
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 1301-1316.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0045
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yue1,2, FENG Yiliao1, WANG Bei2, REN Wenjing1, JIANG Chunyu1, ZHAO Xinyu1, WANG Caihong1, YANG Limei1, ZHUANG Mu1, LÜ Honghao1, WANG Yong1, ZHANG Yangyong1,*( ), JI Jialei1,3,*(
), JI Jialei1,3,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-13
Revised:2025-04-27
Online:2025-05-23
Published:2025-05-21
Contact:
ZHANG Yangyong, JI Jialei
ZHANG Yue, FENG Yiliao, WANG Bei, REN Wenjing, JIANG Chunyu, ZHAO Xinyu, WANG Caihong, YANG Limei, ZHUANG Mu, LÜ Honghao, WANG Yong, ZHANG Yangyong, JI Jialei. Preliminary Transcriptome Analysis of Folate Synthesis and Metabolism in Cabbage[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(5): 1301-1316.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0045
| 样品Sample | 双端序列总数Paired-end reads counts | 总碱基数Clean bases | GC含量/% GC Content | 碱基质量值/% ≥ 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q372-1 | 20 186 702 | 6 043 240 774 | 46.57 | 94.02 |
| Q372-2 | 21 382 384 | 6 402 029 466 | 46.70 | 94.50 |
| Q372-3 | 19 720 185 | 5 902 457 860 | 46.32 | 94.24 |
| Q428-1 | 21 147 787 | 6 332 933 914 | 47.79 | 93.93 |
| Q428-2 | 23 999 831 | 7 185 985 424 | 47.75 | 94.32 |
| Q428-3 | 19 953 645 | 5 975 348 582 | 47.70 | 94.16 |
Table 1 Sequencing data statistics
| 样品Sample | 双端序列总数Paired-end reads counts | 总碱基数Clean bases | GC含量/% GC Content | 碱基质量值/% ≥ 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q372-1 | 20 186 702 | 6 043 240 774 | 46.57 | 94.02 |
| Q372-2 | 21 382 384 | 6 402 029 466 | 46.70 | 94.50 |
| Q372-3 | 19 720 185 | 5 902 457 860 | 46.32 | 94.24 |
| Q428-1 | 21 147 787 | 6 332 933 914 | 47.79 | 93.93 |
| Q428-2 | 23 999 831 | 7 185 985 424 | 47.75 | 94.32 |
| Q428-3 | 19 953 645 | 5 975 348 582 | 47.70 | 94.16 |
| 功能途径 Function pathway | 基因 Gene | 蛋白缩写 Protein abbreviation | 拟南芥ID Arabidopsis thaliana ID | 甘蓝ID Brassica oleracea ID | 相似度/% Similarity | E值 E-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pABA合成 pABA synthesis | ADCL | ADCL | AT1G50090.1 | BolC02g022020.2J | 80.548 | 0 |
| BolC03g082990.2J | 85.955 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g004630.2J | 89.045 | 0 | ||||
| ADCS | ADCS | AT2G28880.1 | BolC04g021330.2J | 84.832 | 0 | |
| BolC04g055450.2J | 81.031 | 0 | ||||
| 喋啶合成 Pteridine synthesis | NUDT | DPP | AT1G68760.1 | BolC02g025120.2J | 82.270 | 9.78E-87 |
| DHNA | DHNA | AT3G11750.1 | BolC01g050940.2J | 87.500 | 3.6E-74 | |
| GCHI | GCHI | AT3G07270.1 | BolC05g058460.2J | 82.303 | 0 | |
| BolC01g053860.2J | 81.023 | 0 | ||||
| 组装加尾 Assembly and taliling | DHTS/DHFR | DHFR | AT2G16370.1 | BolC03g051860.2J | 89.382 | 0 |
| BolC01g004210.2J | 85.246 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g057740.2J | 88.690 | 5.2E-103 | ||||
| DHFS | DHFS | AT5G41480.1 | BolC07g028910.2J | 86.090 | 0 | |
| HPPK/DHPS | HPPK/DHPS | AT4G30000.2 | BolC01g009090.2J | 85.257 | 0 | |
| 分布转运 Distribution and transportation | FPGS | FPGS | AT3G10160.1 | BolC01g052470.2J | 82.083 | 0 |
| GGH | GGH | AT1G78660.1 | BolC02g034750.2J | 85.893 | 0 | |
| 降解回补Degradation and replenishment | PTAR | PTAR | AT1G10310.1 | BolC08g021880.2J | 92.181 | 5.2E-168 |
| C1代谢 C1 metabolism | 5FCL | 5FCL | AT5G13050.1 | BolC09g060020.2J | 85.816 | 4.2E-165 |
| BolC02g005400.2J | 79.196 | 0 | ||||
| 5FCLL | 5FCLL | AT1G76730.1 | BolC06g030250.2J | 86.517 | 0 | |
| DHC | DHC | AT2G38660.1 | BolC04g063230.2J | 88.385 | 0 | |
| FTHS | FTHS | AT1G31220.1 | BolC05g029350.2J | 83.390 | 1.4E-172 | |
| GCSH | GCSH | AT1G32470.1 | BolC08g011080.2J | 94.012 | 3.1E-105 | |
| BolC05g037930.2J | 95.210 | 2.9E-107 | ||||
| BolC05g030770.2J | 93.413 | 6.4E-105 | ||||
| BolC04g013540.2J | 91.018 | 8E-101 | ||||
| GCSL | GCSL | AT1G48030.1 | BolC06g002320.2J | 94.488 | 0 | |
| BolC05g049030.2J | 95.079 | 0 | ||||
| BolC05g049060.2J | 91.262 | 1.94E-57 | ||||
| GCSP | GCSP | AT4G33010.1 | BolC01g005590.2J | 90.172 | 0 | |
| GCST | GCST | AT1G11860.1 | BolC08g055130.2J | 97.066 | 0 | |
| BolC08g023150.2J | 95.854 | 0 | ||||
| MS | MS | AT5G17920.1 | BolC03g009250.2J | 97.781 | 0 | |
| BolC09g055230.2J | 97.520 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g008490.2J | 97.258 | 0 | ||||
| BolC03g036730.2J | 95.953 | 0 | ||||
| BolC05g061690.2J | 95.181 | 0 | ||||
| BolC03g011020.2J | 91.054 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g025710.2J | 95.200 | 8.66E-81 | ||||
| MTHFR | MTHR | AT2G44160.1 | BolC04g005400.2J | 94.454 | 0 | |
| BolC04g066800.2J | 91.611 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g025320.2J | 96.121 | 0 | ||||
| BolC08g043230.2J | 94.098 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g000140.2J | 80.519 | 3.77E-35 | ||||
| PURU | 10-FDF | AT4G17360.1 | BolC01g023770.2J | 93.617 | 0 | |
| BolC07g030320.2J | 93.272 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g042860.2J | 79.688 | 9.51E-27 | ||||
| BolC07g030040.2J | 82.759 | 9.29E-28 | ||||
| SHMT1a | SHMTla | AT4G37930.1 | BolC03g073550.2J | 98.263 | 0 | |
| BolC01g001230.2J | 97.297 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g042720.2J | 91.573 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g033950.2J | 89.513 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g059720.2J | 81.176 | 1.01E-35 | ||||
| SHMT3 | SHMT3 | AT4G32520.1 | BolC01g006620.2J | 91.018 | 0 | |
| BolC03g081120.2J | 88.868 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g056500.2J | 96.970 | 1.9E-14 | ||||
| BolC07g056470.2J | 96.970 | 1.9E-14 |
Table 2 Genes related to folate synthesis and metabolism
| 功能途径 Function pathway | 基因 Gene | 蛋白缩写 Protein abbreviation | 拟南芥ID Arabidopsis thaliana ID | 甘蓝ID Brassica oleracea ID | 相似度/% Similarity | E值 E-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pABA合成 pABA synthesis | ADCL | ADCL | AT1G50090.1 | BolC02g022020.2J | 80.548 | 0 |
| BolC03g082990.2J | 85.955 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g004630.2J | 89.045 | 0 | ||||
| ADCS | ADCS | AT2G28880.1 | BolC04g021330.2J | 84.832 | 0 | |
| BolC04g055450.2J | 81.031 | 0 | ||||
| 喋啶合成 Pteridine synthesis | NUDT | DPP | AT1G68760.1 | BolC02g025120.2J | 82.270 | 9.78E-87 |
| DHNA | DHNA | AT3G11750.1 | BolC01g050940.2J | 87.500 | 3.6E-74 | |
| GCHI | GCHI | AT3G07270.1 | BolC05g058460.2J | 82.303 | 0 | |
| BolC01g053860.2J | 81.023 | 0 | ||||
| 组装加尾 Assembly and taliling | DHTS/DHFR | DHFR | AT2G16370.1 | BolC03g051860.2J | 89.382 | 0 |
| BolC01g004210.2J | 85.246 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g057740.2J | 88.690 | 5.2E-103 | ||||
| DHFS | DHFS | AT5G41480.1 | BolC07g028910.2J | 86.090 | 0 | |
| HPPK/DHPS | HPPK/DHPS | AT4G30000.2 | BolC01g009090.2J | 85.257 | 0 | |
| 分布转运 Distribution and transportation | FPGS | FPGS | AT3G10160.1 | BolC01g052470.2J | 82.083 | 0 |
| GGH | GGH | AT1G78660.1 | BolC02g034750.2J | 85.893 | 0 | |
| 降解回补Degradation and replenishment | PTAR | PTAR | AT1G10310.1 | BolC08g021880.2J | 92.181 | 5.2E-168 |
| C1代谢 C1 metabolism | 5FCL | 5FCL | AT5G13050.1 | BolC09g060020.2J | 85.816 | 4.2E-165 |
| BolC02g005400.2J | 79.196 | 0 | ||||
| 5FCLL | 5FCLL | AT1G76730.1 | BolC06g030250.2J | 86.517 | 0 | |
| DHC | DHC | AT2G38660.1 | BolC04g063230.2J | 88.385 | 0 | |
| FTHS | FTHS | AT1G31220.1 | BolC05g029350.2J | 83.390 | 1.4E-172 | |
| GCSH | GCSH | AT1G32470.1 | BolC08g011080.2J | 94.012 | 3.1E-105 | |
| BolC05g037930.2J | 95.210 | 2.9E-107 | ||||
| BolC05g030770.2J | 93.413 | 6.4E-105 | ||||
| BolC04g013540.2J | 91.018 | 8E-101 | ||||
| GCSL | GCSL | AT1G48030.1 | BolC06g002320.2J | 94.488 | 0 | |
| BolC05g049030.2J | 95.079 | 0 | ||||
| BolC05g049060.2J | 91.262 | 1.94E-57 | ||||
| GCSP | GCSP | AT4G33010.1 | BolC01g005590.2J | 90.172 | 0 | |
| GCST | GCST | AT1G11860.1 | BolC08g055130.2J | 97.066 | 0 | |
| BolC08g023150.2J | 95.854 | 0 | ||||
| MS | MS | AT5G17920.1 | BolC03g009250.2J | 97.781 | 0 | |
| BolC09g055230.2J | 97.520 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g008490.2J | 97.258 | 0 | ||||
| BolC03g036730.2J | 95.953 | 0 | ||||
| BolC05g061690.2J | 95.181 | 0 | ||||
| BolC03g011020.2J | 91.054 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g025710.2J | 95.200 | 8.66E-81 | ||||
| MTHFR | MTHR | AT2G44160.1 | BolC04g005400.2J | 94.454 | 0 | |
| BolC04g066800.2J | 91.611 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g025320.2J | 96.121 | 0 | ||||
| BolC08g043230.2J | 94.098 | 0 | ||||
| BolC02g000140.2J | 80.519 | 3.77E-35 | ||||
| PURU | 10-FDF | AT4G17360.1 | BolC01g023770.2J | 93.617 | 0 | |
| BolC07g030320.2J | 93.272 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g042860.2J | 79.688 | 9.51E-27 | ||||
| BolC07g030040.2J | 82.759 | 9.29E-28 | ||||
| SHMT1a | SHMTla | AT4G37930.1 | BolC03g073550.2J | 98.263 | 0 | |
| BolC01g001230.2J | 97.297 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g042720.2J | 91.573 | 0 | ||||
| BolC06g033950.2J | 89.513 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g059720.2J | 81.176 | 1.01E-35 | ||||
| SHMT3 | SHMT3 | AT4G32520.1 | BolC01g006620.2J | 91.018 | 0 | |
| BolC03g081120.2J | 88.868 | 0 | ||||
| BolC07g056500.2J | 96.970 | 1.9E-14 | ||||
| BolC07g056470.2J | 96.970 | 1.9E-14 |

Fig. 7 Folate biosynthetic pathway in cabbage inbred lines Drawing based on De Lepeleire et al.,2018;Lian et al.,2015 Enzymes involved in folate synthesis. ADCS:Aminodeoxychorismate synthase;ADCL:Aminodeoxychorismate lyase;FPGS:Folylpolyglutamate synthetase;PGH:pABA-Glu hydrolase;GGH:γ-Glutamyl hydrolase;GCHI:GTP cyclohydrolaseⅠ;HPPK/DHPS:Dihydropterin pyrophosphokinase/dihydropteroate synthase;DHFS:Dihydrofolate synthetase;DHFR:Dihydrofolate reductase;GDC:Glycine decarboxylase;SHMT1a:Serine hydroxymethyl transferase 1a;MTHFR:Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase;MS:Methionine synthase;FTHS:10-Formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase;DHC:5,10-Methylene-THF dehydrogenase/5,10-Methenyl-THF cyclohydrolase
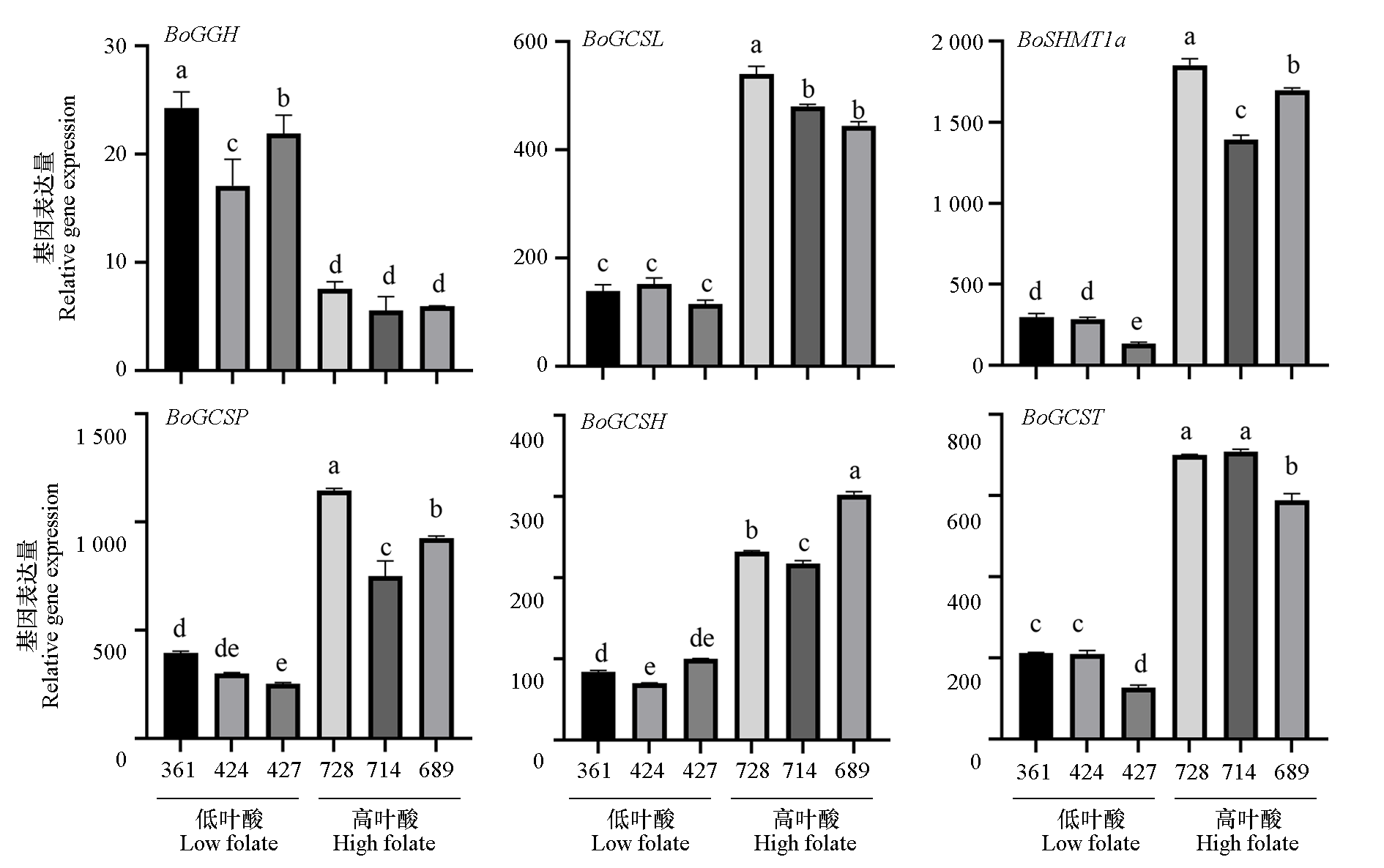
Fig. 8 RT-qPCR validation of differentially expressed genes in cabbage inbred lines Q428 and Q372 Different lowercase letters above the bars mean significantly different at the 0.05 probability level
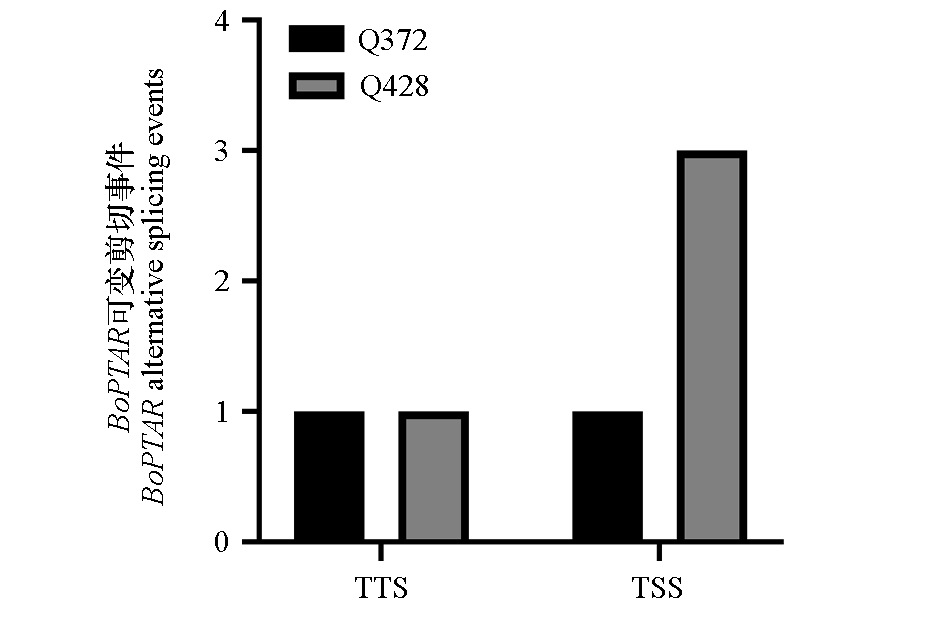
Fig. 9 Differential alternative splicing events between cabbage inbred lines Q428 and Q372 TTS:Transcription termination site;TSS:Transcription start site
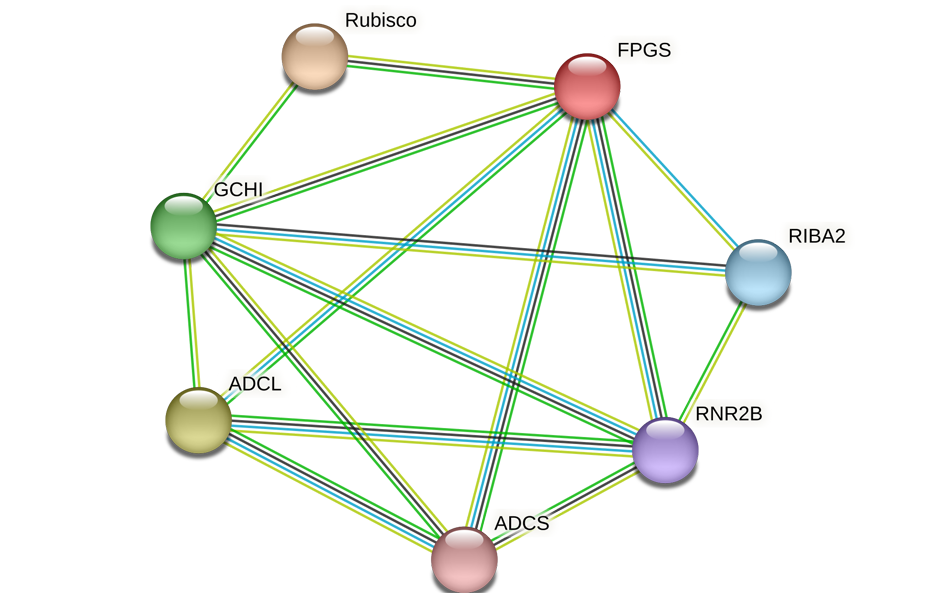
Fig. 10 Network analysis model of folate biosynthesis proteins and one-carbon metabolism key proteins ADCS:BolC04g021330.2J;ADCL:BolC02g022020.2J. Blue Lines:known interactions;Green lines:gene neighborhood;Light green line:text mining;Black line:co-expression
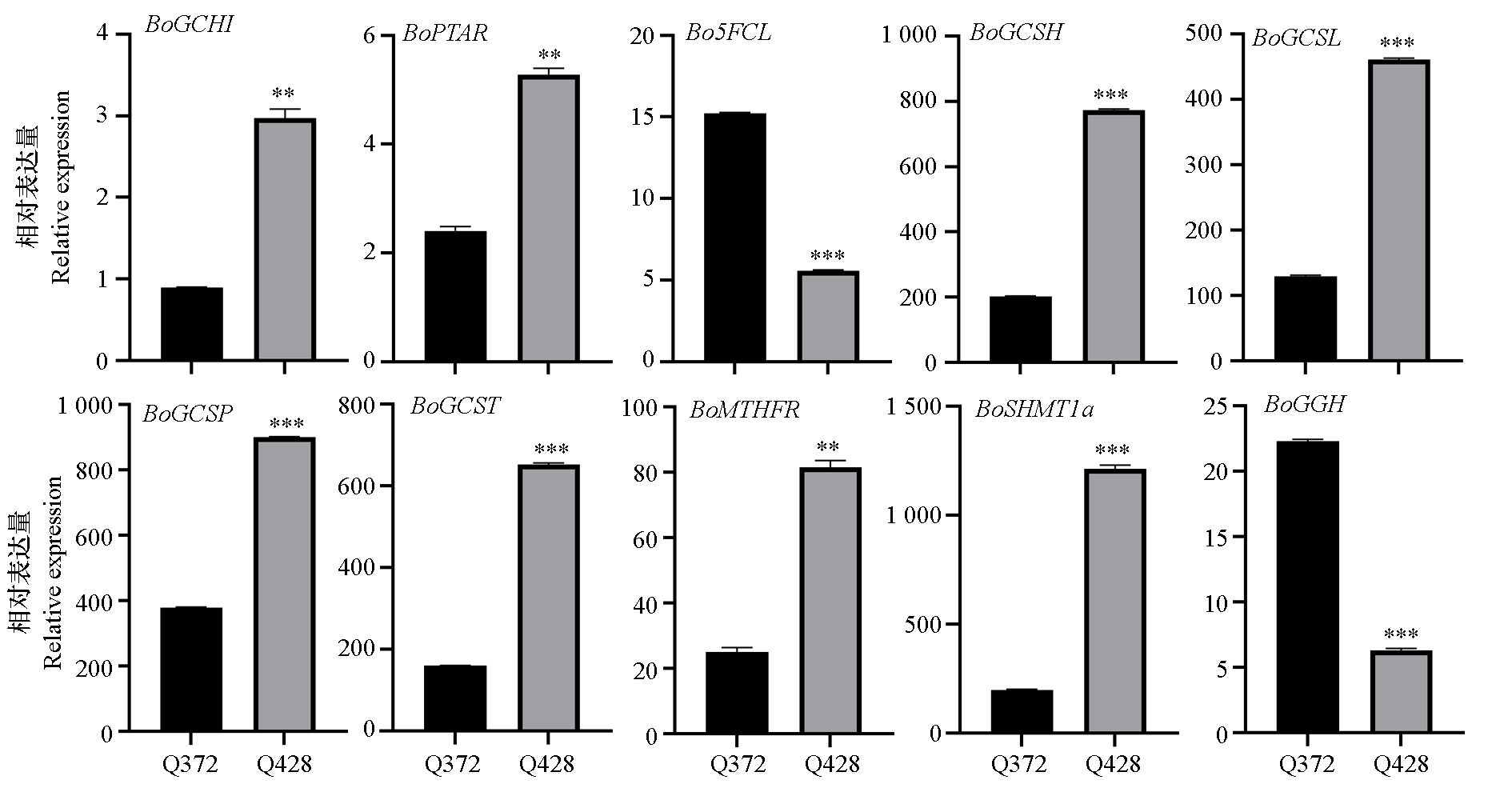
Fig. 11 RT-qPCR verification of folate-related genes BoGCH1:BolC05g058460.2J;BoPTAR:BolC08g021880.2J;Bo5FCL:BolC02g005400.2J;BoGCSH:BolC08g011080.2J;BoGCSL:BolC06g002320.2J;BoGCSP:BolC01g005590.2J;BoGCST:BolC08g055130.2J;BoMTHFR:BolC04g005400.2J;BoSHMT1a:BolC03g073550.2J;BoGGH:BolC02g034750.2J t-test. **:α = 0.01;***:α = 0.001
| [1] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04330.x pmid: 21070406 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert483 pmid: 24574483 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
|
崔亚楠, 韩莉妲, 舒金帅, 王孝宣, 黄泽军, 国艳梅, 刘磊, 杜永臣, 张春义, 李君明. 2020. 不同类型番茄叶酸及其衍生物含量的初步分析. 中国蔬菜,(12):14-21.
|
|
| [7] |
doi: S1674-2052(17)30378-7 pmid: 29277427 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
蒋伟, 李白玉. 2023. 微生物法测定蔬菜中叶酸含量. 食品安全导刊,(13):84-86.
|
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2012.00525 |
|
李莎, 姜凌, 王崇英, 张春义. 2012. 叶酸在植物体内功能的研究进展. 植物学报, 47 (5):525-533.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2012.00525 |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery453 pmid: 30753561 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp152 pmid: 19541855 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04173 |
|
马贵芳, 满夏夏, 张益娟, 高豪, 孙朝霞, 李红英, 韩渊怀, 侯思宇. 2021. 谷子穗发育期转录组与叶酸代谢谱联合分析. 作物学报, 47 (5):837-846.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04173 |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
pmid: 11375437 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
|
杨丽梅, 方智远, 刘玉梅, 庄木, 张扬勇, 孙培田. 2011. “十一五”我国甘蓝遗传育种研究进展. 中国蔬菜,(2):1-10.
|
| [1] | HU Yun, WEN Chunhuai, XIONG Xingcheng, YU Benyu, HE Shenghua. A New Cultivar of Low-Temperature Resistant Chinese Cabbage‘Zhuochunbai 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 81-82. |
| [2] | PANG Wenxing, YE Taining, JIANG Jing, LIANG Yue, WANG Xin, LIU Xin. A New Cultivar of Clubroot-Resistant Chinese Cabbage‘Yuxing 9’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 83-84. |
| [3] | MEN Xuejie, ZHOU Jin, WU Yanghuan, CHEN Fang, YANG Qihang, PARUKE • Aniwaer. A New Seedling-Edible Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Zaokuai 25’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 85-86. |
| [4] | LIU Chong, YI Dandan, ZOU Danrong, ZHOU Lixue, WANG Hui, SHENG Lili, CHEN Xiaofeng, ZHANG Yaming, GUI Hang. A New Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Qingmei 1’of High-Yield and High-Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 87-88. |
| [5] | ZHANG Lei, WANG Qingming, ZHOU Jie, WANG Yue’e, CAI Huaqing, WEI Lijun, LIU Daomin. A New Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Wancuibai’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 89-90. |
| [6] | YU Xiaolin, PING Fan, HUANG Li, CAO Jiashu, SONG Jianwei, LU Gang. A New Early-Mid Maturing Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Qiantangqing’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 91-92. |
| [7] | ZHANG Fenglan, SU Tongbing, ZHANG Bin, YU Shuancang, YU Yangjun, ZHANG Deshuang, ZHAO Xiuyun, WANG Weihong, LI Peirong, XIN Xiaoyun. Review and Prospects of Chinese Cabbage Breeding for the Past 70 Years in China [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(5): 1111-1135. |
| [8] | ZHANG Meidi, MA Ming, LI Xiaonan, JIANG Mingliang. Research Progress on Bolting Resistance Traits in Chinese Cabbage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(5): 1136-1158. |
| [9] | WANG Wenlong, LIU Zhaokun, LU Wenjun, WANG Yaolong, LI Xiaofeng, ZHU Hongfang, LIU Tongkun, LI Ying, HOU Xilin, ZHANG Changwei. Enhancing Ascorbic Acid Content in Non-heading Chinese Cabbage Using Gene Editing Technology [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(5): 1317-1325. |
| [10] | XU Xiuxiu, YE Xinyu, SHI Bo, ZHANG Shujiang, ZHANG Shifan, LI Fei, LI Guoliang, SUN Rifei, WANG Shunli, SUN Huagang, ZHANG Hui. Analysis of Flavor Quality of Chinese Cabbage Yutian Baojian [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(5): 1364-1374. |
| [11] | ZHANG Shuqing, MEN Wanjie, TIAN Tian, CHEN Qiuming, YE Tingyu, YU Hongrui, MA Xinyan, IQBAL Hussain, LEI Na, YU Xiaolin. Identification of Pathotypes of Plasmodiophora brassicae and Study on Green Control in Harbin City [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(5): 1375-1388. |
| [12] | YUAN Juanwei, JIA Li, WANG Han, YAN Congsheng, ZHANG Qi’an, YU Feifei, GAN Defang, JIANG Haikun. Screening of Resistant Germplasm and Identifying Candidate Gene for Phytophthora capsici Resistance in Pepper Germplasm Resources [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 857-871. |
| [13] | TANG Lingli, HE Yuhua, WANG Qingtao, AN Lulu, XU Yongyang, ZHANG Jian, KONG Weihu, HU Keyun, ZHAO Guangwei. Hormonal and Transcriptome Analysis of Ripe Fruits of Non-Climacteric and Climacteric Melon [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 883-896. |
| [14] | SHAO Yifan, ZHU Baoqing, WANG Tongxin, LIAO Jianhe, WU Fanhua, YANG Siyi, FENG Jianhang, YU Xudong. Research of Genetic Regulation of Bombax ceiba Prickle Based on Hormone,Transcriptome and Metabolome [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 933-946. |
| [15] | LI Qiang, WANG Ying, ZHAO Yuqian, SUI Xuelian, CAI Yumei, SU Yanbin, ZHENG Jinglei, SONG Xiaoming. A New Cabbage Cultivar‘Haomei Aoqi’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 1105-1106. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd