
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (11): 2657-2667.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0674
• Cultivation·Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Yajie1, JIAO Yu1, WANG Hailong1, CHEN Zhixing2, PU Hao2, ZHU Zihan1, ZOU Qian1, TANG Shukun3,4, CAO Yanru1,**( )
)
Received:2024-07-10
Revised:2024-08-23
Online:2024-12-12
Published:2024-11-26
Contact:
CAO Yanru
WU Yajie, JIAO Yu, WANG Hailong, CHEN Zhixing, PU Hao, ZHU Zihan, ZOU Qian, TANG Shukun, CAO Yanru. Screening Research and Comprehensive Evaluation of Rooting Agents for Chrysanthemum Cuttings[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2657-2667.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0674
| 药剂分类 Potion classification | 药剂 Potion | 主要成分 Main ingredients | 施用方式 Mode of application | 稀释倍数 Multiple of dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 激素类 Hormone | 吲哚丁酸Indolebutyric acid | 吲哚丁酸Indolebutyric acid | 蘸根Dipping root | 1 000 |
| 吲哚乙酸Indoleacetic acid | 吲哚乙酸Indoleacetic acid | 蘸根Dipping root | 2 500 | |
| 赤霉素Gibberellin | 赤霉素Gibberellin | 蘸根Dipping root | 10 000 | |
| 爱根生Aigensheng | 萘乙酸、吲哚丁酸 Naphthalene acetic acid,indolebutyric acid | 蘸根Dipping root | 400 | |
| ABT生根粉 ABT root growing powder | 萘乙酸、吲哚乙酸 Naphthalene acetic acid,indoleacetic acid | 蘸根 Dipping root | 2 000 | |
| 生根粉Root growing powder | S-诱抗素、吲哚丁酸钾、R诱导剂、扩展渗透剂、萘乙酸钠S-attractant,indolebutyrate potassium, R inducer,expansion osmotic agent,sodium naphthoacetate | 蘸根 Dipping root | 800 | |
| 植物生长调节剂类 Plant growth regulator | 萘乙酸Naphthalene acetic acid | 萘乙酸Naphthalene acetic acid | 蘸根Dipping root | 1 000 |
| 亚精胺Spermidine | 亚精胺Spermidine | 蘸根Dipping root | 137 741 | |
| 复硝酚钠 Compound sodium nitrophenol | 邻硝基苯酚钠、对硝基苯酚钠、5-硝基邻甲氧基苯酚钠O-nitrophenol sodium,p-nitrophenol sodium,5-nitro-o-methoxylphenol sodium | 蘸根Dipping root | 2 000 | |
| 农肥类 Agricultural fertilizer | 强力生根壮苗原液Strong root and strong seedling stock | 氨基酸Amino acid | 灌溉Irrigation | 1 000 |
| 植物生根剂Plant rooting agent | 氨基酸Amino acid | 灌溉Irrigation | 600 | |
| 根多多Genduoduo | 氨基酸Amino acid | 灌溉Irrigation | 600 | |
| 根易生Genyisheng | 微量元素Trace element | 灌溉Irrigation | 800 | |
| 硼锌钙镁铁 Boron,zinc,calcium,magnesium,iron | 硼、锌、钙、镁、铁、铜、锰、氮Boron,zinc,calcium,magnesium,iron,copper,manganese,nitrogen | 灌溉Irrigation | 1 500 | |
| 双吉尔-GGR6号 Double Gil GGR-6 | 氨基酸、微量元素 Amino acid,trace element | 蘸根Dipping root | 10 000 | |
| 壮苗生根剂 Rooting agent for seedling | 氨基酸、矿化碘、黄腐酸、微量元素Amino acid, mineralized iodine,fulvic acid,trace element | 灌溉Irrigation | 1 000 | |
| 根有劲Genyoujin | 黄腐酸钾、氮磷钾Potassium fulvic acid,nitrogen,phosphate,potassium | 灌溉Irrigation | 1 200 | |
| 生根壮苗剂Rooting and seedling strengthening agent | 腐殖酸、氮磷钾 Humic acid,nitrogen,phosphorus,potassium | 灌溉Irrigation | 800 | |
| 甲壳素有机水溶肥料 Chitin organic water soluble fertilizer | 甲壳素 Chitin chitin | 灌溉 Irrigation | 1 000 | |
| 生物酶解海藻精 Enzymatic hydrolysis of alginate | 海藻精 Essence of seaweed | 灌溉 Irrigation | 1 000 | |
| 那氏齐齐发诱导剂 Nashi 778 | 植物提取物Plant extracts | 灌溉Irrigation | 150 | |
| 生根宝Shenggenbao | 无资料 No data | 灌溉Irrigation | 500 | |
| 标典3721 Biaodian 3721 | 无资料 No data | 蘸根Dipping root | 1 500 | |
| 聚无忧Juwuyou | 无资料 No data | 灌溉Irrigation | 1 000 | |
| 微生物菌剂 Microbial inoculant | 三炬灌金液 Three torch filling liquid gold | 胶冻样类芽孢杆菌 Paenibacillus mucilaginosus | 灌溉Irrigation | 500 |
Table 1 Test rooting agent
| 药剂分类 Potion classification | 药剂 Potion | 主要成分 Main ingredients | 施用方式 Mode of application | 稀释倍数 Multiple of dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 激素类 Hormone | 吲哚丁酸Indolebutyric acid | 吲哚丁酸Indolebutyric acid | 蘸根Dipping root | 1 000 |
| 吲哚乙酸Indoleacetic acid | 吲哚乙酸Indoleacetic acid | 蘸根Dipping root | 2 500 | |
| 赤霉素Gibberellin | 赤霉素Gibberellin | 蘸根Dipping root | 10 000 | |
| 爱根生Aigensheng | 萘乙酸、吲哚丁酸 Naphthalene acetic acid,indolebutyric acid | 蘸根Dipping root | 400 | |
| ABT生根粉 ABT root growing powder | 萘乙酸、吲哚乙酸 Naphthalene acetic acid,indoleacetic acid | 蘸根 Dipping root | 2 000 | |
| 生根粉Root growing powder | S-诱抗素、吲哚丁酸钾、R诱导剂、扩展渗透剂、萘乙酸钠S-attractant,indolebutyrate potassium, R inducer,expansion osmotic agent,sodium naphthoacetate | 蘸根 Dipping root | 800 | |
| 植物生长调节剂类 Plant growth regulator | 萘乙酸Naphthalene acetic acid | 萘乙酸Naphthalene acetic acid | 蘸根Dipping root | 1 000 |
| 亚精胺Spermidine | 亚精胺Spermidine | 蘸根Dipping root | 137 741 | |
| 复硝酚钠 Compound sodium nitrophenol | 邻硝基苯酚钠、对硝基苯酚钠、5-硝基邻甲氧基苯酚钠O-nitrophenol sodium,p-nitrophenol sodium,5-nitro-o-methoxylphenol sodium | 蘸根Dipping root | 2 000 | |
| 农肥类 Agricultural fertilizer | 强力生根壮苗原液Strong root and strong seedling stock | 氨基酸Amino acid | 灌溉Irrigation | 1 000 |
| 植物生根剂Plant rooting agent | 氨基酸Amino acid | 灌溉Irrigation | 600 | |
| 根多多Genduoduo | 氨基酸Amino acid | 灌溉Irrigation | 600 | |
| 根易生Genyisheng | 微量元素Trace element | 灌溉Irrigation | 800 | |
| 硼锌钙镁铁 Boron,zinc,calcium,magnesium,iron | 硼、锌、钙、镁、铁、铜、锰、氮Boron,zinc,calcium,magnesium,iron,copper,manganese,nitrogen | 灌溉Irrigation | 1 500 | |
| 双吉尔-GGR6号 Double Gil GGR-6 | 氨基酸、微量元素 Amino acid,trace element | 蘸根Dipping root | 10 000 | |
| 壮苗生根剂 Rooting agent for seedling | 氨基酸、矿化碘、黄腐酸、微量元素Amino acid, mineralized iodine,fulvic acid,trace element | 灌溉Irrigation | 1 000 | |
| 根有劲Genyoujin | 黄腐酸钾、氮磷钾Potassium fulvic acid,nitrogen,phosphate,potassium | 灌溉Irrigation | 1 200 | |
| 生根壮苗剂Rooting and seedling strengthening agent | 腐殖酸、氮磷钾 Humic acid,nitrogen,phosphorus,potassium | 灌溉Irrigation | 800 | |
| 甲壳素有机水溶肥料 Chitin organic water soluble fertilizer | 甲壳素 Chitin chitin | 灌溉 Irrigation | 1 000 | |
| 生物酶解海藻精 Enzymatic hydrolysis of alginate | 海藻精 Essence of seaweed | 灌溉 Irrigation | 1 000 | |
| 那氏齐齐发诱导剂 Nashi 778 | 植物提取物Plant extracts | 灌溉Irrigation | 150 | |
| 生根宝Shenggenbao | 无资料 No data | 灌溉Irrigation | 500 | |
| 标典3721 Biaodian 3721 | 无资料 No data | 蘸根Dipping root | 1 500 | |
| 聚无忧Juwuyou | 无资料 No data | 灌溉Irrigation | 1 000 | |
| 微生物菌剂 Microbial inoculant | 三炬灌金液 Three torch filling liquid gold | 胶冻样类芽孢杆菌 Paenibacillus mucilaginosus | 灌溉Irrigation | 500 |
| 处理 Treatment | Z1 | Z2 | 综合得分 Composite score | 位次 Precedence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O(对照 Control) | -2.77 | -1.49 | -2.21 | 5 |
| 那氏齐齐发诱导剂Nashi 778 | 3.76 | -1.34 | 2.29 | 1 |
| 植物生根剂Plant rooting agent | -0.98 | -0.08 | -0.69 | 4 |
| 双吉尔-GGR6号Double Gil GGR-6 | 0.33 | 1.33 | 0.51 | 2 |
| 萘乙酸Naphthalene acetic acid | -0.86 | 0.33 | -0.51 | 3 |
Table 2 Analysis of principal components(Z1,Z2)of root phenotypic indexes of chrysanthemum cuttings treated with different rooting agents
| 处理 Treatment | Z1 | Z2 | 综合得分 Composite score | 位次 Precedence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O(对照 Control) | -2.77 | -1.49 | -2.21 | 5 |
| 那氏齐齐发诱导剂Nashi 778 | 3.76 | -1.34 | 2.29 | 1 |
| 植物生根剂Plant rooting agent | -0.98 | -0.08 | -0.69 | 4 |
| 双吉尔-GGR6号Double Gil GGR-6 | 0.33 | 1.33 | 0.51 | 2 |
| 萘乙酸Naphthalene acetic acid | -0.86 | 0.33 | -0.51 | 3 |
| 营养物质 Nutrient | 平均数Average | 极差 Extremely poor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O (对照Control) | 那氏齐齐发诱导剂 Nashi 778 | 双吉尔-GGR6号 Double Gil GGR-6 | ||
| 可溶性糖/(mg · g-1)Soluble sugar | 1.85 | 1.90 | 1.92 | 0.07 |
| 淀粉/(mg · g-1)Starch content | 1.26 | 1.32 | 1.33 | 0.08 |
| 可溶性蛋白/(mg · g-1)Soluble proteins | 2.04 | 2.18 | 2.18 | 0.16 |
| 氮素/% Nitrogen | 1.91 | 1.93 | 1.91 | 0.02 |
Table 3 Range analysis of nutrient content of chrysanthemum cuttings treated with different chemicals
| 营养物质 Nutrient | 平均数Average | 极差 Extremely poor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O (对照Control) | 那氏齐齐发诱导剂 Nashi 778 | 双吉尔-GGR6号 Double Gil GGR-6 | ||
| 可溶性糖/(mg · g-1)Soluble sugar | 1.85 | 1.90 | 1.92 | 0.07 |
| 淀粉/(mg · g-1)Starch content | 1.26 | 1.32 | 1.33 | 0.08 |
| 可溶性蛋白/(mg · g-1)Soluble proteins | 2.04 | 2.18 | 2.18 | 0.16 |
| 氮素/% Nitrogen | 1.91 | 1.93 | 1.91 | 0.02 |
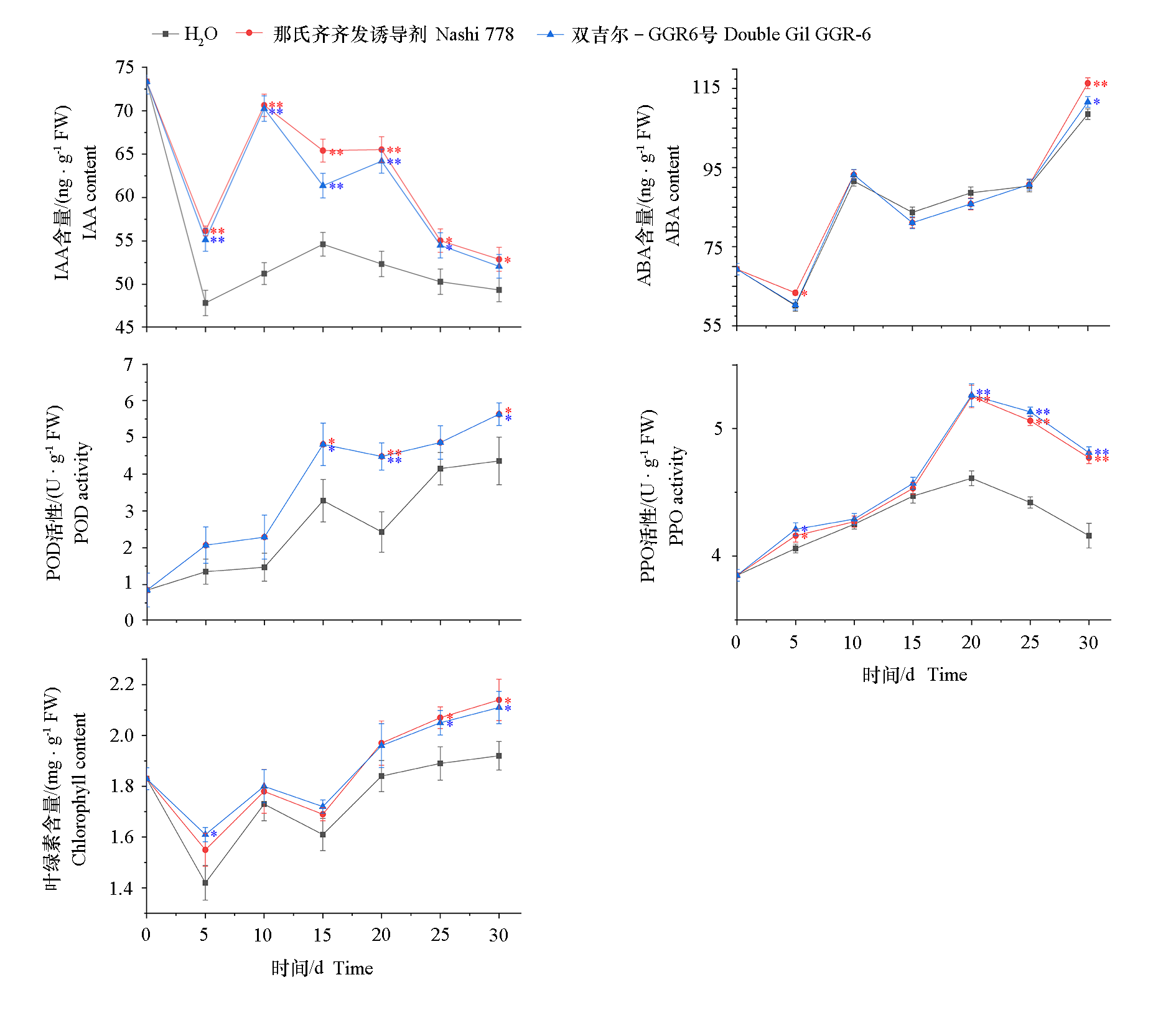
Fig. 4 Effects of rooting agent treatment on IAA,ABA,chlorophyll content,POD and PPO enzyme activities during the rooting process of chrysanthemum cuttings ** P < 0.01,* P < 0.05.
| 因素 Factor | 平均数Average | 极差 Extremely poor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O (对照Control) | 那氏齐齐发诱导剂 Nashi 778 | 双吉尔-GGR6号 Double Gil GGR-6 | ||
| 叶绿素/(mg · g-1)Chlorophyll | 1.74 | 1.87 | 1.88 | 0.15 |
| IAA/(ng · g-1) | 50.95 | 60.94 | 59.58 | 10.51 |
| ABA/(ng · g-1) | 87.15 | 88.42 | 87.12 | 1.75 |
| POD/(U · g-1) | 2.84 | 4.02 | 4.02 | 1.18 |
| PPO/(U · g-1) | 4.33 | 4.67 | 4.71 | 0.38 |
Table 4 The content of IAA,ABA and chlorophyll and the activities of POD and PPO enzymes in chrysanthemum cuttings treated with various rooting agents were extremely poor
| 因素 Factor | 平均数Average | 极差 Extremely poor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O (对照Control) | 那氏齐齐发诱导剂 Nashi 778 | 双吉尔-GGR6号 Double Gil GGR-6 | ||
| 叶绿素/(mg · g-1)Chlorophyll | 1.74 | 1.87 | 1.88 | 0.15 |
| IAA/(ng · g-1) | 50.95 | 60.94 | 59.58 | 10.51 |
| ABA/(ng · g-1) | 87.15 | 88.42 | 87.12 | 1.75 |
| POD/(U · g-1) | 2.84 | 4.02 | 4.02 | 1.18 |
| PPO/(U · g-1) | 4.33 | 4.67 | 4.71 | 0.38 |
| [1] |
|
|
陈晓峰. 2017. 苏州地区多本菊提高扦插成活率试验研究. 现代园艺,(12):6-8.
|
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
贺群. 2019. 外源吲哚乙酸对茶树响应镉胁迫的影响[硕士论文]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
黄正秉. 2011. 优质苗提升切花菊生产水平. 中国花卉报,2011-04-19.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
李合生. 2000. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
李燕, 孙玲, 方明慧, 金志刚. 2019. 赤霉素处理对甜叶菊扦插苗生根的影响初探. 南方农业, 13 (14):117-119.
|
|
| [7] |
|
|
刘萍, 徐克东, 孙莉萍, 丁义峰, 李娜, 李建平. 2007. PCT和N-(DH)AK对菊花水培扦插生理生化的影响. 北方园艺,(5):114-116.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
毛鹏飞, 郭巧生, 汪涛. 2012. 药用杭菊扦插育苗技术研究. 中草药, 43 (8):1611-1614.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
毛一. 2020. 菊花的繁殖与栽培技术要点浅析. 南方农业, 14 (14):5-6.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
裴红美, 张德平, 戴思兰. 2010. 3个中国传统菊花品种扦插繁殖试验. 中国园艺文摘, 26 (11):9-11.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
宋晓斌, 曹支敏, 张学武, 王云芳, 原双进. 2004. 双吉尔-GGR6对油松育苗的作用. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),(10):107-110.
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
王萍, 石鑫, 房伦革. 2012. 那氏齐齐发诱导剂在园林植物上的试验研究及推广应用. 农业科技与信息(现代园林),(4):82-89.
|
|
| [13] |
|
|
王文富, 舒符萝. 1964. 云南旱地红土的利用与改良. 土壤通报,(5):22-26.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
王绍弛. 2019. 食药两用菊花中多农药残留分析方法建立及应用[硕士论文]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
吴春花, 郑成淑, 李莲花, 苏艳敏, 安金花. 2001. IBA和NAA对菊花“秀芳力”扦插生根的影响. 延边大学农学学报,(1):54-57.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
吴颂如, 陈婉芬, 周燮. 1988. 酶联免疫法(ELSA)测定内源激素. 植物生理学通讯,(5):53-57.
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
徐东花. 2015. 亚精胺对菊花不定根发生及生根机理的研究[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
许蕊. 2021. 菊花穴盘扦插育苗技术要点. 南方农业, 15 (15):42-43.
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
杨雪萌. 2009. 菊花扦插生根技术和机理研究[硕士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
于玲, 党佳旗, 程美意, 刘旭富, 姜浩. 2022. 菊花应用价值调查研究. 现代园艺, 45 (13):21-23.
|
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0703 |
|
张会敏, 陈睿, 鲜小林. 2022. 中国功能菊花的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 38 (14):38-46.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0703 |
|
| [22] |
|
|
张黎, 翟彦. 2005. 不同基质不同部位对菊花扦插生根的影响. 西北农业学报,(6):112-114.
|
|
| [23] |
|
|
张颖, 王晓立, 王芳, 胡杰慧. 2017. NAA对菊花扦插繁殖的影响. 安徽农学通报, 23 (24):103-104.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
张远兵, 刘爱荣, 张雪平, 朱庆华, 韩志国. 2001. IAA、NAA和B对菊花扦插苗素质的影响. 安徽农业技术师范学院学报, 15 (1):23-25.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
张志良. 2003. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京:高等教育出版社:123-124,127-134.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
赵艳莉, 曹琴, 熊小强, 李战鸿. 2019. 促进金丝皇菊扦插生根的不同生根剂筛选试验. 农业科技通讯,(9):111-113.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
周凯, 王智芳, 郝峰鸽, 郭维明. 2010. 菊花不同部位及根际土壤水浸液对其扦插苗生长的自毒效应. 西北植物学报, 30 (4):762-768.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
朱维伟, 冯国建, 谭洋洋. 2022. 干湿循环下常春藤根系对云南红土的阻裂效应. 草原与草坪, 42 (2):107-111.
|
| [1] | ZHU Qixuan, LI Xiaoying, WU Junkai, GE Hang, CHEN Junwei, XU Hongxia. Genetic Tendency Analysis and Comprehensive Evaluation of the Fruit Traits in Loquat F1 Generation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1201-1215. |
| [2] | WANG Xiaolong, SHAO Xuedong, ZHANG Zhengwen, ZHONG Xiaomin, LIU Chang, WANG Zhiqiang, WANG Baoliang, JI Xiaohao, SHI Xiangbin, WANG Haibo. Correlation Analysis of Fruit Quality and the Nutrient Level in Plant and Soil of Wine Grape‘Merlot’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2575-2593. |
| [3] | LI Tingting, YUAN Weigao , ZHU Jinru , CAI Jianwu , DENG Weiping , and WU Chuping. A New Zelkova schneideriana Cultivar‘Wanlü’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(S1): 183-184. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xi, ZHAO Qiuyan, GU Zhijia, HUANG Haiquan, YAN Bo, HUANG Meijuan. Studies on Pollen Micromorphology of Impatiens Plants in Southwest Sichuan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(8): 1664-1678. |
| [5] | WANG Hongxiu, ZHOU Shangling, HE Shaoguo, TIAN Zaize, MA Jinghua, PENG Liangzhi, CHUN Changpin. Study on the Standard of Nutrient Elements Contents in Eureka Lemon Leaves [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1535-1546. |
| [6] | DUAN Kaihang, WANG Xiaoling, MAO Yongmin, WANG Yao, REN Yongxiang, REN Liuliu, SHEN Lianying. Analysis of Genetic Diversity of Wild Jujube Germplasm Resources Based on Quantitative Characters [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(12): 2568-2576. |
| [7] | CHEN Sijia, WANG Huan, LI Ruirui, WANG Zhuoyi, LUO Jing, WANG Caiyun. Characterization of CmMYC2 in Formation of Green Color in Ray Florets of Chrysanthemum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2377-2387. |
| [8] | HU Hao, YANG Ting, GAO Liping, Maarten A. Jongsma, WANG Caiyun. Cloning and Characterization of Key Synthase FAS Gene Involved in Terpenoids Pathway of Chrysanthemum morifolium [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(2): 313-324. |
| [9] | WANG Zhenjiang, LUO Guoqing, DAI Fanwei, XIAO Gengsheng, LIN Sen, LI Zhiyi, TANG Cuiming. Genetic Diversity of 569 Fruit Mulberry Germplasm Resources Based on Eight Agronomic Traits [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(12): 2375-2384. |
| [10] | TANG Xiaowei, SU Jiangshuo, GUAN Zhiyong, FANG Weimin, CHEN Fadi, ZHANG Fei. Comprehensive Evaluation of Tea Chrysanthemum’s Drought and Waterlogging Tolerance at Seedling Stage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(12): 2443-2457. |
| [11] | SUN Wei,YU Ruining,ZHANG Fei,JIANG Jiafu,CHEN Fadi,and FANG Weimin*. Quantitative Evaluation on Rooting Capacity for Cutting Propagation of Chrysanthemum [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(3): 540-548. |
| [12] | YAO Chenyang1,2,GE Hong2,WU Hua3,JIA Ruidong2,ZHAO Xin2,Lü Yingmin1,*,and YANG Shuhua2,*. Petal Volatile Components Among Different Varieties of Rosa rugosa [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(2): 375-384. |
| [13] | LIU Xin,LI Xiaotong,JING Xin,WANG Shuoshuo,GONG Biao,WEI Min,and SHI Qinghua*. Effect of S-adenosylmethionine on Growth and Physiological Metabolism of Cucumber Cutting Seedlings [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2018, 45(8): 1513-1522. |
| [14] | ZHANG Binbin1,2,SHEN Zhijun2,MA Ruijuan2,JIANG Hang2,YAN Juan2,and YU Mingliang1,2,*. Antioxidant Capacity Evaluation of Peach Fruit Based on Flesh Individual Phenol and Total Phenol Content [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2018, 45(5): 931-942. |
| [15] | ZOU Jingjing2,*,CAI Xuan1,*,ZENG Xiangling2,ZHENG Riru1,**,and WANG Caiyun1,**. Changes of Aroma-active Compounds in Different Cultivars of Osmanthus fragrans During Flowering [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2017, 44(8): 1517-1534. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd