
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2597-2612.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0850
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Min, HE Han, ZHOU Chenping, KUANG Ruibin, LIU Chuanhe, WU Xiaming, XU Ze, WEI Yuerong**( )
)
Received:2025-03-02
Revised:2025-07-28
Online:2025-10-25
Published:2025-10-28
Contact:
WEI Yuerong
YANG Min, HE Han, ZHOU Chenping, KUANG Ruibin, LIU Chuanhe, WU Xiaming, XU Ze, WEI Yuerong. Development and Application of Insertion-Deletion(InDel)Markers in Papaya(Carica papaya)Based on Whole Genome Re-Sequencing Data[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(10): 2597-2612.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0850
| 染色体编号 Chrosome labels | 标记引物数 Number of InDel primers | 有效引物数 Number of effective primers | 有效扩增率/% Effective amplification ratios | 多态引物数 Number of polymorphic primers | 引物多态率/% Polymorphic primer ratios |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr1 | 40 | 36 | 90.0 | 31 | 77.5 |
| Chr2 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 34 | 85.0 |
| Chr3 | 40 | 39 | 97.5 | 31 | 77.5 |
| Chr4 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 32 | 80.0 |
| Chr5 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 28 | 70.0 |
| Chr6 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 27 | 67.5 |
| Chr7 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 28 | 70.0 |
| Chr8 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 29 | 72.5 |
| Chr9 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 31 | 77.5 |
| 合计Total | 360 | 355 | 98.6 | 271 | 75.3 |
Table 1 Statistics of amplification results of 360 InDel markers
| 染色体编号 Chrosome labels | 标记引物数 Number of InDel primers | 有效引物数 Number of effective primers | 有效扩增率/% Effective amplification ratios | 多态引物数 Number of polymorphic primers | 引物多态率/% Polymorphic primer ratios |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr1 | 40 | 36 | 90.0 | 31 | 77.5 |
| Chr2 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 34 | 85.0 |
| Chr3 | 40 | 39 | 97.5 | 31 | 77.5 |
| Chr4 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 32 | 80.0 |
| Chr5 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 28 | 70.0 |
| Chr6 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 27 | 67.5 |
| Chr7 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 28 | 70.0 |
| Chr8 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 29 | 72.5 |
| Chr9 | 40 | 40 | 100.0 | 31 | 77.5 |
| 合计Total | 360 | 355 | 98.6 | 271 | 75.3 |
| 标记号 InDel labels | 标记类型 Type | 差异长 度/bp Length | 上游扩增引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游扩增引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer | 标记引物扩增位置 Amplification location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr1-09 | 插入 Insertion | 35 | ACCTTGACATACATGCATGCA | TGCCTTGAGTCACACGGA | Chr1:2749817-2750039 |
| Chr1-10 | 插入 Insertion | 36 | GAACCTCCTCCCCCGCTA | TGAACCACCTGCTCGCAT | Chr1:2857128-2857366 |
| Chr1-15 | 插入 Insertion | 49 | TGTTCCATGTGTTATGGACGT | ACAAGCTTGGTGCATATGCT | Chr1:3213152-3213384 |
| Chr1-26 | 缺失 Deletion | -46 | CGCCCTCTCCCGTAAAGC | ACCACAGGTACTTGGCCG | Chr1:7259239-7259506 |
| Chr1-29 | 缺失 Deletion | -30 | CGTGAGGTGCTCGCTGAT | GGGACATCTCGTGCACGT | Chr1:7846667-7846868 |
| Chr1-30 | 插入 Insertion | 42 | GAACGCAAAAGACTGACTCCT | AGGTTCTGAAGACATGCACTT | Chr1:8015769-8016044 |
| Chr1-39 | 插入 Insertion | 39 | GTCCTCAGGACGACCCTAGA | ATCTGGTGGCAGTGGCAG | Chr1:10631445-10631724 |
| Chr2-01 | 插入 Insertion | 37 | GCTCCAACGAGAGAGATGACT | CGGTGCTGGTGACGAAGA | Chr2:307044-307320 |
| Chr2-02 | 插入 Insertion | 31 | CAGGATTTTGCTAGGGTCAGT | AGACTTGCCTGCTGGAGC | Chr2:612393-612613 |
| Chr2-13 | 缺失 Deletion | -34 | ACCAACCGTCGATCCTCA | TGGCAAAACGTCGTGATGT | Chr2:5215597-5215796 |
| Chr2-15 | 插入 Insertion | 44 | TGCTGGGAATGCTTTGTGC | TGGTCCATGATGCCAGCTG | Chr2:5922591-5922860 |
| Chr2-18 | 插入 Insertion | 44 | GGTTAGACTGTCAAGTGGGCT | CGCCCTGAAAACATGGTGC | Chr2:10719434-10719712 |
| Chr2-20 | 缺失 Deletion | -31 | ACAACCTGAGAGCTCTTCCC | AGCTGCTTCTACCTGCTTGA | Chr2:12083278-12083527 |
| Chr2-29 | 插入 Insertion | 48 | TGGAATCAAGATTTGCACCGA | TTCCAGTTTCCGAACAACCA | Chr2:23526410-23526648 |
| Chr2-31 | 缺失 Deletion | -33 | GGCAGCACTTCATTGCCG | GGGTCTTACACTGGTTGCCA | Chr2:28941802-28942025 |
| Chr2-38 | 插入 Insertion | 38 | ACGAGTCTTCAAGCTTGCCA | TGCCAGTCTGTAAATTGCGG | Chr2:34031300-34031578 |
| Chr3-03 | 插入 Insertion | 48 | GCCAACACAAGAACGGAAACT | TGCAGTTCAAGTGGCGCT | Chr3:627145-627348 |
| Chr3-17 | 缺失 Deletion | -44 | CTCCTGCACAGTCGCCAT | GCTTGCTTTGCTCTCCGC | Chr3:6901713-6901929 |
| Chr3-21 | 缺失 Deletion | -46 | CCCTTCCCCCTCCCAAGA | TTCTGCCGTCGGTTGAGC | Chr3:10826323-10826544 |
| Chr3-22 | 插入 Insertion | 39 | TCCCGGACATCTGACCCC | AGCCTTTGATTCCCACTGCA | Chr3:10886342-10886562 |
| Chr3-23 | 插入 Insertion | 31 | GGAGCACAAGCCATGGGT | AGCCACCAGTCAGACCTCT | Chr3:11351904-11352128 |
| Chr3-30 | 插入 Insertion | 34 | ACGGTGACAGCATGAGGC | CACATGCAAGATGCCGGC | Chr3:16193105-16193338 |
| Chr3-31 | 插入 Insertion | 42 | AGCCAACCCACCACAAGT | CTCAGCCTATTTGTTGGTCCA | Chr3:16707449-16707694 |
| Chr3-33 | 插入 Insertion | 33 | TGCTGGAAAACACCCGCA | GCCTCCCCAAGTCAGCTG | Chr3:21024394-21024593 |
| Chr4-03 | 缺失 Deletion | -33 | CCAGCATCAGAACTCGAGGT | TTGGTTGCGGGGAATGCA | Chr4:1324489-1324712 |
| Chr4-08 | 插入 Insertion | 42 | CGAGCCTGTGTACCTGGT | TCACTTTCGTCAGTTGCCTGA | Chr4:4076944-4077153 |
| Chr4-14 | 插入 Insertion | 41 | GCGGTGAGCCTGAGATGA | AGACTCGTGGAGAACAAAGCA | Chr4:9192243-9192474 |
| Chr4-24 | 缺失 Deletion | -40 | ACGGGGCGTACATGTGTG | ACGAGGCCACCCCTAAGA | Chr4:21621919-21622128 |
| Chr4-25 | 插入 Insertion | 45 | TGGTTTCGCAAGTTCGCA | GTGCTAGTTGTTTTGCATGCT | Chr4:22997264-22997514 |
| Chr4-26 | 缺失 Deletion | -46 | AGAGGGGTTAGGCAGGGG | TCCCCACATTGATGTTGACCA | Chr4:23149465-23149734 |
| Chr4-34 | 缺失 Deletion | -32 | TCACGAGTTGAGGGAGGTCT | ACTTGTTGAGGGTTGAAAGCC | Chr4:28955964-28956194 |
| Chr4-40 | 插入 Insertion | 46 | GACGTGGTGCTTATCCCGT | GGCAGTCCAGTTCTATAGGGG | Chr4:34041449-34041703 |
| Chr5-02 | 缺失 Deletion | -49 | TGCGCACAACATTCAGGTC | GGCTATGTTGTGCCTGGGA | Chr5:59655-59828 |
| Chr5-07 | 插入 Insertion | 38 | TGAGTGGAAAGAAGATGCGGA | TCATCCCTCCATCCACAAACT | Chr5:272642-272800 |
| Chr5-08 | 缺失 Deletion | -34 | GACAAAGCAAAACTGCATCGT | TGATTTGGCAGCCCCTGG | Chr5:699745-699920 |
| Chr5-11 | 缺失 Deletion | -35 | GCGGCAATCAGAGGAGCA | GCACCACACAGACAAAAATCA | Chr5:1024290-1024446 |
| Chr5-15 | 缺失 Deletion | -33 | TGGGAGGTAGCTGACGGA | CAGCATGCCTAACCGTGC | Chr5:1509285-1509412 |
| Chr5-18 | 缺失 Deletion | -33 | GACTCCGATGATGTCCTCTGT | CGTGAAGGAAATCGGTGTGC | Chr5:1615976-1616100 |
| Chr5-24 | 插入 Insertion | 31 | GGGCTTGAGTTTGGGCCT | CCCAGTCCCATACCCCGA | Chr5:44035468-44035705 |
| Chr5-29 | 缺失 Deletion | -42 | GGAGGAAATTTTGGCTTGGGG | ACCAAAAACATGGAACCACCT | Chr5:44418169-44418332 |
| Chr5-30 | 插入 Insertion | 34 | GCAACTGTCTGATCCTTTGGG | ACTTCGCATTTCAGGGGAGA | Chr5:45207382-45207589 |
| Chr6-09 | 缺失 Deletion | -38 | CTAGACGCCCACGAAGCC | TCTTCCCTCTGCCGACCA | Chr6:9710183-9710427 |
| Chr6-10 | 插入 Insertion | 46 | ACATGCATGCCTAGTCACGA | GGGTTGTTGGAAGGGTCCT | Chr6:10024162-10024384 |
| Chr6-27 | 插入 Insertion | 45 | ATGTTGGGTCGCAGTGGC | AGGGCGGAGGGGATTTCT | Chr6:26274037-26274275 |
| Chr6-28 | 缺失 Deletion | -32 | TGAAAACAACTGCGAAACACT | ACTTCAGATGGGTACTTCTGC | Chr6:26872028-26872241 |
| Chr6-29 | 缺失 Deletion | -44 | CGGCAAGAGGAGAAGGGC | GGGGTTTCCAAGGAAGGGG | Chr6:28571296-28571513 |
| Chr6-32 | 缺失 Deletion | -43 | ACGCTAATGTTGCCGCCA | CGTCGAGCTTTACCCGCA | Chr6:33681522-33681724 |
| Chr7-01 | 插入 Insertion | 37 | TGCTCGGACGACCACAAC | AGTGGCCAACGAGCAGAG | Chr7:12591-12775 |
| Chr7-02 | 缺失 Deletion | -47 | GCAGCGGCCAATGCTAAG | GGGTGGTTGATGCTTCGC | Chr7:30560-30830 |
| Chr7-06 | 插入 Insertion | 31 | GGGGTTTAGCGTGGGTCC | AATGGCTGGTCTCACGCG | Chr7:449549-449763 |
| Chr7-12 | 缺失 Deletion | -46 | TGCATAAGGTCTGGAGACTGT | ACCCGAGCTACACCACAA | Chr7:2509875-2510036 |
| Chr7-19 | 缺失 Deletion | -41 | GCCTAGAGCCTCCAAACCA | GGAGATCCCTGTGCTGCC | Chr7:5959628-5959858 |
| Chr7-21 | 缺失 Deletion | -45 | ACTGAGTGAGCGATGGCAC | TGGGATGGCAGTAAAGCGG | Chr7:6662961-6663207 |
| Chr7-24 | 缺失 Deletion | -49 | ACCCTGGCTAAACGCGTC | ATGGGGGCGGGTCAACTA | Chr7:8693948-8694111 |
| Chr7-28 | 插入 Insertion | 33 | ACTCGTGTTCCCCAAAACA | ACCTATCAATTCTCCCGTCGA | Chr7:11076056-11076250 |
| Chr7-35 | 缺失 Deletion | -38 | AGAACCCCATCAACGGAAACT | ACCTTCCCACCTCACTCGT | Chr7:15440638-15440766 |
| Chr8-09 | 缺失 Deletion | -42 | ATCAGGCAAATGCATGGTTGA | AACCATCCTGGACCCGGA | Chr8:1320235-1320497 |
| Chr8-16 | 缺失 Deletion | -47 | TGGCTCCACAATCTGGCA | TGCCAACTGGTTTCCTCTTTC | Chr8:3251541-3251789 |
| Chr8-18 | 缺失 Deletion | -44 | CCCGCCTTTTCCACGTGA | AGTCATTCTGGTTCGGGTTGA | Chr8:3574827-3575078 |
| Chr8-19 | 缺失 Deletion | -42 | GCTTGCGGCAATTGGTTTC | ACGAGGATTGACAGGCAGC | Chr8:3680573-3680739 |
| Chr8-26 | 缺失 Deletion | -46 | AGTGGCAAGCAGTGTAGGA | CTTTCACTGCCGGGGAGT | Chr8:6135649-6135902 |
| Chr8-29 | 插入 Insertion | 44 | ACATCAGCTGCTCATTCCAT | TTGTACAGTCCCAAGTTGTGT | Chr8:7246002-7246208 |
| Chr8-30 | 缺失 Deletion | -33 | TGAAGGCCCCAGTTTTCCA | TGCATGTATTCGACCTTGTGG | Chr8:7761356-7761536 |
| Chr8-32 | 插入 Insertion | 36 | ACACTGCACTGCACTAGCT | GGCCAGTTTAGCCCGTCT | Chr8:8396708-8396836 |
| Chr9-09 | 缺失 Deletion | -32 | TCCGTTAACGCTCCGCAG | TGTGGTGGTTCTCTCCTTGTG | Chr9:5206000-5206184 |
| Chr9-15 | 插入 Insertion | 45 | CGACATGCAAGGAACTGGG | GACTTGGGTGCCGAAGCT | Chr9:6742034-6742244 |
| Chr9-17 | 缺失 Deletion | -34 | GGCGTTGTATGGCTCACG | GAGATTGCTCAGGTGTGGGA | Chr9:8310123-8310248 |
| Chr9-22 | 插入 Insertion | 30 | CCAACACCCCATTCCCCA | TGCACTAGACTCCTCCATCCA | Chr9:9397358-9397476 |
| Chr9-25 | 缺失 Deletion | -31 | CTTGTCCACGCGTGAGGT | GCTCGTCCCCTTTGCACA | Chr9:12450328-12450471 |
| Chr9-26 | 缺失 Deletion | -39 | CCGGTATCACTGAGGGCC | CAGTCGTGTGGAGTTGGGA | Chr9:14289457-14289653 |
| Chr9-27 | 缺失 Deletion | -31 | CTAGCACCAGGCCGTCAG | CCGCTGCACCTGGAGAAA | Chr9:14871648-14871817 |
| Chr9-31 | 缺失 Deletion | -45 | AGTTAGCCCATGCGCGTT | AGGGCCTCCTCCACTGAC | Chr9:27896823-27896950 |
Table 2 Location and sequence information of 72 pairs of core InDel primers
| 标记号 InDel labels | 标记类型 Type | 差异长 度/bp Length | 上游扩增引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游扩增引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer | 标记引物扩增位置 Amplification location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr1-09 | 插入 Insertion | 35 | ACCTTGACATACATGCATGCA | TGCCTTGAGTCACACGGA | Chr1:2749817-2750039 |
| Chr1-10 | 插入 Insertion | 36 | GAACCTCCTCCCCCGCTA | TGAACCACCTGCTCGCAT | Chr1:2857128-2857366 |
| Chr1-15 | 插入 Insertion | 49 | TGTTCCATGTGTTATGGACGT | ACAAGCTTGGTGCATATGCT | Chr1:3213152-3213384 |
| Chr1-26 | 缺失 Deletion | -46 | CGCCCTCTCCCGTAAAGC | ACCACAGGTACTTGGCCG | Chr1:7259239-7259506 |
| Chr1-29 | 缺失 Deletion | -30 | CGTGAGGTGCTCGCTGAT | GGGACATCTCGTGCACGT | Chr1:7846667-7846868 |
| Chr1-30 | 插入 Insertion | 42 | GAACGCAAAAGACTGACTCCT | AGGTTCTGAAGACATGCACTT | Chr1:8015769-8016044 |
| Chr1-39 | 插入 Insertion | 39 | GTCCTCAGGACGACCCTAGA | ATCTGGTGGCAGTGGCAG | Chr1:10631445-10631724 |
| Chr2-01 | 插入 Insertion | 37 | GCTCCAACGAGAGAGATGACT | CGGTGCTGGTGACGAAGA | Chr2:307044-307320 |
| Chr2-02 | 插入 Insertion | 31 | CAGGATTTTGCTAGGGTCAGT | AGACTTGCCTGCTGGAGC | Chr2:612393-612613 |
| Chr2-13 | 缺失 Deletion | -34 | ACCAACCGTCGATCCTCA | TGGCAAAACGTCGTGATGT | Chr2:5215597-5215796 |
| Chr2-15 | 插入 Insertion | 44 | TGCTGGGAATGCTTTGTGC | TGGTCCATGATGCCAGCTG | Chr2:5922591-5922860 |
| Chr2-18 | 插入 Insertion | 44 | GGTTAGACTGTCAAGTGGGCT | CGCCCTGAAAACATGGTGC | Chr2:10719434-10719712 |
| Chr2-20 | 缺失 Deletion | -31 | ACAACCTGAGAGCTCTTCCC | AGCTGCTTCTACCTGCTTGA | Chr2:12083278-12083527 |
| Chr2-29 | 插入 Insertion | 48 | TGGAATCAAGATTTGCACCGA | TTCCAGTTTCCGAACAACCA | Chr2:23526410-23526648 |
| Chr2-31 | 缺失 Deletion | -33 | GGCAGCACTTCATTGCCG | GGGTCTTACACTGGTTGCCA | Chr2:28941802-28942025 |
| Chr2-38 | 插入 Insertion | 38 | ACGAGTCTTCAAGCTTGCCA | TGCCAGTCTGTAAATTGCGG | Chr2:34031300-34031578 |
| Chr3-03 | 插入 Insertion | 48 | GCCAACACAAGAACGGAAACT | TGCAGTTCAAGTGGCGCT | Chr3:627145-627348 |
| Chr3-17 | 缺失 Deletion | -44 | CTCCTGCACAGTCGCCAT | GCTTGCTTTGCTCTCCGC | Chr3:6901713-6901929 |
| Chr3-21 | 缺失 Deletion | -46 | CCCTTCCCCCTCCCAAGA | TTCTGCCGTCGGTTGAGC | Chr3:10826323-10826544 |
| Chr3-22 | 插入 Insertion | 39 | TCCCGGACATCTGACCCC | AGCCTTTGATTCCCACTGCA | Chr3:10886342-10886562 |
| Chr3-23 | 插入 Insertion | 31 | GGAGCACAAGCCATGGGT | AGCCACCAGTCAGACCTCT | Chr3:11351904-11352128 |
| Chr3-30 | 插入 Insertion | 34 | ACGGTGACAGCATGAGGC | CACATGCAAGATGCCGGC | Chr3:16193105-16193338 |
| Chr3-31 | 插入 Insertion | 42 | AGCCAACCCACCACAAGT | CTCAGCCTATTTGTTGGTCCA | Chr3:16707449-16707694 |
| Chr3-33 | 插入 Insertion | 33 | TGCTGGAAAACACCCGCA | GCCTCCCCAAGTCAGCTG | Chr3:21024394-21024593 |
| Chr4-03 | 缺失 Deletion | -33 | CCAGCATCAGAACTCGAGGT | TTGGTTGCGGGGAATGCA | Chr4:1324489-1324712 |
| Chr4-08 | 插入 Insertion | 42 | CGAGCCTGTGTACCTGGT | TCACTTTCGTCAGTTGCCTGA | Chr4:4076944-4077153 |
| Chr4-14 | 插入 Insertion | 41 | GCGGTGAGCCTGAGATGA | AGACTCGTGGAGAACAAAGCA | Chr4:9192243-9192474 |
| Chr4-24 | 缺失 Deletion | -40 | ACGGGGCGTACATGTGTG | ACGAGGCCACCCCTAAGA | Chr4:21621919-21622128 |
| Chr4-25 | 插入 Insertion | 45 | TGGTTTCGCAAGTTCGCA | GTGCTAGTTGTTTTGCATGCT | Chr4:22997264-22997514 |
| Chr4-26 | 缺失 Deletion | -46 | AGAGGGGTTAGGCAGGGG | TCCCCACATTGATGTTGACCA | Chr4:23149465-23149734 |
| Chr4-34 | 缺失 Deletion | -32 | TCACGAGTTGAGGGAGGTCT | ACTTGTTGAGGGTTGAAAGCC | Chr4:28955964-28956194 |
| Chr4-40 | 插入 Insertion | 46 | GACGTGGTGCTTATCCCGT | GGCAGTCCAGTTCTATAGGGG | Chr4:34041449-34041703 |
| Chr5-02 | 缺失 Deletion | -49 | TGCGCACAACATTCAGGTC | GGCTATGTTGTGCCTGGGA | Chr5:59655-59828 |
| Chr5-07 | 插入 Insertion | 38 | TGAGTGGAAAGAAGATGCGGA | TCATCCCTCCATCCACAAACT | Chr5:272642-272800 |
| Chr5-08 | 缺失 Deletion | -34 | GACAAAGCAAAACTGCATCGT | TGATTTGGCAGCCCCTGG | Chr5:699745-699920 |
| Chr5-11 | 缺失 Deletion | -35 | GCGGCAATCAGAGGAGCA | GCACCACACAGACAAAAATCA | Chr5:1024290-1024446 |
| Chr5-15 | 缺失 Deletion | -33 | TGGGAGGTAGCTGACGGA | CAGCATGCCTAACCGTGC | Chr5:1509285-1509412 |
| Chr5-18 | 缺失 Deletion | -33 | GACTCCGATGATGTCCTCTGT | CGTGAAGGAAATCGGTGTGC | Chr5:1615976-1616100 |
| Chr5-24 | 插入 Insertion | 31 | GGGCTTGAGTTTGGGCCT | CCCAGTCCCATACCCCGA | Chr5:44035468-44035705 |
| Chr5-29 | 缺失 Deletion | -42 | GGAGGAAATTTTGGCTTGGGG | ACCAAAAACATGGAACCACCT | Chr5:44418169-44418332 |
| Chr5-30 | 插入 Insertion | 34 | GCAACTGTCTGATCCTTTGGG | ACTTCGCATTTCAGGGGAGA | Chr5:45207382-45207589 |
| Chr6-09 | 缺失 Deletion | -38 | CTAGACGCCCACGAAGCC | TCTTCCCTCTGCCGACCA | Chr6:9710183-9710427 |
| Chr6-10 | 插入 Insertion | 46 | ACATGCATGCCTAGTCACGA | GGGTTGTTGGAAGGGTCCT | Chr6:10024162-10024384 |
| Chr6-27 | 插入 Insertion | 45 | ATGTTGGGTCGCAGTGGC | AGGGCGGAGGGGATTTCT | Chr6:26274037-26274275 |
| Chr6-28 | 缺失 Deletion | -32 | TGAAAACAACTGCGAAACACT | ACTTCAGATGGGTACTTCTGC | Chr6:26872028-26872241 |
| Chr6-29 | 缺失 Deletion | -44 | CGGCAAGAGGAGAAGGGC | GGGGTTTCCAAGGAAGGGG | Chr6:28571296-28571513 |
| Chr6-32 | 缺失 Deletion | -43 | ACGCTAATGTTGCCGCCA | CGTCGAGCTTTACCCGCA | Chr6:33681522-33681724 |
| Chr7-01 | 插入 Insertion | 37 | TGCTCGGACGACCACAAC | AGTGGCCAACGAGCAGAG | Chr7:12591-12775 |
| Chr7-02 | 缺失 Deletion | -47 | GCAGCGGCCAATGCTAAG | GGGTGGTTGATGCTTCGC | Chr7:30560-30830 |
| Chr7-06 | 插入 Insertion | 31 | GGGGTTTAGCGTGGGTCC | AATGGCTGGTCTCACGCG | Chr7:449549-449763 |
| Chr7-12 | 缺失 Deletion | -46 | TGCATAAGGTCTGGAGACTGT | ACCCGAGCTACACCACAA | Chr7:2509875-2510036 |
| Chr7-19 | 缺失 Deletion | -41 | GCCTAGAGCCTCCAAACCA | GGAGATCCCTGTGCTGCC | Chr7:5959628-5959858 |
| Chr7-21 | 缺失 Deletion | -45 | ACTGAGTGAGCGATGGCAC | TGGGATGGCAGTAAAGCGG | Chr7:6662961-6663207 |
| Chr7-24 | 缺失 Deletion | -49 | ACCCTGGCTAAACGCGTC | ATGGGGGCGGGTCAACTA | Chr7:8693948-8694111 |
| Chr7-28 | 插入 Insertion | 33 | ACTCGTGTTCCCCAAAACA | ACCTATCAATTCTCCCGTCGA | Chr7:11076056-11076250 |
| Chr7-35 | 缺失 Deletion | -38 | AGAACCCCATCAACGGAAACT | ACCTTCCCACCTCACTCGT | Chr7:15440638-15440766 |
| Chr8-09 | 缺失 Deletion | -42 | ATCAGGCAAATGCATGGTTGA | AACCATCCTGGACCCGGA | Chr8:1320235-1320497 |
| Chr8-16 | 缺失 Deletion | -47 | TGGCTCCACAATCTGGCA | TGCCAACTGGTTTCCTCTTTC | Chr8:3251541-3251789 |
| Chr8-18 | 缺失 Deletion | -44 | CCCGCCTTTTCCACGTGA | AGTCATTCTGGTTCGGGTTGA | Chr8:3574827-3575078 |
| Chr8-19 | 缺失 Deletion | -42 | GCTTGCGGCAATTGGTTTC | ACGAGGATTGACAGGCAGC | Chr8:3680573-3680739 |
| Chr8-26 | 缺失 Deletion | -46 | AGTGGCAAGCAGTGTAGGA | CTTTCACTGCCGGGGAGT | Chr8:6135649-6135902 |
| Chr8-29 | 插入 Insertion | 44 | ACATCAGCTGCTCATTCCAT | TTGTACAGTCCCAAGTTGTGT | Chr8:7246002-7246208 |
| Chr8-30 | 缺失 Deletion | -33 | TGAAGGCCCCAGTTTTCCA | TGCATGTATTCGACCTTGTGG | Chr8:7761356-7761536 |
| Chr8-32 | 插入 Insertion | 36 | ACACTGCACTGCACTAGCT | GGCCAGTTTAGCCCGTCT | Chr8:8396708-8396836 |
| Chr9-09 | 缺失 Deletion | -32 | TCCGTTAACGCTCCGCAG | TGTGGTGGTTCTCTCCTTGTG | Chr9:5206000-5206184 |
| Chr9-15 | 插入 Insertion | 45 | CGACATGCAAGGAACTGGG | GACTTGGGTGCCGAAGCT | Chr9:6742034-6742244 |
| Chr9-17 | 缺失 Deletion | -34 | GGCGTTGTATGGCTCACG | GAGATTGCTCAGGTGTGGGA | Chr9:8310123-8310248 |
| Chr9-22 | 插入 Insertion | 30 | CCAACACCCCATTCCCCA | TGCACTAGACTCCTCCATCCA | Chr9:9397358-9397476 |
| Chr9-25 | 缺失 Deletion | -31 | CTTGTCCACGCGTGAGGT | GCTCGTCCCCTTTGCACA | Chr9:12450328-12450471 |
| Chr9-26 | 缺失 Deletion | -39 | CCGGTATCACTGAGGGCC | CAGTCGTGTGGAGTTGGGA | Chr9:14289457-14289653 |
| Chr9-27 | 缺失 Deletion | -31 | CTAGCACCAGGCCGTCAG | CCGCTGCACCTGGAGAAA | Chr9:14871648-14871817 |
| Chr9-31 | 缺失 Deletion | -45 | AGTTAGCCCATGCGCGTT | AGGGCCTCCTCCACTGAC | Chr9:27896823-27896950 |
| 标记号 InDel labels | 等位基 因数 (Na) Number of alleles | 有效等位基 因数(Ne) Effective number of alleles | 基因多样性 指数(H) Gene diversity index | 多态性信息 含量(PIC) Polymorphic information content | 遗传距离 (Nei’s) Nei’s genetic distance | 标记号 InDel labels | 等位基 因数 (Na) Number of alleles | 有效等位基 因数(Ne) Effective number of alleles | 基因多样 性指数 (H) Gene diversity index | 多态性信息含量(PIC) Polymorphic information content | 遗传距离 (Nei’s) Nei’s genetic distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr1-09 | 2.00 | 1.8579 | 0.6544 | 0.3551 | 0.4617 | Chr5-29 | 2.00 | 1.2605 | 0.3609 | 0.1853 | 0.2067 |
| Chr1-10 | 2.00 | 1.9991 | 0.6929 | 0.3749 | 0.4998 | Chr5-30 | 2.00 | 1.2865 | 0.3819 | 0.1979 | 0.2227 |
| Chr1-15 | 2.00 | 1.3665 | 0.4390 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 | Chr6-09 | 2.00 | 1.9919 | 0.6911 | 0.3740 | 0.4980 |
| Chr1-26 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.2322 | 0.2682 | Chr6-10 | 2.00 | 1.5589 | 0.5441 | 0.2943 | 0.3585 |
| Chr1-29 | 2.00 | 1.1357 | 0.2374 | 0.1124 | 0.1195 | Chr6-27 | 2.00 | 1.3937 | 0.4562 | 0.2426 | 0.2825 |
| Chr1-30 | 2.00 | 1.8776 | 0.6602 | 0.3582 | 0.4674 | Chr6-28 | 2.00 | 1.3937 | 0.4562 | 0.2426 | 0.2825 |
| Chr1-39 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 | Chr6-29 | 2.00 | 1.4761 | 0.5033 | 0.2705 | 0.3225 |
| Chr2-01 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.0957 | 0.1007 | Chr5-30 | 2.00 | 1.2865 | 0.3819 | 0.1979 | 0.2227 |
| Chr2-02 | 2.00 | 2.0000 | 0.6931 | 0.3677 | 0.4855 | Chr6-09 | 2.00 | 1.9919 | 0.6911 | 0.3740 | 0.4980 |
| Chr2-13 | 2.00 | 1.9437 | 0.6786 | 0.3013 | 0.3696 | Chr6-10 | 2.00 | 1.5589 | 0.5441 | 0.2943 | 0.3585 |
| Chr2-15 | 2.00 | 1.6934 | 0.5997 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 | Chr6-27 | 2.00 | 1.3937 | 0.4562 | 0.2426 | 0.2825 |
| Chr2-18 | 2.00 | 1.9856 | 0.6895 | 0.3609 | 0.4726 | Chr6-32 | 2.00 | 1.8579 | 0.6544 | 0.3551 | 0.4617 |
| Chr2-20 | 2.00 | 1.5864 | 0.5564 | 0.3256 | 0.4095 | Chr7-01 | 2.00 | 1.7686 | 0.6262 | 0.2322 | 0.2682 |
| Chr2-29 | 2.00 | 1.1120 | 0.2078 | 0.3732 | 0.4964 | Chr7-02 | 2.00 | 1.8776 | 0.6602 | 0.3013 | 0.3696 |
| Chr2-31 | 2.00 | 2.0000 | 0.6931 | 0.3750 | 0.5000 | Chr7-06 | 2.00 | 1.6136 | 0.5681 | 0.3694 | 0.4889 |
| Chr2-38 | 2.00 | 1.8961 | 0.6655 | 0.3750 | 0.5000 | Chr7-12 | 2.00 | 1.9566 | 0.6820 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 |
| Chr3-03 | 2.00 | 1.1636 | 0.2691 | 0.3709 | 0.4919 | Chr7-19 | 2.00 | 1.7442 | 0.6179 | 0.3402 | 0.4346 |
| Chr3-17 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.2322 | 0.2682 | Chr7-21 | 2.00 | 1.5864 | 0.5564 | 0.2740 | 0.3277 |
| Chr3-21 | 2.00 | 1.7686 | 0.6262 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 | Chr7-24 | 2.00 | 1.3665 | 0.4390 | 0.3356 | 0.4267 |
| Chr3-22 | 2.00 | 1.9679 | 0.6850 | 0.3677 | 0.4855 | Chr7-28 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.3582 | 0.4674 |
| Chr3-23 | 2.00 | 1.9437 | 0.6786 | 0.3402 | 0.4346 | Chr7-35 | 2.00 | 1.4875 | 0.5093 | 0.3080 | 0.3803 |
| Chr3-30 | 2.00 | 1.6672 | 0.5897 | 0.3443 | 0.4421 | Chr8-09 | 2.00 | 1.4210 | 0.4727 | 0.0408 | 0.0416 |
| Chr3-31 | 2.00 | 1.7923 | 0.6340 | 0.3201 | 0.4002 | Chr8-16 | 2.00 | 1.0435 | 0.1030 | 0.1853 | 0.2067 |
| Chr3-33 | 2.00 | 1.3665 | 0.4390 | 0.1307 | 0.1406 | Chr8-18 | 2.00 | 1.3665 | 0.4390 | 0.2524 | 0.2963 |
| Chr4-03 | 2.00 | 1.5589 | 0.5441 | 0.3582 | 0.4674 | Chr8-19 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.3013 | 0.3696 |
| Chr4-08 | 2.00 | 1.5589 | 0.5441 | 0.3551 | 0.4617 | Chr8-26 | 2.00 | 1.5864 | 0.5564 | 0.3740 | 0.4980 |
| Chr4-14 | 2.00 | 1.8579 | 0.6544 | 0.2426 | 0.2825 | Chr8-29 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 |
| Chr4-24 | 2.00 | 1.3937 | 0.4562 | 0.1979 | 0.2227 | Chr8-30 | 2.00 | 1.2605 | 0.3609 | 0.2322 | 0.2682 |
| Chr4-25 | 2.00 | 1.8776 | 0.6602 | 0.2943 | 0.3585 | Chr8-32 | 2.00 | 1.9919 | 0.6911 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 |
| Chr4-26 | 2.00 | 1.8078 | 0.6390 | 0.2943 | 0.3585 | Chr9-09 | 3.00 | 2.0664 | 0.8735 | 0.4523 | 0.5161 |
| Chr4-34 | 2.00 | 1.6672 | 0.5897 | 0.3470 | 0.4468 | Chr9-15 | 2.00 | 1.6405 | 0.5792 | 0.3732 | 0.4964 |
| Chr4-40 | 2.00 | 1.2865 | 0.3819 | 0.3201 | 0.4002 | Chr9-17 | 2.00 | 1.5158 | 0.5236 | 0.3634 | 0.4774 |
| Chr5-02 | 2.00 | 1.4210 | 0.4727 | 0.2524 | 0.2963 | Chr9-22 | 2.00 | 1.5589 | 0.5441 | 0.3142 | 0.3904 |
| Chr5-07 | 2.00 | 1.8961 | 0.6655 | 0.3609 | 0.4726 | Chr9-25 | 2.00 | 1.9856 | 0.6895 | 0.2943 | 0.3585 |
| Chr5-08 | 2.00 | 1.6136 | 0.5681 | 0.3080 | 0.3803 | Chr9-26 | 2.00 | 1.9134 | 0.6703 | 0.2868 | 0.3470 |
| Chr5-11 | 2.00 | 1.3129 | 0.4019 | 0.2099 | 0.2383 | Chr9-27 | 2.00 | 1.5314 | 0.5312 | 0.2824 | 0.3403 |
| Chr5-15 | 2.00 | 1.6934 | 0.5997 | 0.3256 | 0.4095 | Chr9-31 | 2.00 | 1.9097 | 0.6693 | 0.3629 | 0.4764 |
| Chr5-18 | 2.00 | 1.2865 | 0.3819 | 0.1979 | 0.2227 | 平均值 | 2.01 | 1.6692 | 0.5660 | 0.3041 | 0.3828 |
| Chr5-24 | 2.00 | 1.9134 | 0.6703 | 0.3634 | 0.4774 | Average |
Table 3 Genetic diversity analysis of 47 papaya germplasms
| 标记号 InDel labels | 等位基 因数 (Na) Number of alleles | 有效等位基 因数(Ne) Effective number of alleles | 基因多样性 指数(H) Gene diversity index | 多态性信息 含量(PIC) Polymorphic information content | 遗传距离 (Nei’s) Nei’s genetic distance | 标记号 InDel labels | 等位基 因数 (Na) Number of alleles | 有效等位基 因数(Ne) Effective number of alleles | 基因多样 性指数 (H) Gene diversity index | 多态性信息含量(PIC) Polymorphic information content | 遗传距离 (Nei’s) Nei’s genetic distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr1-09 | 2.00 | 1.8579 | 0.6544 | 0.3551 | 0.4617 | Chr5-29 | 2.00 | 1.2605 | 0.3609 | 0.1853 | 0.2067 |
| Chr1-10 | 2.00 | 1.9991 | 0.6929 | 0.3749 | 0.4998 | Chr5-30 | 2.00 | 1.2865 | 0.3819 | 0.1979 | 0.2227 |
| Chr1-15 | 2.00 | 1.3665 | 0.4390 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 | Chr6-09 | 2.00 | 1.9919 | 0.6911 | 0.3740 | 0.4980 |
| Chr1-26 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.2322 | 0.2682 | Chr6-10 | 2.00 | 1.5589 | 0.5441 | 0.2943 | 0.3585 |
| Chr1-29 | 2.00 | 1.1357 | 0.2374 | 0.1124 | 0.1195 | Chr6-27 | 2.00 | 1.3937 | 0.4562 | 0.2426 | 0.2825 |
| Chr1-30 | 2.00 | 1.8776 | 0.6602 | 0.3582 | 0.4674 | Chr6-28 | 2.00 | 1.3937 | 0.4562 | 0.2426 | 0.2825 |
| Chr1-39 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 | Chr6-29 | 2.00 | 1.4761 | 0.5033 | 0.2705 | 0.3225 |
| Chr2-01 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.0957 | 0.1007 | Chr5-30 | 2.00 | 1.2865 | 0.3819 | 0.1979 | 0.2227 |
| Chr2-02 | 2.00 | 2.0000 | 0.6931 | 0.3677 | 0.4855 | Chr6-09 | 2.00 | 1.9919 | 0.6911 | 0.3740 | 0.4980 |
| Chr2-13 | 2.00 | 1.9437 | 0.6786 | 0.3013 | 0.3696 | Chr6-10 | 2.00 | 1.5589 | 0.5441 | 0.2943 | 0.3585 |
| Chr2-15 | 2.00 | 1.6934 | 0.5997 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 | Chr6-27 | 2.00 | 1.3937 | 0.4562 | 0.2426 | 0.2825 |
| Chr2-18 | 2.00 | 1.9856 | 0.6895 | 0.3609 | 0.4726 | Chr6-32 | 2.00 | 1.8579 | 0.6544 | 0.3551 | 0.4617 |
| Chr2-20 | 2.00 | 1.5864 | 0.5564 | 0.3256 | 0.4095 | Chr7-01 | 2.00 | 1.7686 | 0.6262 | 0.2322 | 0.2682 |
| Chr2-29 | 2.00 | 1.1120 | 0.2078 | 0.3732 | 0.4964 | Chr7-02 | 2.00 | 1.8776 | 0.6602 | 0.3013 | 0.3696 |
| Chr2-31 | 2.00 | 2.0000 | 0.6931 | 0.3750 | 0.5000 | Chr7-06 | 2.00 | 1.6136 | 0.5681 | 0.3694 | 0.4889 |
| Chr2-38 | 2.00 | 1.8961 | 0.6655 | 0.3750 | 0.5000 | Chr7-12 | 2.00 | 1.9566 | 0.6820 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 |
| Chr3-03 | 2.00 | 1.1636 | 0.2691 | 0.3709 | 0.4919 | Chr7-19 | 2.00 | 1.7442 | 0.6179 | 0.3402 | 0.4346 |
| Chr3-17 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.2322 | 0.2682 | Chr7-21 | 2.00 | 1.5864 | 0.5564 | 0.2740 | 0.3277 |
| Chr3-21 | 2.00 | 1.7686 | 0.6262 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 | Chr7-24 | 2.00 | 1.3665 | 0.4390 | 0.3356 | 0.4267 |
| Chr3-22 | 2.00 | 1.9679 | 0.6850 | 0.3677 | 0.4855 | Chr7-28 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.3582 | 0.4674 |
| Chr3-23 | 2.00 | 1.9437 | 0.6786 | 0.3402 | 0.4346 | Chr7-35 | 2.00 | 1.4875 | 0.5093 | 0.3080 | 0.3803 |
| Chr3-30 | 2.00 | 1.6672 | 0.5897 | 0.3443 | 0.4421 | Chr8-09 | 2.00 | 1.4210 | 0.4727 | 0.0408 | 0.0416 |
| Chr3-31 | 2.00 | 1.7923 | 0.6340 | 0.3201 | 0.4002 | Chr8-16 | 2.00 | 1.0435 | 0.1030 | 0.1853 | 0.2067 |
| Chr3-33 | 2.00 | 1.3665 | 0.4390 | 0.1307 | 0.1406 | Chr8-18 | 2.00 | 1.3665 | 0.4390 | 0.2524 | 0.2963 |
| Chr4-03 | 2.00 | 1.5589 | 0.5441 | 0.3582 | 0.4674 | Chr8-19 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.3013 | 0.3696 |
| Chr4-08 | 2.00 | 1.5589 | 0.5441 | 0.3551 | 0.4617 | Chr8-26 | 2.00 | 1.5864 | 0.5564 | 0.3740 | 0.4980 |
| Chr4-14 | 2.00 | 1.8579 | 0.6544 | 0.2426 | 0.2825 | Chr8-29 | 2.00 | 1.9293 | 0.6747 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 |
| Chr4-24 | 2.00 | 1.3937 | 0.4562 | 0.1979 | 0.2227 | Chr8-30 | 2.00 | 1.2605 | 0.3609 | 0.2322 | 0.2682 |
| Chr4-25 | 2.00 | 1.8776 | 0.6602 | 0.2943 | 0.3585 | Chr8-32 | 2.00 | 1.9919 | 0.6911 | 0.3657 | 0.4817 |
| Chr4-26 | 2.00 | 1.8078 | 0.6390 | 0.2943 | 0.3585 | Chr9-09 | 3.00 | 2.0664 | 0.8735 | 0.4523 | 0.5161 |
| Chr4-34 | 2.00 | 1.6672 | 0.5897 | 0.3470 | 0.4468 | Chr9-15 | 2.00 | 1.6405 | 0.5792 | 0.3732 | 0.4964 |
| Chr4-40 | 2.00 | 1.2865 | 0.3819 | 0.3201 | 0.4002 | Chr9-17 | 2.00 | 1.5158 | 0.5236 | 0.3634 | 0.4774 |
| Chr5-02 | 2.00 | 1.4210 | 0.4727 | 0.2524 | 0.2963 | Chr9-22 | 2.00 | 1.5589 | 0.5441 | 0.3142 | 0.3904 |
| Chr5-07 | 2.00 | 1.8961 | 0.6655 | 0.3609 | 0.4726 | Chr9-25 | 2.00 | 1.9856 | 0.6895 | 0.2943 | 0.3585 |
| Chr5-08 | 2.00 | 1.6136 | 0.5681 | 0.3080 | 0.3803 | Chr9-26 | 2.00 | 1.9134 | 0.6703 | 0.2868 | 0.3470 |
| Chr5-11 | 2.00 | 1.3129 | 0.4019 | 0.2099 | 0.2383 | Chr9-27 | 2.00 | 1.5314 | 0.5312 | 0.2824 | 0.3403 |
| Chr5-15 | 2.00 | 1.6934 | 0.5997 | 0.3256 | 0.4095 | Chr9-31 | 2.00 | 1.9097 | 0.6693 | 0.3629 | 0.4764 |
| Chr5-18 | 2.00 | 1.2865 | 0.3819 | 0.1979 | 0.2227 | 平均值 | 2.01 | 1.6692 | 0.5660 | 0.3041 | 0.3828 |
| Chr5-24 | 2.00 | 1.9134 | 0.6703 | 0.3634 | 0.4774 | Average |

Fig. 3 Cluster analysis of 47 papaya varieties /germplasm resources based on InDel molecular marker analysis The outer ring heatmap,from the inside out,corresponds to flower color(white flowers and yellow flowers are assigned 0 and 1,respectively),single fruit weight[0,1,and 2 represent light fruits(single fruit weight < 800 g),medium fruits(800 g ≤ single fruit weight ≤ 1 200 g),and heavy fruits(single fruit weight > 1 200 g)in sequence],fruit shape(0,1,2,3,and 4 represent pyriform,round,elliptical,long elliptical,and enlongated shape in sequence),and flesh color(0,1,2,and 3 represent yellow,orange-yellow,orange-red,and red in sequence)
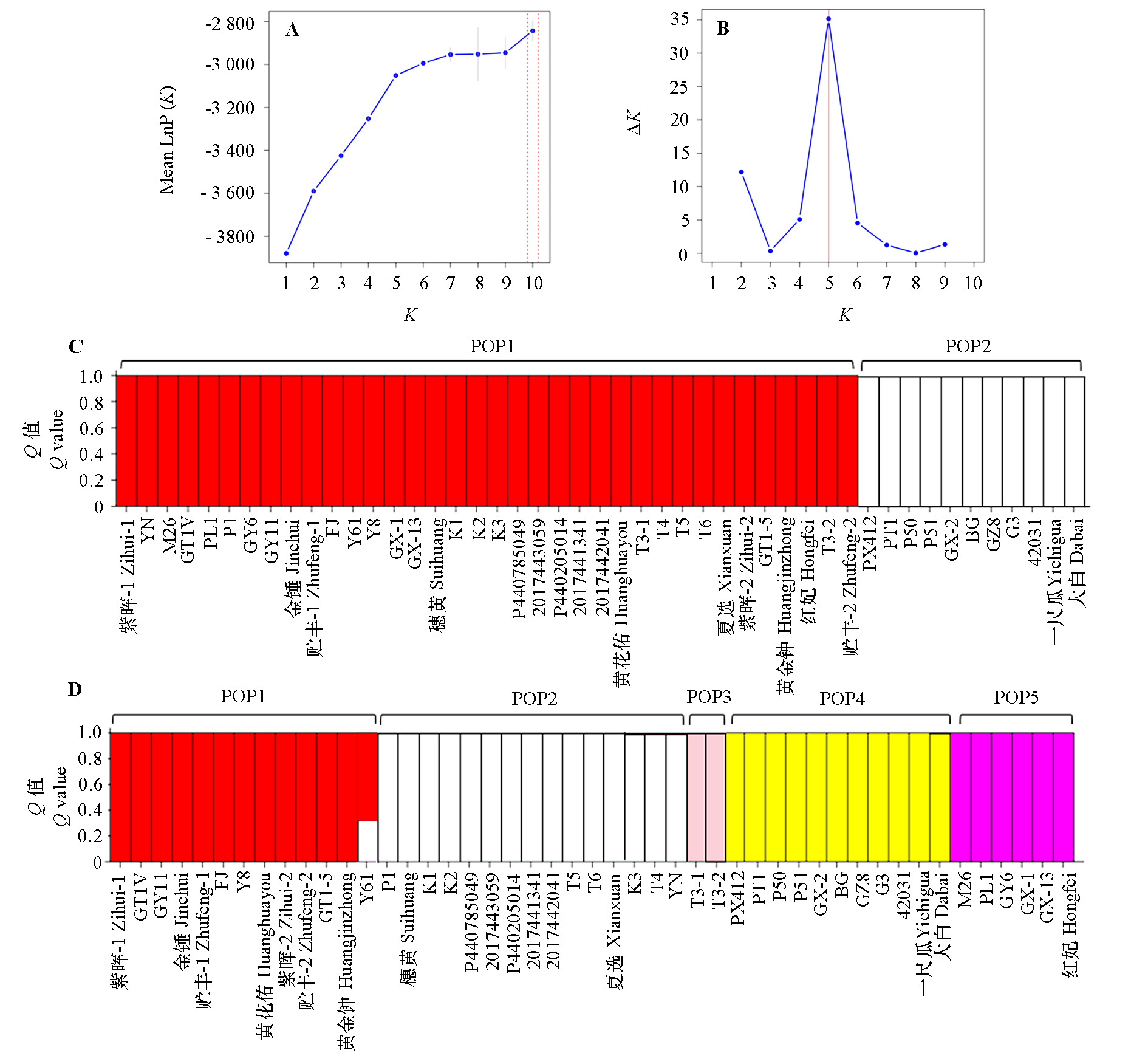
Fig. 4 Population structure analysis of 47 papaya germplasms based on InDel molecular markers A:Line plot of lnP(K)versus K value;B:Line plot of ΔK value versus K value;C:Population structure at K = 2;D:Population structure at K = 5
| 编号 No. | 种质 Germplasm | 花色 Flower color | 单果质量 Fruit weight | 果实形状 Fruit shape | 果肉颜色 Pulp color | 分子身份证编码 Molecular ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PX412 | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 11221101011001101010111001011010100110100111 |
| 2 | 紫晖-1 Zihui-1 | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 11320111010101101111111010101111111101011011 |
| 3 | YN | 白White | 轻Light | 椭圆Ellipse | 黄Yellow | 00200101111101110110111111100111100111111001 |
| 4 | M26 | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01221110101110110111111111011111011011111111 |
| 5 | GT1V | 黄Yellow | 重Heavy | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 12320110110101111010101110100111100101111010 |
| 6 | PL1 | 白White | 轻Light | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 00221110111110100101111111011001110110100101 |
| 7 | PT1 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01321110011011100110101001011111010110100101 |
| 8 | P1 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01320111010101010101101011011010110110111001 |
| 9 | P50 | 白White | 轻Light | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 00321110111011110110100111010111101101110110 |
| 10 | P51 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01311001011011111010100111011111100101100101 |
| 11 | GY6 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01310110101110100111111011011001011001101010 |
| 12 | GY11 | 白White | 重Heavy | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 02321111111111011101101110101110110111111110 |
| 13 | 金锤Jinchui | 黄Yellow | 轻Light | 梨形Pear shaped | 橙红Orange-red | 10021010110101111101101010111110011111111010 |
| 14 | 贮丰-1 Zhufeng-1 | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01221111011010111101100111010111011011011110 |
| 15 | FJ | 白White | 轻Light | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 黄Yellow | 00301111110101011001111010100111010101111010 |
| 16 | Y61 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01320110111110010101101010101011100111111010 |
| 17 | Y8 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01310110110101011010101010100111100101101010 |
| 18 | GX-1 | 白White | 轻Light | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 00221110110110010111101001011111011001100101 |
| 19 | GX-2 | 白White | 轻Light | 椭圆Ellipse | 红Red | 00230110111001101110100101011111100111100101 |
| 20 | GX-13 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01311110110110010111011001011011010111111010 |
| 21 | 穗黄Suihuang | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01311101111111111011011110010110110111100110 |
| 22 | BG | 白White | 轻Light | 梨形Pear shaped | 橙红Orange-red | 00020110101010100110100101010110010101100101 |
| 23 | K1 | 白White | 中Moderate | 圆形Round | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01111011110101010110111011011010100110101001 |
| 24 | K2 | 黄Yellow | 轻Light | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 黄Yellow | 10301011011111011011101011011110100111110111 |
| 25 | K3 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01321111111111110111110110011101111011111110 |
| 26 | P440785049 | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01211010100111110101010110011011111010111110 |
| 27 | 2017443059 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01311011101101100111010111101011110111101110 |
| 28 | P440205014 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01321010111101101101011011101010101010100110 |
| 29 | GZ8 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01311111111010101110101101011110110110100101 |
| 30 | 2017441341 | 白White | 中Moderate | 圆形Round | 橙红Orange-red | 01120111111111010111101011011110100110111101 |
| 31 | 2017442041 | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01221010110101110111011011011011101011111111 |
| 32 | 黄花佑 Huanghuayou | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 梨形 Pear shaped | 橙红Orange-red | 11020111111111011011101010100110101011111111 |
| 33 | G3 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01321010011010100110100111100110111101011010 |
| 34 | T3-1 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 黄Yellow | 01301001010110101010011010101010101001011010 |
| 35 | T4 | 白White | 重Heavy | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 02310111111111110111110110111101111011111110 |
| 36 | T5 | 白White | 重Heavy | 长条形Long strip | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 02411010100110011010100110101011101010011010 |
| 37 | T6 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长条形Long strip | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01411001011001011010011001011011101010101010 |
| 38 | 夏选Xiaxuan | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01220101011111111110011111011111111011100111 |
| 39 | 42031 | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 11321001011010011010101010010111100110100101 |
| 40 | 一尺瓜 Yichigua | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01221001011010100110101001011111010101100101 |
| 41 | 紫晖-2 Zihui-2 | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 11320111010101101111111010101111111101011011 |
| 42 | GT1-5 | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 11320111010101101111111010101111111101011011 |
| 43 | 大白Dabai | 黄Yellow | 轻Light | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 10221111011011111010101111011110100111100101 |
| 44 | 黄金钟 Huangjin- zhong | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 圆形Round | 橙红Orange-red | 11121111110101011001111010110110010101111010 |
| 45 | 红妃Hongfei | 黄Yellow | 重Heavy | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 12321010100110010101011110101001010110011010 |
| 46 | T3-2 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 黄Yellow | 01301001100110101010011010101010101001011010 |
| 47 | 贮丰-2 Zhufeng-2 | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01221111011010111101100111010110011011011110 |
Table 4 Phenotypic and genotypic codes of 47 papaya germplasms
| 编号 No. | 种质 Germplasm | 花色 Flower color | 单果质量 Fruit weight | 果实形状 Fruit shape | 果肉颜色 Pulp color | 分子身份证编码 Molecular ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PX412 | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 11221101011001101010111001011010100110100111 |
| 2 | 紫晖-1 Zihui-1 | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 11320111010101101111111010101111111101011011 |
| 3 | YN | 白White | 轻Light | 椭圆Ellipse | 黄Yellow | 00200101111101110110111111100111100111111001 |
| 4 | M26 | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01221110101110110111111111011111011011111111 |
| 5 | GT1V | 黄Yellow | 重Heavy | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 12320110110101111010101110100111100101111010 |
| 6 | PL1 | 白White | 轻Light | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 00221110111110100101111111011001110110100101 |
| 7 | PT1 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01321110011011100110101001011111010110100101 |
| 8 | P1 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01320111010101010101101011011010110110111001 |
| 9 | P50 | 白White | 轻Light | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 00321110111011110110100111010111101101110110 |
| 10 | P51 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01311001011011111010100111011111100101100101 |
| 11 | GY6 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01310110101110100111111011011001011001101010 |
| 12 | GY11 | 白White | 重Heavy | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 02321111111111011101101110101110110111111110 |
| 13 | 金锤Jinchui | 黄Yellow | 轻Light | 梨形Pear shaped | 橙红Orange-red | 10021010110101111101101010111110011111111010 |
| 14 | 贮丰-1 Zhufeng-1 | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01221111011010111101100111010111011011011110 |
| 15 | FJ | 白White | 轻Light | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 黄Yellow | 00301111110101011001111010100111010101111010 |
| 16 | Y61 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01320110111110010101101010101011100111111010 |
| 17 | Y8 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01310110110101011010101010100111100101101010 |
| 18 | GX-1 | 白White | 轻Light | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 00221110110110010111101001011111011001100101 |
| 19 | GX-2 | 白White | 轻Light | 椭圆Ellipse | 红Red | 00230110111001101110100101011111100111100101 |
| 20 | GX-13 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01311110110110010111011001011011010111111010 |
| 21 | 穗黄Suihuang | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01311101111111111011011110010110110111100110 |
| 22 | BG | 白White | 轻Light | 梨形Pear shaped | 橙红Orange-red | 00020110101010100110100101010110010101100101 |
| 23 | K1 | 白White | 中Moderate | 圆形Round | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01111011110101010110111011011010100110101001 |
| 24 | K2 | 黄Yellow | 轻Light | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 黄Yellow | 10301011011111011011101011011110100111110111 |
| 25 | K3 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01321111111111110111110110011101111011111110 |
| 26 | P440785049 | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01211010100111110101010110011011111010111110 |
| 27 | 2017443059 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01311011101101100111010111101011110111101110 |
| 28 | P440205014 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01321010111101101101011011101010101010100110 |
| 29 | GZ8 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01311111111010101110101101011110110110100101 |
| 30 | 2017441341 | 白White | 中Moderate | 圆形Round | 橙红Orange-red | 01120111111111010111101011011110100110111101 |
| 31 | 2017442041 | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01221010110101110111011011011011101011111111 |
| 32 | 黄花佑 Huanghuayou | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 梨形 Pear shaped | 橙红Orange-red | 11020111111111011011101010100110101011111111 |
| 33 | G3 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01321010011010100110100111100110111101011010 |
| 34 | T3-1 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 黄Yellow | 01301001010110101010011010101010101001011010 |
| 35 | T4 | 白White | 重Heavy | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 02310111111111110111110110111101111011111110 |
| 36 | T5 | 白White | 重Heavy | 长条形Long strip | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 02411010100110011010100110101011101010011010 |
| 37 | T6 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长条形Long strip | 橙黄Orange-yellow | 01411001011001011010011001011011101010101010 |
| 38 | 夏选Xiaxuan | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01220101011111111110011111011111111011100111 |
| 39 | 42031 | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 11321001011010011010101010010111100110100101 |
| 40 | 一尺瓜 Yichigua | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01221001011010100110101001011111010101100101 |
| 41 | 紫晖-2 Zihui-2 | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 11320111010101101111111010101111111101011011 |
| 42 | GT1-5 | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 11320111010101101111111010101111111101011011 |
| 43 | 大白Dabai | 黄Yellow | 轻Light | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 10221111011011111010101111011110100111100101 |
| 44 | 黄金钟 Huangjin- zhong | 黄Yellow | 中Moderate | 圆形Round | 橙红Orange-red | 11121111110101011001111010110110010101111010 |
| 45 | 红妃Hongfei | 黄Yellow | 重Heavy | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 12321010100110010101011110101001010110011010 |
| 46 | T3-2 | 白White | 中Moderate | 长椭圆Long ellipse | 黄Yellow | 01301001100110101010011010101010101001011010 |
| 47 | 贮丰-2 Zhufeng-2 | 白White | 中Moderate | 椭圆Ellipse | 橙红Orange-red | 01221111011010111101100111010110011011011110 |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1139/g09-043 pmid: 19767901 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79401-z pmid: 33431939 |
| [3] |
pmid: 6247908 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0066 |
|
陈方策, 胡平正, 解为玮, 王钲彭, 钟创南, 李海炎, 何业华, 彭泽, 万保雄, 刘朝阳. 2024, 基于重测序的中国李基因组 InDel 标记的开发及应用. 园艺学报, 51 (11):2510-2522.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0066 |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.4238/2015.March.30.8 pmid: 25867396 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2012.01115.x |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
|
胡陶铸, 林丽, 胡继军, 邰连赛, 王圣洁, 刘杨. 2019. 利用InDel标记构建番茄新品种指纹图谱. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 37 (2):24-29.
|
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
pmid: 12033619 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.1534/genetics.166.1.419 pmid: 15020433 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2043-0 pmid: 31655544 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.21021 pmid: 35087324 |
| [22] |
NYT 2519-2013. Guidelines for the testing of distinctness,uniformity and stability —Papaya(Carica papaya L.) (in Chinese)
|
|
NYT 2519-2013. 植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南番木瓜
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0935 URL |
|
汤雨晴, 杨惠栋, 闫承璞, 王斯妤, 王雨亭, 胡钟东, 朱方红. 2023. 基于重测序的‘金兰柚’基因组InDel标记的开发及应用. 园艺学报, 50 (1):15-26.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0935 URL |
|
| [26] |
|
|
仝征, 彭存智, 常丽丽, 王丹, 黄超, 徐兵强. 2024. 一种高浓度琼脂糖电泳凝胶的制备方法及其应用:中国,CN114397350A. 2024-04-12.
|
|
| [27] |
pmid: 12582698 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1101/gr.183905.114 pmid: 25762551 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
|
王珏. 2017. 基于中国樱桃全基因组开发的InDel标记及引物通用性评价[硕士论文]. 雅安: 四川农业大学.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.84100 |
|
吴迷, 汪念, 沈超, 黄聪, 温天旺, 林忠旭. 2019. 基于重测序的陆地棉InDel标记开发与评价. 作物学报, 45 (2):196-203.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.84100 |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
|
杨敏, 周陈平, 李庆萌, 邝瑞彬, 吴夏明, 魏岳荣. 2024. ‘黄花佑’和‘金锤’番木瓜贮藏期品质、贮藏特性及转录组分析. 中国农学通报, 40 (6):57-66.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0118 |
|
| [35] |
|
|
杨易, 黎庭耀, 李国景, 陈汉才, 沈卓, 周轩, 吴增祥, 吴新义, 张艳. 2022. 基于重测序的长豇豆基因组InDel标记开发及应用. 园艺学报, 49 (4):778-790.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0347 URL |
|
| [36] |
|
|
尤园园, 王帅, 方莹莹, 齐诚, 李淑培, 张映, 陈钰辉, 刘伟, 刘富中, 舒金帅. 2024. 茄子全基因组InDel变异特征及分子标记开发和应用. 园艺学报, 51 (3):520-532.
|
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01068-1 pmid: 35551309 |
| [38] |
|
|
张国儒, 唐亚萍, 杨涛, 帕提古丽, 王柏柯, 李宁, 王娟, 李晓琴, 余庆辉, 杨生保. 2019. 基于重测序番茄InDel标记的开发. 分子植物育种, 17 (14):4692-4697.
|
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
|
赵光远. 2020. 番木瓜畸形花叶病毒在寄主基因功能鉴定及交叉保护中的应用[博士论文]. 海口: 海南大学.
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
张颖聪, 任鹏荣, 周常清, 罗金棠, 陈健. 2020. 基于SRAP标记的番木瓜种质资源遗传多样性及亲缘关系分析初报. 中国热带农业,(1):52-59.
|
| [1] | SHI Lanrong, ZHENG Jian, ZHANG Ji, OU Lianghua, GAN Weitang. A New Processed Carica papaya Cultivar‘Guire 3’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 83-84. |
| [2] | DAI Xiaogang, LIANG Qingqing, BI Changwei, WEI Mingchen, LIU Jingsheng. Development of Species-Specific InDel Primers for Magnolia biondii and Their Application in Root Bark Identification [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(9): 2387-2394. |
| [3] | ZHONG Shengyuan, LUO Yuting, CHEN Jianfeng, ZHONG Haifeng, CHEN Yuhua, and LIU Zhonghua. Grading of Quantitative Traits and Genetic Diversity in DUS Test of Phalaenopsis Cultivars [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(7): 1817-1827. |
| [4] | LI Zuo, XIAO Wenfang, CHEN Heming, and LÜ Fubing. Genetic Diversity and Core Collection Construction of Phalaenopsis Germplasm Resources [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1519-1529. |
| [5] | SUN Pei, ZHANG Hong, YANG Yuan, WANG Hua, LI Maofu, KANG Yanhui, SUN Xiangyi, JIN Wanmei. Genetic Diversity Analysis and Fingerprint Construction of Rosa Germplasm Resources Based on SSR Marker [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1539-1552. |
| [6] | BI Qingrui, CUI Dongsheng, MA Xinyuan, XUE Yuran, ZHANG Shikui, FAN Guoquan, NIU Yingying. Genetic Diversity and Genetic Relationship of Local Pear Cultivars in Xinjiang [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 561-574. |
| [7] | LUO Sifang, YAN Xiang, XIE Lifang, SUN Jingxian, GUO Zijing, ZHANG Zuming, CHEN Zhaoxing. Development and Application of Insertion-Deletion(InDel)Markers in Gannan wild Fortunella hindsii Based on Whole Genome Re-sequencing Data [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 267-278. |
| [8] | ZHANG Lu, ZHANG Pingping, XIE Weijia, XU Feng, PENG Lüchun, SONG Jie, DU Guanghui, LI Shifeng. Genetic Diversity Analysis and SSR Fingerprint Construction of Evergreen Rhododendron Germplasms [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 380-394. |
| [9] | XIAO Xi’ou, NIE Heng, LIN Wenqiu, WU Caiyu. Development of Whole-Genome SNP Markers of Eggplant [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 88-100. |
| [10] | QIN Zilu, XU Zhengkang, DAI Xiaogang, CHEN Yingnan. Genetic Diversity Analysis and Core Collection Construction of Magnolia biondii Germplasm [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1823-1832. |
| [11] | QIN Yu, GUO Rongkun, NONG Huilan, WANG Yan, CUI Kai, DONG Ningguang. Using the Fluorescent Labeled SSR Markers to Establish Molecular Identity of Hawthorn [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1227-1240. |
| [12] | YUAN Na, XU Qinyuan, XU Zhaolong, ZHOU Ling, LIU Xiaoqing, CHEN Xin, DU Jianchang. The Development and Verification of SNP Lquid Chips for Common Bean Based on Targeted Sequencing Technology [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1017-1032. |
| [13] | YOU Ping, YANG Jin, ZHOU Jun, HUANG Aijun, BAO Minli, YI Long. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Candidatus Liberibacter Asiaticus Based on Different Types of Prophage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(4): 727-736. |
| [14] | YOU Yuanyuan, WANG Shuai, FANG Yingying, QI Cheng, LI Shupei, ZHANG Ying, CHEN Yuhui, LIU Wei, LIU Fuzhong, SHU Jinshuai. Variation Characteristics of Insertion-Deletion(InDel)and Molecular Markers Development and Application in Eggplant Based on Whole Genome Re-sequencing Data [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 520-532. |
| [15] | CHEN Fangce, HU Pingzheng, XIE Weiwei, WANG Zhengpeng, ZHONG Chuangnan, LI Haiyan, HE Yehua, PENG Ze, WAN Baoxiong, LIU Chaoyang. Development and Application of Prunus salicina InDel Markers Based on Genome Re-sequencing [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2510-2522. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd