
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (10): 2255-2266.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0799
姚远1, 邓利君1, 胡娟2, 唐晓雨1, 王铁1, 李航1, 孙国超1, 熊博1, 廖玲1, 汪志辉1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-30
修回日期:2024-08-08
出版日期:2024-12-13
发布日期:2024-10-21
通讯作者:
基金资助:
YAO Yuan1, DENG Lijun1, HU Juan2, TANG Xiaoyu1, WANG Tie1, LI Hang1, SUN Guochao1, XIONG Bo1, LIAO Ling1, WANG Zhihui1,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-30
Revised:2024-08-08
Published:2024-12-13
Online:2024-10-21
摘要:
为揭示‘脆红李’早熟芽变形成的分子基础,采用高通量重测序技术对‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变材料进行了全基因组重测序,测序深度分别为19.40× 和22.82×,基因组覆盖度85%以上。与参考基因组相比,‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变分别检测到1 860 745和1 931 603个单核苷酸多态性点(SNP),419 134和444 892个小片段插入/缺失位点(InDel),其中发生在编码区的非同义突变位点分别为61 997个和63 498个。分析两者间的差异非同义突变,共引起2 391个基因变异。KEGG代谢通路富集分析发现,基因变异主要富集在真核生物核糖体生物发生、RNA运输、苯丙类生物合成、植物—病原体互作等途径上,此外在植物激素转导通路上共注释到12个变异基因。这些基因和其他相关基因变异后能影响其相应蛋白或酶的活性或特异性,从而导致生长发育过程发生变化,使‘脆红李’早熟芽变单株果实成熟期提前。
姚远, 邓利君, 胡娟, 唐晓雨, 王铁, 李航, 孙国超, 熊博, 廖玲, 汪志辉. ‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变全基因组重测序分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2255-2266.
YAO Yuan, DENG Lijun, HU Juan, TANG Xiaoyu, WANG Tie, LI Hang, SUN Guochao, XIONG Bo, LIAO Ling, WANG Zhihui. Whole Genome Resequencing Analysis of‘Cuihongli’Plum and Its Early-Ripening Bud Sport Mutation[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2255-2266.
| 样品 Sample | 原始测序序列 Raw read | 过滤后剩余序列 Clean read | 过滤剩余序列/% Clean reads rate | 含N > 5%的Reads/% Ns reads rate | Q30/% | GC含量/% GC content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脆红李 Cuihongli | 40 671 358 | 39 919 834 | 98.15 | 0.23 | 87.48 | 38.26 |
| 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 47 401 654 | 46 638 688 | 98.39 | 0.22 | 88.45 | 38.31 |
表1 ‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变单株基因组测序质量情况
Table 1 Clean data for genome sequencing of‘Cuihongli’plum and its early-ripening mutant single plant
| 样品 Sample | 原始测序序列 Raw read | 过滤后剩余序列 Clean read | 过滤剩余序列/% Clean reads rate | 含N > 5%的Reads/% Ns reads rate | Q30/% | GC含量/% GC content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脆红李 Cuihongli | 40 671 358 | 39 919 834 | 98.15 | 0.23 | 87.48 | 38.26 |
| 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 47 401 654 | 46 638 688 | 98.39 | 0.22 | 88.45 | 38.31 |
| 样品 Sample | Clean bases | Mapped bases | Mapped rate/% | Mean depth/× | Coverage 1×/% | Coverage 4×/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脆红李 Cuihongli | 5 987 975 100 | 5 513 839 633 | 92.08 | 19.40 | 92.03 | 85.67 |
| 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 6 995 803 200 | 6 489 148 161 | 92.76 | 22.82 | 92.30 | 86.83 |
表2 ‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变单株测序样本匹配基因组情况
Table 2 Sample alignment information of‘Cuihongli’plum and its early-ripening mutant single plant
| 样品 Sample | Clean bases | Mapped bases | Mapped rate/% | Mean depth/× | Coverage 1×/% | Coverage 4×/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脆红李 Cuihongli | 5 987 975 100 | 5 513 839 633 | 92.08 | 19.40 | 92.03 | 85.67 |
| 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 6 995 803 200 | 6 489 148 161 | 92.76 | 22.82 | 92.30 | 86.83 |
| 类别 Category | 脆红李 Cuihongli | 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 差异数 Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 总数 Total | 1 860 745 | 1 931 603 | 70 858 |
| 基因间区 Intergenic | 1 045 098(56.17%) | 1 093 864(56.63%) | 48 766 |
| 基因上游 Gene upstream | 167 118(8.98%) | 172 580(8.93%) | 5 462 |
| 基因下游 Gene downstream | 129 169(6.94%) | 132 864(6.88%) | 3 695 |
| 外显子 Exon | 118 505(6.37%) | 121 031(6.27%) | 2 526 |
| 内含子 Intron | 296 906(15.96%) | 304 915(15.79%) | 8 009 |
| UTR5′ | 24 210(1.30%) | 24 746(1.28%) | 536 |
| UTR3′ | 45 125(2.43%) | 45 988(2.38%) | 863 |
| 剪切区域 Splicing | 434(0.02%) | 464(0.02%) | 30 |
| 其他 Others | 34 180(1.83%) | 35 151(1.82%) | 971 |
表3 ‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变单株的SNP变异位点分布差异
Table 3 Differences of SNPs distribution in genome of‘Cuihongli’plum and its early-ripening mutant single plant
| 类别 Category | 脆红李 Cuihongli | 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 差异数 Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 总数 Total | 1 860 745 | 1 931 603 | 70 858 |
| 基因间区 Intergenic | 1 045 098(56.17%) | 1 093 864(56.63%) | 48 766 |
| 基因上游 Gene upstream | 167 118(8.98%) | 172 580(8.93%) | 5 462 |
| 基因下游 Gene downstream | 129 169(6.94%) | 132 864(6.88%) | 3 695 |
| 外显子 Exon | 118 505(6.37%) | 121 031(6.27%) | 2 526 |
| 内含子 Intron | 296 906(15.96%) | 304 915(15.79%) | 8 009 |
| UTR5′ | 24 210(1.30%) | 24 746(1.28%) | 536 |
| UTR3′ | 45 125(2.43%) | 45 988(2.38%) | 863 |
| 剪切区域 Splicing | 434(0.02%) | 464(0.02%) | 30 |
| 其他 Others | 34 180(1.83%) | 35 151(1.82%) | 971 |
| 样品 | 转换 | 颠换 | 转换/颠换 | 纯合 | 杂合 | 杂合率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Transition | Transvertion | Ts/Tv | Homozygosity | Heterozygosity | Het-ratio |
| 脆红李 Cuihongli | 1 159 670 | 701 075 | 1.654 | 670 867 | 1 189 878 | 63.95 |
| 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 1 204 261 | 727 342 | 1.656 | 683 247 | 1 248 356 | 64.63 |
表4 ‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变单株的SNP突变模式及杂合率
Table 4 Ts/Tv and Het-ratio of SNPs in genome of‘Cuihongli’plum and its early-ripening mutant single plant
| 样品 | 转换 | 颠换 | 转换/颠换 | 纯合 | 杂合 | 杂合率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Transition | Transvertion | Ts/Tv | Homozygosity | Heterozygosity | Het-ratio |
| 脆红李 Cuihongli | 1 159 670 | 701 075 | 1.654 | 670 867 | 1 189 878 | 63.95 |
| 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 1 204 261 | 727 342 | 1.656 | 683 247 | 1 248 356 | 64.63 |
| 样品 | 总数 | 非同义突变 | 同义突变 | 终止子出现 | 终止子缺失 | 未知类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Total | Nonsynonymous | Synonymous | Stopgain | Stoploss | Unknown |
| 脆红李 Cuihongli | 118 505 | 61 997 | 55 029 | 1 005 | 256 | 218 |
| 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 121 031 | 63 498 | 56 034 | 1 017 | 260 | 222 |
| 差异数 Difference | 2 526 | 1 501 | 1 005 | 12 | 4 | 4 |
表5 ‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变单株的编码区SNP变异类型
Table 5 Categories of SNPs in the coding region of‘Cuihongli’plum and its early-ripening mutant single plant
| 样品 | 总数 | 非同义突变 | 同义突变 | 终止子出现 | 终止子缺失 | 未知类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Total | Nonsynonymous | Synonymous | Stopgain | Stoploss | Unknown |
| 脆红李 Cuihongli | 118 505 | 61 997 | 55 029 | 1 005 | 256 | 218 |
| 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 121 031 | 63 498 | 56 034 | 1 017 | 260 | 222 |
| 差异数 Difference | 2 526 | 1 501 | 1 005 | 12 | 4 | 4 |
| 类别 Category | 脆红李 Cuihongli | 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 差异数 Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 总数 Total | 419 134 | 444 892 | 25 758 |
| 基因间区 Intergenic | 212 581(50.72%) | 227 768(51.20%) | 15 187 |
| 基因上游 Gene upstream | 49 018(11.70%) | 51 934(11.67%) | 2 916 |
| 基因下游 Gene downstream | 36 569(8.72%) | 38 302(8.61%) | 1 733 |
| 外显子 Exon | 9 718(2.32%) | 10 146(2.28%) | 428 |
| 内含子 Intron | 77 778(18.56%) | 81 847(18.40%) | 4 069 |
| UTR5 | 9 246(2.21%) | 9 628(2.16%) | 382 |
| UTR3 | 13 233(3.16%) | 13 768(3.09%) | 535 |
| 剪切区域 Splicing | 273(0.07%) | 292(0.07%) | 19 |
| 其他 Others | 10 718(2.54%) | 11 207(2.52%) | 489 |
表6 ‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变单株的InDel变异位点分布差异
Table 6 Differences of InDels distribution in genome of‘Cuihongli’plum and its early-ripening mutant single plant
| 类别 Category | 脆红李 Cuihongli | 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 差异数 Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 总数 Total | 419 134 | 444 892 | 25 758 |
| 基因间区 Intergenic | 212 581(50.72%) | 227 768(51.20%) | 15 187 |
| 基因上游 Gene upstream | 49 018(11.70%) | 51 934(11.67%) | 2 916 |
| 基因下游 Gene downstream | 36 569(8.72%) | 38 302(8.61%) | 1 733 |
| 外显子 Exon | 9 718(2.32%) | 10 146(2.28%) | 428 |
| 内含子 Intron | 77 778(18.56%) | 81 847(18.40%) | 4 069 |
| UTR5 | 9 246(2.21%) | 9 628(2.16%) | 382 |
| UTR3 | 13 233(3.16%) | 13 768(3.09%) | 535 |
| 剪切区域 Splicing | 273(0.07%) | 292(0.07%) | 19 |
| 其他 Others | 10 718(2.54%) | 11 207(2.52%) | 489 |
| 样品 Sample | 总数 Total | 移码突变 Frameshift | 非移码突变 Nonframeshift | 终止子出现 Stopgain | 终止子缺失 Stoploss | 未知 Unknown | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 插入 Insertion | 缺失 Deletion | 插入 Insertion | 缺失 Deletion | |||||
| 脆红李 Cuihongli | 9 718 | 1 780 | 4 787 | 1 245 | 1 524 | 243 | 123 | 16 |
| 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 10 146 | 1 867 | 4 954 | 1 338 | 1 576 | 262 | 129 | 20 |
| 差异数Difference | 428 | 87 | 167 | 93 | 52 | 19 | 6 | 4 |
表7 ‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变单株的编码区InDel功能注释及统计
Table 7 Function annotation and statistics of InDels in coding region of‘Cuihongli’plum and its early-ripening mutant single plant
| 样品 Sample | 总数 Total | 移码突变 Frameshift | 非移码突变 Nonframeshift | 终止子出现 Stopgain | 终止子缺失 Stoploss | 未知 Unknown | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 插入 Insertion | 缺失 Deletion | 插入 Insertion | 缺失 Deletion | |||||
| 脆红李 Cuihongli | 9 718 | 1 780 | 4 787 | 1 245 | 1 524 | 243 | 123 | 16 |
| 早熟芽变 Early-ripening mutant | 10 146 | 1 867 | 4 954 | 1 338 | 1 576 | 262 | 129 | 20 |
| 差异数Difference | 428 | 87 | 167 | 93 | 52 | 19 | 6 | 4 |
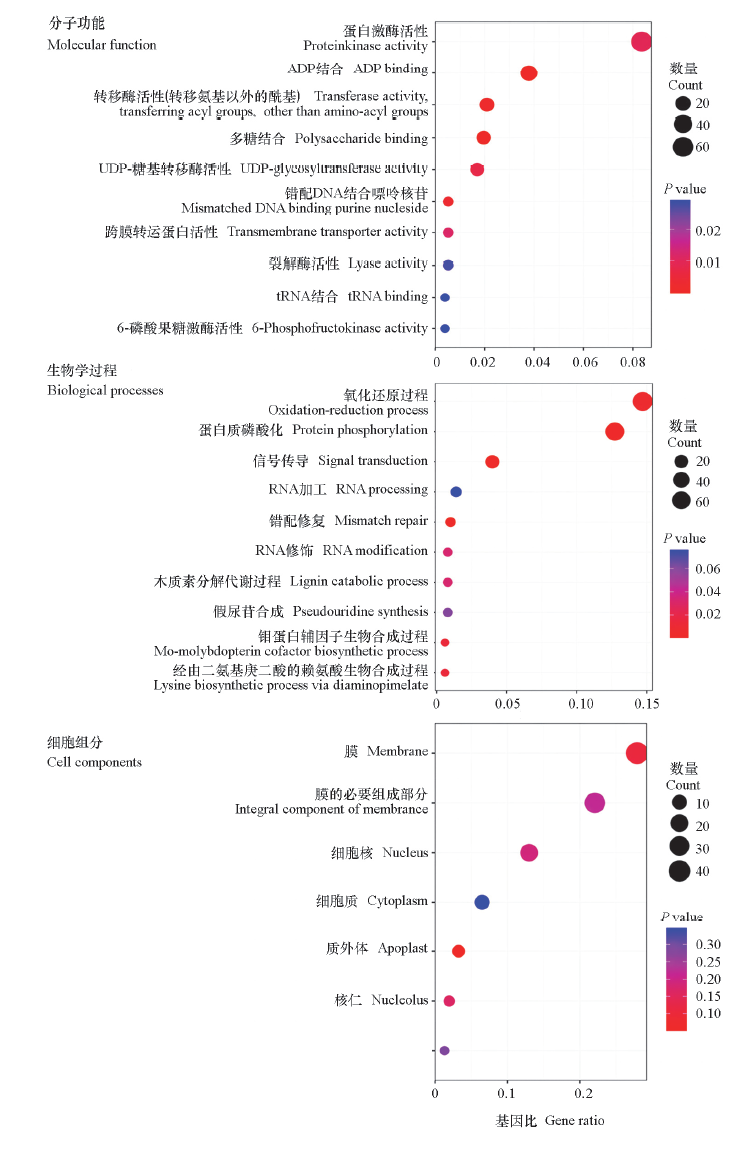
图2 ‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变单株差异基因GO注释与富集分析
Fig. 2 GO annotation and enrichment analysis of differential genes of‘Cuihongli’plum and its early-ripening mutant single plant
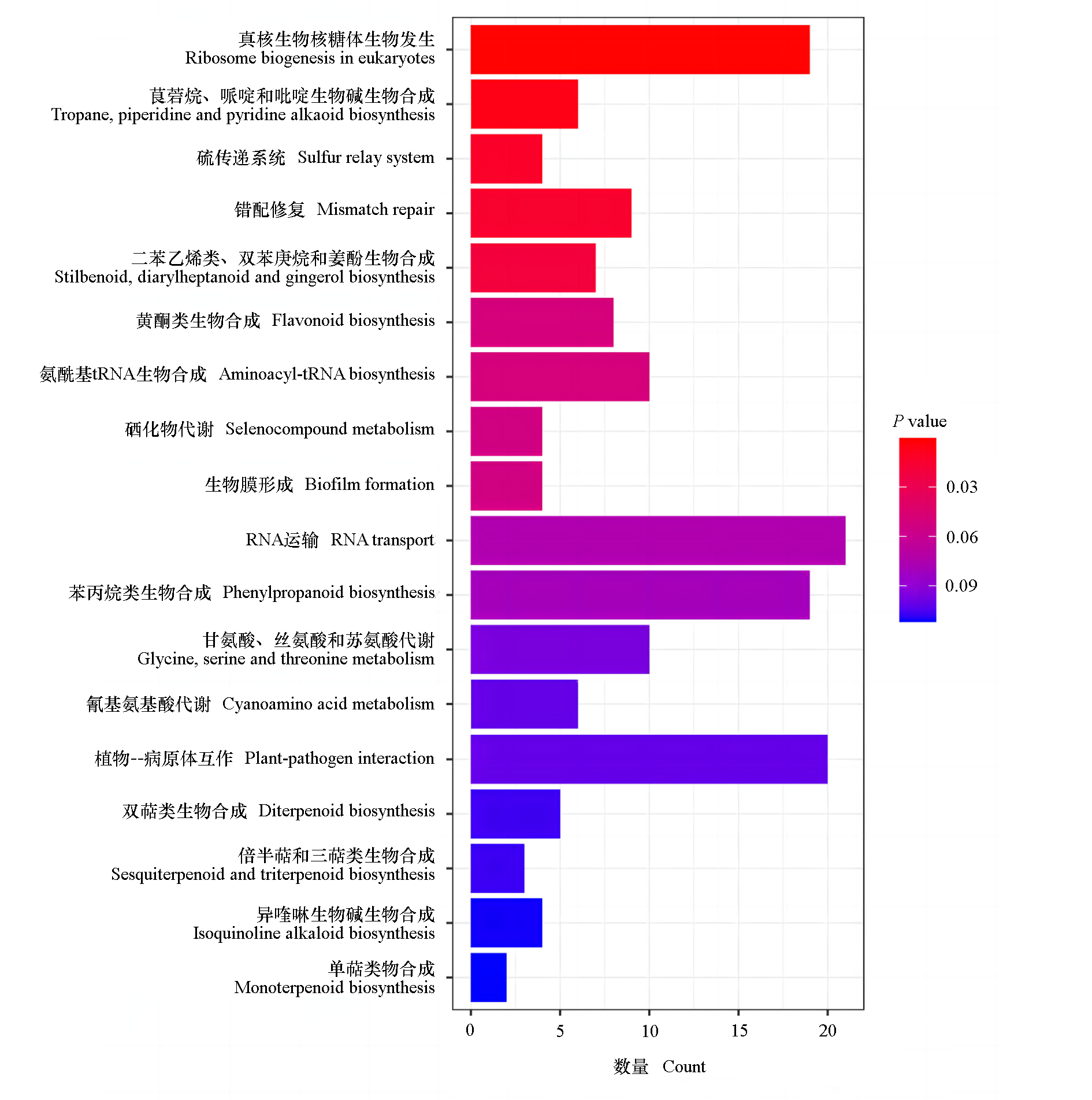
图3 ‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变单株差异基因的KEGG注释分类
Fig. 3 KEGG annotation classification of differential genes of‘Cuihongli’plum and its early-ripening mutant single plant

图4 植物激素信号转导通路示意图 红色标记:注释到的基因。+ p:磷酸化;- p:去磷酸化;+ u:泛素化。
Fig. 4 Plant hormone signaling pathway The red:The annotated gene. + p:Phosphorylation;- p:Dephosphorylation;+ u:Ubiquitylation.
| [1] |
doi: 10.1038/75556 pmid: 10802651 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
常爱玲. 2017. ‘无子瓯柑’InDel和SV标记开发[硕士论文]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
崔璐璐. 2021. 基于分子标记及基因组重测序的‘梨橙’遗传特性分析[硕士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2022.07.1339 |
|
董昳伶, 肖旭腾, 张敏, 沈乐意, 陈天池, 贾永红, 吴月燕. 2022. 环割对葡萄VvNCED基因的表达和果实成熟的影响. 核农学报, 36 (7):1339-1349.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2022.07.1339 |
|
| [6] |
|
|
葛宇, 徐梓宁, 马蔚红, 刘远征, 王步天, 刘毅. 2022. 基于重测序的不同生态型油梨的全基因组变异及进化分析. 热带农业科学, 42 (11):50-57.
|
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.04.006 pmid: 24954581 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
|
李兴武, 章黎黎. 2018. 不同杀菌方式对‘脆红李’低糖果酱营养成分和感官品质的影响. 食品研究与开发, 39 (11):70-75.
|
|
| [13] |
|
|
李兴武, 章黎黎. 2019. 热空气结合乙醇熏蒸保鲜‘脆红李’的工艺优化. 保鲜与加工, 19 (6):34-39.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
林瑶. 2019. 基于重测序的桃SSR位点分析及其在野生资源鉴定评价中的应用[硕士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
李菲菲. 2020. ‘早蜜’椪柑主要品质特征及其形成机理的研究[博士论文]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学.
|
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0549 |
|
谯正林, 胡慧贞, 鄢波, 陈龙清. 2021. 花香挥发性苯/苯丙素类化合物的生物合成及基因调控研究进展. 园艺学报, 48 (9):1815-1826.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0549 |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
王蒙召. 2016. 基因组重测序基础上的早实枳与普通枳部分差异基因比较分析[硕士论文]. 武汉:华中农业大学.
|
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0764 |
|
王智宇, 常贝贝, 刘琦, 程晓帆, 杜晓云, 于晓丽, 宋来庆, 赵玲玲. 2022. 苹果溶质转运蛋白基因MdSLC35F2-like表达与花青苷积累的研究. 园艺学报, 49 (11):2293-2303.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0764 |
|
| [25] |
|
|
魏潇, 章秋平, 吕春晶, 刘晶, 王杰, 杨巍. 2022. 基于重测序的‘香蕉李’及其晚熟芽变全基因组变异分析. 分子植物育种, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.s.20220624.1404.004.html.
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0288 |
|
张印, 胡路艳, 王淑明, 景丹龙, 郭启高, 梁国鲁. 2023. ABA调控果实成熟研究进展. 园艺学报, 50 (9):1889-1898.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0288 |
|
| [32] |
|
|
赵雨桐, 王巍, 穆佳琪, 杨海清, 刘悦萍. 2022. 桃果实成熟过程中激素相关基因表达模式分析. 北京农学院学报, 37 (3):1-8.
|
| [1] | 钟乙中, 汪州, 谢静瑶, 王钲彭, 郝静静, 刘朝阳, 张伟, 吴竞, 钟紫琴, 陈程杰, 何业华. 2个熟期不同的华南李品种在热带北界线附近地区的开花结果行为[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2105-2119. |
| [2] | 黄奕琦, 朱玉琴, 杜肇轩, 徐丰, 陈小怡, 杨国顺, 许延帅. 果树芽变机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1547-1564. |
| [3] | 张红, 王超楠, 范伟强, 黄志银, 刘晓晖, 李梅, 张斌. 早熟微型大白菜新品种‘津娃娃560’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2989-2990. |
| [4] | 岳林清, 吴怡超, 何星星, 向明燕, 王进, 武峥, 朱世国, 丁梦琦, 张建, 方小梅, 易泽林. 李资源果实主要性状的SSR标记关联分析及指纹图谱构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2495-2509. |
| [5] | 陈方策, 胡平正, 解为玮, 王钲彭, 钟创南, 李海炎, 何业华, 彭泽, 万保雄, 刘朝阳. 基于重测序的中国李基因组InDel标记的开发及应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2510-2522. |
| [6] | 刘艳飞, 何昕, 贺浩浩, 刘占德. 早熟黄肉中华猕猴桃新品种‘黑金’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2725-2726. |
| [7] | 雍明丽, 刘晓宏, 冯翠, 刘慧颖, 钱巍, 苏小俊. 早熟耐褐变丝瓜新品种‘苏丝5号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2477-2478. |
| [8] | 孙燕霞, 唐 岩, 刘大亮, 赵玲玲, 张学勇, 刘学卿, Dorota Ewa Kruczynska, 程志娟, Sylwia Keller-Przybylkowicz, 宋来庆, . 早熟苹果新品种‘烟青玉’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 3-4. |
| [9] | 蔚 露, 牛自勉, 郭文龙, 林 琭, 李 全, 李志强, 王红宁, 李鸿雁 . 早熟苹果新品种‘夏露’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 7-8. |
| [10] | 王富荣, 艾小艳, 王会良, 刘 勇, 朱 炜, 张 杨, 顾 霞, 刘模发, 诸小敏, 甘志猛, 何华平 , 龚林忠. 特早熟红肉油桃新品种‘楚红 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 19-20. |
| [11] | 吴伟民 , 王壮伟, 钱亚明, 王西成, 王 博, 闫莉春. 早熟鲜食葡萄新品种‘紫金红霞’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 25-26. |
| [12] | 赵婉彤 , 普金安 , 张翠英 , 杨兆贵 , 江 东 , . 早熟甜橙新品种‘新冰 30’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 33-34. |
| [13] | 张 艳 , 黎庭耀, 沈 卓, 杨 易, 周 轩, 吴增祥. 杂交一代菜薹新品种‘粤翠 1 号菜心’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 47-48. |
| [14] | 王 宏, 张 雅. 茄子新品种‘杭茄 2010’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 61-62. |
| [15] | 张红梅 , 单维奎 , 林大勇 , 张 威 , 王 琼 , 刘晓庆 , 崔晓艳 , 陈 新 , 陈华涛 , . 早熟春播菜用大豆新品种‘苏早 3 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 81-82. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司