
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 693-704.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0021
邢志淦1, 雷向朝1, 王浩臣1, 冯铭鑫1, 李靖雯1, 刘羽佳1, 房玉林1, 孟江飞1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-15
修回日期:2025-01-14
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
XING Zhigan1, LEI Xiangzhao1, WANG Haochen1, FENG Mingxin1, LI Jingwen1, LIU Yujia1, FANG Yulin1, MENG Jiangfei1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-10-15
Revised:2025-01-14
Published:2025-03-25
Online:2025-03-25
摘要:
以1年生‘阳光玫瑰’的5BB、抗砧3号、SO4和101-14砧木嫁接苗为材料进行低温与盐复合胁迫耐受性研究。结果表明,盐胁迫下,与自根苗相比,4种砧木嫁接苗均能不同程度地降低丙二醛(MDA)含量和相对电导率水平,增加脯氨酸、可溶性糖(101-14除外)和可溶性蛋白等渗透调节物质含量,提高POD抗氧化酶活性,其中SO4嫁接苗对盐胁迫的耐受性表现最好。低温胁迫下,嫁接苗与自根苗的各项生理生化指标变化趋势与盐胁迫下相似,但变化幅度不同,5BB嫁接苗表现出更强的低温耐受性。盐与低温复合胁迫下,SO4嫁接苗的MDA含量显著低于其他砧木嫁接苗,受害程度最轻,3种有机渗透调节物质可溶性蛋白、可溶性总糖和游离脯氨酸含量显著高于盐和低温单一胁迫处理,CAT和POD活性也显著升高。隶属函数综合评价,SO4嫁接的‘阳光玫瑰’在盐与低温复合胁迫下抗性最强,更适宜进一步推广使用,砧木5BB更适合在低温冷害环境中使用。
邢志淦, 雷向朝, 王浩臣, 冯铭鑫, 李靖雯, 刘羽佳, 房玉林, 孟江飞. 不同砧木‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄幼树对盐与低温复合胁迫的生理响应[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 693-704.
XING Zhigan, LEI Xiangzhao, WANG Haochen, FENG Mingxin, LI Jingwen, LIU Yujia, FANG Yulin, MENG Jiangfei. Physiological Response of Shine Muscat Grape Seedlings Grafted with Different Rootstocks to Combined Stress of Salt and Low Temperature[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 693-704.

图1 盐与低温复合胁迫下‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄不同砧木嫁接苗叶片表型变化
Fig. 1 Phenotypic changes of leaves of‘Shine Muscat’grape grafted seedlings of different rootstocks under combined stress of salt and low temperature
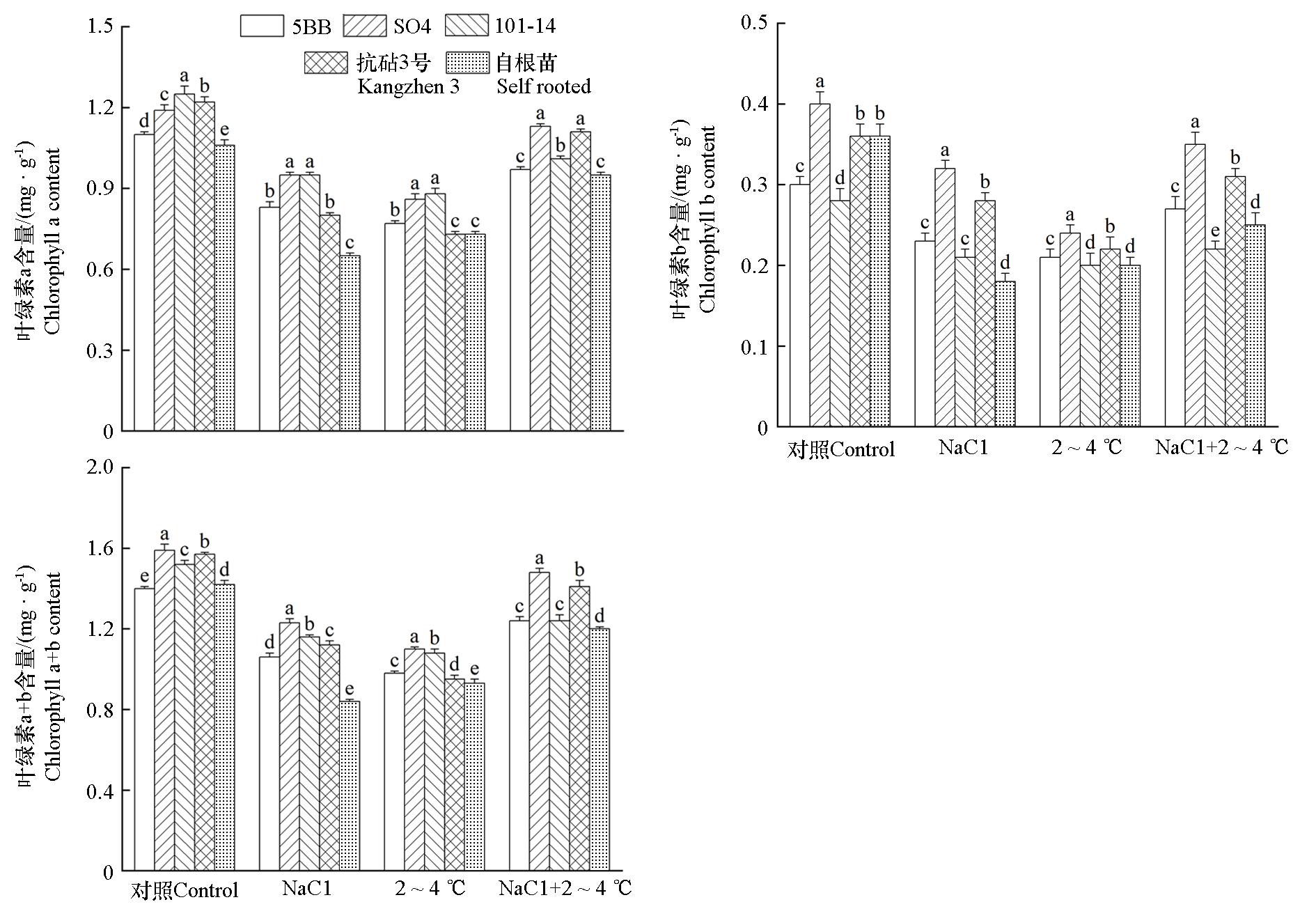
图2 盐与低温复合胁迫对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄不同砧木嫁接苗叶片叶绿素含量的影响 不同小写字母表示相同处理不同砧木间的差异显著性(P < 0.05)。下同
Fig. 2 Effects of combined salt and low temperature stress on chlorophyll content in‘Shine Muscat’grape leaves of different rootstocks of grafted seedlings Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different rootstocks in same treatment(P < 0.05). The same below
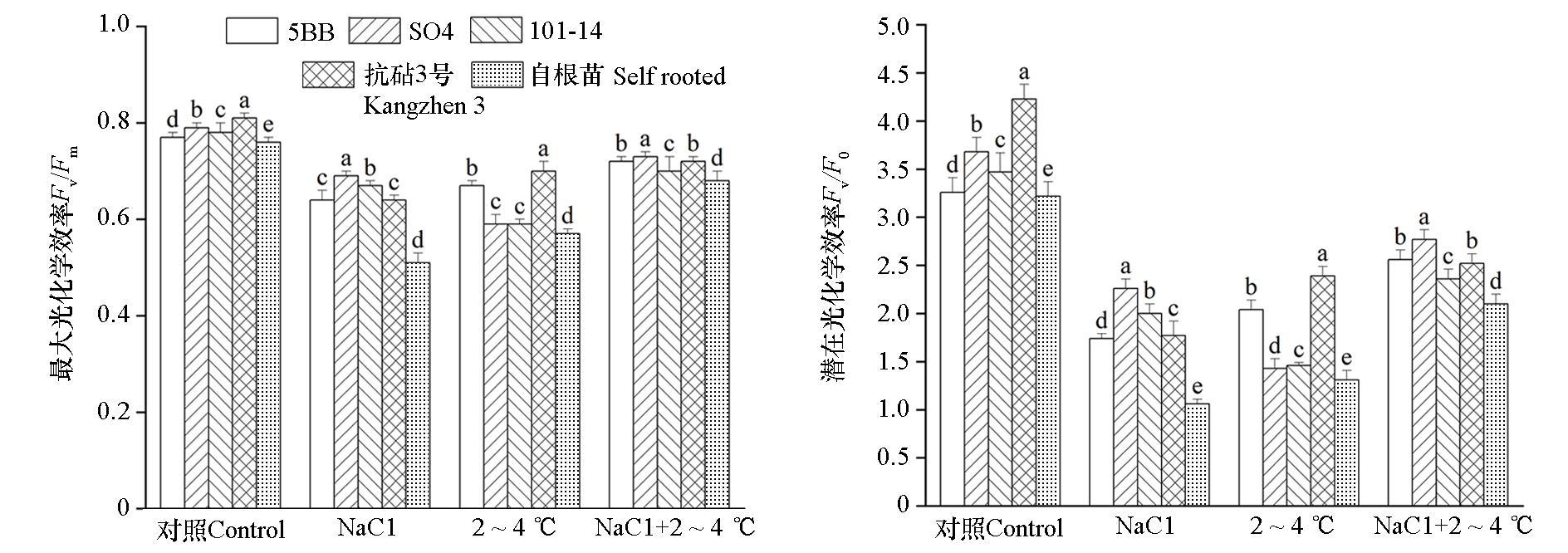
图3 盐与低温复合胁迫对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄不同砧木嫁接苗叶片叶绿素荧光参数的影响
Fig. 3 Effects of combined salt and low temperature stress on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in‘Shine Muscat’grape leaves of different rootstocks of grafted seedlings
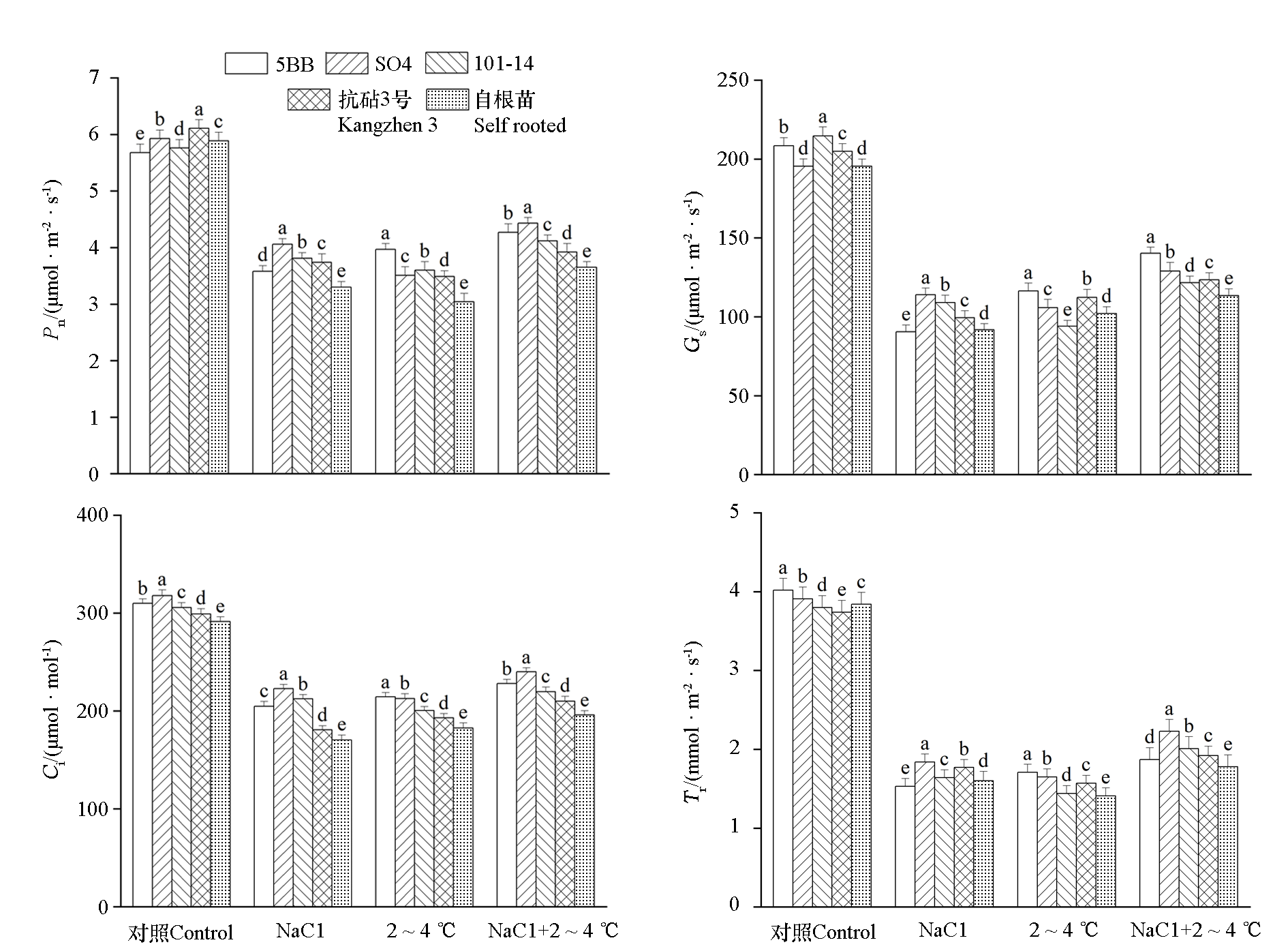
图4 盐与低温复合胁迫对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄不同砧木嫁接苗叶片光合参数的影响
Fig. 4 Effects of combined salt and low temperature stress on photosynthetic parameters in‘Shine Muscat’grape leaves of different rootstocks of grafted seedlings

图5 盐与低温复合胁迫对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄不同砧木嫁接苗叶片相对电导率和丙二醛含量的影响
Fig. 5 Effects of combined salt and low temperature stress on relative electrical conductivity and MDA content in‘Shine Muscat’grape leaves of different rootstocks of grafted seedlings

图6 盐与低温复合胁迫对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄不同砧木嫁接苗叶片渗透调节物质的影响
Fig. 6 Effects of combined salt and low temperature stress on osmotic adjustment substance in‘Shine Muscat’grape leaves of different rootstocks of grafted seedlings
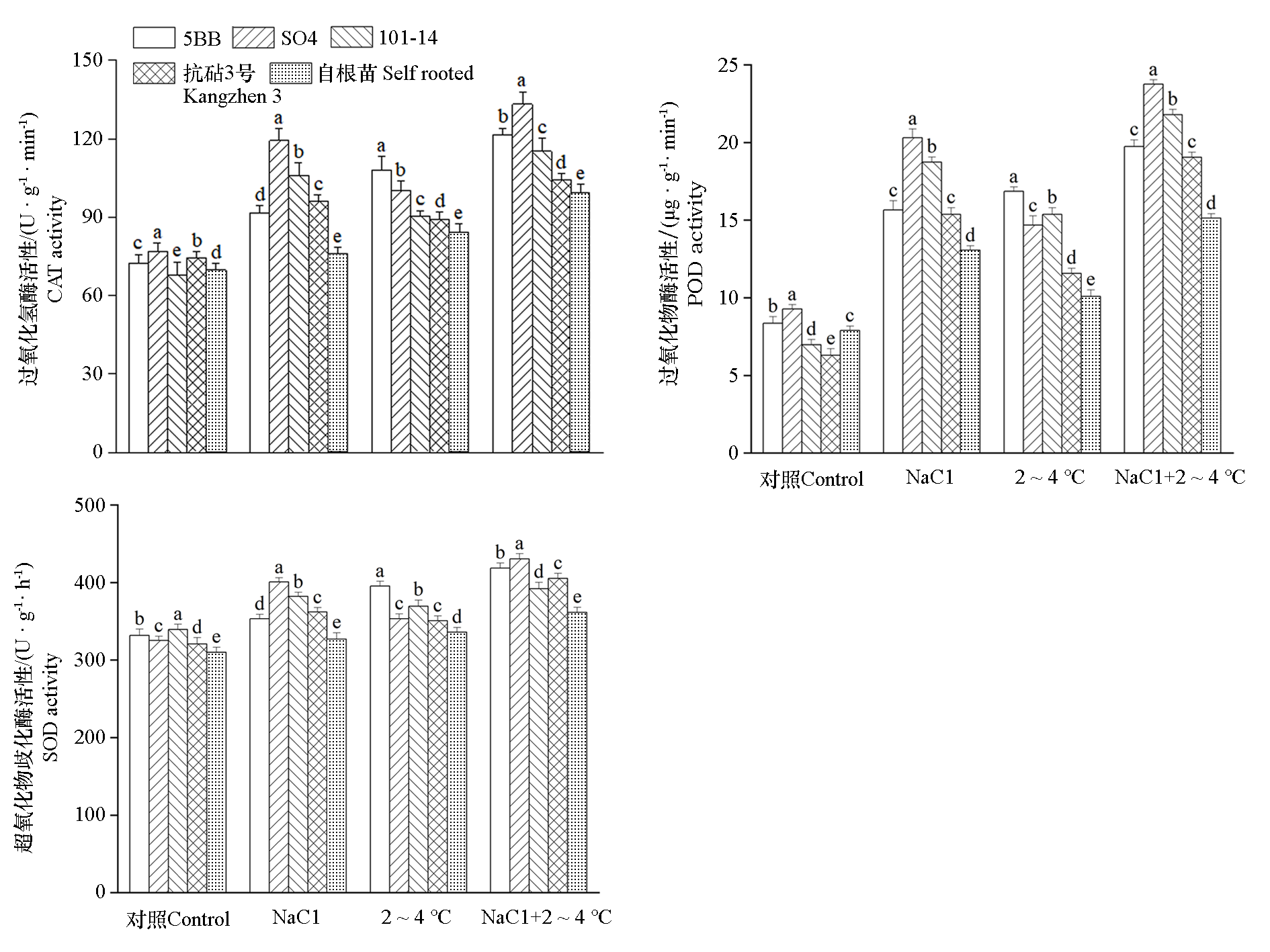
图7 盐与低温复合胁迫对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄不同砧木嫁接苗叶片抗氧化酶活性的影响
Fig. 7 Effects of combined salt and low temperature stress on antioxidant enzyme activity in‘Shine Muscat’grape leaves of different rootstocks of grafted seedlings
| 指标Index | 砧木Rootstock | 自根苗 Self-rooted plants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5BB | SO4 | 101-14 | 抗砧3号Kangzhen 3 | ||
| 相对电导率REC | 0.587 | 0.802 | 0.636 | 0.370 | 0.043 |
| 丙二醛MDA | 0.709 | 0.882 | 0.637 | 0.505 | 0.101 |
| 叶绿素Chl | 0.561 | 0.980 | 0.807 | 0.709 | 0.019 |
| 最大光化学效率Fv/Fm | 0.715 | 0.961 | 0.863 | 0.715 | 0.076 |
| 潜在光化学效率Fv/Fo | 0.572 | 0.963 | 0.767 | 0.595 | 0.061 |
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.385 | 0.912 | 0.637 | 0.560 | 0.077 |
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.149 | 0.860 | 0.708 | 0.416 | 0.185 |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度Ci | 0.619 | 0.901 | 0.738 | 0.243 | 0.082 |
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.163 | 0.884 | 0.419 | 0.721 | 0.326 |
| 可溶性总糖SS | 0.485 | 0.989 | 0.007 | 0.556 | 0.296 |
| 可溶性蛋白SP | 0.069 | 0.947 | 0.561 | 0.301 | 0.031 |
| 游离脯氨酸Pro | 0.619 | 0.952 | 0.286 | 0.417 | 0.119 |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | 0.356 | 0.895 | 0.632 | 0.442 | 0.052 |
| 过氧化物酶POD | 0.355 | 0.917 | 0.694 | 0.320 | 0.042 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 0.405 | 0.916 | 0.714 | 0.500 | 0.119 |
| 平均值Mean | 0.450 | 0.917 | 0.607 | 0.491 | 0.109 |
| 抗性级别Tolerance level | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
表1 ‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄不同砧木嫁接苗耐盐性隶属函数法综合评价
Table 1 Comprehensive evaluation of salt tolerance of different rootstock‘Shine Muscat’grape grafted seedlings
| 指标Index | 砧木Rootstock | 自根苗 Self-rooted plants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5BB | SO4 | 101-14 | 抗砧3号Kangzhen 3 | ||
| 相对电导率REC | 0.587 | 0.802 | 0.636 | 0.370 | 0.043 |
| 丙二醛MDA | 0.709 | 0.882 | 0.637 | 0.505 | 0.101 |
| 叶绿素Chl | 0.561 | 0.980 | 0.807 | 0.709 | 0.019 |
| 最大光化学效率Fv/Fm | 0.715 | 0.961 | 0.863 | 0.715 | 0.076 |
| 潜在光化学效率Fv/Fo | 0.572 | 0.963 | 0.767 | 0.595 | 0.061 |
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.385 | 0.912 | 0.637 | 0.560 | 0.077 |
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.149 | 0.860 | 0.708 | 0.416 | 0.185 |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度Ci | 0.619 | 0.901 | 0.738 | 0.243 | 0.082 |
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.163 | 0.884 | 0.419 | 0.721 | 0.326 |
| 可溶性总糖SS | 0.485 | 0.989 | 0.007 | 0.556 | 0.296 |
| 可溶性蛋白SP | 0.069 | 0.947 | 0.561 | 0.301 | 0.031 |
| 游离脯氨酸Pro | 0.619 | 0.952 | 0.286 | 0.417 | 0.119 |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | 0.356 | 0.895 | 0.632 | 0.442 | 0.052 |
| 过氧化物酶POD | 0.355 | 0.917 | 0.694 | 0.320 | 0.042 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 0.405 | 0.916 | 0.714 | 0.500 | 0.119 |
| 平均值Mean | 0.450 | 0.917 | 0.607 | 0.491 | 0.109 |
| 抗性级别Tolerance level | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| 指标Index | 砧木Rootstock | 自根苗 Self-rooted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5BB | SO4 | 101-14 | 抗砧3号Kangzhen 3 | ||
| 相对电导率REC | 0.764 | 0.541 | 0.205 | 0.591 | 0.164 |
| 丙二醛MDA | 0.981 | 0.792 | 0.540 | 0.396 | 0.115 |
| 叶绿素Chl | 0.288 | 0.940 | 0.831 | 0.125 | 0.016 |
| 最大光化学效率Fv/Fm | 0.735 | 0.321 | 0.231 | 0.923 | 0.105 |
| 潜在光化学效率Fv/Fo | 0.649 | 0.155 | 0.179 | 0.932 | 0.058 |
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.943 | 0.505 | 0.590 | 0.486 | 0.057 |
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.804 | 0.490 | 0.139 | 0.682 | 0.380 |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度Ci | 0.864 | 0.825 | 0.545 | 0.377 | 0.139 |
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.900 | 0.750 | 0.225 | 0.550 | 0.150 |
| 可溶性总糖SS | 0.984 | 0.578 | 0.045 | 0.364 | 0.006 |
| 可溶性蛋白SP | 0.933 | 0.113 | 0.563 | 0.122 | 0.043 |
| 游离脯氨酸Pro | 0.965 | 0.614 | 0.263 | 0.070 | 0.158 |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | 0.831 | 0.598 | 0.292 | 0.252 | 0.108 |
| 过氧化物酶POD | 0.954 | 0.667 | 0.758 | 0.257 | 0.061 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 0.901 | 0.333 | 0.550 | 0.300 | 0.101 |
| 平均值Mean | 0.833 | 0.542 | 0.397 | 0.428 | 0.111 |
| 抗性级别Tolerance level | 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 5 |
表2 ‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄不同砧木嫁接苗低温耐受性的综合评价
Table 2 Comprehensive evaluation of low temperature tolerance of different rootstock‘Shine Muscat’grape grafted seedlings
| 指标Index | 砧木Rootstock | 自根苗 Self-rooted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5BB | SO4 | 101-14 | 抗砧3号Kangzhen 3 | ||
| 相对电导率REC | 0.764 | 0.541 | 0.205 | 0.591 | 0.164 |
| 丙二醛MDA | 0.981 | 0.792 | 0.540 | 0.396 | 0.115 |
| 叶绿素Chl | 0.288 | 0.940 | 0.831 | 0.125 | 0.016 |
| 最大光化学效率Fv/Fm | 0.735 | 0.321 | 0.231 | 0.923 | 0.105 |
| 潜在光化学效率Fv/Fo | 0.649 | 0.155 | 0.179 | 0.932 | 0.058 |
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.943 | 0.505 | 0.590 | 0.486 | 0.057 |
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.804 | 0.490 | 0.139 | 0.682 | 0.380 |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度Ci | 0.864 | 0.825 | 0.545 | 0.377 | 0.139 |
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.900 | 0.750 | 0.225 | 0.550 | 0.150 |
| 可溶性总糖SS | 0.984 | 0.578 | 0.045 | 0.364 | 0.006 |
| 可溶性蛋白SP | 0.933 | 0.113 | 0.563 | 0.122 | 0.043 |
| 游离脯氨酸Pro | 0.965 | 0.614 | 0.263 | 0.070 | 0.158 |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | 0.831 | 0.598 | 0.292 | 0.252 | 0.108 |
| 过氧化物酶POD | 0.954 | 0.667 | 0.758 | 0.257 | 0.061 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 0.901 | 0.333 | 0.550 | 0.300 | 0.101 |
| 平均值Mean | 0.833 | 0.542 | 0.397 | 0.428 | 0.111 |
| 抗性级别Tolerance level | 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 5 |
| 指标 Index | 砧木Rootstock | 自根苗 Self-rooted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5BB | SO4 | 101-14 | 抗砧3号Kangzhen 3 | ||
| 相对电导率REC | 0.506 | 0.796 | 0.333 | 0.423 | 0.075 |
| 丙二醛MDA | 0.894 | 0.992 | 0.618 | 0.417 | 0.008 |
| 叶绿素Chl | 0.144 | 0.988 | 0.144 | 0.742 | 0.004 |
| 最大光化学效率Fv/Fm | 0.712 | 0.858 | 0.420 | 0.712 | 0.128 |
| 潜在光化学效率Fv/Fo | 0.648 | 0.910 | 0.398 | 0.598 | 0.073 |
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.764 | 0.944 | 0.596 | 0.371 | 0.067 |
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.861 | 0.547 | 0.342 | 0.394 | 0.114 |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度Ci | 0.686 | 0.899 | 0.535 | 0.359 | 0.106 |
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.263 | 0.895 | 0.509 | 0.351 | 0.105 |
| 可溶性总糖SS | 0.577 | 0.991 | 0.077 | 0.495 | 0.007 |
| 可溶性蛋白SP | 0.693 | 0.941 | 0.452 | 0.053 | 0.211 |
| 游离脯氨酸Pro | 0.788 | 0.955 | 0.288 | 0.303 | 0.121 |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | 0.600 | 0.870 | 0.448 | 0.192 | 0.077 |
| 过氧化物酶POD | 0.531 | 0.963 | 0.753 | 0.457 | 0.037 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 0.777 | 0.921 | 0.461 | 0.619 | 0.095 |
| 平均值Mean | 0.630 | 0.898 | 0.425 | 0.432 | 0.082 |
| 抗性级别Tolerance level | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
表3 ‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄不同砧木嫁接苗盐与低温复合耐受性的综合评价
Table 3 Comprehensive evaluation of salt tolerance and low temperature tolerance of different rootstock‘Shine Muscat’grape grafted seedlings
| 指标 Index | 砧木Rootstock | 自根苗 Self-rooted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5BB | SO4 | 101-14 | 抗砧3号Kangzhen 3 | ||
| 相对电导率REC | 0.506 | 0.796 | 0.333 | 0.423 | 0.075 |
| 丙二醛MDA | 0.894 | 0.992 | 0.618 | 0.417 | 0.008 |
| 叶绿素Chl | 0.144 | 0.988 | 0.144 | 0.742 | 0.004 |
| 最大光化学效率Fv/Fm | 0.712 | 0.858 | 0.420 | 0.712 | 0.128 |
| 潜在光化学效率Fv/Fo | 0.648 | 0.910 | 0.398 | 0.598 | 0.073 |
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.764 | 0.944 | 0.596 | 0.371 | 0.067 |
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.861 | 0.547 | 0.342 | 0.394 | 0.114 |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度Ci | 0.686 | 0.899 | 0.535 | 0.359 | 0.106 |
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.263 | 0.895 | 0.509 | 0.351 | 0.105 |
| 可溶性总糖SS | 0.577 | 0.991 | 0.077 | 0.495 | 0.007 |
| 可溶性蛋白SP | 0.693 | 0.941 | 0.452 | 0.053 | 0.211 |
| 游离脯氨酸Pro | 0.788 | 0.955 | 0.288 | 0.303 | 0.121 |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | 0.600 | 0.870 | 0.448 | 0.192 | 0.077 |
| 过氧化物酶POD | 0.531 | 0.963 | 0.753 | 0.457 | 0.037 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 0.777 | 0.921 | 0.461 | 0.619 | 0.095 |
| 平均值Mean | 0.630 | 0.898 | 0.425 | 0.432 | 0.082 |
| 抗性级别Tolerance level | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
|
曹建东. 2010. 9个葡萄砧木和品种的抗寒性及耐盐性鉴定[硕士论文]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学.
|
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
高振, 翟衡, 臧兴隆, 朱化平, 杜远鹏. 2014. 低温放热法研究8个葡萄砧木和6个栽培品种芽的抗寒性. 园艺学报, 41 (1):17-25.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
郝燕, 朱燕芳, 张坤, 王玉安. 2022. 不同砧木对两个鲜食葡萄品种生长与果实品质的影响. 经济林研究, 40 (4):246-255.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01130 pmid: 28713405 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
李梦旭, 樊健. 2023. 蔬菜嫁接技术研究现状及发展趋势. 农业工程, 13 (4):140-145.
|
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15050057 |
|
李鹏程, 李铭, 郭绍杰, 苏学德, 张连杰. 2015. 几种葡萄砧木的引种表现及抗寒性分析. 中国农学通报, 31 (34):93-97.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15050057 |
|
| [12] |
|
|
廖祥儒, 贺普超, 万怡震, 朱新产. 1996. 盐胁迫对葡萄离体新梢叶片的伤害作用. 果树科学,(4):211-214.
|
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0165 URL |
|
刘众杰, 郑婷, 赵方贵, 傅伟红, 诸葛雅贤, 张志昌, 房经贵. 2022. 葡萄砧木对渗透胁迫的抗性差异及生理响应机理. 园艺学报, 49 (5):984-994.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0165 URL |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
|
史晓敏. 2021. 13种葡萄砧木耐盐性差异比较研究[硕士论文]. 银川: 宁夏大学.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
束胜, 胡晓辉, 王玉, 张润花, 袁颖辉, 陈长军, 施露, 郭世荣. 2022. 蔬菜作物逆境生理与抗逆栽培研究进展. 南京农业大学学报, 45 (6):1087-1098.
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
王伟军, 郝建宇, 陈文朝, 刘晶晶, 吕丽霞, 杨茜. 2021. 不同砧木对蜜光葡萄物候期和果实品质的影响. 山西农业科学, 49 (7):872-875.
|
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0569 URL |
|
韦建明, 李云洲, 梁燕. 2023. 嫁接技术提高番茄抗病抗逆性的研究进展. 园艺学报, 50 (9):1997-2014.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0569 URL |
|
| [25] |
|
|
袁军伟, 李敏敏, 尹勇刚, 刘长江, 韩斌, 孙艳, 贾楠, 郭紫娟, 赵胜建. 2019. 不同砧木嫁接的赤霞珠葡萄对盐胁迫的生理响应. 中国农业大学学报, 24 (8):48-59.
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
周万海. 2005. 葡萄砧木耐盐性及砧—穗特性研究[硕士论文]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学.
|
| [1] | 丛鑫, 胡乾元, 庞桂斌, 徐立荣, 徐征和, 刘鸿飞, 裴向丽. 灌溉水矿化度对冬枣生长及产量品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 714-726. |
| [2] | 赵钰磊, 李珊, 李承男, 马金龙, 马红义, 尹晓. 灰霉菌侵染葡萄叶片初期的蛋白质组学研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 279-291. |
| [3] | 陈亚娟, 金鑫, 杨江山, 戴子博, 李斗, 邵璋. 黄腐酸钾对‘蛇龙珠’葡萄果实糖酸代谢及香味物质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 406-422. |
| [4] | 李敖, 郑旭, 吴承勖, 聂瑞宁, 姬新颖, 唐佳莉, 张俊佩. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下核桃幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 423-438. |
| [5] | 李晓庆, 闫思远, 顾沛雯. 宁夏地区葡萄灰霉病菌的多样性及致病力分化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 481-490. |
| [6] | 李敏, 李思雨, 施紫涵, 陈爽, 徐炎, 刘国甜. 葡萄GRF/GIF家族基因对遗传转化再生效率的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 51-65. |
| [7] | 王珊珊, 郭瑞, 何棱, 吴春红, 陈禅友, 万何平, 赵慧霞. 长豇豆Lhc家族基因鉴定及其在盐胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 111-122. |
| [8] | 贺丹丹, 何宏泰, 王文庭, 周文美, 刘燕敏, 刘骕骦. 甜瓜GolS家族基因鉴定及其响应低温胁迫的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 136-148. |
| [9] | 梁国平, 曾宝珍, 刘铭, 边志远, 陈佰鸿, 毛娟. 山葡萄VaSR基因家族的鉴定及VaSR1抗寒功能验证与互作蛋白筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 37-50. |
| [10] | 李旭娇, 吕齐, 姚东东, 赵丰云, 王小非, 于坤. ‘烟富3’苹果不同砧木嫁接对其15N–尿素吸收利用的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1868-1880. |
| [11] | 杨敬辉, 许媛, 肖婷, 褚姝频, 刘吉祥, 姚克兵. 葡萄胶孢炭疽病菌复合种(Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complexes)对嘧菌酯的抗药性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1906-1912. |
| [12] | 韩斌, 刘长江, 尹勇刚, 孙艳, 贾楠, 赵胜建, 郭紫娟, 李敏敏. 中晚熟鲜食葡萄新品种‘金光’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1977-1978. |
| [13] | 刘苗苗, 姚锦, 包敏, 楚言言, 王西平. 赤霉素诱导葡萄无核形成机理研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1610-1622. |
| [14] | 张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [15] | 武祥琪, 孙鹂, 俞浙萍, 俞沁佩, 梁森苗, 郑锡良, 戚行江, 张淑文. 杨梅MrSPL4在响应干旱和低温胁迫中的作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 927-938. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司