
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 591-602.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0274
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Rui1,2, WU Hongfei1,3, ZHANG Changyuan1, CAO Haishun1, TAN Delong1, GUO Jinju1, WANG Yunlong1, WANG Rufang1, YUAN Yu1, WU Tingquan1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-30
Revised:2025-02-13
Online:2025-03-25
Published:2025-03-25
Contact:
WU Tingquan
WANG Rui, WU Hongfei, ZHANG Changyuan, CAO Haishun, TAN Delong, GUO Jinju, WANG Yunlong, WANG Rufang, YUAN Yu, WU Tingquan. CsPUB54 Negatively Regulates Cucumber Resistance to Phytophthora Melonis by Interacting with PmRXLR1 Effector[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 591-602.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0274
| 名称Name | 编码序列Coding sequence | 蛋白序列Protein sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CsPUB54 | ATGGATGAACAAATCGAAGTCCCCCACTATTTCCTCTGCCCCATCTCCCTCCAAATCATGAAAGACCCTGTAACTCTTCCCTCCGGCATCACCTACGATCGCCACTCCATTGAAACTTGG CTCTTCTCCGGCAAAAACTCCTCCTGCCCCGTCACTAAACTCCCAGTCTCCGACTCCGATTCCGATCTCCTCACCCCCAACCACACCCTCCGCCGTCTCATCCAAGCTTGGTGTACTTTGA ACTCCTCCCATGGCGTCGAACGTTTCCCCACTCCTAAACCCCCCATTCATAAATCCCAAATCCTTCACATTATTTCCACTTCCAACACTTCCCCTTCTTCCCAAATCTCCTCCATTCGCCG TCTCCGCTCCATTTCCGCCGAGTCTGAAACTAATCGCCGATGCGTTGAATTCGCCGGTGCGCCGGAGTTTTTAGTCTCTGTTATTGTGGGTTCTGATTCCTCGGCTTCTCATGAAGCCCTCT CCACTCTTCATAACCTCCGTCTCTCTGATTCAACGTTTAAATCATTGGCTACCCGCCCTGAATTCCTCGAGTCCTTGACCGATTTCATGAAATTACAACAGGGTACTCATGAATCGTCCAGA ACGTACGCGGTGTTGATTTTGAAATCAATTATTGAAGTCGCTGAACCAATTCAACTAAGCTTCTTGAAACCCGAATTGTTTGTGCAAATCGTTGAGATTTTGAAAGATCGATCATCCTCTCAA CAGATTTTCAAAGCGGCATTGGGTATTTTGATTGCGGTGAGTCCATTGGGGAGAAACA GACTGAAGGCAGTAGAAGCAGGTGGAGTTAGGGCTTTGGTTGAGATTTTACTGTCGTCGCCGGAAAAAAGAGTATGTGAAATGACATTGACGGCGATGGATATACTGTGTGGGTGTGCGGAT GGAAGAGCGGCGCTGTTGGCACACGGCGGAGGGATGGCAGTGGTTTCGAAGAAGATATTGAGAGTGTCGCAATTGGGGAGTGAAAGGGCGGTGAGAATATTGTATTCGGTGGCTAAATTCTCA GGAAGTCCTGCGGTGTTGATGGAAATGGCGCAACTGGGGATTGTGGCAAAGCTATGTTTGGTTCTGCAAATTGAAAATGGAGGCAAGACGAAGGAGAAAGCTAAAGAGATTTTGAAAATGCAT TCTCGTCTTTGGAAGAACTCACCTTGTATTCCTTCTAAATTGGCTTCTTCATATCCTACAAATTAA | MDEQIEVPHYFLCPISLQIMKDPVTLPSGITYDRHSIETWLFSGKNSSCPVTKLPVSDSDSDLLTPNHTLRRLIQAWCTLNSSHGVERFPTPKPPIHKSQILHIISTSNTSPSSQISSIRRLRS ISAESETNRRCVEFAGAPEFLVSVIVGSDSSASHEALSTLHNLRLSDSTFKSLATRPEFLESLTDFMKLQQGTHESSRTYAVLILKSIIEVAEPIQLSFLKPELFVQIVEILKDRSSSQQIFKAA LGILIAVSPLGRNRLKAVEAGGVRALVEILLSSPEKRVCEMTLTAMDILCGCADGRAALLAHGGGMAVVSKKILRVSQLGSERAVRILYSVAKFSGSPAVLMEMAQLGIVAKLCLVLQIENGGKTK EKAKEILKMHSRLWKNSPCIPSKLASSYPTN* |
| PmRXLR1 | ATGCGTCTGTCTTTCATGCTTTCTGTTGCTGTGGTCATCGGCCACCTCGTGGCCTGCAACGCGACTGC GGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCG CTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAG ATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCG CATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA | MRLSFMLSVAVVIGHLVACNATADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKE AYEAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 (无信号肽 No signal peptide) | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGG AGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTA CACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATC TACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEA WAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
Table 1 Gene and protein sequences of CsPUB54 and PmRXLR1
| 名称Name | 编码序列Coding sequence | 蛋白序列Protein sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CsPUB54 | ATGGATGAACAAATCGAAGTCCCCCACTATTTCCTCTGCCCCATCTCCCTCCAAATCATGAAAGACCCTGTAACTCTTCCCTCCGGCATCACCTACGATCGCCACTCCATTGAAACTTGG CTCTTCTCCGGCAAAAACTCCTCCTGCCCCGTCACTAAACTCCCAGTCTCCGACTCCGATTCCGATCTCCTCACCCCCAACCACACCCTCCGCCGTCTCATCCAAGCTTGGTGTACTTTGA ACTCCTCCCATGGCGTCGAACGTTTCCCCACTCCTAAACCCCCCATTCATAAATCCCAAATCCTTCACATTATTTCCACTTCCAACACTTCCCCTTCTTCCCAAATCTCCTCCATTCGCCG TCTCCGCTCCATTTCCGCCGAGTCTGAAACTAATCGCCGATGCGTTGAATTCGCCGGTGCGCCGGAGTTTTTAGTCTCTGTTATTGTGGGTTCTGATTCCTCGGCTTCTCATGAAGCCCTCT CCACTCTTCATAACCTCCGTCTCTCTGATTCAACGTTTAAATCATTGGCTACCCGCCCTGAATTCCTCGAGTCCTTGACCGATTTCATGAAATTACAACAGGGTACTCATGAATCGTCCAGA ACGTACGCGGTGTTGATTTTGAAATCAATTATTGAAGTCGCTGAACCAATTCAACTAAGCTTCTTGAAACCCGAATTGTTTGTGCAAATCGTTGAGATTTTGAAAGATCGATCATCCTCTCAA CAGATTTTCAAAGCGGCATTGGGTATTTTGATTGCGGTGAGTCCATTGGGGAGAAACA GACTGAAGGCAGTAGAAGCAGGTGGAGTTAGGGCTTTGGTTGAGATTTTACTGTCGTCGCCGGAAAAAAGAGTATGTGAAATGACATTGACGGCGATGGATATACTGTGTGGGTGTGCGGAT GGAAGAGCGGCGCTGTTGGCACACGGCGGAGGGATGGCAGTGGTTTCGAAGAAGATATTGAGAGTGTCGCAATTGGGGAGTGAAAGGGCGGTGAGAATATTGTATTCGGTGGCTAAATTCTCA GGAAGTCCTGCGGTGTTGATGGAAATGGCGCAACTGGGGATTGTGGCAAAGCTATGTTTGGTTCTGCAAATTGAAAATGGAGGCAAGACGAAGGAGAAAGCTAAAGAGATTTTGAAAATGCAT TCTCGTCTTTGGAAGAACTCACCTTGTATTCCTTCTAAATTGGCTTCTTCATATCCTACAAATTAA | MDEQIEVPHYFLCPISLQIMKDPVTLPSGITYDRHSIETWLFSGKNSSCPVTKLPVSDSDSDLLTPNHTLRRLIQAWCTLNSSHGVERFPTPKPPIHKSQILHIISTSNTSPSSQISSIRRLRS ISAESETNRRCVEFAGAPEFLVSVIVGSDSSASHEALSTLHNLRLSDSTFKSLATRPEFLESLTDFMKLQQGTHESSRTYAVLILKSIIEVAEPIQLSFLKPELFVQIVEILKDRSSSQQIFKAA LGILIAVSPLGRNRLKAVEAGGVRALVEILLSSPEKRVCEMTLTAMDILCGCADGRAALLAHGGGMAVVSKKILRVSQLGSERAVRILYSVAKFSGSPAVLMEMAQLGIVAKLCLVLQIENGGKTK EKAKEILKMHSRLWKNSPCIPSKLASSYPTN* |
| PmRXLR1 | ATGCGTCTGTCTTTCATGCTTTCTGTTGCTGTGGTCATCGGCCACCTCGTGGCCTGCAACGCGACTGC GGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCG CTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAG ATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCG CATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA | MRLSFMLSVAVVIGHLVACNATADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKE AYEAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 (无信号肽 No signal peptide) | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGG AGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTA CACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATC TACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEA WAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| 用途Usage | 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene cloning | CsPUB54-F (C) CsPUB54-R (C) PmRXLR1-F (C) PmRXLR1-R (C) | ATGGATGAACAAATCGAAGTCCCCCAC TTAATTTGTAGGATATGAAGAAGCCA ATGCGTCTGTCTTTCATGCTTTC TTAATCCTGATACAGGTGAAAGCCG |
| 载体构建 Vector construction | CsPUB54-F (V) CsPUB54-R (V) PmRXLR1-F (V) PmRXLR1-R (V) | CATATGATGGATGAACAAATCG CGCGGATCCTTAATTTGTAGGATATG CCGGAATTCACTGCGGACTTCGACG CGCGGATCCTTAATCCTGATACAGGTG |
| 基因表达 Gene expression | CsPUB54-F (E) CsPUB54-R (E) | CAAATCTCCTCCATTCGCCGTC TCATGAAATCGGTCAAGGACTC |
| 黄瓜内参基因 Cucumber reference gene | CsUBQ-F CsUBQ-R | GCGTAAGAAGAAGACCTACACCA CCTTTCCAGAGTCATCGACCT |
| 瓜类疫霉菌ITS检测 ITS detection of Phytophthora melons | DC6-F ITS4-R | 5′-GAGGGACTTTTGGGTAATCA-3′ 5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′ |
Table 2 The primers used in the experiment
| 用途Usage | 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene cloning | CsPUB54-F (C) CsPUB54-R (C) PmRXLR1-F (C) PmRXLR1-R (C) | ATGGATGAACAAATCGAAGTCCCCCAC TTAATTTGTAGGATATGAAGAAGCCA ATGCGTCTGTCTTTCATGCTTTC TTAATCCTGATACAGGTGAAAGCCG |
| 载体构建 Vector construction | CsPUB54-F (V) CsPUB54-R (V) PmRXLR1-F (V) PmRXLR1-R (V) | CATATGATGGATGAACAAATCG CGCGGATCCTTAATTTGTAGGATATG CCGGAATTCACTGCGGACTTCGACG CGCGGATCCTTAATCCTGATACAGGTG |
| 基因表达 Gene expression | CsPUB54-F (E) CsPUB54-R (E) | CAAATCTCCTCCATTCGCCGTC TCATGAAATCGGTCAAGGACTC |
| 黄瓜内参基因 Cucumber reference gene | CsUBQ-F CsUBQ-R | GCGTAAGAAGAAGACCTACACCA CCTTTCCAGAGTCATCGACCT |
| 瓜类疫霉菌ITS检测 ITS detection of Phytophthora melons | DC6-F ITS4-R | 5′-GAGGGACTTTTGGGTAATCA-3′ 5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′ |
| 突变体Mutant | 序列Sequence |
|---|---|
| PmRXLR1 Δ1 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGA GTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGA TCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAAC GGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAA AAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAA---GGGGACCCCAAGAAC AAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ1 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSH QEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKE---GDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ2 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGG CCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACT GAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGAT GCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCG GCGGAGGCG GCAGCAGCGAACAAGTACACC GGAGTCCAA GGAAAGAAC GCACTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCT ACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ2 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSH QEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAAEAAAANKYT GVQGKNALKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ3 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCG CTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGG AACGGACCTTCATCATTACT GAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCA GATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTAC TCCGCGTGGGCA TCCAACAAGTACACCCTG TCCTCCATCAAG TCCTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAA ATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACG GCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ3 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKND DIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLA RQMLKDPSKEKEAY SAWA SNKYTL SSIK SWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIY NGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ4 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCC GGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGC GGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCA GCGAACAAGTACACCCTG GGCGGTGGAGGGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACC CCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ4 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITE LMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLGGGGNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ5 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGAC GACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATG AACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGC TGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGC AGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAA GGCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAA GAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGC TTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ5 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAE ERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLVQ GKNWLKIGDPKNKGK YDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ6 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAG AACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTT AAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCT GAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAG---GATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ6 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNK AAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPK---D* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ7 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACG ACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCC AGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGA AGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAG AACAAAGGAGCAGCTGCCGCCATCTACGCCGCGTACGGCG CTGCCCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ7 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDD AEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAY EAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGAAAAIYAAYGAALYQD* |
Table 3 Base sequences and amino acid sequences of PmRXLR1 gene mutants
| 突变体Mutant | 序列Sequence |
|---|---|
| PmRXLR1 Δ1 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGA GTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGA TCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAAC GGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAA AAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAA---GGGGACCCCAAGAAC AAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ1 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSH QEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKE---GDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ2 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGG CCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACT GAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGAT GCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCG GCGGAGGCG GCAGCAGCGAACAAGTACACC GGAGTCCAA GGAAAGAAC GCACTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCT ACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ2 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSH QEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAAEAAAANKYT GVQGKNALKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ3 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCG CTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGG AACGGACCTTCATCATTACT GAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCA GATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTAC TCCGCGTGGGCA TCCAACAAGTACACCCTG TCCTCCATCAAG TCCTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAGAACAAAGGAAA ATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACG GCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ3 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKND DIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLA RQMLKDPSKEKEAY SAWA SNKYTL SSIK SWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIY NGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ4 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACGACATTGCC GGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGC GGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCA GCGAACAAGTACACCCTG GGCGGTGGAGGGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACC CCAAGAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGCTTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ4 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITE LMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLGGGGNWLKIGDPKNKGKYDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ5 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGAC GACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATG AACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGC TGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGC AGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAA GGCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAA GAACAAAGGAAAATATGACCGCATCTACAACGGGTACGGC TTTCACCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ5 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAE ERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLVQ GKNWLKIGDPKNKGK YDRIYNGYGFHLYQD* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ6 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAG AACGACGACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTT AAAAAGTTGGCCAGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGAAGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCT GAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAG---GATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ6 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDDAEERTFIITELMNK AAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAYEAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPK---D* |
| PmRXLR1 Δ7 碱基Base | ACTGCGGACTTCGACGGAACTGAAGTGTCCACGATGGAGTCGCCAGACATCGTCCGGCCCTCGCTCAAGAACGACG ACATTGCCGGTGGGAGGTTGCTGCGATCCCACCAAGAGGACGACGCGGAGGAACGGACCTTCATCATTACTGAACTGATGAACAAGGCGGCGGTTAAAAAGTTGGCC AGGCAGATGCTGAAGGACCCATCAAAGGAGA AGGAAGCGTACGAGGCGTGGGCAGCGAACAAGTACACCCTGGTCCAAATCAAGAACTGGCTGAAAATCGGGGACCCCAAG AACAAAGGAGCAGCTGCCGCCATCTACGCCGCGTACGGCG CTGCCCTGTATCAGGATTAA |
| PmRXLR1 Δ7 氨基酸Amino acid | TADFDGTEVSTMESPDIVRPSLKNDDIAGGRLLRSHQEDD AEERTFIITELMNKAAVKKLARQMLKDPSKEKEAY EAWAANKYTLVQIKNWLKIGDPKNKGAAAAIYAAYGAALYQD* |
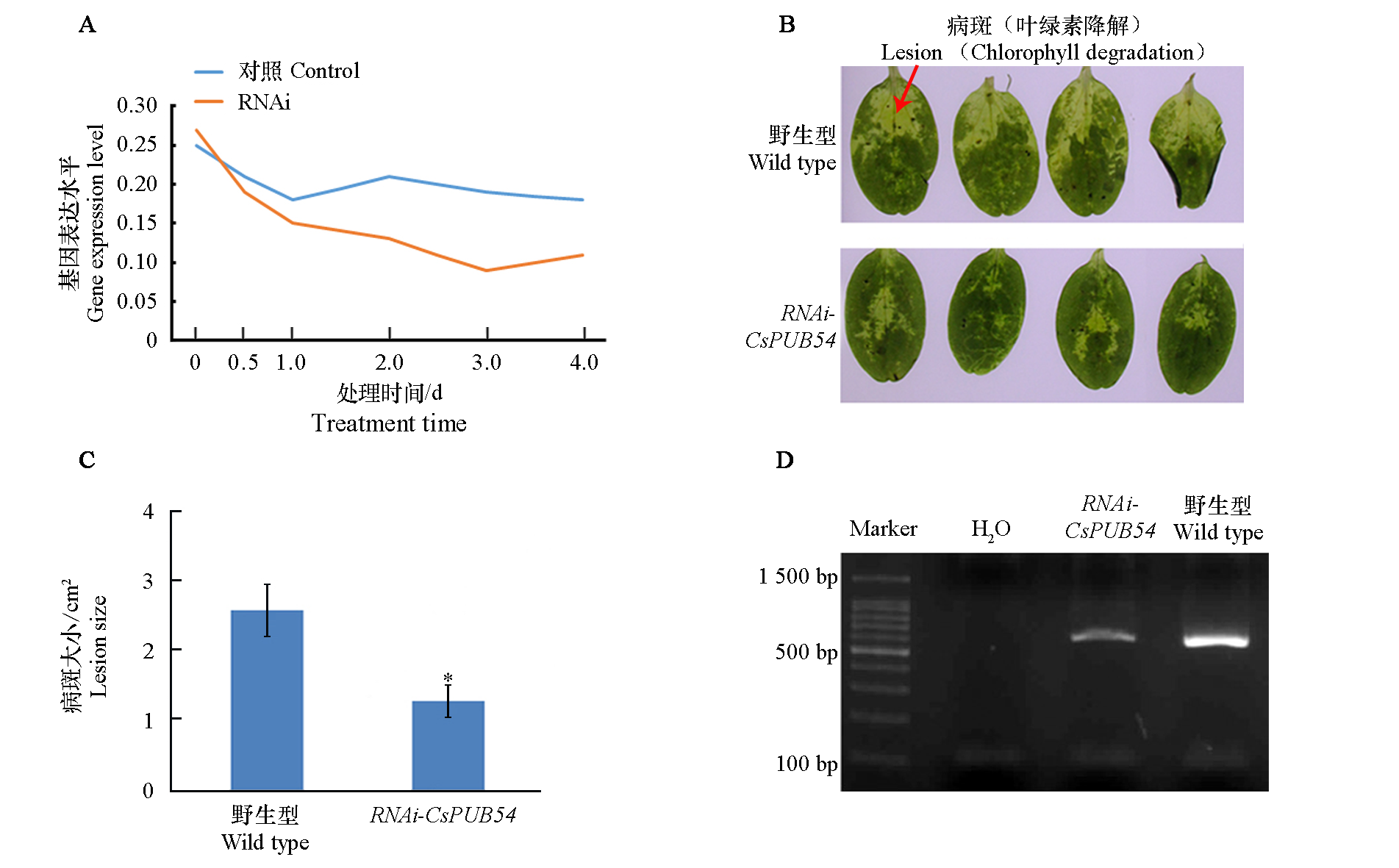
Fig. 5 Detection of disease resistance in cucumber leaves silent with CsPUB54 A. Silencing efficiency analysis of CsPUB54 in cucumber leaves;B:Phenotypes of wild-type and RNAi-CsPUB54 cucumber leaves after inoculation with Phytophthora melonis;C:Statistical analysis of lesion area of wild-type and RNAi-CsPUB54 cucumber inoculated with Phytophthora melonis ;D:Detection of the total number of Phytophthora melonis in inoculated cucumber leaves
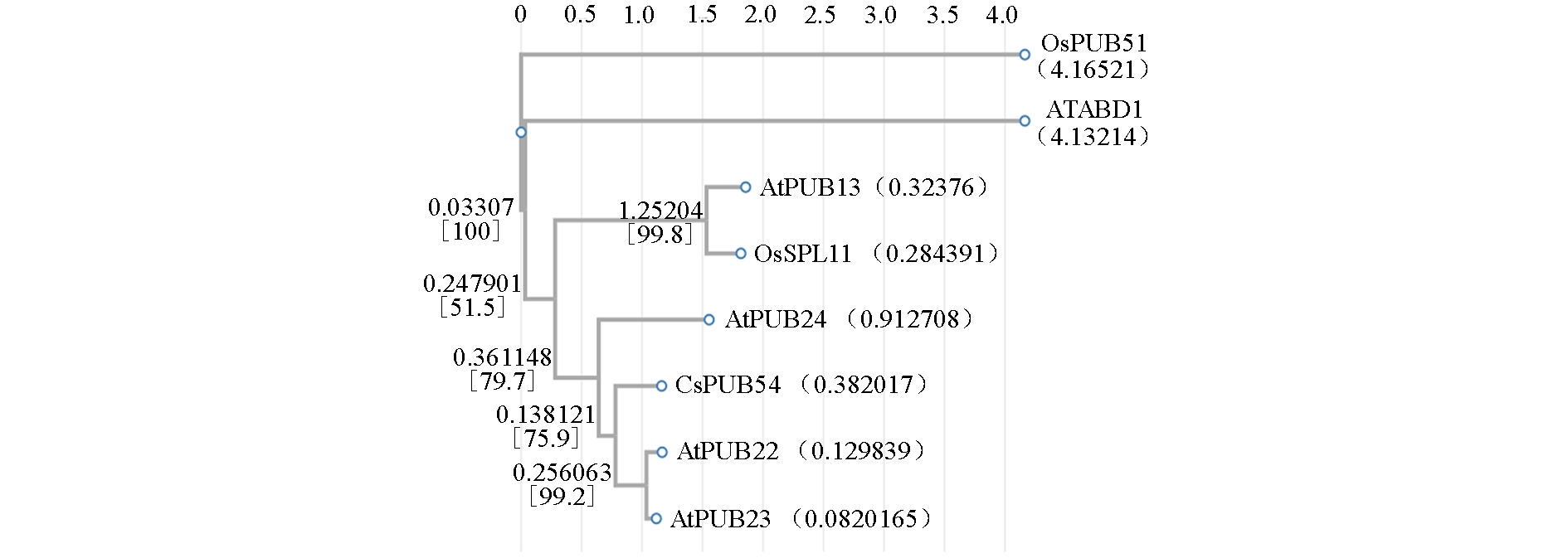
Fig. 6 Sequence alignment of cucumber CsPUB54 with rice(Os),Arabidopsis(At)PUB proteins regulating immune negatively The numbers in parentheses in the figure represent the evolutionary distance,and the smaller the number,the closer the evolutionary distance. The numbers in square brackets are bootstrap values,indicating reliability(reliability greater than 70 is better)
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
胡维炜, 张武, 刘连忠, 蔡芮莹, 朱小倩. 2016. 利用图像处理技术计算大豆叶片相对病斑面积. 江苏农业学报, 32 (4):774-779.
|
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.15414 pmid: 30169906 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0430 URL |
|
齐晨辉, 赵先炎, 韩朋良, 姜翰, 王永旭, 胡大刚, 郝玉金. 2017. 苹果U-box型E3泛素连接酶MdPUB24的耐盐性和ABA敏感性鉴定. 园艺学报, 44 (12):2255-2264.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0430 URL |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00824-y pmid: 30671725 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.104463 pmid: 23170036 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.17660 pmid: 34339518 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
王瑞, 林毓娥, 杜虎, 金庆敏, 杨晓珊, 吴廷全. 2019. 快速鉴定瓜类疫病抗性方法的建立及黄瓜种质资源鉴定. 广东农业科学, 46 (10):13-18.
|
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15070017 |
|
王瑞, 林毓娥, 梁肇均, 金庆敏, 吴廷全. 2016. 广东地区黄瓜疫病病原菌的分离与鉴定. 中国农学通报, 32 (1):76-80.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15070017 |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [1] | ZHANG Shengping, DONG Shaoyun, GUAN Jiantao, MIAO Han, LIU Xiaoping, GU Xingfang. Research Progress on Molecular Breeding of Disease Resistance in Cucumber [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 773-791. |
| [2] | XING Zhigan, LEI Xiangzhao, WANG Haochen, FENG Mingxin, LI Jingwen, LIU Yujia, FANG Yulin, MENG Jiangfei. Physiological Response of Shine Muscat Grape Seedlings Grafted with Different Rootstocks to Combined Stress of Salt and Low Temperature [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 693-704. |
| [3] | WEN Zhengyang, SUN Jingbo, ZHANG Mengxia, ZHANG Feng, DONG Chunjuan. Identification of CsCuAO Gene Family in Cucumber and Their Regulatory Roles in Adventitious Root Formation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 309-321. |
| [4] | CAI Zeyan, ZHANG Mingxing, ZHOU Chi, TAO Yu, YANG Sha, LI Xin, LI Xuefeng. Analysis of Endogenous Microbial Community Diversity,Structure and Function of Pepper Different Resistant Phytophthora Blight Cultivars [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 322-336. |
| [5] | MAO Xin, YUAN Wenfei, GUO Yurun, XU Xinxin, LI Yi, ZHANG Yi, MIAO Yanxiu, BAI Longqiang, LI Yansu. Analysis of the Decomposition of Organic Materials and Nutrients Contents in Root Zone and Leaves of Cucumber Under Organic Substrate Planting Board Cultivation in Solar Greenhouse [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 439-452. |
| [6] | LI Wenjing, SHI Shuo, ZHANG Hao, ZHANG Jiangyan, SONG Sihao, YANG Aizhen, SHEN Yuanyue, GUO Jiaxuan, GAO Fan. Effects of Exogenous Nitric Oxide and Putrescine on Drought Resistance of Strawberry Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2131-2142. |
| [7] | CHEN Ming, ZHANG Jieru, YANG Hangyun, WANG Yinbao, ZHENG Zhiyuan, ZENG Jiaoke, CHEN Jinyin, FU Yongqi, XIANG Miaolian. Induction Mechanism of Methyl Jasmonate on Postharvest Navel Orange Fruit Against Blue Mold [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2183-2194. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yong, MA Jianxiang, WEI Chunhua, LI Hao, YANG Jianqiang, ZHANG Xian. A New Muskmelon Cultivar‘Nongdatian 10’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2225-2226. |
| [9] | QIU Hui, ZHU Dejuan, ZHANG Yongle, GAO Yujie, LI Liu, WANG Guoping, HONG Ni. Interaction Between the Coat Protein of Apple Chlorotic Leaf Spot Virus and Two E3 Ubiquitin Ligases of Pear and Their Subcellular Localization [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1715-1727. |
| [10] | KUANG Meimei, LI Li, MA Jianwei, LIU Yuan, JIANG Hongfei, LEI Rui, MAN Yuping, WANG Yifan, HUANG Bo, WANG Yanchang, LIU Shibiao. Screening of Kiwifruit Canker Resistance-Related Genes Based on the Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis of Hybrids from Actinidia chinensis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1743-1757. |
| [11] | YANG Jinghui, XU Yuan, XIAO Ting, CHU Shupin, LIU Jixiang, YAO Kebing. Resistance of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Species Complexes from Grape to Azoxystrobin [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1906-1912. |
| [12] | GONG Xiaoya, LI Xian, ZHOU Xingang, WU Fengzhi. Effect of Rhizosphere Microorganisms Induced by Potato-Onion on Tomato Root-Knot Nematode Disease [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [13] | DU Meixia, PANG Shuwei, DONG Liting, MO Kaiqin, HOU Mengyuan, WANG Shuai, ZOU Xiuping. Research Progress on the Molecular Mechanisms of Interactions Between Candidatus Liberibacter and Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1623-1638. |
| [14] | SHI Fengyan, WANG Zhidan, ZHANG Xi, WANG Xiuxue, ZOU Chunlei. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Pepper Resistance to Phytophthora Blight [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1665-1682. |
| [15] | YUAN Quan, LU Wei, WANG Jun, CHEN Ru, LI Yansu, YU Xianchang, HE Chaoxing, SUN Mintao, YAN Yan. Effects of Irrigation Lower Limits on Early-Spring Cucumber Grown Under Different Soil Textures in the Solar Greenhouse [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1377-1385. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd