGACGAAGGAGAAAGCTAAAGAGATTTTGAAAATGCAT TCTCGTCTTTGGAAGAACTCACCTTGTATTCCTTCTAAATTGGCTTCTTCATATCCTACAAATTAA | MDEQIEVPHYFLCPISLQIMKDPVTLPSGITYDRHSIETWLFSGKNSSCPVTKLPVSDSDSDLLTPNHTLRRLIQAWCTLNSSHGVERFPTPKPPIHKSQILHIISTSNTSPSSQISSIRRLRS ISAESETNRRCVEFAGAPEFLVSVIVGSDSSASHEALSTLHNLRLSDSTFKSLATRPEFLESLTDFMKLQQGTHESSRTYAVLILKSIIEVAEPIQLSFLKPELFVQIVEILKDRSSSQQIFKAA LGILIAVSPLGRNRLKAVEAGGVRALVEILLSSPEKRVCEMTLTAMDILCGCADGRAALLAHGGGMAVVSKKILRVSQLGSERAVRILYSVAKFSGSPAVLMEMAQLGIVAKLCLVLQIENGGKTK EKAKEILKMHSRLWKNSPCIPSKLASSYPTN* |
| PmRXLR1 | ATGCGTCTGTCTTTCATGCTTTCTGTTGCTGTGGTCATCGGCCACCTCGTGGCCTGCAACGCGACTGC GGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCG CTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAG ATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCG CATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA | MRLSFMLSVAVVIGHLVACNATADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKE AYEAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 (无信号肽 No signal peptide) | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGG AGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTA CACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATC TACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEA WAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| 用途Usage | 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene cloning | CsPUB54-F (C) CsPUB54-R (C) PmRXLR1-F (C) PmRXLR1-R (C) | ATGGATGAACAAATCGAAGTCCCCCAC TTAATTTGTAGGATATGAAGAAGCCA ATGCGTCTGTCTTTCATGCTTTC TTAATCCTGATACAGGTGAAAGCCG |
| 载体构建 Vector construction | CsPUB54-F (V) CsPUB54-R (V) PmRXLR1-F (V) PmRXLR1-R (V) | CATATGATGGATGAACAAATCG CGCGGATCCTTAATTTGTAGGATATG CCGGAATTCACTGCGGACTTCGACG CGCGGATCCTTAATCCTGATACAGGTG |
| 基因表达 Gene expression | CsPUB54-F (E) CsPUB54-R (E) | CAAATCTCCTCCATTCGCCGTC TCATGAAATCGGTCAAGGACTC |
| 黄瓜内参基因 Cucumber reference gene | CsUBQ-F CsUBQ-R | GCGTAAGAAGAAGACCTACACCA CCTTTCCAGAGTCATCGACCT |
| 瓜类疫霉菌ITS检测 ITS detection of Phytophthora melons | DC6-F ITS4-R | 5′-GAGGGACTTTTGGGTAATCA-3′ 5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′ |
表2 本试验中所用引物
Table 2 The primers used in the experiment
| 用途Usage | 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene cloning | CsPUB54-F (C) CsPUB54-R (C) PmRXLR1-F (C) PmRXLR1-R (C) | ATGGATGAACAAATCGAAGTCCCCCAC TTAATTTGTAGGATATGAAGAAGCCA ATGCGTCTGTCTTTCATGCTTTC TTAATCCTGATACAGGTGAAAGCCG |
| 载体构建 Vector construction | CsPUB54-F (V) CsPUB54-R (V) PmRXLR1-F (V) PmRXLR1-R (V) | CATATGATGGATGAACAAATCG CGCGGATCCTTAATTTGTAGGATATG CCGGAATTCACTGCGGACTTCGACG CGCGGATCCTTAATCCTGATACAGGTG |
| 基因表达 Gene expression | CsPUB54-F (E) CsPUB54-R (E) | CAAATCTCCTCCATTCGCCGTC TCATGAAATCGGTCAAGGACTC |
| 黄瓜内参基因 Cucumber reference gene | CsUBQ-F CsUBQ-R | GCGTAAGAAGAAGACCTACACCA CCTTTCCAGAGTCATCGACCT |
| 瓜类疫霉菌ITS检测 ITS detection of Phytophthora melons | DC6-F ITS4-R | 5′-GAGGGACTTTTGGGTAATCA-3′ 5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′ |
| 突变体Mutant | 序列Sequence |
|---|---|
| PmRXLR1 Δ1 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGA GTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGA TCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAAC GGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAA AAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAA---GGGGACCCCAAGAAC AAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ1 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSH QEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKE---GDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ2 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGG CCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACT GAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGAT GCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCG GCGGAGGCG GCAGCAGCGAACAAGTACACC GGAGTCCAA GGAAAGAAC GCACTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCT ACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ2 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSH QEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAAEAAAANKYT GVQGKNALKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ3 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCG CTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGG AACGGACCTTCATCATTACT GAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCA GATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTAC TCCGCGTGGGCA TCCAACAAGTACACCCTG TCCTCCATCAAG TCCTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAA ATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACG GCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ3 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKND DIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLA RQMLKDPSKEKEAY SAWA SNKYTL SSIK SWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIY NGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ4 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCC GGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGC GGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCA GCGAACAAGTACACCCTG GGCGGTGGAGGGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACC CCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ4 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITE LMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLGGGGNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ5 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGAC GACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATG AACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGC TGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGC AGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAA GGCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAA GAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGC TTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ5 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAE ERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLVQ GKNWLKIGDPKNKGK YDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ6 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAG AACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTT AAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCT GAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAG---GATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ6 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNK AAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPK---D* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ7 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACG ACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCC AGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGA AGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAG AACAAAGGAGCAGCTGCCGCCATCTACGCCGCGTACGGCG CTGCCCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ7 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDD AEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAY EAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGAAAAIYAAYGAALYQD* |
表3 PmRXLR1蛋白突变体碱基序列和氨基酸序列
Table 3 Base sequences and amino acid sequences of PmRXLR1 gene mutants
| 突变体Mutant | 序列Sequence |
|---|---|
| PmRXLR1 Δ1 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGA GTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGA TCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAAC GGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAA AAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAA---GGGGACCCCAAGAAC AAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ1 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSH QEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKE---GDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ2 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGG CCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACT GAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGAT GCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCG GCGGAGGCG GCAGCAGCGAACAAGTACACC GGAGTCCAA GGAAAGAAC GCACTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCT ACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ2 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSH QEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAAEAAAANKYT GVQGKNALKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ3 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCG CTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGG AACGGACCTTCATCATTACT GAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCA GATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTAC TCCGCGTGGGCA TCCAACAAGTACACCCTG