
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 491-502.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0282
杨文清, 王嘉荟, 徐秉良, 李惠霞, 梁巧兰, 杨顺义*( ), 牛二波*(
), 牛二波*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-08
修回日期:2024-11-07
出版日期:2025-02-25
发布日期:2025-02-23
通讯作者:
基金资助:
YANG Wenqing, WANG Jiahui, XU Bingliang, LI Huixia, LIANG Qiaolan, YANG Shunyi*( ), NIU Erbo*(
), NIU Erbo*( )
)
Received:2024-05-08
Revised:2024-11-07
Published:2025-02-25
Online:2025-02-23
摘要:
利用高通量测序技术和RT-PCR相结合的方法,对甘肃定西地区感染病毒病的辣椒叶片进行病原鉴定。结果显示染病叶片受黄瓜花叶病毒(cucumber mosaic virus,CMV)和甜菜西方黄化病毒(beet western yellows virus,BWYV)的复合侵染,首次在甘肃发现BWYV侵染辣椒。借助特异性引物克隆BWYV的外壳蛋白(coat protein,CP)和运动蛋白(movement protein,MP)基因深入分析BWYV的分子进化和遗传变异,通过序列比对发现其CP基因与其他物种BWYV分离物的核苷酸和氨基酸相似性分别为93.27% ~ 99.51%和90.10% ~ 99.01%,其MP基因的相似性分别为89.20% ~ 99.05%和86.86% ~ 98.86%。此外,系统发育树分析显示BWYV不同分离物可分为4个类群,无明显地理分布特征,寄主植物多样性分析显示具有显著的寄主关联性。
杨文清, 王嘉荟, 徐秉良, 李惠霞, 梁巧兰, 杨顺义, 牛二波. 甘肃定西地区辣椒病毒病鉴定及BWYV遗传变异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 491-502.
YANG Wenqing, WANG Jiahui, XU Bingliang, LI Huixia, LIANG Qiaolan, YANG Shunyi, NIU Erbo. Identification of Pepper Virus Diseases and Analysis of BWYV Genetic Variation in Dingxi Area of Gansu Province[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 491-502.
| 引物名称 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物/bp Fragment | 退火温度/℃ Tm | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMV-CP | F:GTCGACCATGGACAAAT;R:CCGGGTCAGACTGGTAGCA | 660 | 56 | 王德富 等, |
| CMV-MP- | F:AGGCATGGCTTTCCAAGGTACCAG;R:AGTGCTAAAGACCGTTAACCA | 850 | 55 | 杜江 等, |
| BWYV-CP | F:CCTCAAAATCTCAGCCCACG;R:TGGCATCATCGGTACTCTGG | 780 | 60 | 本试验This study |
| BWYV-MP | F:TGAATACGGTCGTGGGTAGA;R:GGCCATTATACGAGTCGCTG | 725 | 56 | 本试验This study |
表1 辣椒主要病毒检测引物
Table 1 Primers used for detection of key virus in pepper
| 引物名称 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物/bp Fragment | 退火温度/℃ Tm | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMV-CP | F:GTCGACCATGGACAAAT;R:CCGGGTCAGACTGGTAGCA | 660 | 56 | 王德富 等, |
| CMV-MP- | F:AGGCATGGCTTTCCAAGGTACCAG;R:AGTGCTAAAGACCGTTAACCA | 850 | 55 | 杜江 等, |
| BWYV-CP | F:CCTCAAAATCTCAGCCCACG;R:TGGCATCATCGGTACTCTGG | 780 | 60 | 本试验This study |
| BWYV-MP | F:TGAATACGGTCGTGGGTAGA;R:GGCCATTATACGAGTCGCTG | 725 | 56 | 本试验This study |
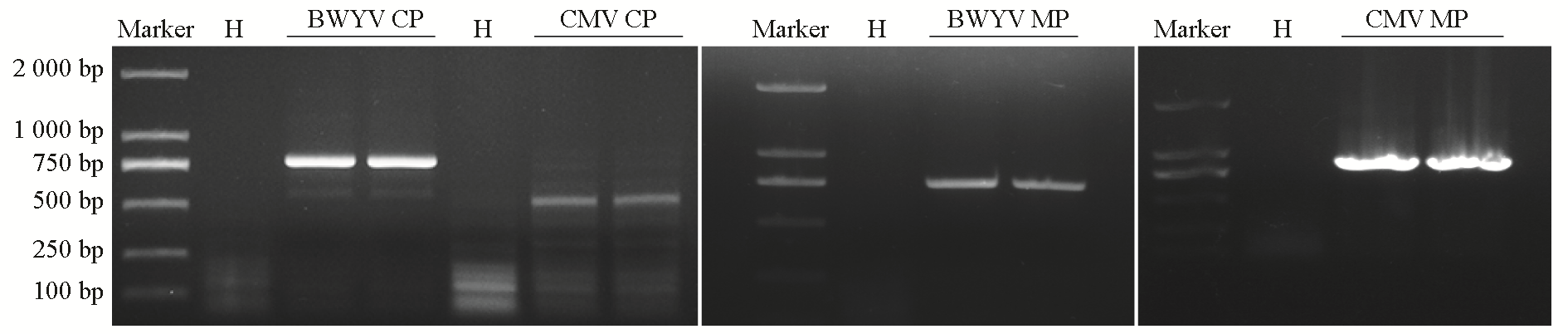
图3 辣椒健康植株(H)与感染病毒植株叶片中BWYV和CMV外壳蛋白(CP)和运动蛋白(MP)基因扩增结果
Fig. 3 Amplification results of BWYV and CMV coat protein(CP)and motor protein(MP)genes in the leaves of pepper healthy plants(H)and virus-infected plants
| 基因登录号 Gene ID | 株系 Strain | 寄主植物 Host plant | 地理来源 Geographical origin | 核苷酸 Nucleotide | 氨基酸 Aminoacid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK307779.1 | SDJN16 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 中国山东Shandong,China | 99.18 | 98.51 |
| MK307780.1 | SDWF16 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 中国山东Shandong,China | 99.01 | 99.01 |
| LC428355.1 | S14 | 菠菜Spinacia oleracea | 日本Japan | 99.51 | 99.01 |
| MW349136.1 | JJ18 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 韩国Korea | 99.18 | 98.51 |
| OQ570952.1 | YA35 | 萝卜Raphanus sativus | 韩国Korea | 99.18 | 98.02 |
| LC592344.1 | ADHS | 北玄参Scrophularia buergeriana | 韩国Korea | 99.01 | 99.01 |
| LC428357.1 | R3a | 萝卜Raphanus sativus | 日本Japan | 98.85 | 98.02 |
| OM419176.1 | — | 香菜Coriandrum sativum | 塞浦路斯Cyprus | 93.92 | 91.09 |
| ON924237.1 | W11 | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 美国USA | 93.76 | 91.58 |
| KU521325.1 | Rouen1 | 猪笼草Nepenthes mirabilis | 法国French | 93.60 | 90.10 |
| ON924244.1 | NYC | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 美国USA | 93.60 | 91.58 |
| NC004756.1 | USA | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 美国USA | 93.60 | 92.08 |
| HM804471.1 | BJA | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国北京Beijing,China | 97.87 | 98.51 |
| HM804472.1 | BJB | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国北京Beijing,China | 95.73 | 96.04 |
| EU636991.1 | IM | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国内蒙古Inner Mongolia,China | 99.18 | 90.10 |
| EU636990.1 | GS | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国甘肃Gansu,China | 93.76 | 93.56 |
| AB903037.1 | KY | 菠菜Spinacia oleracea | 日本Japan | 93.27 | 94.55 |
表2 BWYV-CP-GSDX16与其他地区辣椒及其他物种BWYV CP分离物序列的相似性
Table 2 Sequence similarity between BWYV-CP-GSDX16 and BWYV CP isolates from peppers and other species in other regions %
| 基因登录号 Gene ID | 株系 Strain | 寄主植物 Host plant | 地理来源 Geographical origin | 核苷酸 Nucleotide | 氨基酸 Aminoacid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK307779.1 | SDJN16 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 中国山东Shandong,China | 99.18 | 98.51 |
| MK307780.1 | SDWF16 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 中国山东Shandong,China | 99.01 | 99.01 |
| LC428355.1 | S14 | 菠菜Spinacia oleracea | 日本Japan | 99.51 | 99.01 |
| MW349136.1 | JJ18 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 韩国Korea | 99.18 | 98.51 |
| OQ570952.1 | YA35 | 萝卜Raphanus sativus | 韩国Korea | 99.18 | 98.02 |
| LC592344.1 | ADHS | 北玄参Scrophularia buergeriana | 韩国Korea | 99.01 | 99.01 |
| LC428357.1 | R3a | 萝卜Raphanus sativus | 日本Japan | 98.85 | 98.02 |
| OM419176.1 | — | 香菜Coriandrum sativum | 塞浦路斯Cyprus | 93.92 | 91.09 |
| ON924237.1 | W11 | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 美国USA | 93.76 | 91.58 |
| KU521325.1 | Rouen1 | 猪笼草Nepenthes mirabilis | 法国French | 93.60 | 90.10 |
| ON924244.1 | NYC | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 美国USA | 93.60 | 91.58 |
| NC004756.1 | USA | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 美国USA | 93.60 | 92.08 |
| HM804471.1 | BJA | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国北京Beijing,China | 97.87 | 98.51 |
| HM804472.1 | BJB | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国北京Beijing,China | 95.73 | 96.04 |
| EU636991.1 | IM | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国内蒙古Inner Mongolia,China | 99.18 | 90.10 |
| EU636990.1 | GS | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国甘肃Gansu,China | 93.76 | 93.56 |
| AB903037.1 | KY | 菠菜Spinacia oleracea | 日本Japan | 93.27 | 94.55 |
| 登录号 Gene ID | 株系 Strain | 寄主植物 Host plant | 地理来源 Geographical origin | 核苷酸 Nucleotide | 氨基酸 Aminoacid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK307780.1 | SDWF16 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 中国山东Shandong,China | 99.05 | 98.86 |
| LC428357.1 | R3a | 萝卜Raphanus sativus | 日本Japan | 99.05 | 98.86 |
| OQ625515.1 | NJ22 | 萝卜Raphanus sativus | 韩国Korea | 99.05 | 98.86 |
| LC592344.1 | ADHS | 北玄参Scrophularia buergeriana | 韩国Korea | 97.92 | 94.86 |
| ON759519.1 | P03 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 韩国Korea | 98.86 | 98.29 |
| MK307779.1 | SDJN16 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 中国山东Shandong,China | 98.67 | 98.29 |
| OQ570952.1 | YA35 | 萝卜Raphanus sativus | 韩国Korea | 98.48 | 98.29 |
| KM076647.1 | LS | 益母草Leonurus sibiricus | 韩国Korea | 98.48 | 97.14 |
| HM804471.1 | BJA | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国北京Beijing,China | 96.21 | 93.14 |
| HM804472.1 | BJB | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国北京Beijing,China | 96.02 | 92.57 |
| ON924175.1 | JJ | 小麦Triticum aestivum | 中国江苏Jiangsu,China | 91.29 | 89.14 |
| EU636990.1 | GS | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国甘肃Gansu,China | 89.96 | 87.43 |
| HQ543079.1 | 6pCP | 豌豆Pisum sativum | 澳大利亚Australia | 89.39 | 89.14 |
| EU636991.1 | IM | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国内蒙古Inner Mongolia,China | 89.58 | 86.86 |
| HQ543082.1 | 9p | 豌豆Pisum sativum | 澳大利亚Australia | 89.39 | 88.00 |
| HQ543095.1 | 27p | 豌豆Pisum sativum | 澳大利亚Australia | 89.20 | 86.86 |
| HQ543084.1 | 14p | 豌豆Pisum sativum | 澳大利亚Australia | 89.20 | 87.43 |
表3 BWYV-MP-GSDX16与其他地区辣椒及其他物种BWYV MP分离物序列的相似性
Table 3 Sequence similarity between BWYV-MP-GSDX16 and BWYV MP isolates from peppers and other species in other regions %
| 登录号 Gene ID | 株系 Strain | 寄主植物 Host plant | 地理来源 Geographical origin | 核苷酸 Nucleotide | 氨基酸 Aminoacid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK307780.1 | SDWF16 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 中国山东Shandong,China | 99.05 | 98.86 |
| LC428357.1 | R3a | 萝卜Raphanus sativus | 日本Japan | 99.05 | 98.86 |
| OQ625515.1 | NJ22 | 萝卜Raphanus sativus | 韩国Korea | 99.05 | 98.86 |
| LC592344.1 | ADHS | 北玄参Scrophularia buergeriana | 韩国Korea | 97.92 | 94.86 |
| ON759519.1 | P03 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 韩国Korea | 98.86 | 98.29 |
| MK307779.1 | SDJN16 | 辣椒Capsicum annuum | 中国山东Shandong,China | 98.67 | 98.29 |
| OQ570952.1 | YA35 | 萝卜Raphanus sativus | 韩国Korea | 98.48 | 98.29 |
| KM076647.1 | LS | 益母草Leonurus sibiricus | 韩国Korea | 98.48 | 97.14 |
| HM804471.1 | BJA | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国北京Beijing,China | 96.21 | 93.14 |
| HM804472.1 | BJB | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国北京Beijing,China | 96.02 | 92.57 |
| ON924175.1 | JJ | 小麦Triticum aestivum | 中国江苏Jiangsu,China | 91.29 | 89.14 |
| EU636990.1 | GS | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国甘肃Gansu,China | 89.96 | 87.43 |
| HQ543079.1 | 6pCP | 豌豆Pisum sativum | 澳大利亚Australia | 89.39 | 89.14 |
| EU636991.1 | IM | 甜菜Beta vulgaris | 中国内蒙古Inner Mongolia,China | 89.58 | 86.86 |
| HQ543082.1 | 9p | 豌豆Pisum sativum | 澳大利亚Australia | 89.39 | 88.00 |
| HQ543095.1 | 27p | 豌豆Pisum sativum | 澳大利亚Australia | 89.20 | 86.86 |
| HQ543084.1 | 14p | 豌豆Pisum sativum | 澳大利亚Australia | 89.20 | 87.43 |
| 分组 Group | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | — | — | — | — |
| Ⅱ | 0.0464 | — | — | — |
| Ⅲ | 0.1157 | 0.1367 | — | — |
| Ⅳ | 0.1212 | 0.1470 | 0.1482 | — |
表4 辣椒BWYV CP-GSDX16(所在Ⅰ组)与不同地域BWYV CP分离物的组间遗传距离
Table 4 Genetic distance between pepper BWYV CP-GSDX16(group Ⅰ)and BWYV CP isolates from different regions
| 分组 Group | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | — | — | — | — |
| Ⅱ | 0.0464 | — | — | — |
| Ⅲ | 0.1157 | 0.1367 | — | — |
| Ⅳ | 0.1212 | 0.1470 | 0.1482 | — |
| 分组Group | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | — | — | — | — |
| Ⅱ | 0.0889 | — | — | — |
| Ⅲ | 0.1905 | 0.1981 | — | — |
| Ⅳ | 0.2021 | 0.2229 | 0.1652 | — |
表5 辣椒BWYV-MP-GSDX16(所在Ⅰ组)与不同地域BWYV MP分离物的组间遗传距离
Table 5 Genetic distance between pepper BWYV-MP-GSDX16(groupⅠ)and BWYV MP isolates from different regions
| 分组Group | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | — | — | — | — |
| Ⅱ | 0.0889 | — | — | — |
| Ⅲ | 0.1905 | 0.1981 | — | — |
| Ⅳ | 0.2021 | 0.2229 | 0.1652 | — |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.3.1140-1148.2000 pmid: 10627524 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
陈灵芝, 张茹, 魏兵强, 王兰兰, 高彦萍, 张武. 2018. 辣椒ToMMV的分子鉴定. 中国蔬菜,(6):39-43.
|
|
| [4] |
pmid: 15789270 |
| [5] |
|
|
杜江, 马振男, 王德富, 牛颜冰. 2023. 基于小RNA深度测序和RT-PCR鉴定鹅绒藤花叶病的病毒病原. 草业科学, 41 (10):2229-2239.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
高芳銮. 2019. 中国马铃薯Y病毒群体遗传结构及其分子进化机制[博士论文]. 福州: 福建农林大学.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
郭思瑶, 童艳, 黄娅, 罗信福, 青玲. 2015. 重庆辣椒病毒病病原初步鉴定和分析. 园艺学报, 42 (2):263-270.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
慧芳, 刘秀岩, 李宗谕, 刘福顺, 杨世海. 2019. 转录组测序技术在药用植物研究中的应用. 中草药, 50 (24):6149-6155.
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
|
刘青, 周书玉, 崔冬丽,
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
刘雪建. 2015. 浙江省和江西省蔬菜病毒鉴定与变异研究[硕士论文]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
王德富, 时晓丽, 寇丽莎, 庞小静, 刘勇, 牛颜冰. 2016. 山西西葫芦花叶病病原鉴定与部分序列分析. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 36 (5):310-314,363.
|
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
|
王兰兰. 2015. 甘肃省辣椒生产与科研现状及发展对策. 辣椒杂志, 13 (4):1-3.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
王立浩, 张正海, 曹亚从, 张宝玺. 2016. “十二五”我国辣椒遗传育种研究进展及其展望. 中国蔬菜,(1):1-7.
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
王莉爽, 李淳, 杨学辉, 张松柏, 刘勇. 2020. 贵州辣椒叶脉黄化病毒分离物检测及其P0、CP、MP基因进化分析. 园艺学报, 47 (12):2415-2426.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
王少立, 谭玮萍, 杨园园, 代惠洁, 孙晓辉, 乔宁, 竺晓平. 2017. 山东省辣椒主要病毒种类的分子检测与鉴定. 中国农业科学, 50 (14):2728-2738.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.14.009 |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
向本春, 谢浩, 崔星明, 李春, 刘素萍, 席德慧, 尹玉琦. 1994. 新疆辣椒轻微斑驳病毒的分离鉴定. 病毒学报,(3):240-245.
|
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
徐秉良. 2001. 甘肃省辣椒病毒病原种群鉴定. 甘肃农业大学学报,(专刊):238-243.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
徐秉良, 李敏权, 郁继华. 2002. 甘肃省辣椒病毒病的发生与症状类型. 甘肃农业科技,(2):42-44.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
杨永林, 闫淑珍, 田茹燕, 冯兰香, 梁训生, 王志源. 1995. 中国六省、市辣(甜)椒病毒种群及其分布的研究. 中国病毒学,(4):332-339.
|
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1111/ppa.13023 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
|
臧连毅, 刘晓莹, 孙晓辉, 张先平, 周涛, 竺晓平. 2020. 甜菜西方黄化病毒两个山东辣椒分离物全基因组扩增及序列分析. 植物病理学报, 50 (5):584-591.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
张学慧. 2022. 新疆辣椒病毒病病原鉴定及检测[硕士论文]. 石河子: 石河子大学.
|
|
| [33] |
|
|
赵汝娜, 王蓉, 师迎春, 张桂娟, 原锴, 范在丰, 周涛. 2014. 侵染甜椒的番茄褪绿病毒的分子鉴定. 植物保护, 40 (1):128-130.
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
赵小慧, 刘冲, 郁凯, 钟明娟, 郑佳秋, 邢锦城. 2023. 利用小RNA深度测序技术鉴定江苏盐城辣椒病毒种类. 江苏农业学报, 39 (1):37-43.
|
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0677 URL |
|
邹学校, 胡博文, 熊程, 戴雄泽, 刘峰, 欧立军, 杨博智, 刘周斌, 索欢, 徐昊, 朱凡, 远方. 2022. 中国辣椒育种60年回顾与展望. 园艺学报, 49 (10):2099-2118.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0677 URL |
|
| [38] |
|
|
左琳彧, 雍容婧, 袁雯, 杜开通, 周涛. 2016. 北京地区辣椒上黄瓜花叶病毒和甜菜西方黄化病毒复合侵染的分子鉴定. 植物保护, 42 (3):181-183.
|
| [1] | 蔡泽彦, 张明星, 周池, 陶禹, 杨莎, 李鑫, 李雪峰. 辣椒疫病不同抗性品种内生微生物群落多样性、结构及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 322-336. |
| [2] | 邹学校, 杨莎, 戴雄泽, 胡博文, 徐昊, 朱凡, 裴宋雨, 远方. 中国辣椒产业快速发展40年回顾与展望[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 247-258. |
| [3] | 李怡斐, 杨小苗, 王春萍, 段敏杰, 黄启中, 黄任中, 张世才. 加工型辣椒新品种‘艳椒465’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2223-2224. |
| [4] | 段敏杰, 李怡斐, 王春萍, 杨小苗, 黄任中, 黄启中, 张世才. 辣椒果实类胡萝卜素调控因子转录组和靶向代谢组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1773-1791. |
| [5] | 石凤岩, 王治丹, 张曦, 王秀雪, 邹春蕾. 辣椒疫病抗性机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1665-1682. |
| [6] | 张茹, 陈灵芝, 王兰兰. 辣椒新品种‘陇椒13号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1709-1710. |
| [7] | 郭瑞, 陈高, 赵慧霞, 乾义柯, 兰红, 万何平, 陈禅友. 紫色辣椒新品种‘江大紫椒1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1175-1176. |
| [8] | 侯雪, 王姣姣, 张雯雯, 赵建龙, 茆振川. 辣椒乙烯反应抑制因子Cacl-6468的克隆及其抗根结线虫作用分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 761-772. |
| [9] | 刘艳艳, 丁颖, 刘兴华, 郑佳秋, 刘志钦. 辣椒CaSYT1的鉴定及其在疫霉侵染过程中的功能初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 533-544. |
| [10] | 付稳, 朱程红, 兰嘉仪, 李诗, 张正, 刘峰, 戴雄泽. 鲜食嫩果辣椒‘樟树港’果实品质特性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 616-630. |
| [11] | 张正海, 王永富, 吴华茂, 于海龙, 曹亚从, 冯锡刚, 王立浩. 辣椒重要性状遗传定位与候选基因研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 669-696. |
| [12] | 罗新锐, 张晓旭, 王玉萍, 王智, 马媛媛, 周丙月. 普通菜豆Trihelix基因家族鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2775-2790. |
| [13] | 张少平, 李洲, 鞠玉栋, 练冬梅, 林碧珍, 姚运法, 吴松海, 洪建基, 赖正锋. 鲜食辣椒采后品质劣变伴随膜脂过氧化反应研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2945-2961. |
| [14] | 吴丹, 柳佳欣, 卓林熙, 李钰, 罗英, 周勇, 杨有新, 余婷. CaWRKY39在辣椒响应疫霉菌侵染中的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2297-2310. |
| [15] | 罗银, 罗希榕, 吴诗琪, 李唐燕, 李靖, 邱化荣, 覃成. 基于荧光原位杂交的四种不同栽培种辣椒的核型分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2311-2319. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司