
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 1301-1316.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0045
张悦1,2, 冯一了1, 王蓓2, 任文静1, 姜春昱1, 赵新宇1, 王彩红1, 杨丽梅1, 庄木1, 吕红豪1, 王勇1, 张扬勇1,*( ), 季家磊1,3,*(
), 季家磊1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-13
修回日期:2025-04-27
出版日期:2025-05-23
发布日期:2025-05-21
通讯作者:
基金资助:
ZHANG Yue1,2, FENG Yiliao1, WANG Bei2, REN Wenjing1, JIANG Chunyu1, ZHAO Xinyu1, WANG Caihong1, YANG Limei1, ZHUANG Mu1, LÜ Honghao1, WANG Yong1, ZHANG Yangyong1,*( ), JI Jialei1,3,*(
), JI Jialei1,3,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-13
Revised:2025-04-27
Published:2025-05-23
Online:2025-05-21
摘要:
对127份甘蓝自交系材料的叶酸组分和含量进行了靶向代谢组分析,确定甘蓝中叶酸主要组分为5-甲基-四氢叶酸(占比60% ~ 80%)和5-甲酰-四氢叶酸(占比15% ~ 25%),筛选出早熟圆球型高叶酸自交系材料Q428和低叶酸自交系材料Q372。通过Q428和Q372比较转录组分析,鉴定出10 305个差异表达基因,在Q428中上调和下调表达的基因分别有5 178、5 127个。GO分析显示,差异表达基因与光合作用、光收集、蛋白质—发色团连接和叶绿素结合等相关;KEGG分析表明,差异表达基因主要集中于碳代谢、氨基酸生物合成及淀粉和蔗糖代谢等通路。通过与24个拟南芥叶酸合成代谢基因的共线性分析,在甘蓝中鉴定到叶酸合成代谢相关基因57个,其中12个关键基因在Q428和Q372中显著差异表达。与Q372相比,Q428中BoGCHI、GDC复合体相关编码基因(BoGCSH、BoGCSL、BoGCSP、BoGCST)、BoMTHFR和BoSHMT1a的表达量显著上调,而BoGGH在Q428中表达量显著下调。初步推测上述基因的差异表达是影响甘蓝叶酸含量的关键因素,可作为利用生物育种技术调控甘蓝叶酸含量的分子靶点。
张悦, 冯一了, 王蓓, 任文静, 姜春昱, 赵新宇, 王彩红, 杨丽梅, 庄木, 吕红豪, 王勇, 张扬勇, 季家磊. 甘蓝叶酸合成代谢的转录组初步分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(5): 1301-1316.
ZHANG Yue, FENG Yiliao, WANG Bei, REN Wenjing, JIANG Chunyu, ZHAO Xinyu, WANG Caihong, YANG Limei, ZHUANG Mu, LÜ Honghao, WANG Yong, ZHANG Yangyong, JI Jialei. Preliminary Transcriptome Analysis of Folate Synthesis and Metabolism in Cabbage[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(5): 1301-1316.
| 样品Sample | 双端序列总数Paired-end reads counts | 总碱基数Clean bases | GC含量/% GC Content | 碱基质量值/% ≥ 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q372-1 | 20 186 702 | 6 043 240 774 | 46.57 | 94.02 |
| Q372-2 | 21 382 384 | 6 402 029 466 | 46.70 | 94.50 |
| Q372-3 | 19 720 185 | 5 902 457 860 | 46.32 | 94.24 |
| Q428-1 | 21 147 787 | 6 332 933 914 | 47.79 | 93.93 |
| Q428-2 | 23 999 831 | 7 185 985 424 | 47.75 | 94.32 |
| Q428-3 | 19 953 645 | 5 975 348 582 | 47.70 | 94.16 |
表1 测序数据统计
Table 1 Sequencing data statistics
| 样品Sample | 双端序列总数Paired-end reads counts | 总碱基数Clean bases | GC含量/% GC Content | 碱基质量值/% ≥ 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q372-1 | 20 186 702 | 6 043 240 774 | 46.57 | 94.02 |
| Q372-2 | 21 382 384 | 6 402 029 466 | 46.70 | 94.50 |
| Q372-3 | 19 720 185 | 5 902 457 860 | 46.32 | 94.24 |
| Q428-1 | 21 147 787 | 6 332 933 914 | 47.79 | 93.93 |
| Q428-2 | 23 999 831 | 7 185 985 424 | 47.75 | 94.32 |
| Q428-3 | 19 953 645 | 5 975 348 582 | 47.70 | 94.16 |

图3 甘蓝自交系材料Q428与Q372差异显著的前20个GO功能组
Fig. 3 The top 20 Gene Ontology terms exhibiting significant differential enrichment between cabbage inbred lines Q428 and Q372
| 功能途径 Function pathway | 基因 Gene | 蛋白缩写 Protein abbreviation | 拟南芥ID Arabidopsis thaliana ID | 甘蓝ID Brassica oleracea ID | 相似度/% Similarity | E值 E-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pABA合成 pABA synthesis | ADCL | ADCL | AT1G50090.1 | BolC02g022020.2J | 80.548 | 0 |
| BolC03g082990.2J | 85.955 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g004630.2J | 89.045 | 0 | ||||
| ADCS | ADCS | AT2G28880.1 | BolC04g021330.2J | 84.832 | 0 | |
| BolC04g055450.2J | 81.031 | 0 | ||||
| 喋啶合成 Pteridine synthesis | NUDT | DPP | AT1G68760.1 | BolC02g025120.2J | 82.270 | 9.78E-87 |
| DHNA | DHNA | AT3G11750.1 | BolC01g050940.2J | 87.500 | 3.6E-74 | |
| GCHI | GCHI | AT3G07270.1 | BolC05g058460.2J | 82.303 | 0 | |
| BolC01g053860.2J | 81.023 | 0 | ||||
| 组装加尾 Assembly and taliling | DHTS/DHFR | DHFR | AT2G16370.1 | BolC03g051860.2J | 89.382 | 0 |
| BolC01g004210.2J | 85.246 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g057740.2J | 88.690 | 5.2E-103 | ||||
| DHFS | DHFS | AT5G41480.1 | BolC07g028910.2J | 86.090 | 0 | |
| HPPK/DHPS | HPPK/DHPS | AT4G30000.2 | BolC01g009090.2J | 85.257 | 0 | |
| 分布转运 Distribution and transportation | FPGS | FPGS | AT3G10160.1 | BolC01g052470.2J | 82.083 | 0 |
| GGH | GGH | AT1G78660.1 | BolC02g034750.2J | 85.893 | 0 | |
| 降解回补Degradation and replenishment | PTAR | PTAR | AT1G10310.1 | BolC08g021880.2J | 92.181 | 5.2E-168 |
| C1代谢 C1 metabolism | 5FCL | 5FCL | AT5G13050.1 | BolC09g060020.2J | 85.816 | 4.2E-165 |
| BolC02g005400.2J | 79.196 | 0 | ||||
| 5FCLL | 5FCLL | AT1G76730.1 | BolC06g030250.2J | 86.517 | 0 | |
| DHC | DHC | AT2G38660.1 | BolC04g063230.2J | 88.385 | 0 | |
| FTHS | FTHS | AT1G31220.1 | BolC05g029350.2J | 83.390 | 1.4E-172 | |
| GCSH | GCSH | AT1G32470.1 | BolC08g011080.2J | 94.012 | 3.1E-105 | |
| BolC05g037930.2J | 95.210 | 2.9E-107 | ||||
| BolC05g030770.2J | 93.413 | 6.4E-105 | ||||
| BolC04g013540.2J | 91.018 | 8E-101 | ||||
| GCSL | GCSL | AT1G48030.1 | BolC06g002320.2J | 94.488 | 0 | |
| BolC05g049030.2J | 95.079 | 0 | ||||
| BolC05g049060.2J | 91.262 | 1.94E-57 | ||||
| GCSP | GCSP | AT4G33010.1 | BolC01g005590.2J | 90.172 | 0 | |
| GCST | GCST | AT1G11860.1 | BolC08g055130.2J | 97.066 | 0 | |
| BolC08g023150.2J | 95.854 | 0 | ||||
| MS | MS | AT5G17920.1 | BolC03g009250.2J | 97.781 | 0 | |
| BolC09g055230.2J | 97.520 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g008490.2J | 97.258 | 0 | ||||
| BolC03g036730.2J | 95.953 | 0 | ||||
| BolC05g061690.2J | 95.181 | 0 | ||||
| BolC03g011020.2J | 91.054 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g025710.2J | 95.200 | 8.66E-81 | ||||
| MTHFR | MTHR | AT2G44160.1 | BolC04g005400.2J | 94.454 | 0 | |
| BolC04g066800.2J | 91.611 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g025320.2J | 96.121 | 0 | ||||
| BolC08g043230.2J | 94.098 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g000140.2J | 80.519 | 3.77E-35 | ||||
| PURU | 10-FDF | AT4G17360.1 | BolC01g023770.2J | 93.617 | 0 | |
| BolC07g030320.2J | 93.272 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g042860.2J | 79.688 | 9.51E-27 | ||||
| BolC07g030040.2J | 82.759 | 9.29E-28 | ||||
| SHMT1a | SHMTla | AT4G37930.1 | BolC03g073550.2J | 98.263 | 0 | |
| BolC01g001230.2J | 97.297 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g042720.2J | 91.573 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g033950.2J | 89.513 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g059720.2J | 81.176 | 1.01E-35 | ||||
| SHMT3 | SHMT3 | AT4G32520.1 | BolC01g006620.2J | 91.018 | 0 | |
| BolC03g081120.2J | 88.868 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g056500.2J | 96.970 | 1.9E-14 | ||||
| BolC07g056470.2J | 96.970 | 1.9E-14 |
表2 叶酸合成代谢相关基因
Table 2 Genes related to folate synthesis and metabolism
| 功能途径 Function pathway | 基因 Gene | 蛋白缩写 Protein abbreviation | 拟南芥ID Arabidopsis thaliana ID | 甘蓝ID Brassica oleracea ID | 相似度/% Similarity | E值 E-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pABA合成 pABA synthesis | ADCL | ADCL | AT1G50090.1 | BolC02g022020.2J | 80.548 | 0 |
| BolC03g082990.2J | 85.955 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g004630.2J | 89.045 | 0 | ||||
| ADCS | ADCS | AT2G28880.1 | BolC04g021330.2J | 84.832 | 0 | |
| BolC04g055450.2J | 81.031 | 0 | ||||
| 喋啶合成 Pteridine synthesis | NUDT | DPP | AT1G68760.1 | BolC02g025120.2J | 82.270 | 9.78E-87 |
| DHNA | DHNA | AT3G11750.1 | BolC01g050940.2J | 87.500 | 3.6E-74 | |
| GCHI | GCHI | AT3G07270.1 | BolC05g058460.2J | 82.303 | 0 | |
| BolC01g053860.2J | 81.023 | 0 | ||||
| 组装加尾 Assembly and taliling | DHTS/DHFR | DHFR | AT2G16370.1 | BolC03g051860.2J | 89.382 | 0 |
| BolC01g004210.2J | 85.246 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g057740.2J | 88.690 | 5.2E-103 | ||||
| DHFS | DHFS | AT5G41480.1 | BolC07g028910.2J | 86.090 | 0 | |
| HPPK/DHPS | HPPK/DHPS | AT4G30000.2 | BolC01g009090.2J | 85.257 | 0 | |
| 分布转运 Distribution and transportation | FPGS | FPGS | AT3G10160.1 | BolC01g052470.2J | 82.083 | 0 |
| GGH | GGH | AT1G78660.1 | BolC02g034750.2J | 85.893 | 0 | |
| 降解回补Degradation and replenishment | PTAR | PTAR | AT1G10310.1 | BolC08g021880.2J | 92.181 | 5.2E-168 |
| C1代谢 C1 metabolism | 5FCL | 5FCL | AT5G13050.1 | BolC09g060020.2J | 85.816 | 4.2E-165 |
| BolC02g005400.2J | 79.196 | 0 | ||||
| 5FCLL | 5FCLL | AT1G76730.1 | BolC06g030250.2J | 86.517 | 0 | |
| DHC | DHC | AT2G38660.1 | BolC04g063230.2J | 88.385 | 0 | |
| FTHS | FTHS | AT1G31220.1 | BolC05g029350.2J | 83.390 | 1.4E-172 | |
| GCSH | GCSH | AT1G32470.1 | BolC08g011080.2J | 94.012 | 3.1E-105 | |
| BolC05g037930.2J | 95.210 | 2.9E-107 | ||||
| BolC05g030770.2J | 93.413 | 6.4E-105 | ||||
| BolC04g013540.2J | 91.018 | 8E-101 | ||||
| GCSL | GCSL | AT1G48030.1 | BolC06g002320.2J | 94.488 | 0 | |
| BolC05g049030.2J | 95.079 | 0 | ||||
| BolC05g049060.2J | 91.262 | 1.94E-57 | ||||
| GCSP | GCSP | AT4G33010.1 | BolC01g005590.2J | 90.172 | 0 | |
| GCST | GCST | AT1G11860.1 | BolC08g055130.2J | 97.066 | 0 | |
| BolC08g023150.2J | 95.854 | 0 | ||||
| MS | MS | AT5G17920.1 | BolC03g009250.2J | 97.781 | 0 | |
| BolC09g055230.2J | 97.520 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g008490.2J | 97.258 | 0 | ||||
| BolC03g036730.2J | 95.953 | 0 | ||||
| BolC05g061690.2J | 95.181 | 0 | ||||
| BolC03g011020.2J | 91.054 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g025710.2J | 95.200 | 8.66E-81 | ||||
| MTHFR | MTHR | AT2G44160.1 | BolC04g005400.2J | 94.454 | 0 | |
| BolC04g066800.2J | 91.611 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g025320.2J | 96.121 | 0 | ||||
| BolC08g043230.2J | 94.098 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g000140.2J | 80.519 | 3.77E-35 | ||||
| PURU | 10-FDF | AT4G17360.1 | BolC01g023770.2J | 93.617 | 0 | |
| BolC07g030320.2J | 93.272 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g042860.2J | 79.688 | 9.51E-27 | ||||
| BolC07g030040.2J | 82.759 | 9.29E-28 | ||||
| SHMT1a | SHMTla | AT4G37930.1 | BolC03g073550.2J | 98.263 | 0 | |
| BolC01g001230.2J | 97.297 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g042720.2J | 91.573 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g033950.2J | 89.513 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g059720.2J | 81.176 | 1.01E-35 | ||||
| SHMT3 | SHMT3 | AT4G32520.1 | BolC01g006620.2J | 91.018 | 0 | |
| BolC03g081120.2J | 88.868 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g056500.2J | 96.970 | 1.9E-14 | ||||
| BolC07g056470.2J | 96.970 | 1.9E-14 |

图7 甘蓝自交系叶酸合成代谢通路图 参考De Lepeleire等(2018)和Lian等(2015)绘制 参与叶酸合成代谢的酶。ADCS:氨基脱氧胆酸合成酶;ADCL:氨基脱氧胆酸裂解酶;FPGS:叶酰聚谷氨酸合成酶;PGH:pABA-谷氨酸水解酶;GGH:γ-谷酰基水解酶;GCHI:GTP 环化水解酶Ⅰ;HPPK/DHPS:二氢蝶呤焦磷酸激酶;DHFS:二氢叶酸合成酶;DHFR:二氢叶酸还原酶;GDC:甘氨酸脱羧酶;SHMT1a:丝氨酸羟甲基转移酶1a;MTHFR:亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶;MS:蛋氨酸合成酶;FTHS:10-甲酰基四氢叶酸合成酶;DHC:5,10-亚甲基-四氢叶酸脱氢酶/5,10-亚甲基-四氢叶酸环水解酶
Fig. 7 Folate biosynthetic pathway in cabbage inbred lines Drawing based on De Lepeleire et al.,2018;Lian et al.,2015 Enzymes involved in folate synthesis. ADCS:Aminodeoxychorismate synthase;ADCL:Aminodeoxychorismate lyase;FPGS:Folylpolyglutamate synthetase;PGH:pABA-Glu hydrolase;GGH:γ-Glutamyl hydrolase;GCHI:GTP cyclohydrolaseⅠ;HPPK/DHPS:Dihydropterin pyrophosphokinase/dihydropteroate synthase;DHFS:Dihydrofolate synthetase;DHFR:Dihydrofolate reductase;GDC:Glycine decarboxylase;SHMT1a:Serine hydroxymethyl transferase 1a;MTHFR:Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase;MS:Methionine synthase;FTHS:10-Formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase;DHC:5,10-Methylene-THF dehydrogenase/5,10-Methenyl-THF cyclohydrolase
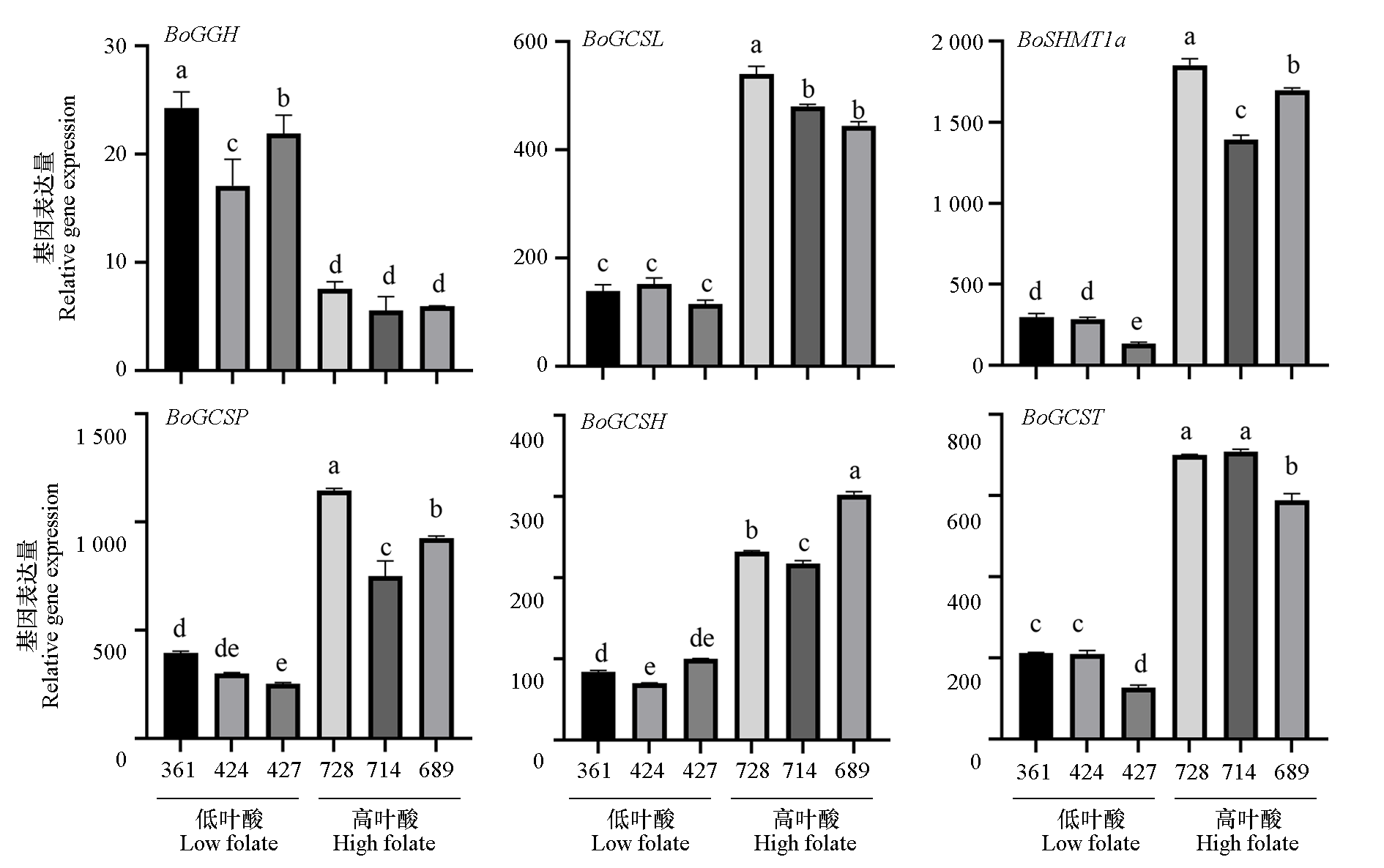
图8 甘蓝自交系材料Q428和Q372差异表达基因RT-qPCR 验证 柱上不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 8 RT-qPCR validation of differentially expressed genes in cabbage inbred lines Q428 and Q372 Different lowercase letters above the bars mean significantly different at the 0.05 probability level
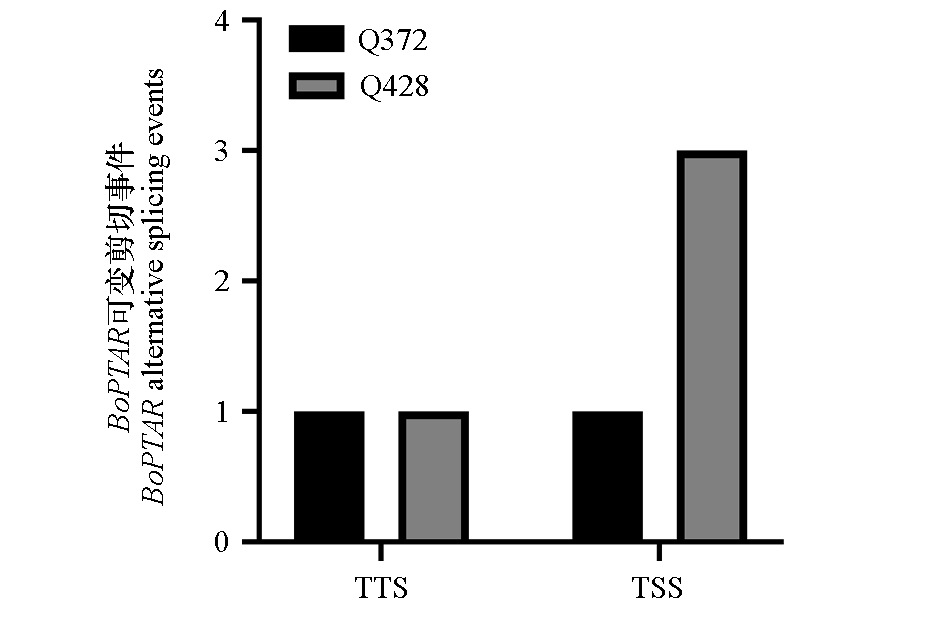
图9 甘蓝自交系材料Q428和Q372差异可变剪接事件 TTS:转录终止位点;TSS:转录起始位点
Fig. 9 Differential alternative splicing events between cabbage inbred lines Q428 and Q372 TTS:Transcription termination site;TSS:Transcription start site
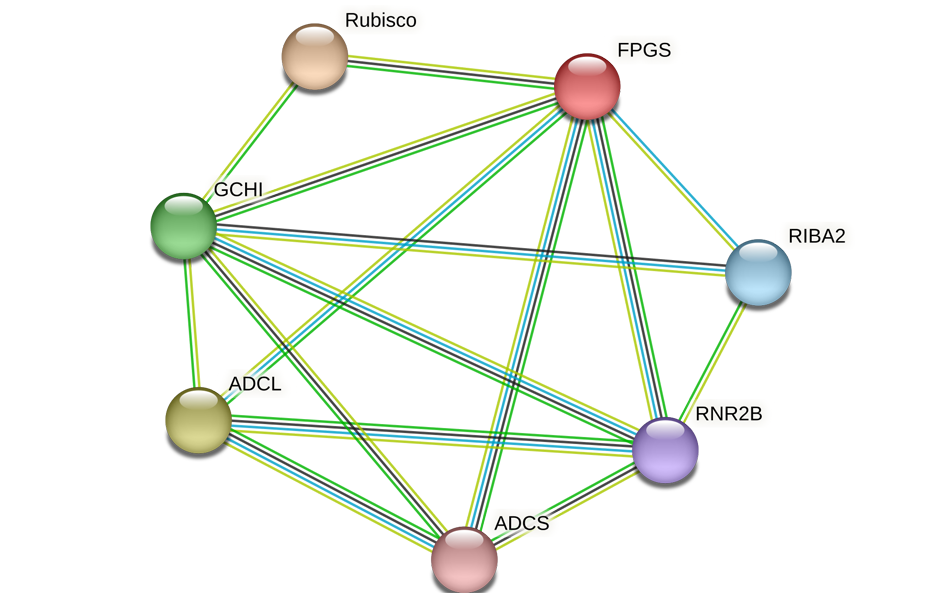
图10 叶酸合成蛋白与一碳代谢关键蛋白网络分析模式图 ADCS:BolC04g021330.2J;ADCL:BolC02g022020.2J 蓝色线条:已知互作蛋白;绿色线条:基因邻域;浅绿线条:文本挖掘;黑色线条:基因共表达
Fig. 10 Network analysis model of folate biosynthesis proteins and one-carbon metabolism key proteins ADCS:BolC04g021330.2J;ADCL:BolC02g022020.2J. Blue Lines:known interactions;Green lines:gene neighborhood;Light green line:text mining;Black line:co-expression
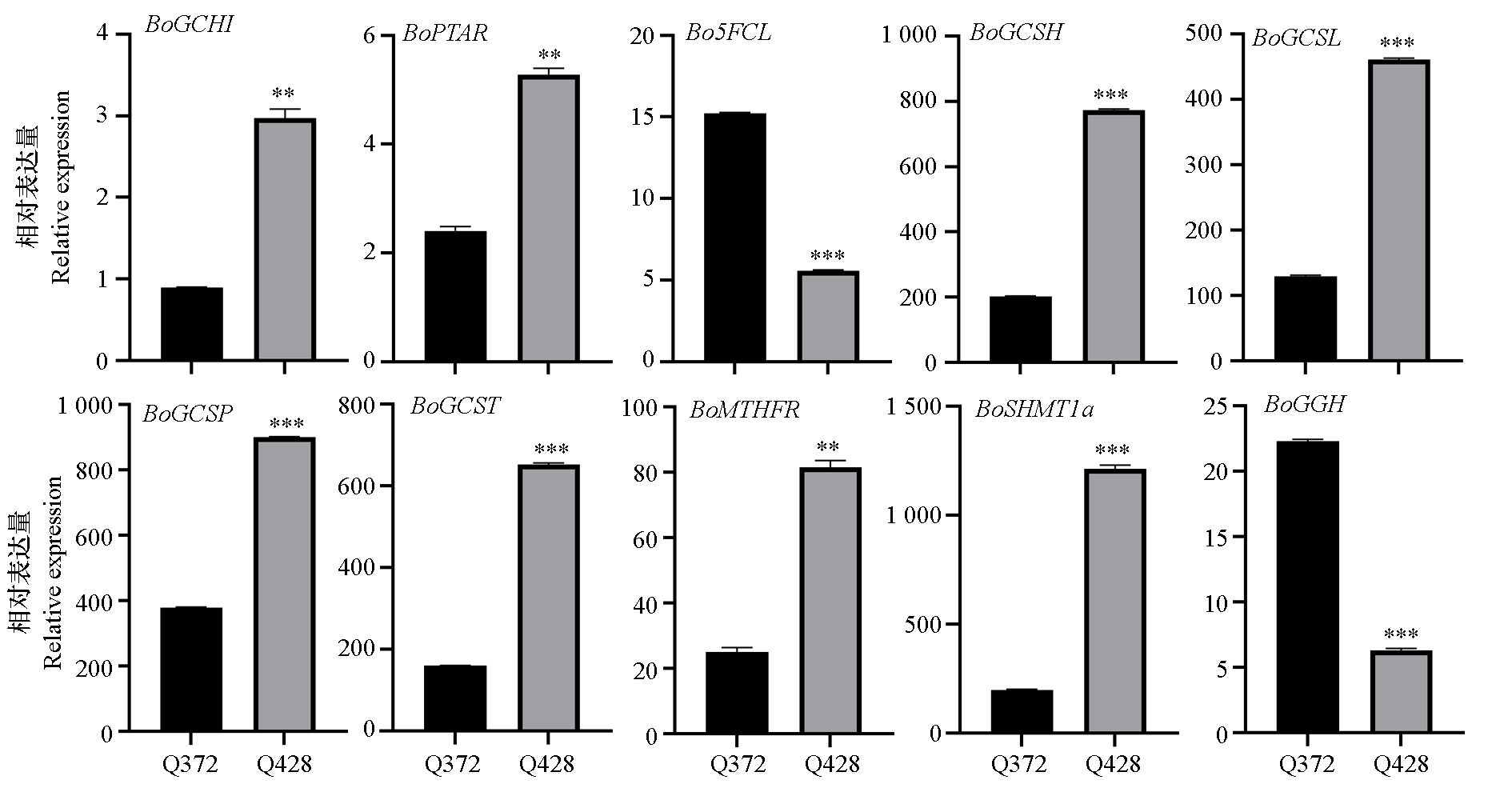
图11 叶酸相关基因RT-qPCR验证
Fig. 11 RT-qPCR verification of folate-related genes BoGCH1:BolC05g058460.2J;BoPTAR:BolC08g021880.2J;Bo5FCL:BolC02g005400.2J;BoGCSH:BolC08g011080.2J;BoGCSL:BolC06g002320.2J;BoGCSP:BolC01g005590.2J;BoGCST:BolC08g055130.2J;BoMTHFR:BolC04g005400.2J;BoSHMT1a:BolC03g073550.2J;BoGGH:BolC02g034750.2J t-test. **:α = 0.01;***:α = 0.001
| [1] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04330.x pmid: 21070406 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert483 pmid: 24574483 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
|
崔亚楠, 韩莉妲, 舒金帅, 王孝宣, 黄泽军, 国艳梅, 刘磊, 杜永臣, 张春义, 李君明. 2020. 不同类型番茄叶酸及其衍生物含量的初步分析. 中国蔬菜,(12):14-21.
|
|
| [7] |
doi: S1674-2052(17)30378-7 pmid: 29277427 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
蒋伟, 李白玉. 2023. 微生物法测定蔬菜中叶酸含量. 食品安全导刊,(13):84-86.
|
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2012.00525 |
|
李莎, 姜凌, 王崇英, 张春义. 2012. 叶酸在植物体内功能的研究进展. 植物学报, 47 (5):525-533.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2012.00525 |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery453 pmid: 30753561 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp152 pmid: 19541855 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04173 |
|
马贵芳, 满夏夏, 张益娟, 高豪, 孙朝霞, 李红英, 韩渊怀, 侯思宇. 2021. 谷子穗发育期转录组与叶酸代谢谱联合分析. 作物学报, 47 (5):837-846.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04173 |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
pmid: 11375437 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
|
杨丽梅, 方智远, 刘玉梅, 庄木, 张扬勇, 孙培田. 2011. “十一五”我国甘蓝遗传育种研究进展. 中国蔬菜,(2):1-10.
|
| [1] | 王清明, 张 雷, 蔡华庆, 周 洁, 韦丽君, 刘道敏. 薹用甘蓝型油菜新品种‘皖薹2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 97-98. |
| [2] | 袁娟伟, 贾利, 王涵, 严从生, 张其安, 俞飞飞, 甘德芳, 江海坤. 辣椒种质资源疫病抗性鉴定及抗病基因挖掘[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 857-871. |
| [3] | 唐伶俐, 贺玉花, 王庆涛, 安璐璐, 徐永阳, 张健, 孔维虎, 户克云, 赵光伟. 非呼吸跃变和呼吸跃变型甜瓜成熟果实的激素与转录组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 883-896. |
| [4] | 邵一帆, 朱宝庆, 王童欣, 廖建和, 吴繁花, 杨思怡, 冯建行, 于旭东. 基于激素、转录组和代谢组研究木棉皮刺的遗传调控[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 933-946. |
| [5] | 李强, 王英, 赵玉倩, 隋雪莲, 蔡玉梅, 苏彦宾, 郑敬蕾, 宋小明. 结球甘蓝新品种‘豪美奥奇’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 1105-1106. |
| [6] | 吝茹雪, 王斐, 张艳杰, 马力, 刘肖烽, 李舒然, 刘亚龙, 王晨, 姜淑苓, 欧春青. 梨矮生相关基因转录组筛选与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 545-560. |
| [7] | 李芮, 王稳, 杜明辉, 刘根忠, 马方放, 包志龙. SlBON1调控番茄植株营养生长机制的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 73-87. |
| [8] | 李洁, 武超, 贾祥堑, 王娟. ‘壶瓶枣’果皮着色物质及其相关基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1728-1742. |
| [9] | 匡美美, 李黎, 马建伟, 刘原, 蒋鸿霏, 雷瑞, 满玉萍, 王一帆, 黄波, 王彦昌, 刘世彪. 利用中华猕猴桃杂交后代转录组测序筛选抗溃疡病相关基因[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1743-1757. |
| [10] | 韩荧, 段颖, 牛一杰, 李衍素, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 王君, 李强, 陈双臣, 闫妍. 腐殖酸生物降解地膜提高番茄品质的转录代谢机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [11] | 段敏杰, 李怡斐, 王春萍, 杨小苗, 黄任中, 黄启中, 张世才. 辣椒果实类胡萝卜素调控因子转录组和靶向代谢组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1773-1791. |
| [12] | 李文远, 林梦桦, 李亚辉, 于全琦, 梁颖, 张志勇. 梨果实代谢组学研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1595-1609. |
| [13] | 姚丰平, 王衍彬, 秦玉川, 王丽玲. 不同干燥处理的树参叶黄酮类成分的非靶向代谢组学分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1069-1082. |
| [14] | 马存发, 武婷, 赵辉, 张天培, 赵立坚, 余永辉, 肖建成, 李军, 巫水钦. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术敲除青花菜BoSP11创制自交亲和系[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 509-519. |
| [15] | 张文昊, 张辉, 刘雨婷, 王艳, 张迎迎, 王馨曼, 王全华, 朱为民, 杨学东. 番茄含糖量不同的两个材料果实转录组初步分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 281-294. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司