
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (8): 1773-1791.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0374
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
DUAN Minjie1, LI Yifei1, WANG Chunping2, YANG Xiaomiao1, HUANG Renzhong1, HUANG Qizhong1, ZHANG Shicai1,*( )
)
Received:2024-02-22
Revised:2024-05-20
Online:2024-08-25
Published:2024-08-21
Contact:
ZHANG Shicai
DUAN Minjie, LI Yifei, WANG Chunping, YANG Xiaomiao, HUANG Renzhong, HUANG Qizhong, ZHANG Shicai. Integrated Transcriptomic and Targeted Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Regulation of Carotenoid Accumulation During Pepper Fruit Development[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1773-1791.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0374
| 基因 Gene | 引物(5′-3′) Forward sequence | 生物学功能 Biological function |
|---|---|---|
| CCS | F:AGCACCCACATCAAAGCCAG R:GTGGTGAAGGGTCAACGCAA | 催化玉米黄质和紫黄质转化为辣椒红素和辣椒玉红素 Catalyzes the conversion of zeaxanthin and vioxanthin to capsanthin and capsorubin |
| PSY1 | F:ACAGGCAGGTCTATCCGACGAAG R:ACAACAGCAGAGATGCCAACACAG | 催化GGPP合成八氢番茄红素 Catalyzes the synthesis of phytoene by GGPP |
| CHYB | F:GCACGAGTCACACCATAGACCAAG R:CGTGAACGAACATGTAGGCCATCC | 催化β-胡萝卜素转化为玉米黄质 Catalyzes the conversion of β-carotene to zeaxanthin |
| NCED1 | F:GACATTCAGGGATAGCAAGGC R:TTGAAATAGACCAAACCAGCGT | 催化紫黄质和新黄质裂解成ABA前体 Catalytic cleavage of vioxanthin and neoxanthin into ABA precursors |
| LCYB | F:GTTGTTGGAATTGGTGGCACAGC R:ATGGCATTGGCAACGACAGGAG | 催化番茄红素生成β-胡萝卜素 Catalyzes the conversion of lycopene to β-carotene |
| ABA2 | F:CCCCTTGTTCAAATATCCTCG R:ACAGACCCTGCTATACTGCCTAA | 参与类胡萝卜素裂解及ABA的生物合成 Involved in carotenoid cleavage and ABA biosynthesis |
| PSY2 | F:AGACAGAGGTGGAATTTTGGGTCT R:CAAATTCCCCGGAAGCACA | 参与植物绿色器官色素积累 Involved in the accumulation of pigment in plant green organs |
| LCYE | F:ACCCTCGGTGTAAGAATTAAAG R:GAGTGATCTGACAACGGAATAA | 催化番茄红素转化为δ-胡萝卜素 Catalyzes the conversion of lycopene to δ-carotene |
| CRTISO | F:CACGGCAGGCGTTCATACA R:TCAGCCAGCAACACCCCAT | 催化八氢番茄红素转化为番茄红素 Catalyzes the conversion of phytoene to lycopene |
| CMB1 | F:CTCTAGTCGTGGCAAGCTTTAT R:CTGATGGTTGGGTTCCTTCA | 番茄:参与果实成熟及调控果实色素积累 Tomato:Involved in fruit ripening and regulating fruit pigment accumulation |
| SEP3 | F:ATCATGGCATTCTGGGGAGC R:TTTCGGTAGCACGGCATCG | 拟南芥:调控花器官发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates the development of floral organs |
| YABBY2 | F:GCGTGTTCCTTCTGCCTACA R:TTGCCCTCCAGCTTGAGTC | 番茄:调节果实心室数和内源赤霉素含量 Tomato:Regulates the number of ventricles and endogenous gibberellin content in the fruit |
| GT-3B | F:CGCAGATAGGTTCCCTCAATG R:TCAGGCTCCAGCGTTTCAC | 拟南芥:调控耐盐相关基因表达 Arabidopsis:Regulation of salt tolerance-related gene expression |
| NF-YA3 | F:AGAAGCCCCAAGAGTCCAAA R:CCGATGCACGATGAGAAGG | 拟南芥:调控早期胚胎发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates early embryonic development |
| NAC2 | F:TCACCCGACTGATGAAGAGC R:TCCCCATACAACGCCAAAT | 拟南芥:调控胚胎发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates embryonic development |
| AGL27 | F:AAACGAAGGAAAGGTCTGATGA R:TCTGCCACGATTGGAGATGAT | 拟南芥:增强植物对环境胁迫的耐受性 Arabidopsis:Enhancing plant tolerance to environmental stresses |
| HOX5 | F:AGGCAGGTGGCTGTATGGTT R:ATCGTTGTCTTTGCGAATGG | 拟南芥:ABA响应的正向调节因子 Arabidopsis:A positive regulator of ABA response |
| GATA26 | F:GCTGGATTCGTTGCGTTTT R:GCTGCTACTGGTGCTTGCTT | 拟南芥:参与光依赖调节 Arabidopsis:Involved in light-dependent regulation |
| bHLH48 | F:AATCCCTACAGCGACAAGTGG R:GTTTGTCCCTCGGTCCAGAT | 拟南芥:与光敏色素互作调控下胚轴伸长 Arabidopsis:Interacts with photosensitizer pigments to regulate hypocotyl elongation |
Table 1 Primers for qRT-PCR
| 基因 Gene | 引物(5′-3′) Forward sequence | 生物学功能 Biological function |
|---|---|---|
| CCS | F:AGCACCCACATCAAAGCCAG R:GTGGTGAAGGGTCAACGCAA | 催化玉米黄质和紫黄质转化为辣椒红素和辣椒玉红素 Catalyzes the conversion of zeaxanthin and vioxanthin to capsanthin and capsorubin |
| PSY1 | F:ACAGGCAGGTCTATCCGACGAAG R:ACAACAGCAGAGATGCCAACACAG | 催化GGPP合成八氢番茄红素 Catalyzes the synthesis of phytoene by GGPP |
| CHYB | F:GCACGAGTCACACCATAGACCAAG R:CGTGAACGAACATGTAGGCCATCC | 催化β-胡萝卜素转化为玉米黄质 Catalyzes the conversion of β-carotene to zeaxanthin |
| NCED1 | F:GACATTCAGGGATAGCAAGGC R:TTGAAATAGACCAAACCAGCGT | 催化紫黄质和新黄质裂解成ABA前体 Catalytic cleavage of vioxanthin and neoxanthin into ABA precursors |
| LCYB | F:GTTGTTGGAATTGGTGGCACAGC R:ATGGCATTGGCAACGACAGGAG | 催化番茄红素生成β-胡萝卜素 Catalyzes the conversion of lycopene to β-carotene |
| ABA2 | F:CCCCTTGTTCAAATATCCTCG R:ACAGACCCTGCTATACTGCCTAA | 参与类胡萝卜素裂解及ABA的生物合成 Involved in carotenoid cleavage and ABA biosynthesis |
| PSY2 | F:AGACAGAGGTGGAATTTTGGGTCT R:CAAATTCCCCGGAAGCACA | 参与植物绿色器官色素积累 Involved in the accumulation of pigment in plant green organs |
| LCYE | F:ACCCTCGGTGTAAGAATTAAAG R:GAGTGATCTGACAACGGAATAA | 催化番茄红素转化为δ-胡萝卜素 Catalyzes the conversion of lycopene to δ-carotene |
| CRTISO | F:CACGGCAGGCGTTCATACA R:TCAGCCAGCAACACCCCAT | 催化八氢番茄红素转化为番茄红素 Catalyzes the conversion of phytoene to lycopene |
| CMB1 | F:CTCTAGTCGTGGCAAGCTTTAT R:CTGATGGTTGGGTTCCTTCA | 番茄:参与果实成熟及调控果实色素积累 Tomato:Involved in fruit ripening and regulating fruit pigment accumulation |
| SEP3 | F:ATCATGGCATTCTGGGGAGC R:TTTCGGTAGCACGGCATCG | 拟南芥:调控花器官发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates the development of floral organs |
| YABBY2 | F:GCGTGTTCCTTCTGCCTACA R:TTGCCCTCCAGCTTGAGTC | 番茄:调节果实心室数和内源赤霉素含量 Tomato:Regulates the number of ventricles and endogenous gibberellin content in the fruit |
| GT-3B | F:CGCAGATAGGTTCCCTCAATG R:TCAGGCTCCAGCGTTTCAC | 拟南芥:调控耐盐相关基因表达 Arabidopsis:Regulation of salt tolerance-related gene expression |
| NF-YA3 | F:AGAAGCCCCAAGAGTCCAAA R:CCGATGCACGATGAGAAGG | 拟南芥:调控早期胚胎发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates early embryonic development |
| NAC2 | F:TCACCCGACTGATGAAGAGC R:TCCCCATACAACGCCAAAT | 拟南芥:调控胚胎发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates embryonic development |
| AGL27 | F:AAACGAAGGAAAGGTCTGATGA R:TCTGCCACGATTGGAGATGAT | 拟南芥:增强植物对环境胁迫的耐受性 Arabidopsis:Enhancing plant tolerance to environmental stresses |
| HOX5 | F:AGGCAGGTGGCTGTATGGTT R:ATCGTTGTCTTTGCGAATGG | 拟南芥:ABA响应的正向调节因子 Arabidopsis:A positive regulator of ABA response |
| GATA26 | F:GCTGGATTCGTTGCGTTTT R:GCTGCTACTGGTGCTTGCTT | 拟南芥:参与光依赖调节 Arabidopsis:Involved in light-dependent regulation |
| bHLH48 | F:AATCCCTACAGCGACAAGTGG R:GTTTGTCCCTCGGTCCAGAT | 拟南芥:与光敏色素互作调控下胚轴伸长 Arabidopsis:Interacts with photosensitizer pigments to regulate hypocotyl elongation |
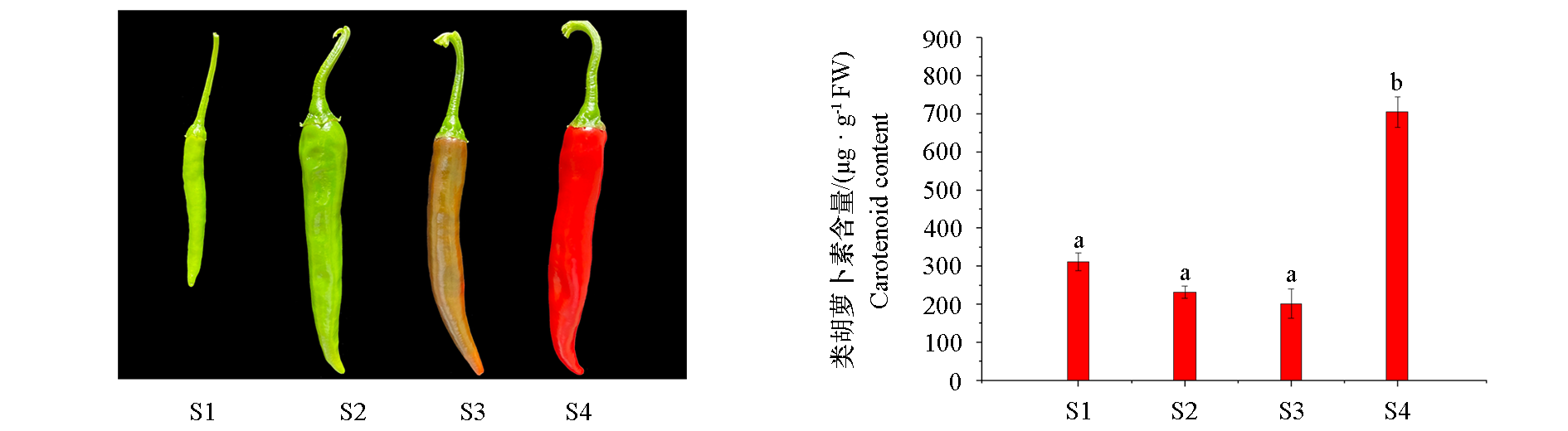
Fig. 1 Carotenoid accumulation(A)and phenotypes(B)of chili pepper fruits at the four ripening stages S1:Young fruit stage;S2:Mature green fruit stage;S3:Color-changed fruit stage;S4:Red ripe fruit stage. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level. The same below.

Fig. 9 Coexpressionnetwork of carotenoid biosynthetic genes and transcription factors in chili pepper fruits Red ellipses indicate the differentially expressed carotenoid biosynthetic genes,and the other squares indicate differentially expressed transcription factors that interact with carotenoid biosynthetic genes. The soild line represents positive regulation,the dashed line represents negative regulation,and the thickness of line represents the weigth.
| 目标 基因 Target gene | 候选转录因子 Transcription factor candidate | 缩写 Abbreviation | 蛋白ID Protein ID | 启动子基序 结合位点 Promoter motif union sites | 拟南芥同源基因 Arabidopsis locus name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCS | 预测:核转录因子Y亚基A-3-like亚型X1 Predicted:Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit A-3-like isoform X1 | NF-YA3 | XP_016562508.1 | 93 | AT1G72830 |
| 含NAC结构域的蛋白2 -like NAC domain-containing protein 2-like | NAC2 | XP_016569664.1 | 1 | AT3G15510 | |
| SEPALLATA-like MADS-box蛋白3 SEPALLATA-like MADS-box protein 3 | SEP3 | AYA60475.1 | 12 | AT1G24260 | |
| 预测:GATA转录因子26亚型X1 Predicted:GATA transcription factor 26 isoform X1 | GATA26 | XP_016575075.1 | 44 | AT4G17570 | |
| PSY | 预测:MADS-box蛋白CMB -like Predicted:MADS-box protein CMB1-like | CMB1 | XP_016547230.1 | 1 | AT2G03710 |
| NCED1 | 三螺旋转录因子GT-3b Trihelix transcription factor GT-3b | GT-3B | XP_016542034.1 | 45 | AT5G01380 |
| CHYB | 预测:无性生殖类似MADS-box蛋白AGL27亚型X5 Predicted:Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL27 isoform X5 | AGL27 | XP_016551041.1 | 2 | AT1G77080 |
| 预测:GATA转录因子26亚型X1 Predicted:GATA transcription factor 26 isoform X1 | GATA26 | XP_016575075.1 | 78 | AT4G17570 | |
| PSY2 | 预测:转录因子bHLH48亚型X2 Predicted:Transcription factor bHLH48 isoform X2 | bHLH48 | XP_016543852.1 | 16 | AT2G42300 |
| CRTISO | 假定的轴向调节YABBY 2亚型X1 Putative axial regulator YABBY 2 isoform X1 | YABBY2 | XP_016548878.1 | 2 | AT2G26580 |
| 同源框亮氨酸拉链蛋白HOX5 Homeobox-leucine zipper protein HOX5 | HOX5 | KAF3660217.1 | 3 | AT5G65310 |
Table 2 Binding site analysis of the promoter of target genes and the candidate transcription
| 目标 基因 Target gene | 候选转录因子 Transcription factor candidate | 缩写 Abbreviation | 蛋白ID Protein ID | 启动子基序 结合位点 Promoter motif union sites | 拟南芥同源基因 Arabidopsis locus name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCS | 预测:核转录因子Y亚基A-3-like亚型X1 Predicted:Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit A-3-like isoform X1 | NF-YA3 | XP_016562508.1 | 93 | AT1G72830 |
| 含NAC结构域的蛋白2 -like NAC domain-containing protein 2-like | NAC2 | XP_016569664.1 | 1 | AT3G15510 | |
| SEPALLATA-like MADS-box蛋白3 SEPALLATA-like MADS-box protein 3 | SEP3 | AYA60475.1 | 12 | AT1G24260 | |
| 预测:GATA转录因子26亚型X1 Predicted:GATA transcription factor 26 isoform X1 | GATA26 | XP_016575075.1 | 44 | AT4G17570 | |
| PSY | 预测:MADS-box蛋白CMB -like Predicted:MADS-box protein CMB1-like | CMB1 | XP_016547230.1 | 1 | AT2G03710 |
| NCED1 | 三螺旋转录因子GT-3b Trihelix transcription factor GT-3b | GT-3B | XP_016542034.1 | 45 | AT5G01380 |
| CHYB | 预测:无性生殖类似MADS-box蛋白AGL27亚型X5 Predicted:Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL27 isoform X5 | AGL27 | XP_016551041.1 | 2 | AT1G77080 |
| 预测:GATA转录因子26亚型X1 Predicted:GATA transcription factor 26 isoform X1 | GATA26 | XP_016575075.1 | 78 | AT4G17570 | |
| PSY2 | 预测:转录因子bHLH48亚型X2 Predicted:Transcription factor bHLH48 isoform X2 | bHLH48 | XP_016543852.1 | 16 | AT2G42300 |
| CRTISO | 假定的轴向调节YABBY 2亚型X1 Putative axial regulator YABBY 2 isoform X1 | YABBY2 | XP_016548878.1 | 2 | AT2G26580 |
| 同源框亮氨酸拉链蛋白HOX5 Homeobox-leucine zipper protein HOX5 | HOX5 | KAF3660217.1 | 3 | AT5G65310 |

Fig. 10 RT-qPCR and RNA-seq analysis of 19 genes at the four stages of chili pepper fruits * and ** mean significantly different in relative expression at the 0.05 and 0.01 probability level,respectively.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
pmid: 7259770 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3317 pmid: 25751142 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(01)00175-3 pmid: 11524116 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0410-2 pmid: 31086351 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.060 pmid: 23692768 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms140919025 pmid: 24065101 |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.122127 pmid: 24858934 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
pmid: 9526511 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1187 |
|
雷建军, 朱张生, 陈长明, 陈国菊, 曹必好, 雷伶刚, 郑婕, 吴昊, 肖艳辉, 邱正坤, 颜爽爽. 2023. 辣椒红色素及其生物合成的分子机理研究进展. 园艺学报, 50 (3):669-684.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1187 |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04064.x pmid: 19891701 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1039/c0np00036a pmid: 21321752 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1038/nbt.3122 pmid: 25690850 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04863.x pmid: 22111515 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.007 pmid: 25578273 |
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
pmid: 16701678 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2012.09.001 pmid: 23043987 |
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1068181 pmid: 11951045 |
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.03.016 pmid: 21514607 |
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [1] | ZHAO Jiaying, ZENG Zhouting, CEN Xinying, SHI Jiaoqi, LI Xiaoxian, SHEN Xiaoxia, and YU Zhenming, . Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CCO Gene Family in Dendrobium officinale During Flower Development [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2075-2088. |
| [2] | A New Processing Pepper Cultivar‘Yanjiao ’. A New Processing Pepper Cultivar‘Yanjiao 465’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2223-2224. |
| [3] | SHI Fengyan, WANG Zhidan, ZHANG Xi, WANG Xiuxue, and ZOU Chunlei, . Research Progress on the Mechanism of Pepper Resistance to Phytophthora Blight [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1665-1682. |
| [4] | ZHAO Zeyang, ZHOU Yuqing, LIN Deshu, and REN Huibo, . Advances in Morphogenesis of Petal Conical Epidermal Cells [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1695-1706. |
| [5] | ZHANG Ru, CHEN Lingzhi, and WANG Lanlan. A New Pepper F1 Hybrid Cultivar‘Longjiao 13’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1709-1710. |
| [6] | DENG Shufang, LIU Qian, LIU Ling, CHEN Ou, WANG Wenjun, ZENG Kaifang, DENG Lili. Cloning of Mandarin Fruit CcHY5 and Its Function in Fruit Coloration [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 939-955. |
| [7] | GUO Rui, CHEN Gao, ZHAO Huixai, QIAN Yike, LAN Hong, WAN Heping, CHEN Chanyou. A New Purple Pepper Cultivar‘Jiangda Zijiao 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1175-1176. |
| [8] | FU Wen, ZHU Chenghong, LAN Jiayi, LI Shi, ZHANG Zheng, LIU Feng, DAI Xiongze. Study on the Quality Characteristics of Fresh and Immature Pepper [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 616-630. |
| [9] | YANG Liang, LIU Huan, MA Yanqin, LI Ju, WANG Hai'e, ZHOU Yujie, LONG Haicheng, MIAO Mingjun, LI Zhi, CHANG Wei. Creating High Lycopene Fruit Using CRISPR/Cas9 Technology in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 253-265. |
| [10] | JIANG Bo, LÜ Yuanda, LIU Shumei, YAN Huaxue. Research Advances in the Regulation of Plant Hormones in Citrus Fruit Maturation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2928-2944. |
| [11] | ZHANG Shaoping, LI Zhou, JU Yudong, LIAN Dongmei, LIN Bizhen, YAO Yunfa, WU Songhai, HONG Jianji, LAI Zhengfeng. Advances in Research on Membrane Lipid Peroxidation Reaction During the Quality Deterioration Period of Fresh Pepper [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2945-2961. |
| [12] | TANG Zheng, CHEN Sique, XU Qian, ZHONG Weijie, LIU Qing, ZHU Shiyang. Functional Study of AP2/ERF in Response to Black Rot at Broccoli Seedling Stage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2523-2539. |
| [13] | WU Dan, LIU Jiaxin, ZHUO Linxi, LI Yu, LUO Ying, ZHOU Yong, YANG Youxin, and YU Ting, . Functional Analysis of CaWRKY39 Under Phytophthora capsici Infection in Pepper [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2297-2310. |
| [14] | LUO Yin, LUO Xirong, WU Shiqi, LI Tangyan, LI Jing, QIU Huarong, and QIN Cheng, . Karyotype Analysis of Four Cultivars of Peppers Based on Fluorescence in situ Hybridization [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2311-2319. |
| [15] | YOU Qian, LIU Xiao, LIU Mengmeng, LIU Dan, BO Chen, ZHU Yanfang, DUAN Yongbo, XUE Jianping, ZHANG Aimin, and XUE Tao. Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of the HSF Family Gene in Pinellia ternata [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2371-2385. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd