
园艺学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 285-302.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0470
赵晓勇1,2, 欧若含1,2, 梅宇洋2, 崔桐灏2, 刘意隆1,2, 谢小东1,3, 曹培健1,3, 李鲜1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-07-16
修回日期:2025-12-16
出版日期:2026-01-25
发布日期:2026-01-26
通讯作者:
基金资助:
ZHAO Xiaoyong1,2, OU Ruohan1,2, MEI Yuyang2, CUI Tonghao2, LIU Yilong1,2, XIE Xiaodong1,3, CAO Peijian1,3, LI Xian1,2,*( )
)
Received:2025-07-16
Revised:2025-12-16
Published:2026-01-25
Online:2026-01-26
摘要:
总结了植物蛋白质N-糖基化修饰相关的N-糖链结构特征及其加工途径,重点梳理了参与N-糖基化修饰的关键酶,包括寡糖转移酶(oligosaccharyltransferase,OST)、α-葡萄糖苷酶(α-glucosidase,GCS)、α-甘露糖苷酶(α-mannosidase,α-Man)及其他N-糖链加工酶的酶学特性与生物学功能研究进展。
赵晓勇, 欧若含, 梅宇洋, 崔桐灏, 刘意隆, 谢小东, 曹培健, 李鲜. 植物蛋白质N-糖基化修饰关键酶及其生物学 功能研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(1): 285-302.
ZHAO Xiaoyong, OU Ruohan, MEI Yuyang, CUI Tonghao, LIU Yilong, XIE Xiaodong, CAO Peijian, LI Xian. Research Progress on Key Enzymes Involved in Protein N-Glycosylation and Their Biological Functions in Plants[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2026, 53(1): 285-302.
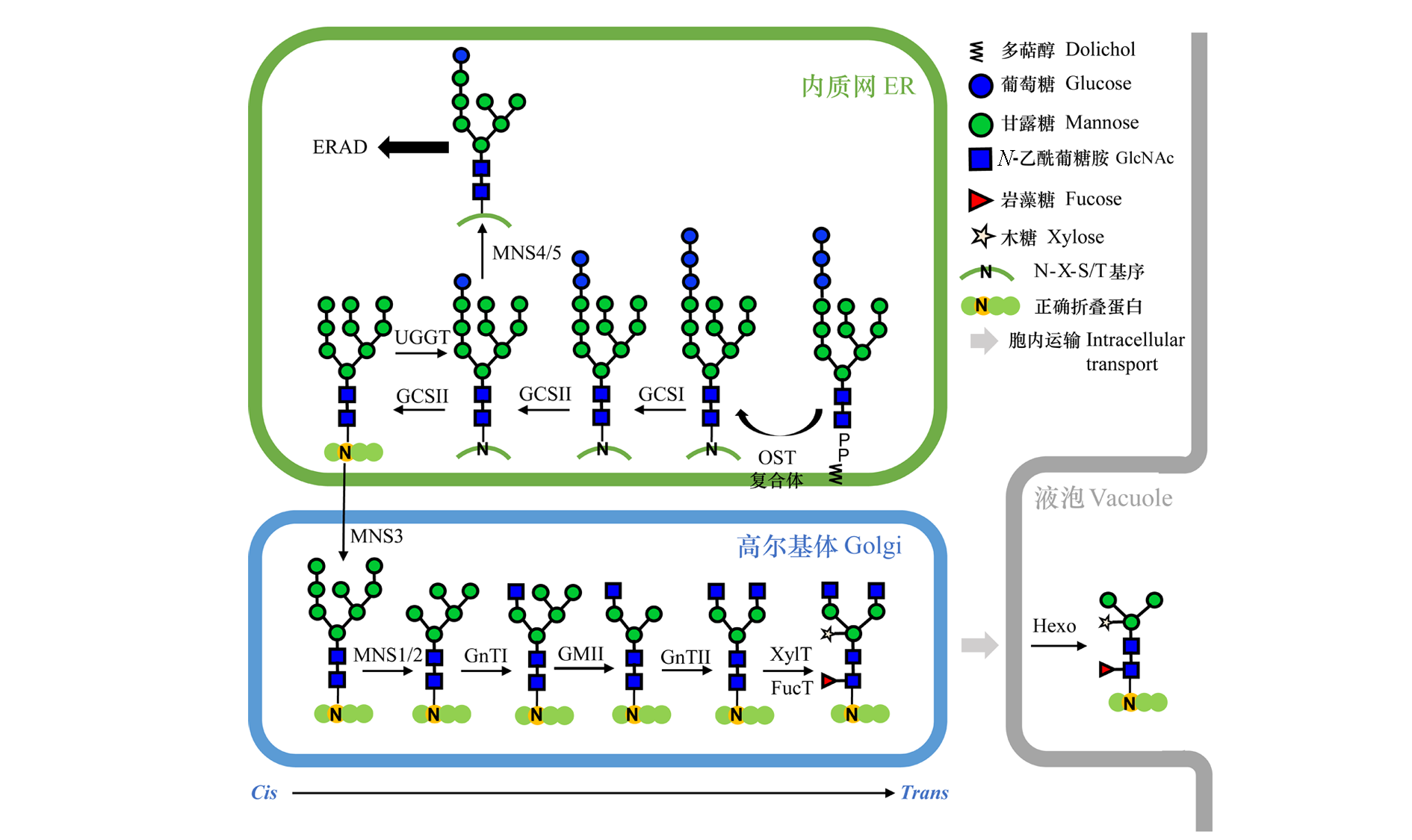
图2 植物蛋白质N-糖基化主要加工途径(Nagashima et al.,2018) OST:寡糖转移酶;GCS:α-葡萄糖苷酶;UGGT:UDP-葡萄糖:糖蛋白葡萄糖基转移酶;MNS3:内质网Ⅰ型α-甘露糖苷酶;MNS1/2:高尔基Ⅰ型α-甘露糖苷酶;GnTI:N-乙酰葡糖胺转移酶Ⅰ;GMⅡ:高尔基Ⅱ型α-甘露糖苷酶;GnTⅡ:N-乙酰葡糖胺转移酶Ⅱ;XylT:β-1,2-木糖转移酶;FucT:α-1,3-岩藻糖转移酶;Hexo:β-D-N-乙酰己糖胺酶;ERAD:内质网相关的降解途径;ER:内质网高尔基体
Fig. 2 Main processing pathways of protein N-glycosylation in plant(Nagashima et al.,2018) OST:Oligosaccharyltransferase;GCS:α-Glucosidase;UGGT:UDP-glucose glycoprotein glucosyltransferase;MNS3:ER-type α-mannosidase Ⅰ;MNS1/2:Golgi α-mannosidaseⅠ;GnTⅠ:N-acetylglucosaminyltransferaseⅠ;GMⅡ:Golgi α-mannosidase Ⅱ;GnTⅡ:N-acetylglucosaminyl- transferase Ⅱ;XylT:β-1,2-Xylosyltransferase;FucT:α-1,3-Fucosyltransferase;Hexo:β-D-N-acetylhexosaminidase;ERAD:Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation;ER:Endoplasmic reticulum
| 酶 Enzyme | 物种 Species | 突变体 Mutant | 技术 Technology | 表型 Phenotype | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OST | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | stt3a | T-DNA | 盐胁迫下根系生长受抑制,根尖肿胀 Root growth is suppressed under salt stress,root tips become swollen | Koiwa et al., |
| stt3b | 不引起盐敏感性Insensitive to salt stress | ||||
| stt3a stt3b | 双突配子体致死Diploid gametophytes lethal | ||||
| dgl1 | 细胞生长和分化缺陷,异位胼胝质积累 Cell growth and differentiation defects,ectopic callose accumulates | Lerouxel et al., | |||
| 互花米草 Spartina alterniflora | stt3a,stt3b | 拟南芥stt3a突变体 中异源表达 overexpression in Arabidopsis stt3a mutant | 显著缓解拟南芥盐敏感表型 Significantly alleviates the salt-sensitive phenotype in Arabidopsis | Jiang et al., | |
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | dgl1 | 甲基磺酸乙酯 | 根细胞长度缩短,根分生组织缩小和细胞死亡 Root cell length shortened,root meristem reduced and cell dies | Qin et al., | |
| (EMS)诱变 ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) mutagenesis | |||||
| GCSI | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | gcs1/knf | T-DNA | 胚胎发育异常,结晶纤维素含量显著下降 Embryo development abnormal,crystalline cellulose content significantly decreased | Boisson et al., Gillmor et al., |
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | mogs | EMS诱变 EMS mutagenesis | 根发育受阻Root development defect | Wang et al., | |
| GCSII | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | rsw3 | T-DNA | 根径向膨胀,纤维素含量降低;抑制幼苗发育 | Burn et al., |
| Roots radially expand,cellulose content decreases; seedling development inhibits | Soussillane et al., | ||||
| α-ManI | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | mns3 | T-DNA | N-聚糖组成异常但无明显植株表型 N-glycan composition abnormal but no obvious plant phenotype | Liebminger et al., |
| mns1 mns2 | T-DNA | 双突根系形态变化 Double mutant root morphology changes | Liebminger et al., | ||
| 对盐和渗透胁迫表现出超敏感性 Hypersensitivity to salt and osmotic stress | Liu et al., | ||||
| 易受丁香假单胞菌番茄致病变种DC3000侵染 Susceptible to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 infection | Jia et al., | ||||
| mns1 mns2 mns3 | T-DNA | 根系变短粗、径向膨大、细胞壁结构异常 Roots become short and thick,radially swollen,cell wall structure abnormal | Liebminger et al., | ||
| mns4 mns5 | T-DNA | 盐胁迫下根系生长受抑制 Root growth is suppressed under salt stress | Hüttner et al., | ||
| 百脉根 Lotus japonicus | man I | LORE1 retrotransposon | 生长受阻,种子减少Growth suppressed,seeds reduced | Pedersen et al., | |
| 人参 Panax ginseng | GH47-E | 拟南芥中异源表达 overexpression in Arabidopsis | 种荚数量、长度和千粒质量增加, 抽薹和开花时间提前,根系变长 silique number,length and thousand-grain weight increased,bolting and flowering time advanced,root system becomes longer | 王铎, | |
| α-ManII | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | hgl1 | T-DNA | 盐敏感性增强Salt sensitivity enhanced | Kang et al., |
| Kaulfürst-Soboll et al., | |||||
| 辣椒 Capsicum annuum | ManII | RNAi | 果实延迟软化Fruit softening delayed | Ghosh et al., | |
| 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum | ManII | RNAi/过表达 RNAi/overexpression | 果实成熟软化进程减缓/果实软化时间提前,软化速率加快 Process of fruit ripening and softening slows down/ accelerates | Meli et al., | |
| RNAi | 种子数量减少,叶片卷曲 Seed number reduced,leaves curl | Kaulfürst-Soboll et al., | |||
| 甜瓜 Cucumis melo | ManII | RNAi/过表达 RNAi/overexpression | 果实延缓成熟,硬度高、质量大/果实提前成熟,硬度小、质量小Fruit ripening delayed,with high hardness,large weight/fruit ripening advanced,with low hardness,small weight | 党维鑫, | |
| GnTI | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | cgl1 | T-DNA | 盐胁迫下根系生长受抑制Root growth suppressed under salt stress | Kang et al., |
| 生长素敏感性增加Auxin sensitivity increased | Frank et al., | ||||
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | gnt1 | T-DNA | 分蘖失败、叶片脆性增加,生殖发育停滞 Tillering fails,leaf brittleness increases,reproductive development stops | Fanata et al., | |
| 百脉根 Lotus japonicus | gnt I | LORE1 retrotransposon | 严重生长缺陷,致死性 Wevere growth defects,lethal | Pedersen et al., | |
| 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum | GNTI | RNAi | 影响果实成熟和脱落 Fruit ripening affected and abscission | Kaulfürst-Soboll et al., | |
| GnTII | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | gnt2 | T-DNA | 胁迫条件下生长发育严重受损,影响植物激素响应 Growth and development severely impaired under stress,plant hormone response affected | Yoo et al., |
| XylT | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | xylT | T-DNA | 无明显表型 no obvious phenotype | Kang et al., |
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | rcn11 | γ射线 | 多种胁迫下生长受到影响,如种子萌发等 Growth(including seed germination)affected under stress conditions | Takano et al., | |
| 番茄 Lycopersicon esculentum | xylT | RNAi | 致敏性降低 Sensitivity reduced | Paulus et al., | |
| FucT | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | fucTa fucTb | T-DNA | 无明显表型 No obvious phenotype | Kang et al., |
| fucTa fucTb xylT | T-DNA | 根系发育受阻,盐胁迫敏感性增加 Root development suppressed,salt stress sensitivity increased | Kang et al., | ||
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | fuct | T-DNA | 花药花粉发育受损,植株生长减弱;发育异常, 对稻瘟病菌的敏感性增加 Anther pollen development impaired,plant growth weakened;development abnormal,susceptibility to Magnaporthe oryzae increased | Sim et al., | |
| Harmoko et al., |
表1 植物N-糖基化相关酶的生物学功能鉴定
Table 1 Biological function identification of enzymes involved in plant N-glycosylation
| 酶 Enzyme | 物种 Species | 突变体 Mutant | 技术 Technology | 表型 Phenotype | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OST | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | stt3a | T-DNA | 盐胁迫下根系生长受抑制,根尖肿胀 Root growth is suppressed under salt stress,root tips become swollen | Koiwa et al., |
| stt3b | 不引起盐敏感性Insensitive to salt stress | ||||
| stt3a stt3b | 双突配子体致死Diploid gametophytes lethal | ||||
| dgl1 | 细胞生长和分化缺陷,异位胼胝质积累 Cell growth and differentiation defects,ectopic callose accumulates | Lerouxel et al., | |||
| 互花米草 Spartina alterniflora | stt3a,stt3b | 拟南芥stt3a突变体 中异源表达 overexpression in Arabidopsis stt3a mutant | 显著缓解拟南芥盐敏感表型 Significantly alleviates the salt-sensitive phenotype in Arabidopsis | Jiang et al., | |
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | dgl1 | 甲基磺酸乙酯 | 根细胞长度缩短,根分生组织缩小和细胞死亡 Root cell length shortened,root meristem reduced and cell dies | Qin et al., | |
| (EMS)诱变 ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) mutagenesis | |||||
| GCSI | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | gcs1/knf | T-DNA | 胚胎发育异常,结晶纤维素含量显著下降 Embryo development abnormal,crystalline cellulose content significantly decreased | Boisson et al., Gillmor et al., |
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | mogs | EMS诱变 EMS mutagenesis | 根发育受阻Root development defect | Wang et al., | |
| GCSII | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | rsw3 | T-DNA | 根径向膨胀,纤维素含量降低;抑制幼苗发育 | Burn et al., |
| Roots radially expand,cellulose content decreases; seedling development inhibits | Soussillane et al., | ||||
| α-ManI | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | mns3 | T-DNA | N-聚糖组成异常但无明显植株表型 N-glycan composition abnormal but no obvious plant phenotype | Liebminger et al., |
| mns1 mns2 | T-DNA | 双突根系形态变化 Double mutant root morphology changes | Liebminger et al., | ||
| 对盐和渗透胁迫表现出超敏感性 Hypersensitivity to salt and osmotic stress | Liu et al., | ||||
| 易受丁香假单胞菌番茄致病变种DC3000侵染 Susceptible to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 infection | Jia et al., | ||||
| mns1 mns2 mns3 | T-DNA | 根系变短粗、径向膨大、细胞壁结构异常 Roots become short and thick,radially swollen,cell wall structure abnormal | Liebminger et al., | ||
| mns4 mns5 | T-DNA | 盐胁迫下根系生长受抑制 Root growth is suppressed under salt stress | Hüttner et al., | ||
| 百脉根 Lotus japonicus | man I | LORE1 retrotransposon | 生长受阻,种子减少Growth suppressed,seeds reduced | Pedersen et al., | |
| 人参 Panax ginseng | GH47-E | 拟南芥中异源表达 overexpression in Arabidopsis | 种荚数量、长度和千粒质量增加, 抽薹和开花时间提前,根系变长 silique number,length and thousand-grain weight increased,bolting and flowering time advanced,root system becomes longer | 王铎, | |
| α-ManII | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | hgl1 | T-DNA | 盐敏感性增强Salt sensitivity enhanced | Kang et al., |
| Kaulfürst-Soboll et al., | |||||
| 辣椒 Capsicum annuum | ManII | RNAi | 果实延迟软化Fruit softening delayed | Ghosh et al., | |
| 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum | ManII | RNAi/过表达 RNAi/overexpression | 果实成熟软化进程减缓/果实软化时间提前,软化速率加快 Process of fruit ripening and softening slows down/ accelerates | Meli et al., | |
| RNAi | 种子数量减少,叶片卷曲 Seed number reduced,leaves curl | Kaulfürst-Soboll et al., | |||
| 甜瓜 Cucumis melo | ManII | RNAi/过表达 RNAi/overexpression | 果实延缓成熟,硬度高、质量大/果实提前成熟,硬度小、质量小Fruit ripening delayed,with high hardness,large weight/fruit ripening advanced,with low hardness,small weight | 党维鑫, | |
| GnTI | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | cgl1 | T-DNA | 盐胁迫下根系生长受抑制Root growth suppressed under salt stress | Kang et al., |
| 生长素敏感性增加Auxin sensitivity increased | Frank et al., | ||||
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | gnt1 | T-DNA | 分蘖失败、叶片脆性增加,生殖发育停滞 Tillering fails,leaf brittleness increases,reproductive development stops | Fanata et al., | |
| 百脉根 Lotus japonicus | gnt I | LORE1 retrotransposon | 严重生长缺陷,致死性 Wevere growth defects,lethal | Pedersen et al., | |
| 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum | GNTI | RNAi | 影响果实成熟和脱落 Fruit ripening affected and abscission | Kaulfürst-Soboll et al., | |
| GnTII | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | gnt2 | T-DNA | 胁迫条件下生长发育严重受损,影响植物激素响应 Growth and development severely impaired under stress,plant hormone response affected | Yoo et al., |
| XylT | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | xylT | T-DNA | 无明显表型 no obvious phenotype | Kang et al., |
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | rcn11 | γ射线 | 多种胁迫下生长受到影响,如种子萌发等 Growth(including seed germination)affected under stress conditions | Takano et al., | |
| 番茄 Lycopersicon esculentum | xylT | RNAi | 致敏性降低 Sensitivity reduced | Paulus et al., | |
| FucT | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | fucTa fucTb | T-DNA | 无明显表型 No obvious phenotype | Kang et al., |
| fucTa fucTb xylT | T-DNA | 根系发育受阻,盐胁迫敏感性增加 Root development suppressed,salt stress sensitivity increased | Kang et al., | ||
| 水稻 Oryza sativa | fuct | T-DNA | 花药花粉发育受损,植株生长减弱;发育异常, 对稻瘟病菌的敏感性增加 Anther pollen development impaired,plant growth weakened;development abnormal,susceptibility to Magnaporthe oryzae increased | Sim et al., | |
| Harmoko et al., |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1021/cr3003714 pmid: 23531120 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b03558 pmid: 31459963 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(99)00165-8 pmid: 10580125 |
| [4] |
pmid: 3609010 |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.5.1010 URL |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01483.x URL |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2018.16.issue-10 URL |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.114.250720 pmid: 25355867 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00633-8 pmid: 37528230 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
党维鑫. 2015. 转α-甘露糖苷酶基因超表达、干扰载体甜瓜株系的生理生化分析[硕士论文]. 内蒙古: 内蒙古大学.
|
|
| [17] |
pmid: 7881169 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)55439-9 URL |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.12087 pmid: 23199012 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.113.215509 pmid: 23493405 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1997.12061411.x URL |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq289 URL |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1083/jcb.200111093 URL |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2013.02.004 pmid: 23422784 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.30.21375 URL |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1093/glycob/6.1.23 pmid: 8991505 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.14031 pmid: 27241276 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1038/nature10317 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.063073 URL |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0250-z |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0101-y pmid: 30733602 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.082 pmid: 27320861 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1271/bbb.80561 URL |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1093/jb/mvq094 pmid: 20798166 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.123216 pmid: 24737672 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2018.06.005 URL |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.13847 pmid: 29385647 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.1186/s40529-015-0111-9 pmid: 28510840 |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.196097 URL |
| [46] |
pmid: 2139344 |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3054.2001.1120103.x URL |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(98)00128-7 pmid: 9878773 |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.013862 URL |
| [51] |
doi: 10.1039/D2CS00764A URL |
| [52] |
pmid: 9719679 |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1134/S1021443724604555 |
| [54] |
pmid: 12070072 |
| [55] |
pmid: 9738959 |
| [56] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2005.42.issue-4 URL |
| [57] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00238 pmid: 30141327 |
| [58] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.072363 pmid: 20023195 |
| [59] |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.178020 URL |
| [60] |
doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)34824-X URL |
| [61] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2018.01.006 URL |
| [62] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.078154 URL |
| [63] |
doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.75 |
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
doi: 10.1007/s10545-011-9337-1 URL |
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01756-5 |
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00729.x pmid: 18315532 |
| [72] |
pmid: 8981089 |
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
doi: 10.1083/jcb.201404075 pmid: 25092655 |
| [75] |
doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwz029 pmid: 30976784 |
| [76] |
doi: 10.1093/glycob/6.6.611 pmid: 8922956 |
| [77] |
doi: 10.1271/bbb.63.35 URL |
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.11.008 pmid: 19162525 |
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.13570 pmid: 28407380 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34438-z pmid: 30382146 |
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.11.017 pmid: 19111666 |
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
pmid: 12770767 |
| [87] |
doi: 10.1038/nature21695 |
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00294-x pmid: 33087899 |
| [90] |
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2017.15.issue-2 URL |
| [91] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms19041225 URL |
| [92] |
doi: 10.1007/s10719-008-9201-1 URL |
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
pmid: 26911286 |
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(04)00150-4 pmid: 15013764 |
| [97] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.052985 URL |
| [98] |
pmid: 10781814 |
| [99] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2006.45.issue-5 URL |
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
pmid: 11229321 |
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
pmid: 12671684 |
| [106] |
doi: 10.1111/brv.v97.2 URL |
| [107] |
pmid: 2271638 |
| [108] |
doi: 10.1093/brain/awu019 pmid: 24566669 |
| [109] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.102.4.1109 pmid: 8278542 |
| [110] |
|
|
王铎. 2018. 人参α-甘露糖苷酶PgGH47基因家族生物信息学分析及转化番茄的研究[硕士论文]. 长春: 吉林农业大学.
|
|
| [111] |
|
|
王铎, 张美萍, 王义. 2018. α-甘露糖苷酶的研究进展. 生命科学, 30 (6):652-658.
|
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2014.78.issue-4 URL |
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
pmid: 11358875 |
| [116] |
doi: 10.1271/bbb.69.1111 URL |
| [117] |
doi: 10.1271/bbb.68.2547 URL |
| [118] |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.R400036200 URL |
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA117.000165 URL |
| [121] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.2c00662 URL |
| [122] |
pmid: 1822240 |
| [123] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.04.031 pmid: 22633491 |
| [1] | 何义仲, 庞尧, 孙浩谦, 李欣宇, 王振豪, 钱卫, 张印, 何发, 尹杭, 赖恒鑫, 淳长品, 付行政, 彭良志. 果实抗坏血酸生物合成、代谢循环及其调控的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1899-1915. |
| [2] | 刘晓梦, 唐宁, 陈泽雄, 罗成荣, 张威威, 许锋. 植物表皮毛发育研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(4): 705-718. |
| [3] | 解林峰,任传宏,张 波,徐昌杰,李 鲜*. 植物类黄酮生物合成相关UDP–糖基转移酶研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(9): 1655-1669. |
| [4] | 高 振1,骆 萌1,王 磊1,宋士任1,赵丽萍1,许文平1,张才喜1,王世平1,2,*,马 超1,*. 植物环状RNA研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(1): 171-181. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司