
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1427-1440.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0746
徐强1, 马全会1, 闫芬芬1,*( ), 吴翠云1, 王玖瑞2, 刘孟军2
), 吴翠云1, 王玖瑞2, 刘孟军2
收稿日期:2024-11-11
修回日期:2025-03-07
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-06-20
通讯作者:
基金资助:
XU Qiang1, MA Quanhui1, YAN Fenfen1,*( ), WU Cuiyun1, WANG Jiurui2, and LIU Mengjun2
), WU Cuiyun1, WANG Jiurui2, and LIU Mengjun2
Received:2024-11-11
Revised:2025-03-07
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-06-20
摘要: 为探究杂交F1代制干枣果实重要性状的遗传变异规律,为制干枣品种选育提供理论依据。以‘雨虹’ב交城5号’的83个F1代株系及亲本为试材,对成熟期鲜果含水率、果实制干率、果实可食率及外观、质构参数、营养品质等14个指标进行测定和综合评价。结果表明,杂交后代果实制干率、可食率及鲜果含水率符合正态分布特征,为微效多基因控制的数量性状,制干率和可食率变异系数较高,为16.11%和7.70%,含水率变异系数最小,为2.05%,表现为趋中遗传。7个质构参数的变异系数在17.50% ~ 144.00%之间,呈现趋高遗传,其中粘附性分离比例接近于1︰1,推测为质量性状;硬度1、硬度2、内聚性、弹性、咀嚼性、粘黏性均符合正态分布,推测为微效多基因控制的性状。果实大小变异系数范围13.31% ~ 35.60%,果实纵径、单果质量和果形指数呈趋中偏低遗传,果实横径呈现趋高遗传。果实糖酸性状遗传变异系数范围18.18% ~ 36.61%,糖酸比表现趋高遗传趋势,可溶性糖、可滴定酸为趋中遗传。以质构参数为依据对F1代株系进行聚类分析,杂交后代群体聚为5个类群,其中Ⅱ类群(包括父本‘交城5号’,果实硬度较高,黏性较低)占比51.81%,表明F1代制干果实口感多数偏向于父本。经灰色关联度分析初步筛选出了5个果实制干品质优良的株系。
徐强, 马全会, 闫芬芬, 吴翠云, 王玖瑞, 刘孟军. 杂交F1代制干枣果实重要性状遗传变异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1427-1440.
XU Qiang, MA Quanhui, YAN Fenfen, WU Cuiyun, WANG Jiurui, and LIU Mengjun. Genetic Variation and Analysis of Important Traits of Dried Fruits in F1 Hybrid Jujube[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1427-1440.
| 性状 Trait | 亲本Parents | F1各性状的数量及比例 F1 fruit traits segregation ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨虹(♀) Yuhong | 交城5号(♂) Jiaocheng 5 | |||||
| 果实颜色 Fruit color | 红Red | 红Red | 橘红色Orang-red 6(7.23%) | 红色Red 65(78.31%) | 紫红色Amaranth 6(7.23%) | 棕红色Brownish-red 6(7.23%) |
| 皱缩程度 Shrinkage | 中等General | 饱满Full | 饱满Full 7(8.43%) | 中等General 58(69.88%) | 皱缩Crumpling 18(21.69%) | |
表1 枣‘雨虹’ב交城5号’F1代制干果实外观性状分离情况
Table 1 Trait segregation in dried fruits of jujube‘Yuhong’בJiaocheng 5’F1 progenies
| 性状 Trait | 亲本Parents | F1各性状的数量及比例 F1 fruit traits segregation ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨虹(♀) Yuhong | 交城5号(♂) Jiaocheng 5 | |||||
| 果实颜色 Fruit color | 红Red | 红Red | 橘红色Orang-red 6(7.23%) | 红色Red 65(78.31%) | 紫红色Amaranth 6(7.23%) | 棕红色Brownish-red 6(7.23%) |
| 皱缩程度 Shrinkage | 中等General | 饱满Full | 饱满Full 7(8.43%) | 中等General 58(69.88%) | 皱缩Crumpling 18(21.69%) | |
| 性状 Trait | 亲本Parents | F1代群体F1 progenies | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨虹 (♀) Yuhong | 交城5号 (♂) Jiaocheng 5 | MP | Mean ± SD | CV/% | VMP/% | Ta/% | HH/% | LL/% | |
| 可食率/% Edible rate | 93.13 | 95.94 | 94.53 | 94.52 ± 2.01 | 2.05 | -0.09 | 99.91 | 16.45 | 34.17 |
| 制干率/% Drying rate | 49.64 | 50.57 | 50.10 | 51.20 ± 8.03 | 16.11 | 2.64 | 102.64 | 42.42 | 49.49 |
| 含水率/% Moisture rate | 64.06 | 62.03 | 63.05 | 62.79 ± 4.84 | 7.70 | -0.40 | 99.59 | 36.27 | 24.50 |
表2 枣‘雨虹’ב交城5号’F1代果实可食率、制干率和含水率遗传变异分析
Table 2 Genetic variability and heritability estimates of edible rate,drying rate,and moisture rate in F1 progenies of jujube‘Yuhong’בJiaocheng 5’
| 性状 Trait | 亲本Parents | F1代群体F1 progenies | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨虹 (♀) Yuhong | 交城5号 (♂) Jiaocheng 5 | MP | Mean ± SD | CV/% | VMP/% | Ta/% | HH/% | LL/% | |
| 可食率/% Edible rate | 93.13 | 95.94 | 94.53 | 94.52 ± 2.01 | 2.05 | -0.09 | 99.91 | 16.45 | 34.17 |
| 制干率/% Drying rate | 49.64 | 50.57 | 50.10 | 51.20 ± 8.03 | 16.11 | 2.64 | 102.64 | 42.42 | 49.49 |
| 含水率/% Moisture rate | 64.06 | 62.03 | 63.05 | 62.79 ± 4.84 | 7.70 | -0.40 | 99.59 | 36.27 | 24.50 |
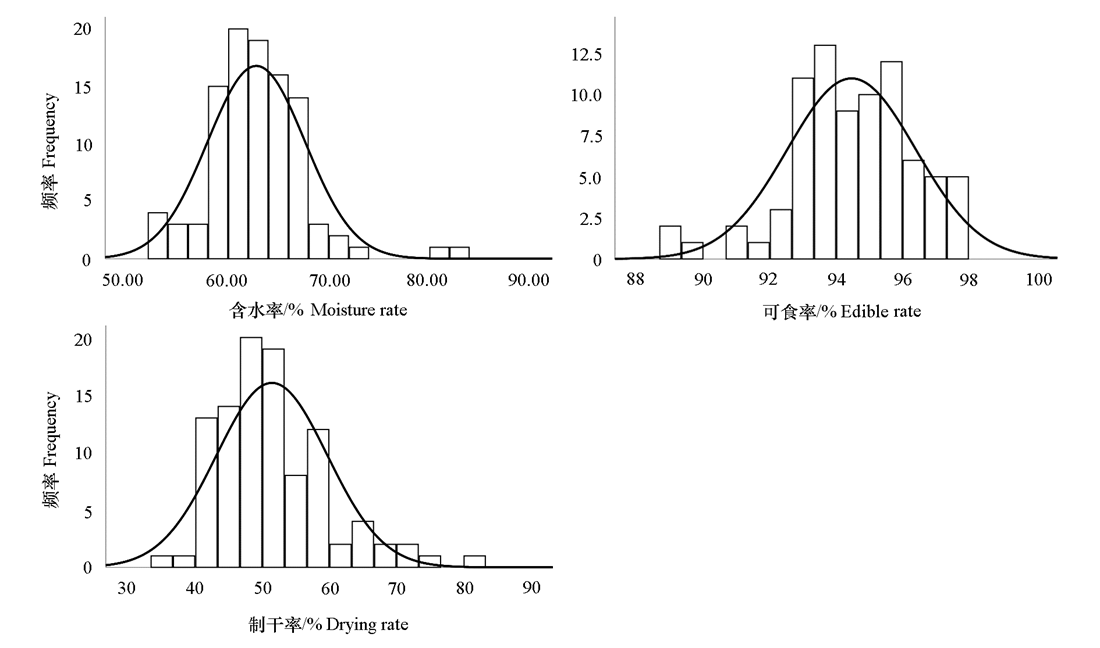
图2 枣‘雨虹’ב交城5号’F1代果实可食率、含水率及制干率的频率分布直方图
Fig. 2 Frequency distribution histograms of edible rate,moisture rate,and drying rate in F1 progenies of jujube‘Yuhong’בJiaocheng 5’
| 性状 Trait | 亲本Parents | F1代群体F1 progenies | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨虹 (♀) Yuhong | 交城5号 (♂) Jiaocheng 5 | MP | Mean ± SD | CV/% | VMP/% | Ta/% | HH/% | LL/% | |
| 硬度1/N Hardness 1 | 50.70 | 78.35 | 64.53 | 88.11 ± 28.91 | 32.82 | 36.54 | 136.54 | 64.29 | 13.09 |
| 硬度2/N Hardness 2 | 31.79 | 50.99 | 41.39 | 57.90 ± 19.37 | 33.46 | 39.89 | 139.89 | 64.28 | 11.90 |
| 内聚性Cohesiveness | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 17.50 | 14.33 | 114.33 | 76.82 | 11.90 |
| 弹性/mm Springiness | 1.47 | 1.62 | 1.54 | 1.87 ± 0.43 | 23.16 | 21.13 | 121.13 | 70.23 | 17.85 |
| 咀嚼性/(N · mm) Chewiness | 14.03 | 29.29 | 21.66 | 43.70 ± 23.60 | 53.99 | 101.76 | 201.76 | 71.42 | 10.71 |
| 粘附性/(N · mm) Adhesiveness | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.75 ± 1.08 | 144.00 | 167.86 | 267.86 | 42.85 | 0.05 | |
| 粘黏性/N Gumminess | 9.80 | 17.40 | 13.67 | 21.58 ± 8.56 | 39.67 | 57.86 | 157.86 | 66.66 | 11.90 |
表3 枣‘雨虹’ב交城5号’F1代制干果实质地参数遗传变异分析
Table 3 Genetic variation analysis of textural parameters in dried fruits of jujube‘Yuhong’בJiaocheng 5’F1 progenies
| 性状 Trait | 亲本Parents | F1代群体F1 progenies | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨虹 (♀) Yuhong | 交城5号 (♂) Jiaocheng 5 | MP | Mean ± SD | CV/% | VMP/% | Ta/% | HH/% | LL/% | |
| 硬度1/N Hardness 1 | 50.70 | 78.35 | 64.53 | 88.11 ± 28.91 | 32.82 | 36.54 | 136.54 | 64.29 | 13.09 |
| 硬度2/N Hardness 2 | 31.79 | 50.99 | 41.39 | 57.90 ± 19.37 | 33.46 | 39.89 | 139.89 | 64.28 | 11.90 |
| 内聚性Cohesiveness | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 17.50 | 14.33 | 114.33 | 76.82 | 11.90 |
| 弹性/mm Springiness | 1.47 | 1.62 | 1.54 | 1.87 ± 0.43 | 23.16 | 21.13 | 121.13 | 70.23 | 17.85 |
| 咀嚼性/(N · mm) Chewiness | 14.03 | 29.29 | 21.66 | 43.70 ± 23.60 | 53.99 | 101.76 | 201.76 | 71.42 | 10.71 |
| 粘附性/(N · mm) Adhesiveness | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.75 ± 1.08 | 144.00 | 167.86 | 267.86 | 42.85 | 0.05 | |
| 粘黏性/N Gumminess | 9.80 | 17.40 | 13.67 | 21.58 ± 8.56 | 39.67 | 57.86 | 157.86 | 66.66 | 11.90 |

图3 枣‘雨虹’ב交城5号’F1代制干果实质地参数频数分布直方图
Fig. 3 Frequency distribution histogram of textural parameters in dried fruits of jujube‘Yuhong’בJiaocheng 5’F1 progenies
| 性状 Trait | 亲本Parents | F1代群体F1 progenies | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨虹 (♀) Yuhong | 交城5号 (♂) Jiaocheng 5 | MP | Mean ± SD | CV/% | VMP/% | Ta/% | HH/% | LL/% | ||
| 果实纵径/mm Fruit length | 31.57 | 38.68 | 35.13 | 33.85 ± 5.18 | 15.30 | -3.63 | 96.37 | 13.63 | 35.22 | |
| 果实横径/mm Fruit diameter | 18.79 | 19.18 | 18.99 | 20.71 ± 2.76 | 13.31 | 9.08 | 109.08 | 66.30 | 25.00 | |
| 单果质量/g Single fruit weight | 4.82 | 7.43 | 6.13 | 5.59 ± 1.99 | 35.60 | -8.73 | 91.27 | 12.28 | 35.96 | |
| 果形指数Fruit shape index | 1.67 | 2.01 | 1.84 | 1.67 ± 0.37 | 22.42 | -9.33 | 90.67 | 15.90 | 53.40 | |
表4 枣‘雨虹’ב交城5号’F1代制干果实大小遗传变异分析
Table 4 Genetic variation analysis of fruit size in dried fruits of jujube‘Yuhong’בJiaocheng 5’F1 progenies
| 性状 Trait | 亲本Parents | F1代群体F1 progenies | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨虹 (♀) Yuhong | 交城5号 (♂) Jiaocheng 5 | MP | Mean ± SD | CV/% | VMP/% | Ta/% | HH/% | LL/% | ||
| 果实纵径/mm Fruit length | 31.57 | 38.68 | 35.13 | 33.85 ± 5.18 | 15.30 | -3.63 | 96.37 | 13.63 | 35.22 | |
| 果实横径/mm Fruit diameter | 18.79 | 19.18 | 18.99 | 20.71 ± 2.76 | 13.31 | 9.08 | 109.08 | 66.30 | 25.00 | |
| 单果质量/g Single fruit weight | 4.82 | 7.43 | 6.13 | 5.59 ± 1.99 | 35.60 | -8.73 | 91.27 | 12.28 | 35.96 | |
| 果形指数Fruit shape index | 1.67 | 2.01 | 1.84 | 1.67 ± 0.37 | 22.42 | -9.33 | 90.67 | 15.90 | 53.40 | |
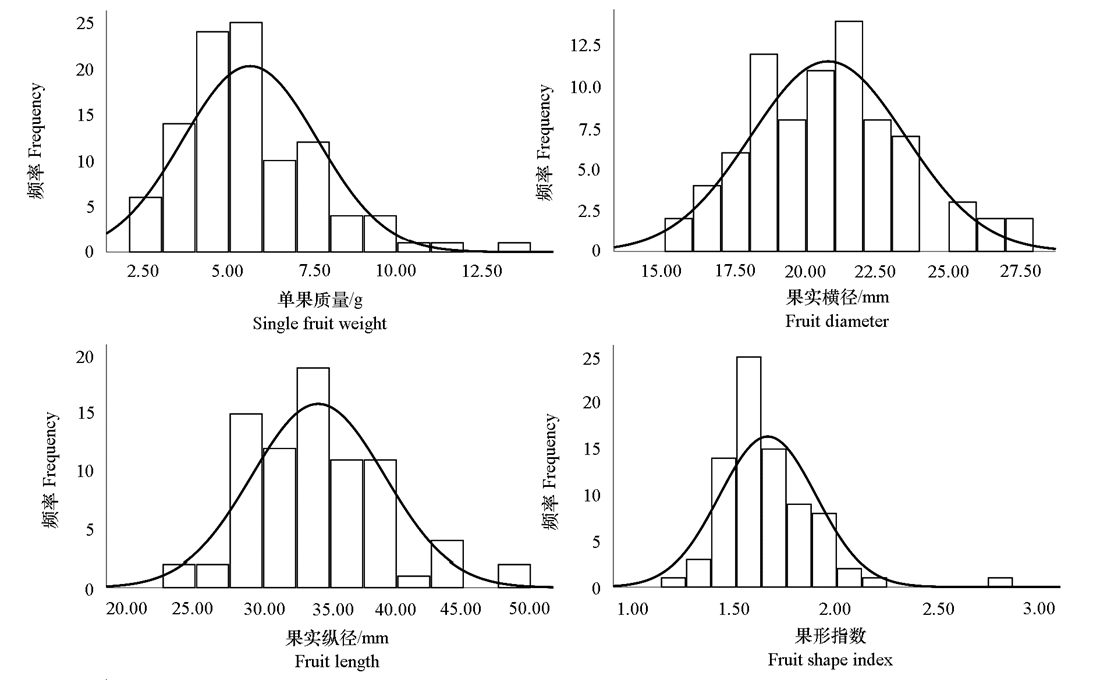
图4 枣‘雨虹’ב交城5号’F1代制干果实大小性状分布频数分布直方图
Fig. 4 frequency distribution histogram of fruit size traits in dried fruits of jujube‘Yuhong’בJiaocheng 5’F1 progenies
| 性状 Trait | 亲本Parents | F1代群体F1 progenies | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨虹 (♀) Yuhong | 交城5号 (♂) Jiaocheng 5 | MP | Mean ± SD | CV/% | VMP/% | Ta/% | HH/% | LL/% | |
| 可滴定酸含量/% Organic acid | 1.05 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.99 ± 0.26 | 18.18 | -1.00 | 55.00 | 40.24 | 48.78 |
| 可溶性糖含量/% Soluble sugar | 66.45 | 45.92 | 56.18 | 55.16 ± 9.88 | 26.26 | -1.82 | 176.00 | 14.63 | 17.07 |
| 糖酸比Sugar/acid | 62.78 | 48.46 | 55.62 | 58.90 ± 21.58 | 36.61 | 6.00 | 106.00 | 37.80 | 31.70 |
表5 枣‘雨虹’ב交城5号’F1代制干果实营养性状遗传变异分析
Table 5 Analysis of genetic variation in nutritional traits of dried fruits of jujube‘Yuhong’בJiaocheng 5’F1 progenies
| 性状 Trait | 亲本Parents | F1代群体F1 progenies | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨虹 (♀) Yuhong | 交城5号 (♂) Jiaocheng 5 | MP | Mean ± SD | CV/% | VMP/% | Ta/% | HH/% | LL/% | |
| 可滴定酸含量/% Organic acid | 1.05 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.99 ± 0.26 | 18.18 | -1.00 | 55.00 | 40.24 | 48.78 |
| 可溶性糖含量/% Soluble sugar | 66.45 | 45.92 | 56.18 | 55.16 ± 9.88 | 26.26 | -1.82 | 176.00 | 14.63 | 17.07 |
| 糖酸比Sugar/acid | 62.78 | 48.46 | 55.62 | 58.90 ± 21.58 | 36.61 | 6.00 | 106.00 | 37.80 | 31.70 |
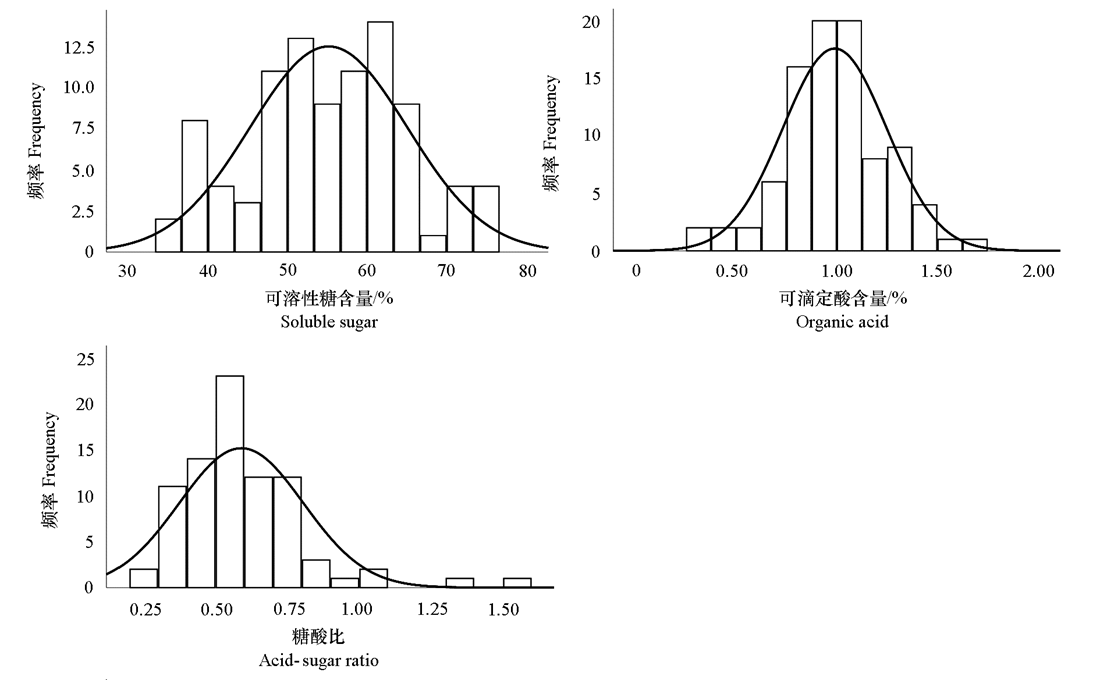
图5 枣‘雨虹’ב交城5号’F1代制干果实营养性状频数分布频数分布直方图
Fig. 5 Frequency distribution histogram of nutritional traits in dried fruits of jujube‘Yuhong’בJiaocheng 5’F1 progenies
| 性状 Trait | 硬度1 Hardness 1 | 粘附性 Gumminess | 硬度2 Hardness 2 | 内聚性 Cohesiveness | 弹性 Springiness | Adhesiveness 粘黏性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 硬度1 Hardness1 | ||||||
| 粘附性Gumminess | -0.238 | |||||
| 硬度2 Hardness2 | 0.981** | -0.221 | ||||
| 内聚性Cohesiveness | 0.439** | -0.157 | 0.518** | |||
| 弹性Springiness | 0.514** | -0.066 | 0.548** | 0.647** | ||
| 粘黏性Adhesiveness | 0.921** | -0.235 | 0.951** | 0.713** | 0.645** | |
| 咀嚼性Chewiness | 0.841** | -0.183 | 0.875** | 0.730** | 0.833** | 0.945** |
表6 F1代制干果实质构相关参数的相关性分析
Table 6 Correlation analysis of dried fruit texture parameters in F1 progenies
| 性状 Trait | 硬度1 Hardness 1 | 粘附性 Gumminess | 硬度2 Hardness 2 | 内聚性 Cohesiveness | 弹性 Springiness | Adhesiveness 粘黏性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 硬度1 Hardness1 | ||||||
| 粘附性Gumminess | -0.238 | |||||
| 硬度2 Hardness2 | 0.981** | -0.221 | ||||
| 内聚性Cohesiveness | 0.439** | -0.157 | 0.518** | |||
| 弹性Springiness | 0.514** | -0.066 | 0.548** | 0.647** | ||
| 粘黏性Adhesiveness | 0.921** | -0.235 | 0.951** | 0.713** | 0.645** | |
| 咀嚼性Chewiness | 0.841** | -0.183 | 0.875** | 0.730** | 0.833** | 0.945** |
| 性状 Traits | 单果质量 Single frut weight | 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar | 可滴定酸 Organic acid conten | 可食率 Edible proportion | 制干率 Drying rate | 硬度 Hardness | 果实口感 Fruit pulp texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 可溶性糖Soluble sugar | -0.008 | ||||||
| 可滴定酸 Organic acid conten | 0.066 | 0.002 | |||||
| 可食率Edible proportion | 0.153* | -0.083 | -0.026 | ||||
| 制干率Drying rate | -0.003 | -0.089 | 0.042 | -0.007 | |||
| 硬度1 Hardness 1 | 0.136 | 0.078 | 0.031 | 0.008 | -0.072 | ||
| 果实口感 Fruit pulp texture | 0.073 | -0.025 | -0.154 | 0.034 | -0.060 | 0.426** | |
| 皱缩程度 Degree of shrinkage | -0.033 | 0.090 | -0.109 | -0.055 | -0.011 | 0.061 | 0.390** |
表7 质构参数与果实性状的相关性分析
Table 7 Correlation analysis of key traits of dried fruit quality
| 性状 Traits | 单果质量 Single frut weight | 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar | 可滴定酸 Organic acid conten | 可食率 Edible proportion | 制干率 Drying rate | 硬度 Hardness | 果实口感 Fruit pulp texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 可溶性糖Soluble sugar | -0.008 | ||||||
| 可滴定酸 Organic acid conten | 0.066 | 0.002 | |||||
| 可食率Edible proportion | 0.153* | -0.083 | -0.026 | ||||
| 制干率Drying rate | -0.003 | -0.089 | 0.042 | -0.007 | |||
| 硬度1 Hardness 1 | 0.136 | 0.078 | 0.031 | 0.008 | -0.072 | ||
| 果实口感 Fruit pulp texture | 0.073 | -0.025 | -0.154 | 0.034 | -0.060 | 0.426** | |
| 皱缩程度 Degree of shrinkage | -0.033 | 0.090 | -0.109 | -0.055 | -0.011 | 0.061 | 0.390** |

图6 质构参数性状的聚类分析 H1:硬度1;Gu:粘附性;H2:硬度2;Co:内聚性;Sp:弹性;Ad:粘黏性;Gh:咀嚼性
Fig. 6 Cluster analysis of fruits texture parameters H1:Hardness 1;Gu:Gumminess;H2:Hardness 2;Co:Cohesiveness;Sp:Springiness;Ad:Adhesiveness;Gh:Chewiness
| 性状 Trait | J44 | J93 | J87 | J254 | J54 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单果质量Single fruit mass | 0.0739 | 0.0932 | 0.0900 | 0.0635 | 0.0826 |
| 可溶性糖Soluble sugar content | 0.0894 | 0.0593 | 0.0706 | 0.0660 | 0.0999 |
| 可滴定酸Organic acid content | 0.0866 | 0.0952 | 0.0709 | 0.0783 | 0.0895 |
| 可食率Edible rate | 0.0731 | 0.0739 | 0.0887 | 0.0883 | 0.0907 |
| 制干率 Drying rate | 0.0974 | 0.0657 | 0.0768 | 0.0985 | 0.0590 |
| 硬度1 Hardness 1 | 0.0852 | 0.0898 | 0.0748 | 0.0949 | 0.0494 |
| 口感Fruit pulp texture | 0.8320 | 0.8320 | 0.8320 | 0.8320 | 0.8320 |
| 皱缩程度Degree of shrinkage | 0.1205 | 0.1383 | 0.1383 | 0.1205 | 0.1383 |
| 加权关联度 Weighted correlation degree | 0.7663 | 0.7557 | 0.7502 | 0.7501 | 0.7496 |
| 排序Rank | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
表8 枣‘雨虹’ב交城5号’F1代5个优株的果实灰色关联加权系数
Table 8 Grey relational weighted coefficients of five superior F1 strains from jujube‘Yuhong’בJiaocheng 5’
| 性状 Trait | J44 | J93 | J87 | J254 | J54 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单果质量Single fruit mass | 0.0739 | 0.0932 | 0.0900 | 0.0635 | 0.0826 |
| 可溶性糖Soluble sugar content | 0.0894 | 0.0593 | 0.0706 | 0.0660 | 0.0999 |
| 可滴定酸Organic acid content | 0.0866 | 0.0952 | 0.0709 | 0.0783 | 0.0895 |
| 可食率Edible rate | 0.0731 | 0.0739 | 0.0887 | 0.0883 | 0.0907 |
| 制干率 Drying rate | 0.0974 | 0.0657 | 0.0768 | 0.0985 | 0.0590 |
| 硬度1 Hardness 1 | 0.0852 | 0.0898 | 0.0748 | 0.0949 | 0.0494 |
| 口感Fruit pulp texture | 0.8320 | 0.8320 | 0.8320 | 0.8320 | 0.8320 |
| 皱缩程度Degree of shrinkage | 0.1205 | 0.1383 | 0.1383 | 0.1205 | 0.1383 |
| 加权关联度 Weighted correlation degree | 0.7663 | 0.7557 | 0.7502 | 0.7501 | 0.7496 |
| 排序Rank | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 性状 Trait | J87 | J44 | J54 | J254 | J93 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单果质量/g Single fruit mass | 5.28 | 6.37 | 3.82 | 7.79 | 4.34 |
| 可溶性糖含量/% Soluble sugar content | 59.04 | 53.01 | 50.61 | 36.41 | 37.57 |
| 可滴定酸/% Organic acid content | 1.07 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 1.07 | 0.72 |
| 可食率/% Edible rate | 93.53 | 95.46 | 94.23 | 92.90 | 95.92 |
| 制干率/% Drying rate | 50.12 | 55.36 | 65.23 | 50.57 | 61.04 |
| 硬度1/N Hardness 1 | 101.44 | 129.71 | 176.59 | 56.84 | 81.03 |
| 口感Fruit pulp texture | 致密Compact | 致密Compact | 致密Compact | 致密Compact | 致密Compact |
| 皱缩程度Degree of shrinkage | 饱满 Full | 中等 General | 饱满 Full | 中等 General | 饱满 Full |
表9 枣‘雨虹’ב交城5号’F1代的优株及亲本制干果实性状指标
Table 9 The dried fruit traits of five superior F1 strains from jujube‘Yuhong’בJiaocheng 5’and parental lines
| 性状 Trait | J87 | J44 | J54 | J254 | J93 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单果质量/g Single fruit mass | 5.28 | 6.37 | 3.82 | 7.79 | 4.34 |
| 可溶性糖含量/% Soluble sugar content | 59.04 | 53.01 | 50.61 | 36.41 | 37.57 |
| 可滴定酸/% Organic acid content | 1.07 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 1.07 | 0.72 |
| 可食率/% Edible rate | 93.53 | 95.46 | 94.23 | 92.90 | 95.92 |
| 制干率/% Drying rate | 50.12 | 55.36 | 65.23 | 50.57 | 61.04 |
| 硬度1/N Hardness 1 | 101.44 | 129.71 | 176.59 | 56.84 | 81.03 |
| 口感Fruit pulp texture | 致密Compact | 致密Compact | 致密Compact | 致密Compact | 致密Compact |
| 皱缩程度Degree of shrinkage | 饱满 Full | 中等 General | 饱满 Full | 中等 General | 饱满 Full |
| [1] |
doi: 10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.20221104002 |
|
陈万年, 鲍荆凯, 潘依玲, 吴翠云, 王玖瑞, 刘孟军, 闫芬芬. 2023. 枣JMS2 × 交城5号F1代糖酸组分遗传变异分析. 植物遗传资源学报, 24 (3):767-779.
doi: 10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.20221104002 |
|
| [2] |
|
|
崔永宁, 陈洁珍, 史发超, 姜永华, 严倩, 欧良喜, 刘海伦, 蔡长河. 2022. 基于TPA法的荔枝资源果肉质地品质分析. 果树学报,(12):2241-2252.
|
|
| [3] |
|
|
樊保国, 李登科. 2011. 制干枣品种品质性状的因子分析与综合评价. 植物遗传资源学报, 12 (5):716-720.
doi: 10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.2011.05.008 |
|
| [4] |
|
|
高俊凤. 2006. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社:144-147.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
李登科. 2006. 枣种质资源描述规范和数据标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社:201-203
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
刘孟军, 王玖瑞. 2019. 新中国果树科学研究70年——枣. 果树学报, 36 (10):1369-1381.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
刘政海, 董志刚, 李晓梅, 谭敏, 杨镕兆, 杨兆亮, 唐晓萍. 2020. ‘威代尔’与‘霞多丽’葡萄杂交F1代果实性状遗传倾向分析. 果树学报, 37 (8):1122-1131.
|
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
罗宇佳. 2024. 枣杂交后代果实性状遗传变异分析及果实大小候选基因的挖掘[硕士论文]. 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
潘依玲, 鲍荆凯, 吴翠云, 王玖瑞, 刘孟军, 闫芬芬. 2023. 雄性不育枣‘JMS2’ב交城5号’杂交F1代花性状遗传变异分析. 西北农业学报, 32 (12):1913-1921.
|
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2014-0867 |
|
齐秀东, 魏建梅, 李永红. 2015. 苹果果实质地软化过程中碳水化合物代谢及其关键酶基因表达的变化. 园艺学报, 42 (3):409-417.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2014-0867 |
|
| [13] |
|
|
石建春, 王愈, 李志刚, 郝晓玲, 高灵芝, 宋长利. 2023. 三种干燥方法对不同采收期木枣干制品质影响. 食品工业科技, 44 (10):98-106.
|
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0056 |
|
唐海霞, 裴广营, 张琼, 王中堂. 2023. 枣果实相关性状QTL 定位分析. 园艺学报, 50 (4):754-764.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0056 |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
王晶晶, 陈奇凌, 王文军. 2022. 兵团红枣种植现状、存在问题及发展建议. 新疆农垦科技, 45 (4):1-3
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
魏利清, 万红军, 许铭强, 李瑾瑜, 逄焕明, 李焕荣. 2011. 枣干制过程中可溶性糖含量变化的规律. 食品与机械, 27 (6):67-70.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
谢欢, 王中堂, 李明玥, 李新岗. 2022. 枣杂交后代果实性状遗传分析. 经济林研究, 40 (2):125-134.
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0070 |
|
谢文杰, 陈西玲, 石国朝, 张鹏, 李新岗, 张睿, 段晓姗. 2024. 设施栽培‘冬枣’花发育和花蜜分泌规律的研究. 园艺学报, 51 (12):2735-2742.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0070 |
|
| [20] |
Xinjiang uygur autonomous region bureau of statistics. 2020 Xinjiang Statistical Yearbook. Beijing: China Statistical Publishing House:2-28. (in Chinese)
|
|
新疆维吾尔自治区统计局. 2020 新疆统计年鉴. 北京: 中国统计出版社:25-28.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
许铭强, 陈恺, 张艳艳, 逄焕明, 李焕荣, 李可. 2012. 干制温度对枣果实质构性能的影响. 食品与机械, 28 (5):59-62,70.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
闫芬芬, 王玖瑞, 冯一峰, 林敏娟, 吴翠云, 刘孟军. 2020. 枣规模化杂种创制技术体系的建立与应用研究进展. 果树学报, 37 (6):929-938.
|
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
|
张宝善, 陈锦屏, 李强. 2004. 干制方式对红枣Vc、还原糖和总酸变化的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),(11):117-121.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
张梅, 王利娜, 王姝婧, 杨智鹏, 马路婷, 刘伟峰, 魏喜喜, 李建贵. 2022. 基于层次—关联度的新疆骏枣品质性状分析及综合评价. 中南林业科技大学学报, 42 (1):78-85.
|
|
| [27] |
|
| [1] | 韩 飞, 张 琼, 李大卫, 吕海燕, 刘小莉, 田 华, 钟彩虹. 软枣猕猴桃授粉专用新品种‘中科猕枣雄1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 55-56. |
| [2] | 张玉平, 武 阳, 路东晔, 潘青华. 鲜食枣新品种‘京玉2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 69-70. |
| [3] | 帕提古丽 • 买买提吐尔逊, 周 斌, 罗青红, 盛 玮, 蒋 腾. 新疆大果沙枣新品种‘金莎’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 71-72. |
| [4] | 刘亚男, 鲍丹丹, 张四普, 牛佳佳, 许志飞, 杨永锋, 鲁云风. 叶面喷施纳米硒对猕猴桃果实氨基酸含量及代谢组的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1575-1587. |
| [5] | 姜凤超, 杨丽, 张俊环, 张美玲, 于文剑, 孙浩元. 杏果实中调控有机酸积累的QTL定位及其主效基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 846-856. |
| [6] | 孔佳涛, 付彩霞, 吴雅诺, 刘园, 胡哲辉, 徐娟, 黄皓, 赵曌, 陈磊, 陈嘉景. 冰糖橙风味组学解析及风味品质差异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 984-996. |
| [7] | 段青青, 韩梅梅, 王友平, 常培培, 谭月强, 张自坤. 外源褪黑素影响盐碱复合胁迫下西瓜种子萌发的综合评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 1020-1036. |
| [8] | 智慧, 杨菁菁, 罗建让. 牡丹96个品种表型多样性分析与观赏性综合评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 635-645. |
| [9] | 丛鑫, 胡乾元, 庞桂斌, 徐立荣, 徐征和, 刘鸿飞, 裴向丽. 灌溉水矿化度对冬枣生长及产量品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 714-726. |
| [10] | 陆秀萍, 汤智超, 唐文琨, 毛妃凤, 张万萍, 李经纬. 13种类病毒RNA/DNA基因组对番茄的侵染性鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 749-760. |
| [11] | 吴悠, 冀宏宇, 邓淑雯, 梁翠怡, 万志庭, 吴沙沙, 翟俊文. 三褶虾脊兰花发育相关基因RT-qPCR内参基因的筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2063-2074. |
| [12] | 刘新月, 翟昭慈, 陶佳淋, 冯坤, 蔡晓腾, 刘志国, 刘孟军. 不同落叶剂对冬枣落叶效果及养分回流的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2120-2130. |
| [13] | 李洁, 武超, 贾祥堑, 王娟. ‘壶瓶枣’果皮着色物质及其相关基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1728-1742. |
| [14] | 匡美美, 李黎, 马建伟, 刘原, 蒋鸿霏, 雷瑞, 满玉萍, 王一帆, 黄波, 王彦昌, 刘世彪. 利用中华猕猴桃杂交后代转录组测序筛选抗溃疡病相关基因[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1743-1757. |
| [15] | 郑传奇, 唐玉超, 杨盼盼, 彭富海, 徐雷锋, 唐乐, 支永明, 明军. 园艺植物苦味研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1529-1546. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司