
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 724-736.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1297
严娟1,*, 赵滨涛1,2,*, 孙朦1, 宋宏峰1, 蔡志翔1, 李垍峣1,2, 宿子文1,2, 张明昊3, 沈志军1, 许建兰1, 马瑞娟1, 俞明亮1,**( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-01
修回日期:2022-11-29
出版日期:2023-04-25
发布日期:2023-04-27
作者简介:第一联系人:*共同第一作者
基金资助:
YAN Juan1,*, ZHAO Bintao1,2,*, SUN Meng1, SONG Hongfeng1, CAI Zhixiang1, LI Jiyao1,2, SU Ziwen1,2, ZHANG Minghao3, SHEN Zhijun1, XU Jianlan1, MA Ruijuan1, YU Mingliang1,**( )
)
Received:2022-09-01
Revised:2022-11-29
Online:2023-04-25
Published:2023-04-27
摘要:
以12个地理位置和气候类型不同的地区2011—2021年气温数据为基本资料,通过0 ~ 7.2 ℃模型对各地区用于打破桃休眠的累积冷量(h)进行评估,同时统计已报道的基于0 ~ 7.2 ℃模型估算的589份桃品种资源的需冷量,分析各地区气温变化情况及其对冷量积累的影响,研判各地区桃品种资源面临的适应性挑战,并提出应对策略。研究结果表明,10年间,在11月初至翌年3月底(桃需冷量积累时间段),12个地区的气温均逐年升高,平均升高2 ℃,部分年份气温波动大。各地区冷量积累差异明显。随着纬度降低,冷量起始日期由早到迟,结束日期则由迟到早,冷量积累时间逐渐减少;各地平均累积冷量4.5 ~ 1 315 h,逐年降低趋势较明显,且纬度越低,降低趋势越明显。另外,气候带类型也对冷量累积有影响。累积冷量降低对各地桃的适应性产生了轻度、中度或重度影响。基于以上结果,对各地适宜生长的桃需冷量区间范围进行了预判,具体为:北京、蒙阴、郑州和南京以 < 1 000 h为宜,上海和杭州以600 ~ 700 h为宜,桂林以 < 400 h为宜,文山和古田以 < 200 h为宜(古田一些高海拔区域需冷量400 h的桃也可适应),福州以 < 100 h为宜,广州以 < 50 h为宜,海南需要基本不休眠、常绿类型的桃。未来桃产业发展需要加大低需冷量桃种质的创制和品种选育,优化主产区品种布局,合理制定南延栽培计划。
中图分类号:
严娟, 赵滨涛, 孙朦, 宋宏峰, 蔡志翔, 李垍峣, 宿子文, 张明昊, 沈志军, 许建兰, 马瑞娟, 俞明亮. 基于桃需冷量探讨气温变化对其适应性的挑战[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 724-736.
YAN Juan, ZHAO Bintao, SUN Meng, SONG Hongfeng, CAI Zhixiang, LI Jiyao, SU Ziwen, ZHANG Minghao, SHEN Zhijun, XU Jianlan, MA Ruijuan, YU Mingliang. Adaptability of Peach Under Air Temperature Change Based on Chilling Requirment[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 724-736.
| 地点 Region | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 气候类型 Climate type | 海拔/m Altitude | 站点号 Site number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北京Beijing | 40°08′ | 116°58′ | 内陆温带季风 Continental temperate monsoon | 35.35 | 54511099999 |
| 山东蒙阴 Mengyin,Shandong | 36°18′ | 118°15′ | 内陆温带季风 Continental temperate monsoon | 302.00 | 54836099999 |
| 郑州Zhengzhou | 34°52′ | 113°84′ | 内陆温带季风 Continental temperate monsoon | 150.87 | 57083099999 |
| 南京Nanjing | 31°74′ | 118°86′ | 内陆亚热带季风 Continental subtropical monsoon | 14.93 | 58238099999 |
| 上海Shanghai | 31°20′ | 121°33′ | 沿海亚热带季风Coastal subtropical monsoon | 3.04 | 58367099999 |
| 杭州Hangzhou | 30°23′ | 120°43′ | 沿海亚热带季风 Coastal subtropical monsoon | 7.01 | 58457099999 |
| 福建古田 Gutian,Fujian | 26°63′ | 118°15′ | 内陆亚热带季风 Continental subtropical monsoon | 153.00 | 58834099999 |
| 福州Fuzhou | 26°08′ | 119°28′ | 沿海亚热带海洋季风 Continental subtropical marine monsoon | 85.00 | 58847099999 |
| 广西桂林 Guilin,Guangxi | 25°22′ | 110°04′ | 内陆亚热带季风 Continental subtropical monsoon | 173.73 | 57957099999 |
| 云南文山 Wenshan,Yunnan | 24°07′ | 105°07′ | 内陆高原中亚热带季风 Continental plateau mid-subtropical monsoon | 1 251.00 | 59007099999 |
| 广州Guangzhou | 23°39′ | 113°30′ | 沿海亚热带季风 Coastal subtropical monsoon | 15.24 | 59287099999 |
| 海南Hainan | 19°93′ | 110°46′ | 沿海热带季风 Coastal tropical monsoon | 22.86 | 47031199999 |
表1 各地区气象站点信息
Table 1 Information of meteorological stations in tested regions
| 地点 Region | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 气候类型 Climate type | 海拔/m Altitude | 站点号 Site number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北京Beijing | 40°08′ | 116°58′ | 内陆温带季风 Continental temperate monsoon | 35.35 | 54511099999 |
| 山东蒙阴 Mengyin,Shandong | 36°18′ | 118°15′ | 内陆温带季风 Continental temperate monsoon | 302.00 | 54836099999 |
| 郑州Zhengzhou | 34°52′ | 113°84′ | 内陆温带季风 Continental temperate monsoon | 150.87 | 57083099999 |
| 南京Nanjing | 31°74′ | 118°86′ | 内陆亚热带季风 Continental subtropical monsoon | 14.93 | 58238099999 |
| 上海Shanghai | 31°20′ | 121°33′ | 沿海亚热带季风Coastal subtropical monsoon | 3.04 | 58367099999 |
| 杭州Hangzhou | 30°23′ | 120°43′ | 沿海亚热带季风 Coastal subtropical monsoon | 7.01 | 58457099999 |
| 福建古田 Gutian,Fujian | 26°63′ | 118°15′ | 内陆亚热带季风 Continental subtropical monsoon | 153.00 | 58834099999 |
| 福州Fuzhou | 26°08′ | 119°28′ | 沿海亚热带海洋季风 Continental subtropical marine monsoon | 85.00 | 58847099999 |
| 广西桂林 Guilin,Guangxi | 25°22′ | 110°04′ | 内陆亚热带季风 Continental subtropical monsoon | 173.73 | 57957099999 |
| 云南文山 Wenshan,Yunnan | 24°07′ | 105°07′ | 内陆高原中亚热带季风 Continental plateau mid-subtropical monsoon | 1 251.00 | 59007099999 |
| 广州Guangzhou | 23°39′ | 113°30′ | 沿海亚热带季风 Coastal subtropical monsoon | 15.24 | 59287099999 |
| 海南Hainan | 19°93′ | 110°46′ | 沿海热带季风 Coastal tropical monsoon | 22.86 | 47031199999 |
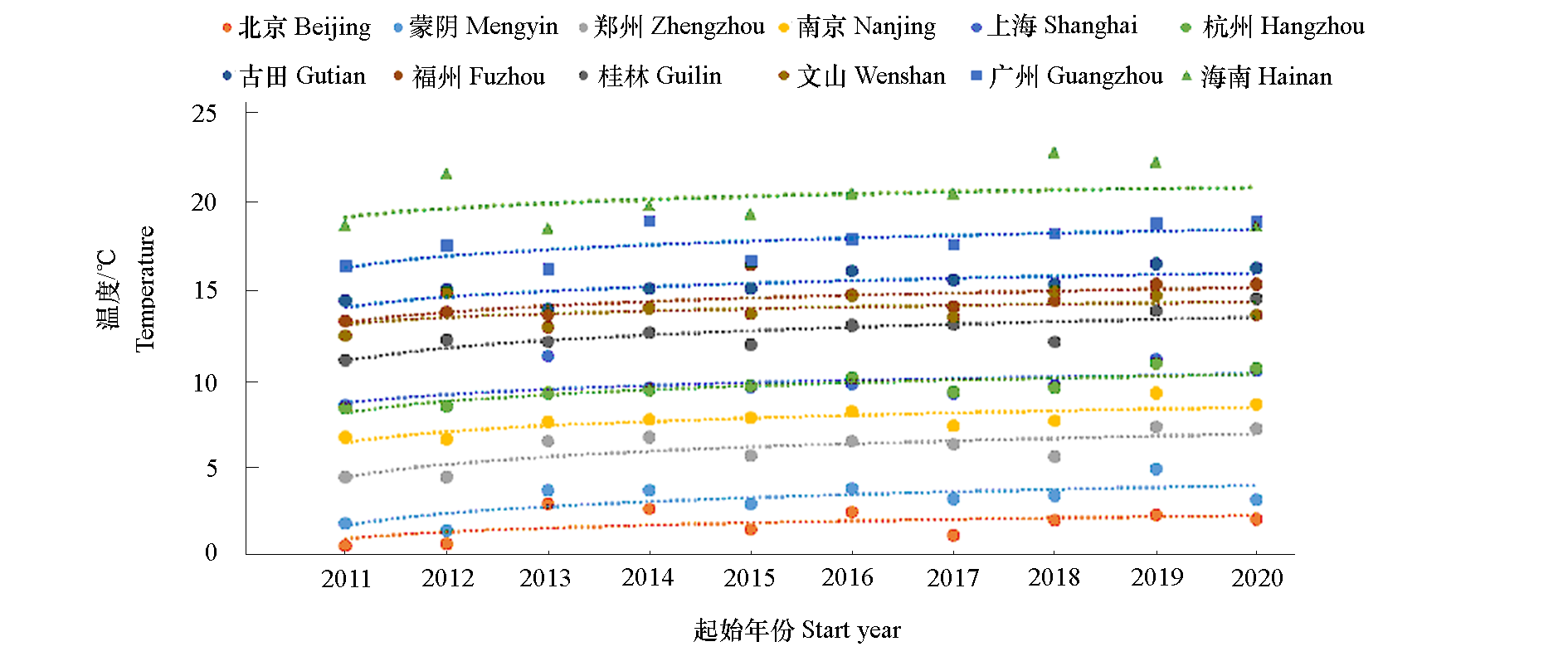
图1 12个地区近10年11月1日—翌年3月31日气温变化 虚线为根据气温变化拟合的对数趋势线。
Fig. 1 Air temperature change from 1st Nov. to 31st Mar. of the next year in recent 10 years in 12 regions The dotted lines in the figure were the logarithmic trend line fitted according to the temperature change.
| 地区 Region | 起始日期/结束日期/区间天数/d Start date/end date/interval days | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011—2012 | 2012—2013 | 2013—2014 | 2014—2015 | 2015—2016 | ||
| 北京Beijing | 11-13/03-22/131 | 11-03/03-31/149 | 11-17/03-13/117 | 11-07/03-15/129 | 11-06/03-17/133 | |
| 蒙阴Mengyin | 11-20/03-26/128 | 11-04/03-27/144 | 11-10/03-15/126 | 11-16/03-15/120 | 11-17/03-17/122 | |
| 郑州Zhengzhou | 11-23/03-22/121 | 11-23/03-26/124 | 11-19/03-09/111 | 11-27/03-12/106 | 11-22/03-01/101 | |
| 南京Nanjing | 11-30/03-14/106 | 11-24/03-21/118 | 12-06/03-08/93 | 12-01/03-13/103 | 11-24/02-26/95 | |
| 上海Shanghai | 12-01/03-13/104 | 12-04/03-04/91 | 11-27/03-11/105 | 12-01/03-11/101 | 12-04/03-14/102 | |
| 杭州Hangzhou | 11-30/03-14/106 | 12-07/03-04/88 | 12-09/03-14/96 | 12-01/03-11/101 | 11-26/03-15/110 | |
| 古田Gutian | 12-23/02-29/68 | 12-30/02-13/44 | 12-19/02-21/65 | — | 01-22/02-17/27 | |
| 福州Fuzhou | 01-04/02-28/56 | — | 02-09/02-21/13 | — | — | |
| 桂林Guilin | 01-03/03-10/68 | 12-18/03-03/76 | 12-20/03-09/79 | 01-28/03-08/40 | 01-12/02-27/47 | |
| 文山Wenshan | 12-09/03-13/96 | 12-29/02-22/56 | 12-15/02-21/69 | 12-11/02-12/64 | 12-15/02-27/75 | |
| 广州Guangzhou | — | — | 02-09/02-20/12 | — | 01-23/02-03/12 | |
| 海南Hainan | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 北京Beijing | 11-01/03-24/144 | 11-03/03-13/131 | 11-13/03-24/132 | 11-18/03-16/120 | 11-02/03-21/140 | |
| 蒙阴Mengyin | 11-22/03-17/116 | 11-17/03-23/127 | 12-03/03-14/102 | 11-25/03-15/112 | 11-19/03-22/124 | |
| 郑州Zhengzhou | 11-21/03-08/108 | 11-29/03-09/101 | 12-04/03-11/98 | 11-29/03-06/96 | 11-20/03-02/103 | |
| 南京Nanjing | 11-22/03-02/101 | 11-30/03-11/102 | 12-06/03-04/89 | 11-27/03-11/105 | 11-27/03-09/103 | |
| 上海Shanghai | 12-14/03-17/94 | 12-05/03-10/96 | 12-06/03-08/93 | 12-18/02-20/65 | 12-13/03-09/87 | |
| 杭州Hangzhou | 12-14/03-16/93 | 12-01/03-21/111 | 12-06/03-10/95 | 12-18/03-06/80 | 12-13/03-09/87 | |
| 古田Gutian | — | 01-08/02-14/38 | 12-29/01-25/28 | — | 12-31/01-20/21 | |
| 福州Fuzhou | — | 01-29/02-09/12 | — | — | 12-31/01-14/15 | |
| 桂林Guilin | 01-11/03-02/51 | 01-04/02-23/51 | 12-08/03-02/85 | 01-14/03-04/51 | 12-29/01-20/23 | |
| 文山Wenshan | 02-09/03-01/21 | 01-08/02-13/37 | 12-28/01-23/27 | 01-25/02-18/25 | 12-14/01-29/47 | |
| 广州Guangzhou | — | 01-28/02-06/10 | — | — | — | |
| 海南Hainan | — | — | — | — | — | |
表2 12个地区不同年度冷量积累起止日期及天数
Table 2 Start and end dates and interval days of chilling accumulation in 12 regions in different years
| 地区 Region | 起始日期/结束日期/区间天数/d Start date/end date/interval days | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011—2012 | 2012—2013 | 2013—2014 | 2014—2015 | 2015—2016 | ||
| 北京Beijing | 11-13/03-22/131 | 11-03/03-31/149 | 11-17/03-13/117 | 11-07/03-15/129 | 11-06/03-17/133 | |
| 蒙阴Mengyin | 11-20/03-26/128 | 11-04/03-27/144 | 11-10/03-15/126 | 11-16/03-15/120 | 11-17/03-17/122 | |
| 郑州Zhengzhou | 11-23/03-22/121 | 11-23/03-26/124 | 11-19/03-09/111 | 11-27/03-12/106 | 11-22/03-01/101 | |
| 南京Nanjing | 11-30/03-14/106 | 11-24/03-21/118 | 12-06/03-08/93 | 12-01/03-13/103 | 11-24/02-26/95 | |
| 上海Shanghai | 12-01/03-13/104 | 12-04/03-04/91 | 11-27/03-11/105 | 12-01/03-11/101 | 12-04/03-14/102 | |
| 杭州Hangzhou | 11-30/03-14/106 | 12-07/03-04/88 | 12-09/03-14/96 | 12-01/03-11/101 | 11-26/03-15/110 | |
| 古田Gutian | 12-23/02-29/68 | 12-30/02-13/44 | 12-19/02-21/65 | — | 01-22/02-17/27 | |
| 福州Fuzhou | 01-04/02-28/56 | — | 02-09/02-21/13 | — | — | |
| 桂林Guilin | 01-03/03-10/68 | 12-18/03-03/76 | 12-20/03-09/79 | 01-28/03-08/40 | 01-12/02-27/47 | |
| 文山Wenshan | 12-09/03-13/96 | 12-29/02-22/56 | 12-15/02-21/69 | 12-11/02-12/64 | 12-15/02-27/75 | |
| 广州Guangzhou | — | — | 02-09/02-20/12 | — | 01-23/02-03/12 | |
| 海南Hainan | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 北京Beijing | 11-01/03-24/144 | 11-03/03-13/131 | 11-13/03-24/132 | 11-18/03-16/120 | 11-02/03-21/140 | |
| 蒙阴Mengyin | 11-22/03-17/116 | 11-17/03-23/127 | 12-03/03-14/102 | 11-25/03-15/112 | 11-19/03-22/124 | |
| 郑州Zhengzhou | 11-21/03-08/108 | 11-29/03-09/101 | 12-04/03-11/98 | 11-29/03-06/96 | 11-20/03-02/103 | |
| 南京Nanjing | 11-22/03-02/101 | 11-30/03-11/102 | 12-06/03-04/89 | 11-27/03-11/105 | 11-27/03-09/103 | |
| 上海Shanghai | 12-14/03-17/94 | 12-05/03-10/96 | 12-06/03-08/93 | 12-18/02-20/65 | 12-13/03-09/87 | |
| 杭州Hangzhou | 12-14/03-16/93 | 12-01/03-21/111 | 12-06/03-10/95 | 12-18/03-06/80 | 12-13/03-09/87 | |
| 古田Gutian | — | 01-08/02-14/38 | 12-29/01-25/28 | — | 12-31/01-20/21 | |
| 福州Fuzhou | — | 01-29/02-09/12 | — | — | 12-31/01-14/15 | |
| 桂林Guilin | 01-11/03-02/51 | 01-04/02-23/51 | 12-08/03-02/85 | 01-14/03-04/51 | 12-29/01-20/23 | |
| 文山Wenshan | 02-09/03-01/21 | 01-08/02-13/37 | 12-28/01-23/27 | 01-25/02-18/25 | 12-14/01-29/47 | |
| 广州Guangzhou | — | 01-28/02-06/10 | — | — | — | |
| 海南Hainan | — | — | — | — | — | |
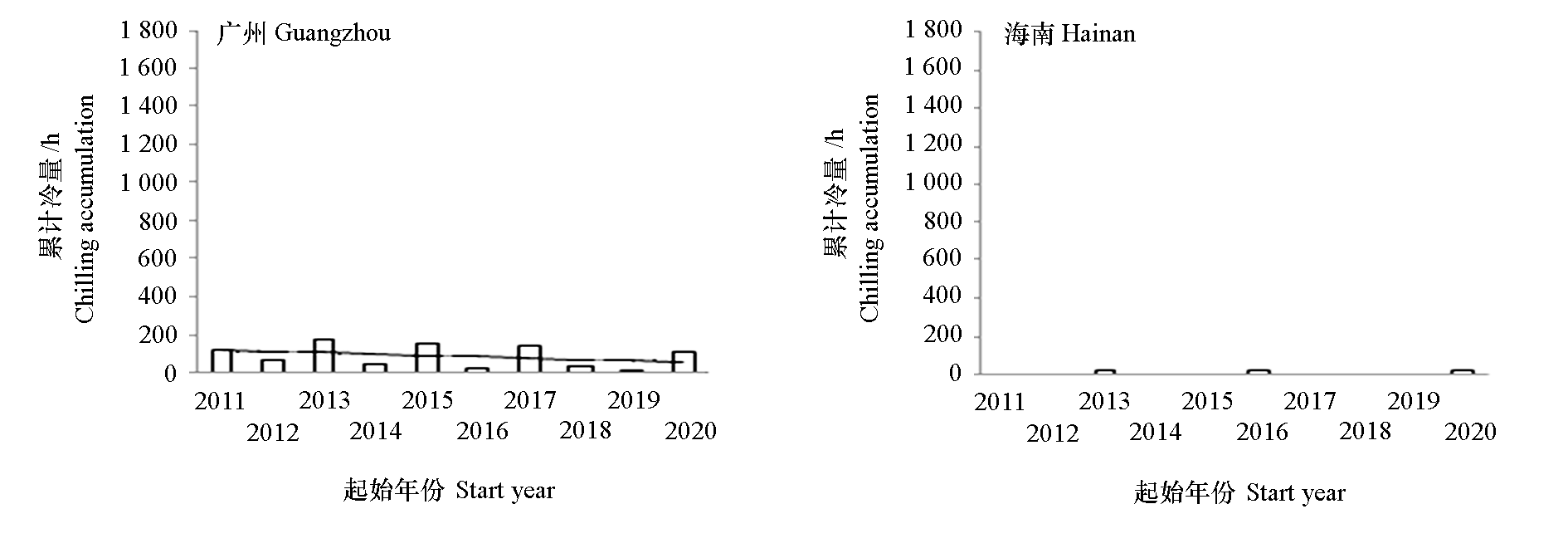
图2 12个地区累积冷量 为了数据的可比性,部分无法确定冷量积累起始期的地区年份直接用11月1日至翌年3月31日的气温在0 ~ 7.2 ℃之间的小时数之和来代表累积冷量。图中斜线为根据气温变化拟合的线性趋势线。
Fig. 2 Chilling accumulation in 12 regions For the sake of data comparability,in some regions where the initial period of chilling accumulation cannot be determined,the sum of the hours when the temperature is between 0 and 7.2 ℃ from November 1 to March 31 is used to represent the chilling accumulation. The oblique lines in the figure were a linear trend line fitted according to the temperature change.
| 地方 Region | 不同等级需冷量桃适应性挑战 Adaptability challenge of peach with different chilling requirement | 适应的需冷量范围预判 Prediction of peach with suitable chilling requirement range | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 300 h | 300 ~ 600 h | 600 ~ 900 h | 900 ~ 1200 h | ≥1 200 h | ||
| 北京Beijing | √ | √ | √ | √ | * | < 1 200 h(考虑到有特殊年份,< 1 000 h为最佳) < 1 200 h(< 1 000 h is the best considering special years) |
| 蒙阴Mengyin | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 基本不受限(考虑到有特殊年份,< 1 000 h为最佳)Basically unlimited(< 1 000 h is the best considering special years) |
| 郑州Zhengzhou | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 基本不受限,(考虑到有特殊年份 < 1 000 h为最佳)Basically unlimited(< 1 000 h is the best considering special years) |
| 南京Nanjing | √ | √ | √ | * | × | < 1 000 h |
| 上海Shanghai | √ | √ | * | ** | × | < 700 h |
| 杭州Hangzhou | √ | √ | * | ** | × | < 600 h |
| 古田Gutian | * | ** | × | × | × | < 200 h(海拔高的区域,可放宽到 < 400 h) < 200 h(< 400 h is ok in areas with high altitude) |
| 福州Fuzhou | * | × | × | × | × | < 100 h |
| 桂林Guilin | √ | * | *** | × | × | < 400 h |
| 文山Wenshan | * | ** | *** | × | × | < 200 h |
| 广州Guangzhou | *** | × | × | × | × | < 50 h |
| 海南Hainan | × | × | × | × | × | 基本不休眠的桃(如常绿系列) Non-dormant peach(for example:evergreen peach) |
表3 桃适应性挑战和应对策略
Table 3 Peach adaptability challenge and strategy
| 地方 Region | 不同等级需冷量桃适应性挑战 Adaptability challenge of peach with different chilling requirement | 适应的需冷量范围预判 Prediction of peach with suitable chilling requirement range | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 300 h | 300 ~ 600 h | 600 ~ 900 h | 900 ~ 1200 h | ≥1 200 h | ||
| 北京Beijing | √ | √ | √ | √ | * | < 1 200 h(考虑到有特殊年份,< 1 000 h为最佳) < 1 200 h(< 1 000 h is the best considering special years) |
| 蒙阴Mengyin | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 基本不受限(考虑到有特殊年份,< 1 000 h为最佳)Basically unlimited(< 1 000 h is the best considering special years) |
| 郑州Zhengzhou | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 基本不受限,(考虑到有特殊年份 < 1 000 h为最佳)Basically unlimited(< 1 000 h is the best considering special years) |
| 南京Nanjing | √ | √ | √ | * | × | < 1 000 h |
| 上海Shanghai | √ | √ | * | ** | × | < 700 h |
| 杭州Hangzhou | √ | √ | * | ** | × | < 600 h |
| 古田Gutian | * | ** | × | × | × | < 200 h(海拔高的区域,可放宽到 < 400 h) < 200 h(< 400 h is ok in areas with high altitude) |
| 福州Fuzhou | * | × | × | × | × | < 100 h |
| 桂林Guilin | √ | * | *** | × | × | < 400 h |
| 文山Wenshan | * | ** | *** | × | × | < 200 h |
| 广州Guangzhou | *** | × | × | × | × | < 50 h |
| 海南Hainan | × | × | × | × | × | 基本不休眠的桃(如常绿系列) Non-dormant peach(for example:evergreen peach) |
| [1] | Bielenberg D G, Wang Y E, Li Z, Zhebentyayeva Z, Fan S, Reighard G L. 2008. Sequencing and annotation of the evergrowing locus in peach [Prunus persica(L.)Batsch]reveals a cluster of six MADS-box transcription factors as candidate genes for regulation of terminal bud formation. Tree Genetics & Genomes, 4 (3):495-507. |
| [2] |
Cantin C M, Wang X W, Almira M, Arús, Eduardo I. 2020. Inheritance and QTL analysis of chilling and heat requirements for flowering in an interspecific almond × peach(Texas × Earlygold)F2 population. Euphytica, 216 (3):51.
doi: 10.1007/s10681-020-02588-9 |
| [3] | Chen Mao-quan, Ye Wei-qi, Liu Zhuo-xiang, Zhong Han-chun, Liu Xu-bo, Pan Zhi-mei. 2012. The requirements of chilling for bud dormancy and caloric for blooming for 12 peach varieties. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 48 (1):86-90. (in Chinese) |
| 陈茂铨, 叶伟其, 刘卓香, 钟汉春, 柳旭波, 潘芝梅. 2012. 12个桃品种的花芽休眠需冷量和开花需热量. 林业科学, 48 (1):86-90. | |
| [4] |
Citadin I, Raseira M, Herter F G, Da S J B. 2001. Heat requirement for blooming and leafing in peach. HortScience, 36 (2):305-307.
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.36.2.305 URL |
| [5] |
Erica F, Eduardo F, Helen B, Eike L. 2020. A conceptual framework for winter dormancy in deciduous trees. Agronomy, 10 (2):241.
doi: 10.3390/agronomy10020241 URL |
| [6] |
Evangelina M, Gabriel H V, Leandro K, Marcos P, Laura L M, María E D, Marta Q, Gerardo D L C. 2014. Comparison of methods for estimation of chilling and heat requirements of nectarine and peach genotypes for flowering. Scientia Horticulturae, 177 (2):112-117.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2014.07.042 URL |
| [7] | Gao Zhi-hong, Zhang Jun-yi, Qiao Yu-Shan, Chang You-hong, Lin Jing, Zhang Zhen. 2004. Study on the chilling requirement of peach and plum varieties. China Fruits, 7 (3):20-23. (in Chinese) |
| 高志红, 张君毅, 乔玉山, 常有宏, 蔺经, 章镇. 2004. 桃和李品种需冷量研究. 中国果树, 7 (3):20-23. | |
| [8] |
Guillamón J G, Prudencio Á S, Yuste J E, Dicenta F, Sánchez-Pérez R. 2020. Ascorbic acid and prunasin,two candidate biomarkers for endodormancy release in almond flower buds identified by a nontargeted metabolomic study. Horticulture Research, 7 (1):117-129.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-0338-9 |
| [9] |
Hernandez J A, Diaz V P, Martinez S G, Alburquerque N, Martinez S G, Barba E G, Acosta M J R, Carrera E, Garcia B J. 2021. Physiological and biochemical characterization of bud dormancy:evolution of carbohydrate and antioxidant metabolisms and hormonal profile in a low chill peach variety. Scientia Horticulturae, 281:109957.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.109957 URL |
| [10] | Hu Rui-lan, Jia Yong-xiang. 2002. Study on the causes of ripening stage of peach in shadow and temperature. Shanxi Fruits, 19 (3):4-5. (in Chinese) |
| 胡瑞兰, 贾永祥. 2002. 影响温室桃成熟期的因子研究. 山西果树, 19 (3):4-5. | |
| [11] | Jiang Wei-bing, Han Hao-zhang, Dai Mei-song, Wang Liang-ju, Ma Kai. 2005. Study on the chilling requirement of leading deciduous fruit cultivars in southern part of Jiangsu Province. Journal of Fruit Science, 22 (1):75-77. (in Chinese) |
| 姜卫兵, 韩浩章, 戴美松, 汪良驹, 马凯. 2005. 苏南地区主要落叶果树的需冷量. 果树学报, 22 (1):75-77. | |
| [12] |
Jiménez S, Reighard G L, Bielenberg D G. 2010. Gene expression of DAM5 and DAM6 is suppressed by chilling temperatures and inversely correlated with bud break rate. Plant Molecular Biology, 73 (1-2):157-167.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-010-9608-5 pmid: 20143130 |
| [13] |
Leida C, Romeu J F, Garcia-Brunton J, Rios G, Badenes M L. 2012. Gene expression analysis of chilling requirements for flower bud break in peach. Plant Breeding, 131:329-334.
doi: 10.1111/pbr.2012.131.issue-2 URL |
| [14] | Li Wen-gui, Deng Jia-lin, Zhang Quan-jun, Zhong Bi-feng. 2011. Studies on chilling requirements and chilling requirement of peach in Chengdu. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 38 (19):47-49. (in Chinese) |
| 李文贵, 邓家林, 张全军, 钟必凤. 2011. 成都桃自然休眠与需冷量研究. 广东农业科学, 38 (19):47-49. | |
| [15] |
Ma Rong, Li Dao-gao. 2005. A study on chilling requirement of peach varieties in south of sichuan basin. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 21 (10):248-250,298. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.0510248 |
| 马融, 李道高. 2005. 川南地区引种桃品种的需冷量研究. 中国农学通报, 21 (10):248-250,298. | |
| [16] | Ouyang Ru-xin. 2011. Study on buds chilling requirements of several nectarine cultivars. Northern Horticulture,(1):59-60. (in Chinese) |
| 欧阳汝欣. 2011. 几个油桃品种需冷量的研究. 北方园艺,(1):59-60. | |
| [17] |
Qian C L, Ji Z J, Zhu Q, Qi X H, Li Q Q, Yin J D, Liu J, Kan J, Zhang M, Jin C H, Xiao L X. 2021. Effects of 1-MCP on proline,polyamine,and nitric oxide metabolism in postharvest peach fruit under chilling stress. Horticultural Plant Journal, 7 (3):188-196.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.12.007 URL |
| [18] | Razavi F, Hajilou J, Tabatabaei S J, Dadpour M. 2011. Comparison of chilling and heat requirement in some peach and apricot cultivars. Research in Plant Biology, 1 (2):40-47. |
| [19] | Richardson E A, Seeley S D, Walker D R. 1974. A model for estimating the completion of rest for‘Redhaven’and‘Elberta’peach trees. Horticultural Science, 9 (4):331-332. |
| [20] | Shen Yuan-yue, Guo Jia-xuan, Jia Ke-gong. 1998. Studies on the rest release period and the chilling requirerement of peach varieties. Journal of Laiyang Agricultural College, (1):8-11. (in Chinese) |
| 沈元月, 郭家选, 贾克功. 1998. 桃品种自然休眠结束期及需冷量. 莱阳农学院学报,(1):8-11. | |
| [21] | Shen Yuan-yue, Guo Jia-xuan, Zhu Jun, Jia Ke-gong. 1999. Preliminary report on chilling and heat requirements of early peach varieties. China Fruits, 13 (2):21-22. (in Chinese) |
| 沈元月, 郭家选, 祝军, 贾克功. 1999. 早熟桃品种需冷量和需热量的研究初报. 中国果树, 13 (2):21-22. | |
| [22] | Song Ying, Shi Zuo-an, Gao Dong-sheng. 2002. Chilling requirement by fruit trees in south-west Shandong Province. Deciduous Fruits,(6):1-3. (in Chinese) |
| 宋颖, 史作安, 高东升. 2002. 鲁西南地区果树需冷量的研究. 落叶果树,(6):1-3. | |
| [23] | Sun Wan-xia, Liu Xun-ju, Wang Li, Wang Ji-yuan, Jiu Song-tao, Wang Lei, Wang Shi-ping, Zhang Cai-xi. 2021. Haracteristics of low temperature and its impact on chilling accumulation of sweet cherries in the Yangtze River Delta. Journal of Fruit Science, 38 (11):1900-1910. (in Chinese) |
| 孙菀霞, 刘勋菊, 王丽, 王继源, 纠松涛, 王磊, 王世平, 张才喜. 2021. 长三角地区低温特征及其对甜樱桃蓄冷量的影响. 果树学报, 38 (11):1900-1910. | |
| [24] | Swapnil P, Singh A T H, Vikal Y, Thakur A. 2019. Intraspecific hybridization of low chill peach cultivars for superior fruit quality and their hybridity confirmation by SSR markers. Indian Jounal of Horticulture, 76:199-205. |
| [25] |
Tadeu M H, Pio R, Silva G N, Olmstead M, Cruz C D, Souza F B M D, Bisi R B, Locatelli G. 2020. Duration of the phenological stages of peach trees at tropics. Scientia Horticulturae, 261:108976.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108976 URL |
| [26] | Thurow L B, Gasic K, Raseira M, Bonow S, Castro C. 2020. Genome-wide SNP discovery through genotyping by sequencing,population structure,and linkage disequilibrium in Brazilian peach breeding germplasm. Tree Genetics & Genomes, 16:10. |
| [27] | Topp B L, Sherman W B, Raseira M. 2008. Low-chill cultivar development. Australia: CABI Publishing. |
| [28] |
Vanalli C, Casagrandi R, Gatto M, Bevacqua D. 2021. Shifts in the thermal niche of fruit trees under climate change:the case of peach cultivation in France. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 300:108327.
doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108327 URL |
| [29] | Wang Li-rong, Hu Ni-yun. 1992. Low chilling requriment of peach cultivars. Journal of Fruit Science,(1):39-42. (in Chinese) |
| 王力荣, 胡霓云. 1992. 桃品种的低温需求量. 果树科学,(1):39-42. | |
| [30] |
Wang Lirong, Wu Jinlong. 2021. Review for the research of fruit tree germplasm and breeding of new varieties in the past seven decades in China. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (4):749-758. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0616 URL |
|
王力荣, 吴金龙. 2021. 中国果树种质资源研究与新品种选育70年. 园艺学报, 48 (4):749-758.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0616 URL |
|
| [31] | Wang Li-rong, Zhu Geng-rui. 2005. Description specification and data standard of peach germplasm resources. Beijing: China Agriculture Press:29. (in Chinese) |
| 王力荣, 朱更瑞. 2005. 桃种质资源描述规范和数据标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社:29. | |
| [32] | Wang Li-rong, Zhu Geng-rui, Fang Wei-chao, Chen Chang-wen, Cao Ke, Wang Xin-wei. 2021. Breeding of a new peach cultivar‘Zhongtaohongyu’with low chilling requirement. China Fruits,(3):79-80. (in Chinese) |
| 王力荣, 朱更瑞, 方伟超, 陈昌文, 曹珂, 王新卫. 2021. 低需冷量桃新品种‘中桃红玉’的选育. 中国果树,(3):79-80. | |
| [33] | Wang Li-rong, Zhu Geng-rui, Fang Wei-chao, Zuo Qin-yuan. 2003. Estimating models of the chilling requirement for peach. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 30 (4):379-383. (in Chinese) |
| 王力荣, 朱更瑞, 方伟超, 左覃元. 2003. 桃品种需冷量评价模式的探讨. 园艺学报, 30 (4):379-383. | |
| [34] | Wang Li-rong, Zhu Geng-rui, Zuo Qin-yuan. 1997. Studies on the chilling requirement of peach varieties. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 24 (2):194-196. (in Chinese) |
| 王力荣, 朱更瑞, 左覃元. 1997. 中国桃品种需冷量的研究. 园艺学报, 24 (2):194-196. | |
| [35] | Wang Zu-hua, Zhuang En-ji. 2001. Chinese fruit tree annals. Peach. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House:74-89. (in Chinese) |
| 汪祖华, 庄恩及. 2001. 中国果树志. 桃卷. 北京: 中国林业出版社:74-89. | |
| [36] | Xiao Xiao, Zhang Ji-jun, Zhang Li-bin, Yao Xiao-xia. 2007. A study on buds chilling requirements of several new peach cultivars. Joumal of Inner Mongo Lia Agricultural Nuniversity,(3):77-79. (in Chinese) |
| 肖啸, 张吉军, 张立彬, 姚晓霞. 2007. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版),(3):77-79. | |
| [37] |
Yamane H, Ooka T, Jotatsu H, Hosaka Y, Sasaki R, Tao R. 2011. Expressional regulation of PpDAM5 and PpDAM6,peach(Prunus persica)dormancy-associated MADS-box genes,by low temperature and dormancy-breaking reagent treatment. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62 (10):3481-3488.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/err028 URL |
| [38] |
Yan J, Zhang M H, Peng B, Su Z W, Xu Z Y, Cai Z X, Yang J, Ma R J, Yu M L, Shen Z J. 2021. Predicting chilling requirement of peach floral buds using electronic nose. Scientia Horticulturae, 290 (2):110517.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110517 URL |
| [39] | Yan Juan, Zhang Ming-hao, Cai Zhi-xiang, Shen Zhi-jun, Ma Rui-juan, Xu Zi-yuan, Su Zi-wen, Yu Ming-liang. 2021. Effects of chilling and heat requirement differences between peach floral bud and leaf bud on their phenological process. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 22 (5):1281-1292. (in Chinese) |
| 严娟, 张明昊, 蔡志翔, 沈志军, 马瑞娟, 徐子媛, 宿子文, 俞明亮. 2021. 需冷量和需热量差异对桃花叶物候进程的影响. 植物遗传资源学报, 22 (5):1281-1292. | |
| [40] | Zhang Ming-hao, Yan Juan, Cai Zhi-xiang, Shen Zhi-jun, Ma Rui-juan, Zhang Chun-hua, Xu Zhi-yuan, Yu Ming-liang. 2021. Chilling and heat requirements of 103 germplasms of peach in Nanjing. Journal of Fruit Science, 38 (1):29-39. (in Chinese) |
| 张明昊, 严娟, 蔡志翔, 沈志军, 马瑞娟, 张春华, 徐子媛, 俞明亮. 2021. 103份桃种质在南京地区的需冷量和需热量研究. 果树学报, 38 (1):29-39. | |
| [41] |
Zhang X H, Shen H Y, Wen B B, Li S, Xu C, Gai Y, Meng X G, He H J, Wang N, Li D M, Chen X D, Xiao W, Fu X L, Tan Q P, Li L. 2021. BTB-TAZ domain protein PpBT 3 modulates peach bud endodormancy by interacting with PpDAM5. Plant Sci, 310 (4):110956.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.110956 URL |
| [42] | Zhu Geng-rui, Fang Wei-chao, Wang Li-rong. 2004. Chilling requirement of oranamental peach. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,(2):176-178. (in Chinese) |
| 朱更瑞, 方伟超, 王力荣. 2004. 观赏桃品种需冷量的研究. 植物遗传资源学报,(2):176-178. | |
| [43] | Zhu Geng-rui, Wang Li-rong, Fang Wei-chao, Chen Chang-wen, Cao Ke, Wang Xiao-li, Wang Xin-wei. 2016. A new low chilling requirement ornamental flower peach cultivar‘Yingchun’. Journal of Fruit Science, 33 (6):770-772. (in Chinese) |
| 朱更瑞, 王力荣, 方伟超, 陈昌文, 曹珂, 王小丽, 王新卫. 2016. 低需冷量、早花观赏桃新品种‘迎春’的选育. 果树学报, 33 (6):770-772. |
| [1] | 郑锦荣, 聂俊, 李艳红, 谭德龙, 谢玉明, 张长远. 樱桃番茄新品种‘粤科达101’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 909-910. |
| [2] | 毛可欣, 安淼, 王海荣, 王世金, 吕巍, 郭盈添, 李健, 李国田. 猕猴桃MYB家族成员鉴定及其低温表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 534-548. |
| [3] | 翟含含, 翟宇杰, 田义, 张叶, 杨丽, 温陟良, 陈海江. 桃SAUR家族基因分析及PpSAUR5功能鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 1-14. |
| [4] | 袁馨, 徐云鹤, 张雨培, 单楠, 陈楚英, 万春鹏, 开文斌, 翟夏琬, 陈金印, 甘增宇. 猕猴桃后熟过程中ABA响应结合因子AcAREB1调控AcGH3.1的表达[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 53-64. |
| [5] | 邢柱东, 吕福堂, 郭尚敬, 张演义. 新品种‘聊大红金’桃[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 225-226. |
| [6] | 杨兴旺, 王海波, 王莹莹, 王小龙, 王志强, 刘培培, 刘万春, 王孝娣. 中熟抗寒桃新品种‘中农甘爽’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 15-16. |
| [7] | 杨兴旺, 王海波, 王莹莹, 张艺灿, 王宝亮, 刘培培, 史祥宾, 刘万春, 王孝娣. 中熟抗寒桃新品种‘中农白干’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 17-18. |
| [8] | 杨兴旺, 刘凤之, 王海波, 王莹莹, 王志强, 史祥宾, 冀晓昊, 刘万春, 王孝娣. 中熟抗寒桃新品种‘中农寒水蜜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 19-20. |
| [9] | 杨兴旺, 刘凤之, 王海波, 王莹莹, 张艺灿, 李 鹏, 王小龙, 刘万春, 王孝娣. 晚熟抗寒桃新品种‘中农秋香’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 21-22. |
| [10] | 王莹莹, 刘立常, 刘志伍, 杨兴旺, 刘万春, 王孝娣, . 极晚熟桃新品种‘中农冬蜜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 23-24. |
| [11] | 王莹莹, 刘立常, 刘志伍, 杨兴旺, 刘万春, 王孝娣, . 小果油桃新品种‘中农珍珠’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 25-26. |
| [12] | 吴延军, 刘庆忠, 陈鸿才, 戚行江, 朱东姿, 郑家祥, 曹学敏, 方丹燕. 甜樱桃新品种‘江南锦’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 29-30. |
| [13] | 张晓明, 闫国华, 周 宇, 王 晶, 段续伟, 吴传宝, 张开春. 甜樱桃砧木新品种‘京春2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 31-32. |
| [14] | 宋 放, 陈 奇, 袁炎良, 陈 沙, 尹海军, 蒋迎春, . 黄肉猕猴桃新品种‘先沃1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 47-48. |
| [15] | 齐永杰, 高正辉, 马 娜, 王清明, 柯凡君, 陈 钱, 徐义流, . 黄肉抗溃疡病猕猴桃新品种‘皖农金果’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 49-50. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司