
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 671-692.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0355
• Cultivation·Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHENG Xiaogai, WAN Yuan, LIN Lu*( ), XIE Peng, LI Zhiqiang, LI Mi, WANG Pengpeng, NIU Zimian
), XIE Peng, LI Zhiqiang, LI Mi, WANG Pengpeng, NIU Zimian
Received:2024-10-14
Revised:2025-01-17
Online:2025-03-25
Published:2025-03-25
Contact:
LIN Lu
CHENG Xiaogai, WAN Yuan, LIN Lu, XIE Peng, LI Zhiqiang, LI Mi, WANG Pengpeng, NIU Zimian. Influences of Trunk Heights on Leaf Photosynthesis and Fruit Qualities at Different Canopy Locations in Open-Central Canopy of Apple[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 671-692.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0355
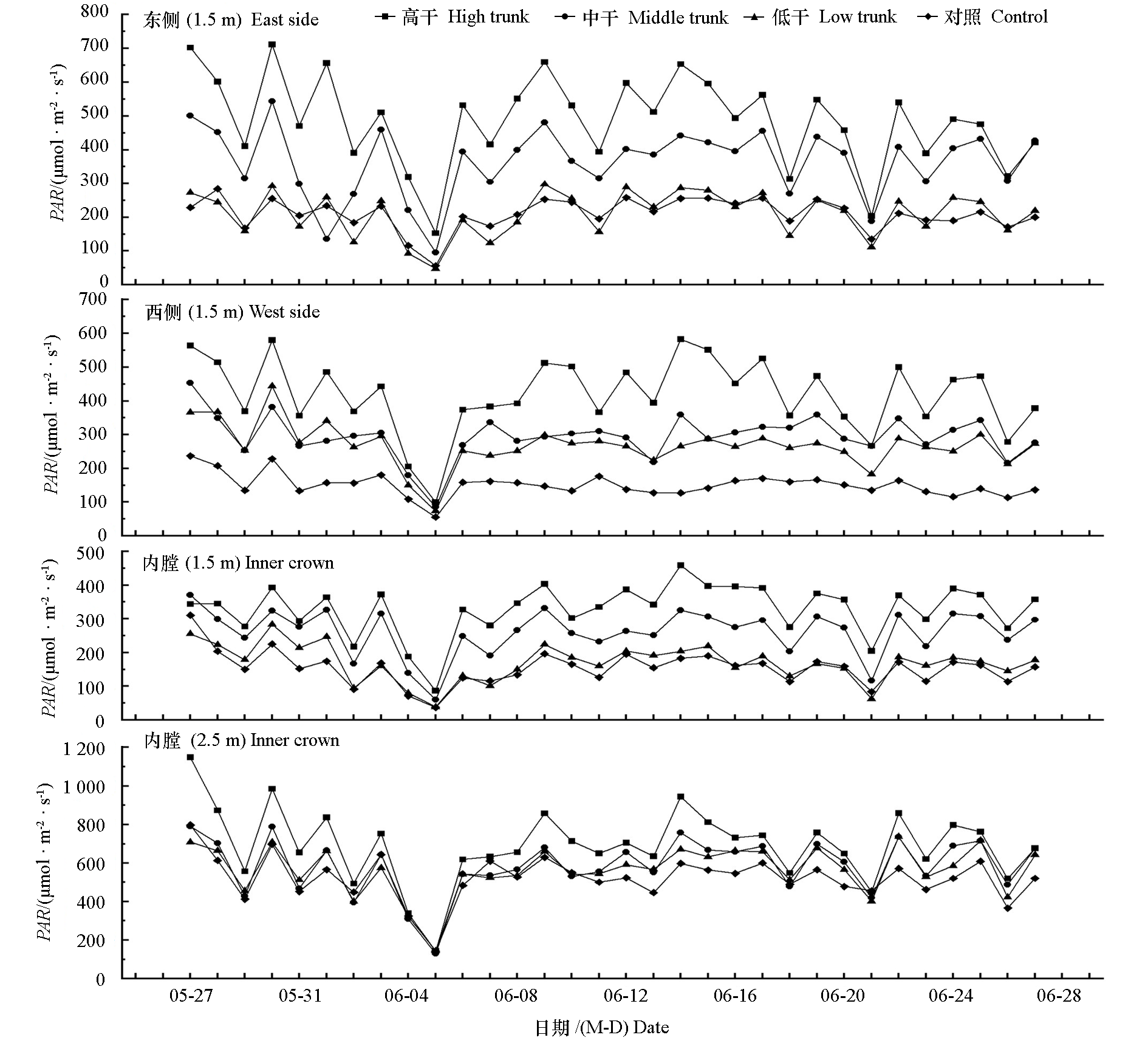
Fig. 1 Changes in daily means of photosynthetically active radiation(PAR)at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights
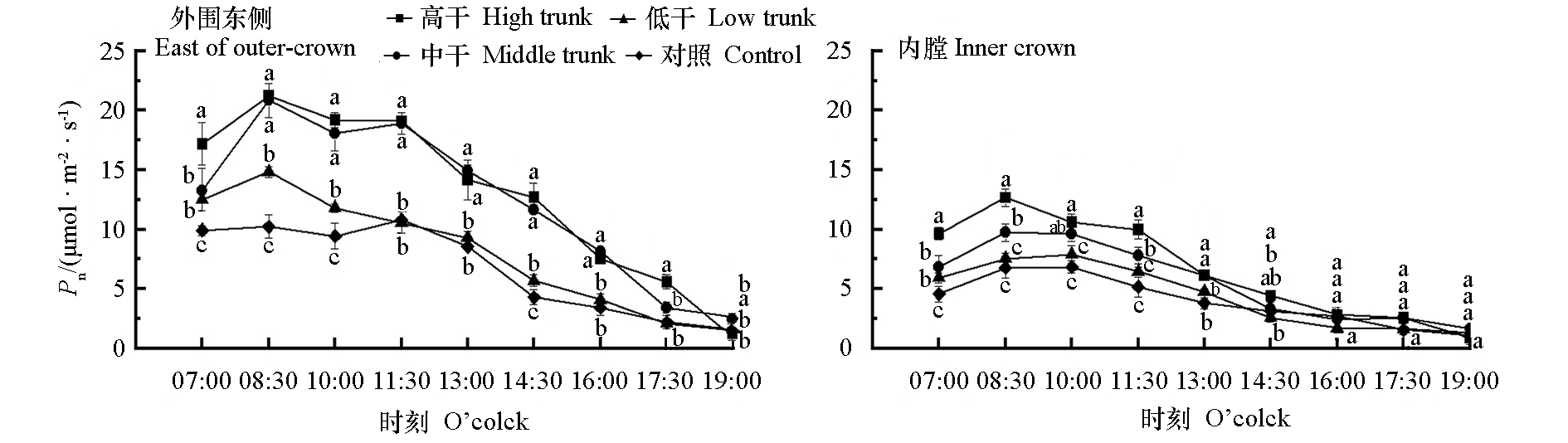
Fig. 2 Diurnal changes of leaf net photosynthetic rate(Pn)at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights The different lowercase letters indicate significant differences(P < 0.05). The same below

Fig. 3 Light response curves of leaf net photosynthetic rate(Pn),stomatal conductance(Gs),intercellular CO2 concentration(Ci)and instantaneous transpiration rate(Tr)at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights

Fig. 4 Differences of characteristic parameters derived from Pn-PAR response curves at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights Amax:Maximum net photosynthetic rate;AQE:Apparent quantum efficiency;LSP:Light saturation point;LCP:Light compensation point;LUR:Light utilization range;Rd:Dark respiration rate

Fig. 5 Response curves of leaf net photosynthetic rate(Pn)to intercellular CO2 concentration(Ci)at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights
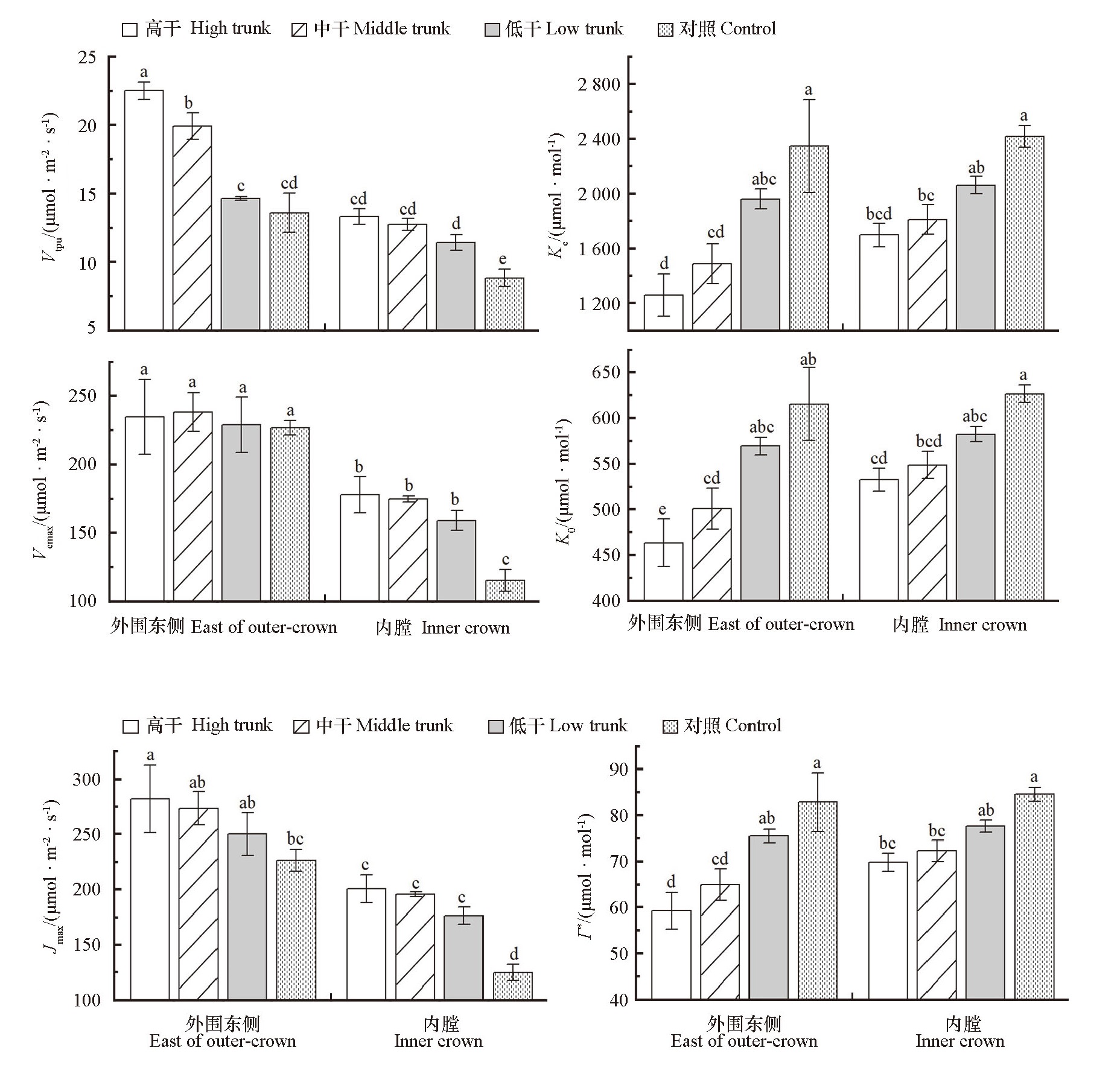
Fig.6 Differences of characteristic parameters derived from Pn-Ci response curves at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights Vcmax-maximum carboxylation rate under the restriction of Rubisco,Jmax-maximum rate of electron transfer under light saturation,Vtpu-supplying rate of triose phosphate,Kc-Michaelis constant of Rubisco to CO2,Ko-Michaelis constant of Rubisco to O2,Γ*-CO2 compensation point of dark respiration under light

Fig. 7 Kinetics curves of Fv′/Fm′,qP,NPQ and ΦPSII during the process of fluorescence quenching at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights

Fig. 13 Differences in contents of total phenols and total flavonoids in peel and flesh at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights. GAE:Gallic acid equivalent;RE:Rutin equivalent

Fig. 14 Differences in antioxidant capacity of peel and flesh at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights TE:Trolox E quivalent
| [1] |
|
|
安佰义, 谷娜, 刘晓嘉, 张艳波, 宋宏伟, 李锋. 2019. 不同树形对李树冠层结构和光合特性的影响. 北方园艺,(3):29-35.
|
|
| [2] |
|
|
白岗栓, 杜社妮, 王建平. 2021. 陕北山地苹果树形改造研究. 中国农业大学学报, 26 (12):54-66.
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00904 pmid: 29018097 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
高方胜, 王明友, 潘恩敬, 苏荣存. 2011. 红富士苹果不同树形冠层光照参数与果实品质产量关系的研究. 中国果树,(1):14-17.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
高照全, 赵晨霞, 李志强, 张显川. 2013. 我国4种主要苹果树形光合能力差异研究. 中国生态农业学报, 21 (7):853-859.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.09.019 |
|
胡德玉, 刘雪峰, 何绍兰, 谢让金, 钱春, 吕强, 易时来, 郑永强, 邓烈. 2017. 郁闭柑橘园整形改造对植株冠层生理特性、产量和果实品质的影响. 中国农业科学, 50 (9):1734-1746.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.09.019 |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
贾浩, 郝建博, 曹洪波, 韩艳, 李丹, 陈海江. 2015. 遮荫对‘保佳红’桃树叶片快速叶绿素荧光诱导动力学曲线的影响. 西北植物学报, 35 (9):1861-1867.
|
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
林琭, 李志强, 蔚露, 王红宁, 牛自勉. 2020a. 苹果两种树形叶片对光强和CO2浓度互作的光合响应及光抑制特性. 园艺学报, 47 (11):2073-2085.
|
|
| [20] |
pmid: 26710629 |
|
林琭, 汤昀, 张纪涛, 闫万丽, 肖建红, 丁超, 董川, 籍增顺. 2015. 不同水势对黄瓜花后叶片气体交换及叶绿素荧光参数的影响. 应用生态学报, 26 (7):2030-2040.
pmid: 26710629 |
|
| [21] |
|
|
林琭, 蔚露, 王红宁, 牛自勉, 谢鹏. 2020b. 冠层结构对梨叶片光合特性及果实品质的影响. 西北植物学报, 40 (7):1180-1191.
|
|
| [22] |
pmid: 14759845 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202011.030 |
|
牛军强, 孙文泰, 董铁, 尹晓宁, 刘兴禄, 马明. 2020. 间伐改形对陇东高原密闭富士苹果园冠层微域环境及叶片生理特性的影响. 应用生态学报, 31 (11):3681-3690.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202011.030 |
|
| [24] |
|
|
牛自勉, 孙俊宝, 蔚露, 郭爱珍, 王建新. 2011. 树干高度对苹果开心形树产量及品质的影响. 山西农业科学, 39 (10):1067-1069,1091.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
牛自勉, 蔚露, 谢鹏, 韩苹苹, 李全. 2015. 干高对梨树开心树形产量与品质的影响. 山西农业科学, 43 (10):1272-1275.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
牛自勉, 蔚露, 张文和. 2012. 开心树形叶幕结构对苹果园地面太阳辐射的影响. 山西农业科学, 40 (11):1164-1168.
|
|
| [27] |
pmid: 26915197 |
|
屈振江, 尚小宁, 王景红, 梁轶, 高峰, 杨芳. 2015. 黄土高原两种树形苹果园花期温度垂直变化特征及预测. 应用生态学报,(11):3405-3412.
pmid: 26915197 |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1093/treephys/tps020 pmid: 22491489 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.18.011 |
|
阮班录, 刘建海, 李雪薇, 李丙智, 韩明玉, 张林森, 周永博. 2011. 乔砧苹果郁闭园不同改造方法对冠层光照和叶片状况及产量品质的影响. 中国农业科学, 44 (18):3805-3811.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.18.011 |
|
| [30] |
|
|
苏渤海, 范崇辉, 李国栋, 张军科, 韩明玉. 2008. 红富士苹果改形过程中不同树形光照分布及其对产量品质的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 36 (1):158-162.
|
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201809.026 |
|
孙文泰, 牛军强, 董铁, 刘兴禄, 尹晓宁, 马明. 2018. 间伐改形对陇东旱塬密闭苹果园树体冠层结构和发育后期叶片质量的影响. 应用生态学报, 29 (9):3008-3016.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201809.026 |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
|
王建新, 牛自勉, 李志强, 郭爱萍, 高慧卿. 2011. 乔砧富士苹果不同冠形相对光照强度的差异及对果实品质的影响. 果树学报, 28 (1):8-14.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
王文军, 陈奇凌, 郑强卿, 王晶晶, 王振东. 2021. 不同树形对灰枣叶片光合及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 新疆农业科学, 58 (4):616-624.
doi: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2021.04.004 |
|
| [36] |
|
|
王琰, 范崇辉, 江道伟, 李丙智, 杜荣. 2011. 苹果不同树形树冠特性和果实品质的比较. 西北农业学报, 20 (12):93-97.
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
魏钦平, 鲁韧强, 张显川, 王小伟, 高照全, 刘军. 2004. 富士苹果高干开心形光照分布与产量品质的关系研究. 园艺学报, 31 (3):291-296.
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
|
闫小莉, 王德炉. 2014. 遮荫对苦丁茶树叶片特征及光合特性的影响. 生态学报, 34 (13):3538-3547.
|
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0146 URL |
|
蔚露, 牛自勉, 林琭, 姜闯道, 王红宁, 谢鹏, 李志强, 郭晋鸣. 2020. 小冠开心形和细型主干形‘玉露香’梨光能截获与光合作用差异. 园艺学报, 47 (1):11-22.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0146 URL |
|
| [42] |
|
|
蔚露, 牛自勉, 林琭, 谢鹏, 李小平. 2017. 树干高度对苹果开心形叶幕PPFD与UV的影响. 山西农业科学, 45 (11):1755-1759.
|
|
| [43] |
|
|
张显川, 高照全, 付占方, 方建辉, 李天红. 2007. 苹果树形改造对树冠结构和冠层光合能力的影响. 园艺学报, 34 (3):537-542.
|
|
| [44] |
|
|
张显川, 高照全, 舒先迂, 魏钦平. 2005. 苹果开心形树冠不同部位光合与蒸腾能力的研究. 园艺学报, 42 (6):975-979.
|
|
| [45] |
|
| [1] | LI Ao, ZHENG Xu, WU Chengxu, NIE Ruining, JI Xinying, TANG Jiali, ZHANG Junpei. The Effect of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Walnut Seedlings Under Salt Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 423-438. |
| [2] | SHI Xingxiu, FENG Beibei, YAN Peng, GENG Wenjuan, Jumazira Sharshanmukhan. Physiological Changes Associated with Early Watercore in‘Orin’Apples [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 171-184. |
| [3] | ZHANG Songyan, DIE Pengxiang, SONG Mengting, LI Zhijian, ZHOU Jian. Effect of Overexpression of Robinia pseudoacacia RpACBP3 Gene on Photosynthetic Physiological Characteristics of Nicotiana tabacum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2155-2167. |
| [4] | JIA Linguang, ZHANG He, ZHANG Xueying, SUN Jianshe, GAO Yi, LI Guofang, TAN Ming, SHAO Jianzhu. A New Edible Crabapple Cultivar‘Jinxing’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2227-2228. |
| [5] | QIU Hui, ZHU Dejuan, ZHANG Yongle, GAO Yujie, LI Liu, WANG Guoping, HONG Ni. Interaction Between the Coat Protein of Apple Chlorotic Leaf Spot Virus and Two E3 Ubiquitin Ligases of Pear and Their Subcellular Localization [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1715-1727. |
| [6] | LIU Yinghao, LI Yun, LÜ Weijing, CHEN Ran, JIANG Weitao, YIN Chengmiao, MAO Zhiquan, WANG Yanfang. Effects of Different Temperatures’ Biochar on Soil Fungi Community Structure Under Apple Replantation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1853-1867. |
| [7] | LI Xujiao, LÜ Qi, YAO Dongdong, ZHAO Fengyun, WANG Xiaofei, YU Kun. Effect of‘Yanfu 3’Apple Grafted with Different Rootstocks on Absorption and Utilization of 15N-urea [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1868-1880. |
| [8] | TIAN Wen, LI Zichen, WANG Lin, WANG Dajiang, WANG Kun, SUN Simiao, WANG Guangyi, LIU Zhao, LU Xiang, FENG Jianrong, GAO Yuan. Advances in Genome-Wide Association Study Associated Important Traits in Apple [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1565-1579. |
| [9] | LIU Chenglong, FAN Xudong, REN Fang, ZHANG Zunping, HU Guojun, DONG Yafeng. Detection Methods of Apple Tree Viruses [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1580-1594. |
| [10] | QIN Genhong, YUAN Hongbo, WANG Zhuoni, SHI Bingke, FAN Yangyang, WANG Li, ZHANG Meng, TU Hongtao, XU Chao, HOU Hui. Antagonistic Activity of Volatile Organic Compounds of Bacillus cereus Strain G3-17 Against Apple Ring Rot [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1403-1412. |
| [11] | SHI Bingke, WANG Zhuoni, QIN Genhong, HUANG Tianxiang, WANG Li, TU Hongtao, YUAN Hongbo, HOU Hui. Isolation and Identification of Endophytic Fungus Pa2 Antagonistic Against Apple Ring Rot Caused by Botryosphaeria dothidea [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1113-1125. |
| [12] | LUO Jiandong, QIU Mengqing, ZHOU Huimin, XIE Weiwei, Huang Haixin, LIU Jieqi, ZHANG Zimin, XU Jian, CHEN Chengjie, HE Yehua, LIU Chaoyang. Cloning and Functional Analysis of Pineapple AcZFP1 Gene Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 495-508. |
| [13] | XIA Hongyi, LIU Qiao, PENG Jiaqing, WU Wei, GONG Linzhong. Effects of f-Shaped Tree Shape on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Fruit Quality in‘Shine Muscat’Grapevines with Rain-Shelter Cultivation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 560-570. |
| [14] | GAO Yongchen, SU Xinjian, YU Cheng, LIU Zhu, MAO Ke, ZOU Yangjun, GONG Xiaoqing. Effects of Black Nonwovens and Herb Residue Mulching on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Microorganisms in the Apple Orchard [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 587-600. |
| [15] | SUN Quan, HE Zhengchen, YE Junli, WEI Ranran, YIN Yingzi, CHAI Lijun, XIE Zongzhou, XU Qiang, XU Juan, GUO Wenwu, CHENG Yunjiang, DENG Xiuxin. Storage with Climacteric Fruits Improves Color and Quality of Citrus Fruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 601-615. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd