
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 2410-2424.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0858
• Cultivation·Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
DU Lijun, LIU Yingcai, SHI Yanyan, WANG Yang, LI Chunhui, HE Yintao, WANG Xu, BIAN Chuanjie, ZHANG Manrang*( )
)
Received:2025-01-24
Revised:2025-03-15
Online:2025-09-25
Published:2025-09-24
Contact:
ZHANG Manrang
DU Lijun, LIU Yingcai, SHI Yanyan, WANG Yang, LI Chunhui, HE Yintao, WANG Xu, BIAN Chuanjie, ZHANG Manrang. Effect of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on the Growth and Mechanism of Different Apple Cultivar Under Salt-Alkali Stress[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(9): 2410-2424.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0858
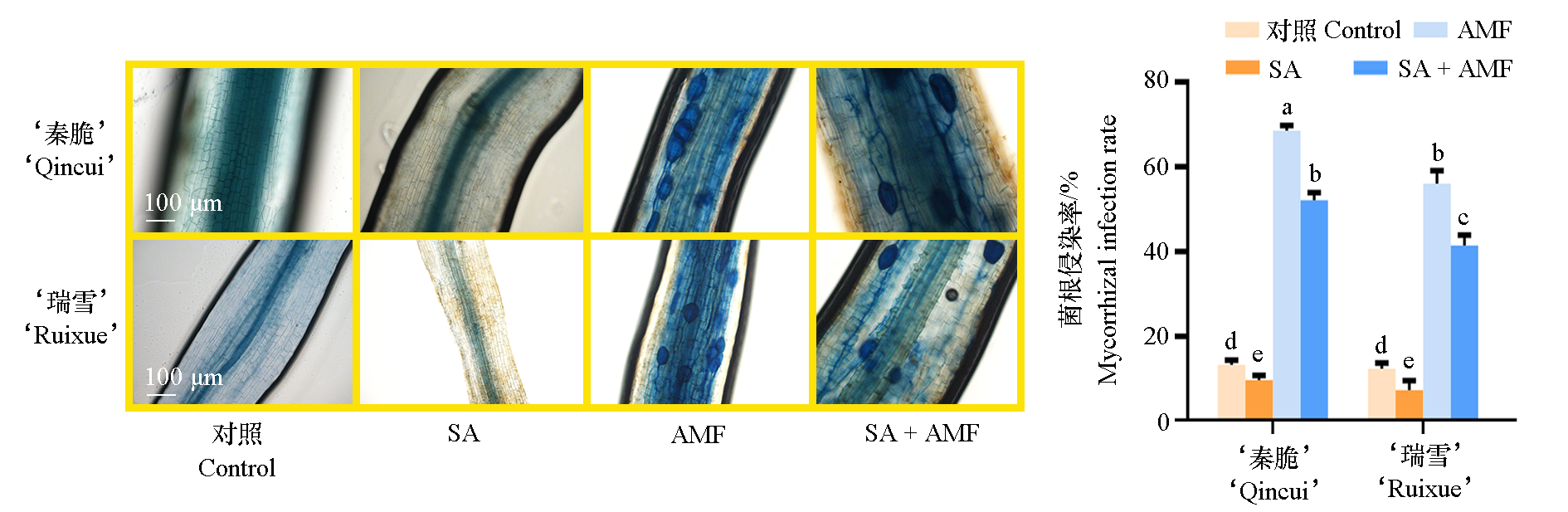
Fig. 1 The Phenotype and mycorrhizal infection rate of‘Qincui’and‘Ruixue’apples SA:0.2 mol · L-1 NaHCO3 + NaCl;AMF:Inoculation with Rhizophagus intraradices;SA + AMF:SA treatment applied 60 days after AMF inoculation. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 probability level. The same below
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 株高/cm Height | 茎粗/mm Stem diameter | 新梢生长量/cm Shoot growth | 根面积/cm2 Root area | 根长/cm Root length | 根体积/cm3 Root volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘秦脆’ ‘Qincui’ | 对照Control | 106.0 ± 2.6 b | 7.3 ± 0.3 b | 82.3 ± 2.5 b | 96.1 ± 3.5 b | 3 294.6 ± 74.8 b | 2 630.6 ± 187.5 b |
| SA | 83.0 ± 4.4 d | 6.4 ± 0.2 c | 71.3 ± 2.3 c | 77.1 ± 1.3 d | 2 672.1 ± 180.5 d | 1 924.0 ± 155.8 c | |
| AMF | 120.7 ± 5.6 a | 8.1 ± 0.5 a | 100.7 ± 2.1 a | 117.1 ± 5.3 a | 3 509.4 ± 110.3 a | 3 061.3 ± 161.4 a | |
| SA + AMF | 97.0 ± 5.2 c | 7.2 ± 0.3 b | 80.3 ± 2.5 b | 83.6 ± 2.5 c | 3 056.6 ± 19.1 c | 2 437.3 ± 231.1 b | |
| ‘瑞雪’ ‘Ruixue’ | 对照Control | 81.0 ± 1.7 b | 7.1 ± 0.2 c | 73.9 ± 2.0 b | 91.4 ± 0.6 b | 3 060.0 ± 122.6 b | 2 592.3 ± 133.2 b |
| SA | 70.0 ± 1.7 d | 6.3 ± 0.2 d | 66.6 ± 1.4 c | 72.7 ± 2.2 c | 2 551.1 ± 174.8 d | 1 914.3 ± 124.1 c | |
| AMF | 89.0 ± 3.6 a | 8.1 ± 0.2 a | 98.2 ± 0.2 a | 102.9 ± 3.0 a | 3 441.2 ± 136.5 a | 3 030.0 ± 123.1 a | |
| SA + AMF | 77.7 ± 1.5 c | 7.6 ± 0.2 b | 71.3 ± 0.6 b | 91.7 ± 8.2 b | 2 706.4 ± 272.3 c | 2 347.7 ± 186.9 b |
Table 1 Physiological indexes of‘Qincui’and‘Ruixue’apple grafted seedings after 20 days under salt-alkali treatment
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 株高/cm Height | 茎粗/mm Stem diameter | 新梢生长量/cm Shoot growth | 根面积/cm2 Root area | 根长/cm Root length | 根体积/cm3 Root volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘秦脆’ ‘Qincui’ | 对照Control | 106.0 ± 2.6 b | 7.3 ± 0.3 b | 82.3 ± 2.5 b | 96.1 ± 3.5 b | 3 294.6 ± 74.8 b | 2 630.6 ± 187.5 b |
| SA | 83.0 ± 4.4 d | 6.4 ± 0.2 c | 71.3 ± 2.3 c | 77.1 ± 1.3 d | 2 672.1 ± 180.5 d | 1 924.0 ± 155.8 c | |
| AMF | 120.7 ± 5.6 a | 8.1 ± 0.5 a | 100.7 ± 2.1 a | 117.1 ± 5.3 a | 3 509.4 ± 110.3 a | 3 061.3 ± 161.4 a | |
| SA + AMF | 97.0 ± 5.2 c | 7.2 ± 0.3 b | 80.3 ± 2.5 b | 83.6 ± 2.5 c | 3 056.6 ± 19.1 c | 2 437.3 ± 231.1 b | |
| ‘瑞雪’ ‘Ruixue’ | 对照Control | 81.0 ± 1.7 b | 7.1 ± 0.2 c | 73.9 ± 2.0 b | 91.4 ± 0.6 b | 3 060.0 ± 122.6 b | 2 592.3 ± 133.2 b |
| SA | 70.0 ± 1.7 d | 6.3 ± 0.2 d | 66.6 ± 1.4 c | 72.7 ± 2.2 c | 2 551.1 ± 174.8 d | 1 914.3 ± 124.1 c | |
| AMF | 89.0 ± 3.6 a | 8.1 ± 0.2 a | 98.2 ± 0.2 a | 102.9 ± 3.0 a | 3 441.2 ± 136.5 a | 3 030.0 ± 123.1 a | |
| SA + AMF | 77.7 ± 1.5 c | 7.6 ± 0.2 b | 71.3 ± 0.6 b | 91.7 ± 8.2 b | 2 706.4 ± 272.3 c | 2 347.7 ± 186.9 b |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
高华, 赵政阳. 2016. 苹果新品种——瑞雪. 中国果业信息, 33 (4):57.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0348 |
|
李敖, 郑旭, 吴承勖, 聂瑞宁, 姬新颖, 唐佳莉, 张俊佩. 2025. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下核桃幼苗生长及生理的影响. 园艺学报, 52 (2):423-438.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0348 |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1036 |
|
梁圣敏, 张菲, 吴强盛. 2023. 丛枝菌根真菌通过调节枳根系多胺提高抗旱性. 园艺学报, 50 (12):2680-2688.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1036 |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
刘燕湘, 杨海萌, 赖燕芬, 郑杰娜, 张福平. 2013. 杨桃果实过氧化氢酶活性研究. 南方农业学报, 44 (2):304-307.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
陆建增, 周丽颜, 黄馨仪, 吴凤芝, 高丹美. 2024. 番茄碳库强度对其与伴生分蘖洋葱和AMF的关系及钾吸收的影响. 园艺学报, 51 (11):1-13.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03234-7 pmid: 38764051 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
孙志娟, 刘文杰, 郑晓东, 袭祥利, 马长青, 刘晓丽, 王彩虹, 田义轲. 2023. 褪黑素对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及其机制. 园艺学报, 50 (8):1697-1710.
|
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
|
翟书林, 刘晓琳, 姚璐莹, 詹文晶, 高文俊. 2023. 混合盐碱下接种丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)对紫花苜蓿根系构型的影响. 饲料研究, 46 (21):90-94.
|
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0499 |
|
郑晓东, 袭祥利, 李玉琪, 孙志娟, 马长青, 韩明三, 李少旋, 田义轲, 王彩虹. 2022. 油菜素内酯对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及调控机理研究. 园艺学报, 49 (7):1401-1414.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0499 |
|
| [49] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0368 |
|
邹养军, 马锋旺, 符轩畅, 李翠英, 安贵阳, 李明军, 李超, 党志明. 2019. 晚熟苹果新品种‘秦脆’. 园艺学报, 46 (5):1011-1012.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0368 |
| [1] | ZHANG Zongying, WANG Nan, LIU Wenjun, ZOU Qi, WANG Ping, MA Mingfu, XU Yuehua, CHEN Xiaoliu, MAO Zhiquan, CHEN Xuesen. A New Purple-Red Bud Apple Cultivar‘Baxian Xinfu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 1-2. |
| [2] | ZHU Yu, LIU Xiaofeng, ZHOU Jia, LI Jing, WANG Qiang. A New Apple Cultivar‘Huayou Baofeng’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 3-4. |
| [3] | SUN Jilu, ZHANG Ruifen, SHA Guangli, MA Rongqun, HUANG Yue, WANG Xiongwei, MA Minxia, GE Hongjuan. A New Ornamental Crabapple Cultivar‘Datang Laofeng’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 227-228. |
| [4] | ZHANG Ruifen, SUN Jilu, GE Hongjuan, MA Rongqun, HUANG Yue, SUN Hongtao, SHA Guangli. A New Ornamental Crabapple Cultivar‘Ziyu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 229-230. |
| [5] | XU Gongxun, YAN Shuai, HE Meiqi, MA Huaiyu, LÜ Deguo, QIN Sijun, CHENG Cungang, ZHAO Deying. Advances in the Research on Cold Resistance of Apple [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(8): 2021-2045. |
| [6] | ZHAO Yupu, BAI Yihan, HOU Saisai, PU Zitian, NIE Lanchun, LI Qingyun, and WANG Xinxin. Research Progress of Alleviating Continuous Cropping Obstacles in Facilities Vegetables Soil Using Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(8): 2166-2186. |
| [7] | SUN Dongyu, WEI Dong, YANG Yinyan, HU Caizhu, HU Zhiqun, ZHOU Donghui, and ZHOU Biyan. Physiological Response and Transcriptome Analysis of Wax Apple Flowering to Foliar Application of Chlorpyrifos [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(7): 1718-1732. |
| [8] | CHEN Xuesen, WANG Nan, ZHANG Zongying, ZHANG Shuhui, LIU Wenjun, ZOU Qi, YU Lei, ZHANG Jing, JIANG Yuanmao, HU Dagang, LI Yuanyuan, and MAO Zhiquan. Research Progress on Breeding Nutrient-Rich,Strong Flavored,Simplified Management,and Mechanization-adapted Apple Varieties [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1661-1676. |
| [9] | TIAN Yufeng, MA Songya, YANG An, HAN Xiaolei, ZHANG Caixia. Establishment and Optimization of Regeneration System for Apple Rootstock B9 [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 947-958. |
| [10] | CHENG Xiaogai, WAN Yuan, LIN Lu, XIE Peng, LI Zhiqiang, LI Mi, WANG Pengpeng, NIU Zimian. Influences of Trunk Heights on Leaf Photosynthesis and Fruit Qualities at Different Canopy Locations in Open-Central Canopy of Apple [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 671-692. |
| [11] | LI Ao, ZHENG Xu, WU Chengxu, NIE Ruining, JI Xinying, TANG Jiali, ZHANG Junpei. The Effect of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Walnut Seedlings Under Salt Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 423-438. |
| [12] | LI Chaonan, LI Lu, GAO Danlei, QIAO Hongyong, YUAN Tao. Differences in Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Community in the Roots and Rhizosphere Soil of Paeonia ludlowii Between Original Site and Introduction Site [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 467-480. |
| [13] | SHI Xingxiu, FENG Beibei, YAN Peng, GENG Wenjuan, Jumazira Sharshanmukhan. Physiological Changes Associated with Early Watercore in‘Orin’Apples [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 171-184. |
| [14] | JIA Linguang, ZHANG He, ZHANG Xueying, SUN Jianshe, GAO Yi, LI Guofang, TAN Ming, SHAO Jianzhu. A New Edible Crabapple Cultivar‘Jinxing’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2227-2228. |
| [15] | QIU Hui, ZHU Dejuan, ZHANG Yongle, GAO Yujie, LI Liu, WANG Guoping, HONG Ni. Interaction Between the Coat Protein of Apple Chlorotic Leaf Spot Virus and Two E3 Ubiquitin Ligases of Pear and Their Subcellular Localization [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1715-1727. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd