
园艺学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4): 759-777.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0425
收稿日期:2020-08-14
出版日期:2021-04-25
发布日期:2021-04-29
通讯作者:
张绍铃
E-mail:nnzsl@njau.edu.cn
基金资助:
HE Min, GU Chao, WU Juyou, ZHANG Shaoling( )
)
Received:2020-08-14
Online:2021-04-25
Published:2021-04-29
Contact:
ZHANG Shaoling
E-mail:nnzsl@njau.edu.cn
摘要:
苹果、梨等果树均具有典型的配子体型自交不亲和性,该性状是由单一位点(S-locus)上的分别控制花柱和花粉特异性的复等位基因(S-allele)所决定的。其中,控制花柱自交不亲和性的决定因子被确定为S-RNase,而花粉决定因子则可能是由SLF(S-locus F-box)/SFB(S-haplotype-specific F-box)控制。以蔷薇科果树和芸香科果树为例,从自交不亲和反应雌、雄决定子的发现、自交亲和突变机制研究、S-RNase介导的花粉管信号转导,以及自交亲和种质在果树育种中的应用等方面综述果树自交不亲和机制研究进展,以期为后续自交不亲和性研究提供一定参考。
中图分类号:
何敏, 谷超, 吴巨友, 张绍铃. 果树自交不亲和机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(4): 759-777.
HE Min, GU Chao, WU Juyou, ZHANG Shaoling. Recent Advances on Self-incompatibility Mechanism in Fruit Trees[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(4): 759-777.
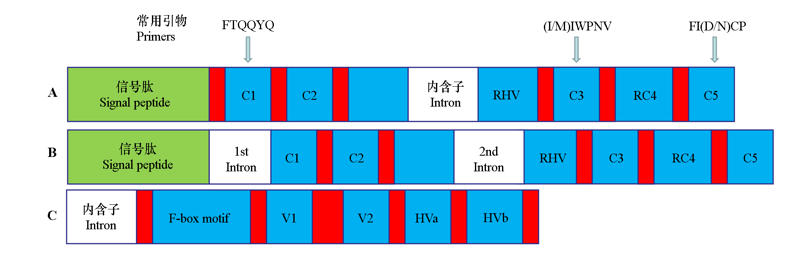
图1 蔷薇科果树S基因及SFB基因结构图 A:梨属和苹果属S-Rnase基因结构(李天忠 等,2011);B:李属S-Rnase基因结构(Wu,2013)。C:李属SFB基因结构图(Wu et al.2013)。
Fig. 1 The basic structure of S-RNase and SFB in Rosaceae fruit trees A: The basic structure of S-Rnase inPyrus and Malus(Li Tianzhong et al.2011);B:The basic structure of S-Rnase in Prunus(Wu et al.2013); C:SFB gene structure ofPrunus(Wu et al.2013).

图2 梨中S-RNase介导的花粉管信号转导过程 在梨自交不亲和反应中,梨花柱S-RNase进入到花粉管内,能降解花粉管的RNA和细胞核,破坏花粉管的线粒体,减少花粉管尖端的活性氧梯度,同时还能抑制Ca2+内流,解聚花粉管的微丝骨架,使花粉管发生细胞程序死亡的现象,同时花粉管会启动防御机制,通过增加磷脂酸来延缓细胞程序性死亡的进程。
Fig. 2 S-RNase mediates the signal transduction process of pear pollen tube During the self-incompatible reaction,S-RNase is transported into the pollen tube,triggers RNA and nuclei degradation,mitochondria collapse,specifically disrupts tiplocalized ROS of incompatible pollen tube. Thus the pollen tube plasma membrane Ca2+ current decreases. It can also depolymerizes the actin cytoskeleton,finally causes the pollen tube programmed cell death. At the same time,the pollen tube initiates a defense mechanism to delay the process of programmed cell death by increasing phosphatidic acid.
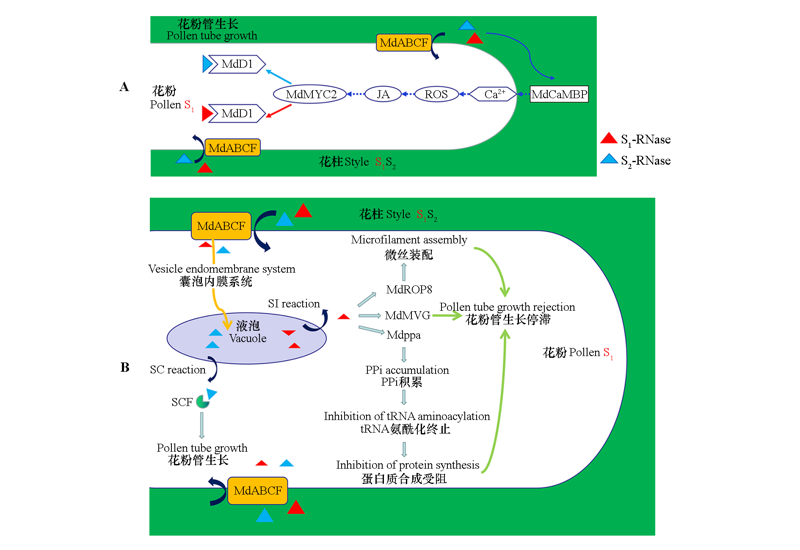
图3 S-RNase介导的苹果花粉管信号转导过程 A:自交不亲和(SI)反应早期花粉管正常生长;B:自交不亲和反应致使花粉管生长停止。MdCaMBP:苹果钙调素结合蛋白;ROS:活性氧;JA:茉莉酸;MdMYC:苹果髓细胞组织增生蛋白;MdD1:苹果γ-硫堇蛋白;tRNA:转运RNA;PPi:无机焦磷酸盐;Mdppa:苹果无机焦磷酸酶;MdMVG:苹果肌动蛋白结合蛋白;MdROP8:苹果小GTP结合蛋白;MdABCF:苹果ABCF转运蛋白;SC:自交亲和。
Fig. 3 S-RNase mediates the signal transduction process of apple pollen tube A:Normal growth of pollen tubes in the early stage of self-incompatibility(SI)reaction. B:Self-incompatibility reaction causes pollen tube growth rejection. MdCaMBP:Malus × domasticacalmodulin-binding protein;ROS:Reactive oxygen species;JA:Jasmonic acid;MdMYC:Malus × domasticamyelocytomatosis protein;MdD1:Malus × domastica gamma-thionin protein;tRNA:transfer RNA;PPi:Pyrophosphate;Mdppa:Malus×domastica inorganic pyrophosphatase;MdMVG:Malus × domastica actin-binding protein;MdROP8:Malus × domasticasmall GTP binding protein;MdABCF:Malus × domastica ATP-binding cassette transporter;SC:Self-compatibility.
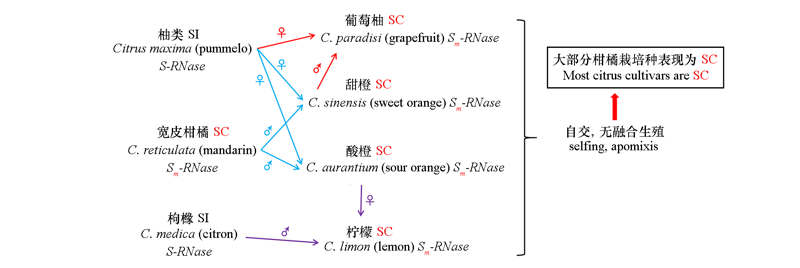
图4 柑橘自交亲和的演变过程[参考梁梅(2019)的文献修改] SI:自交不亲和;SC:自交亲和。红色,蓝色,紫色的箭头,表示两个亲本杂交。变异的S基因Sm-RNase使宽皮柑橘表现为自交亲和,并通过基因渗透和种间杂交在其他杂种中得以保留,后代杂种通过自交或无融合生殖使之固定,故大部分品种表现为自交亲和。
Fig. 4 Evolution process of citrus self-compatibility(Liang Mei,2019) SI:Self-incompatible;SC:Self-compatible. The red,blue,and purple arrows drawn in this figure represent the hybridization process between the two parents. The mutatedS gene Sm-RNase makes mandarin appear to be self-compatible,and is retained in other hybrids through gene penetration and interspecific hybridization. The progeny hybrids can fix the trait of self-compatibility through selfing or apomixis and this is the reason why most citrus cultivars are self-compatible.
| [1] |
Broothaerts W, Keulemans J, van Nerum I. 2004. Self-fertile apple resulting from S-RNase gene silencing. Plant Cell Reports, 22 (7):497-501.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-003-0716-4 URL |
| [2] |
Burgos L, Pereztornero O, Ballester J, Olmos E. 1998. Detection and inheritance of stylar ribonucleases associated with incompatibility alleles in apricot. Sexual Plant Reproduction, 11 (3):153-158.
doi: 10.1007/s004970050133 URL |
| [3] |
Chen J, Wang P, De Graaf B H J, Zhang H, Jiao H, Tang C, Zhang S, Wu J. 2018. Phosphatidic acid counteracts S-RNase signaling in pollen by stabilizing the actin cytoskeleton. The Plant Cell, 30 (5):1023-1039.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00021 URL |
| [4] | Chen Di-xin, Zhang Shao-ling, Tao Shu-tian. 2004. Characteristics of pollen germination and pollen tube growth in in vivo sand pear styles. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,(3):34-37. (in Chinese) |
| 陈迪新, 张绍铃, 陶书田. 2004. 沙梨花粉原位萌发与花粉管生长特性. 南京农业大学学报,(3):34-37. | |
| [5] |
Cui Y N, Zhuang M, Wu J, Liu J S, Zhang Y Y, Zhang L K, Huang Y L, Cai X, Liang J L, Zhang K, Wang X W, Cheng F. 2020. Segmental translocation contributed to the origin of the Brassica S-locus. Horticultural Plant Journal, 6 (3):167-178.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.04.005 URL |
| [6] | Dayton D F. 1974. Overcoming self-incompatibility in apple with killed compatible pollen. Journal of America Social Horticulture Science, 99:190-192. |
| [7] |
Entani T, Iwano M, Shiba H, Che F, Isogai A, Takayama S. 2003. Comparative analysis of the self-incompatibility ( S-) locus region of Prunus mume:identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with allelic diversity. Genes to Cells, 8 (3):203-213.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2003.00626.x URL |
| [8] |
Entani T, Kubo K, Isogai S, Fukao Y, Shirakawa M, Isogai A, Takayama S. 2014. Ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated degradation of S-RNase in a solanaceous cross-compatibility reaction. Plant Journal, 78 (6):1014-1021.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.12528 URL |
| [9] |
Fernández i Martí A, Gradziel T M, Socias i Company R. 2014. Methylation of the S f locus in almond is associated with S-RNase loss of function. Plant Molecular Biology, 86 (6):681-689.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-014-0258-x URL pmid: 25326263 |
| [10] |
Franklin-Tong V E, Franklin F C H. 1992. Gametophytic self-incompatibility in Papaver rhoeas L. Sexual Plant Reproduction, 5 (1):1-7.
doi: 10.1007/BF00714552 URL |
| [11] | Gao Qiguo, Lei Zhenze, Liang Yunfei, Jiang Yupeng, Zhu Liquan. 2019. Screening of Brassica oleracea MLPK-interacting PUB proteins based on gene family analysis. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (4):714-722. (in Chinese) |
| 高启国, 雷镇泽, 梁云飞, 姜宇鹏, 朱利泉. 2019. 基于家族基因分析的甘蓝MLPK互作PUB蛋白的筛选. 园艺学报, 46 (4):714-722. | |
| [12] |
Goldraij A, Kondo K, Lee C B, Hancock C N, Sivaguru M, Vazquezsantana S, Kim S, Phillips T E, Cruzgarcia F, Mcclure B. 2006. Compartmentalization of S-RNase and HT-B degradation in self-incompatible Nicotiana. Nature, 439 (7078):805-810.
pmid: 16482149 |
| [13] |
Gray J E, Mcclure B, Bonig I, Anderson M A, Clarke A E. 1991. Action of the style product of the self-incompatibility gene of Nicotiana alata( S-RNase)on in vitro-grown pollen tubes. The Plant Cell, 3 (3):271-283.
pmid: 12324597 |
| [14] | Gu C, Zhang S, Huang S, Heng W, Liu Q, Wu H, Wu J. 2010. Identification of S-genotypes in Chinese cherry cultivars( Prunus pseudocerasus Lindl.). Tree Genetics & Genomes, 6 (4):579-590. |
| [15] |
Gu Z, Li W, Doughty J, Meng D, Yang Q, Yuan H, Li Y, Chen Q, Yu J, Liu C, Li T. 2019. A gamma-thionin protein from apple, MdD1,is required for defence against S-RNase-induced inhibition of pollen tube prior to self/non-self recognition. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 17 (11):2184-2198.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.v17.11 URL |
| [16] |
Hancock C N, Kent L, Mcclure B. 2005. The stylar 120 kDa glycoprotein is required for S-specific pollen rejection in Nicotiana. Plant Journal, 43 (5):716-723.
pmid: 16115068 |
| [17] |
Haring V, Gray J E, Mcclure B, Anderson M A, Clarke A E. 1990. Self-incompatibility:a self-recognition system in plants. Science, 250 (4983):937-941.
doi: 10.1126/science.2237440 URL |
| [18] |
Hauck N R, Yamane H, Tao R, Iezzoni A F. 2002. Self-compatibility and incompatibility in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.). Sexual Plant Reproduction, 15 (1):39-46.
doi: 10.1007/s00497-002-0136-6 URL |
| [19] |
Hauck N R, Yamane H, Tao R, Iezzoni A F. 2006. Accumulation of nonfunctional S-haplotypes results in the breakdown of gametophytic self-incompatibility in tetraploid Prunus. Genetics, 172 (2):1191-1198.
doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.049395 URL |
| [20] | Heng W, Wu H, Chen Q, Wu J, Huang S, Zhang S. 2008. Identification of S-genotypes and novel S-RNase alleles in Prunus mume. Journal of Horticultural Science & Biotechnology, 83 (6):689-694. |
| [21] | Heng Wei, Zhang Shao-ling, Fang Cheng-quan, Wu Hua-qing, Wu Jun. 2008. Identification of 20 S-genotypes and cloning novel S-RNases in Pyrus. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 35 (3):313-318. (in Chinese) |
| 衡伟, 张绍铃, 方成泉, 吴华清, 吴俊. 2008. 梨20个品种 S基因型的鉴定及新 S-RNases基因的克隆. 园艺学报, 35 (3):313-318. | |
| [22] | Hiratsuka S, Kitoh Y, Matsushima J. 1991. Induction of deformed pollen tube tips and their morphological characteristics in self-incompatible Japanese pear. Journal of The Japanese Society for Horticultural Science, 60 (2):257-265. |
| [23] |
Hiratsuka S, Nakashima M, Kamasaki K, Kubo T, Kawai Y. 1999. Comparison of an S-protein expression between self-compatible and -incompatible Japanese pear cultivars. Sexual Plant Reproduction, 12 (2):88-93.
doi: 10.1007/s004970050176 URL |
| [24] | Hu Rong-mei, Meng Dong, Bai Song-ling, Hu Jian-fang, Li Tian-zhong. 2012. Preliminary study of calmodulin binding protein with stylar S-RNase in apple‘Ralls Genet’. Journal of China Agricultural University, 17 (4):62-67. (in Chinese) |
| 呼荣媚, 孟冬, 白松龄, 胡建芳, 李天忠. 2012. 苹果‘国光’花柱中与S-RNase互作的钙调素结合蛋白研究. 中国农业大学学报, 17 (4):62-67. | |
| [25] |
Hua Z, Kao T. 2006. Identification and characterization of components of a putative petunia S-locus F-box-containing E 3 ligase complex involved in S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. The Plant Cell, 18 (10):2531-2553.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.041061 URL |
| [26] |
Huang J, Lan Z, Yang Q, Xue Y. 2006. AhSSK1,a novel SKP1-like protein that interacts with the S-locus F-box protein SLF. Plant Journal, 46 (5):780-793.
pmid: 16709194 |
| [27] |
Huang S, Wu H, Li Y, Wu J, Zhang S, Heng W, Zhang S. 2008. Competitive interaction between two functional S-haplotypes confer self-compatibility on tetraploid Chinese cherry( Prunus pseudocerasus Lindl. cv. Nanjing Chuisi). Plant Cell Reports, 27 (6):1075-1085.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-008-0528-7 URL |
| [28] |
Ishimizu T, Endo T, Yamaguchikabata Y, Nakamura K T, Sakiyama F, Norioka S. 1998. Identification of regions in which positive selection may operate in S-RNase of Rosaceae:implication for S-allele-specific recognition sites in S-RNase. FEBS Letters, 440 (3):337-342.
doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(98)01470-7 URL |
| [29] |
Janssens G A, Goderis I J, Broekaert W F, Broothaerts W. 1995. A molecular method for S-allele identification in apple based on allele-specific PCR. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 91 (4):691-698.
doi: 10.1007/BF00223298 pmid: 24169899 |
| [30] | Jiang Nan, Tan Xiao-feng, Zhang Lin, Zhang Jing-guo, Hu Hong-ju. 2015. Preparation of S-RNase cDNA microarray and its application in identifying pear cultivars S-genotypes. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 42 (12):2341-2352. (in Chinese) |
| 江南, 谭晓风, 张琳, 张靖国, 胡红菊. 2015. 梨自交不亲和基因cDNA芯片制备及对部分砂梨品种 S基因型的鉴定. 园艺学报, 42 (12):2341-2352. | |
| [31] | Jiang Nan, Zhang Lin, Tan Xiao-feng, Tan Hui, Zhang Jing-guo. 2017. Detection of pear S-genotypes and evolutionary analysis of novel S-RNase genes identified by cDNA microarray-based method. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 18 (3):520-529. (in Chinese) |
| 江南, 张琳, 谭晓风, 谭慧, 张靖国. 2017. 基于cDNA芯片的梨品种 S基因型鉴定及新 S-RNase基因进化分析. 植物遗传资源学报, 18 (3):520-529. | |
| [32] | Jin Zi-ming, Wang Guo-ming, Ke Ya-qi, Shi Su-li, Wu Lei, Gu Chao. 2008. Study on in situ pollen germination and self-incompatibility strength of pear. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 46 (12):86-91. (in Chinese) |
| 金子明, 王国明, 柯亚琪, 石苏利, 吴磊, 谷超. 2018. 梨自交花粉原位萌发观察及不亲和性强度研究. 江苏农业科学, 46 (12):86-91. | |
| [33] |
Kim H, Park J, Hirata Y, Nou I. 2008. Molecular characterization of new S-Rnases(‘S 31’and‘S 32’)in apple(Malus × domestica Borkh.). Journal of Plant Biology, 51 (3):202-208.
doi: 10.1007/BF03030699 URL |
| [34] |
Kubo K, Entani T, Takara A, Wang N, Fields A M, Hua Z H, Toyoda M, Kawashima S, Ando T, Isogai A, Kao T, Takayama S. 2010. Collaborative non-self recognition system in S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Science, 330 (6005):796-799.
doi: 10.1126/science.1195243 URL |
| [35] |
Liang M, Cao Z, Zhu A, Liu Y, Tao M, Yang H, Chai L. 2020. Evolution of self-compatibility by a mutant S m-RNase in citrus. Nature Plants, 6 (2):131-142.
doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0597-3 pmid: 32055045 |
| [36] |
Lee H, Huang S, Kao T. 1994. Sproteins control rejection of incompatible pollen in Petunia inflata. Nature, 367 (6463):560-563.
pmid: 7509041 |
| [37] |
Lewis D. 1947. Competition and dominance of incompatibility alleles in diploid pollen. Heredity, 1 (1):85-108.
doi: 10.1038/hdy.1947.5 URL |
| [38] |
Li M, Li X, Han Z, Shu H, Li T. 2009. Molecular analysis of two Chinese pear( Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.)spontaneous self-compatible mutants,Yan Zhuang and Jin Zhui. Plant Biology, 11 (5):774-783.
doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2008.00180.x pmid: 19689786 |
| [39] |
Li M, Zhu K, Bai S, Zhi L, Li T. 2011. Isolation and S-genotyping application of S-allelic polymorphic MdSLFBs in apple( Malus domestica Borkh.). Molecular Breeding, 28 (2):171-180.
doi: 10.1007/s11032-010-9471-8 URL |
| [40] | Li Tian-zhong, Long Shen-shan, Li Mao-fu, Bai Song-ling, Meng Dong. 2011. Advances in research of the self-incompatibility genotypes( S-genotypes)in apple. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 44 (6):1173-1183. (in Chinese) |
| 李天忠, 龙慎山, 李茂福, 白松龄, 孟冬. 2011. 苹果自交不亲和基因型( S基因)研究进展. 中国农业科学, 44 (6):1173-1183. | |
| [41] |
Li W, Meng D, Gu Z, Yang Q, Yuan H, Li Y, Chen Q, Yu J, Liu C, Li T. 2018. Apple S-RNase triggers inhibition of tRNA aminoacylation by interacting with a soluble inorganic pyrophosphatase in growing self-pollen tubes in vitro. New Phytologist, 218 (2):579-593.
doi: 10.1111/nph.15028 URL |
| [42] |
Li W, Yang Q, Gu Z, Wu C, Meng D, Yu J, Chen Q, Li Y, Yuan H, Wang D, Li T. 2016. Molecular and genetic characterization of a self-compatible apple cultivar,‘CAU-1’. Plant Science, 252:162-175.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.07.010 URL |
| [43] | Li Xiao-fang, Li Mao-fu, Han Zhen-hai, Xu Xue-feng, Li Tian-zhong. 2008. Self-compatible pear cultivar‘Yanzhuang’resulting from S-RNase mutation of‘Ya Li’(Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.). Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 35 (1):13-18. (in Chinese) |
| 李晓芳, 李茂福, 韩振海, 许雪峰, 李天忠. 2008. ‘鸭梨’芽变‘闫庄梨’自交亲和性分子机制初步研究. 园艺学报, 35 (1):13-18. | |
| [44] |
Li Y, Wu J, Wu C, Yu J, Liu C, Fan W, Li T, Li W. 2020. A mutation near the active site of S-RNase causes self-compatibility in S-RNase-based self-incompatible plants. Plant Molecular Biology, 103:129-139.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-020-00979-z URL |
| [45] | Liang Mei. 2019. Gene identification and evolution of self-incompatibility of citrus[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 梁梅. 2019. 柑橘自交不亲和相关基因鉴定及其演化[博士论文]. 武汉:华中农业大学. | |
| [46] |
Liang M, Cao Z, Zhu A, Liu Y, Tao M, Yang H, Franklin-Tong V E, Chai L. 2020. Evolution of self-compatibility by a mutant Sm-RNase in citrus. Nature Plants, 6 (2):131-142.
doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0597-3 pmid: 32055045 |
| [47] | Liu Zhu-qin, Zhang Shao-ling, Xu Guo-hua. 2007. Effect of pear stylar S-RNase on self-pollen tube ultrastructure in vitro. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 34 (4):841-846. (in Chinese) |
| 刘珠琴, 张绍铃, 徐国华. 2007. 离体梨花柱S-RNase对自体花粉管超微结构变化的影响. 园艺学报, 34 (4):841-846. | |
| [48] | Liu Zhu-qin, Zhang Shao-ling, Xu Guo-hua, Zhao Cai-ping, Wu Jun. 2005. In vitro effects of stylar S-RNase of pear on the ultra-structure of its pollen tubes. Acta Botanica Boreali-occidentalia Sinica,(7):1357-1361. (in Chinese) |
| 刘珠琴, 张绍铃, 徐国华, 赵彩平, 吴俊. 2005. 梨花柱S-RNase对花粉管超微结构的影响. 西北植物学报,(7):1357-1361. | |
| [49] | Long S, Li M, Han Z, Wang K, Li T. 2010. Characterization of three new S-alleles and development of an S-allele-specific PCR system for rapidly identifying the S-genotype in apple cultivars. Tree Genetics & Genomes, 6 (2):161-168. |
| [50] | Long Shen-shan, Li Mao-fu, Han Zhen-hai, Zhang Bing-bing, Wang Kun, Li Tian-zhong. 2010. Characterization of two novel S-RNase genes and PCR analyzing of S-genotypes of 46 cultivars in Malus domestica Borkh. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 18 (2):265-271. (in Chinese) |
| 龙慎山, 李茂福, 韩振海, 张冰冰, 王昆, 李天忠. 2010. 苹果两个新 S-RNase基因克隆与46个品种 S基因型的PCR分析. 农业生物技术学报, 18 (2):265-271. | |
| [51] |
Marchese A, Boskovic R I, Caruso T, Raimondo A, Cutuli M, Tobutt K R. 2007. A new self-compatibility haplotype in the sweet cherry‘Kronio’,S5′,attributable to a pollen-part mutation in theSFB gene. Journal of Experimental Botany, 58:4347-4356.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm322 URL |
| [52] |
Matsuura T, Sakai H, Unno M, Ida K, Sato M, Sakiyama F, Norioka S. 2001. Crystal structure at 1.5-Å resolution ofPyrus pyrifolia pistil ribonuclease responsible for gametophytic self-incompatibility. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276 (48):45261-45269.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107617200 URL |
| [53] |
Mcclure B, Gray J E, Anderson M A, Clarke A E. 1990. Self-incompatibility in Nicotiana alata involves degradation of pollen rRNA. Nature, 347 (6295):757-760.
doi: 10.1038/347757a0 URL |
| [54] |
Meng D, Gu Z, Li W, Wang A, Yuan H, Yang Q, Li T. 2014a. Apple MdABCF assists in the transportation of S-RNase into pollen tubes. Plant Journal, 78 (6):990-1002.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.12524 URL |
| [55] |
Meng D, Gu Z, Wang A, Yuan H, Li W, Yang Q, Duan X, Li T. 2014b. Screening and characterization of apple Rho-like GTPase(MdROPs)genes related to S-RNase mediated self-incompatibility. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture, 117 (3):465-476.
doi: 10.1007/s11240-014-0457-9 URL |
| [56] |
Meng D, Gu Z, Yuan H, Wang A, Li W, Yang Q, Zhu Y, Li T. 2014c. The microtubule cytoskeleton and pollen tube golgi vesicle system are required for in vitro S-RNase internalization and gametic self-incompatibility in apple. Plant and Cell Physiology, 55 (5):977-989.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu031 URL |
| [57] | Meng Dong. 2014. Apple ABCF transport S-RNase into pollen tube effecting self-incompatibility[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Beijing:China Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 孟冬. 2014. 苹果MdABCF转运 S-RNase至花粉管影响自交不亲和反应[博士论文]. 北京:中国农业大学. | |
| [58] | Meng X, Hua Z, Sun P, Kao T. 2011. The amino terminal F-box domain of Petunia inflata S-locus F-box protein is involved in the S-RNase-based self-incompatibility mechanism. Aob Plants, 11:1-14. |
| [59] |
Murfett J, Atherton T L, Mou B, Gassert C S, Mcclure B. 1994. S-RNase expressed in transgenic Nicotiana causes S-allele-specific pollen rejection. Nature, 367 (6463):563-566.
pmid: 8107825 |
| [60] |
Muñoz-Sanz J V, Zuriaga E, Lopez I, Badenes M L, Romero C. 2017. Self-(in)compatibility in apricot germplasm is controlled by two major loci, S and M. BMC Plant Biology, 17 (1):82.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1027-1 pmid: 28441955 |
| [61] |
Ngo B X, Wakana A, Park S M, Nada Y, Fukudome I. 2001. Pollen tube behaviors in self-incompatible and self-compatible citrus cultivars. Journal of The Faculty of Agriculture Kyushu University, 45 (2):443-457.
doi: 10.5109/24394 URL |
| [62] |
Norioka N, Norioka S, Ohnishi Y, Ishimizu T, Oneyama C, Nakanishi T, Sakiyama F. 1996. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequences of cDNAs encoding S-allele specific stylar RNases in a self-incompatible cultivar and its self-compatible mutant of Japanese pear, Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai. Journal of Biochemistry, 120 (2):335-345.
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021418 URL |
| [63] | Nyska R, Raz A, Baras Z, Shafir S, Goldway M, Schneider D. 2013. Self-compatibility in loquat( Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.)is possibly due to S 6-RNase mutation. Scientia Horticulturae, 161 (Complete):43-48. |
| [64] |
Okada K, Tonaka N, Moriya Y, Norioka N, Sawamura Y, Matsumoto T, Takasaki-Yasuda T. 2008. Deletion of a 236 kb region around S 4-RNase in a stylar-part mutant S 4 sm- haplotype of Japanese pear. Plant Molecular Biology, 66 (4):389-400.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-007-9277-1 URL |
| [65] |
Okada K, Tonaka N, Taguchi T, Ichikawa T, Sawamura Y, Nakanishi T, Takasakiyasuda T. 2011. Related polymorphic F-box protein genes between haplotypes clustering in the BAC contig sequences around the S-RNase of Japanese pear. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62 (6):1887-1902.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq381 URL |
| [66] |
Ortega E, Sutherland B G, Dicenta F, Boskovic R I, Tobutt K R. 2005. Determination of incompatibility genotypes in almond using first and second intron consensus primers:detection of new S alleles and correction of reported S genotypes. Plant Breeding, 124 (2):188-196.
doi: 10.1111/pbr.2005.124.issue-2 URL |
| [67] |
Qi Y, Wang Y, Han Y, Qiang S, Wu J, Tao S, Zhang S, Wu H. 2011a. Self-compatibility of‘Zaoguan’(Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.)is associated with style-part mutations. Genetica, 139 (9):1149-1158.
doi: 10.1007/s10709-011-9617-6 URL |
| [68] | Qi Y, Wu H, Cao Y, Wu J, Tao S, Zhang S. 2011b. Heteroallelic diploid pollen led to self-compatibility in tetraploid cultivar‘Sha 01’(Pyrus sinkiangensis Yü). Tree Genetics & Genomes, 7 (4):685-695. |
| [69] | Qi Yong-jie. 2011. Mutant mechanism analyses of self-compatible pear and creation of self-fruitful germplasm resources in Pyrus[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 齐永杰. 2011. 梨自交亲和性突变机制及自花结实性种质的创制[博士论文]. 南京:南京农业大学. | |
| [70] |
Sanzol J. 2009. Pistil-function breakdown in a new S-allele of European pear,S 21,confers self-compatibility. Plant Cell Reports, 28 (3):457-467.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-008-0645-3 URL |
| [71] | Sapir G, Stern R A, Eisikowitch D, Goldway M. 2004. Cloning of four new Japanese plum S-alleles and determination of the compatibility between cultivars by PCR analysis. Journal of Horticultural Science & Biotechnology, 79 (2):223-227. |
| [72] | Sassa H, Hirano H, Ikehashi H. 1993. Identification and characterization of stylar glycoproteins associated with self-incompatibility genes of Japanese pear, Pyrus serotina Rehd. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 241 (1):17-25. |
| [73] |
Sassa H, Kakui H, Miyamoto M, Suzuki Y, Hanada T, Ushijima K, Kusaba M, Hirano H, Koba T. 2007. S locus F-box brothers:multiple and pollen-specific F-box genes with S haplotype-specific polymorphisms in apple and Japanese pear. Genetics, 175 (4):1869-1881.
doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.068858 URL |
| [74] |
Shi S, Cheng H, Wu L, Xie Z, Gu C, Zhang S. 2018. Identification of S-genotypes in 18 pear accessions and exploration of the breakdown of self-incompatibility in the pear cultivar Xinxue. Scientia Horticulturae, 238:350-355.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.05.003 URL |
| [75] | Shi Songmei, Gao Qiguo, Zuo Tonghong, Pu Quanming, Liu Yudong, Liu Guixi, Zhu Liquan, He Xinhua. 2019. Cloning and functional analysis of BoMLPKn1’s orthologs gene AtAPK1b in Arabidopsis. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (11):2164-2175. (in Chinese) |
| 施松梅, 高启国, 左同鸿, 蒲全明, 刘豫东, 刘贵喜, 朱利泉, 何新华. 2019. 甘蓝 BoMLPKn1的克隆及其拟南芥同源基因 AtAPK1b的功能研究. 园艺学报, 46 (11):2164-2175. | |
| [76] |
Sonneveld T, Robbins T P, Boskovic R, Tobutt K R. 2001. Cloning of six cherry self-incompatibility alleles and development of allele-specific PCR detection. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 102 (6):1046-1055.
doi: 10.1007/s001220000525 URL |
| [77] |
Sonneveld T, Tobutt K R, Vaughan S P, Robbins T P. 2005. Loss of pollen- S function in two self-compatible selections of Prunus avium is associated with deletion/mutation of an S haplotype-specific F-box gene. The Plant Cell, 17 (1):37-51.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.026963 URL |
| [78] | Sun Hui-ling, Meng Dong, Bai Song-ling, Hu Jian-fang, Li Tian-zhong. 2011. Screen and identification of pollen γ-thionin interacting with style S-RNase in apple. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 38 (8):1437-1446. (in Chinese) |
| 孙会玲, 孟冬, 白松龄, 胡建芳, 李天忠. 2011. 苹果花粉中与花柱 S-RNase互作的 γ-硫堇筛选及鉴定. 园艺学报, 38 (8):1437-1446. | |
| [79] |
Tao R, Watari A, Hanada T, Habu T, Yaegaki H, Yamaguchi M, Yamane H. 2007. Self-compatible peach( Prunus persica)has mutant versions of the S haplotypes found in self-incompatible Prunus species. Plant Molecular Biology, 63 (1):109-123.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-006-9076-0 URL |
| [80] |
Tao R, Yamane H, Sugiura A, Murayama H, Sassa H, Mori H. 1999. Molecular typing of S-alleles through identification,characterization and cDNA cloning for S-RNases in sweet cherry. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 124 (3):224-233.
doi: 10.21273/JASHS.124.3.224 URL |
| [81] |
Tsukamoto T, Hauck N R, Tao R, Jiang N, Iezzoni A F. 2006. Molecular characterization of three non-functional S-haplotypes in sour cherry (Prunus cerasus). Plant Molecular Biology, 62 (3):371-383.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-006-9026-x URL |
| [82] |
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Dandekar A M, Gradziel T M, Tao R, Hirano H. 2003. Structural and transcriptional analysis of the self-incompatibility locus of almond:identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with haplotype-specific polymorphism. The Plant Cell, 15 (3):771-781.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.009290 URL |
| [83] |
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tamura M, Kusaba M, Tao R, Gradziel T M, Hirano H. 2001. Characterization of the S-locus region of almond( Prunus dulcis):analysis of a somaclonal mutant and a cosmid contig for an S haplotype. Genetics, 158 (1):379-386.
pmid: 11333246 |
| [84] |
Ushijima K, Yamane H, Watari A, Kakehi E, Ikeda K, Hauck N R, Iezzoni A F, Tao R. 2004. The S haplotype-specific F-box protein gene, SFB,is defective in self-compatible haplotypes of Prunus avium and P. mume. Plant Journal, 39 (4):573-586.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2004.39.issue-4 URL |
| [85] |
Vieira J, Fonseca N A, Vieira C P. 2009. RNase-based gametophytic self-incompatibility evolution:questioning the hypothesis of multiple independent recruitments of the S-pollen gene. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 69 (1):32-41.
doi: 10.1007/s00239-009-9249-y URL pmid: 19495553 |
| [86] |
Vilanova S, Badenes M L, Burgos L, Martínez-Calvo J, Llácer G, Romero C. 2006. Self-compatibility of two apricot selections is associated with two pollen-part mutations of different nature. Plant Physiology, 142 (2):629-641.
doi: 10.1104/pp.106.083865 URL |
| [87] |
Wang C, Wu J, Xu G, Gao Y, Chen G, Wu J, Wu H, Zhang S. 2010. S-RNase disrupts tip-localized reactive oxygen species and induces nuclear DNA degradation in incompatible pollen tubes of Pyrus pyrifolia. Journal of Cell Science, 123 (24):4301-4309.
doi: 10.1242/jcs.075077 URL |
| [88] |
Wang C, Xu G, Jiang X, Chen G, Wu J, Wu H, Zhang S. 2009. S-RNase triggers mitochondrial alteration and DNA degradation in the incompatible pollen tube of Pyrus pyrifolia in vitro. Plant Journal, 57 (2):220-229.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2009.57.issue-2 URL |
| [89] |
Wang P, Gao Z, Ni Z, Zhang Z, Cai B. 2013. Self-compatibility in‘Zaohong’Japanese apricot is associated with the loss of function of pollenS genes. Molecular Biology Reports, 40 (11):6485-6493.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2765-2 URL |
| [90] |
Wang S, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Qie H, Wang H. 2017. Identification of two new S-RNases and molecular S-genotyping of twenty loquat cutivars [ Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl.]. Scientia Horticulturae, 218:48-55.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.02.002 URL |
| [91] | Wu Hua-qing, Heng Wei, Li Xiao, Huang Shao-xi, Zhang Shao-ling. 2007a. Mutational analysis of self-compatible mutant of Daguohuanghua (Pyrus pyrifolia). Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,(2):33-37. |
| 吴华清, 衡伟, 李晓, 黄绍西, 张绍铃. 2007a. 大果黄花梨自交亲和性变异机制研究. 南京农业大学学报,(2):33-37. | |
| [92] | Wu Hua-qing, Qi Yong-jie, Zhang Shao-ling. 2008. Molecular mechanism and genetic characterization of self-compatibility in pear‘Osa-Nijisseiki’. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 35 (8):1109-1116. (in Chinese) |
| 吴华清, 齐永杰, 张绍铃. 2008. ‘奥嗄二十世纪’梨自交亲和性分子机制及遗传特性研究. 园艺学报, 35 (8):1109-1116. | |
| [93] | Wu Hua-qing, Zhang Shao-ling, Wu Ju-you, Wang Ying-tao, Wu Jun. 2007b. Mutational mechanism of self-compatible pear cultivar‘Jinzhuili’ (Pyrus bretschneideri). Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 34 (2):295-300. (in Chinese) |
| 吴华清, 张绍铃, 吴巨友, 王迎涛, 吴俊. 2007b. ‘金坠梨’自交亲和性突变机制的初步研究. 园艺学报, 34 (2):295-300. | |
| [94] |
Wu J, Gu C, Du Y, Wu H, Liu W, Liu N, Lu J, Zhang S. 2011. Self-compatibility of‘Katy’apricot(Prunus armeniaca L.)is associated with pollen-part mutations. Sexual Plant Reproduction, 24 (1):23-35.
doi: 10.1007/s00497-010-0148-6 URL |
| [95] |
Wu J, Gu C, Khan M A, Wu J, Gao Y, Wang C, Zhang S. 2013. Molecular determinants and mechanisms of gametophytic self-incompatibility in fruit trees of Rosaceae. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 32 (1):53-68.
doi: 10.1080/07352689.2012.715986 URL |
| [96] | Wu J, Gu C, Zhang S, Zhang S, Wu H, Heng W. 2009. Identification of S-haplotype-specific S-RNase and SFB alleles in native Chinese apricot( Prunus armeniaca L.). Journal of Horticultural Science & Biotechnology, 84 (6):645-652. |
| [97] |
Wu J, Li M, Li T. 2013. Genetic features of the spontaneous self-compatible mutant,‘Jin Zhui’(Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.). PLoS ONE, 8 (10):e76509.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076509 URL |
| [98] | Wu Ju-you, Li Qi-ming, Wang Peng, Zhang Shao-ling. 2018. Actin cytoskeleton is a new target of S-RNase in self-incompatibility of pear. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 41 (5):775-777. (in Chinese) |
| 吴巨友, 李启明, 王鹏, 张绍铃. 2018. 梨自交不亲和性反应S-RNase新靶点—微丝骨架. 南京农业大学学报, 41 (5):775-777. | |
| [99] | Wu Ju-you, Zhang Shao-ling, Jiang Da-hua, Wu Jun, Liu Lian-mei. 2006. In situ germination and pollen tube growth of distant pollens in pear. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,(11):2197-2201. (in Chinese) |
| 吴巨友, 张绍铃, 蒋大华, 吴俊, 刘连妹. 2006. 梨远缘花粉原位萌发及生长特性. 西北植物学报,(11):2197-2201. | |
| [100] |
Xu G, Zhang S, Yang Y. 2008. Influence of endogenous and exogenous RNases on the variation of pollen cytosolic-free Ca2+ in Pyrus serotina Rehd. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 30 (2):233-241.
doi: 10.1007/s11738-007-0112-8 URL |
| [101] | Xu Guo-hua, Zhang Shao-ling, Zhang Chao-ying, Chen Di-xin. 2003. Changes in free Ca2+distribution in pollen cell after self-and cross-pollination in Pyrus serotina Rehd. Acta Photophysiologica Sinica,(2):97-103. (in Chinese) |
| 徐国华, 张绍铃, 张超英, 陈迪新. 2003. 梨自花与异花授粉后花粉胞内游离Ca2+分布的变化. 植物生理与分子生物学学报,(2):97-103. | |
| [102] | Xu Yi-liu, Zhang Shao-ling. 2003. Charaterization and molecular mechanism of gametophytic self-incompatibility in pears. Journal of Fruit Science,(1):59-63. (in Chinese) |
| 徐义流, 张绍铃. 2003. 梨配子体型自交不亲和性及其分子机理. 果树学报,(1):59-63. | |
| [103] |
Yaegaki H, Shimada T, Moriguchi T, Hayama H, Haji T, Yamaguchi M. 2001. Molecular characterization of S-RNase genes and S-genotypes in the Japanese apricot( Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc.). Sexual Plant Reproduction, 13 (5):251-257.
doi: 10.1007/s004970100064 URL |
| [104] |
Yang Q, Meng D, Gu Z, Li W, Chen Q, Li Y, Yuan H, Yu J, Liu C, Li T. 2018. Apple S-RNase interacts with an actin-binding protein,MdMVG,to reduce pollen tube growth by inhibiting its actin-severing activity at the early stage of self-pollination induction. Plant Journal, 95 (1):41-56.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2018.95.issue-1 URL |
| [105] |
Yuan H, Meng D, Gu Z, Li W, Wang A, Yang Q, Zhu Y, Li T. 2014. A novel gene, MdSSK1,as a component of the SCF complex rather than MdSBP1 can mediate the ubiquitination of S-RNase in apple. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65 (12):3121-3131.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru164 URL pmid: 24759884 |
| [106] | Zhang Shao-ling, Hiratsuka Shin. 2000. Effects of the stylar S glycoproteins on the pollen germination and the tube growth in pears( Pyrus serotina Rhed.) in vitro. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 27 (4):251-256. (in Chinese) |
| 张绍铃, 平塚伸. 2000. 梨花柱S糖蛋白对离体花粉萌发及花粉管生长的影响. 园艺学报, 27 (4):251-256. | |
| [107] | Zhang Shao-ling, Hiratsuka Shin, Xu Guo-hua, Fang Jing-gui, Liu You-liang. 2001. Expression and possible role of S 4(S 4 SM)genes in the styles of self-incompatible pear cultivar and its self-compatible mutant. Acta Botanica Sinica,(11):1172-1178. (in Chinese) |
| 张绍铃, 平塚伸, 徐国华, 房经贵, 刘友良. 2001. 梨自交不亲和及其亲和突变品种花柱内S4(S4SM)基因的表达与作用的比较. 植物学报,(11):1172-1178. | |
| [108] | Zhang Shao-ling, Wu Ju-you, Wu Jun, Qi Yong-jie, Gao Yong-bin. 2012. Advance in molecular mechanisms of self-incompatibility in Rosaceae fruit trees. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 35 (5):53-63. (in Chinese) |
| 张绍铃, 吴巨友, 吴俊, 齐永杰, 高永彬. 2012. 蔷薇科果树自交不亲和性分子机制研究进展. 南京农业大学学报, 35 (5):53-63. | |
| [109] | Zhang Shao-ling, Yang Ji-gun, Li Xiu-gen, Hiratsuka Shin, Joseph Ngwela Wolukau. 2002. Differences of S-glycoprotein content in the styles among pear cultivars differing in self-incompatible strength. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 29 (2):165-167. (in Chinese) |
| 张绍铃, 杨记磙, 李秀根, 平塚伸, Joseph Ngwela Wolukau. 2002. 梨自交不亲和强度不同品种花柱S糖蛋白含量的差异. 园艺学报, 29 (2):165-167. | |
| [110] | Zhang Xiao-li, AIshajiang· Maimaiti, Xu Ye-ting, Deng Li, Wang Ji-xun. 2018. Present advance of S-gene genotype and S-genotypes in pear. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica,(8):1077-1087. (in Chinese) |
| 张校立, 艾沙江·买买提, 徐叶挺, 邓莉, 王继勋. 2018. 梨 S基因与 S基因型鉴定的研究进展. 西北农业学报,(8):1077-1087. | |
| [111] | Zhang Ying. 2017. Identification of S genotypes in loquat based on AS-PCR and study on the mechanism of self-compatibility of‘Zaohuang’loquat[M. D. Dissertation]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 张颖. 2017. 基于AS-PCR鉴定枇杷 S基因型及‘早黄’枇杷自交亲和机制的研究[硕士论文]. 南京:南京农业大学. | |
| [112] | Zhou Jian-tao, Jiang Xue-ting, Liu Zhu-qin, Zhang Shao-ling. 2008. The variation of style auto-fluorescence after calmodulin treatment on self-and cross-pollination in Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 35 (6):781-786. (in Chinese) |
| 周建涛, 姜雪婷, 刘珠琴, 张绍铃. 2008. 钙调素对梨自花及异花授粉后花柱自发荧光变化的影响. 园艺学报, 35 (6):781-786. | |
| [113] |
Zuriaga E, Muñoz-Sanz J V, Molina L, Gisbert A D, Badenes M L, Romero C. 2013. An S-locus independent pollen factor confers self-compatibility in‘Katy’apricot. PLoS ONE, 8 (1):e53947.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053947 URL |
| [1] | 方天, 刘继红. 主要果树重要性状QTL鉴定研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(12): 2622-2640. |
| [2] | 王力荣, 吴金龙. 中国果树种质资源研究与新品种选育70年[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(4): 749-758. |
| [3] | 王 珏1,*,王 燕1,2,*,张 静2,陈 涛1,3,王 磊2,陈 清1,汤浩茹1,2,王小蓉1,2,**. 中国樱桃InDel标记开发及其在蔷薇科果树中通用性评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(1): 98-110. |
| [4] | 王玉柱*. 水热因子影响果实品质的研究进展及其对栽培的启示[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(9): 1681-1690. |
| [5] | 党江波1,梁国鲁1,李 彩2,吴 頔1,郭启高1,*,梁森林1,王 鹏1. 果树多倍体砧木的研究现状与展望[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(9): 1701-1710. |
| [6] | 任 芳,张尊平,范旭东,胡国君,李正男,董雅凤*. 主要果树病毒实时荧光定量PCR检测技术研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2018, 45(9): 1688-1700. |
| [7] | 李坤坤,徐昌杰*. 蔷薇科果树离体再生与遗传转化研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2017, 44(9): 1633-1644. |
| [8] | 何 文1,2,潘鹤立1,潘腾飞1,汤浩茹2,王小蓉2,*,潘东明1,*. 果树砧穗互作研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2017, 44(9): 1645-1657. |
| [9] | 徐国锋,聂继云*,李海飞,闫 震,叶孟亮. 衍生化结合分散固相萃取–UPLC–MS/MS法测定果品中EBDCs类农药残留[J]. 园艺学报, 2017, 44(2): 391-398. |
| [10] | 吴 潇,齐开杰,殷 豪*,张绍铃*. 诱变技术在落叶果树育种中的应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(9): 1633-1652. |
| [11] | 宁留芳,杨洪强*,曹 辉,周春然,张玮玮,孟凡尧. 发酵果树枝碎屑对苹果幼树根系特征及叶片光合蒸腾的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(10): 1989-1994. |
| [12] | 靳 娟, 鲁晓燕, 王 依. 果树耐盐性研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2014, 41(9): 1761-1776. |
| [13] | 刘慧芹, 韩巨才, 赵廷昌, 温祥珍, 刘艳, 刘慧平, 王远宏. 果树内生拮抗细菌的筛选鉴定及其生防作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2014, 41(2): 335-342. |
| [14] | 乔 鑫, 李 梦, 殷 豪, 李雷廷, 吴 俊, 张绍铃. 果树全基因组测序研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2014, 41(1): 165-177. |
| [15] | 刘有春, 陶承光, 刘威生, 刘 宁, 刘 硕, 章秋平, 郁香荷, 张玉萍, 徐 铭, 张同喜. 花粉形态在核果类果树遗传起源和系统关系研究中的应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2013, 40(9): 1701-1709. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司