
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (10): 2281-2296.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0569
韩世文1, 刘涛1, 王丽萍1,2, 李楠洋1,2, 王素娜1,2, 王星1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-31
修回日期:2024-07-22
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2024-10-21
通讯作者:
基金资助:
HAN Shiwen1, LIU Tao1, WANG Liping1,2, LI Nanyang1,2, WANG Suna1,2, WANG Xing1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-10-31
Revised:2024-07-22
Published:2024-10-25
Online:2024-10-21
摘要:
短节间基因家族[SHORT INTERNODES(SHI)-related sequence,SRS]是植物生长和发育重要的转录因子家族。对黄瓜SRS基因家族进行了全基因组筛选和功能特征分析,鉴定到9个SRS成员,不均匀地分布于7条染色体上。根据系统发生关系,CsSRS被分为3个亚族。基因结构和基序组成表明,同一亚族中的CsSRS成员具有类似的内含子/外显子和基序。序列分析发现CsSRS氨基酸N-末端具有高度保守的RING结构域,C-末端IGGH结构域在进化中有丢失现象。CsSRS的启动子区域存在多种与生长、发育和逆境应答相关的顺式作用元件。组织表达模式分析发现CsSRS表现出显著组织特异性。此外,转录组表达分析表明CsSRS对多种生物和非生物胁迫表现出不同的响应,表明它们在功能上发生了分化。其中,CsSRS6在大部分组织中都有表达,且在逆境胁迫下均发生差异表达。
韩世文, 刘涛, 王丽萍, 李楠洋, 王素娜, 王星. 黄瓜SRS基因家族鉴定及胁迫响应表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2281-2296.
HAN Shiwen, LIU Tao, WANG Liping, LI Nanyang, WANG Suna, WANG Xing. Genome-Wide Identification and Stress-Responsive Expression Analysis of the Cucumber SRS Gene Family[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2281-2296.
| 基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | CDS碱基数/bp CDS size | 氨基酸数量/aa Number of amino acids | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 等电点 pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsSRS1 CsSRS2 CsSRS3 CsSRS4 CsSRS5 CsSRS6 CsSRS7 CsSRS8 CsSRS9 | CsaV3_1G043360.1 CsaV3_2G029220.1 CsaV3_3G002100.1 CsaV3_3G045570.1 CsaV3_4G005360.1 CsaV3_5G036780.1 CsaV3_6G039030.1 CsaV3_6G046800.1 CsaV3_7G006060.1 | 939 646 1 186 1 006 805 927 1 116 1 012 969 | 307 211 388 329 263 303 365 331 317 | 31.147 21.978 43.201 37.237 28.683 32.074 37.662 35.897 35.222 | 8.90 6.87 8.93 9.00 6.24 8.89 7.15 7.00 7.13 |
| 基因名称 Gene name | 不稳定系数 Instability index | 脂肪族氨基酸指数 Aliphatic index | 平均亲水性 Grand average of hydropathicity | 亚细胞定位 Prediction of subcellular location | |
| CsSRS1 CsSRS2 CsSRS3 CsSRS4 CsSRS5 CsSRS6 CsSRS7 CsSRS8 CsSRS9 | 41.44 44.57 49.09 48.97 61.27 41.15 37.75 54.07 53.15 | 58.18 57.63 67.16 60.09 45.59 62.21 61.21 50.45 60.88 | 1.460 -0.225 -0.865 -0.806 -0.751 -0.493 -0.417 -0.769 -0.736 | 核内Nuclear 核内、核外Nuclear,extracellular 核内Nuclear 核内Nuclear 核内Nuclear 核内Nuclear 核外、核内Extracellular,nuclear 核内Nuclear 核内Nuclear | |
表1 黄瓜SRS基因家族成员蛋白信息
Table 1 The information of SRS proteins in cucumber
| 基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | CDS碱基数/bp CDS size | 氨基酸数量/aa Number of amino acids | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 等电点 pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsSRS1 CsSRS2 CsSRS3 CsSRS4 CsSRS5 CsSRS6 CsSRS7 CsSRS8 CsSRS9 | CsaV3_1G043360.1 CsaV3_2G029220.1 CsaV3_3G002100.1 CsaV3_3G045570.1 CsaV3_4G005360.1 CsaV3_5G036780.1 CsaV3_6G039030.1 CsaV3_6G046800.1 CsaV3_7G006060.1 | 939 646 1 186 1 006 805 927 1 116 1 012 969 | 307 211 388 329 263 303 365 331 317 | 31.147 21.978 43.201 37.237 28.683 32.074 37.662 35.897 35.222 | 8.90 6.87 8.93 9.00 6.24 8.89 7.15 7.00 7.13 |
| 基因名称 Gene name | 不稳定系数 Instability index | 脂肪族氨基酸指数 Aliphatic index | 平均亲水性 Grand average of hydropathicity | 亚细胞定位 Prediction of subcellular location | |
| CsSRS1 CsSRS2 CsSRS3 CsSRS4 CsSRS5 CsSRS6 CsSRS7 CsSRS8 CsSRS9 | 41.44 44.57 49.09 48.97 61.27 41.15 37.75 54.07 53.15 | 58.18 57.63 67.16 60.09 45.59 62.21 61.21 50.45 60.88 | 1.460 -0.225 -0.865 -0.806 -0.751 -0.493 -0.417 -0.769 -0.736 | 核内Nuclear 核内、核外Nuclear,extracellular 核内Nuclear 核内Nuclear 核内Nuclear 核内Nuclear 核外、核内Extracellular,nuclear 核内Nuclear 核内Nuclear | |
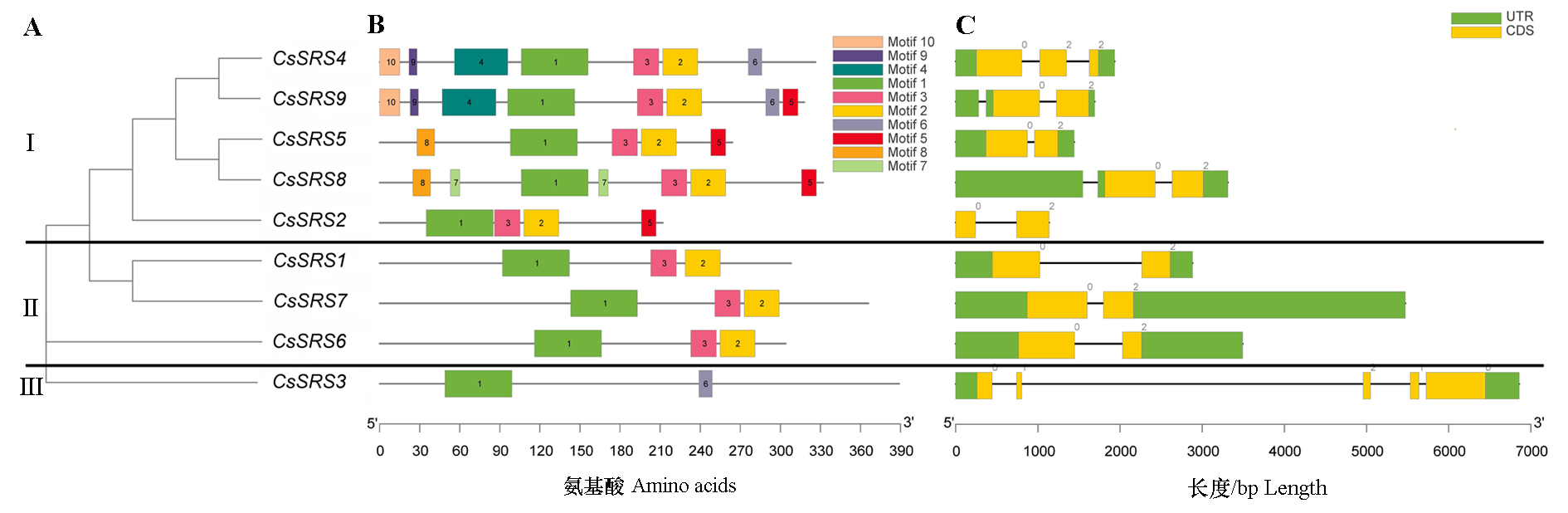
图3 黄瓜SRS家族进化分析(A)、保守序列(B)与基因结构(C)示意图
Fig. 3 Evolutionary analysis(A),conserved sequence of SRS proteins(B)and exon-intron structures of SRS genes(C)in cucumber

图4 黄瓜(Cs)、拟南芥(At)、番茄(Sl)、水稻(Os)和玉米(Zm)SRS家族成员系统发育树
Fig. 4 Phylogenetic tree of SRS family members in Cucumis sativus(Cs),Arabidopsis thaliana(At),Solanum lycopersicum(Sl),Oryza sativa(Os)and Zea mays(Zm)

图6 黄瓜SRS基因启动子顺式作用元件热图 颜色代表顺式作用元件数量,红色越深表示数量越多,蓝色越深表示数量越少,图中数字表示元件数。
Fig. 6 The heatmap of various cis-elements in the promoters of each cucumber SRS gene Colors represent the quantity of cis elements,with deeper red indicating higher quantities and deeper blue indicating lower quantities. The numbers in the image represent the counts of cis-elements.
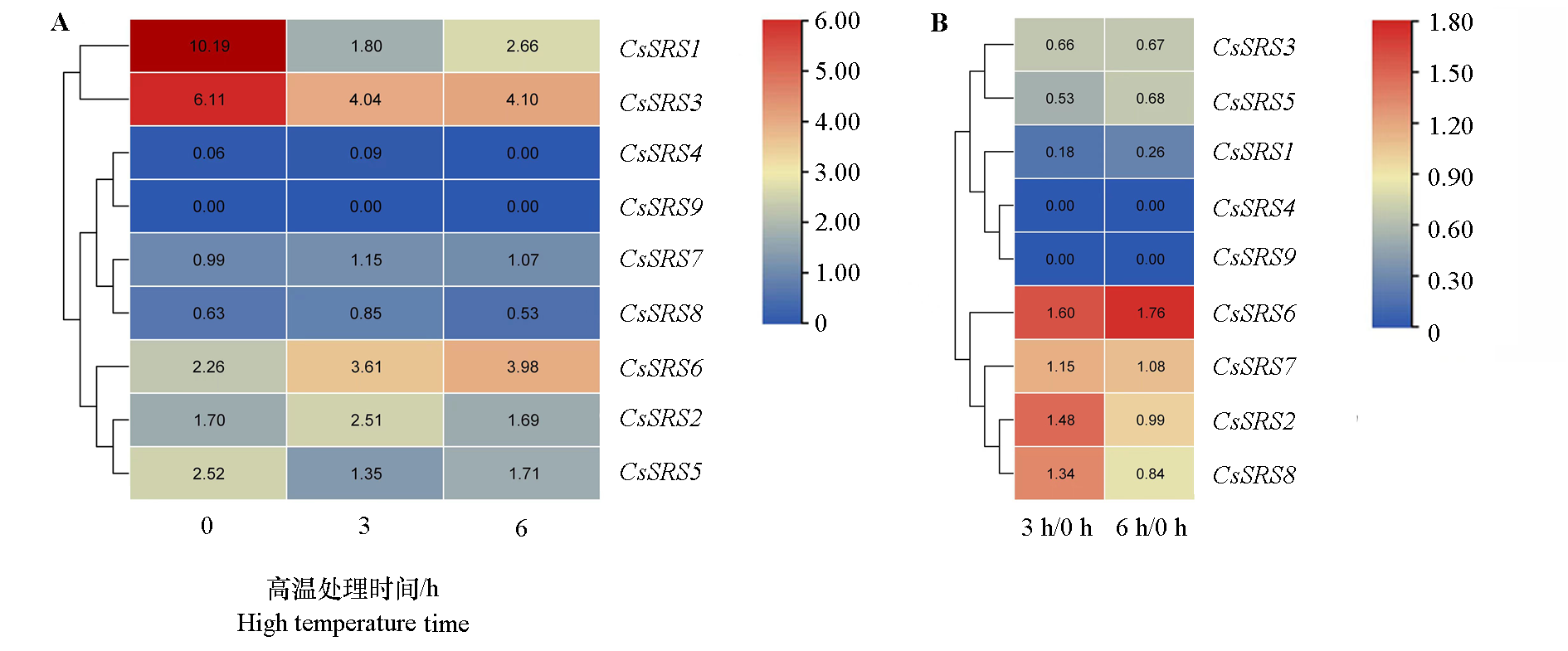
图8 黄瓜SRS家族基因在高温胁迫下的表达热图 A:表格中的数据是原始的FPKM值。B:表格中的数据是原始的FPKM值的差异倍数。
Fig. 8 Expression heatmap of cucumber SRS family genes under high-temperature stress A:The data in the table represents the raw FPKM values;B:The data in the table represents the fold change of raw FPKM values.
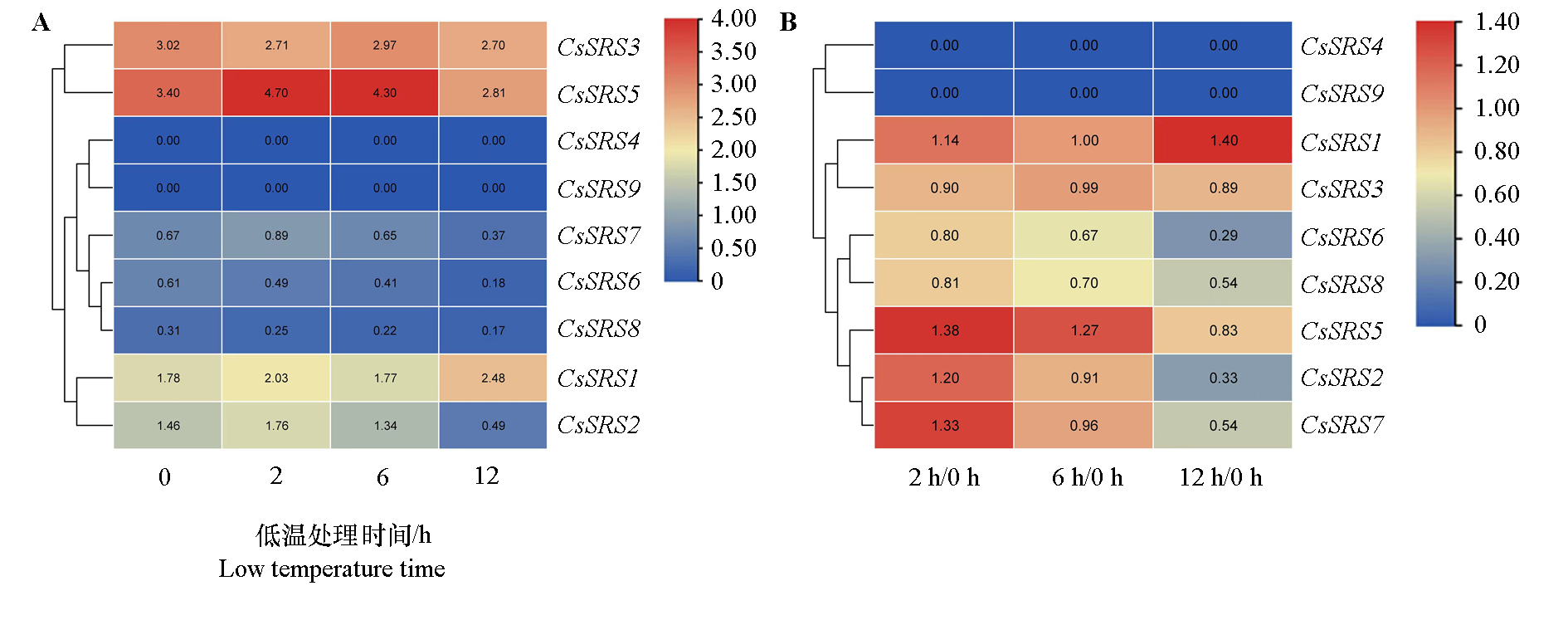
图9 黄瓜SRS家族基因在低温胁迫下的表达热图 A:表格中的数据是原始的FPKM值。B:表格中的数据是原始的FPKM值的差异倍数。
Fig. 9 Expression heatmap of cucumber SRS family genes under low-temperature stress A:The data in the table represents the raw FPKM values;B:The data in the table represents the fold change of raw FPKM values.

图10 黄瓜SRS家族基因在盐和硅处理下的表达热图 A:表格中的数据是原始的FPKM值。B:表格中的数据是原始的FPKM值的差异倍数。
Fig. 10 Expression heatmap of cucumber SRS family genes under salt and silicon stress treatments A:The data in the table represents the raw FPKM values;B:The data in the table represents the fold change of raw FPKM values.

图11 黄瓜SRS家族基因在霜霉病胁迫下的表达模式 A:表格中的数据是原始的FPKM值。B:表格中的数据是原始的FPKM值的差异倍数。
Fig. 11 Expression patterns of cucumber SRS family genes under downy mildew stress treatment A:The data in the table represents the raw FPKM values;B:The data in the table represents the multiples of the raw FPKM values.

图12 黄瓜SRS家族基因在南方根结线虫病胁迫下的表达模式 A:表格中的数据是原始的FPKM值。B:表格中的数据是原始的FPKM值的差异倍数。
Fig. 12 Expression patterns of cucumber SRS family genes under southern root-knot nematode stress treatment A:The data in the table represents the raw FPKM values;B:The data in the table represents the multiples of the raw FPKM values.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
pmid: 8827714 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
pmid: 11706176 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1038/nbt.3122 pmid: 25690850 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0674 |
|
宋蒙飞, 查高辉, 陈劲枫, 娄群峰. 2022. 黄瓜株型性状分子基础研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (12):2683-2702.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0674 |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1093/jhered/93.1.77 pmid: 12011185 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
|
王锦锋. 2022. 苹果SRS基因家族的鉴定与功能分析. 西北植物学报, 42 (6):943-951.
|
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1038/ng.3717 pmid: 27841879 |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [1] | 任思源, 陈森, 龙治坚, 王博雅, 唐登国, 王正前, 杨斌, 胡尚连, 曹颖. 花魔芋球茎发育期氮分配变化和相关基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2019-2030. |
| [2] | 袁泉, 卢威, 王君, 陈茹, 李衍素, 于贤昌, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 闫妍. 日光温室不同土质灌水下限对早春黄瓜生长、产量和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1377-1385. |
| [3] | 王文娇, 邢军杰, 申成丞, 李斌. 黄瓜蜡质基因CsCER1调控因子CsCOL5的筛选及其功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1005-1016. |
| [4] | 张丛莹, 顾兴芳, 苗晗, 董邵云, 刘小萍, 官健涛, 张圣平. 黄瓜新品种‘中农脆玉1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1173-1174. |
| [5] | 于静, 冯向君, 金英学, 丁国华. 焦脱镁叶绿酸a对黄瓜枯萎病菌的抑制作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 859-874. |
| [6] | 张丛莹, 顾兴芳, 苗晗, 董邵云, 刘小萍, 官健涛, 张圣平. 黄瓜新品种‘中农脆绿2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 919-920. |
| [7] | 周平, 颜少宾, 郭瑞, 金光. 桃镁离子转运蛋白MGT基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 463-478. |
| [8] | 刘梦, 贾惠婷, 周新刚. 黄瓜枯萎病菌共生细菌的分离鉴定及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 643-655. |
| [9] | 崔一琼, 李菊, 刘晓奇, 王俊文, 唐中祺, 武玥, 肖雪梅, 郁继华. 水分亏缺对设施基质栽培番茄果实蔗糖和淀粉代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2607-2619. |
| [10] | 冯一清, 仇胜囡, 吴月, 解阳, 张晓伟, 毕焕改, 艾希珍. 褪黑素对日光温室黄瓜耐冷性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2633-2644. |
| [11] | 尤倩, 刘晓, 刘梦梦, 刘丹, 伯晨, 朱艳芳, 段永波, 薛建平, 张爱民, 薛涛. 半夏热激因子HSF家族基因鉴定及生物信息分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2371-2385. |
| [12] | 吴琼, 张甜甜, 李茂营, 吴慧玲, 郭绍贵, 张洁, 任毅, 张海英, 宫国义. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌5号防控西瓜CGMMV机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2427-2438. |
| [13] | 叶玙璠, 王誉洁, 傅前媛, 王璐, 郝心愿, 丁长庆, 王新超, 曹红利, 李娜娜. 茶树镁离子螯合酶H亚基基因CsChlH的克隆及其表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 91-102. |
| [14] | 蒋素华, 王林青, 吴景亮, 牛苏燕, 刘军, 崔波. 黄瓜新品种‘优NT603’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1807-1808. |
| [15] | 王泉城, 武军, 李磊, 石延霞, 谢学文, 李宝聚, 柴阿丽. 多主棒孢菌CcTLS1对黄瓜的致病机理分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 569-582. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司