TCCTCCATCAAG TCCTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAA ATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACG GCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ3 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKND DIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLA RQMLKDPSKEKEAY SAWA SNKYTL SSIK SWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIY NGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ4 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCC GGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGC GGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCA GCGAACAAGTACACCCTG GGCGGTGGAGGGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACC CCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ4 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITE LMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLGGGGNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ5 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGAC GACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATG AACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGC TGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGC AGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAA GGCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAA GAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGC TTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ5 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAE ERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLVQ GKNWLKIGDPKNKGK YDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ6 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAG AACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTT AAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCT GAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAG---GATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ6 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNK AAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPK---D* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ7 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACG ACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCC AGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGA AGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAG AACAAAGGAGCAGCTGCCGCCATCTACGCCGCGTACGGCG CTGCCCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ7 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDD AEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAY EAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGAAAAIYAAYGAALYQD* |
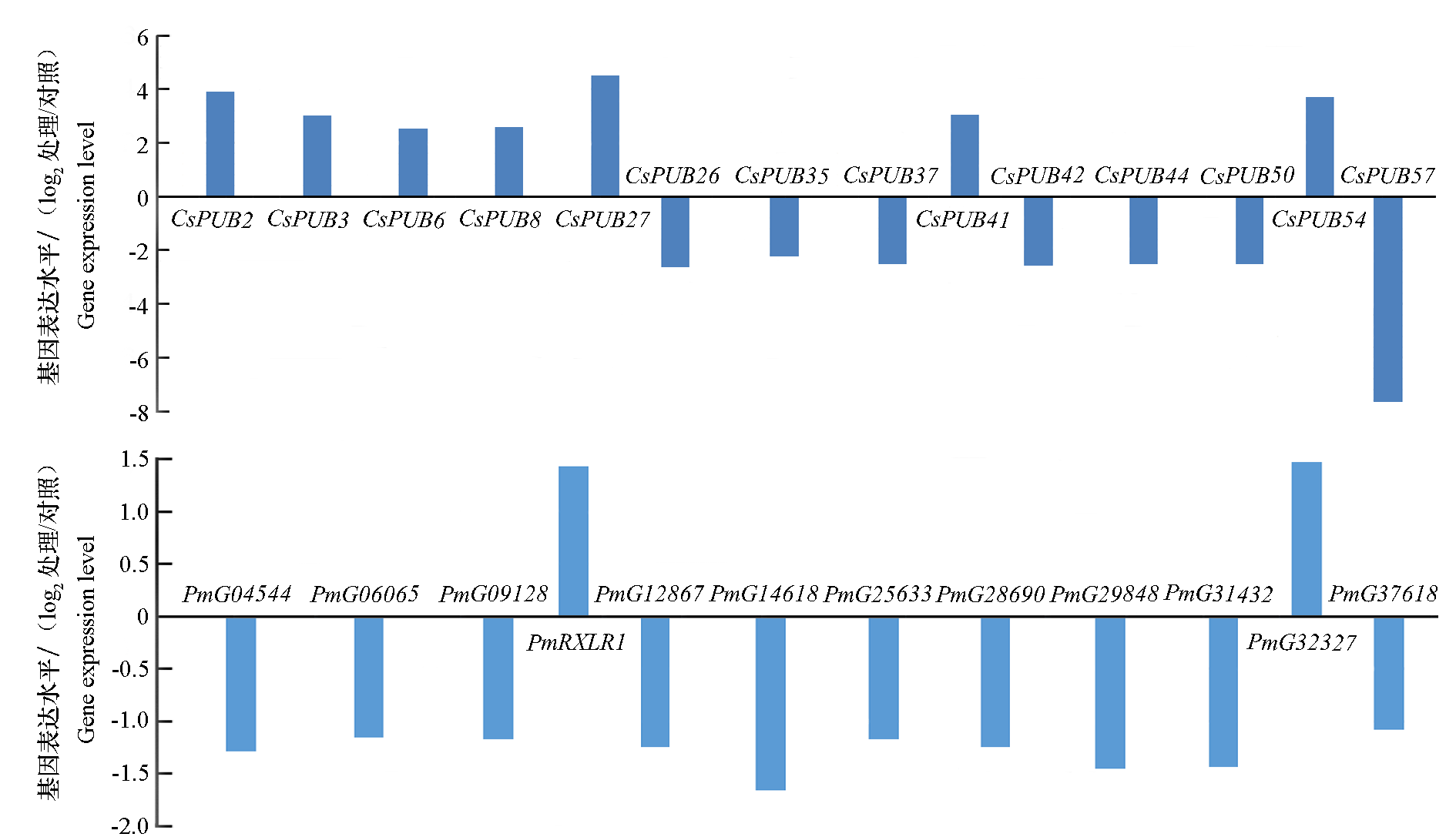
图1 B80黄瓜接种瓜类疫霉菌0 h与24 h后差异显著的PUB和RXLR的表达量
Fig. 1 Expression analysis of PUBs and RXLRs with significant differences at 0 h and 24 h inoculation with Phytophthora melonis
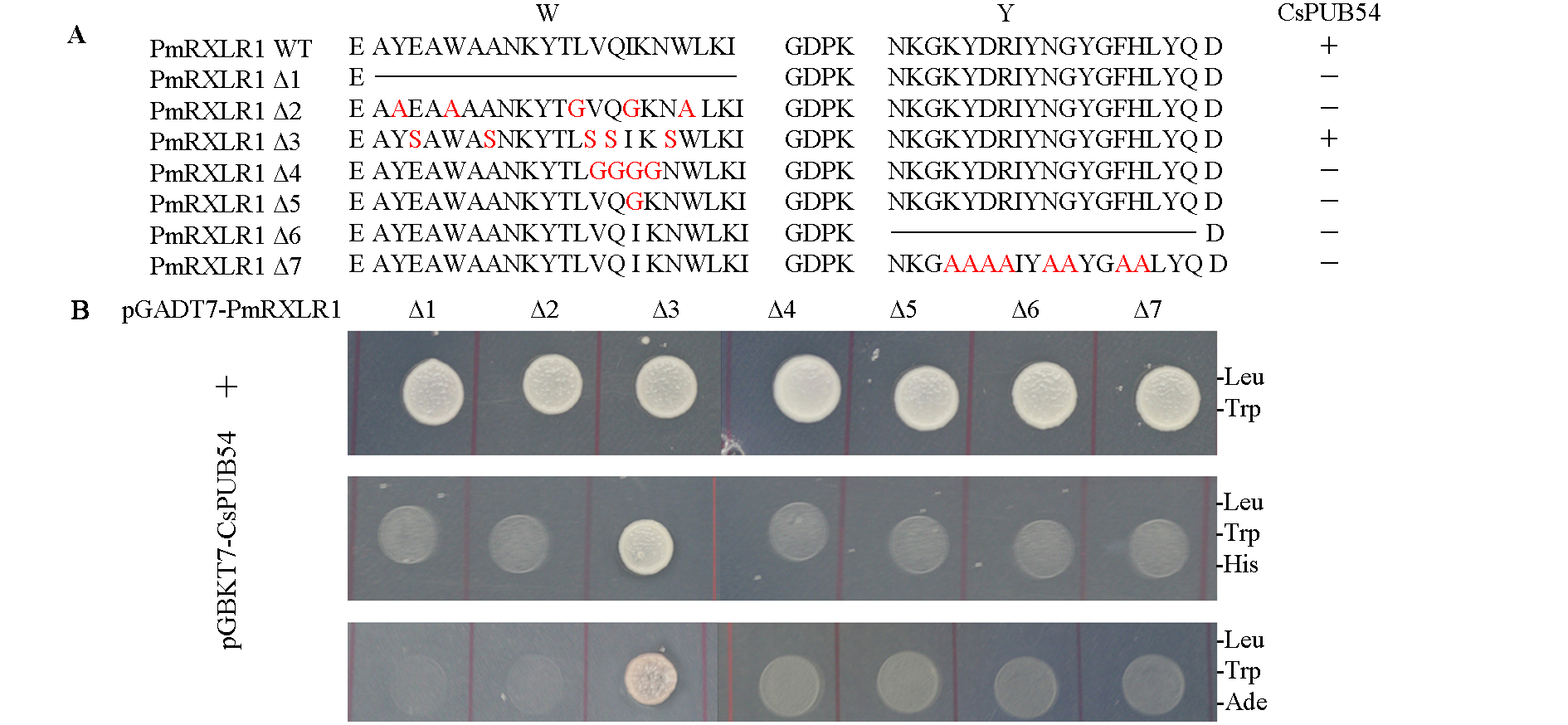
图4 PmRXLR1突变体Δ1 ~ Δ7的W和Y基序序列(A)和突变体与CsPUB54的酵母双杂交结果(B)
Fig. 4 The W and Y motif sequences of PmRXLR1 mutant Δ1-Δ7(A)and the yeast two hybrid of the mutants and CsPUB54(B)
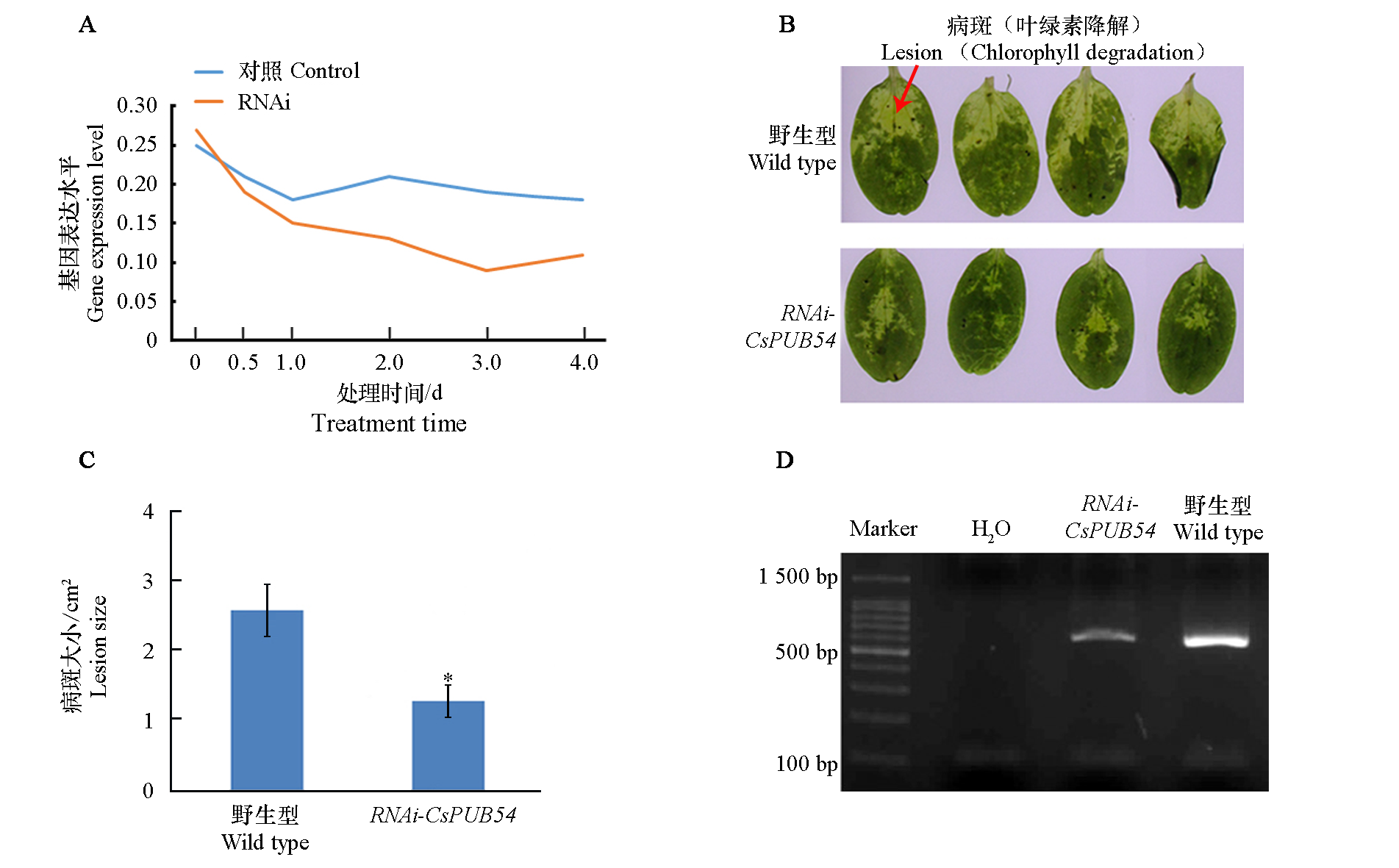
图5 黄瓜CsPUB54沉默的叶片的抗病性检测 A:CsPUB54在黄瓜叶片中的沉默效率;B:接种瓜类疫霉菌后野生型和RNAi-CsPUB54黄瓜叶片表型;C:接种瓜类疫霉菌后野生型和RNAi-CsPUB54黄瓜叶片病斑面积统计分析;D:接种瓜类疫霉菌的叶片中菌量的检测
Fig. 5 Detection of disease resistance in cucumber leaves silent with CsPUB54 A. Silencing efficiency analysis of CsPUB54 in cucumber leaves;B:Phenotypes of wild-type and RNAi-CsPUB54 cucumber leaves after inoculation with Phytophthora melonis;C:Statistical analysis of lesion area of wild-type and RNAi-CsPUB54 cucumber inoculated with Phytophthora melonis ;D:Detection of the total number of Phytophthora melonis in inoculated cucumber leaves
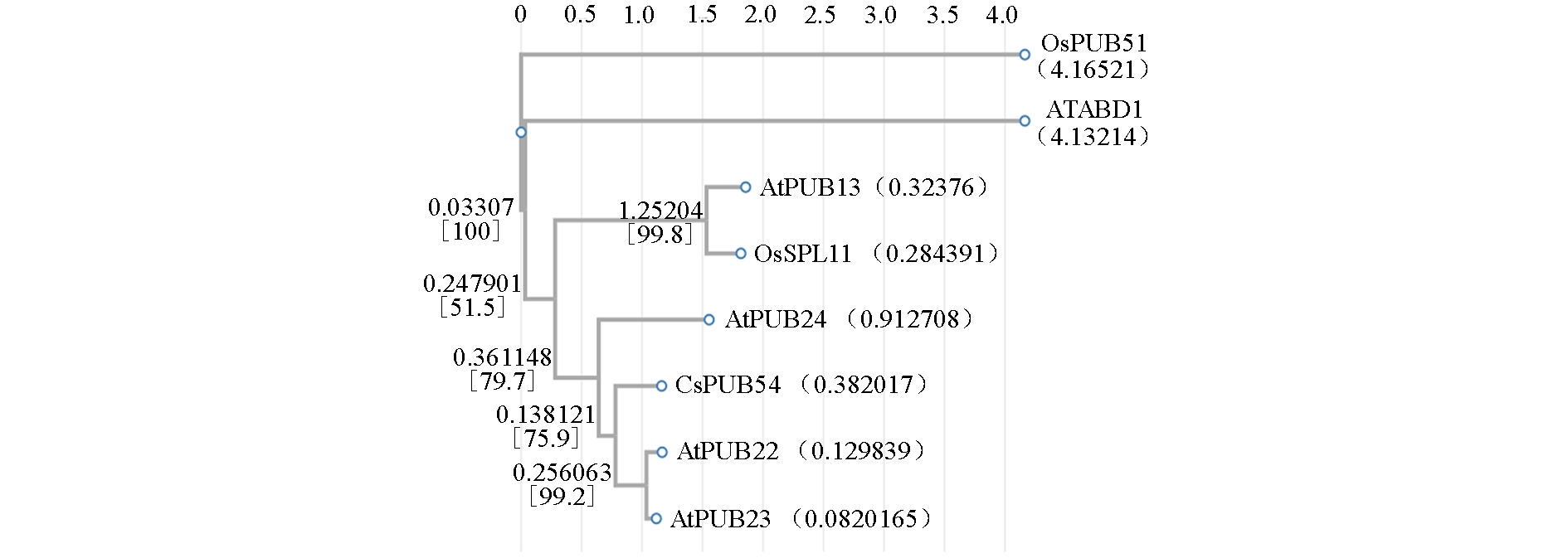
图6 黄瓜CsPUB54与水稻(Os)、拟南芥(At)免疫负向调控PUB蛋白序列比对 图中小括号中的数字表示进化距离,数字越小进化距离越近;中括号中的数字为自展值,表示可靠度(大于70可靠度较好)
Fig. 6 Sequence alignment of cucumber CsPUB54 with rice(Os),Arabidopsis(At)PUB proteins regulating immune negatively The numbers in parentheses in the figure represent the evolutionary distance,and the smaller the number,the closer the evolutionary distance. The numbers in square brackets are bootstrap values,indicating reliability(reliability greater than 70 is better)
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
胡维炜, 张武, 刘连忠, 蔡芮莹, 朱小倩. 2016. 利用图像处理技术计算大豆叶片相对病斑面积. 江苏农业学报, 32 (4):774-779.
|
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.15414 pmid: 30169906 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0430 URL |
|
齐晨辉, 赵先炎, 韩朋良, 姜翰, 王永旭, 胡大刚, 郝玉金. 2017. 苹果U-box型E3泛素连接酶MdPUB24的耐盐性和ABA敏感性鉴定. 园艺学报, 44 (12):2255-2264.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0430 URL |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00824-y pmid: 30671725 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.104463 pmid: 23170036 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.17660 pmid: 34339518 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
王瑞, 林毓娥, 杜虎, 金庆敏, 杨晓珊, 吴廷全. 2019. 快速鉴定瓜类疫病抗性方法的建立及黄瓜种质资源鉴定. 广东农业科学, 46 (10):13-18.
|
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15070017 |
|
王瑞, 林毓娥, 梁肇均, 金庆敏, 吴廷全. 2016. 广东地区黄瓜疫病病原菌的分离与鉴定. 中国农学通报, 32 (1):76-80.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15070017 |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [1] | 张圣平, 董邵云, 官健涛, 苗晗, 刘小萍, 顾兴芳. 黄瓜抗病分子育种研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 773-791. |
| [2] | 荆永琳, 陈浪欣, 李俊国, 王加宾, 王小冰, 杨庆全, 孟春阳, 徐立. 菠萝AcKNOX1影响叶缘发育的功能研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 292-308. |
| [3] | 温正阳, 孙靖博, 张梦夏, 张锋, 董春娟. 黄瓜CsCuAO家族基因鉴定及其在不定根形成中的作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 309-321. |
| [4] | 蔡泽彦, 张明星, 周池, 陶禹, 杨莎, 李鑫, 李雪峰. 辣椒疫病不同抗性品种内生微生物群落多样性、结构及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 322-336. |
| [5] | 毛欣, 元文飞, 郭雨润, 徐欣欣, 李艺, 张毅, 苗妍秀, 白龙强, 李衍素. 日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培中有机物料腐解及根区和叶片养分含量的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 439-452. |
| [6] | 陈明, 张洁茹, 杨航云, 王印宝, 郑致远, 曾教科, 陈金印, 付永琦, 向妙莲. 茉莉酸甲酯诱导采后脐橙抗青霉病的机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2183-2194. |
| [7] | 邱辉, 朱德娟, 张永乐, 高玉洁, 李柳, 王国平, 洪霓. ACLSV外壳蛋白与梨两种E3泛素连接酶互作及亚细胞定位[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1715-1727. |
| [8] | 龚小雅, 李贤, 周新刚, 吴凤芝. 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对根结线虫病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [9] | 石凤岩, 王治丹, 张曦, 王秀雪, 邹春蕾. 辣椒疫病抗性机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1665-1682. |
| [10] | 袁泉, 卢威, 王君, 陈茹, 李衍素, 于贤昌, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 闫妍. 日光温室不同土质灌水下限对早春黄瓜生长、产量和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1377-1385. |
| [11] | 彭爱红, 张婧芸, 陈志毅, 苏娟, 何永睿, 姚利晓. CsEXPA8过表达对‘晚锦橙’生长及溃疡病抗性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 971-981. |
| [12] | 王文娇, 邢军杰, 申成丞, 李斌. 黄瓜蜡质基因CsCER1调控因子CsCOL5的筛选及其功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1005-1016. |
| [13] | 杨婷, 席德慧, 夏明, 李佳楠. α-苦瓜素基因提高番茄对烟草花叶病毒抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [14] | 王青, 胡燕, 陈姗, 陆景伟, 郑阳, 陶伟林, 孙现超, 周娜, 陈国康. 绛红褐链霉菌CC2-6抑制大白菜根肿病的效果及机制分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1137-1150. |
| [15] | 张丛莹, 顾兴芳, 苗晗, 董邵云, 刘小萍, 官健涛, 张圣平. 黄瓜新品种‘中农脆玉1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1173-1174. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司