
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 3322-3334.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-1051
• Cultivation·Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HAN Shou’an, WANG Min, XIE Hui, ZHU Xuehui, WANG Yanmeng, LIU Xupeng, ZHANG Wen*( )
)
Received:2025-08-05
Revised:2025-11-01
Online:2025-12-25
Published:2025-12-20
Contact:
ZHANG Wen
HAN Shou’an, WANG Min, XIE Hui, ZHU Xuehui, WANG Yanmeng, LIU Xupeng, ZHANG Wen. Impact of GA3-CPPU Combined Fruit Retention Treatments on Berry Quality in Protected Cultivation of‘Wuhe Cuibao’Grape[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(12): 3322-3334.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-1051
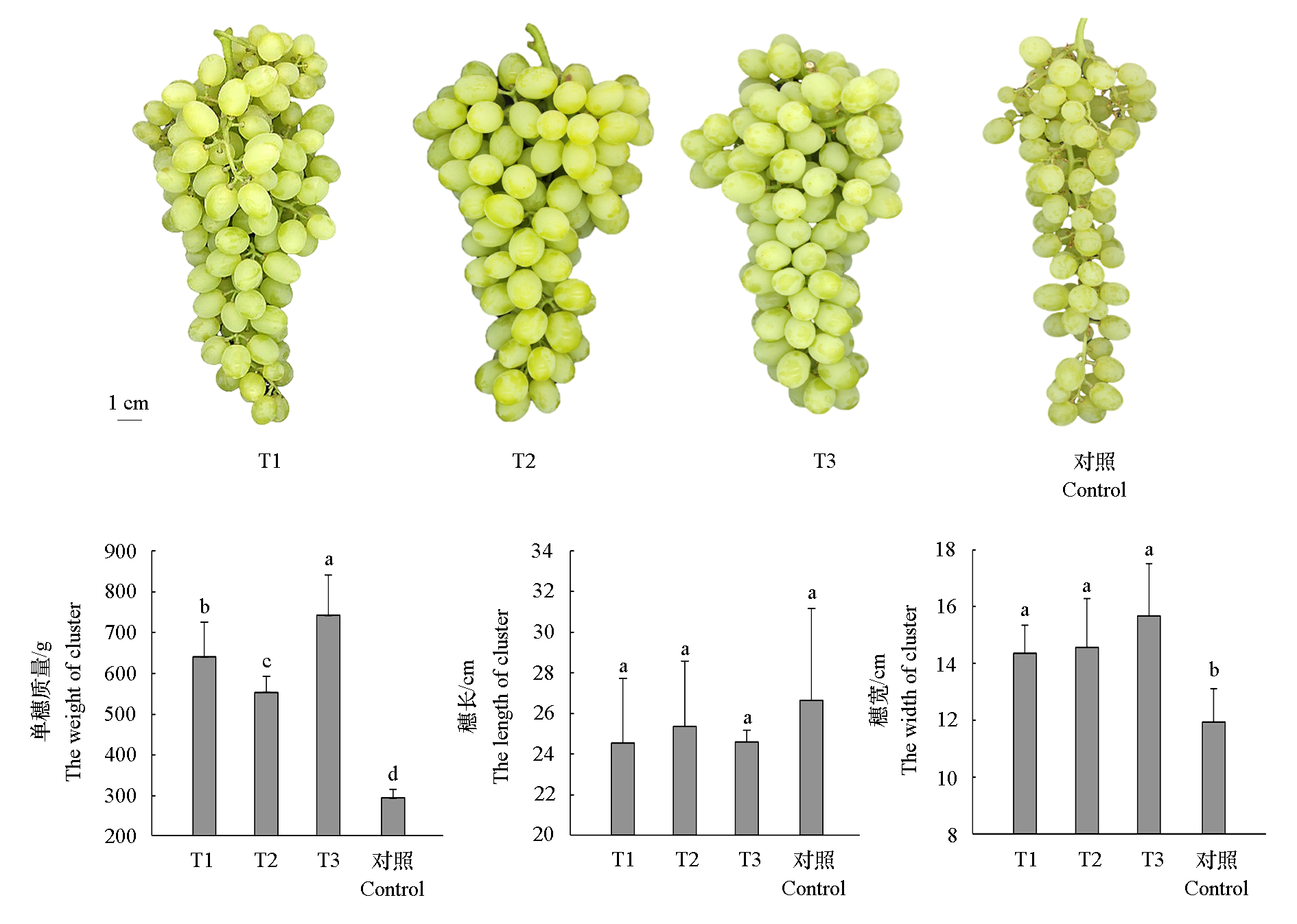
Fig. 1 Effects of combined GA3 and CPPU fruit retention treatments on cluster morphology and size of‘Wuhe Cuibao’grapes T1:5 mg · L-1 GA3 + 0.5 mg · L-1 CPPU;T2:10 mg · L-1 GA3 + 0.5 mg · L-1 CPPU;T3:15 mg · L-1 GA3 + 0.5 mg · L-1 CPPU. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at 0.05 level. The same below
| 处理 Treat- ment | 单粒质 量/g Weight of berry | 皮质量/单 粒质量 Peel weight/ berry weight | 果形指数 shape index | 可溶性固形物/% TSS | 总酸/% TA | 固酸比 TSS/TA | 穗轴直径/ mm Diameter of spike- stalk | 果柄直径/mm Diameter of stalk | 果蒂直径/ mm Diameter of pedicel | 硬度/N Firmness of berry | 果柄耐拉力/N Pulling resistance of stalk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 4.81 b | 0.09 b | 1.33 a | 19.60 c | 0.50 a | 38.91 b | 4.61 b | 1.53 b | 2.61 b | 1.41 b | 1.66 b |
| T2 | 5.02 a | 0.11 a | 1.26 b | 21.20 b | 0.54 a | 38.97 b | 5.26 a | 1.87 a | 3.40 a | 1.63 a | 2.24 a |
| T3 | 5.15 a | 0.10 a | 1.31 a | 21.05 b | 0.56 a | 37.34 b | 4.41 b | 1.93 a | 3.23 a | 1.43 b | 1.90 b |
| H2O | 3.90 c | 0.09 b | 1.26 b | 22.23 a | 0.46 b | 48.18 a | 3.30 c | 1.31 c | 2.55 b | 1.09 c | 1.91 b |
Table 1 Effects of combined GA3 and CPPU fruit retention treatments on the fundamental quality indicators of‘Wuhe Cuibao’grape berries
| 处理 Treat- ment | 单粒质 量/g Weight of berry | 皮质量/单 粒质量 Peel weight/ berry weight | 果形指数 shape index | 可溶性固形物/% TSS | 总酸/% TA | 固酸比 TSS/TA | 穗轴直径/ mm Diameter of spike- stalk | 果柄直径/mm Diameter of stalk | 果蒂直径/ mm Diameter of pedicel | 硬度/N Firmness of berry | 果柄耐拉力/N Pulling resistance of stalk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 4.81 b | 0.09 b | 1.33 a | 19.60 c | 0.50 a | 38.91 b | 4.61 b | 1.53 b | 2.61 b | 1.41 b | 1.66 b |
| T2 | 5.02 a | 0.11 a | 1.26 b | 21.20 b | 0.54 a | 38.97 b | 5.26 a | 1.87 a | 3.40 a | 1.63 a | 2.24 a |
| T3 | 5.15 a | 0.10 a | 1.31 a | 21.05 b | 0.56 a | 37.34 b | 4.41 b | 1.93 a | 3.23 a | 1.43 b | 1.90 b |
| H2O | 3.90 c | 0.09 b | 1.26 b | 22.23 a | 0.46 b | 48.18 a | 3.30 c | 1.31 c | 2.55 b | 1.09 c | 1.91 b |
| 处理 Treatment | L* | a* | b* | C* | h° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 34.92 ± 1.15 a | -0.14 ± 0.67 a | 9.04 ± 0.73 a | 9.07 ± 0.72 a | 91.11 ± 4.39 a |
| T2 | 34.65 ± 0.97 a | -0.28 ± 0.37 a | 9.00 ± 0.98 a | 9.03 ± 0.97 a | 92.07 ± 2.68 a |
| T3 | 35.26 ± 1.22 a | -0.57 ± 0.52 a | 9.03 ± 0.94 a | 9.09 ± 0.91 a | 94.12 ± 3.88 a |
| H2O | 35.17 ± 1.10 a | -0.01 ± 0.52 a | 8.60 ± 0.67 a | 8.64 ± 0.65 a | 90.41 ± 3.85 a |
Table 2 Effects of combined GA3 and CPPU fruit retention treatments on color parameters of‘Wuhe Cuibao’grape berries
| 处理 Treatment | L* | a* | b* | C* | h° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 34.92 ± 1.15 a | -0.14 ± 0.67 a | 9.04 ± 0.73 a | 9.07 ± 0.72 a | 91.11 ± 4.39 a |
| T2 | 34.65 ± 0.97 a | -0.28 ± 0.37 a | 9.00 ± 0.98 a | 9.03 ± 0.97 a | 92.07 ± 2.68 a |
| T3 | 35.26 ± 1.22 a | -0.57 ± 0.52 a | 9.03 ± 0.94 a | 9.09 ± 0.91 a | 94.12 ± 3.88 a |
| H2O | 35.17 ± 1.10 a | -0.01 ± 0.52 a | 8.60 ± 0.67 a | 8.64 ± 0.65 a | 90.41 ± 3.85 a |
| 处理 Treatment | 类黄酮/(mg · g-1) Flavonoid | 单宁/(mg · g-1) Tannin | 黄酮/(mg · g-1)Flavone | 原花青素/(mg · g-1)Proanthocyadin | 多酚/(mg · g-1)Polyphenol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.74 ± 0.10 ab | 5.67 ± 0.21 a | 0.28 ± 0.01 a | 2.09 ± 0.16 a | 1.55 ± 0.01 a |
| T2 | 0.76 ± 0.12 ab | 5.49 ± 0.06 a | 0.25 ± 0.02 a | 2.39 ± 0.30 a | 1.69 ± 0.19 a |
| T3 | 0.57 ± 0.07 b | 5.42 ± 0.39 ab | 0.26 ± 0.00 a | 2.64 ± 0.26 a | 1.78 ± 0.37 a |
| H2O | 0.94 ± 0.23 a | 4.93 ± 0.12 b | 0.28 ± 0.01 a | 2.04 ± 0.35 a | 1.82 ± 0.27 a |
Table 3 Impact of GA3 and CPPU treatments on phenolic content in the berry skins of‘Wuhe Cuibao’grapes berries
| 处理 Treatment | 类黄酮/(mg · g-1) Flavonoid | 单宁/(mg · g-1) Tannin | 黄酮/(mg · g-1)Flavone | 原花青素/(mg · g-1)Proanthocyadin | 多酚/(mg · g-1)Polyphenol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.74 ± 0.10 ab | 5.67 ± 0.21 a | 0.28 ± 0.01 a | 2.09 ± 0.16 a | 1.55 ± 0.01 a |
| T2 | 0.76 ± 0.12 ab | 5.49 ± 0.06 a | 0.25 ± 0.02 a | 2.39 ± 0.30 a | 1.69 ± 0.19 a |
| T3 | 0.57 ± 0.07 b | 5.42 ± 0.39 ab | 0.26 ± 0.00 a | 2.64 ± 0.26 a | 1.78 ± 0.37 a |
| H2O | 0.94 ± 0.23 a | 4.93 ± 0.12 b | 0.28 ± 0.01 a | 2.04 ± 0.35 a | 1.82 ± 0.27 a |
| 处理 Treatment | 果糖Fructose | 葡萄糖Glucose | 总糖/(mg · g-1) Total sugar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量/(mg · g-1) Content | 占总糖比例/% Fructose/total sugar | 含量/(mg · g-1) Content | 占总糖比例/% Glucose/total sugar | ||
| T1 | 23.31 ± 1.67 b | 34.55 ± 0.34 a | 44.21 ± 3.70 b | 65.45 ± 0.34 a | 67.52 ± 4.38 b |
| T2 | 23.40 ± 1.98 b | 33.68 ± 1.46 a | 46.13 ± 4.05 b | 66.32 ± 1.46 a | 69.53 ± 4.39 b |
| T3 | 22.58 ± 0.01 b | 33.24 ± 0.70 a | 45.37 ± 1.72 b | 66.76 ± 0.70 a | 67.95 ± 1.40 b |
| H2O | 27.14 ± 1.50 a | 34.64 ± 1.96 a | 51.63 ± 1.97 a | 65.36 ± 1.96 a | 78.77 ± 4.62 a |
Table 4 Effects of combined GA3 and CPPU fruit retention treatments on sugar composition content in‘Wuhe Cuibao’grape berries
| 处理 Treatment | 果糖Fructose | 葡萄糖Glucose | 总糖/(mg · g-1) Total sugar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量/(mg · g-1) Content | 占总糖比例/% Fructose/total sugar | 含量/(mg · g-1) Content | 占总糖比例/% Glucose/total sugar | ||
| T1 | 23.31 ± 1.67 b | 34.55 ± 0.34 a | 44.21 ± 3.70 b | 65.45 ± 0.34 a | 67.52 ± 4.38 b |
| T2 | 23.40 ± 1.98 b | 33.68 ± 1.46 a | 46.13 ± 4.05 b | 66.32 ± 1.46 a | 69.53 ± 4.39 b |
| T3 | 22.58 ± 0.01 b | 33.24 ± 0.70 a | 45.37 ± 1.72 b | 66.76 ± 0.70 a | 67.95 ± 1.40 b |
| H2O | 27.14 ± 1.50 a | 34.64 ± 1.96 a | 51.63 ± 1.97 a | 65.36 ± 1.96 a | 78.77 ± 4.62 a |
| 处理 Treat- ment | 酒石酸 Tartaric acid | 苹果酸 Malic acid | 柠檬酸 Citric acid | 草酸 Oxalic acid | 总酸/(mg · g-1)Total acid | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量/(mg · g-1)Content | 占总酸比例/% Tartaric acid/ total acid | 含量/(mg · g-1)Content | 占总酸比例/% Malic acid/total acid | 含量/(mg · g-1)Content | 占总酸比例/% Citric acid/ total acid | 含量/(mg · g-1)Content | 占总酸比例/% Oxalic acid/ total acid | ||
| T1 | 9.52 ± 0.16 b | 79.99 ± 2.73 b | 1.38 ± 0.23 b | 11.48 ± 1.44 a | 0.63 ± 0.23 ab | 5.28 ± 1.35 a | 0.39 ± 0.02 a | 3.25 ± 0.13 a | 11.92 ± 0.34 b |
| T2 | 11.46 ± 0.14 a | 80.17 ± 0.72 b | 1.65 ± 0.10 a | 11.54 ± 0.71 a | 0.78 ± 0.02 a | 5.43 ± 0.07 a | 0.41 ± 0.01 a | 2.86 ± 0.01 b | 14.29 ± 0.14 a |
| T3 | 8.24 ± 0.27 b | 80.17 ± 0.96 b | 1.30 ± 0.11 b | 13.33 ± 0.74 a | 0.28 ± 0.09 c | 3.41 ± 0.24 b | 0.32 ± 0.05 ab | 3.10 ± 0.06 a | 10.14 ± 0.21 c |
| H2O | 7.12 ± 0.90 c | 84.68 ± 0.16 a | 0.61 ± 0.08 c | 7.32 ± 0.22 b | 0.41 ± 0.09 bc | 4.86 ± 0.30 a | 0.27 ± 0.05 b | 3.14 ± 0.12 a | 8.41 ± 1.07 d |
Table 5 Effects of combined GA3 and CPPU fruit retention treatments on organic acid composition content in‘Wuhe Cuibao’grape berries
| 处理 Treat- ment | 酒石酸 Tartaric acid | 苹果酸 Malic acid | 柠檬酸 Citric acid | 草酸 Oxalic acid | 总酸/(mg · g-1)Total acid | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量/(mg · g-1)Content | 占总酸比例/% Tartaric acid/ total acid | 含量/(mg · g-1)Content | 占总酸比例/% Malic acid/total acid | 含量/(mg · g-1)Content | 占总酸比例/% Citric acid/ total acid | 含量/(mg · g-1)Content | 占总酸比例/% Oxalic acid/ total acid | ||
| T1 | 9.52 ± 0.16 b | 79.99 ± 2.73 b | 1.38 ± 0.23 b | 11.48 ± 1.44 a | 0.63 ± 0.23 ab | 5.28 ± 1.35 a | 0.39 ± 0.02 a | 3.25 ± 0.13 a | 11.92 ± 0.34 b |
| T2 | 11.46 ± 0.14 a | 80.17 ± 0.72 b | 1.65 ± 0.10 a | 11.54 ± 0.71 a | 0.78 ± 0.02 a | 5.43 ± 0.07 a | 0.41 ± 0.01 a | 2.86 ± 0.01 b | 14.29 ± 0.14 a |
| T3 | 8.24 ± 0.27 b | 80.17 ± 0.96 b | 1.30 ± 0.11 b | 13.33 ± 0.74 a | 0.28 ± 0.09 c | 3.41 ± 0.24 b | 0.32 ± 0.05 ab | 3.10 ± 0.06 a | 10.14 ± 0.21 c |
| H2O | 7.12 ± 0.90 c | 84.68 ± 0.16 a | 0.61 ± 0.08 c | 7.32 ± 0.22 b | 0.41 ± 0.09 bc | 4.86 ± 0.30 a | 0.27 ± 0.05 b | 3.14 ± 0.12 a | 8.41 ± 1.07 d |

Fig. 4 Effects of combined GA3 and CPPU fruit retention treatments on the content of differential volatile aroma compounds in Wuhe Cuibao grape berries A:Alcohols,aldehydes,and ketones;B:Hydrocarbons and heterocyclic compounds;C:Esters;D:Terpenes. The data shown in the figure represent the average peak area values normalized by row using log10 transformation. * indicates a significant difference between the treatment and the control at P < 0.05
| 物质 Volatile aroma components | CAS号 CAS number | 阈值/(μg · g-1) Threshold | 相对气味活度值/(μg · g-1) Relative odor activity value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | 对照Control | |||
| 壬醇 1-Nonanol | 143-08-8 | 0.0053 | 268.86 a | 251.55 a | 215.11 b | 207.62 b |
| 苯甲醇 Benzyl alcohol | 100-51-6 | 0.1 | 0.17 a | 0.17 a | 0.17 a | 0.13 a |
| 2-壬醇 2-Nonanol | 628-99-9 | 0.058 | 0.20 a | 0.19 a | 0.19 a | 0.20 a |
| 甲酸香叶酯 Geranyl formate | 105-86-2 | 0.2 | 0.15 a | 0.15 a | 0.16 a | 0.16 a |
| 大马士酮 (E)-1-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1,3- cyclohexadien-1-yl)-2-Buten-1-one | 23726-93-4 | 0.0015 | 32.41 b | 32.56 b | 30.64 b | 43.13 a |
| (R)-3,7-二甲基-6-辛烯醇 (R)-3,7-dimethyl-6-Octen-1-ol | 1117-61-9 | 0.04 | 0.17 a | 0.16 a | 0.20 a | 0.20 a |
| 香茅醇 Citronellol | 106-22-9 | 0.04 | 0.17 a | 0.16 a | 0.20 a | 0.20 a |
| 香叶醇 Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0.0066 | 615.29 a | 383.95 ab | 500.32 a | 237.07 b |
| 苯乙醛 Benzeneacetaldehyde | 122-78-1 | 0.0063 | 14.97 a | 17.07 a | 12.84 a | 16.91 a |
Table 6 Differences in relative odor activity values(rOAVs)of rose-scented characteristic aroma compounds in ‘Wuhe Cuibao’ grape berries under combined GA3 and CPPU fruit retention treatments
| 物质 Volatile aroma components | CAS号 CAS number | 阈值/(μg · g-1) Threshold | 相对气味活度值/(μg · g-1) Relative odor activity value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | 对照Control | |||
| 壬醇 1-Nonanol | 143-08-8 | 0.0053 | 268.86 a | 251.55 a | 215.11 b | 207.62 b |
| 苯甲醇 Benzyl alcohol | 100-51-6 | 0.1 | 0.17 a | 0.17 a | 0.17 a | 0.13 a |
| 2-壬醇 2-Nonanol | 628-99-9 | 0.058 | 0.20 a | 0.19 a | 0.19 a | 0.20 a |
| 甲酸香叶酯 Geranyl formate | 105-86-2 | 0.2 | 0.15 a | 0.15 a | 0.16 a | 0.16 a |
| 大马士酮 (E)-1-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1,3- cyclohexadien-1-yl)-2-Buten-1-one | 23726-93-4 | 0.0015 | 32.41 b | 32.56 b | 30.64 b | 43.13 a |
| (R)-3,7-二甲基-6-辛烯醇 (R)-3,7-dimethyl-6-Octen-1-ol | 1117-61-9 | 0.04 | 0.17 a | 0.16 a | 0.20 a | 0.20 a |
| 香茅醇 Citronellol | 106-22-9 | 0.04 | 0.17 a | 0.16 a | 0.20 a | 0.20 a |
| 香叶醇 Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0.0066 | 615.29 a | 383.95 ab | 500.32 a | 237.07 b |
| 苯乙醛 Benzeneacetaldehyde | 122-78-1 | 0.0063 | 14.97 a | 17.07 a | 12.84 a | 16.91 a |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
郭淑萍, 杨顺林, 杨玉皎, 张永辉, 孟富宣, 何建军, 张俊松, 金杰. 2022. GA3和CPPU对无核翠宝葡萄果实品质的影响. 果树学报, 39(10):1834-1844.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
韩守安, 张雯, 张捷, 钟海霞, 谢辉, 张付春, 王敏, 潘明启. 2021. 无核翠宝葡萄在新疆的种植特点及关键栽培技术. 农村科技,(1):53-55.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
黄海娜, 程大伟, 顾红, 张洋, 郭西智, 陈锦永. 2019. GA3和TDZ对‘巨玫瑰’葡萄果皮涩味的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 21(2):120-132.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
侯旭东, 谭佳欣. 2021. CPPU与GA3对“妮娜皇后”葡萄果实品质的影响. 安徽农业科学, 49(21):65-69.
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
李辉, 李超, 张梦园, 孙佳莹, 张军翔. 2017. 葡萄酒中单宁涩感评价及结构分析研究进展. 中国酿造, 36(6):14-18.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
刘巧, 彭家清, 程均欢, 肖涛, 朱先波, 夏宏义. 2019. 植物生长调节剂在葡萄生产中的应用研究进展. 黑龙江农业科学,(8):169-174.
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
刘三军, 贺亮亮, 宋银花, 章鹏. 2016. 植物生长调节剂在葡萄上的应用//第五届全国现代果业标准化示范区创建暨果树优质高效生产技术交流会论文汇编. 中国园艺学会:30-33.
|
|
| [13] |
|
|
吕科, 张建海, 董雪洁, 胡小南, 刘帅, 王会学. 2020. GA3和CPPU对‘无核翠宝’葡萄果实膨大及果实品质的影响. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒,(3):24-27.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
穆维松, 冯建英, 田东, 牟鑫. 2019. 我国鲜食葡萄产业的国际贸易与国内需求形势. 中国果树,(2):5-10.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
邱家洪, 陶慧慧, 曾明, 杨思潮, 王凌娇, 袁九香. 2022. 夏黑葡萄保花保果试验初报. 江西科学, 40(4):674-676,723.
|
|
| [16] |
Statistical Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. 2022. Xinjiang Statistical Yearbook 2022. Beijing: China Statistics Press. (in Chinese)
|
|
新疆维吾尔自治区统计局. 2022. 2022年新疆统计年鉴. 北京: 中国统计出版社.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
|
唐晓萍, 陈俊, 马小河, 赵旗峰, 董志刚, 李晓梅. 2012. 早熟无核葡萄新品种‘无核翠宝’. 园艺学报, 39(11):2307-2308.
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
王剑功, 吴金焕, 褚伟雄, 王晖, 朱其林, 吴剑. 2023. 复合调节剂对阳光玫瑰葡萄品质和香气成分影响. 食品工业, 44(10):149-154.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
王继源, 冯娇, 侯旭东, 陶建敏. 2016. CPPU对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄品质及香气合成相关基因表达的影响. 南京农业大学学报, 39(6):915-923.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
王敏, 韩守安, 刘旭鹏, 张雯, 张付春, 钟海霞, 伍新宇, 潘明启. 2024. 新疆葡萄产业发展现状分析. 新疆农业科学, 61(S1):127-130.
|
|
| [22] |
|
|
王西成, 王壮伟, 吴伟民, 赵密珍, 钱亚明. 2018. 植物生长调节剂对葡萄果实品质影响的研究进展. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒,(4):103-107.
|
|
| [23] |
|
|
王颖, 荀志丽, 黄丽萍, 王敏, 马小河, 许艺凡, 王环, 赵旗峰. 2023. 赤霉素处理对葡萄果实发育及品质的影响. 中国果树,(5):43-49,55.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
王永荟, 秦曙. 2023. 植物生长调节剂对葡萄品质影响的研究进展. 农产品质量与安全,(3):22-27.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
魏玲玲, 王武, 陶建敏. 2018. 葡萄香气物质研究进展. 中国南方果树, 47(3):159-165.
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
|
吴玉森. 2019. 鲜食葡萄特征香气物质及根域限制栽培与植物生长调节剂对其影响[博士论文]. 上海: 上海交通大学.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
张泉, 刘婧汇, 姜建福, 刘崇怀. 2023. 国内无核葡萄育种成果及特性分析. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒,(2):73-79,88.
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
张雯, 潘明启, 努里阿 · 阿合买提, 韩守安, 王敏, 艾尔买克 · 才卡斯木. 2022. 西北干旱产区葡萄新梢与花果生长期管理技术要点. 农村科技,(6):39-42.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
钟海霞, 丁祥, 周晓明, 潘明启, 张付春, 韩守安, 张雯, 谢辉, 王敏, 艾尔买克 · 才卡斯木, 伍新宇. 2021. 新疆10个酿酒葡萄品种(系)可溶性糖组分及含量分析. 新疆农业科学, 58(7):1323-1331.
|
| [1] | GENG Hao, GE Mengqing, DING Yunlong, XU Weidong, CONG Chunlei, YAN Hongwei, QIAN Yu, LIU Yufeng. A New Medium Ripening Table Grape Cultivar‘Yuanjinxiang’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 31-32. |
| [2] | GAO Min, ZHAO Ning, LI Zhi, WANG Xianhang, TU Mingxing, GUO Junqiang, WANG Xiping. A New Table Grape Cultivar‘Qinpu 3 Hao’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 33-34. |
| [3] | WEI Xixi, ZHAO Ning, LI Zhi, WANG Xianhang, TU Mingxing, GAO Min, WANG Xiping. A New Table Grape Cultivar‘Qinpu 4 Hao’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 35-36. |
| [4] | HAO Yan, ZHU Yanfang, GAO Bo. A New Seedless Table Grape Cultivar‘Ziyan’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 37-38. |
| [5] | NI Peijin, AI Jun, SHI Guangli, WANG Zhenxing, SUN Dan, SUN Yanfeng, LIU Xiaoying. A New Cold-Resistant Wine Grape Cultivar‘Fuhong’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 39-40. |
| [6] | SHU Nan, LU Wenpeng, FAN Shutian, WANG Yanli, LIU Guoliang, LI Changyu, SUN Bowei, LIU Xinhua, WANG Yue, TAN Yue, ZHANG Baoxiang, TIAN Taiping. A New Wine Grape Cultivar‘Zijing Xianglu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 43-44. |
| [7] | LI Ying, ZHANG Shuhang, GUO Yan, ZHANG Xinfang, LIU Jinyu, FAN Liying, WANG Guangpeng. A New Chestnut Cultivar‘Yanli 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 67-68. |
| [8] | LIU Zhaokun, WANG Huan, HAN Jianjun, WANG Yingying, ZHOU Hongzhang. A New Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Suqing 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 101-102. |
| [9] | ZHENG Mengfan, XIE Yong, ZHENG Wei, LI Guangqian, CHEN Gang, WANG Yushuang, LI Cong, ZHANG Yuyang. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Minfeng 698’with High Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 125-126. |
| [10] | ZHU Pengyu, XIE Yong, ZHENG Wei, LI Guangqian, CHEN Gang, WANG Yushuang, LI Cong, ZHANG Yuyang. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Xiweimei 191’with High Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 127-128. |
| [11] | HUANG Zhen, ZHENG Yansong, LI Guangguang. A New Hot Pepper Cultivar‘Layou 22’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 145-146. |
| [12] | SHI Bo, GUAN Feng, ZHANG Jingyun, YANG Xuetong, XIE Yuanyuan, WANG Kai, WAN Xinjian. A New Processed Wax Gourd Cultivar‘Zaoyoufen’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 163-164. |
| [13] | ZHU Dening, WU Yujun, YU Bingwei, LI Lianfang. A New Luffa acutangula Cultivar‘Xiasheng 6’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 167-168. |
| [14] | HAN Jiayu, GUO Rongrong, ZHANG Ying, SHI Xiaofang, CAO Xiongjun, HUANG Guiyuan, BAI xianjin, XIE Taili, YU Huan, XIE Shuyu, LIN Ling. Low Chilling Requirement Grape New Cultivar‘Guipu 9’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 45-46. |
| [15] | SHU Nan, LU Wenpeng, YANG Yiming, XU Peilei, LI Jiaqi, LIU Tao, QU Bingzhang. A New Wine Grape Cultivar‘Zijinglu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 47-48. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd