
园艺学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (9): 1665-1679.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0636
张春渝, 许小琼, 徐小萍, 赵鹏程, 申序, MunirNigarish, 张梓浩, 林玉玲, 陈振光, 赖钟雄*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-02-09
修回日期:2021-08-11
出版日期:2021-09-25
发布日期:2021-09-30
通讯作者:
赖钟雄
E-mail:Laizx01@163.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Chunyu, XU Xiaoqiong, XU Xiaoping, ZHAO Pengcheng, SHEN Xu, Munir Nigarish, ZHANG Zihao, LIN Yuling, Chen Zhenguang, LAI Zhongxiong*( )
)
Received:2021-02-09
Revised:2021-08-11
Online:2021-09-25
Published:2021-09-30
Contact:
LAI Zhongxiong
E-mail:Laizx01@163.com
摘要:
为研究S-phase kinase-associated protein 1-like(SKP1-like)在龙眼中的分子特性以及其在体胚发生早期的表达模式,基于模式植物拟南芥SKP1-like的氨基酸序列,在龙眼基因组数据库中进行SKP1-like成员的鉴定。同时,通过生物信息学方法对其蛋白理化性质、系统进化特征、染色体定位、共线性与选择压力、基因结构、保守基序、蛋白结构、蛋白互作网络、启动子顺式元件进行分析,并结合龙眼转录组数据分析其在体胚发生早期的表达模式。研究结果表明:龙眼SKP1-like家族基因共有14个成员,分别将其命名为DlSKP1-1 ~ DlSKP1-14。龙眼SKP1-like(DlSKP1)家族基因编码蛋白质的氨基酸数、分子量以及等电点分别为75 ~ 399 aa、8.29 ~ 45.34 kD、4.44 ~ 5.76,均不含信号肽,可能主要定位于叶绿体中。DlSKP1家族存在1对串联重复基因以及4对片段重复基因。蛋白互作结果提示,DlSKP1家族成员可能与多种蛋白(尤其F-Box家族蛋白)存在互作关系。启动子顺式作用元件的结果表明,DlSKP1家族成员启动子含有较多脱落酸(Abscisic acid,ABA)与茉莉酸甲酯(Methyl jasmonate,MeJA)响应元件。此外,DlSKP1成员在龙眼体胚发生早期存在5种不同的表达模式,其中3个成员(DlSKP1-6、DlSKP1-8、DlSKP1-13)在各阶段的表达量较其他成员较高。研究结果显示,DlSKP1家族成员可能与F-Box蛋白存在互作作用,并且可能参与ABA、MeJA的调控过程,还可能在龙眼体胚的形态建成中发挥重要作用。
中图分类号:
张春渝, 许小琼, 徐小萍, 赵鹏程, 申序, MunirNigarish, 张梓浩, 林玉玲, 陈振光, 赖钟雄. 龙眼SKP1-like家族成员鉴定及体胚发生早期表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(9): 1665-1679.
ZHANG Chunyu, XU Xiaoqiong, XU Xiaoping, ZHAO Pengcheng, SHEN Xu, Munir Nigarish, ZHANG Zihao, LIN Yuling, Chen Zhenguang, LAI Zhongxiong. Genome-wide Identification of the SKP1-like Family and Analysis of Their Expression During Early Somatic Embryogenesis in Longan[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(9): 1665-1679.
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 基因位置 Location | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acids | 等电点 pI | 分子量/kD Molecule weight | 不稳定 系数 Instability index | 平均亲水性 Grand average of hydropathicity | 亚细胞定位预测 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dlo004376 | DlSKP1-1 | Chr2:8659065:8659292:+ | 75 | 5.62 | 8.29 | 55.10 | 0.189 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo006336 | DlSKP1-2 | Chr3:3247223:3247714:- | 163 | 4.51 | 18.34 | 40.04 | -0.421 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo006338 | DlSKP1-3 | Chr3:3263169:3263666:- | 165 | 4.81 | 18.88 | 48.13 | -0.503 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo006553 | DlSKP1-4 | Chr3:5966103:5966600:+ | 165 | 4.45 | 18.64 | 50.31 | -0.441 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo012745 | DlSKP1-5 | Chr5:31590465:31597118:+ | 345 | 5.54 | 39.60 | 44.69 | -0.823 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| Dlo013346 | DlSKP1-6 | Chr6:1792674:1794424:- | 158 | 4.59 | 17.83 | 41.09 | -0.494 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo013634 | DlSKP1-7 | Chr6:4396612:4402101:- | 147 | 4.83 | 16.40 | 44.76 | -0.334 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| Dlo015478 | DlSKP1-8 | Chr7:1231833:1233731:- | 209 | 5.12 | 23.37 | 44.46 | -0.498 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo019333 | DlSKP1-9 | Chr9:805779:806249:- | 156 | 4.44 | 17.93 | 34.47 | -0.220 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo019334 | DlSKP1-10 | Chr9:812332:812819:- | 124 | 4.62 | 14.46 | 53.90 | -0.764 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo019594 | DlSKP1-11 | Chr9:4007573:4010954:+ | 399 | 5.76 | 45.34 | 56.04 | -0.647 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo022243 | DlSKP1-12 | Chr10:12177605:12182053:+ | 172 | 5.15 | 19.43 | 40.72 | -0.305 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| Dlo023134 | DlSKP1-13 | Chr11:1244155:1245940:- | 176 | 4.52 | 20.16 | 52.48 | -0.561 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo034799 | DlSKP1-14 | unanchor445_1_409426:233674:234129:- | 182 | 4.96 | 20.68 | 49.36 | -0.565 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
表1 DlSKP1家族蛋白基本理化性质分析
Table 1 Analysis of the basic physical and chemical properties of DlSKP1 family proteins
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 基因位置 Location | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acids | 等电点 pI | 分子量/kD Molecule weight | 不稳定 系数 Instability index | 平均亲水性 Grand average of hydropathicity | 亚细胞定位预测 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dlo004376 | DlSKP1-1 | Chr2:8659065:8659292:+ | 75 | 5.62 | 8.29 | 55.10 | 0.189 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo006336 | DlSKP1-2 | Chr3:3247223:3247714:- | 163 | 4.51 | 18.34 | 40.04 | -0.421 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo006338 | DlSKP1-3 | Chr3:3263169:3263666:- | 165 | 4.81 | 18.88 | 48.13 | -0.503 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo006553 | DlSKP1-4 | Chr3:5966103:5966600:+ | 165 | 4.45 | 18.64 | 50.31 | -0.441 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo012745 | DlSKP1-5 | Chr5:31590465:31597118:+ | 345 | 5.54 | 39.60 | 44.69 | -0.823 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| Dlo013346 | DlSKP1-6 | Chr6:1792674:1794424:- | 158 | 4.59 | 17.83 | 41.09 | -0.494 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo013634 | DlSKP1-7 | Chr6:4396612:4402101:- | 147 | 4.83 | 16.40 | 44.76 | -0.334 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| Dlo015478 | DlSKP1-8 | Chr7:1231833:1233731:- | 209 | 5.12 | 23.37 | 44.46 | -0.498 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo019333 | DlSKP1-9 | Chr9:805779:806249:- | 156 | 4.44 | 17.93 | 34.47 | -0.220 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo019334 | DlSKP1-10 | Chr9:812332:812819:- | 124 | 4.62 | 14.46 | 53.90 | -0.764 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo019594 | DlSKP1-11 | Chr9:4007573:4010954:+ | 399 | 5.76 | 45.34 | 56.04 | -0.647 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo022243 | DlSKP1-12 | Chr10:12177605:12182053:+ | 172 | 5.15 | 19.43 | 40.72 | -0.305 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| Dlo023134 | DlSKP1-13 | Chr11:1244155:1245940:- | 176 | 4.52 | 20.16 | 52.48 | -0.561 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo034799 | DlSKP1-14 | unanchor445_1_409426:233674:234129:- | 182 | 4.96 | 20.68 | 49.36 | -0.565 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
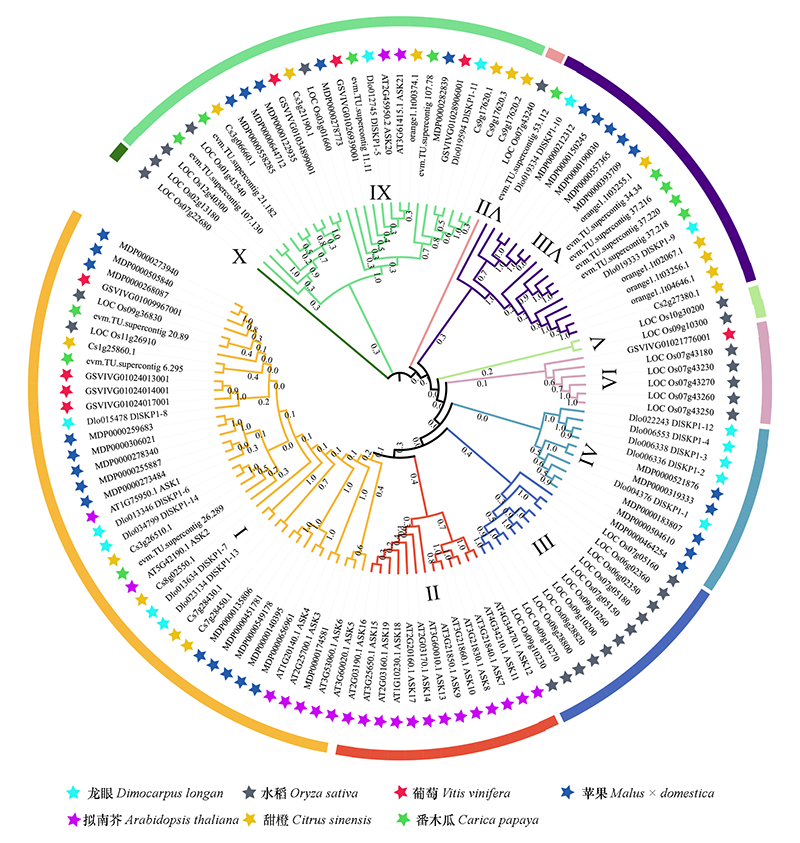
图2 龙眼、拟南芥、甜橙、番木瓜、水稻、葡萄、苹果的SKP1-like家族成员系统进化树 图中显示的数字为基于Bootstrap = 1 000迭代的自展值。
Fig. 2 Phylogenetic tree of the SKP1-like family members:longan,Arabidopsis,sweet orange,papaya,rice,grape,and apple The numbers are bootstrap values based on 1 000 iterations.
| 物种种类 Species | 物种成员 Species member | 龙眼成员 longan members | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | ASK1 | DlSKP1-6 | 0.11 | 2.18 | 0.05 |
| ASK4 | DlSKP1-6 | 0.22 | — | — | |
| ASK20 | DlSKP1-5 | 0.20 | 1.75 | 0.11 | |
| ASK21 | DlSKP1-5 | 0.18 | 1.43 | 0.12 | |
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | Os09t0539500-01 | DlSKP1-8 | 0.25 | 0.63 | 0.40 |
| 甜橙 Citrus sinensis | Cs9g17620.3 | DlSKP1-11 | 0.09 | 0.61 | 0.15 |
| orange1.1t00374.1 | DlSKP1-5 | 0.10 | 0.67 | 0.16 | |
| orange1.1t00374.1 | DlSKP1-11 | 0.19 | 2.17 | 0.09 | |
| Cs8g02550.1 | DlSKP1-13 | 0.14 | 1.26 | 0.11 | |
| Cs8g02550.1 | DlSKP1-6 | 0.12 | 1.89 | 0.06 | |
| Cs8g02550.1 | DlSKP1-8 | 0.21 | 1.75 | 0.12 | |
| Cs3g26510.1 | DlSKP1-13 | 0.14 | 3.07 | 0.05 | |
| Cs3g26510.1 | DlSKP1-6 | 0.03 | 0.82 | 0.03 | |
| Cs3g26510.1 | DlSKP1-8 | 0.17 | 1.04 | 0.16 | |
| Cs1g25860.1 | DlSKP1-13 | 0.23 | 1.76 | 0.13 | |
| Cs1g25860.1 | DlSKP1-6 | 0.11 | 1.47 | 0.07 | |
| Cs1g25860.1 | DlSKP1-8 | 0.23 | 0.94 | 0.25 |
表2 龙眼与拟南芥、水稻以及甜橙SKP1-like共线性成员进化选择压力分析
Table 2 Evolutionary selection pressure analysis of SKP1-like family collinear members in longan and Arabidopsis,longan and rice,and longan and sweet orange
| 物种种类 Species | 物种成员 Species member | 龙眼成员 longan members | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | ASK1 | DlSKP1-6 | 0.11 | 2.18 | 0.05 |
| ASK4 | DlSKP1-6 | 0.22 | — | — | |
| ASK20 | DlSKP1-5 | 0.20 | 1.75 | 0.11 | |
| ASK21 | DlSKP1-5 | 0.18 | 1.43 | 0.12 | |
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | Os09t0539500-01 | DlSKP1-8 | 0.25 | 0.63 | 0.40 |
| 甜橙 Citrus sinensis | Cs9g17620.3 | DlSKP1-11 | 0.09 | 0.61 | 0.15 |
| orange1.1t00374.1 | DlSKP1-5 | 0.10 | 0.67 | 0.16 | |
| orange1.1t00374.1 | DlSKP1-11 | 0.19 | 2.17 | 0.09 | |
| Cs8g02550.1 | DlSKP1-13 | 0.14 | 1.26 | 0.11 | |
| Cs8g02550.1 | DlSKP1-6 | 0.12 | 1.89 | 0.06 | |
| Cs8g02550.1 | DlSKP1-8 | 0.21 | 1.75 | 0.12 | |
| Cs3g26510.1 | DlSKP1-13 | 0.14 | 3.07 | 0.05 | |
| Cs3g26510.1 | DlSKP1-6 | 0.03 | 0.82 | 0.03 | |
| Cs3g26510.1 | DlSKP1-8 | 0.17 | 1.04 | 0.16 | |
| Cs1g25860.1 | DlSKP1-13 | 0.23 | 1.76 | 0.13 | |
| Cs1g25860.1 | DlSKP1-6 | 0.11 | 1.47 | 0.07 | |
| Cs1g25860.1 | DlSKP1-8 | 0.23 | 0.94 | 0.25 |
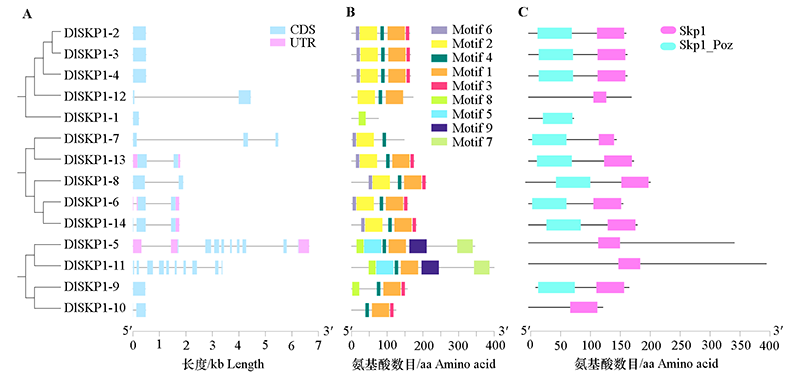
图3 DlSKP1家族成员基因结构位置(A)、保守基序motif(B)及蛋白保守结构域(C)分布图
Fig. 3 Distribution map of gene structure position(A),conserved motif (B),and protein conserved domain(C)of DlSKP1 family members
| 顺式作用元件种类 Kinds of cis-acting elements | DlSKP1-1 | DlSKP1-2 | DlSKP1-3 | DlSKP1-4 | DlSKP1-5 | DlSKP1-6 | DlSKP1-7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TATA-box | 38 | 29 | 36 | 46 | 57 | 48 | 64 |
| CAAT-box | 35 | 34 | 41 | 37 | 43 | 52 | 28 |
| 光响应Light responsiveness | 10 | 7 | 13 | 7 | 3 | 23 | 19 |
| MYB结合情况下的光响应 MYB binding site involved in light responsiveness | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MYB结合情况下的干旱胁迫 MYB binding site involved in drought inducibility | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 压力胁迫 Defense and stress | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 厌氧反应 Anaerobic response | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| 缺氧诱导 Anoxic specific inducibility | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 低温 Low-temperature | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 机械损伤 Wound-responsive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 赤霉素 Gibberellin | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 脱落酸 Abscisic acid | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 7 |
| 水杨酸 Salicylic acid | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 生长素 Auxin | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 茉莉酸甲酯 MeJA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 |
| 胚乳 Endosperm | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 光敏色素下调 Phytochrome down-regulation | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 分生组织表达Meristem expression | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 细胞周期 Cell cycle regulation | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 昼夜节律调控 Circadian control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 栅栏叶肉细胞的分化 Differentiation of the palisade mesophyll cells | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 种子特异调控 Seed-specific regulation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MYBHv1结合位点 MYBHv1 binding site | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 顺式作用元件种类 Kinds of cis-acting elements | DlSKP1-8 | DlSKP1-9 | DlSKP1-10 | DlSKP1-11 | DlSKP1-12 | DlSKP1-13 | DlSKP1-14 |
| TATA-box | 52 | 47 | 77 | 41 | 80 | 32 | 32 |
| CAAT-box | 33 | 46 | 58 | 45 | 40 | 66 | 53 |
| 光响应Light responsiveness | 9 | 5 | 13 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 22 |
| MYB结合情况下的光响应 MYB binding site involved in light responsiveness | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MYB结合情况下的干旱胁迫 MYB binding site involved in drought inducibility | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 压力胁迫 Defense and stress | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 厌氧反应 Anaerobic response | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 3 |
| 缺氧诱导 Anoxic specific inducibility | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 低温 Low-temperature | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 机械损伤 Wound-responsive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 赤霉素 Gibberellin | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 脱落酸 Abscisic acid | 1 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 5 |
| 水杨酸 Salicylic acid | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 生长素 Auxin | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 茉莉酸甲酯 MeJA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 胚乳 Endosperm | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 光敏色素下调 Phytochrome down-regulation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 分生组织表达Meristem expression | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 细胞周期 Cell cycle regulation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 昼夜节律调控 Circadian control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 栅栏叶肉细胞的分化 Differentiation of the palisade mesophyll cells | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 种子特异调控 Seed-specific regulation | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MYBHv1结合位点 MYBHv1 binding site | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
表3 DlSKP1基因家族顺式作用元件分析
Table 3 Analysis of cis-acting elements of the DlSKP1 gene family
| 顺式作用元件种类 Kinds of cis-acting elements | DlSKP1-1 | DlSKP1-2 | DlSKP1-3 | DlSKP1-4 | DlSKP1-5 | DlSKP1-6 | DlSKP1-7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TATA-box | 38 | 29 | 36 | 46 | 57 | 48 | 64 |
| CAAT-box | 35 | 34 | 41 | 37 | 43 | 52 | 28 |
| 光响应Light responsiveness | 10 | 7 | 13 | 7 | 3 | 23 | 19 |
| MYB结合情况下的光响应 MYB binding site involved in light responsiveness | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MYB结合情况下的干旱胁迫 MYB binding site involved in drought inducibility | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 压力胁迫 Defense and stress | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 厌氧反应 Anaerobic response | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| 缺氧诱导 Anoxic specific inducibility | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 低温 Low-temperature | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 机械损伤 Wound-responsive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 赤霉素 Gibberellin | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 脱落酸 Abscisic acid | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 7 |
| 水杨酸 Salicylic acid | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 生长素 Auxin | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 茉莉酸甲酯 MeJA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 |
| 胚乳 Endosperm | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 光敏色素下调 Phytochrome down-regulation | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 分生组织表达Meristem expression | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 细胞周期 Cell cycle regulation | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 昼夜节律调控 Circadian control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 栅栏叶肉细胞的分化 Differentiation of the palisade mesophyll cells | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 种子特异调控 Seed-specific regulation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MYBHv1结合位点 MYBHv1 binding site | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 顺式作用元件种类 Kinds of cis-acting elements | DlSKP1-8 | DlSKP1-9 | DlSKP1-10 | DlSKP1-11 | DlSKP1-12 | DlSKP1-13 | DlSKP1-14 |
| TATA-box | 52 | 47 | 77 | 41 | 80 | 32 | 32 |
| CAAT-box | 33 | 46 | 58 | 45 | 40 | 66 | 53 |
| 光响应Light responsiveness | 9 | 5 | 13 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 22 |
| MYB结合情况下的光响应 MYB binding site involved in light responsiveness | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MYB结合情况下的干旱胁迫 MYB binding site involved in drought inducibility | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 压力胁迫 Defense and stress | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 厌氧反应 Anaerobic response | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 3 |
| 缺氧诱导 Anoxic specific inducibility | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 低温 Low-temperature | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 机械损伤 Wound-responsive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 赤霉素 Gibberellin | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 脱落酸 Abscisic acid | 1 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 5 |
| 水杨酸 Salicylic acid | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 生长素 Auxin | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 茉莉酸甲酯 MeJA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 胚乳 Endosperm | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 光敏色素下调 Phytochrome down-regulation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 分生组织表达Meristem expression | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 细胞周期 Cell cycle regulation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 昼夜节律调控 Circadian control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 栅栏叶肉细胞的分化 Differentiation of the palisade mesophyll cells | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 种子特异调控 Seed-specific regulation | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MYBHv1结合位点 MYBHv1 binding site | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
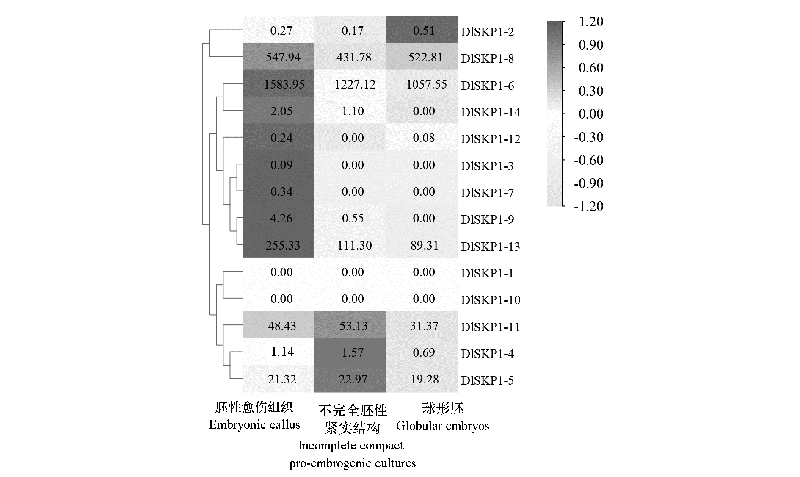
图4 DlSKP1家族成员体胚发生早期不同阶段特异表达分析 图中数值表示DlSKP1成员在体胚发生早期对应的FPKM值。
Fig. 4 Analysis of specific expressions of DlSKP1 family members at different stages of early embryogenesis The values in the figure indicate the FPKM values of DlSKP1 members during early somatic embryogenesis.
| [1] |
Cha J Y, Kim J, Kim T S, Zeng Q N, Wang L, Lee S Y, Kim W Y, Somers D E. 2017. GIGANTEA is a co-chaperone which facilitates maturation of ZEITLUPE in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Nature Communications, 8(1):3-15.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-016-0014-9 URL |
| [2] | Chen C J, Xia R, Chen H, He Y H. 2018. TBtools,a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various biological data handling tools with a user-friendly interface. BioRxiv:289660. |
| [3] |
Cheng C, Wang Z, Ren Z, Zhi L, Yao B, Su C, Liu L, Li X. 2017. SCFAtPP2-B11 modulates ABA signaling by facilitating SnRK2.3 degradation in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genetics, 13(8):e1006947.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006947 URL |
| [4] |
Derenzo C, Seydoux G. 2004. A clean start:degradation of maternal proteins at the oocyte-to-embryo transition. Trends in Cell Biology, 14(8):420-426.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.07.005 URL |
| [5] |
Deshaies R J. 1999. SCF and Cullin/Ring H2-based ubiquitin ligases. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 15(15):435-467.
doi: 10.1146/cellbio.1999.15.issue-1 URL |
| [6] |
Dezfulian M H, Soulliere D M, Dhaliwal R K, Sareen M, Crosby W L. 2012. The SKP1-like gene family of Arabidopsis exhibits a high degree of differential gene expression and gene product interaction during development. PLoS ONE, 7(11):e50984.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050984 URL |
| [7] |
Dindas J, Scherzer S, Roelfsema M R G, von Meyer K, Müller H M, Al-Rasheid K A S, Palme K, Dietrich P, Becker D, Bennett M J, Hedrich R. 2018. AUX1-mediated root hair auxin influx governs SCFTIR1/AFB-type Ca2+ signaling. Nature Communications, 9:1174.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03582-5 URL |
| [8] |
Elzanati O, Roche J, Boulaflous-Stevens A, Mouzeyar S, Bouzidi M F. 2017. Genome-wide analysis,classification,expression and interaction of Physcomitrella patens SKP1-like(PpSKP)and F-box(FBX)genes. Plant Gene, 12:13-22.
doi: 10.1016/j.plgene.2017.05.015 URL |
| [9] | Gray W M, Kepinski S, Rouse D, Leyser O, Estelle M. 2001. Auxin regulates SCFTIR1-dependent degradation of AUX/IAA proteins. Nature, 14:271-276. |
| [10] |
Hellmann H, Hobbie L, Chapman A, Dharmasiri S, Dharmasiri N, Pozo C D, Reinhardt D, Estelle M. 2003. Arabidopsis AXR6 encodes CUL1 implicating SCF E3 ligases in auxin regulation of embryogenesis. The EMBO Journal, 22(13):3314-3325.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg335 URL |
| [11] |
Hershko A, Ciechanover A. 1998. The ubiquitin system. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 67:425-479.
pmid: 9759494 |
| [12] |
Hong M J, Kim D Y, Seo Y W. 2013. SKP1-like-related genes interact with various F-box proteins and may form SCF complexes with Cullin-F-box proteins in wheat. Molecular Biology Reports, 40(2):969-981.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2139-1 URL |
| [13] |
Hu D L, Chen Q Z, Zhang C J, Wang Y, Zhang B J, Tang C M. 2013. Identification of cotton SKP1-like gene GhSKP1 and its function in seed germination and taproot growth in tobacco. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 93(5):817-825.
doi: 10.4141/cjps2012-312 URL |
| [14] | Huang J, Zhu C, Li X. 2018. SCFSNIPER4 controls the turnover of two redundant TRAF proteins in plant immunity. Plant Journal for Cell & Molecular Biology, 95:504-515. |
| [15] | Huang S, Chen X, Zhong X, Li M, Ao K, Huang J, Li X. 2016. Plant TRAF proteins regulate NLR immune receptor turnover. Cell Host & Microbe, 19(2):204-215. |
| [16] |
Iglesias M J, Terrile M C, Correaaragunde N, Colman S L, Izquierdoalvarez A, Fiol D F, Parísa R, Sánchez-Lópezb N, Marinac A, Calderón Villalobos L I A, Estellee F M, Lamattinaa L, Martínez-Ruizb A, Casalongue C A. 2018. Regulation of SCFTIR1/AFBs E3 ligase assembly by S-nitrosylation of Arabidopsis SKP1-like1 impacts on auxin signaling. Redox Biology, 18:200-210.
doi: S2213-2317(18)30414-2 pmid: 30031268 |
| [17] |
Kahloul S, Imen H S E B, Boulaflous A, Ferchichi A, Kong H, Mouzeyar S, Bouzidi M F. 2012. Structural,expression and interaction analysis of rice SKP1-Like genes. DNA Research, 20(1):67-78.
doi: 10.1093/dnares/dss034 URL |
| [18] |
Kim D H, Zhang W, Koepp D M. 2012. The hect domain E3 ligase tom1 and the F-box protein Dia2 control Cdc6 degradation in G1 Phase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287(53):44212-44220.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.401778 URL |
| [19] |
Kinterova V, Kanka J, Petruskova V, Toralova T. 2019. Inhibition of Skp1-Cullin-F-box complexes during bovine oocyte maturation and preimplantation development leads to delayed development of embryos. Biology of Reproduction, 100(4):896-906.
doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy254 pmid: 30535233 |
| [20] |
Koltai , Hinanit . 2014. Receptors,repressors,PINs:a playground for strigolactone signaling. Trends in Plant Science, 19(11):727-733.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2014.06.008 URL pmid: 25037847 |
| [21] |
Kong H, Landherr L L, Frohlich M W, Leebens-Mack J, Depamphilis C W. 2007. Patterns of gene duplication in the plant SKP1 gene family in angiosperms:evidence for multiple mechanisms of rapid gene birth. The Plant Journal, 50(5):873-885.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03097.x URL |
| [22] |
Lai C P, Lee C L, Chen P H, Wu S H, Yang C C, Shaw J F. 2004. Molecular analyses of the Arabidopsis TUBBY-Like protein gene family. Plant Physiology, 134(4):1586-1597.
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.037820 URL |
| [23] | Lai Zhong-xiong, Pan Liang-zhen, Chen Zhen-guang. 1997. Establishment and maintenance of longan embryogenic cell line. Journal of Fujian Agricultural University, 26(2):160-167. (in Chinese) |
| 赖钟雄, 潘良镇, 陈振光. 1997. 龙眼胚性细胞系的建立与保持. 福建农业大学学报, 26(2):160-167. | |
| [24] |
Lee B D, Kim M R, Kang M Y, Cha J Y, Han S H, Nawkar G M, Sakuraba Y, Lee S Y, Imaizumi T, McClung C R, Kim W Y, Paek N C. 2018. The F-box protein FKF1 inhibits dimerization of COP1 in the control of photoperiodic flowering. Nature Communications, 9(1):553.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-02966-x URL |
| [25] |
Li C J, Liu Z J, Zhang Q R, Wang R Z, Xiao L T, Ma H, Chong K, Xu Y Y. 2012. SKP1 is involved in abscisic acid signalling to regulate seed germination,stomatal opening and root growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ, 35(5):952-965.
doi: 10.1111/pce.2012.35.issue-5 URL |
| [26] |
Li P, Miao H, Ma Y, Wang L, Hu G, Ye Z, Zhao J, Qin Y. 2015. CrWSKP1,an SKP1-like gene,is involved in the self-incompatibility reaction of“Wuzishatangju”(Citrus reticulata Blanco). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(9):21695-21710.
doi: 10.3390/ijms160921695 URL |
| [27] |
Li Y, Zhang L, Li D K, Liu Z B, Wang J M, Li X F, Yang Y. 2016. The Arabidopsis F-box E3 ligase RIFP1 plays a negative role in abscisic acid signalling by facilitating ABA receptor RCAR3 degradation. Plant Cell and Environment, 39(3):571-582.
doi: 10.1111/pce.12639 URL |
| [28] | Li Yang, Li Dong. 2015. Research progress on the relationship between ubiquitin ligase and substrate selection. Biotechnology Bulletin, 31(1):11-20. (in Chinese) |
| 李杨, 李栋. 2015. 泛素连接酶—底物选择关系的研究进展. 生物技术通报, 31(1):11-20. | |
| [29] |
Liu A L, Yu Y, Duan X B, Sun X L, Duanmu H Z, Zhu Y M. 2015. GsSKP21,a Glycine soja S-phase kinase-associated protein,mediates the regulation of plant alkaline tolerance and ABA sensitivity. Plant Molecular Biology, 87:111-124.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-014-0264-z URL |
| [30] |
Liu F Q, Ni W M, Griffith M E, Huang Z Y, Chang C Q, Peng W, Ma H, Xie D X. 2004. The ASK1 and ASK2 genes are essential for Arabidopsis early development. The Plant Cell, 16(1):5-20.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.017772 URL |
| [31] |
Lu D, Ni W, Stanley B A, Ma H. 2016. Proteomics and transcriptomics analyses of Arabidopsis floral buds uncover important functions of Arabidopsis SKP1-like1. BMC Plant Biology, 16(1):61.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0571-9 URL |
| [32] |
Matsumoto D, Yamane H, Abe K, Tad R. 2012. Identification of a SKP1-Like protein interacting with SFB,the pollen S determinant of the gametophytic self-incompatibility in Prunus. Plant Physiology, 159(3):1252-1262.
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.197343 URL pmid: 22548785 |
| [33] |
McGinnis K M, Thomas S G, Soule J D, Strader L C, Zale J M, Sun T P, Steber C M. 2003. The Arabidopsis SLEEPY1 gene encodes a putative F-Box subunit of an SCF E3 ubiquitin ligase. The Plant Cell, 15(5):1120-1130.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.010827 URL |
| [34] | Mei Xu, Yu Xiao-min, Pang Ya-fei, Sun Cheng-li. 2019. Overview of the medicinal value of longan core. Chinese Folk Therapy, 27(13):104-105. (in Chinese) |
| 梅徐, 俞晓敏, 庞亚飞, 孙成力. 2019. 龙眼核药用价值概述. 中国民间疗法, 27(13):104-105. | |
| [35] |
Patton E E, Willems A R, Tyers M. 1998. Combinatorial control in ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis:don’t Skp the F-box hypothesis. Trends in Genetics, 14(6):236-243.
pmid: 9635407 |
| [36] |
Rao V, Petla B P, Verma P, Salvi P, Majee M. 2018. Arabidopsis SKP1-like protein 13(ASK13)positively regulates seed germination and seedling growth under abiotic stresses. Journal of Experimental Botany, 69(16):3899-3915.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery191 URL |
| [37] |
Ren C, Pan J, Peng W, Genschik P, Hobbie L, Hellmann H, Estelle M, Gao B, Peng J, Sun C, Xie D. 2005. Point mutations in Arabidopsis Cullin1 reveal its essential role in jasmonate response. Plant Journal, 42:514-524.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2005.42.issue-4 URL |
| [38] |
Smalle J, Vierstra R D. 2004. The ubiquitin 26S proteasome proteolytic pathway. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 55:555-590.
pmid: 15377232 |
| [39] |
Thines B, Katsir L, Melotto M, Niu Y, Mandaokar A, Liu G, Nomura K, He S Y, Howe G A, Browse J. 2007. JAZ repressor proteins are targets of the SCFCOI1 complex during jasmonate signalling. Nature, 448(7154):661-665.
doi: 10.1038/nature05960 URL |
| [40] |
Veronika B, Veronika K, Jiri K, Toralova T. 2016. Characterization of SCF-Complex during bovine preimplantation development. PLoS ONE, 11(1):e0147096.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147096 URL |
| [41] |
Wang L, Wen R, Wang J, Xiang D, Wang Q, Zang Y, Wang Z, Huang S, Li X, Datla R, Fobert P R, Wang H, Wei Y, Xiao W. 2019. Arabidopsis UBC13 diferentially regulates two programmed cell death pathways in responses to pathogen and low-temperature stress. New Phytologist, 221:919-934.
doi: 10.1111/nph.2019.221.issue-2 URL |
| [42] | Wei Chun-ru, Meng Yu-yu, Fan Run-qiao, Li Hu-ying, Zhao Wei-quan, Yu Xiu-mei, Kang Zhen-sheng, Liu Da-qun. 2020. The expression pattern and interaction protein identification of wheat F-box/LRR gene TaFBL14. Chinese Journal of Plant Physiology, 56(4):886-894. (in Chinese) |
| 魏春茹, 孟钰玉, 范润侨, 李虎滢, 赵伟全, 于秀梅, 康振生, 刘大群. 2020. 小麦F-box/LRR类基因TaFBL14的抗逆相关表达模式及互作蛋白鉴定. 植物生理学报, 56(4):886-894. | |
| [43] |
Woo O G, Kim H, Lee J H. 2020. Current understanding of the CRL1 complex in Arabidopsis. Journal of Plant Biology, 64:1-12.
doi: 10.1007/s12374-020-09274-2 URL |
| [44] | Xu Ke-heng, Zhang Yun-tong, Zhang Ying, Wang Bin, Wang Fa-wei, Li Hai-yan. 2018. Research progress of plant F-box gene family. Biotechnology Bulletin, 34(1):26-32. (in Chinese) |
| 许克恒, 张云彤, 张莹, 王彬, 王法微, 李海燕. 2018. 植物F-box基因家族的研究进展. 生物技术通报, 34(1):26-32. | |
| [45] |
Yan J B, Zhang C, Gu M, Bai Z Y, Zhang W G, Qi T C, Cheng Z W, Peng W, Luo H B, Nan F J, Wang Z, Xie D X. 2009. The Arabidopsis coronatine insensitive1 protein is a jasmonate receptor. The Plant Cell, 21(8):2220-2236.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.065730 URL |
| [46] | Ye You-pi. 2014. Advances in the study of Arabidopsis ASK genes. Chinese Journal of Plant Physiology, 50(6):683-690. (in Chinese) |
| 叶佑丕. 2014. 拟南芥ASK基因研究进展. 植物生理学报, 50(6):683-690. | |
| [47] | Yin Shan-shan, Li Mao-fu, Wang Hua, Li Yang, Zhang Qiu-lei, Jin Wan-mei, Li Tian-zhong. 2016. Cloning and expression analysis of strawberry FaSKP1-1 gene. Journal of China Agricultural University, 21(12):28-34. (in Chinese) |
| 殷姗姗, 李茂福, 王华, 李洋, 张秋雷, 金万梅, 李天忠. 2016. 草莓FaSKP1-1基因的克隆与表达分析. 中国农业大学学报, 21(12):28-34. | |
| [48] | Zhang Y, Zhang J, Guo J, Zhou F, Singh S, Xu X, Xie Q, Yang Z, Huang C F. 2018. F-box protein RAE1 regulates the stability of the aluminum-resistance transcription factor STOP1 in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116:319-327. |
| [49] |
Zhang Y Q, Wang C P, Lin Q F, Gao F H, Ma Y, Zhang M, Lin Y H, Ma Q H, Hua X J. 2015. Genome-wide analysis of phylogeny,expression profile and sub-cellular localization of SKP1-Like genes in wild tomato. Plant Science, 238:105-114.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.06.005 URL |
| [50] |
Zhao D Z, Yang M Y, Solava J, Ma H. 1999. The ASK1 gene regulates development and interacts with the UFO gene to control floral organ identity in Arabidopsis. Developmental Genetics, 25(3):209-223.
pmid: 10528262 |
| [51] | Zhou Xu-hong, Zhao Xue-yan, Yang Xiao-mi, Wu Xue-wei, Qu Su-ping. 2020. Carnation DcSKP1 gene cloning and expression analysis. Guangxi Plants, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/45.1134.Q.20200708.1145.032.html . (in Chinese) |
| 周旭红, 赵雪艳, 杨晓密, 吴学尉, 瞿素萍. 2020. 香石竹DcSKP1基因克隆及表达分析. 广西植物, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/45.1134.Q.20200708.1145.032.html . | |
| [52] | Zuo Yue, Xu Yong-hua. 2020. Research progress on the mechanism of GA and ABA during seed germination. Molecular Plant Breeding. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20200727.1446.008.html . (in Chinese) |
| 佐月, 许永华. 2020. 种子萌发过程中GA与ABA的作用机制研究进展. 分子植物育种, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20200727.1446.008.html . |
| [1] | 邓朝军, 许奇志, 蒋际谋, 胡文舜, 郑少泉, 陈秀萍, 姜 帆, 许家辉, 苏文炳, 张雅玲, 黄敬峰. 浓香型龙眼新品种‘醇香’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 75-76. |
| [2] | 邓朝军, 陈秀萍, 许奇志, 蒋际谋, 郑少泉, 胡文舜, 姜 帆, 许家辉, 苏文炳, 张雅玲, 黄敬峰. 浓香型龙眼新品种‘福香’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 77-78. |
| [3] | 徐小萍, 曹清影, 蔡柔荻, 官庆栩, 张梓浩, 陈裕坤, 徐涵, 林玉玲, 赖钟雄. 龙眼miR408与DlLAC12克隆及其在球形胚发生和非生物胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1866-1882. |
| [4] | 陶鑫, 朱荣香, 贡鑫, 吴磊, 张绍铃, 赵建荣, 张虎平. 梨果糖激酶基因PpyFRK5在果实蔗糖积累中的作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1429-1440. |
| [5] | 梁沁, 张延晖, 康开权, 刘瑾航, 李亮, 冯宇, 王超, 杨超, 李永裕. miR168家族进化特性及其在砂梨休眠期的表达模式分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 958-972. |
| [6] | 肖学宸, 刘梦雨, 蒋梦琦, 陈燕, 薛晓东, 周承哲, 吴兴健, 吴君楠, 郭寅生, 叶开温, 赖钟雄, 林玉玲. 龙眼褪黑素合成途径SNAT、ASMT和COMT家族基因鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1031-1046. |
| [7] | 潘鑫峰, 叶方婷, 毛志君, 李兆伟, 范凯. 睡莲WRKY家族的全基因组鉴定和分子进化分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1121-1135. |
| [8] | 刘梦雨, 蒋梦琦, 陈燕, 张舒婷, 薛晓东, 肖学宸, 赖钟雄, 林玉玲. 龙眼GDSL酯酶/脂肪酶基因的全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 597-612. |
| [9] | 申序, 陈晓慧, 张婧, 陈荣珠, 徐小萍, 李晓斐, 蒋梦琦, 刘蒲东, 倪珊珊, 林玉玲, 赖钟雄. 龙眼染色质重塑因子Snf2基因家族的进化动力学研究及在体胚发生早期的表达[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 41-61. |
| [10] | 谢思艺, 周承哲, 朱晨, 詹冬梅, 陈兰, 吴祖春, 赖钟雄, 郭玉琼. 茶树CsTIFY家族全基因组鉴定及非生物胁迫和激素处理中主要基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 100-116. |
| [11] | 杨为海, 曾利珍, 肖秋生, 石胜友. 饥饿胁迫下龙眼落果与果皮和离区糖、ABA及相关基因表达的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(8): 1457-1469. |
| [12] | 俞沁含, 焦淑珍, 吴楠, 张宁波, 徐伟荣. 葡萄E3泛素酶HOS1基因克隆、表达及抗血清制备[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(6): 1173-1180. |
| [13] | 苏立遥, 王培育, 蒋梦琦, 黄倏祺, 薛晓东, 刘梦雨, 肖学宸, 赖春旺, 张梓浩, 陈裕坤, 赖钟雄, 林玉玲. 龙眼pri-miR319a编码短肽活性的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(5): 908-920. |
| [14] | 蔡柔荻, 厉雪, 陈燕, 徐小萍, 陈晓慧, 赖钟雄, 林玉玲. 龙眼DRB家族全基因组鉴定及其表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(5): 921-933. |
| [15] | 牛西强, 罗潇云, 康凯程, 黄先忠, 胡能兵, 隋益虎, 艾昊. 辣椒PEBP基因家族的全基因组鉴定、比较进化与组织表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(5): 947-959. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司