
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 365-379.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0970
收稿日期:2024-09-15
修回日期:2024-12-23
出版日期:2025-02-25
发布日期:2025-02-23
通讯作者:
基金资助:
YAN Xu, LI Yue, FU Xiaopeng, NING Guogui, LIANG Mei*( )
)
Received:2024-09-15
Revised:2024-12-23
Published:2025-02-25
Online:2025-02-23
摘要:
利用已报道的中国古老月季‘月月粉’(Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’)的两套单倍型基因组——RcOB_hap1与RcOB_hap2,对其基因组进行全面的比较分析。同时利用生物信息方法鉴定‘月月粉’中的不平衡等位基因,开发相应的分子标记。结果表明,两套单倍型基因组共线性较好,但RcOB_hap2组装的完整性明显优于RcOB_hap1。‘月月粉’杂合度为3.48%,含有大量的单碱基变异、小片段插入或缺失以及大片段染色体变异。全基因组范围可能存在1 157对蛋白功能差异的等位基因,720对表达显著差异的等位基因。GO注释以及KEGG富集结果表明,不平衡等位基因主要参与了代谢合成调控、生长发育以及环境适应等过程。围绕‘月月粉’的花器官发育、挥发物质合成与抗病免疫反应,分别挑选了不平衡等位基因AP2、MBY4、DSC1进行分子标记开发。在183份月季材料中的分子标记结果显示,蛋白功能不完整的Hap2型AP2在现代栽培月季中被强选择,使月季具有重瓣性状;表达量低的Hap2型MBY4被多数现代月季选择,可能导致栽培月季品种酚类物质合成减少;针对DSC1,现代月季品种广泛携带了表达量低且蛋白功能受影响的Hap1型,可能使现代月季抗病性降低。
阎旭, 李月, 傅小鹏, 宁国贵, 梁梅. 中国古老月季‘月月粉’等位基因不平衡分析与分子标记开发利用[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 365-379.
YAN Xu, LI Yue, FU Xiaopeng, NING Guogui, LIANG Mei. Allele-specific Imbalance Analysis and Related Molecular Marker Development in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 365-379.
| 引物 Primer | 正引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer | 片段大小/bp Fragment size | 基因ID Gene ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP2 | TCATCTATGAAAGAATTTGGAG | GAAGGAATGCGACTGTTAGG | Hap1:962 Hap2:807 | Rc3g0243000 Rc3g0468481 |
| MYB4 | TAGGACTCAAGT TACCACAA | TCGTGAGGTACATTATCATCTA | Hap1:240 Hap2:430 | Rc7g0018900 Rc7g0178681 |
| DSC1 | CGTGAGGTACAT TATCATCTA | AAGATGACTGGACCAGAGCAA | Hap1:599 Hap2:1051 | Rc3g0384800 Rc3g0451671 |
表1 分子标记引物序列
Table 1 Primers sequence of molecular marker
| 引物 Primer | 正引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer | 片段大小/bp Fragment size | 基因ID Gene ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP2 | TCATCTATGAAAGAATTTGGAG | GAAGGAATGCGACTGTTAGG | Hap1:962 Hap2:807 | Rc3g0243000 Rc3g0468481 |
| MYB4 | TAGGACTCAAGT TACCACAA | TCGTGAGGTACATTATCATCTA | Hap1:240 Hap2:430 | Rc7g0018900 Rc7g0178681 |
| DSC1 | CGTGAGGTACAT TATCATCTA | AAGATGACTGGACCAGAGCAA | Hap1:599 Hap2:1051 | Rc3g0384800 Rc3g0451671 |

图1 ‘月月粉’不同单倍型基因组比较与杂合度分析 A:RcOB_hap1和RcOB_hap2大片段比对结果;B:两个单倍型基因组特有染色体区域上的基因与转座子占比;C:RcOB_hap1和RcOB_hap2共线性基因点阵图;D:‘月月粉’重测序数据的读段频率分布图(K = 17)
Fig. 1 Comparative analysis of the RcOB_hap1 and RcOB_hap2 genomes in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ A:Large segment alignment of RcOB_hap1 and RcOB_hap2;B:Distribution percentage of the gene and transposon on the specific chromosome regions for two genomes;C:Dot-plots of the whole-genomic gene alignment between RcOB_hap1 and RcOB_hap2;D:Distribution survey of the K-mer for‘Old Blush’re-sequence genome(K = 17)
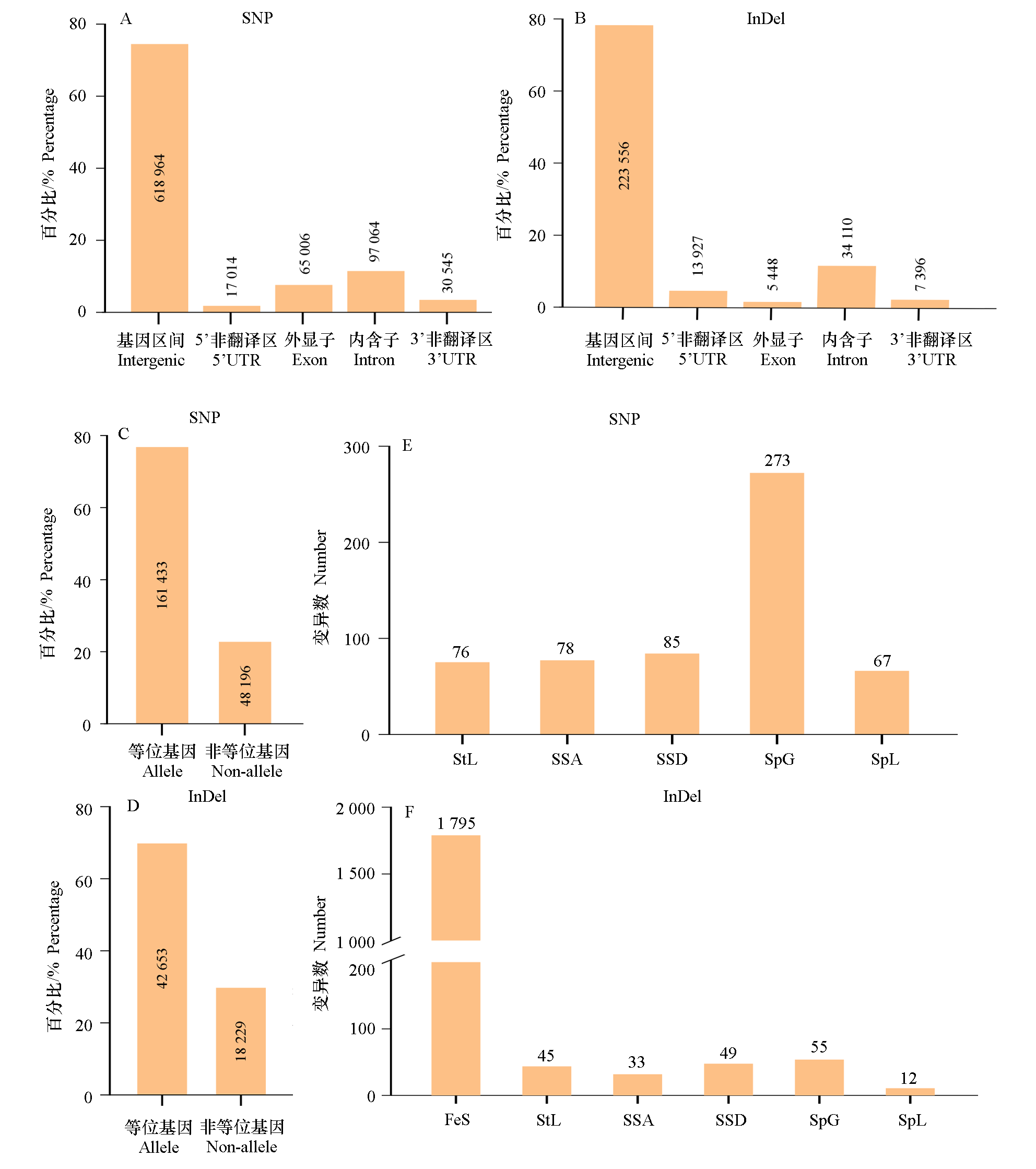
图2 ‘月月粉’单倍型基因组RcOB_hap1和RcOB_hap2之间DNA序列变异 SNP:单核苷酸多态性;InDel:小片段插入/缺失;FeS:移码突变;StL:起始密码子丢失突变;SSA:剪接受体位点突变;SSD:剪接供体位点突变;SpG:终止密码子获得/提前终止突变;SpL:终止密码子丢失突变
Fig. 2 The DNA sequence variation between RcOB_hap1 and RcOB_hap2 genomes in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ SNP:Single nucleotide polymorphism;InDel:Insertion or deletion;FeS:Frame shift;SpL:Stop codon lost;SSA:Splice site acceptor;SSD:Splice site donor;SpG:Stop codon gained or premature stop;StL:Start codon lost
| 基因 Gene | SNP编号 SNP ID | Hap1型读长数 Hap1-type read number | Hap2型读长数 Hap2-type read number | 变化倍数的log2值 log2 fold change | ASE基因 (是/否) ASE gene (yes/no) | P值 P-value | 基因注释 Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc1g0350201 | Chr01_43344427 | 0 | 131 | -10.17 | 是 Yes | 8.28e-108 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr01_43344491 | 0 | 149 | |||||
| Chr01_43344521 | 0 | 136 | |||||
| Chr01_43344550 | 0 | 158 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 0 | 574 | |||||
| Rc2g0129651 | Chr02_45318393 | 31 | 53 | -0.83 | 否 No | 1.15e-4 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr02_45318518 | 30 | 53 | |||||
| Chr02_45318530 | 30 | 56 | |||||
| Chr02_45318549 | 30 | 53 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 121 | 215 | |||||
| Rc3g0468121 | Chr03_14202662 | 86 | 13 | 2.83 | 是 Yes | 1.70e-47 | 磷酸酶 Protein phosphatase |
| Chr03_14202709 | 81 | 13 | |||||
| Chr03_14202963 | 69 | 10 | |||||
| Chr03_14203072 | 75 | 8 | |||||
| Chr03_14204073 | 84 | 11 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 395 | 55 | |||||
| Rc5g0077891 | Chr05_83740197 | 173 | 133 | 0.35 | 否 No | 2.74e-4 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr05_83740290 | 132 | 107 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 305 | 240 |
表3 示例基因在花瓣组织中的ASE分析结果
Table 3 ASE analysis result of gene examples in petal
| 基因 Gene | SNP编号 SNP ID | Hap1型读长数 Hap1-type read number | Hap2型读长数 Hap2-type read number | 变化倍数的log2值 log2 fold change | ASE基因 (是/否) ASE gene (yes/no) | P值 P-value | 基因注释 Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc1g0350201 | Chr01_43344427 | 0 | 131 | -10.17 | 是 Yes | 8.28e-108 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr01_43344491 | 0 | 149 | |||||
| Chr01_43344521 | 0 | 136 | |||||
| Chr01_43344550 | 0 | 158 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 0 | 574 | |||||
| Rc2g0129651 | Chr02_45318393 | 31 | 53 | -0.83 | 否 No | 1.15e-4 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr02_45318518 | 30 | 53 | |||||
| Chr02_45318530 | 30 | 56 | |||||
| Chr02_45318549 | 30 | 53 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 121 | 215 | |||||
| Rc3g0468121 | Chr03_14202662 | 86 | 13 | 2.83 | 是 Yes | 1.70e-47 | 磷酸酶 Protein phosphatase |
| Chr03_14202709 | 81 | 13 | |||||
| Chr03_14202963 | 69 | 10 | |||||
| Chr03_14203072 | 75 | 8 | |||||
| Chr03_14204073 | 84 | 11 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 395 | 55 | |||||
| Rc5g0077891 | Chr05_83740197 | 173 | 133 | 0.35 | 否 No | 2.74e-4 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr05_83740290 | 132 | 107 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 305 | 240 |
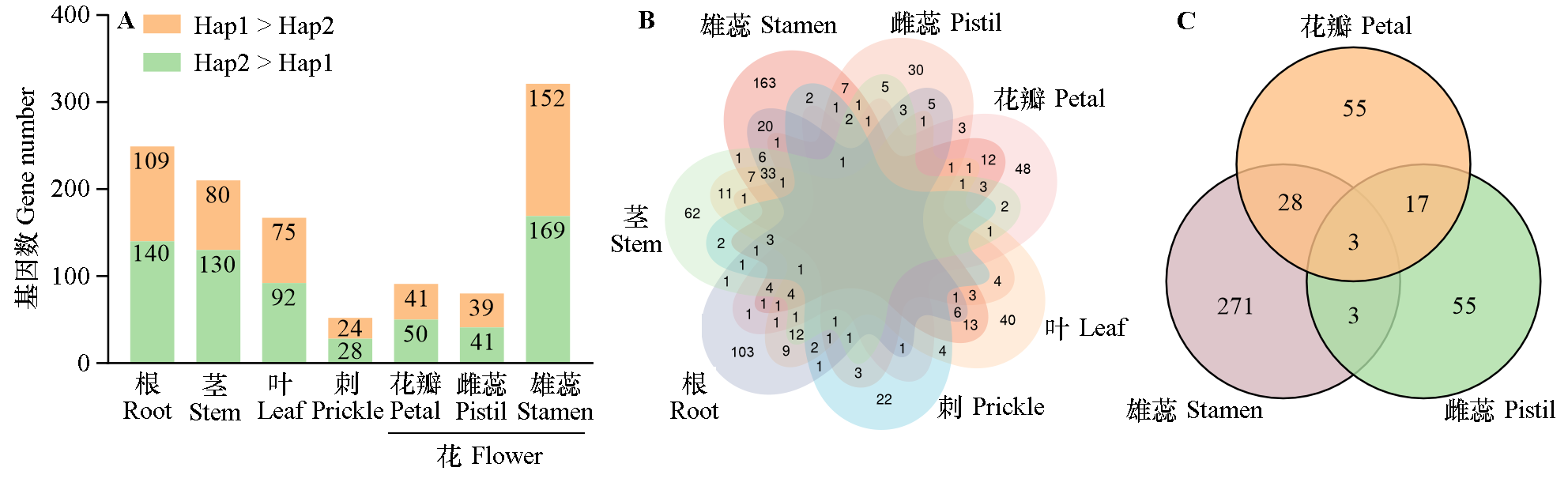
图3 ‘月月粉’不同组织中的ASE基因数(A)、七维韦恩图(B)和三维韦恩图(C)
Fig. 3 ASE genes in different tissues of Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’(A),seven-dimensional Venn diagram(B)and three-dimensional Venn diagram(C)
| 基因 Gene | 等位基因比较 Allele comparison | 基因型频率 Frequency of different genotypes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因表达(有/无差异) Gene expression(DIF./No DIF.) | 蛋白功能(有/无差异) Protein function(DIF./No DIF.) | 36份野生种 36 wild species | 147份栽培种 147 cultivated varieties | ||
| AP2 | 有差异(茎和刺:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in stem & prickle) | 有差异(Hap2型:提前终止) DIF.(Hap2-type:Premature) | Hap2: 8 Hap1&2: 6 Hap2&3: 6 Hap3: 9 No band: 7 | Hap2: 45 Hap1&2: 18 Hap2&3: 70 Hap3: 5 Hap1&3: 6 No band: 3 | |
| MYB4 | 有差异(茎和雌蕊:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in stem & pistil) | 无差异 No DIF. | Hap1: 17 Hap2: 1 Hap1&2: 11 No band: 7 | Hap1: 94 Hap2: 5 Hap1&2: 47 No band: 1 | |
| DSC1 | 有差异(所有组织:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in all tissues) | 有差异(Hap1型:移码) (Hap1-type:Frame shift) | Hap1: 3 Hap2: 3 Hap1&2: 6 No band: 24 | Hap1: 83 Hap2: 5 Hap1&2: 30 No band: 29 | |
表4 AP2、MYB4与DSC1的两个等位拷贝比较与在183份材料中的频率
Table 4 Comparison of two alleles of AP2,MYB4 and DSC1 and their frequency in 183 materials
| 基因 Gene | 等位基因比较 Allele comparison | 基因型频率 Frequency of different genotypes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因表达(有/无差异) Gene expression(DIF./No DIF.) | 蛋白功能(有/无差异) Protein function(DIF./No DIF.) | 36份野生种 36 wild species | 147份栽培种 147 cultivated varieties | ||
| AP2 | 有差异(茎和刺:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in stem & prickle) | 有差异(Hap2型:提前终止) DIF.(Hap2-type:Premature) | Hap2: 8 Hap1&2: 6 Hap2&3: 6 Hap3: 9 No band: 7 | Hap2: 45 Hap1&2: 18 Hap2&3: 70 Hap3: 5 Hap1&3: 6 No band: 3 | |
| MYB4 | 有差异(茎和雌蕊:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in stem & pistil) | 无差异 No DIF. | Hap1: 17 Hap2: 1 Hap1&2: 11 No band: 7 | Hap1: 94 Hap2: 5 Hap1&2: 47 No band: 1 | |
| DSC1 | 有差异(所有组织:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in all tissues) | 有差异(Hap1型:移码) (Hap1-type:Frame shift) | Hap1: 3 Hap2: 3 Hap1&2: 6 No band: 24 | Hap1: 83 Hap2: 5 Hap1&2: 30 No band: 29 | |
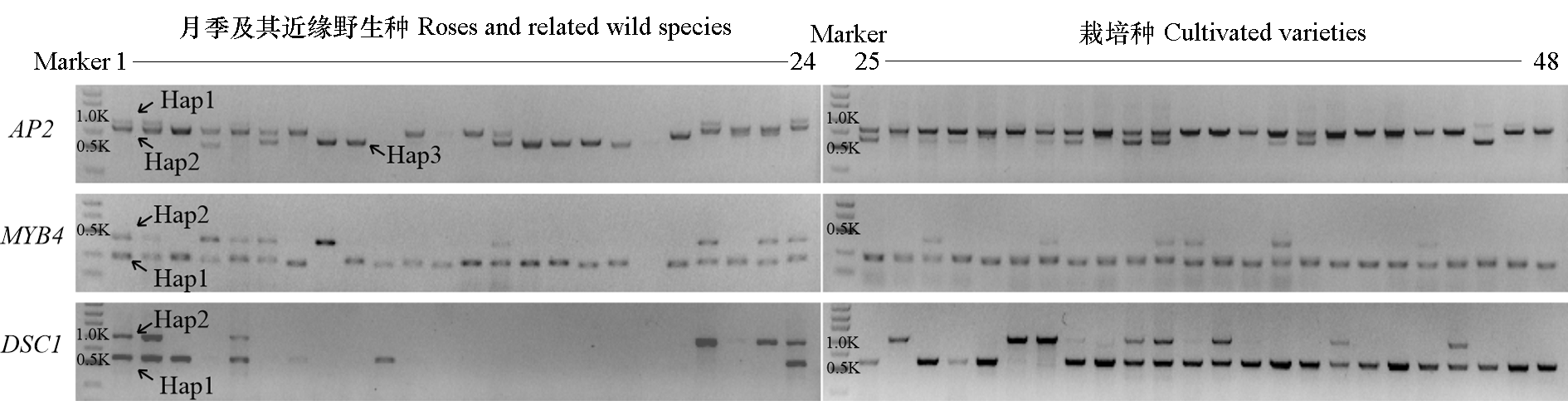

图6 分子标记在月季及近缘野生种(泳道1 ~ 24)与栽培月季(泳道25 ~ 48)中的扩增图谱 泳道1为‘月月粉’月季;泳道46为单瓣‘甜美人’月季
Fig. 6 Amplification results of molecular markers among roses and related wild species(line 1 to 24) and cultivated varieties(line 25 to 48) Line 1 is Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’;Line 46 is Rosa hybrida var.‘Sweet Pretty’with simple flower
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab293 pmid: 34597405 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq342 pmid: 21068208 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30918-4 pmid: 30150746 |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.022087 pmid: 15194819 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00971-3 pmid: 34980919 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
焦文标. 2013. 基于二代测序技术的甜橙基因组杂合度与起源研究[硕士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.9.1211 pmid: 7919989 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.177246 pmid: 27765809 |
| [22] |
pmid: 15049300 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-0428-4 pmid: 32161269 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
李淑斌, 周宁宁, 周青, 晏慧君, 蹇洪英, 王其刚, 陈敏, 邱显钦, 张颢, 王书芳, 李树发, 唐开学. 2015. ‘月月粉’连续开花习性遗传规律分析. 园艺学报, 42 (11):2223-2228.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
李叶飞. 2020. 迷人的英国玫瑰. 天津: 天津人民出版社.
|
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0597-3 pmid: 32055045 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa115 pmid: 32096823 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1038/nrg2815 pmid: 20567245 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv074 pmid: 25819081 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1153917 pmid: 18436778 |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
doi: 10.1111/pbi.13806 pmid: 35258172 |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-00941-x pmid: 34140668 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-2285-x pmid: 32054439 |
| [49] |
|
|
文晓鹏, 邓秀新. 2002. 五种蔷薇属植物基因组DNA的提取及鉴定. 种子,(6):18-21.
|
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.103499 pmid: 19474198 |
| [53] |
|
|
张佐双, 朱秀珍. 2006. 中国月季. 北京: 中国林业出版社.
|
| [1] | 刘港运, 段世享, 许娜娜, 郭姚淼, 豆峻岭, 杨森, 牛欢欢, 刘东明, 杨路明, 胡建斌, 朱华玉. 分子标记辅助构建甜瓜矮化基因Cmerecta近等基因系[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2048-2062. |
| [2] | 杨碧楠, 李博文, 杨振宇, 徐奕芃, 阎韵清, 娄玉霞, 奉树成, 明凤. 月季‘安吉拉’热胁迫反应机制及功能基因的挖掘[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1284-1296. |
| [3] | 王雯雨, 王家荫, 杜婷婷, 张晶晶, 张超, 辛翠花, 郭江波, 裴海霞. 月季RhRNF185-like的克隆及其对花瓣衰老影响分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1047-1055. |
| [4] | 阳茜, 饶得花, 刘洪, 杨哲, 苏镇柱, 江院, 殷纪伟, 徐振江. 卡特兰DUS测试性状与SSR标记的关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 787-803. |
| [5] | 兰伟, 孟艳琼, 宣云, 朱糠宁, 丁晓浩, 樊德新, 康丽云. 月季新品种‘颍荷’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 925-926. |
| [6] | 徐琴, 王嘉颖, 张曼楠, 萧志浩, 郑涵楷, 卢永恩, 王涛涛, 张余洋, 张俊红, 叶志彪, 叶杰. 番茄苗期耐盐相关遗传位点鉴定及分子标记开发[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 239-252. |
| [7] | 李春牛, 苏群, 李先民, 黄展文, 孙明艳, 卢家仕, 王虹妍, 卜朝阳. 茉莉花全基因组SSR标记开发及其亲缘关系鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2343-2357. |
| [8] | 吕红豪, 张扬勇, $\boxed{\hbox{方智远}}$, 杨丽梅, 庄木, 刘玉梅, 王勇, 季家磊, 李占省, 韩风庆. 春甘蓝新品种‘中甘D22’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 213-214. |
| [9] | 周 燕 , 高述民 , 崔荣峰 , 孙丽萍 , 付子豪 , . 月季新品种‘燕京黄’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 149-150. |
| [10] | 马梦宇, 胡耀芳, 古琳, 李振坚, 钱永强, 巨关升, 刘俊祥, 孙振元. 瓶插月季枝条光照处理对切花寿命的延长效应[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1343-1354. |
| [11] | 刘嘉琦, 公菲菲, 张颢, 景维坤, 瞿素萍, 马男, 高俊平, 孙小明. 月季茉莉酸羧基甲基转移酶基因RhJMT对花瓣衰老的调控[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1025-1036. |
| [12] | 高俊平, 马男, 周厚高, 王嘉曦, 张常青, 李永红, 周晓锋, 孙小明. 切花月季新品种‘菲韵’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 915-916. |
| [13] | 申玉晓, 邹金玉, 罗平, 尚文倩, 李永华, 何松林, 王政, 石力匀. ‘月月粉’月季PP2C家族基因鉴定及非生物胁迫响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(10): 2139-2156. |
| [14] | 崔建, 钟雄辉, 刘泽慈, 陈登辉, 李海龙, 韩睿, 乐祥庆, 康俊根, 王超. 结球甘蓝染色体片段替换系构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 65-78. |
| [15] | 刘艺平, 倪梦辉, 吴芳芳, 刘红利, 贺丹, 孔德政. 荷花花器官性状与SSR标记的关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 103-115. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司