
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (10): 2091-2103.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0761
杨江伟1,2, 段小琴2, 张飞燕2, 张丽3, 邓玉荣2, 王晓凤2, 郑智勇2, 张宁2, 司怀军1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-12
修回日期:2023-07-13
出版日期:2023-10-25
发布日期:2023-10-30
通讯作者:
*(E-mail:hjsi@gsau.edu.cn)
基金资助:
YANG Jiangwei1,2, DUAN Xiaoqin2, ZHANG Feiyan2, ZHANG Li3, DENG Yurong2, WANG Xiaofeng2, ZHENG Zhiyong2, ZHANG Ning2, SI Huaijun1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-12
Revised:2023-07-13
Published:2023-10-25
Online:2023-10-30
Contact:
*(E-mail:hjsi@gsau.edu.cn)
摘要:
通过检测26个StIAA家族基因在马铃薯根系发育过程中的表达发现:18个StIAA基因在根系成熟后的表达量比发育初期显著上调,8个StIAA基因变化不显著。利用人工microRNA(artificial microRNA,amiRNA)技术对上调表达最为显著的StIAA22做进一步的功能研究:构建干扰表达载体pBI121-amiRIAA,通过根癌农杆菌介导法转入马铃薯栽培品种‘Dèsirèe’。经定量PCR检测,StIAA22在所有转基因株系中的表达均受到明显抑制;其根系形态构型与非转基因植株差异明显,根系生长受到抑制,根长明显变短,侧根数量增加,根系生物量减少。以上结果表明StIAA22在调节马铃薯根系形态建成中起关键作用。
杨江伟, 段小琴, 张飞燕, 张丽, 邓玉荣, 王晓凤, 郑智勇, 张宁, 司怀军. 利用人工miRNA沉默StIAA22对马铃薯根系构型的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(10): 2091-2103.
YANG Jiangwei, DUAN Xiaoqin, ZHANG Feiyan, ZHANG Li, DENG Yurong, WANG Xiaofeng, ZHENG Zhiyong, ZHANG Ning, SI Huaijun. Root Architecture Alteration by Down-regulation of the StIAA22 Gene Using Artificial MicroRNA in Potato[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(10): 2091-2103.
| 引物名称 Primers name | 引物(5′-3′) Primers sequence |
|---|---|
| amiR-IAA-I | GATAGACCCTTTATAGGCTTCGCTCTCTCTTTTGTATTCC |
| amiR-IAA-II | GAGCGAAGCCTATAAAGGGTCTATCAAAGAGAATCAATGA |
| amiR-IAA-III | GAGCAAAGCCTATAATGGGTCTTTCACAGGTCGTGATATG |
| amiR-IAA-IV | GAAAGACCCATTATAGGCTTTGCTCTACATATATATTCCT |
表1 巢式PCR构建amiR-IAA载体所需引物
Table 1 Primers for construction of amiR-IAA vector using overlapping PCR
| 引物名称 Primers name | 引物(5′-3′) Primers sequence |
|---|---|
| amiR-IAA-I | GATAGACCCTTTATAGGCTTCGCTCTCTCTTTTGTATTCC |
| amiR-IAA-II | GAGCGAAGCCTATAAAGGGTCTATCAAAGAGAATCAATGA |
| amiR-IAA-III | GAGCAAAGCCTATAATGGGTCTTTCACAGGTCGTGATATG |
| amiR-IAA-IV | GAAAGACCCATTATAGGCTTTGCTCTACATATATATTCCT |
| PCR反应 PCR reaction | 正向引物 Forward oligo | 反向引物 Reverse oligo | 模板 Template | 产物长度/bp Length of PCR product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | A | Ⅳ | pRS300 | 272 |
| (b) | Ⅲ | Ⅱ | pRS300 | 171 |
| (c) | Ⅰ | B | pRS300 | 298 |
| (d) | A | B | (a) + (b) + (c) | 701 |
表2 产生amiRNA前体的标准反应体系
Table 2 Standard reaction system of amiRNA precursor
| PCR反应 PCR reaction | 正向引物 Forward oligo | 反向引物 Reverse oligo | 模板 Template | 产物长度/bp Length of PCR product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | A | Ⅳ | pRS300 | 272 |
| (b) | Ⅲ | Ⅱ | pRS300 | 171 |
| (c) | Ⅰ | B | pRS300 | 298 |
| (d) | A | B | (a) + (b) + (c) | 701 |
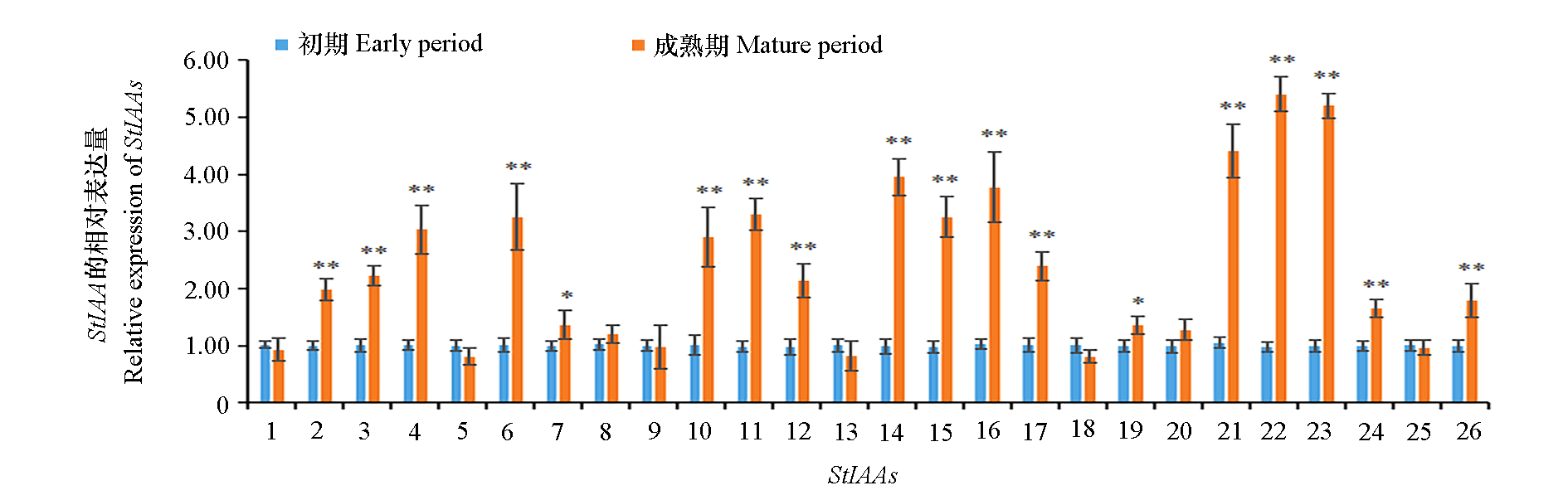
图3 马铃薯StIAA基因在根系不同发育阶段的表达模式 * 表示P < 0.05时差异显著,** 表示P < 0.01 时差异显著。
Fig. 3 Expression pattern of StIAAs in potato root development * indicates signifificant difference(P < 0.05),** indicates signifificant difference(P < 0.01).
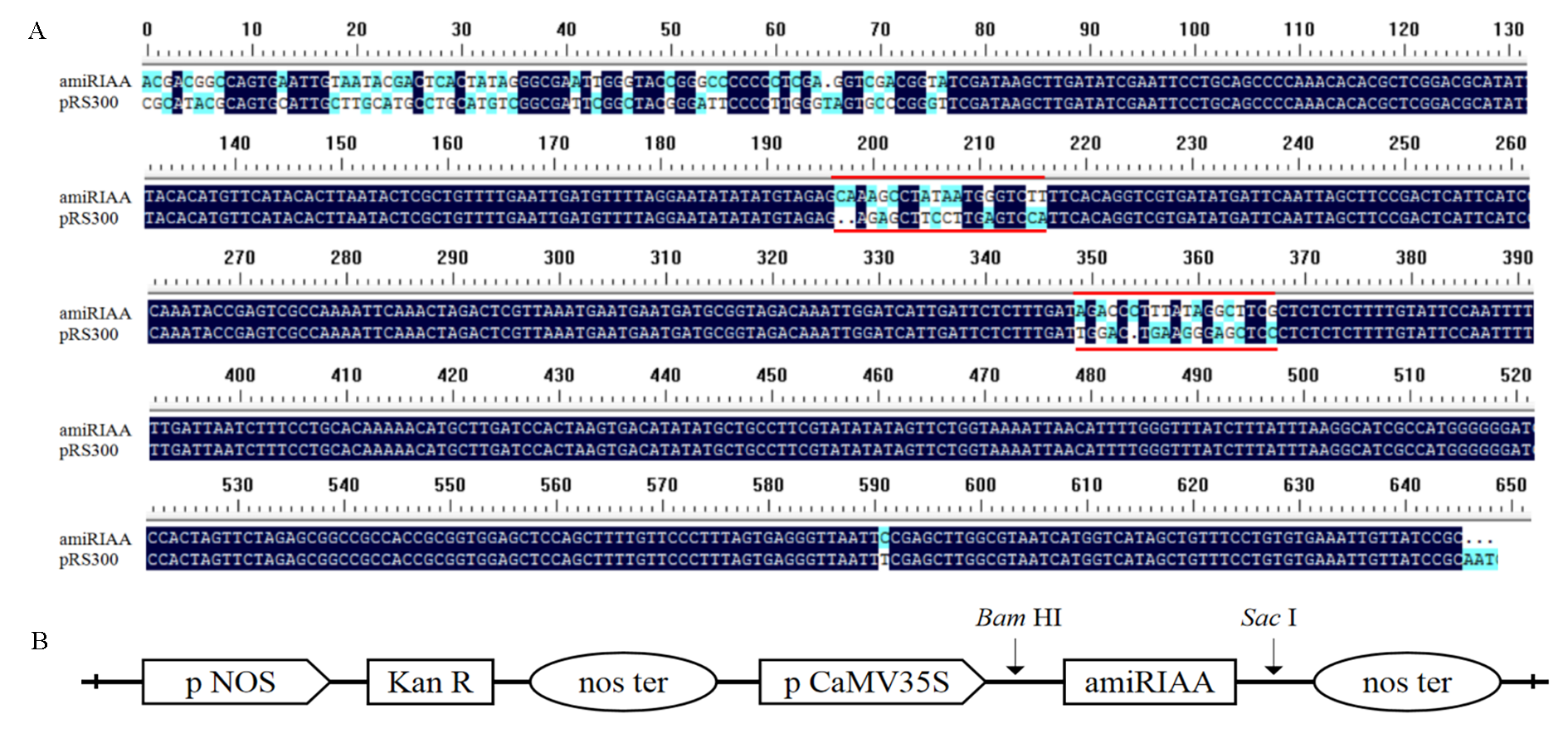
图4 马铃薯StIAA22基因amiRNA载体的构建 A:d片段测序结果,红色线条代表pRS300载体上ath-miR319a的成熟序列和其反向序列经重叠PCR扩增后替换为amiRIAA成熟序列和其反向序列;B:pBI121-amiRIAA表达载体的结构。
Fig. 4 Construction of suppress expression vector of StIAA22 with amiRNA A:Sequencing of the d fragment,the red lines represent mature sequence of miR319a and its reverse sequence on original pRS300 vector,and amiRIAA mature sequence and its reverse sequence after PCR amplification;B:Construction of pBI121-amiRIAA expression vector.

图5 转基因植株NPTII基因的PCR检测 M:DL2 000 marker;V:载体质粒;CK:未转基因植株;T1 ~ T10:转基因植株。
Fig. 5 PCR detection of NPTII gene in the transgenic plants M:DL2 000 marker;V:Vector;CK:Non-transgenic plants;T1-T10:Transgenic plants.
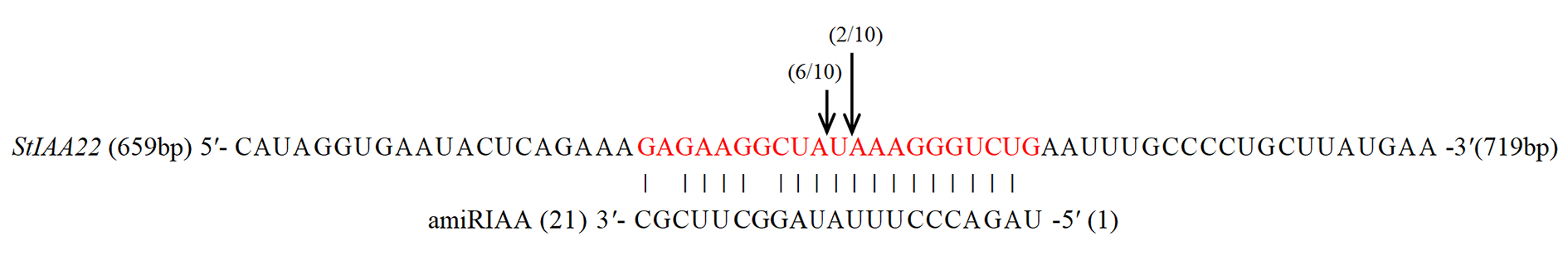
图6 RLM-5° RACE验证amiRIAA对StIAA22基因mRNA的降解位点 括号内的分数表示所有测序克隆中显示断裂位点的克隆比例。
Fig. 6 RLM-5° RACE verification of StIAA22 gene mRNA cleavage sites generated by amiRIAA Fraction within parentheses means the proportions of 5°RACE clones showing these cleavage sites out of all sequenced clones.
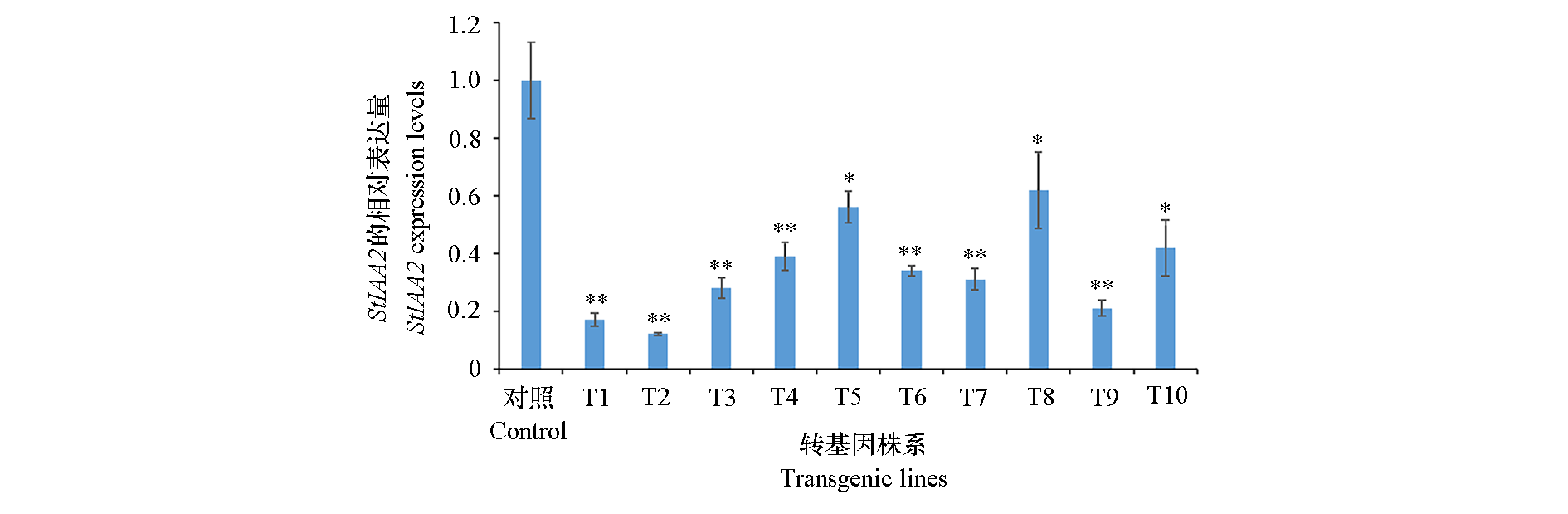
图7 人工miRNA抑制了马铃薯StIAA22的表达 CK:未转基因植株;T1 ~ T10:转基因植株,* 表示P < 0.05 时差异显著,** 表示P < 0.01 时差异显著。
Fig. 7 Artifificial miRNAs silence the expression of the StIAA22 in potato CK:Non-transgenic plants;T1-T10:Transgenic plants,* indicates signifificant difference(P < 0.05),** indicates signifificant difference(P < 0.01).

图8 转基因马铃薯植株(T1,T2和T9)与非转基因植株(CK)的表型特征
Fig. 8 Phenotypic characteristics of transgenic potato plants(T1,T2 and T9)and non-transgenic(CK) * P < 0.05,** P < 0.01.
| [1] |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.326 pmid: 8278386 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043414 URL |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcs022 pmid: 22368074 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcs101 URL |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.4161/psb.4.6.8748 URL |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erp009 URL |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/S1369526602000031 URL |
| [9] |
pmid: 10809445 |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.037192 pmid: 16829592 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1023/A:1015207114117 URL |
| [13] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0700 URL |
|
胡若琳, 王佳丽, 杨慧勤, 袁超, 牛义, 汤青林, 魏大勇, 田时炳, 杨洋, 王志敏. 2022. 茄子生长素响应因子SmARF5对分枝发育的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (9):1895-1906.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0700 URL |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1007/s10142-005-0005-0 URL |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1242/dev.01952 URL |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01450.x URL |
| [17] |
pmid: 17986329 |
| [18] |
pmid: 15797014 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.09.008 URL |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2008.07.006 URL |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2007.08.002 URL |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404 pmid: 17846036 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2005.06.010 pmid: 15964756 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1023/A:1015255030047 URL |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1080/21655979.2019.1692610 URL |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [27] |
|
|
马红媛, 梁正伟, 黄立华, 闫超, 孔祥军. 2008. 4种外源激素处理对羊草种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 26:69-73.
|
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2011.01050.x |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1007/s11032-015-0202-z URL |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2008.53.issue-4 URL |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.08.053 URL |
| [33] |
doi: 10.4161/psb.6.10.17326 URL |
| [34] |
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2014.02059 |
|
乔麟轶, 李欣, 畅志坚, 张晓军, 詹海仙, 郭慧娟, 李建波, 常建忠, 郑军. 2014. 粗山羊草全基因组Aux/IAA基因家族的分离、染色体定位及序列分析. 作物学报, 40:2059-2069.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2014.02059 |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(01)02042-8 pmid: 11544131 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.13.3.465 pmid: 11251090 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01156 pmid: 26734051 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1007/s10265-007-0121-0 pmid: 17987258 |
| [39] |
|
|
司怀军, 谢丛华, 柳俊. 2003. 农杆菌介导的马铃薯试管薯遗传转化体系的优化及反义class I patatin基因的导入. 作物学报, 29:801-805.
|
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erl182 URL |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1080/15592324.2015.1071001 URL |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu124 URL |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.010289 pmid: 11752389 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.017384 pmid: 14742873 |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.001 pmid: 19303845 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.033415 pmid: 16126837 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0039-y URL |
| [49] |
|
|
王垒, 陈劲枫, 贾利. 2010. 黄瓜Aux/IAA 基因家族的生物信息学分析. 中国瓜菜,(23):1-4.
|
|
| [50] |
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2010.00688 |
|
王益军, 吕燕萍, 谢秦, 邓德祥, 卞云龙. 2010. 高粱全基因组生长素原初响应基因Aux/IAA的序列特征分析. 作物学报, 36:688-694.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2010.00688 |
|
| [51] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2022.06.009 URL |
| [52] |
doi: 10.1007/s00438-012-0675-y URL |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1007/s00438-015-1063-1 URL |
| [54] |
|
|
徐丽萍, 刘建兵, 喻方圆. 2019. 东京野茉莉授粉前后花瓣的生理生化变化. 江西农业大学学报, 41:464-475.
|
|
| [55] |
|
|
杨晓婉, 郑国琦, 许兴, 胡美娟, 封美琦. 2013. 宁夏枸杞果实生长发育期内源激素变化及关系研究. 西北植物学报, 33:116-122.
|
|
| [56] |
|
|
张俊红. 2006. 番茄Aux/IAA基因的克隆与功能分析[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [57] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2021.01.010 URL |
| [58] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0380 URL |
|
张倩雯, 杨希航, 李峰, 邓颖天. 2022. miRNA调控园艺作物生长发育研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (5):1145-1161.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0380 URL |
|
| [59] |
|
|
张晓辉, 邹哲, 李汉霞, 叶志彪. 2009. 从反义RNA到人工miRNA的植物基因沉默技术革新. 自然科学进展, 19:1029-1037. (in Chinese)
|
|
| [60] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0692 URL |
|
张彦苹, 刘照坤, 朱旭东, 王晨, 李庆魁, 袁卫明, 娄晓鸣. 2019. 桃果实中miR160a与其靶基因ARF的鉴定及对IAA的响应分析. 园艺学报, 46 (4):613-622.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0692 URL |
|
| [61] |
|
|
张志勇, 王素芳, 田晓莉, 汤菊香. 2009. 生长素调节植物侧根发育过程的机制. 作物杂志,(1):11-13.
|
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
|
郑小敏, 赵敬会, 李荣冲, 王瑞雪, 张涛. 2012. 芸薹属大白菜Aux/IAA基因家族的生物信息学分析. 北方园艺,(14):109-113.
|
|
| [64] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0388 |
|
曾文芳, 王小贝, 潘磊, 牛良, 鲁振华, 崔国朝, 王志强. 2017. 桃Aux/IAA家族基因鉴定及在果实成熟过程中的表达分析. 园艺学报, 44:233-244.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0388 |
| [1] | 王荣艳, 李清, 徐灵, 王秋洁, 宋昱, 母昌冉, 唐唯, 郝大海. 马铃薯‘合作88’自交分离群体叶绿体基因组遗传组成分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1649-1663. |
| [2] | 潘佳佳, 张东梅, 孟建, 高苏南, 朱凯杰, 刘军伟, 李国怀. 李坏死环斑病毒诱导的桃PpPDS沉默体系的优化及验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1587-1600. |
| [3] | 贡丹敏, 蔡林志, 丁仁, 马燕燕, 王万兴, 熊兴耀, 胡新喜. 钾肥种类对马铃薯生长和镉吸收积累的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1332-1342. |
| [4] | 谭杰, 刘建刚, 刘菊, 简银巧, 李广存, 金黎平, 徐建飞. 适合马铃薯块茎计算机断层扫描原位观察的栽培基质筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1085-1094. |
| [5] | 尹健, 朱曦鉴, 吴瑶瑶, 李灿辉, 张金喆. 马铃薯miR319基因家族靶基因预测及其功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 583-595. |
| [6] | 王 宽, 祁利潘, 吴桂丽, 冯 琰, 王 磊, 尹 江, 罗亚婷, 王 燕, 刘 畅, 龚学臣, 王海军. 中早熟马铃薯新品种‘北方002’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 141-142. |
| [7] | 祁利潘, 冯 琰, 王 磊, 尹 江, 王 宽, 罗亚婷, 龚学臣, 刘 畅, 王 燕. 马铃薯新品种‘北方004’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 143-144. |
| [8] | 李燕山, 隋启君, 蒋 伟, 杨琼芬, 白建明. 鲜食、淀粉兼用型马铃薯新品种‘云薯113’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 145-146. |
| [9] | 邹 雪, 丁 凡, 刘丽芳, 余韩开宗, 陈年伟, 饶莉萍. 紫色马铃薯新品种‘绵紫芋1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 93-94. |
| [10] | 闫文渊, 秦军红, 段绍光, 徐建飞, 简银巧, 金黎平, 李广存. 水氮耦合对马铃薯光合特性、块茎形成和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1491-1504. |
| [11] | 邱可立, 王玉民, 何金铃, 俞红, 潘海发, 盛玉, 谢庆梅, 陈红莉, 周晖, 张金云. 桃漆酶家族基因鉴定及PpLAC21功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1351-1362. |
| [12] | 祁利潘, 李越, 王磊, 冯琰, 王宽, 尹江, 郭华春. 马铃薯与枸杞嫁接愈合过程的解剖学观察[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 868-874. |
| [13] | 戴文珊, 吴玥, 王敏. 金柑FcRGA1抗溃疡病机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2325-233. |
| [14] | 叶广继, 郑贞贞, 纳添仓, 王舰. 马铃薯资源糖苷生物碱含量评价及合成相关基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2357-2366. |
| [15] | 齐希梁, 刘聪利, 宋露露, 李明. 甜樱桃磷酸蔗糖合酶基因PavSPS的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(8): 1446-1456. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司