
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (9): 2105-2119.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0865
钟乙中1,*, 汪州1,*, 谢静瑶2, 王钲彭1, 郝静静1, 刘朝阳1, 张伟1, 吴竞1, 钟紫琴1, 陈程杰1, 何业华1,**( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-20
修回日期:2024-07-05
出版日期:2024-09-25
发布日期:2024-09-19
通讯作者:
作者简介:*共同第一作者
基金资助:
ZHONG Yizhong1, WANG Zhou1, XIE Jingyao2, WANG Zhengpeng1, HAO Jingjing1, LIU Chaoyang1, ZHANG Wei1, WU Jing1, ZHONG Ziqin1, CHEN Chengjie1, HE Yehua1,**( )
)
Received:2024-03-20
Revised:2024-07-05
Published:2024-09-25
Online:2024-09-19
摘要:
李属于温带果树,南亚热带秋冬季高温气候对其正常生长发育产生严重影响。为探讨李在热带气候北界线附近的适应性,以2个成熟期不同的华南李品种‘从早1号’(三月李类型,早熟)和‘云开1号’(三华李类型,中熟)为材料,对其在广东省信宜市境内的花芽分化、开花、坐果及果实发育等开花结果行为开展了研究。结果表明:2个品种春梢的花芽形态分化都始于正造果成熟时(分别为4月20日、6月10日),单个花芽形态分化期约60 d;除春梢外,夏梢和秋梢亦能在当年启动并完成花芽分化过程。‘从早1号’和‘云开1号’新梢分别于7月中旬、8月下旬首次出现开花,此后持续到次年1月下旬的正常花期,整个花期长达6个月左右;按开花季节可划分为夏花(7月)、秋花(8—10月)、冬花(11—12月)、早花(1月中旬)和主花期(1月下旬至花期结束)等5个时期,2个品种副花期(7月—次年1月中旬)的开花量分别占18.83%和19.36%;夏花和秋花多畸形,不能正常坐果或不能正常发育;冬花果分别在2月初、3月初成熟,果实虽较小较酸,但仍具市场价值;早花果品质明显改善,具有较高商品价值,冬花果和早花果产量约占总产的5% ~ 10%。2个华南李品种在热带气候北界线附近表现出了花芽分化速度快、9月底前抽生的各级梢能完成花芽分化、花期与成熟期交错、成熟果与不同发育阶段幼果同枝等现象,其对秋冬季高温气候所展现的适应能力,可为李的设施栽培技术和华南李品种演化研究提供启发。
钟乙中, 汪州, 谢静瑶, 王钲彭, 郝静静, 刘朝阳, 张伟, 吴竞, 钟紫琴, 陈程杰, 何业华. 2个熟期不同的华南李品种在热带北界线附近地区的开花结果行为[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2105-2119.
ZHONG Yizhong, WANG Zhou, XIE Jingyao, WANG Zhengpeng, HAO Jingjing, LIU Chaoyang, ZHANG Wei, WU Jing, ZHONG Ziqin, CHEN Chengjie, HE Yehua. Flowering and Fruiting Behaviour of Two South China Plum Cultivars with Different Ripening Stages in an Area Near the Northern Boundary of the Tropics[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2105-2119.

图2 华南李腋芽发育及花芽分化过程的组织形态观察 A ~ E:‘从早1号’春梢展叶后60 d(4月10日)、70 d(4月20日)、85 d(5月5日)、100 d(5月20日)和130 d(6月20日)腋芽外部形态。A:“V”形区内为露出的叶芽先端;B:箭头所指为总芽鳞;C:腋芽分离为3个芽;D:花芽逐渐圆润饱满;E:花芽鳞片掉落,雌雄器官分化完毕。A1:未分化状态;B1:花芽分化始期;C1:小花分化期;D1:小花花器官原基分化期;E1:花芽中已经完成分化的2个小花原基。F ~ J:分别为‘云开1号’10月中旬的花束状枝、短枝春梢、长枝春梢、夏梢和秋梢上花芽分化的情况。
Fig. 2 Histomorphological observation of axillary bud development and the process of flower bud differentiation of south China plum A-E:External morphology of axillary buds of‘Congzao 1’at 60 d(10 April),70 d(20 April),85 d(5 May),100 d(20 May)and 130 d(20 June)after spring leaf expansion. A:Exposed leaf bud apex in the“V”shaped area;B:Total bud scale indicated by arrow;C:Axillary buds separate into three buds;D:Flower buds become gradually rounded and full;E:Flower bud scales fall off and differentiation of male and famle organs is complete;A1:Undifferentiated state;B1:Beginning of floral bud differentiation;C1:Floret differentiation;D1:Floret floral organ primordia differentiation;E1:Two floret primordia in the floral bud that have already completed differentiation. F-J:Flower bud differentiation on bouquet-like branches,short-branch spring tips,long-branch spring tips,summer tips and autumn tips of‘Yunkai 1’in mid-October,respectively.

图3 华南李‘从早1号’开花及果实发育动态与特征 A:7月15日部分花束状枝上叶片开始黄化脱落(白色箭头所指),花芽萌发产生的2朵夏花,基部有2 ~ 3枚苞叶(红色箭头所指);B:8月20日春梢上的早秋花;C:9月20日春梢1个花芽产生的2朵秋花;D:10月10日中枝春梢上2个花芽各自产生了3朵秋花(蕾);E:11月10日中枝春梢上不同时期的冬花蕾;F:12月15日春梢上的正常芽、花蕾和盛开的冬花,基部已无小苞叶;G:1月15日正在开放的早花;H:1月15日正造花的花蕾。A1:春梢上10月下旬的晚秋花坐果(11月10日);B1:春梢上的晚秋花果(11月20日);C1:春、夏梢上的晚秋花果和冬花果(12月15日);D1:1月15日春梢上的冬花果(果龄约70 d);E1:2月5日成熟的冬花果(果龄约90 d的红熟果、果龄约80 d的黄熟果)和正常开放的花;F1:3月10日长果枝成熟的早花果(黄红色)和正造果(绿色);G1:4月25日红熟的正造果。
Fig. 3 Dynamics and characteristics of flowering and fruit development in‘Congzao 1’plum A:Two summer flowers produced by sprouting flower buds with 2-3 bracts at the base of the flower(indicated by red arrows)on some bouquet-like branches(indicated by white arrows) starting to yellow and fall off on 15 July;B:Early autumn flowers on spring tips on 20 August;C:Two autumn flowers produced by 1 flower bud on a spring tips on 20 September;D:Two flower buds on spring tips of the mid-branch on 10 October each produced three autumn flowers(buds);E:Winter flower buds at various times on mid-branch spring tips on 10 November;F:Normal buds,buds,and blooming winter flowers on spring tips on 15 December,no longer with small bracts of leaves at the base;G:Early flowers that were opening on 15 January;H:Buds that were making flowers on 15 January. A1:Late autumn flowers on spring tips that were sitting in late October(10 November);B1:Late autumn flowers and fruits on spring tips(20 November);C1:Late autumn and winter flowering fruits on spring and summer tips(15 December);D1:Winter flowering fruits on spring tips on 15 January(about 70 d of fruit age);E1:Winter flowering fruits(red ripe fruits about 90 d of fruit age,yellow ripe fruits about 80 d of fruit age)and normal open flowers ripening on 5 February;F1:Early flowering fruits(yellowish-red)and normal season fruits(green)ripening on long fruiting shoots on 10 March;G1:Red ripe normal season fruits ripening on 25 April.

图4 华南李‘云开1号’不同时期的开花结果状态 A:10月15日春梢上的秋花和正常芽;B:11月15日春梢上的芽、冬花和秋花果(果龄约1个月);C1:12月15日正常的花束状枝(左箭头所指)、长枝(红框内枝段,为春梢)和二次枝(右箭头所指,为夏梢)的发育状态;C2:12月15日中枝上的芽、冬花和幼果(果龄约1 ~ 2个月);D1:1月15日春梢上正造花芽;D2:1月15日春梢及其二次枝(夏梢)不同开花状态的早花;D3:1月15日短枝上的果实(果龄约3个月)和萌动的花芽;E:2月5日正造花和果实(果龄约2.5个月);F1:3月10日成熟的冬花果(果龄约4个月);F2:3月10日的不同生长发育阶段的幼果(果龄1.0 ~ 2.5个月);G:4月15日成熟的早花果(果龄约4个月)和主花期的幼果(果龄约2个月);H:5月15日成熟的早花果(1月中旬坐果)和主花期的幼果(果龄约3个月)。
Fig. 4 Flowering and fruiting states of‘Yunkai 1’plum at different periods A:Autumn flowers and normal buds on October 15th on the spring shoots;B:Buds,winter flowers,and autumn fruit(fruit age approximately 1 month)on November 15th on the spring shoots. C1:Developmental state of normal bouquet-shaped branches(indicated by left arrow),long branches (branches in red boxes are spring tips),and secondary branches(indicated by right arrow,representing summer tips)on December 15th.C2:Buds,winter flowers,and young fruit(fruit age approximately 1-2 months)on the mid-shoots on December 15th. D1:Flower buds forming on the spring shoots on January 15th. D2:Early flowers in different blooming states on the spring shoots and secondary branches(summer shoots)on January 15th. D3:Fruits(fruit age approximately 3 months)and budding flower buds on the short shoots on January 15th.E:Developing flowers and fruits(fruit age approximately 2.5 months)on February 5th. F1:Mature winter fruits(fruit age approximately 4 months)on March 10th. F2:Immature fruits at different stages of growth and development(fruit age 1.0-2.5 months)on March 10th.G:Mature early fruits(fruit age approximately 4 months)and young fruits during the main flowering period(fruit age approximately 2 months)on April 15th. H:Mature early fruits(set in mid-January)and young fruits during the main flowering period(fruit age approximately 3 months)on May 15th.

图5 2个华南李品种的开花坐果动态 开花率(%)= 当月开花的花芽数/花芽总数 × 100;坐果率(%)= 坐果数/当月开花数 × 100,以谢花后20 d为准。‘从早1号’主花期从1月21日开始,‘云开1号’主花期从1月25日开始。
Fig. 5 Flowering and fruiting dynamics of two cultivars of South China plum Flowering rate(%)= number of flowering buds/total number of buds × 100;Fruiting rate(%)= number of fruit sittings/number of flowering buds in the month × 100,based on 20 d after flower shedding. The main flowering period started from 21st January for the‘Congzao 1’,and from 25th January for the‘Yunkai 1’.
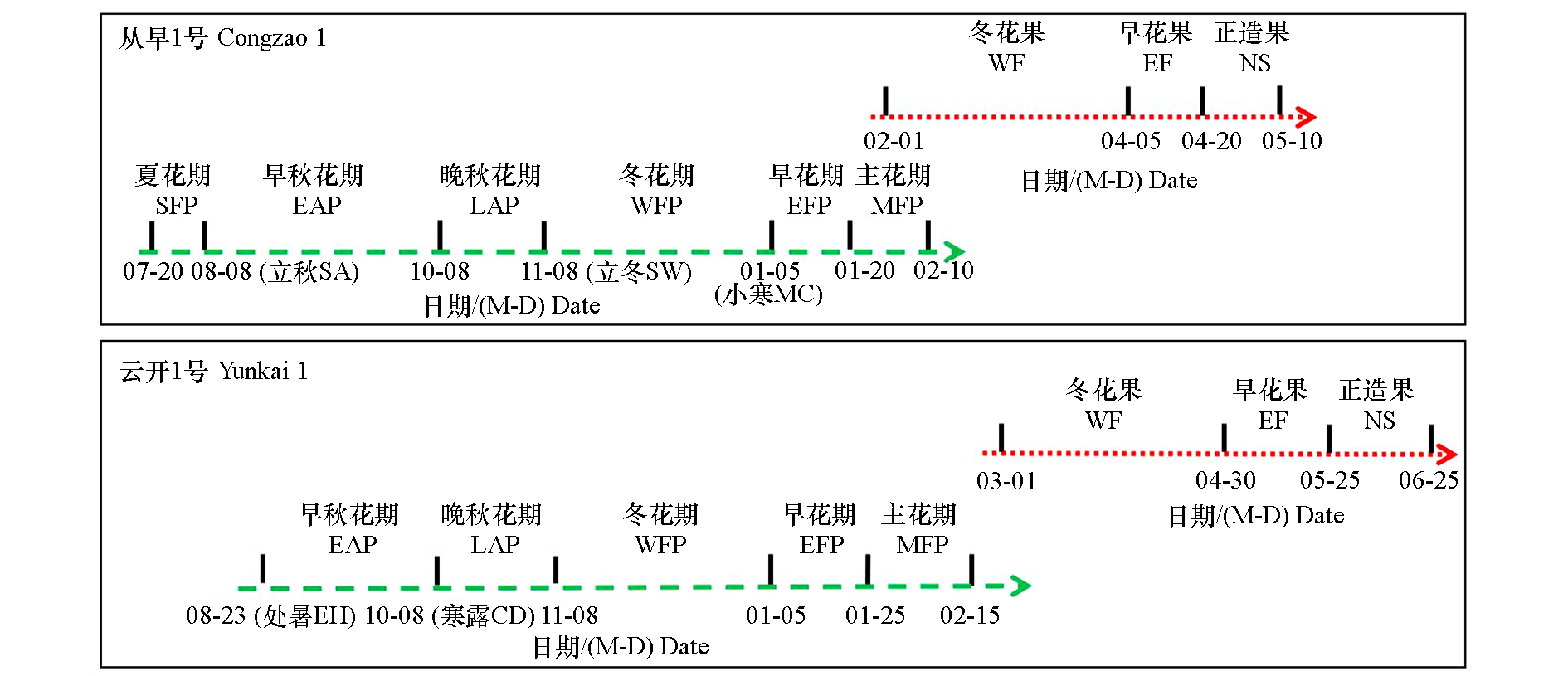
图6 2个华南李品种在广东信宜开花时期及果实成熟类型的划分
Fig. 6 Division of flowering period and fruit maturation types for two South China plum cultivars in Xinyi,Guangdong SFP:Summer flowering period;EAP:Early autumn blooming period;LFP:Late flowering period;WFP:Winter flowering period;EFP:Early flowering period;MFP:Main flowering period;WF:Fruits of winter flowers;EF:Early-flowering fruit;NS:Normal season fruit;SA:Start of autumn;SW:Start of winter;MC:Minor cold;EH:End of heat;CD:Cold dew.
| 品种 Cultivar | 采收时间/(M-D) Harvest time | 单果质量/g Single fruit weight | 总酸/% Total acidity | 可溶性糖/% Soluble sugar | 可溶性固形物/% TSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 从早1号 | 02-15 | 8.6 | 2.2 | 4.0 | 6.3 |
| Congzao 1 | 03-15 | 15.8 | 1.9 | 4.3 | 7.2 |
| 04-15(正造果 Normal season fruits) | 25.3 | 1.7 | 5.3 | 8.0 | |
| 云开1号 | 03-15 | 28.5 | 1.7 | 4.8 | 7.4 |
| Yunkai 1 | 04-15 | 40.8 | 1.4 | 5.3 | 8.0 |
| 05-15 | 50.8 | 1.3 | 6.0 | 8.8 | |
| 06-15(正造果 Normal season fruits) | 52.7 | 1.1 | 7.5 | 11.2 |
表1 2个华南李品种不同时间成熟的果实品质比较
Table 1 Comparison of fruit quality of two cultivars of South China plums ripening at different times
| 品种 Cultivar | 采收时间/(M-D) Harvest time | 单果质量/g Single fruit weight | 总酸/% Total acidity | 可溶性糖/% Soluble sugar | 可溶性固形物/% TSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 从早1号 | 02-15 | 8.6 | 2.2 | 4.0 | 6.3 |
| Congzao 1 | 03-15 | 15.8 | 1.9 | 4.3 | 7.2 |
| 04-15(正造果 Normal season fruits) | 25.3 | 1.7 | 5.3 | 8.0 | |
| 云开1号 | 03-15 | 28.5 | 1.7 | 4.8 | 7.4 |
| Yunkai 1 | 04-15 | 40.8 | 1.4 | 5.3 | 8.0 |
| 05-15 | 50.8 | 1.3 | 6.0 | 8.8 | |
| 06-15(正造果 Normal season fruits) | 52.7 | 1.1 | 7.5 | 11.2 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
蔡兴元, 虞锦星. 1984. 李花芽分化物候期的观察. 中国果树,(2):15-16.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
陈杰忠. 2011. 果树栽培学各论. 北京: 中国农业出版社.
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
Editorial Committee of Flora of China. 1986. Flora Reipublicase Popularis Sinicae. Beijing:Science Press. (in Chinese)
|
|
中国植物志编辑委员会. 1986. 中国植物志. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
|
郝静静. 2020. 李PsMYB-75的功能鉴定及李花芽萌动前后差异基因筛选[硕士论文]. 广州: 华南农业大学.
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
郝静静, 何业华, 杨向晖, 潘建君, 徐荣波, 彭伟卓, 刘朝阳. 2019. 广东冬季低温不足对‘三月李’和‘三华李’开花结果的影响//中国园艺学会2019年学术年会暨成立90周年纪念大会. 郑州:中国园艺学会:2509.
|
|
| [13] |
|
|
何大章, 何东. 1988. 我国热带气候的北界问题. 地理学报, 43 (2):176-182.
doi: 10.11821/xb198802010 |
|
| [14] |
|
|
何业华, 韩景忠, 刘成明, 林顺权, 胡桂兵, 欧阳若, 叶自行, 余小玲, 谢志亮, 徐永炉, 何海波, 张利添. 2009a. 南亚热带李新品种‘华蜜大蜜李’. 园艺学报, 36 (11):1709-1710.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
何业华, 谢志亮, 刘成明, 林顺权, 胡桂兵, 欧阳若, 叶自行, 余小玲, 韩景忠, 徐永炉, 何海波, 何永胜. 2009b. 南亚热带李新品种‘白脆鸡麻李’. 园艺学报, 36 (12):1837-1838.
|
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0067 |
|
何业华, 杨向晖, 栾爱萍, 刘成明, 胡桂兵, 林顺权, 秦永华, 夏靖娴, 傅嘉欣, 赵杰堂, 高用顺, 张志珂, 温瑞明, 陈世凯, 罗学优, 池琼云, 卢仕威. 2020. 华南李新品种‘云开1号’. 园艺学报, 47 (S2):2891-2892.
|
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1093/treephys/25.1.109 pmid: 15519992 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpx169 pmid: 29370432 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
李楚豪. 2018. 广东省主要李种质收集评价及基于果实性状和SNP的分类[硕士论文]. 广州: 华南农业大学.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
梁艳, 刘德强, 潘朋, 张妍, 唐美璇. 2022. 带有愈伤组织的红松种子石蜡切片制作方法改良. 分子植物育种, 20 (13):4455-4461.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
刘振亚. 1981. 两汉时期黄河中下游果树秋花冬实原因的探讨. 河南农学院学报, 12 (1):80-85.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
龙兴桂, 冯殿齐, 苑兆和, 林顺权, 颜昌瑞. 2020. 中国现代果树栽培(上). 北京:中国农业出版社:480-499.
|
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1126/science.171.3966.29 pmid: 17737985 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.111.181982 pmid: 21795580 |
| [30] |
|
|
时晓芳, 韦荣福, 黄桂媛, 张瑛, 林玲, 韩佳宇, 曹雄军, 周思泓, 王博, 白先进, 郭荣荣. 2021. 矮壮素处理促进葡萄二季果成花的分子机制研究. 果树学报, 38 (2):153-167.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
帅焕丽, 杨途熙, 魏安智, 王佳, 李晓, 张莹. 2011. 杏花芽石蜡切片方法的改良. 果树学报, 28 (3):536-539.
|
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
|
涂翠琴, 裘敏和, 过文珍, 任寿金. 1995. 李树花芽分化观察. 果树科学,(12):116-118.
|
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
|
王晴芳, 周级, 肖春桥, 葛双桃. 2000. 砂梨资源返青二次开花调查及其预防. 中国南方果树, 29 (2):44.
|
|
| [38] |
|
|
魏雅君, 廖康, 李雯雯, 冯贝贝, 徐业勇, 王明, 杨红丽, 牛莹莹. 2017. 杏李花芽分化的组织解剖学研究. 果树学报, 34 (7):843-850.
|
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
|
张超, 刘玉平. 2014. 苹果二次开花的原因与防控技术. 北方果树,(2):29-30.
|
|
| [43] |
|
|
张加延, 何跃, 李体智, 彭晓东, 郭忠仁, 李峰. 1988. 我国热带——亚热带地区李的种质资源及地理分布. 山西果树,(3):11-14.
|
|
| [44] |
|
|
张加延, 周恩. 1998. 中国果树志 · 李卷. 北京: 中国林业出版社.
|
|
| [45] |
|
|
张林平, 杨建民, 白志英, 黄文玉. 1998. 大石早生李花芽分化研究. 河北林果研究, 13 (2):174-177.
|
|
| [46] |
|
|
张全军. 2015. 砂梨二次花发生的生理特征及基因表达谱分析[博士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学.
|
|
| [47] |
|
|
钟乙中. 2022. 李翻花现象的调查及PsDAM6在调控李休眠中的作用[硕士论文]. 广州: 华南农业大学.
|
|
| [48] |
|
|
周光理. 2020. 食品分析与检验技术(4版). 北京: 化学工业出版社.
|
|
| [49] |
|
|
周俊辉. 1999. 果树的多次开花结实现象. 江西农业学报, 11 (4):64-68.
|
| [1] | 赵静一, 吴小旭, 胡云捷, 盖淑婷, 朱志浩, 秦蕾, 王勇. 洋葱AcGAI的克隆及其在开花途径的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1792-1802. |
| [2] | 文宋琴, 李佳霖, 池卓恒, 夏燕, 王淑明, 吴頔, 郝雅雯, 郭启高, 梁国鲁, 景丹龙. 光和温度对开花时间基因可变剪接的影响研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1949-1963. |
| [3] | 熊志伟, 李智龙, 尹晖, 高玉霞. 柑橘黄龙病菌亚洲种的泛基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 737-747. |
| [4] | 岳林清, 吴怡超, 何星星, 向明燕, 王进, 武峥, 朱世国, 丁梦琦, 张建, 方小梅, 易泽林. 李资源果实主要性状的SSR标记关联分析及指纹图谱构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2495-2509. |
| [5] | 陈方策, 胡平正, 解为玮, 王钲彭, 钟创南, 李海炎, 何业华, 彭泽, 万保雄, 刘朝阳. 基于重测序的中国李基因组InDel标记的开发及应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2510-2522. |
| [6] | 姚远, 邓利君, 胡娟, 唐晓雨, 王铁, 李航, 孙国超, 熊博, 廖玲, 汪志辉. ‘脆红李’及其早熟芽变全基因组重测序分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2255-2266. |
| [7] | 关夏玉, 陈细红, 郭菁, 吕浩阳, 梁晨媛, 高芳銮. 建兰花叶病毒的遗传变异及其寄主适应性[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 203-212. |
| [8] | 裴芸, 虞夏清, 赵晓坤, 张万萍, 陈劲枫. 多倍化与植物新表型关联性的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1854-1866. |
| [9] | 张悦, 张云春, 党江波, 林授锴, 吴頔, 景丹龙, 郭启高, 梁国鲁, 向素琼. 枇杷花序发育及形成机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1929-1943. |
| [10] | 潘佳佳, 张东梅, 孟建, 高苏南, 朱凯杰, 刘军伟, 李国怀. 李坏死环斑病毒诱导的桃PpPDS沉默体系的优化及验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1587-1600. |
| [11] | 陈欣晨, 赵慧敏, 王森, 邬思敏, 向林, 产祝龙, 王艳平. 不同温度对郁金香花芽分化的影响及相关基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1037-1047. |
| [12] | 严娟, 赵滨涛, 孙朦, 宋宏峰, 蔡志翔, 李垍峣, 宿子文, 张明昊, 沈志军, 许建兰, 马瑞娟, 俞明亮. 基于桃需冷量探讨气温变化对其适应性的挑战[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 724-736. |
| [13] | 宋艳红, 陈亚铎, 张晓玉, 宋盼, 刘丽锋, 李刚, 赵霞, 周厚成. 森林草莓FvbHLH130转录因子调控植株提前开花[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 295-306. |
| [14] | 何业华, 潘建君, 杨向晖, 刘朝阳, 李楚豪, 夏靖娴, 张伟, 彭伟卓, 郝静静, 徐荣波, 孔文辉, 钟乙中. 李新品种‘从早1号早李'[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(12): 2765-2766. |
| [15] | 杨禹妍, 段新圆, 何治霖, 邴起浩, 陈锁英, 刘晓曼, 曾明, 刘小刚. 金柑UDP-鼠李糖合成酶基因的克隆与功能解析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1663-1672. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司