
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (7): 1505-1518.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0474
钱婕妤, 蒋玲莉, 郑钢, 陈佳红, 赖吴浩, 许梦晗, 付建新, 张超( )
)
收稿日期:2022-02-27
修回日期:2022-04-24
出版日期:2022-07-25
发布日期:2022-07-29
基金资助:
QIAN Jieyu, JIANG Lingli, ZHENG Gang, CHEN Jiahong, LAI Wuhao, XU Menghan, FU Jianxin, ZHANG Chao( )
)
Received:2022-02-27
Revised:2022-04-24
Online:2022-07-25
Published:2022-07-29
摘要:
以百日草‘梦境红色’作为试验材料,基于其转录组初步鉴定出33个MYB转录因子。系统进化树分析,鉴定出10个可能参与调控花青素苷合成的R2R3-MYB蛋白,其中S4亚族5个、S6亚族3个、S7亚族2个。结合这10个MYB基因表达和花瓣花青素苷含量变化结果,推测S4亚族ZeMYB32可能负调控花青素苷的合成,而ZeMYB3和ZeMYB16可能促进花青素苷的积累。此外,S6亚族ZeMYB9和ZeMYB10可能正调控花青素苷的合成。进一步研究发现,ZeMYB9定位于细胞核内。烟草中过表达ZeMYB9显著促进其叶片花青素苷的积累,花青素苷合成相关基因上调表达,表明ZeMYB9正向调控花青素合成。
中图分类号:
钱婕妤, 蒋玲莉, 郑钢, 陈佳红, 赖吴浩, 许梦晗, 付建新, 张超. 百日草花青素苷合成相关MYB转录因子筛选及ZeMYB9功能研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1505-1518.
QIAN Jieyu, JIANG Lingli, ZHENG Gang, CHEN Jiahong, LAI Wuhao, XU Menghan, FU Jianxin, ZHANG Chao. Identification and Expression Analysis of MYB Transcription Factors Regulating the Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Zinnia elegans and Function Research of ZeMYB9[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1505-1518.
| 材料 Material | 基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 百日草Zinnia elegans | ZeMYB3 | CGGGCCGTACAGATAACGAGAT | TGTTGGGATTTGTTGCGAGTG |
| ZeMYB6 | GACGGCTGAAGAAGATGAGAAGT | TCCGACCTCAAGTAGTTAATCCA | |
| ZeMYB9 | ACCAGGAAGAACTGCTAATGATGT | TGTGACCGCTCGTGGTTGTTA | |
| ZeMYB10 | ATGGTGCGGAAGGGTGTATG | GCTCGGAGTGGAACAAGGTG | |
| ZeMYB16 | AAAGCTCACGGTGAAGGTTGC | AAGGCTGTGGAGTTTGATGATAAGT | |
| ZeMYB20 | GTGGTCGTTGATTGCTGGAAG | TGAAGATCGCAGTCGTCGTAG | |
| ZeMYB22 | AGTTGTAGGTTGCGGTGGTTA | ATTGGCGGTTCTTCCTGGTAT | |
| ZeMYB23 | GGTCGTTGATTGCTGGAAGGT | TGAAGATCGCAGTCGTCGTAG | |
| ZeMYB32 | CGTCAAGGCTACCAGGAAGGA | ACTCAACGACCTGTGCGGAAT | |
| ZeMYB33 | TACCTGGACGAACAGACAACG | ACTCGACTGCTACGCCTGGAT | |
| ZeACT | TTGTGCTGGATTCTGGGGATGGT | GCAGTTTCAAGCTCTTGCTCGTAGTC | |
| 烟草Nicotiana tabacum | NtEF1α | TGGTTGTGACTTTTGGTCCCA | ACAAACCCACGCTTGAGATCC |
| NtCHS | AAGCAAGAGAAACTAAAGGCTACAAG | AAATCCAAAAAGCACACCCCAT | |
| NtCHI | CGGGTGCCTCCATTCTTTTTACT | CCTGACACTCTTTCGGCGATACTAC | |
| NtF3H | CCAGACAAACCAGATGGATGGATAG | CAAGGGTAAGGTCGGGCTGTG | |
| NtF3'H | TGGCTATTTCATTCCAAAAGGCTCA | CTTCAAAGTCATTTCCTCGCACATC | |
| NtDFR | GCAGTTGCTTCCCTTTTCTACC | TTCCCCATTGGTTGACTTTCC | |
| NtANS | GTGCCTGGGTTACAACTTTTCTATG | CATTGCTTAGGATTTCAAGGGTGTC | |
| NtUFGT | GAGTGCATTGGATGCCTTTT | CCAGCTCCATTAGGTCCTTG | |
| NtAN1a | ACCATTCTCGAACACCGAAG | TGCTAGGGCACAATGTGAAG | |
| NtAN1b | CTTGAACACTTCTCAAACCGA | TGCTAGGGCACAATGTGAAG |
表1 本研究中所用的qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 1 qRT-PCR primer sequences used in this study
| 材料 Material | 基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 百日草Zinnia elegans | ZeMYB3 | CGGGCCGTACAGATAACGAGAT | TGTTGGGATTTGTTGCGAGTG |
| ZeMYB6 | GACGGCTGAAGAAGATGAGAAGT | TCCGACCTCAAGTAGTTAATCCA | |
| ZeMYB9 | ACCAGGAAGAACTGCTAATGATGT | TGTGACCGCTCGTGGTTGTTA | |
| ZeMYB10 | ATGGTGCGGAAGGGTGTATG | GCTCGGAGTGGAACAAGGTG | |
| ZeMYB16 | AAAGCTCACGGTGAAGGTTGC | AAGGCTGTGGAGTTTGATGATAAGT | |
| ZeMYB20 | GTGGTCGTTGATTGCTGGAAG | TGAAGATCGCAGTCGTCGTAG | |
| ZeMYB22 | AGTTGTAGGTTGCGGTGGTTA | ATTGGCGGTTCTTCCTGGTAT | |
| ZeMYB23 | GGTCGTTGATTGCTGGAAGGT | TGAAGATCGCAGTCGTCGTAG | |
| ZeMYB32 | CGTCAAGGCTACCAGGAAGGA | ACTCAACGACCTGTGCGGAAT | |
| ZeMYB33 | TACCTGGACGAACAGACAACG | ACTCGACTGCTACGCCTGGAT | |
| ZeACT | TTGTGCTGGATTCTGGGGATGGT | GCAGTTTCAAGCTCTTGCTCGTAGTC | |
| 烟草Nicotiana tabacum | NtEF1α | TGGTTGTGACTTTTGGTCCCA | ACAAACCCACGCTTGAGATCC |
| NtCHS | AAGCAAGAGAAACTAAAGGCTACAAG | AAATCCAAAAAGCACACCCCAT | |
| NtCHI | CGGGTGCCTCCATTCTTTTTACT | CCTGACACTCTTTCGGCGATACTAC | |
| NtF3H | CCAGACAAACCAGATGGATGGATAG | CAAGGGTAAGGTCGGGCTGTG | |
| NtF3'H | TGGCTATTTCATTCCAAAAGGCTCA | CTTCAAAGTCATTTCCTCGCACATC | |
| NtDFR | GCAGTTGCTTCCCTTTTCTACC | TTCCCCATTGGTTGACTTTCC | |
| NtANS | GTGCCTGGGTTACAACTTTTCTATG | CATTGCTTAGGATTTCAAGGGTGTC | |
| NtUFGT | GAGTGCATTGGATGCCTTTT | CCAGCTCCATTAGGTCCTTG | |
| NtAN1a | ACCATTCTCGAACACCGAAG | TGCTAGGGCACAATGTGAAG | |
| NtAN1b | CTTGAACACTTCTCAAACCGA | TGCTAGGGCACAATGTGAAG |
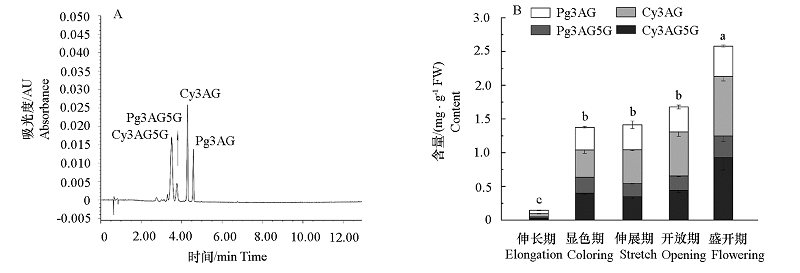
图2 百日草‘梦境红色’不同开放阶段花青素苷UPLC色谱图(A)和含量变化(B)
Fig. 2 UPLC chromatogram(A)and content changes(B)of anthocyanin in Zinnia elegans‘Dreamland Red’at different flower developmental stages
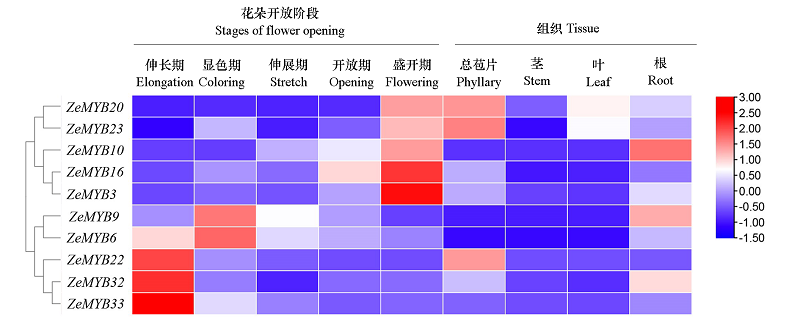
图5 百日草R2R3-MYB基因在花发育阶段表达的热图聚类基因表达数据换算成以2为底的对数进行计算和层次聚类。红框和蓝框分别表示高表达水平和低表达水平。
Fig. 5 Heatmap clustering analysis of R2R3-MYB expression in during flower development stages flowers of Zinnia elegansThe gene expression data was converted into the base-2 logarithm for calculation and hierarchical clustering. Red and blue boxes indicated high and low expression levels correspondingly.
| 基因 Gene | S4 | S6 | S7 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZeMYB3 | ZeMYB16 | ZeMYB20 | ZeMYB23 | ZeMYB32 | ZeMYB9 | ZeMYB10 | ZeMYB22 | ZeMYB6 | ZeMYB33 | |
| ZeCHS | -0.529* | -0.614* | -0.427 | -0.584* | 0.940** | 0.084 | -0.687** | 0.987** | 0.420 | 0.983** |
| ZeCHI | -0.684** | -0.727** | -0.628* | -0.594* | 0.835** | 0.425 | -0.883** | 0.911** | 0.620* | 0.935** |
| ZeF3H | -0.616* | -0.563* | -0.520* | -0.229 | 0.170 | 0.877** | -0.747** | 0.277 | 0.673** | 0.363 |
| ZeF3'H | -0.814** | -0.880** | -0.896** | -0.693** | 0.050 | 0.785** | -0.820** | 0.215 | 0.522 | 0.262 |
| ZeDFR | -0.312 | -0.346 | -0.451 | -0.264 | -0.686** | 0.511 | -0.128 | -0.564* | 0.047 | -0.532* |
| ZeANS | -0.677** | -0.610* | -0.812** | -0.487 | -0.185 | 0.806** | -0.633* | -0.069 | 0.459 | -0.035 |
| Ze3GT | 0.207 | 0.350 | 0.610* | 0.574* | 0.410 | -0.045 | 0.078 | 0.346 | 0.147 | 0.391 |
| Ze5GT | -0.622* | -0.634* | -0.671** | -0.463 | 0.274 | 0.680** | -0.703** | 0.349 | 0.413 | 0.397 |
| ZeAT1 | -0.553* | -0.632* | -0.529* | -0.622* | 0.556* | 0.258 | -0.548* | 0.607* | 0.315 | 0.617* |
| ZeAT2 | -0.281 | -0.336 | -0.217 | -0.332 | 0.708** | 0.062 | -0.379 | 0.654** | 0.440 | 0.641* |
| ZeAT3 | 0.105 | 0.241 | 0.423 | 0.531* | -0.102 | 0.263 | 0.077 | -0.098 | 0.056 | -0.008 |
表2 百日草ZeMYB基因表达量与结构基因表达量相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of expression level of ZeMYB genes with expression level of structural genes in Zinnia elegans
| 基因 Gene | S4 | S6 | S7 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZeMYB3 | ZeMYB16 | ZeMYB20 | ZeMYB23 | ZeMYB32 | ZeMYB9 | ZeMYB10 | ZeMYB22 | ZeMYB6 | ZeMYB33 | |
| ZeCHS | -0.529* | -0.614* | -0.427 | -0.584* | 0.940** | 0.084 | -0.687** | 0.987** | 0.420 | 0.983** |
| ZeCHI | -0.684** | -0.727** | -0.628* | -0.594* | 0.835** | 0.425 | -0.883** | 0.911** | 0.620* | 0.935** |
| ZeF3H | -0.616* | -0.563* | -0.520* | -0.229 | 0.170 | 0.877** | -0.747** | 0.277 | 0.673** | 0.363 |
| ZeF3'H | -0.814** | -0.880** | -0.896** | -0.693** | 0.050 | 0.785** | -0.820** | 0.215 | 0.522 | 0.262 |
| ZeDFR | -0.312 | -0.346 | -0.451 | -0.264 | -0.686** | 0.511 | -0.128 | -0.564* | 0.047 | -0.532* |
| ZeANS | -0.677** | -0.610* | -0.812** | -0.487 | -0.185 | 0.806** | -0.633* | -0.069 | 0.459 | -0.035 |
| Ze3GT | 0.207 | 0.350 | 0.610* | 0.574* | 0.410 | -0.045 | 0.078 | 0.346 | 0.147 | 0.391 |
| Ze5GT | -0.622* | -0.634* | -0.671** | -0.463 | 0.274 | 0.680** | -0.703** | 0.349 | 0.413 | 0.397 |
| ZeAT1 | -0.553* | -0.632* | -0.529* | -0.622* | 0.556* | 0.258 | -0.548* | 0.607* | 0.315 | 0.617* |
| ZeAT2 | -0.281 | -0.336 | -0.217 | -0.332 | 0.708** | 0.062 | -0.379 | 0.654** | 0.440 | 0.641* |
| ZeAT3 | 0.105 | 0.241 | 0.423 | 0.531* | -0.102 | 0.263 | 0.077 | -0.098 | 0.056 | -0.008 |
| [1] |
Aharoni A, Vos C, Wein M, Sun Z, O'Connell A P. 2010. The strawberry FaMYB1 transcription factor suppresses anthocyanin and flavonol accumulation in transgenic tobacco. The Plant Journal, 28 (3):319-332.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2001.01154.x URL |
| [2] |
Boyle T H, Stimart D P. 1989. Anatomical and biochemical factors determining ray floret color of Zinnia angustifolia,Z. elegans,and their interspecific hybrids. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 114:499-505.
doi: 10.21273/JASHS.114.3.499 URL |
| [3] |
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L. 2010. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends in Plant Science, 15:573-581.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.06.005 URL |
| [4] |
Gerats A G M, Farcy E, Wallroth M, Groot S P C, Schram A. 1984. Control of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Petunia hybrida by multiple allelic series of the genes An1and An2. Genetics, 106 (3):501-508.
doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.3.501 pmid: 17246198 |
| [5] |
Gonzalez A, Zhao M, Leavitt J M, Lloyd A M. 2010. Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/MYB transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. The Plant Journal, 53:814-827.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03373.x URL |
| [6] |
Grotewold E. 2006. The genetics and biochemistry of floral pigments. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 57:761-780.
pmid: 16669781 |
| [7] |
Heppel S C, Jaffé F W, Takos A M, Schellmann S, Bogs J. 2013. Identification of key amino acids for the evolution of promoter target specificity of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin regulating MYB factors. Plant Molecular Biology, 82:457-471.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0074-8 pmid: 23689818 |
| [8] | Hong Yanhong, Ye Qinghua, Li Zekun, Wang Wei, Xie Qian, Chen Qingxi, Chen Jianqing. 2021. Accumulation of anthocyanins in red-flowered strawberry‘Meihong’petals and expression analysis of MYB gene. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (8):1470-1484. |
| 洪燕红, 叶清华, 李泽坤, 王威, 谢倩, 陈清西, 陈建清. 2021. 红花草莓‘莓红’花瓣花色苷积累及其MYB基因的表达分析. 园艺学报, 48 (8):1470-1484. | |
| [9] |
Jin H, Cominelli E, Bailey P, Parr A, Mehrtens F, Jones J, Tonelli C, Weisshaar B, Martin C. 2000. Transcriptional repression by AtMYB4 controls production of UV-protecting sunscreens in Arabidopsis. The EMBO Journal, 19:6150-6161.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.22.6150 URL |
| [10] | Ke Yujie, Chen Mingkun, Ma Shanhu, Ou Yue, Wang Yi, Zheng Qingdong, Liu Zhongjian, Ai Ye. 2021. Research progress of MYB transcription factors in Orchidaceae. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (11):2311-2320. (in Chinese) |
| 柯玉洁, 陈明堃, 马山虎, 欧悦, 王艺, 郑清冬, 刘仲健, 艾叶. 2021. 兰科植物MYB 转录因子研究进展. 园艺学报, 48 (11):2311-2320. | |
| [11] |
Li C, Qiu J, Yang G, Huang S, Yin J. 2016. Isolation and characterization of a R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in the spathes of Anthurium andraeanum(Hort.). Plant Cell Reports, 35 (10):2151-2165.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-016-2025-8 URL |
| [12] | Li Chonghui, Yang Guangsui, Zhang Zhiqun, Yin Junmei. 2021. A novel R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene AaMYB6involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in Anthurium andraeanum. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (10):1859-1872. (in Chinese) |
| 李崇晖, 杨光穗, 张志群, 尹俊梅. 2021. 红掌R2R3-MYB转录因子基因AaMYB6调控花青素苷合成. 园艺学报, 48 (10):1859-1872. | |
| [13] | Li Guisheng. 2021. Comparative analysis of‘Jinyan’and‘Hongyang’kiwifruit transcriptomes. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (6):1183-1196. (in Chinese) |
| 李贵生. 2021. 猕猴桃‘金艳’和‘红阳’果实转录组的比较分析. 园艺学报, 48 (6):1183-1196. | |
| [14] |
Li M, Li Y, Guo L, Gong N, Pang Y, Jiang W, Liu Y, Jiang X, Zhao L, Wang Y, Xie D-Y, Gao L, Xia T. 2017. Functional characterization of tea(Camellia sinensis)MYB4a transcription factor using an integrative approach. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8:943-960.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00943 URL |
| [15] | Li Mou-liang, Zhang Xiao-ni, Lin Sheng-nan, Wu Quan-shu, Bao Man-zhu, Fu Xiao-peng. 2020. Genome-wide Identification and Analysis of R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor in Rosa chinensis. Molecular Plant Breeding(online), 18 (33):1-11. (in Chinese) |
| 李谋亮, 张晓妮, 林胜男, 吴全淑, 包满珠, 傅小鹏. 2020. 月季R2R3-MYB转录因子全基因组鉴定与分析. 分子植物育种(网络版), 18 (33):1-11. | |
| [16] |
Li Y, Liang J, Zeng X, Guo H, Luo Y, Kear P, Zhang S, Zhu G. 2021. Genome-wide analysis of MYB gene family in potato provides insights into tissue-specific regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Horticultural Plant Journal, 7 (2):129-141.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.12.001 URL |
| [17] |
Li Y, Shan X, Tong L, Wei C, Lu K, Li S, Kimani S, Wang S, Wang L, Gao X. 2020. The conserved and particular roles of the R2R3-MYB regulator FhPAP1 from Freesia hybrida in flower anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant and Cell Physiology, 61:1365-1380.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcaa065 URL |
| [18] |
Matus J T, Aquea F, Arce-Johnson P. 2008. Analysis of the grape MYB R2R3 subfamily reveals expanded wine quality-related clades and conserved gene structure organization across Vitis and Arabidopsis genomes. BMC Plant Biology, 8 (1):83.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-8-83 URL |
| [19] |
Qian J, Lai W, Jiang L, Zhan H, Zhai M, Fu J, Zhang C. 2021. Association between differential gene expression and anthocyanin biosynthesis underlying the diverse array of petal colors in Zinnia elegans. Scientia Horticulturae, 277:109809.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109809 URL |
| [20] |
Shen H, He X, Poovaiah C R, Wuddineh W A, Ma J, Mann D G, Wang H, Jackson L, Tang Y, Fang C, Richard A D. 2012. Functional characterization of the switchgrass(Panicum virgatum)R2R3-MYB transcription factor PvMYB4for improvement of lignocellulosic feedstocks. New Phytologist, 193:121-136.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03922.x pmid: 21988539 |
| [21] |
Stevenson C C, Harrington G N. 2009. The impact of supplemental carbon sources on Arabidopsis thaliana growth,chlorophyll content and anthocyanin accumulation. Plant Growth Regulation, 59 (3):255.
doi: 10.1007/s10725-009-9412-x URL |
| [22] |
Stracke R, Ishihara H, Huep G, Barsch A, Mehrtens F, Niehaus K, Weisshaar B. 2007. Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. The Plant Journal, 50:660-677.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03078.x URL |
| [23] |
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B. 2001. The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 4 (5):447-456.
pmid: 11597504 |
| [24] |
Sun B, Zhu Z, Cao P, Chen H, Chen C, Zhou X, Mao Y, Lei J, Jiang Y, Meng W, Wang Y, Liu S. 2016. Purple foliage coloration in tea (Camellia sinensis L.)arises from activation of the R2R3-MYB transcription factor CsAN1. Scientific Reports, 6:32534.
doi: 10.1038/srep32534 URL |
| [25] |
Tanaka Y, Sasaki N, Ohmiya A. 2008. Biosynthesis of plant pigments: anthocyanins,betalains and carotenoids. The Plant Journal, 54:733-749.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03447.x URL |
| [26] |
Viegas P, Mathews H, Bhatia C R, Notani N K. 1987. Monohybrid and dihybrid segregations in the progenies of tobacco transformed for kanamycin resistance with a Ti-vector system. Journal of Genetics, 66 (1):25-31.
doi: 10.1007/BF02934453 URL |
| [27] |
Vimolmangkang S, Han Y, Wei G, Korban S S. 2013. An apple MYB transcription factor,MdMYB3,is involved in regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis and flower development. BMC Plant Biology, 13 (1):176-188.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-13-176 URL |
| [28] |
Xu H, Wang N, Liu J, Qu C, Wang Y, Jiang S, Lu N, Wang D, Zhang Z, Chen X. 2017. The molecular mechanism underlying anthocyanin metabolism in apple using the MdMYB16 and MdbHLH33genes. Plant Molecular Biology, 94:149-165.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-017-0601-0 URL |
| [29] |
Yan H, Pei X, Zhang H, Li X, Zhang X, Zhao M, Chiang V, Sederoff R R, Zhao X. 2021. MYB-mediated regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22 (6):3103.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22063103 URL |
| [30] |
Yang C Q, Sha G Y, Wei T, Ma B Q, Li C Y, Li P M, Zou Y J, Xu L F, Ma F W. 2021. Linkage map and QTL mapping of red flesh locus in apple using a R1R1 × R6R6 population. Horticultural Plant Journal, 7 (5):393-400.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.12.008 URL |
| [31] | Yao Yifan, Dong Bin, Feng Chengyong, Yang Liyuan, Zhao Hongbo. 2020. Identification of R2R3-MYB family genes in Osmanthus fragrans and analysis of their expression during flower opening. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (10):164-176. (in Chinese) |
| 姚亦凡, 董彬, 冯成庸, 杨丽媛, 赵宏波. 2020. 桂花R2R3-MYB家族基因鉴定及其在花开放过程中的表达分析. 园艺学报, 47 (10):2027-2039. | |
| [32] | Zhao Jia, Liu Rong, Yang Fan, Li Xin, Liu Housheng, Yan Qian, Xiao Yuehua. 2015. Cloning and expression analysis of anthocyanidin-related R2R3-MYB protein gene from Rosa chinensis. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 48 (7):1392-1404. (in Chinese) |
| 赵佳, 刘荣, 杨帆, 李鑫, 刘厚生, 严倩, 肖月华. 2015. 月季花青素苷相关R2R3-MYB蛋白基因的克隆和表达分析. 中国农业科学, 48 (7):1392-1404. | |
| [33] | Zheng Qingdong, Wang Yi, Ou Yue, Ke Yujie, Yao Yahe, Wang Mengjie, Chen Jiayi, Ai Ye. 2021. Research advances of genes responsible for flower colors in Orchidaceae. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (10):2057-2072. (in Chinese) |
| 郑清冬, 王艺, 欧悦, 柯玉洁, 姚亚合, 王梦洁, 陈嘉忆, 艾叶. 2021. 兰科植物花色相关基因研究进展. 园艺学报, 48 (10):2057-2072. | |
| [34] |
Zhong C, Tang Y, Pang B, Li X, Yang Y, Deng J, Feng C, Li L, Ren G, Wang Y, Peng J, Sun S, Liang S, Wang X. 2020. The R2R3-MYB transcription factor GhMYB1a regulates flavonol and anthocyanin accumulation in Gerbera hybrida. Horticulture Research, 7:78.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-0296-2 URL |
| [35] | Zhou Yang-Li, Hou Shuo, Zheng Zhengquan, Gao Yan-hui, Tong Zaikang. 2020. Functional study of LsMYBs gene in VIGS gene silencing system. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 28 (6):974-983. (in Chinese) |
| 周洋丽, 侯朔, 郑正权, 高燕会, 童再康. 2020. 基于VIGS基因沉默体系的换锦花LsMYBs基因功能研究. 农业生物技术学报, 28 (6):974-983. |
| [1] | 叶子茂, 申晚霞, 刘梦雨, 王 彤, 张晓楠, 余 歆, 刘小丰, 赵晓春, . R2R3-MYB转录因子CitMYB21对柑橘类黄酮生物合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 250-264. |
| [2] | 黄玲, 胡先梅, 梁泽慧, 王艳平, 产祝龙, 向林. 郁金香花青素合成酶基因TgANS的克隆与功能鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1935-1944. |
| [3] | 李茂福, 杨媛, 王华, 范又维, 孙佩, 金万梅. 月季中R2R3-MYB基因RhMYB113c调控花青素苷合成[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1957-1966. |
| [4] | 许海峰, 王中堂, 陈新, 刘志国, 王利虎, 刘平, 刘孟军, 张琼. 冬枣果皮着色相关类黄酮靶向代谢组学及潜在MYB转录因子分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1761-1771. |
| [5] | 陈道宗, 刘镒, 沈文杰, 朱博, 谭晨. 白菜、甘蓝和甘蓝型油菜PAP1/2同源基因的鉴定及分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1301-1312. |
| [6] | 朱自果, 张庆田, 韩真, 李勃, 李国栋, 李秀杰. 欧洲葡萄VvMYB6正向调控花青素合成[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(3): 465-476. |
| [7] | 杨婷, 薛珍珍, 李娜, 郎校安, 李凌飞, 钟春梅. 铁十字秋海棠斑叶发育过程内参基因筛选及验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(11): 2251-2261. |
| [8] | 柯玉洁, 陈明堃, 马山虎, 欧悦, 王艺, 郑清冬, 刘仲健, 艾叶. 兰科植物MYB转录因子研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(11): 2311-2320. |
| [9] | 李崇晖, 杨光穗, 张志群, 尹俊梅. 红掌R2R3-MYB转录因子基因AaMYB6调控花青素苷合成[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(10): 1859-1872. |
| [10] | 殷涵泰, 尹俊梅, 廖易, 陆顺教, 李崇晖. 基于秋石斛花朵颜色、色素分布及表皮细胞形态的表型分类[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(10): 1907-1920. |
| [11] | 张倩, 杨楠, 桑海煜, 赵荣, 宋晓惜, 陈龙清, 向林, 赵凯歌. 蜡梅花青素苷合成相关基因CpTT8的克隆和功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(10): 1945-1955. |
| [12] | 洪艳, 武宇薇, 宋想, 李梦灵, 戴思兰. 光照调控园艺作物花青素苷生物合成的分子机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(10): 1983-2000. |
| [13] | 钟春梅, 王小菁. 非洲菊花色形成调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(10): 2031-2043. |
| [14] | 郑清冬, 王艺, 欧悦, 柯玉洁, 姚亚合, 王梦洁, 陈嘉忆, 艾叶. 兰科植物花色相关基因研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(10): 2057-2072. |
| [15] | 毕蒙蒙, 曹雨薇, 宋蒙, 唐玉超, 何国仁, 杨悦, 杨盼盼, 徐雷锋, 明军. 百合花色研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(10): 2073-2086. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司