
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 292-308.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0304
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
JING Yonglin1,2, CHEN Langxin1,2, LI Junguo1,2, WANG Jiabin1,2, WANG Xiaobing1,2, YANG Qingquan1,2, MENG Chunyang1,2, XU Li1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-08-21
Revised:2024-10-18
Online:2025-02-25
Published:2025-02-23
Contact:
XU Li
JING Yonglin, CHEN Langxin, LI Junguo, WANG Jiabin, WANG Xiaobing, YANG Qingquan, MENG Chunyang, XU Li. Functional Studies of Pineapple AcKNOX1 on Leaf Margin Development[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 292-308.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0304
| 用途 Application | 序列名称 Sequence name | 上游引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| AcKNOX1克隆 Cloning of AcKNOX1 | AcKNOX1 | CCCTTTCCCAAAACCCTACC | CGCCTTCATCGATTGATCGT |
| AcKNOX1+ | GGGGTACCCCCTTTCCCAAAACCCTACC | GCTCTAGACGCCTTCATCGATTGATCGT | |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | pBI221-AcKNOX1 | GACTCTAGAGGATCCATGGATGAGCAACTTTACCAAGTTA | CTCCGCGGCGGATCCTGCGCTTCTTGGTCACATCTATCG |
| 启动子克隆 Cloning of promoter | AcKNOX1-promoter | CAAAATAATGAAATCTATGGCCAAA | AAAAGGAAACCACACCCGAAA |
| qRT-PCR | qPCR-AcKNOX1 | TGCCGTTTTGATGTTCTCACTAAG | CGATTGATCGTATACCCAGTTTG |
Table 1 Primers for cloning and expression analysis of AcKNOX1
| 用途 Application | 序列名称 Sequence name | 上游引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| AcKNOX1克隆 Cloning of AcKNOX1 | AcKNOX1 | CCCTTTCCCAAAACCCTACC | CGCCTTCATCGATTGATCGT |
| AcKNOX1+ | GGGGTACCCCCTTTCCCAAAACCCTACC | GCTCTAGACGCCTTCATCGATTGATCGT | |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | pBI221-AcKNOX1 | GACTCTAGAGGATCCATGGATGAGCAACTTTACCAAGTTA | CTCCGCGGCGGATCCTGCGCTTCTTGGTCACATCTATCG |
| 启动子克隆 Cloning of promoter | AcKNOX1-promoter | CAAAATAATGAAATCTATGGCCAAA | AAAAGGAAACCACACCCGAAA |
| qRT-PCR | qPCR-AcKNOX1 | TGCCGTTTTGATGTTCTCACTAAG | CGATTGATCGTATACCCAGTTTG |
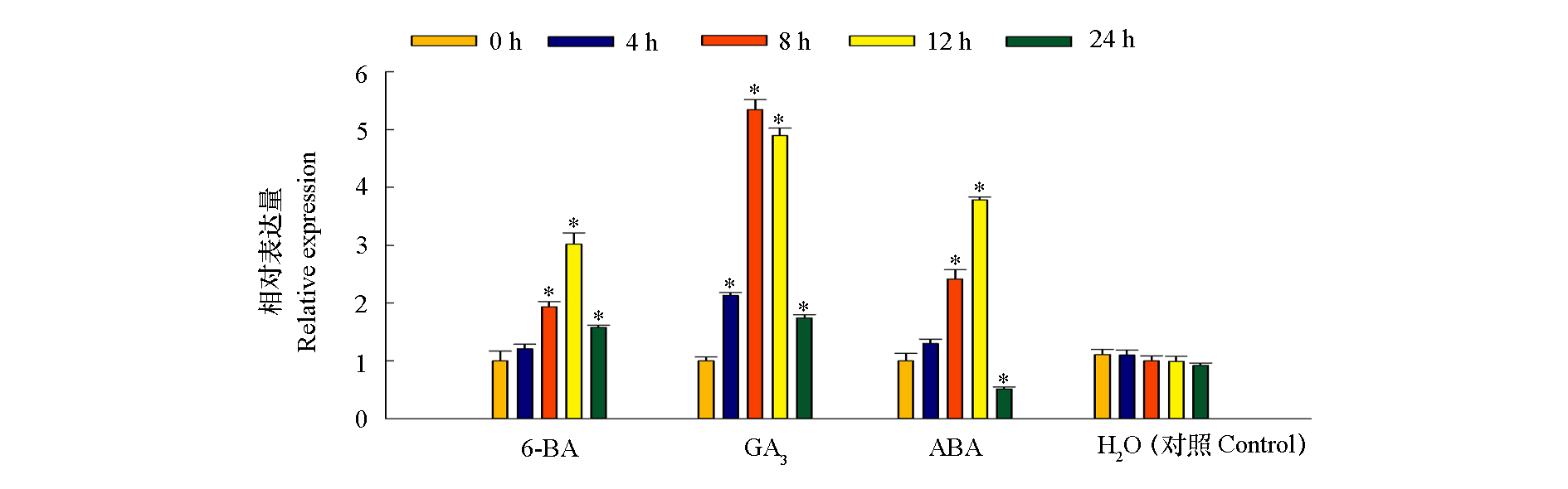
Fig. 6 Expression level of AcKNOX1 in pineapple seedlings after exogenous GA3,ABA and 6-BA treatments * Indicates a significant difference between treatment and control at the 0.05 level at the same time

Fig. 9 The phenotype of wild-type(WT),trans-empty vector(Vector)and transgenic(AcKNOX1-OE)lines of Arabidopsis A:The leaf margin of cotyledon,the red triangle shows serration at the leaf margin;B:The hypocotyl of cotyledon,the white triangles indicate the junction of the hypocotyl and root;C:The hypocotyl length;D:The leaf phenotype during bolting;E:The phenotype of the sixth rosette leaf;F:Quantification of serration in the sixth rosette leaf;G:The leaf phenotype after podding. L1,L2,L3,L4 indicate four lines of transgenic plants
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1070343 pmid: 12052958 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
丛汉卿, 信彩云, 张银东, 李志英, 徐立. 2013. ‘阿蒂擎天’凤梨谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶基因的克隆与乙烯诱导表达特性的\初步分析. 分子植物育种, 11 (3):365-370.
|
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.073601 pmid: 20435903 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.11.037 pmid: 21129970 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.3732/ajb.1700251 pmid: 29885230 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1007/s00299-010-0993-7 pmid: 21212958 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0477 |
|
袁静, 周冰莹. 2021. 植物叶缘锯齿发育调控的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 37 (26):24-31.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0477 |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
doi: 10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.20221220002 |
|
郑健, 潘继红, 余卫霖, 宋云连, 毕珏, 凌铭蔚, 王跃全, 高贤玉, 张惠云, 罗心平. 2023. 植物叶缘锯齿调控的研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报, 24 (4):927-936.
doi: 10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.20221220002 |
| [1] | HE Yehua, LIU Chaoyang, LUAN Aiping, GONG Xue, LIU Jiarou, Zhang Wei, LIN Shunquan, HU Guibing, LIU Chengming, XIA Jingxian, LIN Wenqiu, CHEN Chengjie, XIE Tao, MA Jun, HE Jianchi, CHEN Shaohua. A New Pineapple Cultivar‘Jintong Boluo’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 453-454. |
| [2] | WANG Min, YANG Songguang, LIU Wei, HE Xiaoming, SHI Shaoqi, LIU Wenrui, CHEN Lin, JIANG Biao, PENG Qingwu. Response to Low Temperature Stress and Screening and Validation of Interaction Protein of CqCHP1 in Chieh-qua [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(11): 2376-2386. |
| [3] | ZHOU Xuzixin, YANG Wei, MAO Meiqin, XUE Yanbin, MA Jun. Identification of Pigment Components and Key Genes in Carotenoid Pathway in Mutants of Chimeric Ananas comosus var. bracteatus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1081-1091. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd