
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 842-852.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1221
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
HOU Yixuan1,2,3, ZHANG Ling2,3,4, LÜ Mengwen2,3,5, WU Yaoxing1,2,3, WANG Liangsheng2,3,4, ZHANG Xiuqing1,*( ), LI Shanshan2,3,4,*(
), LI Shanshan2,3,4,*( )
)
Received:2022-10-17
Revised:2022-12-06
Online:2023-04-25
Published:2023-04-27
Contact:
*(E-mail:shshli@ibcas.ac.cn,18686081487@163.com)
CLC Number:
HOU Yixuan, ZHANG Ling, LÜ Mengwen, WU Yaoxing, WANG Liangsheng, ZHANG Xiuqing, LI Shanshan. Analysis of Volatile Components from the Petal of Intersectional Hybrids of Paeonia[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 842-852.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1221
| 成分 Compounds | 组间杂种 Intersectional hybrids | 合计 Total | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 | C12 | C13 | C14 | C15 | C16 | C17 | C18 | C19 | ||
| 单萜Monoterpenoids | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 桉叶油醇Eucalyptol | 0.01 | - | 1.03 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.04 |
| 芳樟醇Linalool | - | 5.74 | - | 30.40 | 8.13 | 0.21 | 11.13 | 18.38 | 12.19 | 5.53 | 6.53 | 26.10 | 30.75 | 3.00 | 18.69 | 3.14 | 23.48 | 17.24 | 18.52 | 239.16 |
| 香叶醇Geraniol | - | - | 13.60 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 13.60 |
| 香叶醛Geranial | - | - | 3.45 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3.45 |
| p-薄荷-1(7),8-二烯-2-醇p-mentha-1(7),8-dien-2-ol | - | - | - | - | - | 1.40 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.40 |
| 倍半萜Sesquiterpenoids | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 人参烯Panaginsene | 0.17 | 0.20 | - | 0.48 | 0.10 | - | 0.17 | - | - | 0.51 | 0.25 | - | 0.93 | 0.59 | 0.41 | - | - | 0.19 | 0.40 | 4.40 |
| β-愈创木烯β-Guaiene | - | 0.90 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.62 | 0.89 | - | 0.82 | 0.45 | 1.28 | - | - | 0.43 | - | 6.39 |
| 5,6-二氢-1,1,3,4-四甲基-(3aR,6aS)-1H,4H-3a,6a-丙戊烯 Modhephene | 0.48 | 0.93 | - | 2.10 | 0.41 | - | 0.65 | - | - | 1.83 | 0.93 | - | 3.82 | 2.17 | 1.21 | 1.75 | - | 0.63 | 1.42 | 18.33 |
| α-愈创木烯α-Guaiene | - | - | - | 2.76 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.76 |
| Ginsinsene | 0.29 | - | - | - | 0.30 | - | 0.64 | - | - | - | - | - | 3.70 | 1.98 | - | - | - | - | 1.34 | 8.25 |
| β-石竹烯 β-Caryophyllene | 1.61 | 1.16 | 3.73 | 42.58 | 2.27 | 2.42 | 8.26 | 3.51 | 1.73 | 33.83 | 7.88 | 4.07 | 48.63 | 15.12 | 10.20 | 43.86 | 1.85 | 2.57 | 11.57 | 246.85 |
| 大根香叶烯D Germacrene D | - | 0.94 | 0.18 | 8.52 | - | 0.19 | 2.83 | 0.28 | 0.06 | - | 0.77 | - | - | - | 0.57 | - | - | - | - | 14.34 |
| 蛇麻烯Humulene | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 2.99 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.63 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 1.46 | 0.38 | 0.16 | 2.74 | 0.69 | 0.45 | 1.84 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.44 | 12.72 |
| γ-雪松烯 γ-himachalene | - | 0.33 | 0.13 | 1.49 | - | 0.17 | 0.58 | 0.08 | - | - | 0.31 | - | - | - | 0.34 | - | - | - | - | 3.43 |
| 不规则萜类 Irregular terpenes | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (E)-4,8-二甲基-1,3,7-壬二烯(E)-4,8-Dimethylnona-1,3,7-Triene | - | - | - | 1.16 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.16 |
| 苯环型/苯丙素类 Benzenoids/ phenylpropanoids | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 苯甲醛Benzaldehyde | 0.39 | - | - | 0.79 | - | - | 0.10 | 0.39 | 0.91 | 1.30 | - | 3.71 | 0.57 | - | - | 2.09 | - | 1.93 | 1.63 | 13.81 |
| 水杨醛Salicylaldehyde | - | 0.21 | - | 0.72 | 1.88 | - | 0.23 | 0.64 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.28 | - | 1.60 | 0.50 | 0.66 | 7.72 |
| 苯乙醇2-Phenylethanol | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.95 | - | 0.85 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4.12 | - | - | 5.92 |
| 水杨酸甲酯 Methyl salicylate | 0.07 | - | 0.82 | 0.16 | 0.47 | - | 0.04 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.56 |
| 1,3,5-三甲氧基苯1,3,5-Trimethoxybenzene | 0.43 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.11 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.15 | 0.56 | - | - | - | - | 1.25 |
| 杂环Miscellaneous cyclic | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6,6-二甲基-双环[3.1.1]庚烷-2-甲醛6,6-Dimethyl-bicyclo[3.1.1]heptane-2-carboxaldehyde | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.09 | - | - | - | - | 1.09 |
| 10-羟基三环[4.2.1.1 (2,5)]癸-3-烯-9-酮10-Hydroxytricyclo[4.2.1.1 (2,5)]dec-3-en-9-one | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.42 | - | - | - | - | 2.42 |
| 脂肪族类Aliphatics | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 己醛Hexanal | 2.31 | - | 3.09 | 1.36 | 1.60 | 0.84 | - | 2.37 | 2.78 | - | - | 1.14 | - | - | - | 2.14 | - | - | 1.45 | 19.08 |
| 2-甲基-1-壬烯 2-Methyl-1-nonene | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.99 | - | - | - | - | 1.04 | - | 0.67 | - | - | 2.70 |
| (E)-2-己烯醛 (E)-2-Hexenal | 1.57 | - | 1.84 | 0.56 | 1.69 | 1.46 | - | 1.59 | 1.32 | - | - | - | 0.68 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10.71 |
| (E)-壬烯醛 (E)-2-Nonenal | 0.90 | - | 0.14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.04 |
| 十五烷Pentadecane | - | - | 4.42 | - | 0.33 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.80 | 3.36 | 0.20 | - | - | - | - | - | 9.11 |
| 十七烷Heptadecane | - | - | 0.53 | 0.75 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.16 | 0.84 | 0.17 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.45 |
Table 1 The components and contents of main volatiles in petals of 19 intersectional hybrids of Paeonia μg · g-1 · h-1
| 成分 Compounds | 组间杂种 Intersectional hybrids | 合计 Total | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 | C12 | C13 | C14 | C15 | C16 | C17 | C18 | C19 | ||
| 单萜Monoterpenoids | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 桉叶油醇Eucalyptol | 0.01 | - | 1.03 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.04 |
| 芳樟醇Linalool | - | 5.74 | - | 30.40 | 8.13 | 0.21 | 11.13 | 18.38 | 12.19 | 5.53 | 6.53 | 26.10 | 30.75 | 3.00 | 18.69 | 3.14 | 23.48 | 17.24 | 18.52 | 239.16 |
| 香叶醇Geraniol | - | - | 13.60 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 13.60 |
| 香叶醛Geranial | - | - | 3.45 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3.45 |
| p-薄荷-1(7),8-二烯-2-醇p-mentha-1(7),8-dien-2-ol | - | - | - | - | - | 1.40 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.40 |
| 倍半萜Sesquiterpenoids | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 人参烯Panaginsene | 0.17 | 0.20 | - | 0.48 | 0.10 | - | 0.17 | - | - | 0.51 | 0.25 | - | 0.93 | 0.59 | 0.41 | - | - | 0.19 | 0.40 | 4.40 |
| β-愈创木烯β-Guaiene | - | 0.90 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.62 | 0.89 | - | 0.82 | 0.45 | 1.28 | - | - | 0.43 | - | 6.39 |
| 5,6-二氢-1,1,3,4-四甲基-(3aR,6aS)-1H,4H-3a,6a-丙戊烯 Modhephene | 0.48 | 0.93 | - | 2.10 | 0.41 | - | 0.65 | - | - | 1.83 | 0.93 | - | 3.82 | 2.17 | 1.21 | 1.75 | - | 0.63 | 1.42 | 18.33 |
| α-愈创木烯α-Guaiene | - | - | - | 2.76 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.76 |
| Ginsinsene | 0.29 | - | - | - | 0.30 | - | 0.64 | - | - | - | - | - | 3.70 | 1.98 | - | - | - | - | 1.34 | 8.25 |
| β-石竹烯 β-Caryophyllene | 1.61 | 1.16 | 3.73 | 42.58 | 2.27 | 2.42 | 8.26 | 3.51 | 1.73 | 33.83 | 7.88 | 4.07 | 48.63 | 15.12 | 10.20 | 43.86 | 1.85 | 2.57 | 11.57 | 246.85 |
| 大根香叶烯D Germacrene D | - | 0.94 | 0.18 | 8.52 | - | 0.19 | 2.83 | 0.28 | 0.06 | - | 0.77 | - | - | - | 0.57 | - | - | - | - | 14.34 |
| 蛇麻烯Humulene | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 2.99 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.63 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 1.46 | 0.38 | 0.16 | 2.74 | 0.69 | 0.45 | 1.84 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.44 | 12.72 |
| γ-雪松烯 γ-himachalene | - | 0.33 | 0.13 | 1.49 | - | 0.17 | 0.58 | 0.08 | - | - | 0.31 | - | - | - | 0.34 | - | - | - | - | 3.43 |
| 不规则萜类 Irregular terpenes | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (E)-4,8-二甲基-1,3,7-壬二烯(E)-4,8-Dimethylnona-1,3,7-Triene | - | - | - | 1.16 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.16 |
| 苯环型/苯丙素类 Benzenoids/ phenylpropanoids | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 苯甲醛Benzaldehyde | 0.39 | - | - | 0.79 | - | - | 0.10 | 0.39 | 0.91 | 1.30 | - | 3.71 | 0.57 | - | - | 2.09 | - | 1.93 | 1.63 | 13.81 |
| 水杨醛Salicylaldehyde | - | 0.21 | - | 0.72 | 1.88 | - | 0.23 | 0.64 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.28 | - | 1.60 | 0.50 | 0.66 | 7.72 |
| 苯乙醇2-Phenylethanol | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.95 | - | 0.85 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4.12 | - | - | 5.92 |
| 水杨酸甲酯 Methyl salicylate | 0.07 | - | 0.82 | 0.16 | 0.47 | - | 0.04 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.56 |
| 1,3,5-三甲氧基苯1,3,5-Trimethoxybenzene | 0.43 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.11 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.15 | 0.56 | - | - | - | - | 1.25 |
| 杂环Miscellaneous cyclic | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6,6-二甲基-双环[3.1.1]庚烷-2-甲醛6,6-Dimethyl-bicyclo[3.1.1]heptane-2-carboxaldehyde | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.09 | - | - | - | - | 1.09 |
| 10-羟基三环[4.2.1.1 (2,5)]癸-3-烯-9-酮10-Hydroxytricyclo[4.2.1.1 (2,5)]dec-3-en-9-one | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.42 | - | - | - | - | 2.42 |
| 脂肪族类Aliphatics | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 己醛Hexanal | 2.31 | - | 3.09 | 1.36 | 1.60 | 0.84 | - | 2.37 | 2.78 | - | - | 1.14 | - | - | - | 2.14 | - | - | 1.45 | 19.08 |
| 2-甲基-1-壬烯 2-Methyl-1-nonene | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.99 | - | - | - | - | 1.04 | - | 0.67 | - | - | 2.70 |
| (E)-2-己烯醛 (E)-2-Hexenal | 1.57 | - | 1.84 | 0.56 | 1.69 | 1.46 | - | 1.59 | 1.32 | - | - | - | 0.68 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10.71 |
| (E)-壬烯醛 (E)-2-Nonenal | 0.90 | - | 0.14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.04 |
| 十五烷Pentadecane | - | - | 4.42 | - | 0.33 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.80 | 3.36 | 0.20 | - | - | - | - | - | 9.11 |
| 十七烷Heptadecane | - | - | 0.53 | 0.75 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.16 | 0.84 | 0.17 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.45 |
| 组间杂种 Intersectional hybrid | 萜类 Terpenoids | 苯环型/苯丙素类 Benzenoids/ phenylpropanoids | 脂肪酸衍生物 Fatty acid derivatives | 杂环类 Miscellaneous cyclics | 含氮类 Nitrogen-containings | 总数 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 9 | 5 | 14 | 5 | - | 33 |
| C2 | 10 | 1 | 3 | - | - | 14 |
| C3 | 7 | 3 | 5 | - | - | 15 |
| C4 | 9 | 5 | 4 | - | - | 18 |
| C5 | 6 | 2 | 4 | - | - | 12 |
| C6 | 8 | - | 2 | 1 | - | 11 |
| C7 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 24 |
| C8 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | 11 |
| C9 | 4 | 3 | 2 | - | - | 9 |
| C10 | 6 | 1 | 4 | - | - | 11 |
| C11 | 9 | - | - | - | - | 9 |
| C12 | 3 | 1 | 3 | - | - | 7 |
| C13 | 8 | 1 | 4 | - | - | 13 |
| C14 | 8 | 1 | 4 | - | 1 | 14 |
| C15 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 16 |
| C16 | 5 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 7 |
| C17 | 2 | 3 | 1 | - | - | 6 |
| C18 | 6 | 2 | - | - | - | 8 |
| C19 | 6 | 3 | 2 | - | - | 11 |
Table 2 Classification and the number of main volatile components in petals of 19 intersectional hybrids of Paeonia
| 组间杂种 Intersectional hybrid | 萜类 Terpenoids | 苯环型/苯丙素类 Benzenoids/ phenylpropanoids | 脂肪酸衍生物 Fatty acid derivatives | 杂环类 Miscellaneous cyclics | 含氮类 Nitrogen-containings | 总数 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 9 | 5 | 14 | 5 | - | 33 |
| C2 | 10 | 1 | 3 | - | - | 14 |
| C3 | 7 | 3 | 5 | - | - | 15 |
| C4 | 9 | 5 | 4 | - | - | 18 |
| C5 | 6 | 2 | 4 | - | - | 12 |
| C6 | 8 | - | 2 | 1 | - | 11 |
| C7 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 24 |
| C8 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | 11 |
| C9 | 4 | 3 | 2 | - | - | 9 |
| C10 | 6 | 1 | 4 | - | - | 11 |
| C11 | 9 | - | - | - | - | 9 |
| C12 | 3 | 1 | 3 | - | - | 7 |
| C13 | 8 | 1 | 4 | - | - | 13 |
| C14 | 8 | 1 | 4 | - | 1 | 14 |
| C15 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 16 |
| C16 | 5 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 7 |
| C17 | 2 | 3 | 1 | - | - | 6 |
| C18 | 6 | 2 | - | - | - | 8 |
| C19 | 6 | 3 | 2 | - | - | 11 |
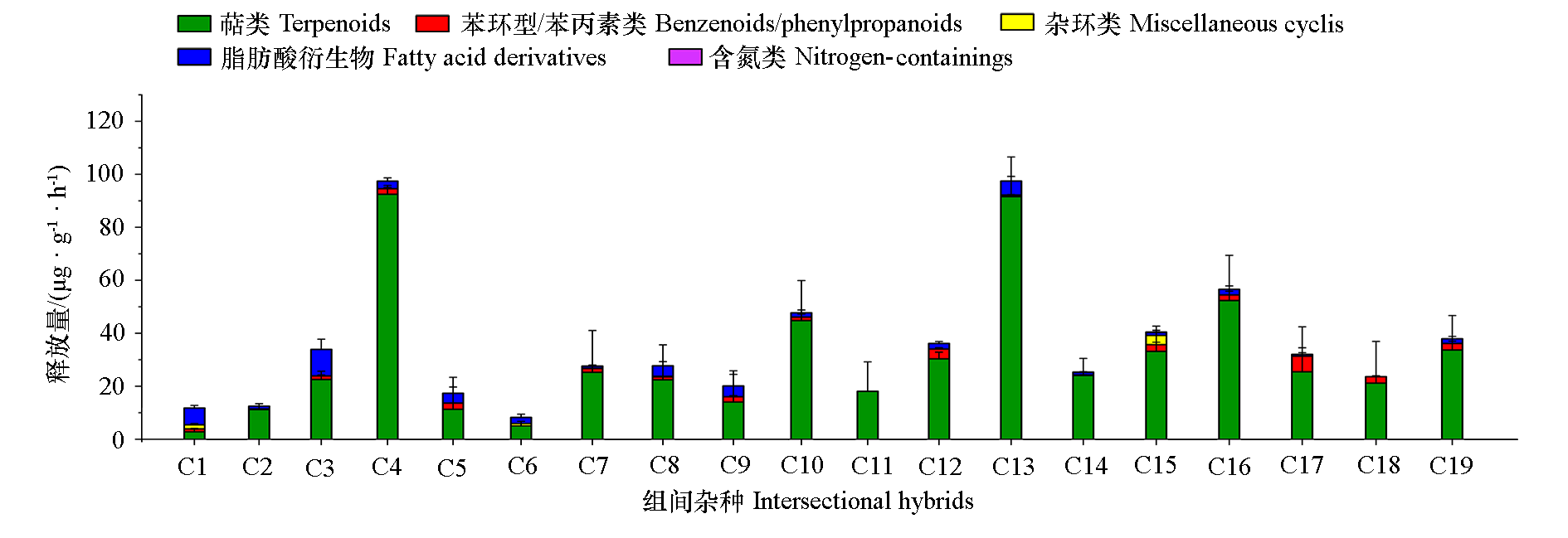
Fig. 2 The amounts of volatiles in 19 intersectional hybrids of Paeonia The names of intersectional hybrids of Paeonia represented by C1-C19 are the same as in Figure 1. The same below.
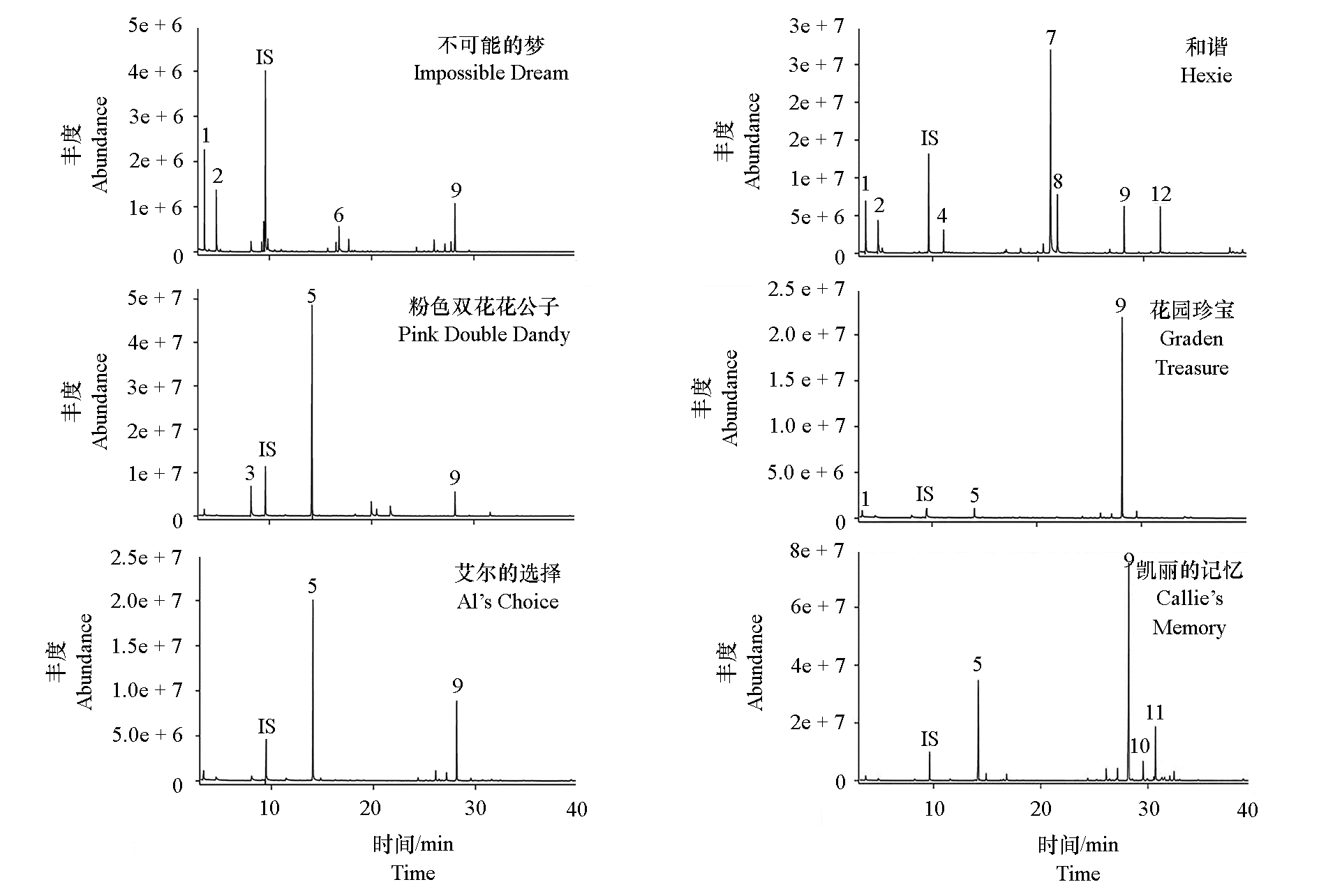
Fig.3 Total ionic chromatograms of volatile components in six intersectional hybrids of Paeonia IS:Internal Standard(3-octanol);1:Hexanal;2:(E)-2-Hexenal;3:Benzaldehyde;4:Eucalyptol;5:Linalool;6:(E)-2-Nonenal;7:Geraniol;8:Geranial;9:β-Caryophyllene;10:Humulene;11:Germacrene D;12:Pentadecane.
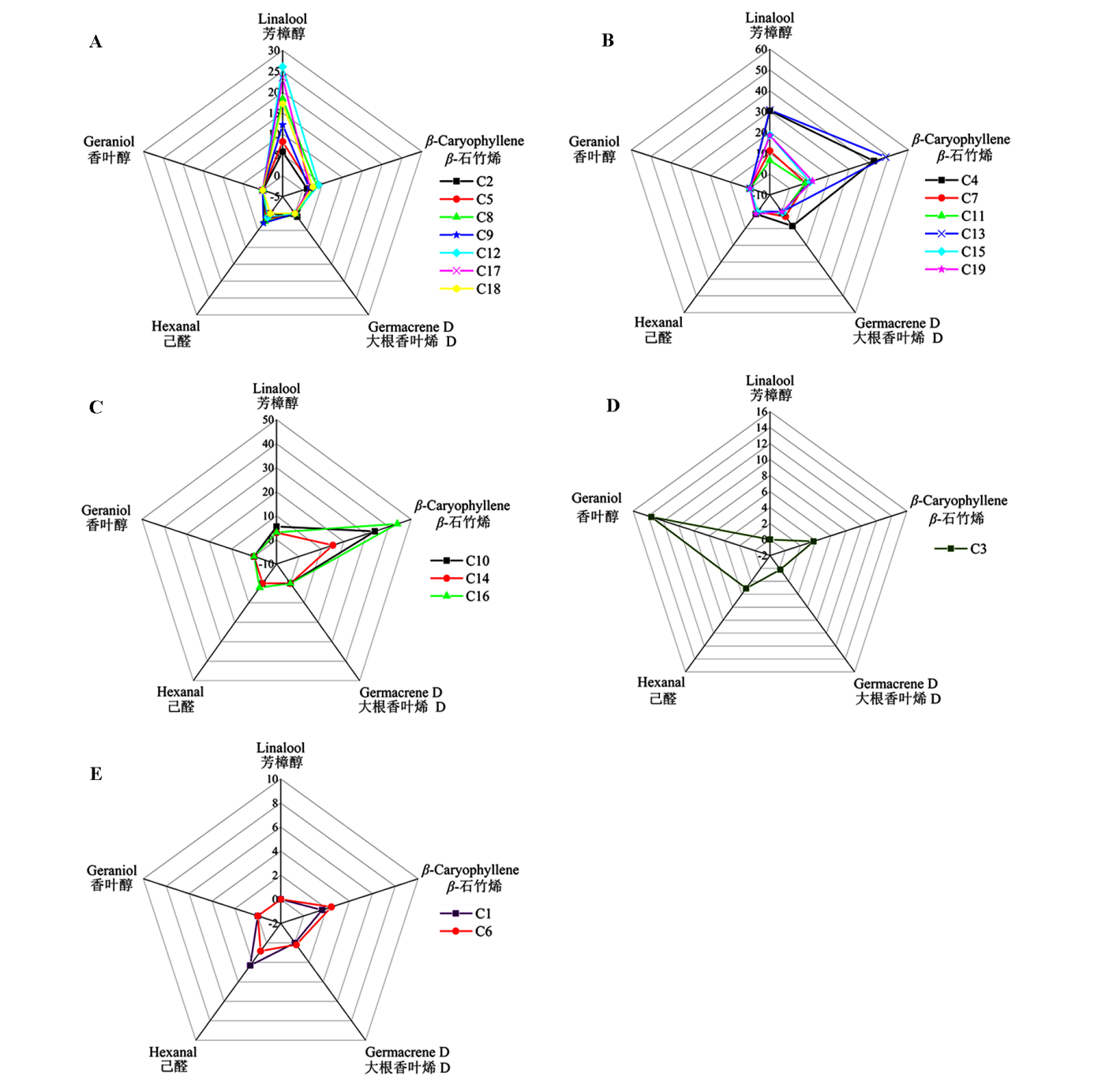
Fig. 4 Five groups classified according to the content of main volatiles among 19 intersectional hybrids of Paeonia A:β-Caryophyllene as the main volatile compounds;B:β-Caryophyllene and linalool as the main volatile compounds;C:Linalool as the main volatile compounds;D:Geraniol as the main volatile compounds;E:The contents are extremely low.
| [1] |
Dudareva N, Klempien A, Muhlemann J K, Kaplan I. 2013. Biosynthesis,function and metabolic engineering of plant volatile organic compounds. New Phytologist, 198 (1):16-32.
doi: 10.1111/nph.12145 pmid: 23383981 |
| [2] |
Fan Z Q, Li J Y, Li X L, Yin H F. 2019. Composition analysis of floral scent within genus Camellia uncovers substantial interspecific variations. Scientia Horticulturae, 250:207-213.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2019.02.050 URL |
| [3] |
Feng L G, Li Y M, Sheng L X, Li T L, Zhao D Q, Tao J. 2016. Comparative analysis of headspace volatiles of different herbaceous peony(Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) cultivars. Journal of Essential Oil Bearing Plants, 19 (1):167-175.
doi: 10.1080/0972060X.2014.1000391 URL |
| [4] |
Ghadiriasli R, Mahmoud M A A, Wagenstaller M, van de Kuilen J W, Buettner A. 2020. Molecular and sensory characterization of odorants in Cembran pine(Pinus cembra L.)from different geographic regions. Talanta, 220:121380.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121380 URL |
| [5] | He Gui-mei. 2006. Studies on distant cross-breeding and embryo in vitro culture and somatic embryogenesis in tree peonies[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. (in Chinese) |
| 何桂梅. 2006. 牡丹远缘杂交育种及其胚培养与体细胞胚发生的研究[博士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学. | |
| [6] |
Hu D, Guo J, Li T, Zhao M, Zou T, Song H, Alim A. 2019. Comparison and identification of the aroma-active compounds in the root of angelica dahurica. Molecules, 24 (23):4352.
doi: 10.3390/molecules24234352 URL |
| [7] | Li Jia-yu. 2005. China peony variety atlas:northwest,southwest,jiangnan volume. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. (in Chinese) |
| 李嘉珏. 2005. 中国牡丹品种图志:西北西南江南卷. 北京: 中国林业出版社. | |
| [8] |
Li Ruiya, Song Chengwei, Niu Tongfei, Wei Zhenzhen, Guo Lili, Hou Xiaogai. 2023. The emitted pattern analysis of flower volatiles and cloning of PsGDS gene in tree peony cultivar‘High Noon’. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 50 (2):331-344. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0870 |
|
李瑞雅, 宋程威, 牛童非, 魏祯祯, 郭丽丽, 侯小改. 2023. ‘海黄’牡丹花挥发性物质释放规律及PsGDS的克隆与表达分析. 园艺学报, 50 (2):331-344.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0870 URL |
|
| [9] |
Li S S, Chen L G, Xu Y J, Wang L J, Wang L S. 2012. Identification of floral fragrances in tree peony cultivars by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Scientia Horticulturae, 142:158-165.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2012.05.015 URL |
| [10] |
Li S S, Zhang L, Sun M, Lv M W, Yang Y, Xu W Z, Wang L S. 2023. Biogenesis of flavor-related linalool is diverged and genetically conserved in tree peony(Paeonia × suffruticosa). Horticulture Research, 10 (2):uhac253.
doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac253 URL |
| [11] | Liao Jian-jun, Qi Zeng-xiang, Li Tao, Wang Kuan. 2016. Research advances in volatile organic compounds in plant. Journal of University of South China(Science and Technology), 30 (3):119-123. (in Chinese) |
| 廖建军, 齐增湘, 李涛, 王宽. 2016. 植物挥发性有机物研究进展. 南华大学学报(自然科学版), 30 (3):119-123. | |
| [12] |
Luo X N, Yuan M, Li B J, Li C Y, Zhang Y L, Shi Q Q. 2019. Variation of floral volatiles and fragrance reveals the phylogenetic relationship among nine wild tree peony species. Flavour and Fragrance Journal, 35:227-241.
doi: 10.1002/ffj.v35.2 URL |
| [13] |
Mączka W, Wińska K, Grabarczyk M. 2020. One hundred faces of geraniol. Molecules, 25 (14):3303.
doi: 10.3390/molecules25143303 URL |
| [14] |
Muhlemann J K, Klempien A, Dudareva N. 2014. Floral volatiles:from biosynthesis to function. Plant Cell Environment, 37 (8):1936-1949.
doi: 10.1111/pce.12314 URL |
| [15] |
Noman A, Aqeel M, Deng J, Khalid N, Sanaullah T, Shuilin H. 2017. Biotechnological advancements for improving floral attributes in ornamental plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8:530.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00530 pmid: 28473834 |
| [16] |
Qiao Zhenglin, Hu Huizhen, Yan Bo, Chen Longqing. 2021. Advances of researches on biosynthesis and regulation of floral volatile benzenoids/phenylpropanoids. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (9):1815-1826. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0549 URL |
|
谯正林, 胡慧贞, 鄢波, 陈龙清. 2021. 花香挥发性苯/苯丙素类化合物的生物合成及基因调控研究进展. 园艺学报, 48 (9):1815-1826.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0549 URL |
|
| [17] |
Song C W, Wang Q, Teixeira da Silva J A, Yu X N. 2018. Identification of floral fragrances and analysis of fragrance patterns in herbaceous peony cultivars. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 143 (4):248-258.
doi: 10.21273/JASHS04420-18 URL |
| [18] | Wang Lian-ying. 2015. Sequel of Chinese Tree Peony. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. (in Chinese) |
| 王莲英. 2015. 中国牡丹品种图志:续著. 北京: 中国林业出版社. | |
| [19] | Wang Yue-lan. 2009. Cross-breeding in tree peony and fertility research of intersectional hybrids[M. D. Dissertation]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. (in Chinese) |
| 王越岚. 2009. 牡丹的杂交育种及组间杂种育性的研究[硕士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学. | |
| [20] | Xiang Lin, Chen Long-qing. 2009. Advances in genetic engineering of floral fragrance. Agricultural Sciences in China, 42 (6):2076-2084. (in Chinese) |
| 向林, 陈龙清. 2009. 花香的基因工程研究进展. 中国农业科学, 42 (6):2076-2084. | |
| [21] | Yu Xiao-nan. 2019. Herbaceous Peonies. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. (in Chinese) |
| 于晓南. 2019. 观赏芍药. 北京: 中国林业出版社. | |
| [22] |
Zhang Y, Li C, Wang S, Yuan M, Li B, Niu L, Shi Q. 2021a. Transcriptome and volatile compounds profiling analyses provide insights into the molecular mechanism underlying the floral fragrance of tree peony. Industrial Crops and Products, 162:113286.
doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113286 URL |
| [23] |
Zhang Y, Luo J, Zeng F. 2021b. Volatile composition analysis of tree peony(Paeonia section Moutan DC.)seed oil and the effect of oxidation during storage. Journal of Food Science, 86 (8):3467-3479.
doi: 10.1111/jfds.v86.8 URL |
| [24] | Zheng Wei-ying, Yu Zhi-gang, Chen Yan-hui, He Jing. 2016. Analysis of volatile components in five different varieties of paony flowers by HS-SPME/GC-MS. Chemical Research and Application, 28 (3):355-359. (in Chinese) |
| 郑伟颖, 俞志刚, 陈延辉, 何敬. 2016. HS-SPME/GC-MS法分析5个不同品种芍药花挥发性成分. 化学研究与应用, 28 (3):355-359. | |
| [25] | Zhong Yuan, Cheng Fang-yun, He Gui-mei, Gao Jing, Wang Rong, Du Xiujuan, Wang Yue-ying, Liu Yu-ying, Cao Xi-jun, Wang Ying. 2016. Five new peony cultivars bred from inter-sectional hybrids in Paeonia. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 52 (6):164. (in Chinese) |
| 钟原, 成仿云, 何桂梅, 高静, 王荣, 杜秀娟, 王越岚, 刘玉英, 曹羲君, 王莹. 2016. 5个芍药属组间杂交新品种. 林业科学, 52 (6):164. | |
| [26] |
Zhuang Yueying, Zhou Lijun, Cheng Bixuan, Yu Chao, Luo Le, Pan Huitang, Zhang Qixiang. 2021. Study on the fragrance metabolic genes of Rosa odorata based on transcriptome sequencing. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (11):2262-2274. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0944 URL |
|
庄玥莹, 周利君, 程璧瑄, 于超, 罗乐, 潘会堂, 张启翔. 2021. 基于转录组测序的香水月季花香代谢基因研究. 园艺学报, 48 (11):2262-2274.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0944 URL |
| [1] | WANG Xiaochen, NIE Ziye, LIU Xianju, DUAN Wei, FAN Peige, LIANG Zhenchang. Effects of Abscisic Acid on Monoterpene Synthesis in‘Jingxiangyu’Grape Berries [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 237-249. |
| [2] | QIANG Wenyan, MENG Qingran, ZHANG Zhiguo, GAO Wenjie. Analysis of Petal Volatile Components Among Different Hemerocallis Cultivars Based on HS-SPME-GC-MS [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 116-130. |
| [3] | ZHU Linlin, ZHOU Wanfei, NING Xuan, ZHU Jun, XI Wan, ZENG Xumei, XIONG Kangshun, WANG Caiyun, LUO Jing, ZHENG Riru. Analysis of Free Aromatic Components of Different Osmanthus fragrans Cultivars [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2395-2406. |
| [4] | CHU Sasa, FAN Xiangzhen, QIU Zhaokai, YANG Qi, ZHANG Yuting, WANG Yang, XU Xiaoshan, TONG Zaikang, ZHANG Junhong. Determination of Leaf Volatile Components from Five Phoebe Species [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(8): 1552-1564. |
| [5] | CHEN Zumin, XIAO Nuoya, ZHANG Yanxia, SHI Xiaomin, GUO Shuaiqi, GAO Hu, WANG Zhenping. Effects of Water Stress on the Volatile Compounds and Related Biosynthetic Genes Expression in‘Muscat Hamburg’Grape Berries [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(5): 883-896. |
| [6] | WANG Junwen, WU Yue, YU Jihua, ZHANG Jing, XIE Jianming, FENG Zhi, TANG Zhongqi, LIU Xiaoqi, LI Jing, ZHONG Yuan. Soluble Sugar,Organic Acid Quality and Volatile Compounds Contents in Tomato Fruits can be Promoted by Exogenous ALA [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(5): 973-986. |
| [7] | HU Hao, YANG Ting, GAO Liping, Maarten A. Jongsma, WANG Caiyun. Cloning and Characterization of Key Synthase FAS Gene Involved in Terpenoids Pathway of Chrysanthemum morifolium [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(2): 313-324. |
| [8] | ZHANG Haipeng1,LIU Cuihua2,LIU Yuan1,WEN Huan1,SHI Yaoqiang3,ZHANG Hongyan1,and XU Juan1,*. Research Advances of Volatile Terpenoids Metabolism in Citrus [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(8): 1610-1624. |
| [9] | DONG Fei1,WANG Chuanzeng2,SUN Xiudong1, ZHANG Qing3,DONG Yuhui1,WANG Lixia1,and LIU Shiqi1,*. Volatile Compounds in Tomato Fruits Under Different Light Qualities Revealed by Proteomic Analyses [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(2): 280-294. |
| [10] | LI Xiaoying1,WU JunKai1,WANG Haijing1,ZHANG Hongxia2,and GUO Xuemin2,*. Analysis of Volatile Components in Whorl Tepals of Magnolia denudata ‘Feihuang’During Its Development [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(10): 2009-2020. |
| [11] | ZHAO Hu*,TANG Kaijing,FAN Xiaoying,and Lü Weijian. High-throughput Transcriptome Sequencing and Primary Analysis of Terpenoids Metabolism in Toona sinensis‘Heiyouchun’Sprout [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2017, 44(11): 2135-2149. |
| [12] | WU Lei1,LIU Hong-ru1,CHEN Miao-jin2,WU Da-jun2,ZHANG Bo1,*,YIN Xue-ren1,XU Chang-jie1,and CHEN Kun-song1. Effects of Rain-shelter Cultivation on Formation of Peach Fruit Volatile Compounds [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2015, 42(3): 535-544. |
| [13] | WANG Hua-lei;FENG Jian-rong;FAN Xin-min;and HE Feng-jiang. Study on Volatile Constituents in Mainly Cultivated Apricot Native to Xinjiang [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2009, 36(7): 1043-1048. |
| [14] | ZHU Hong;CHEN Yu-fen;LI Xue-ping;LI Jun;HAN Dong-fang;and CHEN Wei-xin. Determ ina tion of Volatiles in Harvested Banana Fruit by HS-SPME andGC-MS [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2007, 34(2): 485-488. |
| [15] | ZHANG Ling-zhi;WANG Deng-liang;CHEN Wei-xin;and CHEN Yu-fen. Determination of Volatiles of Puer Tea Stored for Different Lengths of Time [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2007, 34(2): 504-506. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd