
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 705-713.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0273
• Cultivation·Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HU Yawei1, MA Jinlong2, ZHONG Balian2, YAO Fengxian1,2, LIU Guidong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-19
Revised:2025-01-13
Online:2025-03-25
Published:2025-03-25
Contact:
LIU Guidong
HU Yawei, MA Jinlong, ZHONG Balian, YAO Fengxian, LIU Guidong. Preliminary Study on Utilization of 15N-urea Applied to Young Navel Orange Trees in Summer and Its Residual in Soil[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 705-713.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0273
| 器官 Organ | 干质量/(g · plant-1) Dry weight | 在整株中的占比/% Proportion in the whole plant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早 Gannanzao | 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早Gannanzao | ||
| 当年生叶片 1-Year leaf | 795.9 ± 52.5 | 453.7 ± 34.1* | 27.58 ± 0.59 | 27.04 ± 2.17 | |
| 当年生枝条 1-Year branch | 377.6 ± 15.3 | 227.7 ± 18.0* | 13.11 ± 0.48 | 13.54 ± 0.64 | |
| 二年生叶片 2-Year leaf | 73.8 ± 15.7 | 54.7 ± 6.4* | 2.54 ± 0.46 | 3.26 ± 0.14 | |
| 二年生枝条 2-Year branch | 312.4 ± 18.1 | 203.9 ± 24.6* | 10.83 ± 0.24 | 12.12 ± 1.26 | |
| 主干 Trunk | 380.8 ± 47.9 | 252.0 ± 16.2* | 13.15 ± 0.98 | 14.99 ± 0.58 | |
| 主根 Main root | 260.7 ± 21.1 | 138.5 ± 5.0* | 9.03 ± 0.34 | 8.26 ± 0.52 | |
| 粗根 Coarse root | 481.5 ± 9.0 | 250.5 ± 30.9* | 16.76 ± 1.21 | 14.91 ± 1.69 | |
| 细根 Fine root | 201.7 ± 19.6 | 99.0 ± 12.2* | 7.00 ± 0.59 | 5.88 ± 0.55 | |
| 整株 Whole plant | 2 884.4 ± 157.7 | 1 680.1 ± 62.8* | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
Table 1 Dry weight of various parts of young navel orange plants and their proportion in the whole plant
| 器官 Organ | 干质量/(g · plant-1) Dry weight | 在整株中的占比/% Proportion in the whole plant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早 Gannanzao | 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早Gannanzao | ||
| 当年生叶片 1-Year leaf | 795.9 ± 52.5 | 453.7 ± 34.1* | 27.58 ± 0.59 | 27.04 ± 2.17 | |
| 当年生枝条 1-Year branch | 377.6 ± 15.3 | 227.7 ± 18.0* | 13.11 ± 0.48 | 13.54 ± 0.64 | |
| 二年生叶片 2-Year leaf | 73.8 ± 15.7 | 54.7 ± 6.4* | 2.54 ± 0.46 | 3.26 ± 0.14 | |
| 二年生枝条 2-Year branch | 312.4 ± 18.1 | 203.9 ± 24.6* | 10.83 ± 0.24 | 12.12 ± 1.26 | |
| 主干 Trunk | 380.8 ± 47.9 | 252.0 ± 16.2* | 13.15 ± 0.98 | 14.99 ± 0.58 | |
| 主根 Main root | 260.7 ± 21.1 | 138.5 ± 5.0* | 9.03 ± 0.34 | 8.26 ± 0.52 | |
| 粗根 Coarse root | 481.5 ± 9.0 | 250.5 ± 30.9* | 16.76 ± 1.21 | 14.91 ± 1.69 | |
| 细根 Fine root | 201.7 ± 19.6 | 99.0 ± 12.2* | 7.00 ± 0.59 | 5.88 ± 0.55 | |
| 整株 Whole plant | 2 884.4 ± 157.7 | 1 680.1 ± 62.8* | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
| 器官 Organ | 15N分配率/% 15N distribution ratio | 15N利用率/% 15N utilization rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早 Gannanzao | 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早Gannanzao | ||
| 当年生叶片 1-Year leaf | 65.89 ± 2.42 | 60.06 ± 4.46 | 4.25 ± 0.61 | 2.03 ± 0.29* | |
| 当年生枝条 1-Year branch | 8.35 ± 1.45 | 12.58 ± 2.35* | 0.54 ± 0.13 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | |
| 二年生叶片 2-Year leaf | 7.90 ± 0.47 | 3.72 ± 0.47* | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 0.12 ± 0.02* | |
| 二年生枝条 2-Year branch | 5.02 ± 0.49 | 7.20 ± 0.48* | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | |
| 主干 Trunk | 3.44 ± 0.66 | 5.45 ± 0.64* | 0.23 ± 0.07 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | |
| 主根 Main root | 3.58 ± 0.52 | 3.69 ± 0.54 | 0.23 ± 0.04 | 0.12 ± 0.02* | |
| 粗根 Coarse root | 6.29 ± 0.44 | 4.60 ± 0.58* | 0.41 ± 0.08 | 0.15 ± 0.02* | |
| 细根 Fine root | 4.53 ± 1.39 | 2.69 ± 1.17 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 0.09 ± 0.03* | |
| 整株 Whole plant | 100.00 | 100.00 | 6.45 ± 0.89 | 3.36 ± 0.28* | |
Table 2 15N distribution ratio and utilization of different parts in young naval orange plants
| 器官 Organ | 15N分配率/% 15N distribution ratio | 15N利用率/% 15N utilization rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早 Gannanzao | 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早Gannanzao | ||
| 当年生叶片 1-Year leaf | 65.89 ± 2.42 | 60.06 ± 4.46 | 4.25 ± 0.61 | 2.03 ± 0.29* | |
| 当年生枝条 1-Year branch | 8.35 ± 1.45 | 12.58 ± 2.35* | 0.54 ± 0.13 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | |
| 二年生叶片 2-Year leaf | 7.90 ± 0.47 | 3.72 ± 0.47* | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 0.12 ± 0.02* | |
| 二年生枝条 2-Year branch | 5.02 ± 0.49 | 7.20 ± 0.48* | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | |
| 主干 Trunk | 3.44 ± 0.66 | 5.45 ± 0.64* | 0.23 ± 0.07 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | |
| 主根 Main root | 3.58 ± 0.52 | 3.69 ± 0.54 | 0.23 ± 0.04 | 0.12 ± 0.02* | |
| 粗根 Coarse root | 6.29 ± 0.44 | 4.60 ± 0.58* | 0.41 ± 0.08 | 0.15 ± 0.02* | |
| 细根 Fine root | 4.53 ± 1.39 | 2.69 ± 1.17 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 0.09 ± 0.03* | |
| 整株 Whole plant | 100.00 | 100.00 | 6.45 ± 0.89 | 3.36 ± 0.28* | |

Fig. 2 Ndff of soil in different soil layers The different letters indicate that there are significant differences in different soil layers of the same variety
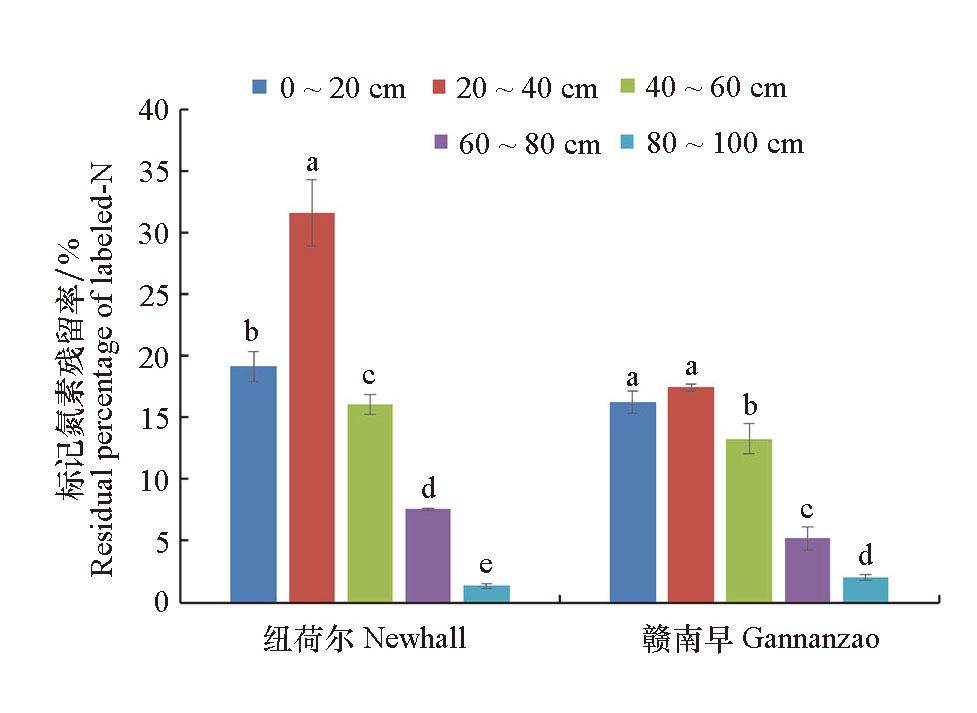
Fig. 3 Residual percentage of 15N in different soil layers The different letters indicate that there are significant differences in different soil layers of the same variety
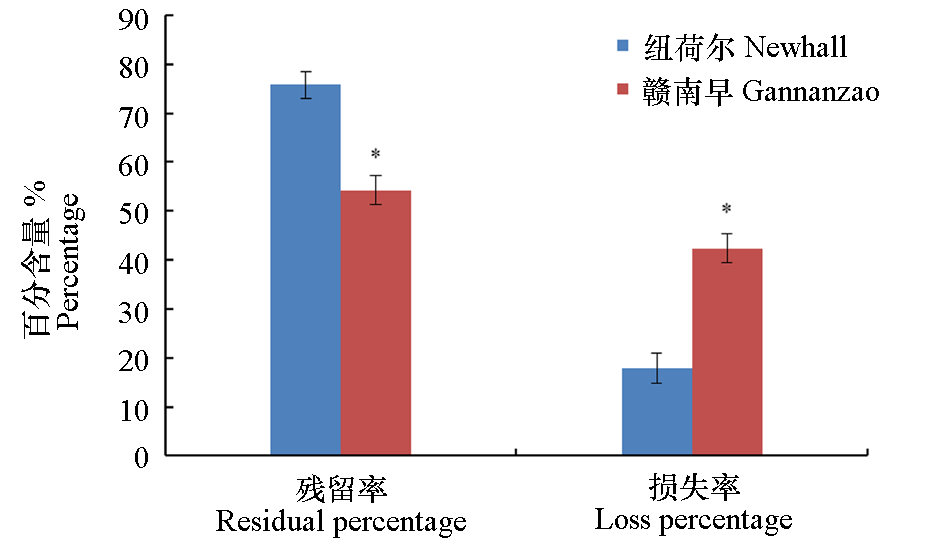
Fig. 4 Residual and loss percentage of 15N in soil Asterisk above the same index indicate that there is a significant difference between the two cultivars
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
杜思婕, 张艺磊, 张志勇, 吉艳芝, 尹兴, 韩建, 张丽娟. 2021. 冬小麦-夏玉米轮作体系不同新型尿素的氮素利用率及去向. 植物营养与肥料学报, 27 (1):24-34.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
范玉兰, 薛珺, 梁梅青, 李勋, 彭良志, 淳长品. 2012. 赣南脐橙果园土壤有机质变化特征研究. 中国南方果树, 41 (4):18-20.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
葛顺峰, 姜远茂, 魏绍冲, 房祥吉. 2011. 不同供氮水平下幼龄苹果园氮素去向初探. 植物营养与肥料学报, 17 (4):949-955.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
黄成能, 卢晓鹏, 李静, 肖玉明, 孙敏红, 谢深喜. 2013. 柑橘氮素营养生理研究进展. 湖南农业科学, 15:76-79.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
柯健. 2017. 氮肥种类和施肥方式对水稻产量及氮素去向的影响[博士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
雷靖, 梁珊珊, 谭启玲, 胡承孝, 孙学成, 赵小虎. 2019. 我国柑橘氮磷钾肥用量及减施潜力. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25 (9):1504-1513.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
李旭. 2020. 减氮施肥对柑橘树体氮素含量、果实品质产量和氮肥利用的影响[硕士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0110 URL |
|
梁振旭, 孙明德, 武阳, 田海青, 杜瑞瑞, 赵艳艳, 刘松忠. 2021. 梨幼树到结果初期春施15N-尿素的利用及其在土壤的残留与损失. 园艺学报, 48 (1):137-145.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0110 URL |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
刘桂东, 姜存仓, 王运华, 彭抒昂, 鲁剑巍. 2010. 柑橘对不同矿质营养元素效应的研究进展. 土壤通报, 41 (6):1547-1552.
|
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0280 URL |
|
刘照霞, 张鑫, 王璐, 马玉婷, 陈倩, 朱占玲, 葛顺峰, 姜远茂. 2022. 肥料穴施位点对苹果细根生长、15N吸收利用及产量品质的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (7):1545-1556.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0280 URL |
|
| [16] |
pmid: 14717433 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
|
孙秋玲, 戴思兰, 张春英, 魏翔莺. 2012. 菌根真菌促进植物吸收利用氮素机制的研究进展. 生态学杂志, 31 (5):1302-1310.
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0126 URL |
|
王芬, 田歌, 于波, 何流, 刘晓霞, 葛顺峰, 姜远茂. 2017. 富士苹果果实膨大期肥料氮去向及土壤氮素平衡的研究. 园艺学报, 44 (8):1569-1578.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0126 URL |
|
| [20] |
|
|
王海宁, 葛顺峰, 姜远茂, 魏绍冲, 陈倩, 孙聪伟. 2013. 不同砧木嫁接的富士苹果幼树13C和15N分配利用特性比较. 园艺学报, 40 (4):733-738.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
王前登, 刘雪艳, 何雪菲, 王成, 柴仲平. 2019. 基于15N示踪的库尔勒香梨园氮素去向研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25 (9):1523-1531.
|
|
| [22] |
|
|
王瑞东, 姜存仓, 刘桂东, 王运华, 彭抒昂, 钟八莲, 曾庆銮. 2011. 赣南脐橙园立地条件及种植现状调查与分析. 中国南方果树, 40 (1):1-3.
|
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0350 |
|
王晓荣, 唐万鹏, 付甜, 黄志霖, 何伟, 刘常富. 2021. 不同管理措施对三峡库区柑橘园土壤养分和径流氮磷流失的影响. 中国农学通报, 37 (11):95-102.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0350 |
|
| [24] |
|
|
吴梦娜, 王少杰, 兰唱, 闫旭, 冯国忠, 高强. 2024. 不同秸秆还田方式下黑土玉米田肥料氮素去向. 土壤学报, 61 (2):506-514.
|
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0063 |
|
武阳, 孙明德, 刘军, 田海青, 王文娟, 刘松忠. 2017. 施氮深度对‘黄金梨’树氮素吸收、分配及利用效率的影响. 园艺学报, 44 (11):2171-2178.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0063 |
|
| [26] |
|
|
徐明杰, 董娴娴, 刘会玲, 张丽娟, 巨晓棠. 2014. 不同管理方式对小麦氮素吸收、分配及去向的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 20 (5):1084-1093.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
徐明杰, 张琳, 汪新颖, 彭亚静, 张丽娟, 巨晓棠. 2015. 不同管理方式对夏玉米氮素吸收、分配及去向的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 21 (1):36-45.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
赵环宇. 2023. 我国柑橘生产的环境代价及氮素优化措施研究[博士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
钟八莲, 赖晓桦, 杨斌华, 米兰芳, 谢上海, 黄彩英, 杨文侠, 张湟. 2013. 纽荷尔脐橙芽变早熟品种—赣南早脐橙. 中国南方果树, 42 (2):48-51.
|
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.08.010 |
|
周丽平, 杨俐苹, 白由路, 卢艳丽, 王磊. 2018. 夏玉米施用不同缓释化处理氮肥的效果及氮肥去向. 中国农业科学, 51 (8):1527-1536.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.08.010 |
| [1] | ZHANG Shuning, ZHENG Shuqi, WANG Xinsheng, KE Fuzhi, ZHANG Lanlan, SUN Xuepeng, GONG Jinli. Advances in the Relationship Between Cell Wall Metabolism and Physiological Diseases of Citrus Peel [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 513-525. |
| [2] | YANG Jinlei, LÜ Biwen, CHEN Yuewen, JIN Yan, YANG Junfeng, ZHOU Tie, TANG Jun, CHANG Yuanyuan, YANG Changyao, LU Xiaopeng. Status of Cadmium Pollution in the Main Citrus Producing Areas of Hunan Province and the Effects of Cadmium Stress on Citrus Development [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 200-212. |
| [3] | REN Siyuan, CHEN Sen, LONG Zhijian, WANG Boya, TANG Dengguo, WANG Zhengqian, YANG Bin, HU Shanglian, CAO Ying. Nitrogen Allocation Characteristics and Expression of Related Genes During Corm-Forming Stage of Amorphophallus konjac [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2019-2030. |
| [4] | DONG Liting, QU Rongrong, PANG Shuwei, MO Kaiqin, CHEN Shuang, SHANG Lanyue, ZOU Xiuping. Expression Characteristics and Function Analysis of CsMEKK1-1 Gene in Response to Huanglongbing in Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2168-2182. |
| [5] | ZHANG Wenlong, WAN Runchu, ZHENG Ni, CHEN Yan, LAI Hengxin, YU Xin, QIAN Chun, CAO Li. ‘Yangguang 1’-a New Monoembryonic Sterile Line of Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2221-2222. |
| [6] | LI Xujiao, LÜ Qi, YAO Dongdong, ZHAO Fengyun, WANG Xiaofei, YU Kun. Effect of‘Yanfu 3’Apple Grafted with Different Rootstocks on Absorption and Utilization of 15N-urea [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1868-1880. |
| [7] | DU Meixia, PANG Shuwei, DONG Liting, MO Kaiqin, HOU Mengyuan, WANG Shuai, ZOU Xiuping. Research Progress on the Molecular Mechanisms of Interactions Between Candidatus Liberibacter and Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1623-1638. |
| [8] | CAO Huixiang, LUO Xin, LIU Wanrong, GUAN Shuping, WANG Tingting, WU Xiaomeng, GUO Wenwu, XIE Kaidong. Evaluation of Fruit Segmental Membrane Development and Mastication in Two Citrus Triploids [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1179-1188. |
| [9] | ZHOU Huizhen, ZHANG Jia, HU Junhua, LI Baixue, CAO Li, YU Xin, WANG Fusheng, ZOU Xiuping, ZHOU Yan. The Role of BAG1 in the Infection of Citrus with Alternaria Brown Spot [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 956-970. |
| [10] | PENG Aihong, ZHANG Jingyun, CHEN Zhiyi, SU Juan, HE Yongrui, YAO Lixiao. Effects of Overexpression of CsEXPA8 on Growth and Canker Disease Resistance in‘Wanjincheng’Orange [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 971-981. |
| [11] | YOU Ping, YANG Jin, ZHOU Jun, HUANG Aijun, BAO Minli, YI Long. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Candidatus Liberibacter Asiaticus Based on Different Types of Prophage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(4): 727-736. |
| [12] | XIONG Zhiwei, LI Zhilong, YIN Hui, GAO Yuxia. Pan-Genome Analysis of Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus Causing Huanglongbing of Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(4): 737-747. |
| [13] | YI Qian, ZHANG Manman, WANG Xiaoli, FENG Jipeng, ZHU Shiping, WANG Fusheng, ZHAO Xiaochun. CclSAUR49 Affects Growth and Limonoids Metabolism in Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 479-494. |
| [14] | SUN Quan, HE Zhengchen, YE Junli, WEI Ranran, YIN Yingzi, CHAI Lijun, XIE Zongzhou, XU Qiang, XU Juan, GUO Wenwu, CHENG Yunjiang, DENG Xiuxin. Storage with Climacteric Fruits Improves Color and Quality of Citrus Fruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 601-615. |
| [15] | LIU Meng, JIA Huiting, ZHOU Xingang. Isolation,Identification and Functional Analysis of Symbiotic Bacteria of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerium [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 643-655. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd