
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 322-336.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0620
蔡泽彦1, 张明星2,3, 周池2,3, 陶禹2,3, 杨莎1, 李鑫2,3,*( ), 李雪峰1,2,*(
), 李雪峰1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-30
修回日期:2024-12-23
出版日期:2025-02-25
发布日期:2025-02-23
通讯作者:
基金资助:
CAI Zeyan1, ZHANG Mingxing2,3, ZHOU Chi2,3, TAO Yu2,3, YANG Sha1, LI Xin2,3,*( ), LI Xuefeng1,2,*(
), LI Xuefeng1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-30
Revised:2024-12-23
Published:2025-02-25
Online:2025-02-23
摘要:
以辣椒感疫病品种(伏地尖和茄门)和抗疫病品种(CM334和SJ-0948)为试验材料,分别提取根、茎、叶部位的DNA,并利用Illumina平台进行细菌16S rRNA基因v3-v4区域和真菌ITS1区域测序。结果表明,不同抗性品种在自然种植状态下内生微生物组成存在明显差异。易感品种伏地尖的根、茎和叶真菌群落的多样性、丰富度指数均显著低于抗病品种。门水平,不同抗性品种根、茎、叶的细菌和真菌优势菌门组成一致,但易感品种伏地尖根、茎、叶的子囊菌门(Ascomycota)真菌丰度均远高于抗病品种。属水平,抗病品种CM334根中优势细菌属有分枝杆菌属(Mycobacterium,相对丰度36.96%),茎中有2013Ark19i(15.21%)、发光杆菌属(Photobacterium,5.50%)、甲基杆菌属(Methylobacterium_ Methylorubrum,4.11%),叶中有金色单胞菌属(Aureimonas,3.02%)。易感品种伏地尖中存在较多的有害真菌属,其中镰刀菌属(Fusarium)在根、茎中的占比分别为9.50%和4.23%,枝孢菌属(Cladosporium)在茎、叶中的占比分别为45.46%和51.74%,均显著高于抗性品种。真菌属中,只发现抗性品种中异壳二孢属(Neoascochyta)(根、叶)和被孢霉属(Mortierella)(根)的相对丰度稍高于感病品种。此外,通过Funguild数据库对真菌群落营养型进行分析,易感品种伏地尖的茎、叶中病理营养型真菌的相对丰度较抗性品种(SJ-0948和CM334)高。
蔡泽彦, 张明星, 周池, 陶禹, 杨莎, 李鑫, 李雪峰. 辣椒疫病不同抗性品种内生微生物群落多样性、结构及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 322-336.
CAI Zeyan, ZHANG Mingxing, ZHOU Chi, TAO Yu, YANG Sha, LI Xin, LI Xuefeng. Analysis of Endogenous Microbial Community Diversity,Structure and Function of Pepper Different Resistant Phytophthora Blight Cultivars[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 322-336.

图1 辣椒疫病不同抗性品种3个生态位的细菌和真菌稀释曲线图
Fig. 1 Endophytic bacterial and fungal rarefaction curves of plant tissues samples from three ecological niches of resistant and susceptible pepper cultivars
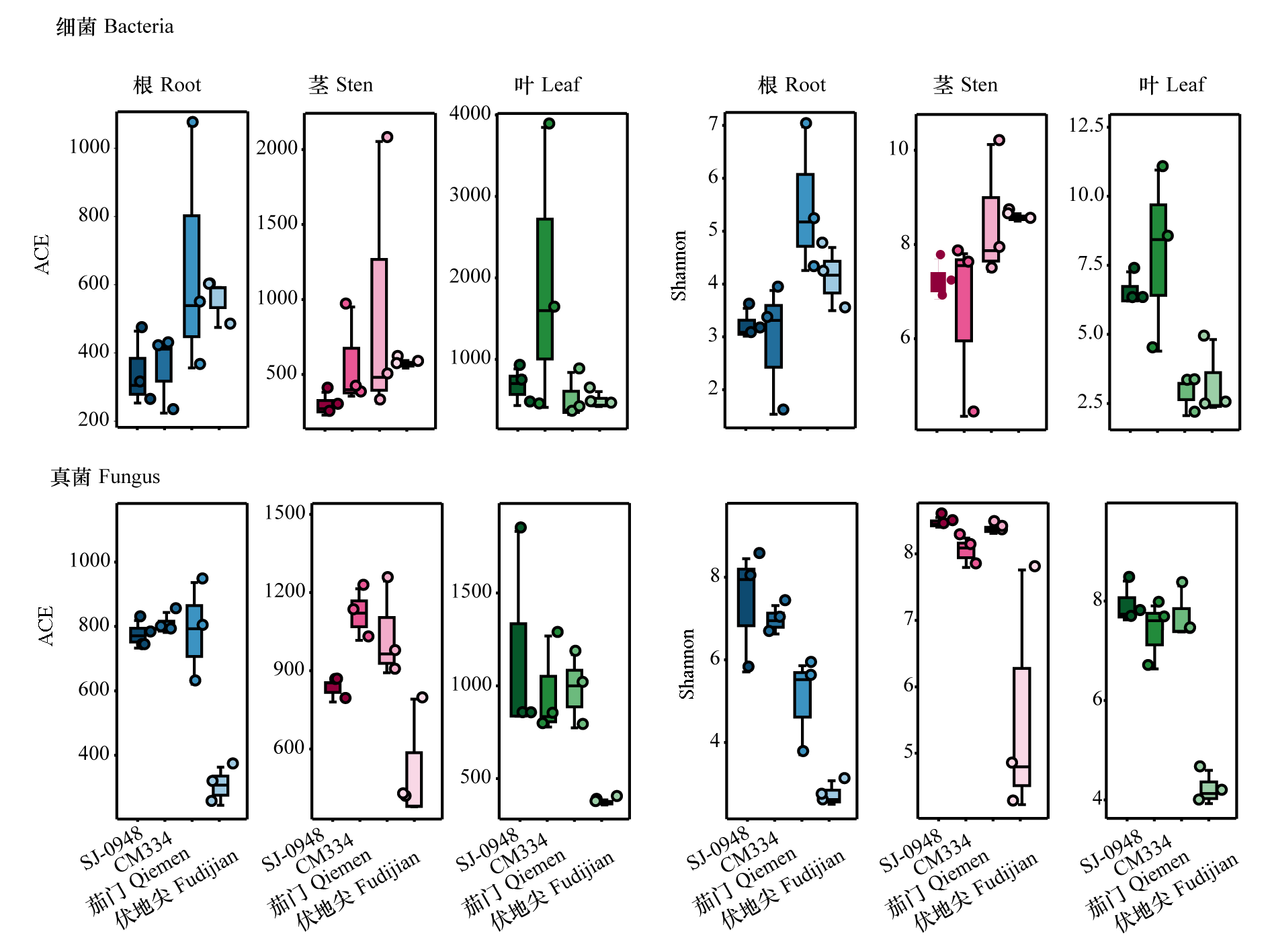
图2 辣椒疫病不同抗性品种3个生态位的微生物群落多样性
Fig. 2 Diversity of endophytic bacterial and fungal communities in three ecological niches of resistant and susceptible pepper cultivars
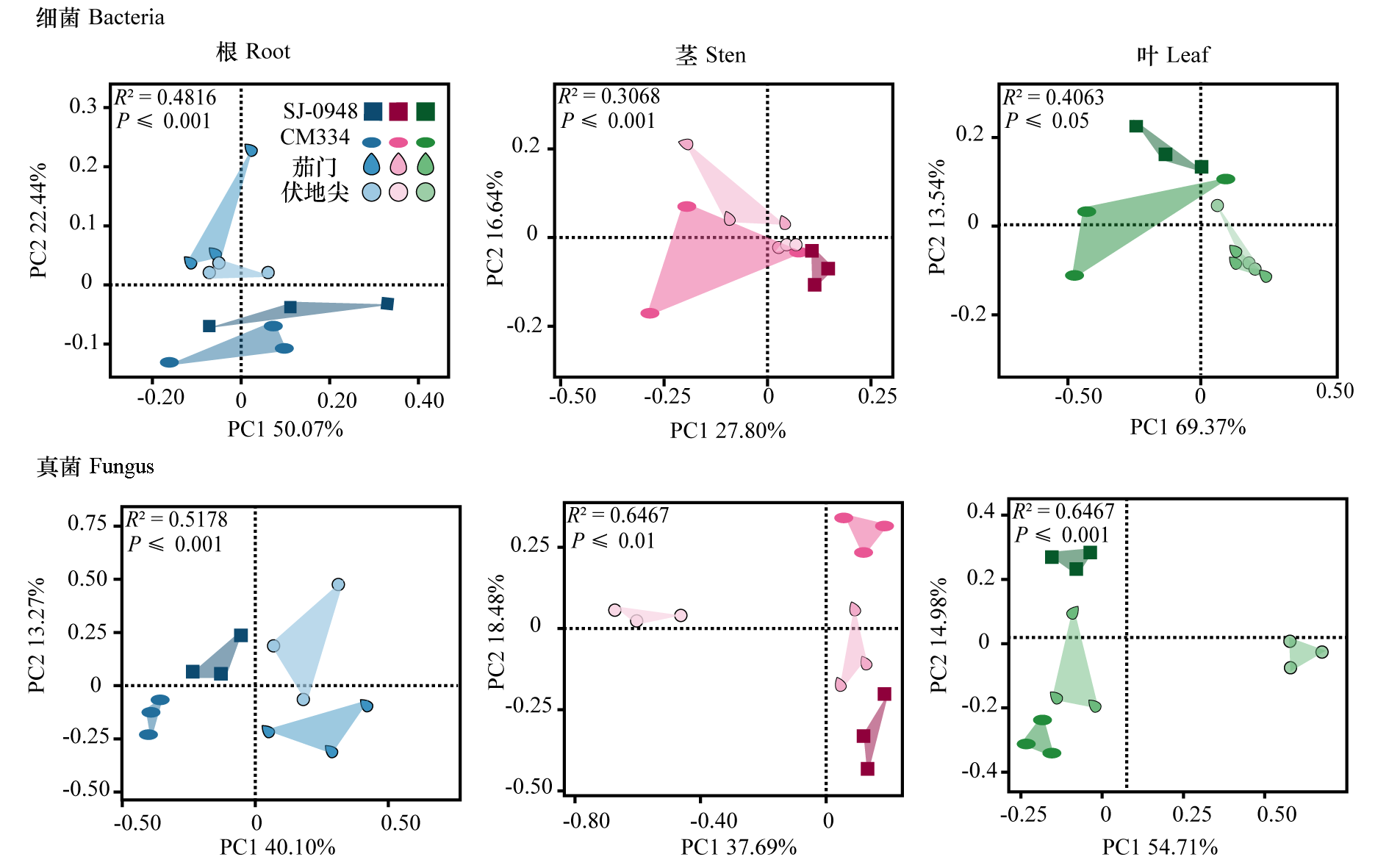
图3 辣椒疫病不同抗性品种3个生态位的细菌和真菌PCoA分析
Fig. 3 PCoA Analysis of bacterial and fungal communities in three ecological niches of resistant and susceptible pepper cultivars
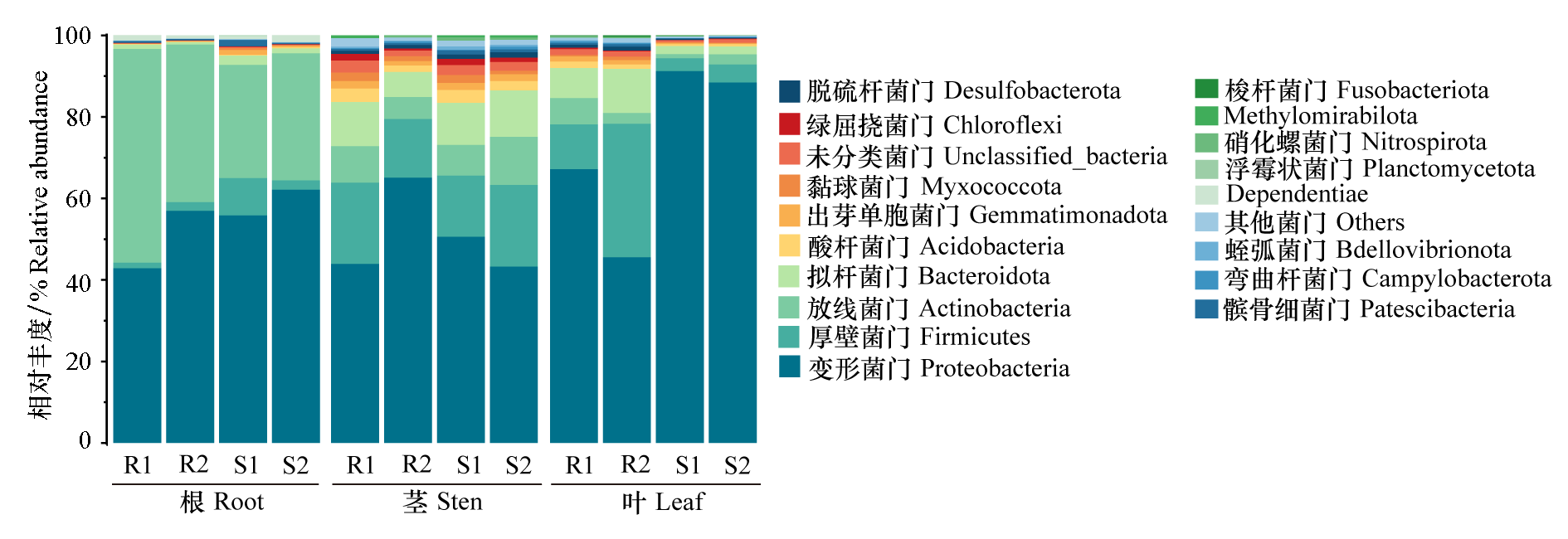
图4 辣椒疫病不同抗性品种各生态位细菌群落门水平的相对丰度 R1:SJ-0948;R2:CM334;S1:茄门;S2:伏地尖。下同
Fig. 4 Relative abundance of bacterial communities at the phylum level in three niches of resistant and susceptible pepper cultivars R1:SJ-0948;R2:CM334;S1:Qiemen;S2:Fudijian. The same below
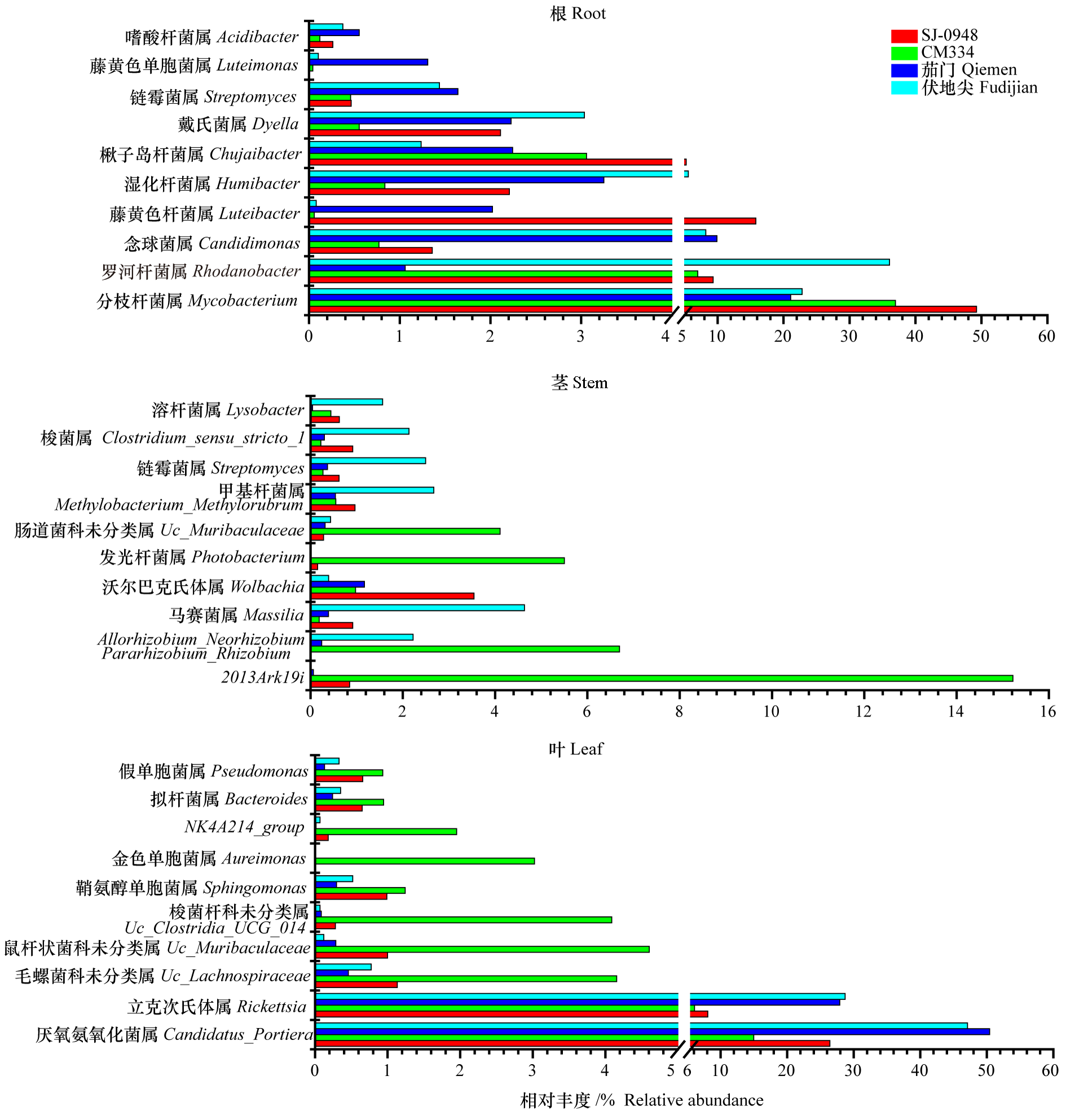
图5 辣椒疫病不同抗性品种各生态位细菌群落属水平的相对丰度
Fig. 5 Relative abundance of bacterial communities at the genus level in three niches of resistant and susceptible pepper cultivars

图6 辣椒疫病不同抗性品种各生态位真菌群落门水平的相对丰度
Fig. 6 Relative abundance of fungal communities at the phylum level in three niches of resistant and susceptible pepper cultivars
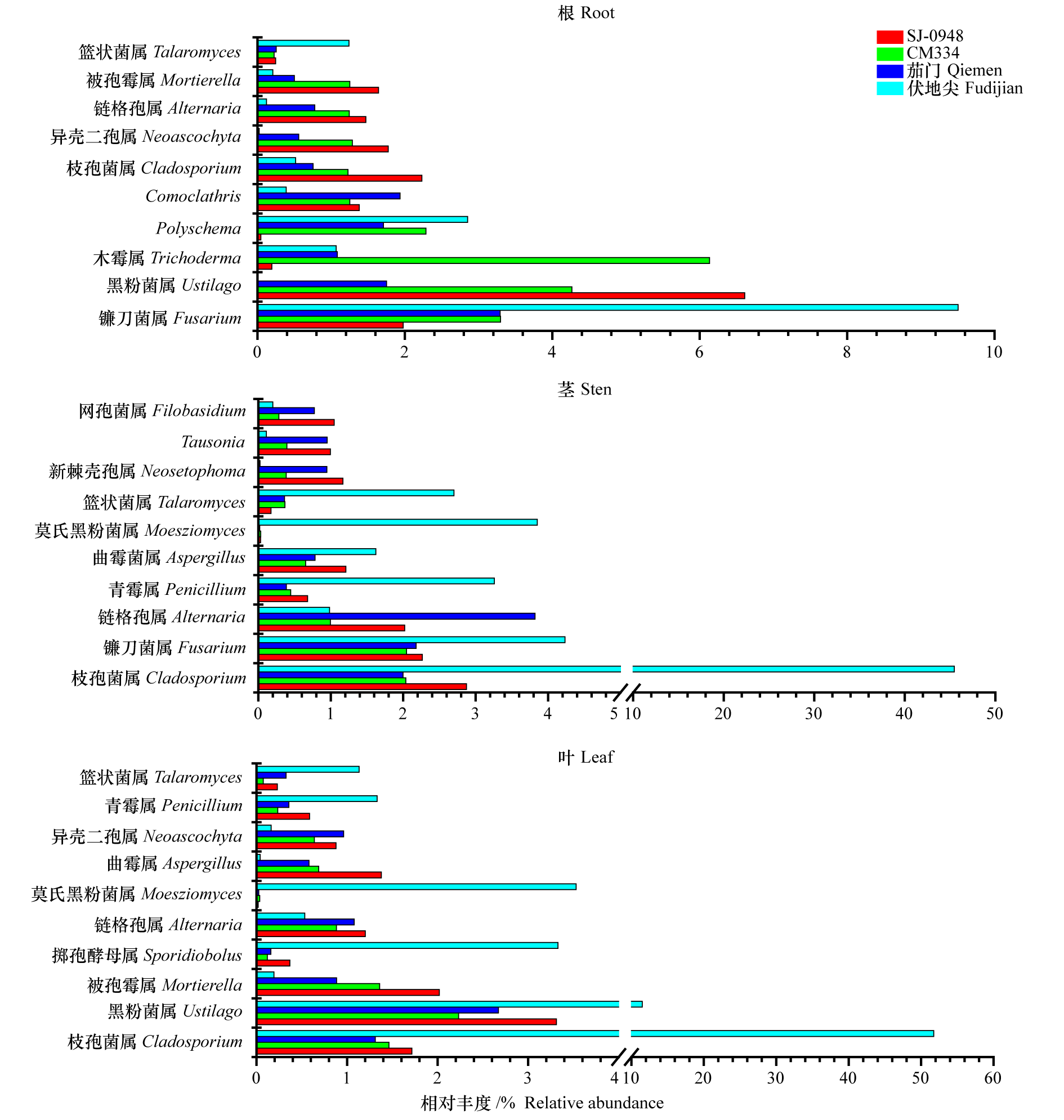
图7 辣椒疫病不同抗性品种各生态位真菌群落属水平的相对丰度
Fig. 7 Relative abundance of fungal communities at the genus level in three niches of resistant and susceptible pepper cultivars
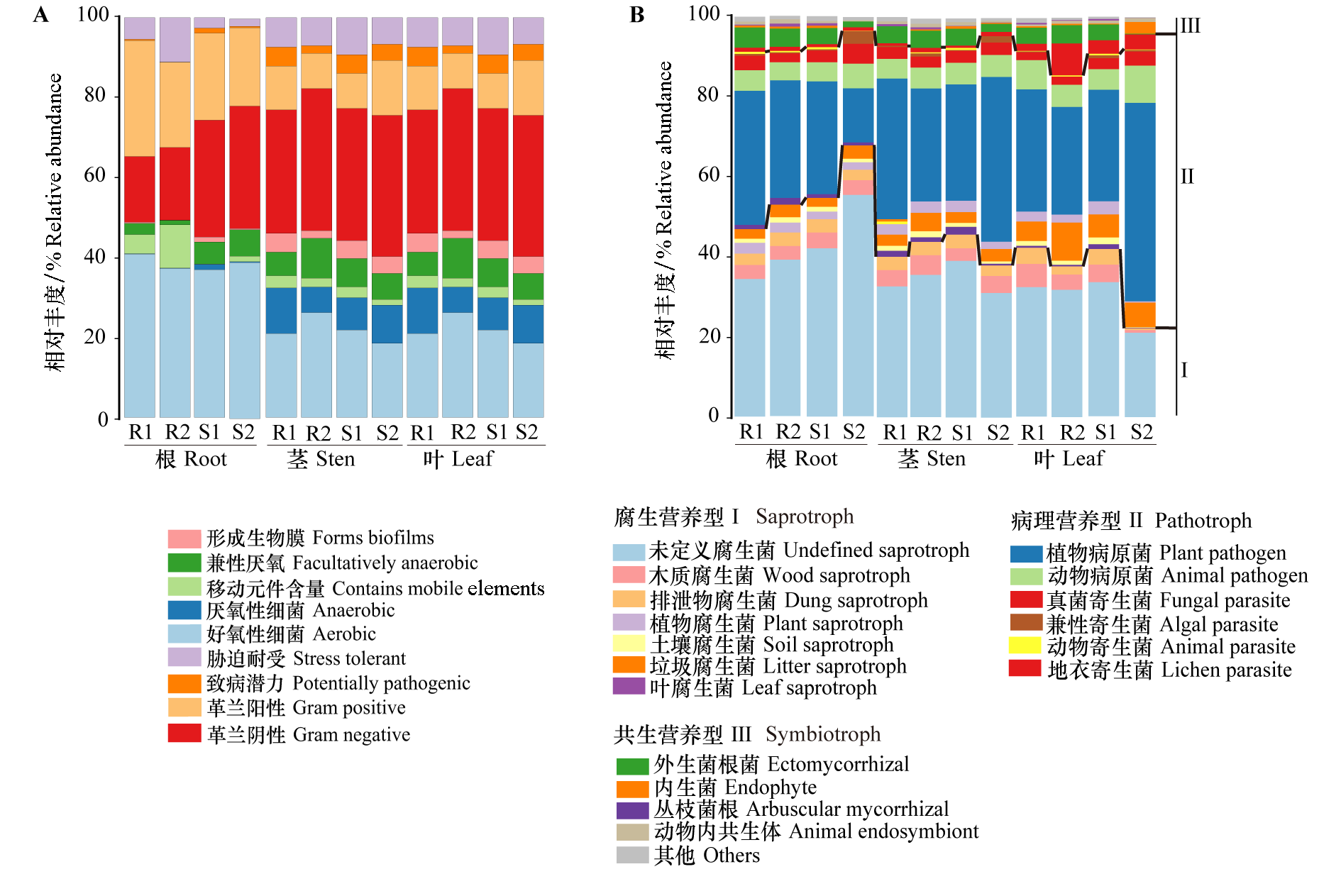
图8 辣椒疫病不同抗性品种细菌群落Bugbase表型预测(A)和真菌群落Funguild营养类型分析(B)
Fig. 8 Phenotypic prediction of bacterial community by Bugbase database(A)and trophic type analysis of fungal community by Funguild database(B)of resistant and susceptible pepper cultivars
| [1] |
|
|
陈力, 王中康, 黄冠军, 曹月青, 夏玉先, 殷幼平. 2008. 柑橘溃疡病生防菌株CQBS03的鉴定及其培养特性研究. 中国农业科学, 41 (8):2537-2545.
|
|
| [2] |
|
|
崔凌霄. 2022. 马铃薯疮痂病菌(Streptomyces galilaeus)的细胞壁降解酶及其致病机制研究[博士论文]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学.
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1000 URL |
|
崔雪婧, 张家宁, 陈江华, 贾纪春, 林杨, 付艳苹. 2023. 纽荷尔脐橙内生真菌参与生理落果的研究. 园艺学报, 50 (12):2713-2722.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1000 URL |
|
| [4] |
|
|
高小宁, 刘睿, 吴自林, 吴嘉云. 2022. 宿根矮化病抗感甘蔗品种茎部内生真菌和细菌群落特征分析. 生物技术通报, 38 (6):166-173.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2021-1197 |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
贾方方, 许跃奇, 阎海涛, 何晓冰, 李俊营, 刘冬梅, 王亚月, 常栋. 2023. 烟草镰刀菌根腐病(Fusarium spp.)拮抗菌L210的鉴定及生防潜力评价. 烟草科技, 56 (10):40-48.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
贾淑鑫, 李金, 闫思远, 郭苗苗, 王若彤, 顾沛雯. 2024. 嗜线虫镰刀菌NQ8GⅡ4 对枸杞根腐病的防效及其机制研究. 园艺学报, 51 (3):631-642.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
雷刚, 周坤华, 陈学军, 黄月琴, 袁欣捷, 李歌歌. 2023. 辣椒疫病研究进展. 江西农业学报, 35 (6):39-48.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
李智敏, 严理, 严准. 2016. 玉米瘤黑粉菌的寄生策略及其调控机制. 微生物学报, 56 (9):13.
|
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02530-0 pmid: 34406444 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
|
刘雨静, 韩升才, 高聚林, 于晓芳, 青格尔, 胡树平, 郭江岸, 赵晓宇. 2024. 不同耕作方式结合秸秆还田对玉米内生细菌多样性的影响. 微生物学报, 64 (7):2522-2538.
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.13346/j.mycosystema.210043 |
|
刘宇星, 邵秋雨, 葛伟, 董醇波, 张芝元, 任玉连, 罗力, 郑鲁平, 韩燕峰. 2021. 健康与患病刺梨植株可培养叶际真菌菌群差异比较. 菌物学报, 40 (10):2620-2640.
doi: 10.13346/j.mycosystema.210043 |
|
| [20] |
|
|
鲁振航, 张慧, 赵佳音, 赵杰, 薛怀丽. 2024. 兰州百合采后贮藏期间青霉病病原Talaromyces adpressus的分离、鉴定及生物学特性研究. 甘肃农业大学学报, https://link.cnki.net/urlid/62.1055.S.20240428.1645.077.
|
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-00826-5 pmid: 33398157 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.16409/j.cnki.2095-039x.2019.06.022 |
|
千慧敏, 文艺, 赵辉, 倪云霞, 刘新涛, 邱睿, 李小杰, 赵新贝, 李淑君, 刘红彦. 2019. 烟草黑胫病和根黑腐病生防假单胞杆菌的筛选与鉴定. 中国生物防治学报, 35 (6):940-948.
doi: 10.16409/j.cnki.2095-039x.2019.06.022 |
|
| [24] |
|
|
乔宁, 马蓉丽, 王瑞丽, 成妍, 焦彦生. 2016. 辣椒疫病的发生及抗性研究进展. 山西农业科学, 44 (6):885-888.
|
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0350 URL |
|
石凤岩, 王治丹, 张曦, 王秀雪, 邹春蕾. 2024. 辣椒疫病抗性机制研究进展. 园艺学报, 51 (7):1665-1682.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
田龙艳, 黄华, 杨华, 黎子君, 邱华龙, 张春花, 徐金柱, 徐长生. 2022. 假单胞菌T1-3-2的抑菌特性及其对杉木的抗病促生作用. 微生物学通报, 49 (11):4752-4765.
|
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0361-8 pmid: 32346148 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
王利群, 戴雄泽, 马艳青, 李雪峰, 张竹青, 陈文超, 欧立军, 邹学校. 2015. 利用‘伏地尖’辣椒选育的骨干亲本与品种的系谱分析. 园艺学报, 42 (11):2267-2277.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
王生萍, 卓玛曲措, 陈娟, 蒋先芝, 旺姆. 2022. 抗感白粉病青稞的内生真菌群落差异分析. 菌物学报, 41 (12):1950-1959.
doi: 10.13346/j.mycosystema.220071 |
|
| [31] |
|
|
王帅鑫. 2020. 沼泽红假单胞菌PSB-06对番茄褪绿病毒的防效及作用机制研究[博士论文]. 湖南: 湖南大学.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
许乐, 阮小蕾, 李冬丽, 李华平. 2012. 对枯萎病不同抗性的香蕉品种的内生细菌多样性及群落结构. 微生物学通报, 39 (9):1250-1259.
|
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0340 |
|
徐明玉, 杜春梅. 2021. 柑橘青霉病防治的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 37 (9):142-148.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0340 |
|
| [34] |
|
|
徐小万, 曾莉, 曹必好, 王恒明, 田永红, 李颖. 2011. 辣椒疫病抗性资源‘CM334’的抗性遗传分析. 植物保护, 37 (5):184-186.
|
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
|
郑迪文, 周游, 谢芳玲, 谢宗宝, 刘峰, 宏建. 2023. 辣椒疫霉病菌拮抗菌的筛选鉴定及生防潜力. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 49 (4):442-447.
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
周黎, 丁建军, 李国英. 2011. 新疆加工番茄根腐病主要致病菌的生物学特性. 新疆农业科学, 48 (4):739-743.
|
| [1] | 杨文清, 王嘉荟, 徐秉良, 李惠霞, 梁巧兰, 杨顺义, 牛二波. 甘肃定西地区辣椒病毒病鉴定及BWYV遗传变异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 491-502. |
| [2] | 邹学校, 杨莎, 戴雄泽, 胡博文, 徐昊, 朱凡, 裴宋雨, 远方. 中国辣椒产业快速发展40年回顾与展望[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 247-258. |
| [3] | 陈明, 张洁茹, 杨航云, 王印宝, 郑致远, 曾教科, 陈金印, 付永琦, 向妙莲. 茉莉酸甲酯诱导采后脐橙抗青霉病的机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2183-2194. |
| [4] | 李怡斐, 杨小苗, 王春萍, 段敏杰, 黄启中, 黄任中, 张世才. 加工型辣椒新品种‘艳椒465’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2223-2224. |
| [5] | 段敏杰, 李怡斐, 王春萍, 杨小苗, 黄任中, 黄启中, 张世才. 辣椒果实类胡萝卜素调控因子转录组和靶向代谢组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1773-1791. |
| [6] | 龚小雅, 李贤, 周新刚, 吴凤芝. 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对根结线虫病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [7] | 石凤岩, 王治丹, 张曦, 王秀雪, 邹春蕾. 辣椒疫病抗性机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1665-1682. |
| [8] | 张茹, 陈灵芝, 王兰兰. 辣椒新品种‘陇椒13号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1709-1710. |
| [9] | 彭爱红, 张婧芸, 陈志毅, 苏娟, 何永睿, 姚利晓. CsEXPA8过表达对‘晚锦橙’生长及溃疡病抗性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 971-981. |
| [10] | 杨婷, 席德慧, 夏明, 李佳楠. α-苦瓜素基因提高番茄对烟草花叶病毒抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [11] | 王青, 胡燕, 陈姗, 陆景伟, 郑阳, 陶伟林, 孙现超, 周娜, 陈国康. 绛红褐链霉菌CC2-6抑制大白菜根肿病的效果及机制分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1137-1150. |
| [12] | 郭瑞, 陈高, 赵慧霞, 乾义柯, 兰红, 万何平, 陈禅友. 紫色辣椒新品种‘江大紫椒1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1175-1176. |
| [13] | 侯雪, 王姣姣, 张雯雯, 赵建龙, 茆振川. 辣椒乙烯反应抑制因子Cacl-6468的克隆及其抗根结线虫作用分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 761-772. |
| [14] | 刘艳艳, 丁颖, 刘兴华, 郑佳秋, 刘志钦. 辣椒CaSYT1的鉴定及其在疫霉侵染过程中的功能初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 533-544. |
| [15] | 付稳, 朱程红, 兰嘉仪, 李诗, 张正, 刘峰, 戴雄泽. 鲜食嫩果辣椒‘樟树港’果实品质特性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 616-630. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司