
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 123-135.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0801
张子鑫*, 陈淑婷*, 周伟欣, 张意涵, 鲁倩, 李中义, 吴昕扬, 徐沛**( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-21
修回日期:2024-10-18
出版日期:2025-01-25
发布日期:2025-01-19
通讯作者:
作者简介:基金资助:
ZHANG Zixin, CHEN Shuting, ZHOU Weixin, ZHANG Yihan, LU Qian, LI Zhongyi, WU Xinyang, XU Pei**( )
)
Received:2024-08-21
Revised:2024-10-18
Published:2025-01-25
Online:2025-01-19
Contact:
** E-mail:peixu@cjlu.edu.cn
摘要:
2022年10—11月,在浙江省杭州市钱塘区观察到疑似病毒侵染的菜豆植株,病毒组测序和PCR技术检测出豇豆轻斑驳病毒(cowpea mild mottle virus,CPMMV)、黄瓜花叶病毒(cucumber mosaic virus,CMV)和紫云英矮缩病毒(milk vetch dwarf virus,MDV),并将CPMMV命名为CPMMV-ZJ(GenBank:OR667247)。利用病毒鉴定、全基因组序列扩增、系统发育分析及亚细胞定位等方法,明确了CPMMV-ZJ的全基因组序列特征、病毒演化及其病毒三联蛋白(triple gene block protein,TGB)的亚细胞定位。结果表明,CPMMV-ZJ的基因组全长为8 226 bp,包含6个开放阅读框。3′和5′区域分别有1个147 bp和75 bp的非编码区(untranslated regions,UTR)。序列分析结果表明,CPMMV浙江分离物与CPMMV安徽分离物的全基因组序列一致性最高(98.03%),并与国内分离物共同聚类在一个小分支上,但与国外分离物(美国、印度、巴西等地)序列一致性较低(63.71% ~ 82.49%),提示病毒变异与地理因素密切相关。对浙江分离物与江苏分离物TGB蛋白的亚细胞定位比较分析发现,二者无明显差异,但TGB2浙江分离物在叶片中的表达导致明显的叶绿体核周聚集现象,推测与植物防御反应有关。
张子鑫, 陈淑婷, 周伟欣, 张意涵, 鲁倩, 李中义, 吴昕扬, 徐沛. 浙江菜豆CPMMV变异株的鉴定及其TGB蛋白定位[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 123-135.
ZHANG Zixin, CHEN Shuting, ZHOU Weixin, ZHANG Yihan, LU Qian, LI Zhongyi, WU Xinyang, XU Pei. Identification of Cowpea Mild Mottle Virus Variants in Zhejiang and Localization of TGB Proteins[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 123-135.
| 用途 Usage | 引物 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primers sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 5′端快速cDNA扩增 5′RACE | 5AP | GGTCTCAAGGGCTCTAAACATTT |
| GSP1 | CAACTCATGACCAGCTCAGC | |
| GSP2 | TTCCCTTGGCAGAACGAGAC | |
| 序列扩增 Sequence amplification | CPMMV-F1 | GTTTACCCACCGGAGTTGCT |
| CPMMV-R2 | AATCACTTTGGCAGGGATCC | |
| CPMMV-F2 | TCAAAGCTAGAATGTCTAGG | |
| 序列扩增;病毒检测 Sequence amplification;Virus detection | CPMMV-R2 | CTGTCAATACAGTTTTGGAG |
| CPMMV-F3 | AGATGAAGGAATTAGAGAGG | |
| 序列扩增 Sequence amplification | CPMMV-R3 | AGAACCTCAGCTACGTGCTC |
| 3′端快速cDNA扩增 3′RACE | 3AP | GTTTTCCCAGTCACGACAC |
| GSP3 | GCCCTTCCAGACATTGATGC | |
| GSP4 | TCAAATAACATGGCCACAGCTG | |
| 亚细胞定位载体构建 Subcellular localization vector construction | TGB1-F | ATGAATGAACTGATCAGTAA |
| TGB1-R | CTCAGAGTTTGGATAGGTTG | |
| TGB2-F | ATGCCACTGACTCCACCA | |
| TGB2-R | GTGAACCCTATTGCAGA | |
| TGB3-F | ATGTCTGCAATAGGGTTCAC | |
| TGB3-R | CAACCTACAACTTAGGCTA | |
| 病毒检测 Virus detection | MDV-F | ACTCAAGGAGAGGCAAGAGC |
| MDV-R | ATGTCGGCTGTCTTTCCACC | |
| CMV-F | AAGTGGTTTGCAGCGTTGAC | |
| CMV-R | TGTTGCAAATCACGCACTCG |
表1 本试验中所用到的引物
Table 1 Primers sequences used in this study
| 用途 Usage | 引物 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primers sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 5′端快速cDNA扩增 5′RACE | 5AP | GGTCTCAAGGGCTCTAAACATTT |
| GSP1 | CAACTCATGACCAGCTCAGC | |
| GSP2 | TTCCCTTGGCAGAACGAGAC | |
| 序列扩增 Sequence amplification | CPMMV-F1 | GTTTACCCACCGGAGTTGCT |
| CPMMV-R2 | AATCACTTTGGCAGGGATCC | |
| CPMMV-F2 | TCAAAGCTAGAATGTCTAGG | |
| 序列扩增;病毒检测 Sequence amplification;Virus detection | CPMMV-R2 | CTGTCAATACAGTTTTGGAG |
| CPMMV-F3 | AGATGAAGGAATTAGAGAGG | |
| 序列扩增 Sequence amplification | CPMMV-R3 | AGAACCTCAGCTACGTGCTC |
| 3′端快速cDNA扩增 3′RACE | 3AP | GTTTTCCCAGTCACGACAC |
| GSP3 | GCCCTTCCAGACATTGATGC | |
| GSP4 | TCAAATAACATGGCCACAGCTG | |
| 亚细胞定位载体构建 Subcellular localization vector construction | TGB1-F | ATGAATGAACTGATCAGTAA |
| TGB1-R | CTCAGAGTTTGGATAGGTTG | |
| TGB2-F | ATGCCACTGACTCCACCA | |
| TGB2-R | GTGAACCCTATTGCAGA | |
| TGB3-F | ATGTCTGCAATAGGGTTCAC | |
| TGB3-R | CAACCTACAACTTAGGCTA | |
| 病毒检测 Virus detection | MDV-F | ACTCAAGGAGAGGCAAGAGC |
| MDV-R | ATGTCGGCTGTCTTTCCACC | |
| CMV-F | AAGTGGTTTGCAGCGTTGAC | |
| CMV-R | TGTTGCAAATCACGCACTCG |
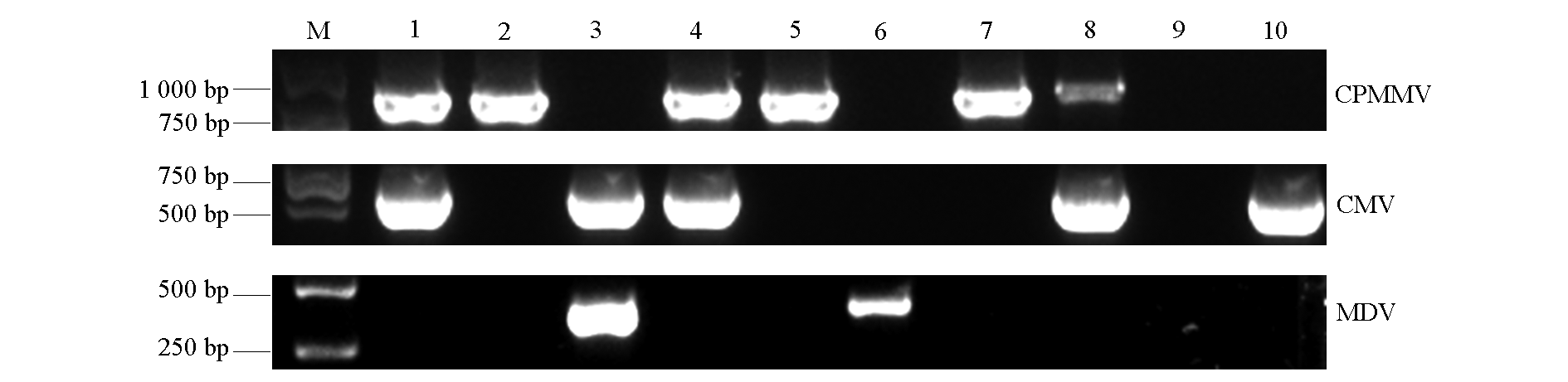
图2 菜豆田间样品中CPMMV、CMV、MDV的RT-PCR检测 M:DL2 000 DNA marker;1 ~ 10:随机挑选的10份田间感染病毒的菜豆叶片样品
Fig. 2 RT-PCR detection of CPMMV,CMV and MDV from samples randomly selected in field of common bean M:DL2 000 DNA marker;1-10:Ten randomly selected common bean leaf samples from virus-infected field plants
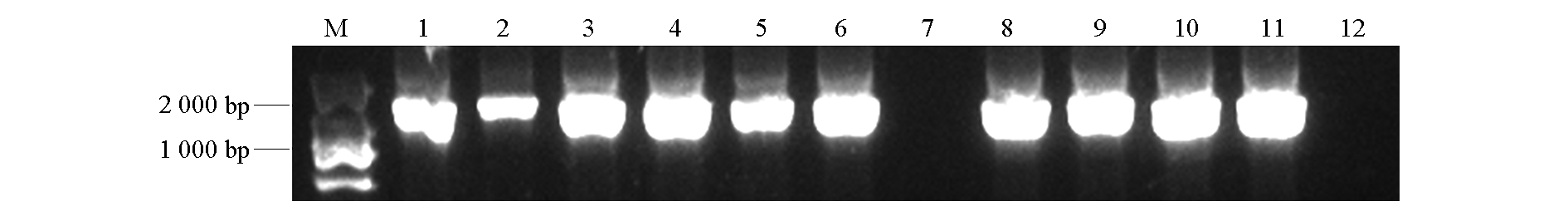
图4 CPMMV-ZJ机械接种健康菜豆叶片后的RT-PCR检测 M:DL2 000 DNA marker;1 ~ 10:接种CPMMV的菜豆叶片样品;11:阳性对照;12:阴性对照
Fig. 4 RT-PCR detection of CPMMV in common bean leaves mechanically inoculated with CPMMV-ZJ M:DL2 000 DNA marker;1-10:Common bean leaf samples inoculated with CPMMV;11:Positive control;12:Negative control

图8 CPMMV浙江分离物(CPMMV-ZJ)与江苏分离物(CPMMV-JS)的TGB蛋白亚细胞定位(A)及TGB2-ZJ引起的叶绿体核周聚集现象(B) 白色箭头指示叶绿体在核周聚集
Fig. 8 Subcellular localization analysis of TGBs of CPMMV Zhejiang(CPMMV-ZJ)and Jiangsu(CPMMV-JS)isolate(A)and the clustering of chloroplasts around the nuclei caused by TGB2-ZJ(B) White arrows represents perinuclear aggregation of chloroplasts
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
pmid: 4701691 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.05.011 pmid: 26120031 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1007/s00705-022-05576-7 pmid: 36269413 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0165 URL |
|
崔甜甜, 王艳娇, 李中安, 周常勇, 宋震. 2017. 柑橘黄化脉明病毒的TGB基因生物信息学分析及亚细胞定位. 园艺学报, 44 (8):1579-1588.
|
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1111/mpp.12840 pmid: 31257720 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20193080 |
|
吉颖, 孙枫, 吴淑华, 李硕, 涂丽琴, 高丹娜, 崔晓艳, 陈新, 季英华, 郭青云. 2022. 江苏大豆上分离的豇豆轻斑驳病毒基因组序列克隆及特征分析. 华北农学报, 37 (3):200-205.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20193080 |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1094/PDIS-04-17-0562-PDN |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.02.005 |
|
刘勇, 李凡, 李月月, 张松柏, 高希武, 谢艳, 燕飞, 张安盛, 戴良英, 程兆榜, 丁铭, 牛颜冰, 王升吉, 车海彦, 江彤, 史晓斌, 何自福, 吴云锋, 张德咏, 青玲, 严婉荣, 杨学辉, 汤亚飞, 郑红英, 唐前君, 章松柏, 章东方, 蔡丽, 陶小荣. 2019. 侵染我国主要蔬菜作物的病毒种类、分布与发生趋势. 中国农业科学, 52 (2):239-261.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.02.005 |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1007/s00705-010-0821-y pmid: 20890716 |
| [25] |
pmid: 9638146 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
pmid: 17610926 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0401 URL |
|
卫甜, 李宏伟, 苏建坤, 刘建凤, 刘红霞. 2016. 黄瓜绿斑驳花叶病毒病生防菌株的分离与筛选. 园艺学报, 43 (12):2391-2400.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0401 URL |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1007/s00705-013-1879-0 pmid: 24142270 |
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
pmid: 27757106 |
| [1] | 邱辉, 朱德娟, 张永乐, 高玉洁, 李柳, 王国平, 洪霓. ACLSV外壳蛋白与梨两种E3泛素连接酶互作及亚细胞定位[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1715-1727. |
| [2] | 袁娜, 徐勤圆, 徐照龙, 周玲, 刘晓庆, 陈新, 杜建厂. 基于靶向测序技术的菜豆SNP液相芯片开发及验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1017-1032. |
| [3] | 孙挺, 蒋茹佳, 施政, Menachem Moshelion, 孙玉东, 程瑞, 徐沛. 菜豆“水分利用效率黄金时段”量化解析方法的建立及应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 656-668. |
| [4] | 罗新锐, 张晓旭, 王玉萍, 王智, 马媛媛, 周丙月. 普通菜豆Trihelix基因家族鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2775-2790. |
| [5] | 吴丹, 柳佳欣, 卓林熙, 李钰, 罗英, 周勇, 杨有新, 余婷. CaWRKY39在辣椒响应疫霉菌侵染中的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2297-2310. |
| [6] | 李宇腾, 陈瑶, 任恒泽, 李聪聪, 王浩乾, 曹红利, 岳川, 郝心愿, 王新超. 茶树CsIDM的鉴定、表达分析及互作验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1679-1696. |
| [7] | 陈玲, 郭铖, 贾安宁, 邓丛良, 种焱, 史喜菊, 李永强. 侵染牡丹的苹果茎沟病毒分离物基因组测序及分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(12): 2735-2747. |
| [8] | 刘志远, 徐兆生, 张合龙, 钱 伟. 无筋菜豆新品种‘蔬豆6号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 135-136. |
| [9] | 王沙, 张心慧, 赵玉洁, 李变变, 招雪晴, 沈雨, 董建梅, 苑兆和. 石榴花青苷合成相关基因PgMYB111的克隆与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1883-1894. |
| [10] | 钟静, 赵丽玲, 李婷婷, 张水英, 陈越, 丁铭. 侵染凤仙花的菜豆金色花叶病毒的鉴定及基因组结构分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1136-1144. |
| [11] | 相立, 赵蕾, 王玫, 吕毅, 王艳芳, 沈向, 陈学森, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 苹果MdWRKY74的克隆和功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 482-492. |
| [12] | 贾瑾, 徐云龙, 周佳乐, 杨小芬, 钟永辉, 曾继吾, 洪霓, 王国平, 彭抒昂, 丁芳. ‘Cocktail’葡萄柚黄龙病菌检测及鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 590-596. |
| [13] | 宋放, 李子璇, 王策, 王志静, 何利刚, 蒋迎春, 吴黎明, 白福玺. 柑橘菌根信号受体蛋白基因LYK2的克隆及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 281-292. |
| [14] | 卢甜甜, 刘志远, 徐兆生, 张合龙, 李国亮, 折红兵, 钱伟. 菜豆花色全基因组关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 332-340. |
| [15] | 谢思艺, 周承哲, 朱晨, 詹冬梅, 陈兰, 吴祖春, 赖钟雄, 郭玉琼. 茶树CsTIFY家族全基因组鉴定及非生物胁迫和激素处理中主要基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 100-116. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司