
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 395-405.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0413
• Cultivation·Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
XU Tong1, WANG Yue1, WU Lina1,2, ZHANG Hang1, YIN Lilai1, XU Keyu1, ZHENG Xiaolin1,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-04
Revised:2024-12-09
Online:2025-02-25
Published:2025-02-23
Contact:
ZHENG Xiaolin
XU Tong, WANG Yue, WU Lina, ZHANG Hang, YIN Lilai, XU Keyu, ZHENG Xiaolin. Effects of Melatonin Treatment on Fruit Quality and Anthocyanin Metabolism of Postharvest‘Taoxingli’Plum[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 395-405.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0413
| 基因名 Gene | 基因号 Gene ID | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物长度/bp Production length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PsPAL | KT601054 | F:CAGGATTACGGAATGCAGGTCT | 22 | |
| R:CCCTCGCAGATAGCTGAGAACACCT | 25 | |||
| PsCHS | KT597917 | F:G AGGAAGTTCGCAAGGCTCAGCGGG | 25 | |
| R:GAAGTAGTAGTCAGGGTAGGTG | 22 | |||
| PsCHI | KP266867 | F:CTGGAGATTCAGGGGAAAGTCA | 22 | |
| R:CGGTTAGTGGCAGTATCGTTGT | 22 | |||
| PsF3H | KP266870 | F:GACATACTTTTCATACCCAATCCG | 24 | |
| R:ATCAGCTCGTCGCTGTACTTCT | 22 | |||
| PsDFR | KT597918 | F:CAGGAACCGTGAATATCGAAGA | 22 | |
| R:GGAGACGAAGTACATCCAACCA | 22 | |||
| PsANS | KT601053 | F:GTGCTGTCACTTGGGTTGGGATT | 23 | |
| R:GCAAACTGGGTAGTAGTTGATTTTC | 25 | |||
| PsUFGT | KT597919 | F:CTTTCAACCTAGCTGCTACTGC | 22 | |
| R:TGACCCAAAACTAACATACACC | 22 | |||
| PsACT | EF585293 | F:CTTCCAACCATCACTCATT | 19 | |
| R:CCTAATATCCACATCACACTT | 21 |
Table 1 Real-Time PCR Primers
| 基因名 Gene | 基因号 Gene ID | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物长度/bp Production length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PsPAL | KT601054 | F:CAGGATTACGGAATGCAGGTCT | 22 | |
| R:CCCTCGCAGATAGCTGAGAACACCT | 25 | |||
| PsCHS | KT597917 | F:G AGGAAGTTCGCAAGGCTCAGCGGG | 25 | |
| R:GAAGTAGTAGTCAGGGTAGGTG | 22 | |||
| PsCHI | KP266867 | F:CTGGAGATTCAGGGGAAAGTCA | 22 | |
| R:CGGTTAGTGGCAGTATCGTTGT | 22 | |||
| PsF3H | KP266870 | F:GACATACTTTTCATACCCAATCCG | 24 | |
| R:ATCAGCTCGTCGCTGTACTTCT | 22 | |||
| PsDFR | KT597918 | F:CAGGAACCGTGAATATCGAAGA | 22 | |
| R:GGAGACGAAGTACATCCAACCA | 22 | |||
| PsANS | KT601053 | F:GTGCTGTCACTTGGGTTGGGATT | 23 | |
| R:GCAAACTGGGTAGTAGTTGATTTTC | 25 | |||
| PsUFGT | KT597919 | F:CTTTCAACCTAGCTGCTACTGC | 22 | |
| R:TGACCCAAAACTAACATACACC | 22 | |||
| PsACT | EF585293 | F:CTTCCAACCATCACTCATT | 19 | |
| R:CCTAATATCCACATCACACTT | 21 |
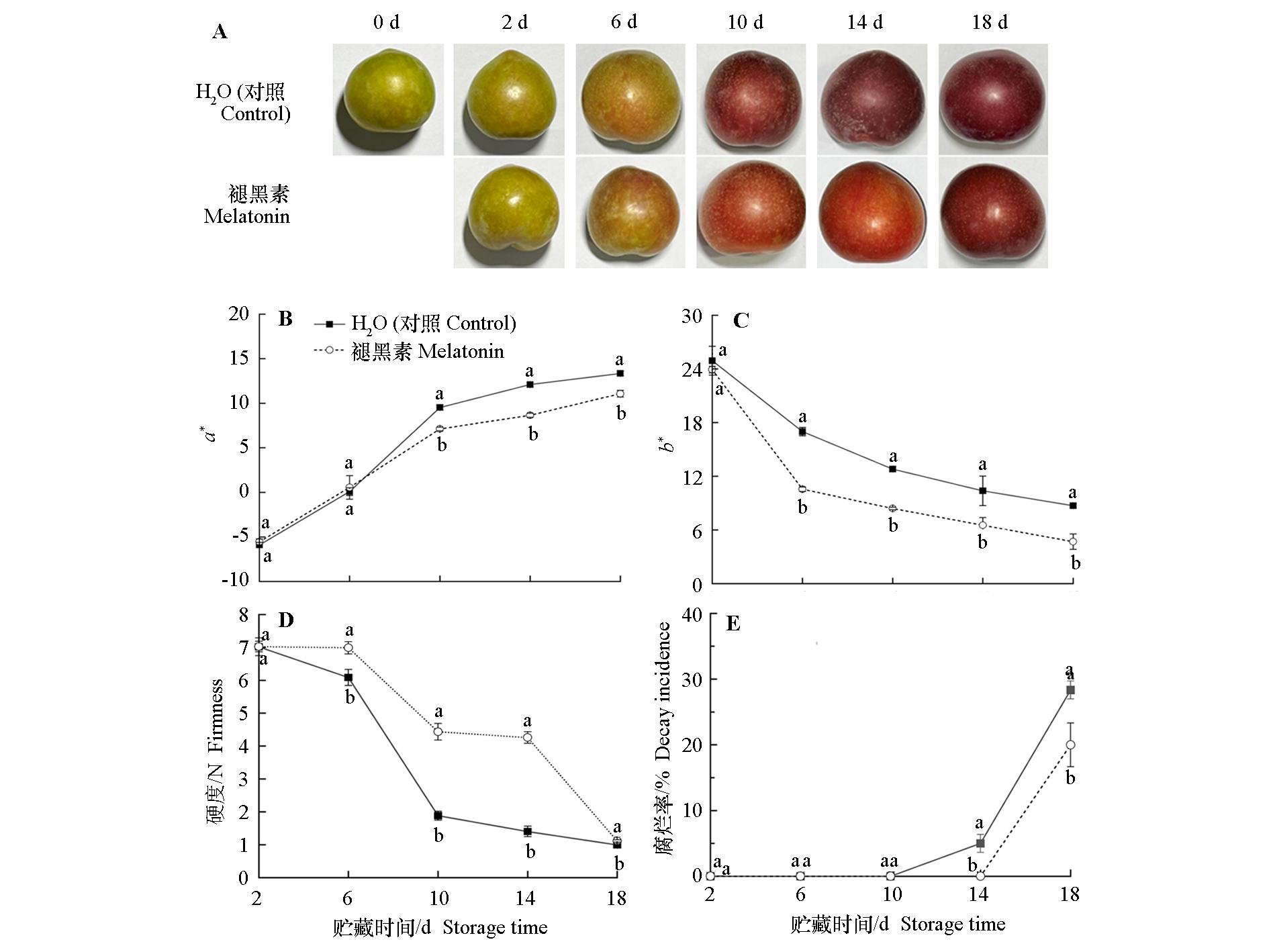
Fig. 1 Effect of melatonin treatment on the color(A),a*(B),b*(C)of the peel,fruit firmness(D)and decay incidence(E)of ‘Taoxingli’plum during storage at ambient temperature Different lowercase letters represented significant differences(P ≤ 0.05). The same below
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
邓长江, 李长清, 朱希强, 郭学平. 2006. 蒽酮—硫酸法测定出芽短梗霉发酵液残糖和总糖含量的研究. 食品与药品,11:54-56.
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
pmid: 23023689 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
|
吴建峰. 2022. 嵊州桃形李不同栽培模式对裂果及效益的影响. 中国南方果树, 51 (2):151-153,159.
|
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [1] | TONG Zongjun, HAN Xing, DUAN Xinlian, LIU Yuanyuan, LIN Junbin, GAN Ying, CHEN Jie, XIE Baogui, GAN Bingcheng, YAN Junjie. Sequence Characterization of PRX Family and Expression Analysis in the Process of Fruiting Body Development in Flammulina filiformis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 337-348. |
| [2] | CHEN Yajuan, JIN Xin, YANG Jiangshan, DAI Zibo, LI Dou, SHAO Zhang. Effects of Fulvic Acid Potassium on Sugar-Acid Metabolism and Aroma Substances in‘Cabernet Gernischt’Grape Berries [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 406-422. |
| [3] | ZHANG Shuning, ZHENG Shuqi, WANG Xinsheng, KE Fuzhi, ZHANG Lanlan, SUN Xuepeng, GONG Jinli. Advances in the Relationship Between Cell Wall Metabolism and Physiological Diseases of Citrus Peel [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 513-525. |
| [4] | REN Xiliang, WANG Yuhong, GAO Tianyi, WANG Jie, HUANG Yunping. A New High-Quality Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Yongqing 8’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 541-542. |
| [5] | ZHANG Shiqi, HUANG Lu, CHENG Xi, ZHANG Xiaoyan, YUAN Yuting, HOU Yichen, DAI Dongqing, XIA Xiudong, YUAN Xingxing, CHEN Xin, ZHU Yuelin, XUE Chenchen. Influence of Different Sowing Dates on the Quality of Vegetable Soybeans [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 213-228. |
| [6] | ZOU Xuexiao, YANG Sha, DAI Xiongze, HU Bowen, XU Hao, ZHU Fan, PEI Songyu, YUAN Fang. The Rapid Development of China’s Chili Pepper Industry Over the Past 40 Years [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 247-258. |
| [7] | LI Guoliang, ZHANG Shifan, LI Fei, ZHANG Hui, SUN Rifei, ZHANG Shujiang. A New Brassica juncea Cultivar for Edible Stems‘Yuya 702’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 261-262. |
| [8] | XIA Zhilei, YU Bingxin, YANG Meng, LIAN Zilin, GUAN Lilan, HE Yichao, YAN Shuangshuang, CAO Bihao, QIU Zhengkun. Fine-Mapping and KASP Marker Development for the Gene Underlying Green Fruit in Eggplant [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2008-2018. |
| [9] | ZHONG Yizhong, WANG Zhou, XIE Jingyao, WANG Zhengpeng, HAO Jingjing, LIU Chaoyang, ZHANG Wei, WU Jing, ZHONG Ziqin, CHEN Chengjie, HE Yehua. Flowering and Fruiting Behaviour of Two South China Plum Cultivars with Different Ripening Stages in an Area Near the Northern Boundary of the Tropics [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2105-2119. |
| [10] | LIU Yanfei, HE Xin, TIAN Ailin, LIU Zhande. A New High-Quality Kiwifruit Cultivar with Better Storability‘Jinfu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2219-2220. |
| [11] | LI Xujiao, LÜ Qi, YAO Dongdong, ZHAO Fengyun, WANG Xiaofei, YU Kun. Effect of‘Yanfu 3’Apple Grafted with Different Rootstocks on Absorption and Utilization of 15N-urea [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1868-1880. |
| [12] | JIANG Biao, XIE Dasen, LIU Wenrui, YAN Jinqiang, WANG Min, He Xiaoming, PENG Qingwu, LIN Yu’e, Liang Zhaojun, CHEN Lin. A New Hybrid Wax Gourd Cultivar‘Yacui 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1979-1980. |
| [13] | ZHANG Lihua, XU Yu, Zheng Litong, Wang Changzhi, ZHU Lingcheng, MA Baiquan, LI Mingjun. The Relevance Research Between Acid Transporters and Fruit Acidity [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1474-1488. |
| [14] | LI Yachen, ZHENG Yanmei, SONG Wenpei, LI Dawei, LIANG Hong, ZHANG Xianzhi. Research Progress on the Role of Hydrogen-Rich Water in Plant Growth and Development and Stress Response [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1489-1500. |
| [15] | LI Xin, CHAI Yingfang, TIAN Zhen, WANG Pengwei, CHENG Yunjiang. Isolation and Purification of Mitochondria and Its Application in Research on Fruit Ripening and Senescence [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1516-1528. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd