
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 3219-3228.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0124
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
QI Yujie1, ZHAO Shiqi1, SUN Shuai1, WANG Haijing1, CUI Xia1,2,*( ), LI Ren1,*(
), LI Ren1,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-02
Revised:2025-05-08
Online:2025-12-25
Published:2025-12-20
Contact:
CUI Xia, LI Ren
QI Yujie, ZHAO Shiqi, SUN Shuai, WANG Haijing, CUI Xia, LI Ren. Mapping of Genes Regulating Tomato Fruit Skin Toughness[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(12): 3219-3228.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0124
| 分子标记 Marker | 物理位置/bp Position on SL2.5 | 引物序列(3′-5′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | 59 530 615 | GTGAGGAAGATGGTGTGTACTTGGTG |
| GACGAATATGTGAAAATAGTGATTTC | ||
| M2 | 59 991 416 | GACGGAGGAAGTAATTAATG |
| CGGTGGTGGTAGTGGTGAAACG | ||
| M3 | 60 031 030 | GTTCAAATATACTCCTC |
| GTAGCTTCTATGCTCCTCT | ||
| M4 | 60 309 325 | GATAAGAGTCTCAAATTTCTATTGCG |
| GTTTTTCTTATAGGGCAAGTATGATC | ||
| M5 | 60 326 153 | CAAAGGAAGTGAAGCAACTAAGTCA |
| GGAGATAGCCAACCGCATATGCAAC | ||
| M6 | 60 920 438 | GTGGATTTGTCGGCACTGTTGATGG |
| GAGAATGAAGTATAGTACTTACACTT | ||
| M7 | 61 340 455 | CAGTGATAGACGTGAATTCGAAATAGCCG |
| TGCGACATTGAGATCTGACTATTTCAGAATTC |
Table 1 Primer sequences of major markers
| 分子标记 Marker | 物理位置/bp Position on SL2.5 | 引物序列(3′-5′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | 59 530 615 | GTGAGGAAGATGGTGTGTACTTGGTG |
| GACGAATATGTGAAAATAGTGATTTC | ||
| M2 | 59 991 416 | GACGGAGGAAGTAATTAATG |
| CGGTGGTGGTAGTGGTGAAACG | ||
| M3 | 60 031 030 | GTTCAAATATACTCCTC |
| GTAGCTTCTATGCTCCTCT | ||
| M4 | 60 309 325 | GATAAGAGTCTCAAATTTCTATTGCG |
| GTTTTTCTTATAGGGCAAGTATGATC | ||
| M5 | 60 326 153 | CAAAGGAAGTGAAGCAACTAAGTCA |
| GGAGATAGCCAACCGCATATGCAAC | ||
| M6 | 60 920 438 | GTGGATTTGTCGGCACTGTTGATGG |
| GAGAATGAAGTATAGTACTTACACTT | ||
| M7 | 61 340 455 | CAGTGATAGACGTGAATTCGAAATAGCCG |
| TGCGACATTGAGATCTGACTATTTCAGAATTC |

Fig. 2 Cellular structure(A)and cuticle thickness(B)of TS12 and TS292 at different stages Blue arrow:Cutinization of epidermal cell wall;Black arrow:Degree of invagination. ** P < 0.01,* P < 0.05
| 成分 Ingredient | 绿熟果实 Mature green fruit | 红熟果实 Red fruit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS292 | TS12 | TS292 | TS12 | |
| 十六烷 Hexadecane | 3.08 ± 0.28 a | 3.09 ± 0.73 a | 3.41 ± 0.79 a | 3.07 ± 0.08 a |
| 9-十八烯酰胺 9-Octadecylamide | 4.86 ± 1.75 ab | 3.64 ± 0.09 ab | 2.35 ± 1.95 b | 6.53 ± 1.87 a |
| 16-羟基十六烷 16-OH hexadecanoic | 26.17 ± 2.22 a | 26.23 ± 6.07 a | 21.04 ± 10.23 a | 25.99 ± 1.75 a |
| 十六烷二酸 Hexadecanedioic acid | 4.84 ± 0.95 b | 2.09 ± 0.87 c | 6.92 ± 0.41 a | 4.45 ± 0.14 b |
| 十六碳-7-烯酸 Hexadec-7-enoate | 3.80 ± 1.88 ab | 5.17 ± 1.23 a | 2.83 ± 0.06 ab | 2.45 ± 0.12 b |
| 7-甲基-Z-十四烯-1-醇 7-Methyl-Z-tetradene-1-ol | 3.60 ± 0.38 a | 4.02 ± 0.74 a | 2.84 ± 1.18 a | 2.76 ± 0.26 a |
| 10-羟基十六烷酸 10-OH hexadecanoic | 324.13 ± 39.36 b | 305.78 ± 17.68 b | 481.46 ± 68.36 a | 325.07 ± 73.82 b |
| 9,10-二羟基十八烷酸 9,10-DiOH octadecanoic | 22.04 ± 0.57 a | 21.56 ± 2.00 a | 39.25 ± 1.02 b | 30.33 ± 0.29 b |
| (Z)-十八碳-9-烯酸(Z)-9-Octadecenoic acid | 14.10 ± 3.86 b | 10.05 ± 3.20 b | 43.24 ± 18.88 a | 18.07 ± 1.06 b |
| 11-环戊基十一酸 11-Cyclopentylundecanoic | 30.87 ± 1.26 bc | 21.02 ± 2.11 c | 46.47 ± 0.61 a | 42.64 ± 3.10 ab |
| Z,Z,Z-4,6,9-十九碳三烯 Z,Z,Z-4,6,9-Nonadecatriene | 3.41 ± 0.12 b | 3.34 ± 0.52 b | 5.46 ± 0.30 a | 4.87 ± 0.47 a |
| 9,12-二羟基十八烷酸 9,12-DiOH octadecanoic | 3.30 ± 0.27 b | 3.37 ± 0.60 b | 5.32 ± 0.19 a | 4.55 ± 0.43 a |
| 顺式-3-辛基环氧辛酸 cis-3-Octyl epoxycapic acid | 3.96 ± 0.64 bc | 3.21 ± 0.07 c | 5.91 ± 0.10 a | 4.64 ± 0.35 b |
| 合计 Total | 448.17 | 412.56 | 666.51 | 475.4 |
Table 2 Contents of each component of TS12 and TS292 cutin μg · cm-2
| 成分 Ingredient | 绿熟果实 Mature green fruit | 红熟果实 Red fruit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS292 | TS12 | TS292 | TS12 | |
| 十六烷 Hexadecane | 3.08 ± 0.28 a | 3.09 ± 0.73 a | 3.41 ± 0.79 a | 3.07 ± 0.08 a |
| 9-十八烯酰胺 9-Octadecylamide | 4.86 ± 1.75 ab | 3.64 ± 0.09 ab | 2.35 ± 1.95 b | 6.53 ± 1.87 a |
| 16-羟基十六烷 16-OH hexadecanoic | 26.17 ± 2.22 a | 26.23 ± 6.07 a | 21.04 ± 10.23 a | 25.99 ± 1.75 a |
| 十六烷二酸 Hexadecanedioic acid | 4.84 ± 0.95 b | 2.09 ± 0.87 c | 6.92 ± 0.41 a | 4.45 ± 0.14 b |
| 十六碳-7-烯酸 Hexadec-7-enoate | 3.80 ± 1.88 ab | 5.17 ± 1.23 a | 2.83 ± 0.06 ab | 2.45 ± 0.12 b |
| 7-甲基-Z-十四烯-1-醇 7-Methyl-Z-tetradene-1-ol | 3.60 ± 0.38 a | 4.02 ± 0.74 a | 2.84 ± 1.18 a | 2.76 ± 0.26 a |
| 10-羟基十六烷酸 10-OH hexadecanoic | 324.13 ± 39.36 b | 305.78 ± 17.68 b | 481.46 ± 68.36 a | 325.07 ± 73.82 b |
| 9,10-二羟基十八烷酸 9,10-DiOH octadecanoic | 22.04 ± 0.57 a | 21.56 ± 2.00 a | 39.25 ± 1.02 b | 30.33 ± 0.29 b |
| (Z)-十八碳-9-烯酸(Z)-9-Octadecenoic acid | 14.10 ± 3.86 b | 10.05 ± 3.20 b | 43.24 ± 18.88 a | 18.07 ± 1.06 b |
| 11-环戊基十一酸 11-Cyclopentylundecanoic | 30.87 ± 1.26 bc | 21.02 ± 2.11 c | 46.47 ± 0.61 a | 42.64 ± 3.10 ab |
| Z,Z,Z-4,6,9-十九碳三烯 Z,Z,Z-4,6,9-Nonadecatriene | 3.41 ± 0.12 b | 3.34 ± 0.52 b | 5.46 ± 0.30 a | 4.87 ± 0.47 a |
| 9,12-二羟基十八烷酸 9,12-DiOH octadecanoic | 3.30 ± 0.27 b | 3.37 ± 0.60 b | 5.32 ± 0.19 a | 4.55 ± 0.43 a |
| 顺式-3-辛基环氧辛酸 cis-3-Octyl epoxycapic acid | 3.96 ± 0.64 bc | 3.21 ± 0.07 c | 5.91 ± 0.10 a | 4.64 ± 0.35 b |
| 合计 Total | 448.17 | 412.56 | 666.51 | 475.4 |
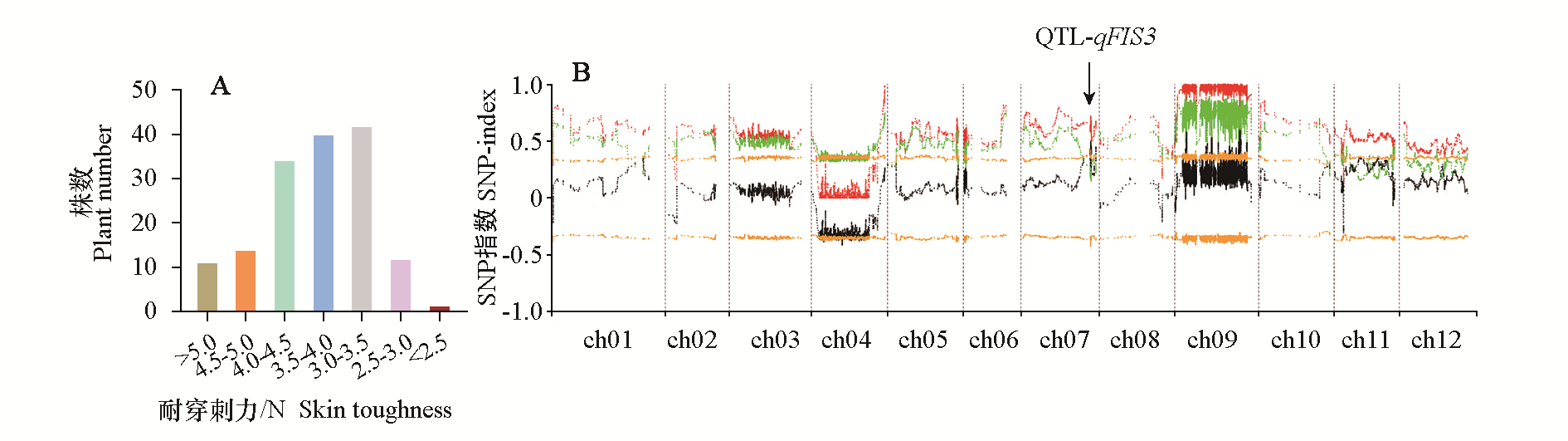
Fig. 4 Skin toughness distribution of RIL lines(A)and BSA pooling sequencing results(B) Black line representation Δ(SNP-index)value,red line indicated high skin toughness pool SNP-index values,green line indicated low skin toughness pool SNP-index values,orange line represents the 95% confidence interval. Arrows indicate the regions that may contain QTL for fruit firmness
| 染色体Chromosome | 物理位置/bp Postion on SL2.50 | SNP指数 ΔSNP-index | 表型变异贡献率/% PVE | 长度/bp length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL2.50ch07 | 59 991 671 ~ 60 990 579 | 0.501089 | 30.12 | 998 908 |
| SL2.50ch09 | 9 731 112 ~ 9 957 832 | 0.58164 | 17.03 | 226 720 |
| SL2.50ch09 | 32 049 034 ~ 32 184 175 | 0.53399 | 17.02 | 135 141 |
| SL2.50ch09 | 47 052 310 ~ 47 360 989 | 0.456416 | 13.15 | 308 679 |
| SL2.50ch09 | 55 337 072 ~ 57 388 709 | 0.604067 | 1.99 | 2 051 637 |
Table 3 QTL loci obtained from BSA sequencing
| 染色体Chromosome | 物理位置/bp Postion on SL2.50 | SNP指数 ΔSNP-index | 表型变异贡献率/% PVE | 长度/bp length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL2.50ch07 | 59 991 671 ~ 60 990 579 | 0.501089 | 30.12 | 998 908 |
| SL2.50ch09 | 9 731 112 ~ 9 957 832 | 0.58164 | 17.03 | 226 720 |
| SL2.50ch09 | 32 049 034 ~ 32 184 175 | 0.53399 | 17.02 | 135 141 |
| SL2.50ch09 | 47 052 310 ~ 47 360 989 | 0.456416 | 13.15 | 308 679 |
| SL2.50ch09 | 55 337 072 ~ 57 388 709 | 0.604067 | 1.99 | 2 051 637 |
| 基因编号 Gene ID | 变异位置 Change position | 在果实中表达 Expression in fruit | 基因注释 Annotation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solyc07g049680 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 凝缩蛋白复合体亚基2 Condensin complex subunit 2 | |
| Solyc07g049690 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 氢过氧化物裂解酶 Hydroperoxide lyase | |
| Solyc07g049700 | 编码区,启动子 CDS,promoter | 是Yes | 抗病蛋白 Disease resistance protein | |
| Solyc07g049710 | 启动子,内含子 Promoter,intron | 是Yes | ATP酶亚基e1 ATPase subunit e1 | |
| Solyc07g049720 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 光系统Ⅱ的10 kD多肽前体 10 kD polypeptide precursor of photosystem 2 | |
| Solyc07g049730 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 预测的跨膜蛋白 Transmembrane protein,putative | |
| Solyc07g049740 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 脂质A二糖合酶 Lipid-A-disaccharide synthase | |
| Solyc07g049750 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 牙本质涎磷蛋白样蛋白 Dentin sialophosphoprotein-like protein | |
| Solyc07g049760 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 否No | CCR4-NOT转录复合物亚基 CCR4-NOT transcription complex subunit 9-like | |
| Solyc07g049770 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 否No | 细胞分化,Rcd1样蛋白 Cell differentiation,Rcd1-like protein | |
| Solyc07g049780 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 细胞分化,Rcd1样蛋白 Cell differentiation,Rcd1-like protein | |
| Solyc07g049790 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 否No | 细胞分化,Rcd1样蛋白 Cell differentiation,Rcd1-like protein | |
| Solyc07g049800 | CDS,promoter,intron,UTR 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 | 是Yes | 细胞分化,Rcd1样蛋白 Cell differentiation,Rcd1-like protein | |
| Solyc07g051800 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 否No | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein | |
| Solyc07g051810 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 否No | 细胞分化,Rcd1样蛋白 Cell differentiation,Rcd1-like protein | |
| Solyc07g051820 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 纤维素合酶 Cellulose synthase | |
Table 4 Gene list and annotation information in the mapped regions
| 基因编号 Gene ID | 变异位置 Change position | 在果实中表达 Expression in fruit | 基因注释 Annotation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solyc07g049680 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 凝缩蛋白复合体亚基2 Condensin complex subunit 2 | |
| Solyc07g049690 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 氢过氧化物裂解酶 Hydroperoxide lyase | |
| Solyc07g049700 | 编码区,启动子 CDS,promoter | 是Yes | 抗病蛋白 Disease resistance protein | |
| Solyc07g049710 | 启动子,内含子 Promoter,intron | 是Yes | ATP酶亚基e1 ATPase subunit e1 | |
| Solyc07g049720 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 光系统Ⅱ的10 kD多肽前体 10 kD polypeptide precursor of photosystem 2 | |
| Solyc07g049730 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 预测的跨膜蛋白 Transmembrane protein,putative | |
| Solyc07g049740 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 脂质A二糖合酶 Lipid-A-disaccharide synthase | |
| Solyc07g049750 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 牙本质涎磷蛋白样蛋白 Dentin sialophosphoprotein-like protein | |
| Solyc07g049760 | 启动子,内含子,非翻译区 Promoter,intron,UTR | 否No | CCR4-NOT转录复合物亚基 CCR4-NOT transcription complex subunit 9-like | |
| Solyc07g049770 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 否No | 细胞分化,Rcd1样蛋白 Cell differentiation,Rcd1-like protein | |
| Solyc07g049780 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 细胞分化,Rcd1样蛋白 Cell differentiation,Rcd1-like protein | |
| Solyc07g049790 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 否No | 细胞分化,Rcd1样蛋白 Cell differentiation,Rcd1-like protein | |
| Solyc07g049800 | CDS,promoter,intron,UTR 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 | 是Yes | 细胞分化,Rcd1样蛋白 Cell differentiation,Rcd1-like protein | |
| Solyc07g051800 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 否No | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein | |
| Solyc07g051810 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 否No | 细胞分化,Rcd1样蛋白 Cell differentiation,Rcd1-like protein | |
| Solyc07g051820 | 编码区,启动子,内含子,非翻译区 CDS,promoter,intron,UTR | 是Yes | 纤维素合酶 Cellulose synthase | |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
付稳, 朱程红, 兰嘉仪, 李诗, 张正, 刘峰, 戴雄泽. 2024. 鲜食嫩果辣椒‘樟树港’果实品质特性研究. 园艺学报, 51(3):616-630.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
郜海燕, 杨帅, 陈杭君, 楚文靖, 穆宏磊, 葛林梅. 2014. 蓝莓外表皮蜡质及其对果实软化的影响. 中国食品学报, 14(2):102-108.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
李宏建, 刘志, 王宏, 徐贵轩, 宋哲, 何明莉, 张春波. 2013. 苹果果实组织结构与果实失重率和硬度变化的关系. 果树学报, 30(5):753-758.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
李肯, 张伟, 武云鹏, 彭冬秀, 张若纬. 2024. 甜瓜果肉硬度KASP 标记的开发与应用. 园艺学报, 51(4):773-786.
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
刘磊, 宋燕, 郑峥, 李君明. 2015. 利用Solanum pennellii LA0716渐渗系群体初步定位番茄果实硬度QTL. 植物遗传资源学报, 16(2):323-329.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
刘泽营, 孙帅, 刘志强, 崔霞, 李仁. 2024. 番茄尖果脐突变体的生理特性及其候选基因分析. 园艺学报, 51(5):982-992. (in Chinese)
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
罗斌, 赵有斌, 尹学清, 赵东林, 杜志龙, 何江涛. 2019. 质构仪在果蔬品质评定中应用的研究进展. 食品研究与开发, 40(5):209-213.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
吴萌萌, 张瑞萍, 史亚娟, 董海清, 丁体玉, 张恒涛, 高启明, 周喆, 阎振立. 2020. 4个苹果品种贮藏期间果实质地和营养成分的变化. 果树学报, 37(9):1404-1412.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
杨玲, 张彩霞, 丛佩华, 程云, 王强. 2014. 基于质地多面分析法对不同苹果品种果肉质构特性的分析. 食品科学, 35(21):57-62.
|
|
| [22] |
|
|
杨涛, 杨生保, 唐亚萍, 李宁, 许娟, 王柏柯, 帕提古丽, 余庆辉. 2017. 番茄果实耐压QTL遗传效应初步分析. 园艺学报, 44(7):1371-1378.
|
| [1] | ZAI Wenshan, CHEN Xianzhi, FU Cunnian, SU Shiwen, SHI Jianlei, XIONG Zili, HUANG Shaoyong. A New Taste Tomato Cultivar‘Ouxiu 901’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 121-122. |
| [2] | WANG Rongqing, YAO Zhuping, CHENG Yuan, YE Qingjing, RUAN Meiying, WAN Hongjian, LI Zhimiao, LIU Chenxu, ZHOU Guozhi. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Zhefen 718’with High Quality and Storage Properties [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 123-124. |
| [3] | ZHENG Mengfan, XIE Yong, ZHENG Wei, LI Guangqian, CHEN Gang, WANG Yushuang, LI Cong, ZHANG Yuyang. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Minfeng 698’with High Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 125-126. |
| [4] | ZHU Pengyu, XIE Yong, ZHENG Wei, LI Guangqian, CHEN Gang, WANG Yushuang, LI Cong, ZHANG Yuyang. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Xiweimei 191’with High Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 127-128. |
| [5] | CUI Aihua, ZHU Moyong, ZHANG Yangdong, WU Qi, LIU Shuai, HU Qixing, HUANG Jigang, LIU Jiaxin, LIU Weisheng, SUN Julong. A New Large Fruit Tomato Cultivar‘Aoliya’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 129-130. |
| [6] | ZHENG Yuli, LIU Yan, PAN Ziwang, HAN Lanlan, LI Kai, LIU Dan, CAO Yang, LU Xinzhe, KANG Yongsheng. A New Multi-Resistant Hard-Flesh Hybrid Tomato‘BY002’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 131-132. |
| [7] | SU Shiwen, FU Cunnian, CHEN Xianzhi, CUI Lili, SHI Jianlei, HUANG Shaoyong, XIONG Zili, ZAI Wenshan. A New Cherry Tomato Cultivar‘Ouxiu Hongying 5’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 133-134. |
| [8] | FU Cunnian, SU Shiwen, CHEN Xianzhi, CUI Lili, SHI Jianlei, HUANG Shaoyong, XIONG Zili, ZAI Wenshan. A New Cherry Tomato Cultivar‘Ouxiu Chengying 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 135-136. |
| [9] | XIONG Zili, SU Shiwen, SHI Jianlei, ZHANG Haili, ZAI Wenshan, CUI Lili. A New Tomato Rootstock Cultivar‘Ouzhen 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 137-138. |
| [10] | SHI Bo, GUAN Feng, ZHANG Jingyun, YANG Xuetong, XIE Yuanyuan, WANG Kai, WAN Xinjian. A New Processed Wax Gourd Cultivar‘Zaoyoufen’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 163-164. |
| [11] | FAN Huidong, ZHENG Shijin, TIAN song, ZHENG Jianchao. A New Tomato F1 Hybrid‘Jifen 7’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 109-110. |
| [12] | ZHANG Liwei, DAI Zhongren, CHEN Qingqi, LEI Na, HUANG Jun, Hu Haijiang, MEN Wanjie. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Hayan Zhongfenguo 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 111-112. |
| [13] | XIONG Zili, SHI Jianlei, CHEN Yongbing, ZHANG Haili, SU Shiwen, ZAI Wenshan, YE Shuguang. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Ouxiu 202’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 113-114. |
| [14] | WANG Baochen, LUO Chen, YAN Jinqiang, CHENG Xiaoxin, MO Renlian, LIU Wenrui, ZHANG Yuyang, JIANG Biao. Cloning,Expression,and Functional Research of BhYAB4b in Wax Gourd [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(9): 2353-2362. |
| [15] | ZHANG Ting, WANG Botao, ZHANG Lei, SONG Lihua, CAO Bing, MA Yaping. Identification of the LbWaxy Gene Family in Lycium barbarum and Analysis of Gene Expression Characteristics Under High Concentrations of CO2 [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(9): 2395-2409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd