
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2737-2747.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0867
• Cultivation·Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Meihua1, SUN Huixian1, ZHAO Yanli1, LI Jing1, TIAN Linlin1, MIAO Yanxiu1, BAI Longqiang1, HOU Leiping1, ZHANG Yi1, LI Tianlai2,**( )
)
Received:2024-10-31
Revised:2025-06-01
Online:2025-10-25
Published:2025-10-28
Contact:
LI Tianlai
SUN Meihua, SUN Huixian, ZHAO Yanli, LI Jing, TIAN Linlin, MIAO Yanxiu, BAI Longqiang, HOU Leiping, ZHANG Yi, LI Tianlai. Effects of Different Nitrogen Concentration on the Locule Number in Tomato Fruit[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(10): 2737-2747.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0867
| 氮水平N level | KNO3 | Ca(NO3)2 · 4H2O | NaH2PO4 · 4H2O | KH2PO4 | NH4NO3 | CaCl2 | MgSO4 | N | P2O5 | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标准Normal | 301 | 912 | 395.5 | -- | -- | -- | 400 | 150 | 180 | 140 |
| 多High | 301 | 912 | 395.5 | -- | 286 | -- | 400 | 250 | 180 | 140 |
| 少Low | 301 | 70 | 395.5 | -- | -- | 748 | 400 | 50 | 180 | 140 |
Table 1 Nutrient solution formulations for different treatments(large elements) mg · L-1
| 氮水平N level | KNO3 | Ca(NO3)2 · 4H2O | NaH2PO4 · 4H2O | KH2PO4 | NH4NO3 | CaCl2 | MgSO4 | N | P2O5 | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标准Normal | 301 | 912 | 395.5 | -- | -- | -- | 400 | 150 | 180 | 140 |
| 多High | 301 | 912 | 395.5 | -- | 286 | -- | 400 | 250 | 180 | 140 |
| 少Low | 301 | 70 | 395.5 | -- | -- | 748 | 400 | 50 | 180 | 140 |
| 目的基因Target gene | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| GA2ox2 | F:ATTCGGGCTGCGGTTAATGA | R:TCAATCTCTGAGCATGGCGG |
| TLOG1 | F:AAGAGCAGTGTCTGGGATGC | R:AATGATGTGACGGGCAGAGG |
| CKX2 | F:CAAGAGGCCACGGTCATTCT | R:TGTCCACTGATGCCAGCATT |
| PRX44 | F:GGGCCTAGTATAACGGTGCC | R:TGGCGACCCACCATTAGAAC |
| PRX3 | F:ATGCACCATCTCTTGCTGCT | R:GCACATGACACAATCCCAGG |
| PRX66 | F:CTCGAAAAGGCTTGCCCAAC | R:CCAAGTGTGTGTCCACCAGA |
| ACTIN | F:GATCAGCGTATCCTTCAGAG | R:GGCATTGTAGCAGAGAAAAC |
Table 2 Primers used in real-time fluorescence quantitative experiments
| 目的基因Target gene | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| GA2ox2 | F:ATTCGGGCTGCGGTTAATGA | R:TCAATCTCTGAGCATGGCGG |
| TLOG1 | F:AAGAGCAGTGTCTGGGATGC | R:AATGATGTGACGGGCAGAGG |
| CKX2 | F:CAAGAGGCCACGGTCATTCT | R:TGTCCACTGATGCCAGCATT |
| PRX44 | F:GGGCCTAGTATAACGGTGCC | R:TGGCGACCCACCATTAGAAC |
| PRX3 | F:ATGCACCATCTCTTGCTGCT | R:GCACATGACACAATCCCAGG |
| PRX66 | F:CTCGAAAAGGCTTGCCCAAC | R:CCAAGTGTGTGTCCACCAGA |
| ACTIN | F:GATCAGCGTATCCTTCAGAG | R:GGCATTGTAGCAGAGAAAAC |

Fig. 1 Effects of different nitrogen concentrations on tomato flowers bud differentiation process(A,B),flower size(C,D)and number of floral organs(E) Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatments(P < 0.05)according to Duncan’s multiple range tests
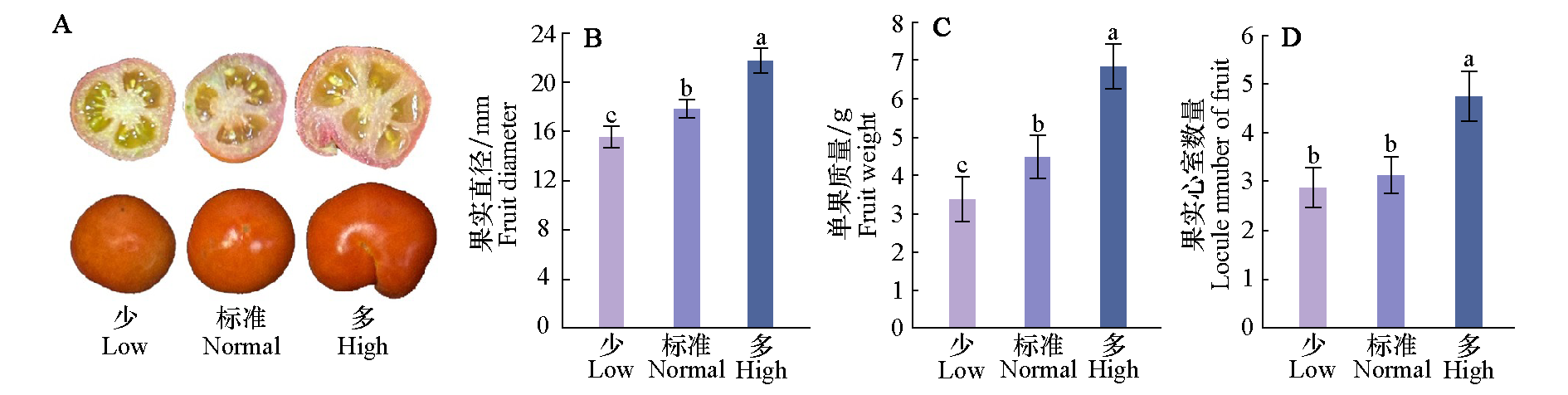
Fig. 2 Effects of different nitrogen concentrations on tomato fruit(A),fruit size(B),fruit weight(C)and locule number(D) Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatments(P < 0.05)according to Duncan’s multiple range tests
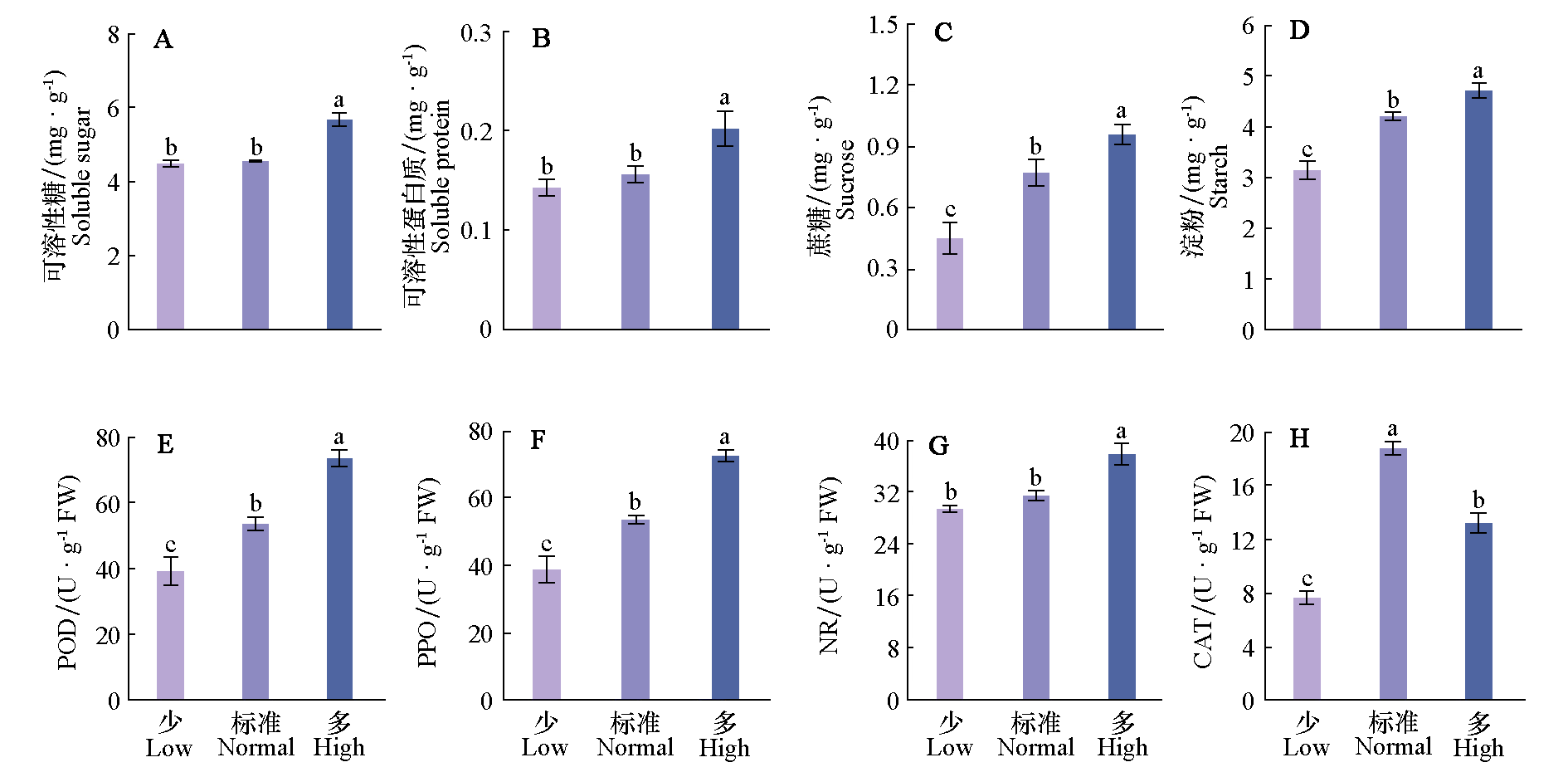
Fig. 3 Effects of different nitrogen concentrations on nutrient content and enzyme activity in stem apex of tomato seedlings Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatments(P < 0.05)according to Duncan’s multiple range tests
| 性状 Trait | 可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein | 淀粉 Starch | 蔗糖 Sucrose | 可溶性糖 Solube sugar | POD | NR | CAT | PPO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花直径Flower size | 0.964** | 0.014 | 0.821** | 0.969** | 0.929** | 0.963** | 0.152 | 0.929** |
| 果实直径Fruit size | 0.961** | 0.080 | 0.876** | 0.868** | 0.934** | 0.919** | 0.379 | 0.968** |
| 单果质量Single fruit weight | 0.942** | 0.129 | 0.910** | 0.880** | 0.960** | 0.913** | 0.445 | 0.986** |
| 心室数量Locule number | 0.845** | -0.277 | 0.642 | 0.812** | 0.770* | 0.939** | -0.040 | 0.785* |
Table 3 Correlation analysis of nutrient content and enzyme activity in stem apex of seedlings with flower and fruit traits
| 性状 Trait | 可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein | 淀粉 Starch | 蔗糖 Sucrose | 可溶性糖 Solube sugar | POD | NR | CAT | PPO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花直径Flower size | 0.964** | 0.014 | 0.821** | 0.969** | 0.929** | 0.963** | 0.152 | 0.929** |
| 果实直径Fruit size | 0.961** | 0.080 | 0.876** | 0.868** | 0.934** | 0.919** | 0.379 | 0.968** |
| 单果质量Single fruit weight | 0.942** | 0.129 | 0.910** | 0.880** | 0.960** | 0.913** | 0.445 | 0.986** |
| 心室数量Locule number | 0.845** | -0.277 | 0.642 | 0.812** | 0.770* | 0.939** | -0.040 | 0.785* |
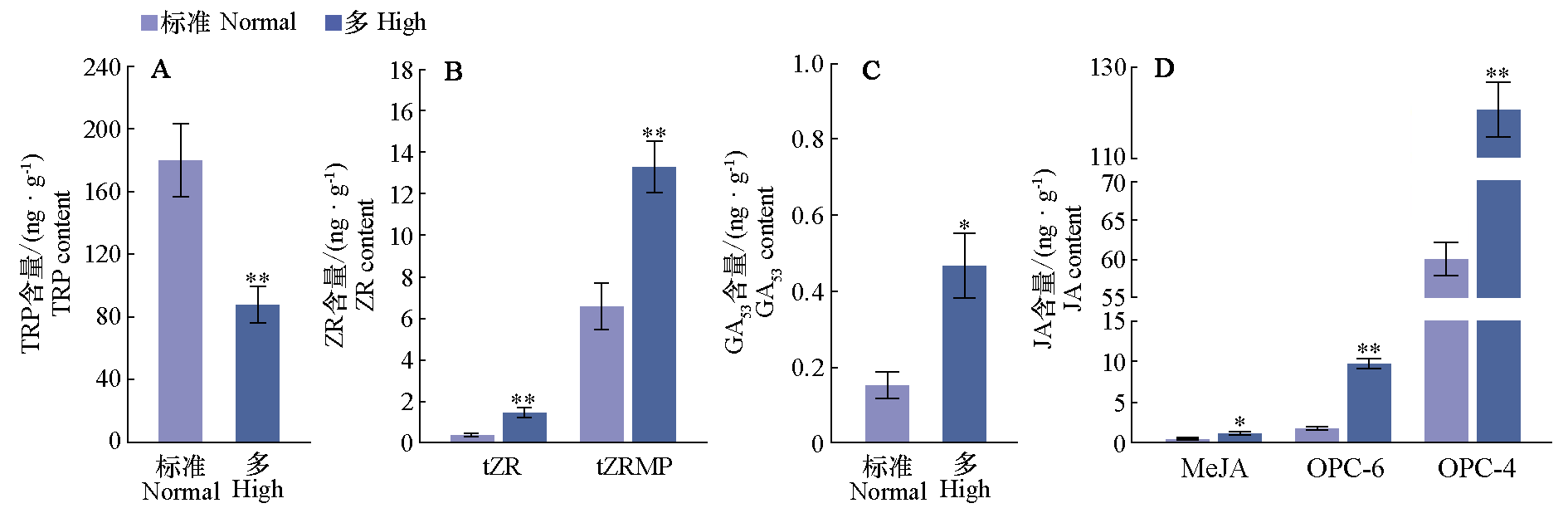
Fig. 4 Effects of high nitrogen concentration on hormone content in stem apex of tomato seedlings * means significant at P < 0.05 level,** means significant at P < 0.01 level according to the Independent t-test
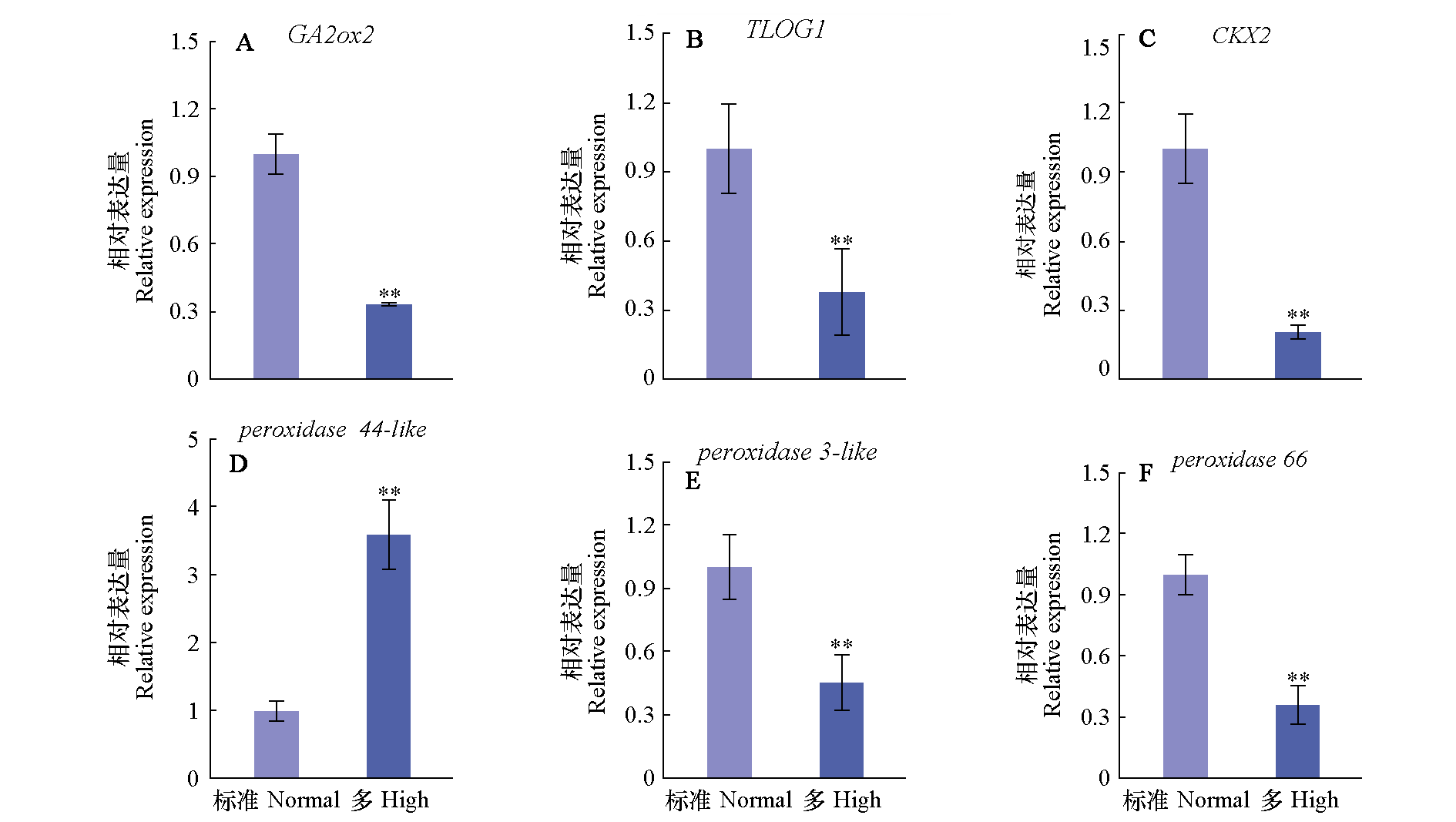
Fig. 5 Effects of high nitrogen concentration on gene expression in stem apex of tomato seedlings * means significant at P < 0.05 level,** means significant at P < 0.01 level
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
|
陈先知. 2005. 苗期光、温、养分对“川番杂交一号”番茄畸形果发生的影响研究[硕士论文]. 成都: 四川农业大学.
|
|
| [3] |
|
|
陈先知, 李能芳, 朱剑桥, 朱隆静. 2006. 苗期夜温对番茄畸形果发生的影响. 四川农业大学学报, 24 (3):309-312.
|
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1038/ng.144 pmid: 18469814 |
| [5] |
|
|
高俊凤. 2006. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京:高等教育出版社:210-217.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
胡静, 饶桦静, 裴瑾, 唐小慧, 刘钰萍, 魏担, 耿福昌. 2018. 西红花花芽分化的形态发育及生理生化变化研究. 中药材, 41 (12):2748-2752.
|
|
| [7] |
|
|
黄洁衔, 李腾基, 黄紫钦, 逯有法, 张建霞. 2023. 墨兰花芽形态分化及生理特性研究. 北方园艺,(3):56-63.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
孔德政, 靳丹丹, 孙丽娜, 管志涛, 毛瑞丽. 2008. 碗莲花芽分化过程中酶活性的变化. 河南农业科学,(4):97-99.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3268.2008.04.028 |
|
| [9] |
|
|
李会. 2018. lc位点通过SlWUS基因调控番茄子房心室形成的研究[博士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
李天来, 房思强, 郭泳, 杨延杰, 藤少明. 1997. 植物生长调节剂对番茄畸形果发生的影响. 沈阳农业大学学报, 28 (3):30-34.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
李天来, 须晖, 郭泳, 姜涛. 2000. 苗期不同灌水点对番茄畸形果发生的影响//中国园艺学会第四届青年学术讨论会论文集:358-361.
|
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
|
李艳冰. 2021. 苗期低夜温诱导番茄心室增多的赤霉素作用机制[博士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
李悦, 李天来, 王丹. 2008. 番茄花芽分化期茎尖内源激素水平与果实心室数目的相关性研究. 中国农业科学,(9):2727-2733.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
刘爽. 2012. 赤霉素与fasciated在调控番茄心室形成中的作用关系分析[博士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
孟思达, 韩磊磊, 相恒佐, 朱美玉, 冯珍, 叶云珠, 孙美华, 李艳冰, 赵利萍, 谭昌华, 齐明芳, 李天来. 2024. 番茄心室数的调控机制研究进展. 园艺学报, 51 (7):1649-1664.
|
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.111.173997 pmid: 21673133 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2010.37 pmid: 20448544 |
| [19] |
|
|
乔双. 2014. 生长素与fasciated在调控番茄心室形成中的作用关系[硕士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
王学奎, 黄见良. 2015. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社.
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
|
吴洁秋, 朱根发, 王凤兰, 杨凤玺. 2021. 竹叶兰花器官发育过程及生理特性研究. 热带作物学报, 42 (1):140-148.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.01.020 |
|
| [25] |
|
|
吴新亮. 2020. 细胞分裂素对番茄多心室畸形果的调控作用研究[硕士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
吴志斌. 2022. 生长素缓解低夜温下番茄多心室畸形果发生的机制解析[硕士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1038/ng.3309 pmid: 26005869 |
| [28] |
|
|
须晖, 李天来, 郭泳, 杨丽娟. 1997. 苗期营养水平对番茄畸形果发生的影响. 中国蔬菜,(5):12-14.
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
须晖, 孙红梅, 郭泳, 杨丽娟, 李天来, 房思强. 1999. 番茄苗期营养及其幼苗茎尖物质含量与畸形果发生的关系//中国园艺学会成立70周年纪念优秀论文选编:476-480.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
须晖, 李天来, 郭泳, 陈伟之, 杨丽娟, 鄂文伟. 2000. 番茄幼苗体内激素含量与畸形果发生的关系//中国园艺学会第四届青年学术讨论会论文集:360-364.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
姚凯, 牛晓娟, 徐僡, 敖家林. 2019. 锶对菠菜幼苗生长、光合和抗氧化酶活性的影响. 核农学报, 33 (6):1225-1231.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2019.06.1225 |
| [1] | ZAI Wenshan, CHEN Xianzhi, FU Cunnian, SU Shiwen, SHI Jianlei, XIONG Zili, HUANG Shaoyong. A New Taste Tomato Cultivar‘Ouxiu 901’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 121-122. |
| [2] | WANG Rongqing, YAO Zhuping, CHENG Yuan, YE Qingjing, RUAN Meiying, WAN Hongjian, LI Zhimiao, LIU Chenxu, ZHOU Guozhi. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Zhefen 718’with High Quality and Storage Properties [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 123-124. |
| [3] | ZHENG Mengfan, XIE Yong, ZHENG Wei, LI Guangqian, CHEN Gang, WANG Yushuang, LI Cong, ZHANG Yuyang. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Minfeng 698’with High Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 125-126. |
| [4] | ZHU Pengyu, XIE Yong, ZHENG Wei, LI Guangqian, CHEN Gang, WANG Yushuang, LI Cong, ZHANG Yuyang. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Xiweimei 191’with High Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 127-128. |
| [5] | CUI Aihua, ZHU Moyong, ZHANG Yangdong, WU Qi, LIU Shuai, HU Qixing, HUANG Jigang, LIU Jiaxin, LIU Weisheng, SUN Julong. A New Large Fruit Tomato Cultivar‘Aoliya’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 129-130. |
| [6] | ZHENG Yuli, LIU Yan, PAN Ziwang, HAN Lanlan, LI Kai, LIU Dan, CAO Yang, LU Xinzhe, KANG Yongsheng. A New Multi-Resistant Hard-Flesh Hybrid Tomato‘BY002’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 131-132. |
| [7] | SU Shiwen, FU Cunnian, CHEN Xianzhi, CUI Lili, SHI Jianlei, HUANG Shaoyong, XIONG Zili, ZAI Wenshan. A New Cherry Tomato Cultivar‘Ouxiu Hongying 5’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 133-134. |
| [8] | FU Cunnian, SU Shiwen, CHEN Xianzhi, CUI Lili, SHI Jianlei, HUANG Shaoyong, XIONG Zili, ZAI Wenshan. A New Cherry Tomato Cultivar‘Ouxiu Chengying 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 135-136. |
| [9] | XIONG Zili, SU Shiwen, SHI Jianlei, ZHANG Haili, ZAI Wenshan, CUI Lili. A New Tomato Rootstock Cultivar‘Ouzhen 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S2): 137-138. |
| [10] | FAN Huidong, ZHENG Shijin, TIAN song, ZHENG Jianchao. A New Tomato F1 Hybrid‘Jifen 7’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 109-110. |
| [11] | ZHANG Liwei, DAI Zhongren, CHEN Qingqi, LEI Na, HUANG Jun, Hu Haijiang, MEN Wanjie. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Hayan Zhongfenguo 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 111-112. |
| [12] | XIONG Zili, SHI Jianlei, CHEN Yongbing, ZHANG Haili, SU Shiwen, ZAI Wenshan, YE Shuguang. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Ouxiu 202’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 113-114. |
| [13] | CHEN Shuting, WU Mumian, LI Tao, LI Zhenxing, MAI Peiting, SUN Baojuan, HAO Yanwei, GONG Chao. Effects of EM Bacteria on Tomato Yield and Soil Bacterial Community [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(9): 2477-2490. |
| [14] | SU Xiumin, WANG Jiao, HAN Wenqing, LI Peng, WANG Qiulan, LI Wanxing. Isolation,Biological Characteristics of the Pathogen Causing Fusarium Wilt on Tomato and Antagonistic Fungus Screening [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(9): 2532-2544. |
| [15] | SONG Qi, SONG Xiaoya, JIAO Yongxin, MAO Ziyue, WU Xiaogang, ZHANG Qingxia. Antifungal Activity of Pseudomonas protegens FD6 Against Botrytis cinerea and Optimization of Its Culture Conditions [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(9): 2545-2553. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd