
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 185-199.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0985
• Cultivation·Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
DU Haowei, LIAO Wei, HUANG Xue, YANG Jinzhi, SHEN Wanqi, ZHANG Dongmei, LIU Junwei*( ), LI Guohuai
), LI Guohuai
Received:2024-06-17
Revised:2024-10-24
Online:2025-01-25
Published:2025-01-19
Contact:
LIU Junwei
DU Haowei, LIAO Wei, HUANG Xue, YANG Jinzhi, SHEN Wanqi, ZHANG Dongmei, LIU Junwei, LI Guohuai. Intercropping of Allium,Mustard,and Alfalfa on the Growth Performance and Soil Environment of Replant Soil-Cultivated Peach Plants[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 185-199.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0985
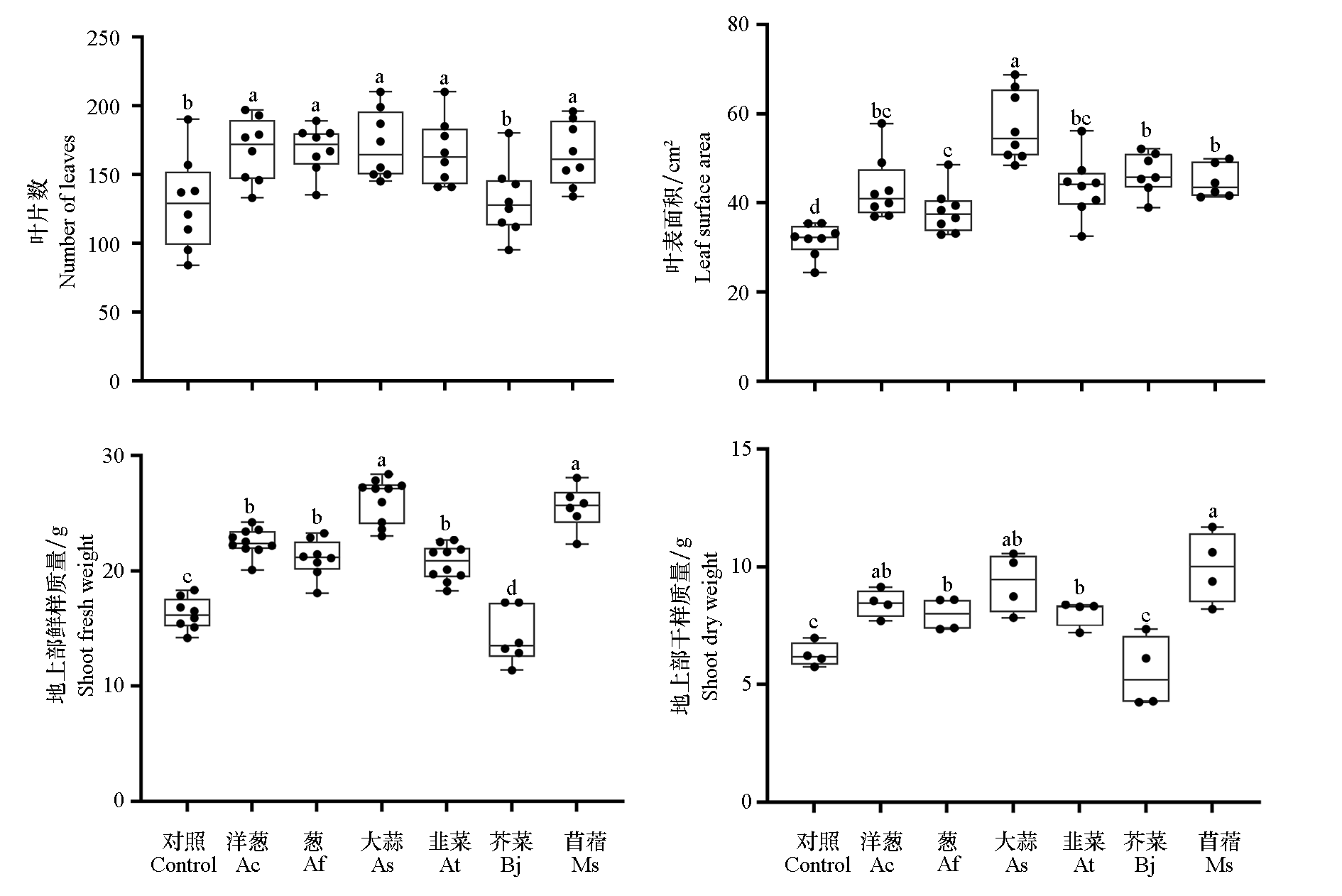
Fig. 2 Growth performance of replant soil-potted peach seedlings under different mixed cropping treatments Ac:Allium cepa;Af:A. fistulosum;At:A. tuberosum;As:A. sativum;Bj:Brassica juncea;Ms:Medicago sativa. Different letters indicate significant differences as conducted by Duncan’s multiple range test at P < 0.05. The same below
| 作物 Crop | 有机质/% Ogranic matter | mg · kg-1 | pH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碱解氮 Alkali- hydrolyzable N | 速效磷 Available P | 速效钾 Available K | 有效钙 Available Ca | 有效镁 Available Mg | 有效钠 Available Na | |||
| 对照Control | 4.05 ± 0.11 b | 71.93 ± 3.86 b | 19.20 ± 0.92 a | 98.58 ± 5.86 b | 2 602.74 ± 66.78 b | 546.72 ± 17.42 b | 120.09 ± 1.22 c | 5.90 ± 0.09 a |
| 芥菜Brassica juncea | 3.89 ± 0.04 b | 80.78 ± 3.75 a | 16.27 ±0.72 b | 103.90 ± 3.29 b | 2 894.05 ± 146.79 a | 632.42 ± 25.21 a | 128.86 ± 2.19 b | 5.77 ± 0.07 b |
| 苜蓿Medicago sativa | 3.62 ± 0.03 c | 74.46 ± 2.48 ab | 17.62 ±0.62 ab | 120.49 ± 3.11 a | 2 702.73 ± 62.20 ab | 617.22 ± 17.11 a | 137.67 ± 3.16 a | 5.72 ± 0.02 b |
| 大蒜Allium sativum | 4.24 ± 0.16 a | 74.48 ± 2.77 ab | 17.64 ±1.13 ab | 118.94 ± 5.80 a | 2 246.67 ± 112.66 c | 532.36 ± 28.34 b | 122.44 ± 2.81 c | 5.81 ± 0.07 ab |
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of peach replanted soil under different mixed cropping treatments with peach seedlings
| 作物 Crop | 有机质/% Ogranic matter | mg · kg-1 | pH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碱解氮 Alkali- hydrolyzable N | 速效磷 Available P | 速效钾 Available K | 有效钙 Available Ca | 有效镁 Available Mg | 有效钠 Available Na | |||
| 对照Control | 4.05 ± 0.11 b | 71.93 ± 3.86 b | 19.20 ± 0.92 a | 98.58 ± 5.86 b | 2 602.74 ± 66.78 b | 546.72 ± 17.42 b | 120.09 ± 1.22 c | 5.90 ± 0.09 a |
| 芥菜Brassica juncea | 3.89 ± 0.04 b | 80.78 ± 3.75 a | 16.27 ±0.72 b | 103.90 ± 3.29 b | 2 894.05 ± 146.79 a | 632.42 ± 25.21 a | 128.86 ± 2.19 b | 5.77 ± 0.07 b |
| 苜蓿Medicago sativa | 3.62 ± 0.03 c | 74.46 ± 2.48 ab | 17.62 ±0.62 ab | 120.49 ± 3.11 a | 2 702.73 ± 62.20 ab | 617.22 ± 17.11 a | 137.67 ± 3.16 a | 5.72 ± 0.02 b |
| 大蒜Allium sativum | 4.24 ± 0.16 a | 74.48 ± 2.77 ab | 17.64 ±1.13 ab | 118.94 ± 5.80 a | 2 246.67 ± 112.66 c | 532.36 ± 28.34 b | 122.44 ± 2.81 c | 5.81 ± 0.07 ab |

Fig. 6 Relative abundance of rhizosphere fungal(A,C)and bacterial(B,D-F)communities of peach plants grown in replanted soil under different mixed cropping treatments Asterisks indicate significant differences between treatments and the control as conducted by Tukey test at * P < 0.05,** P < 0.01
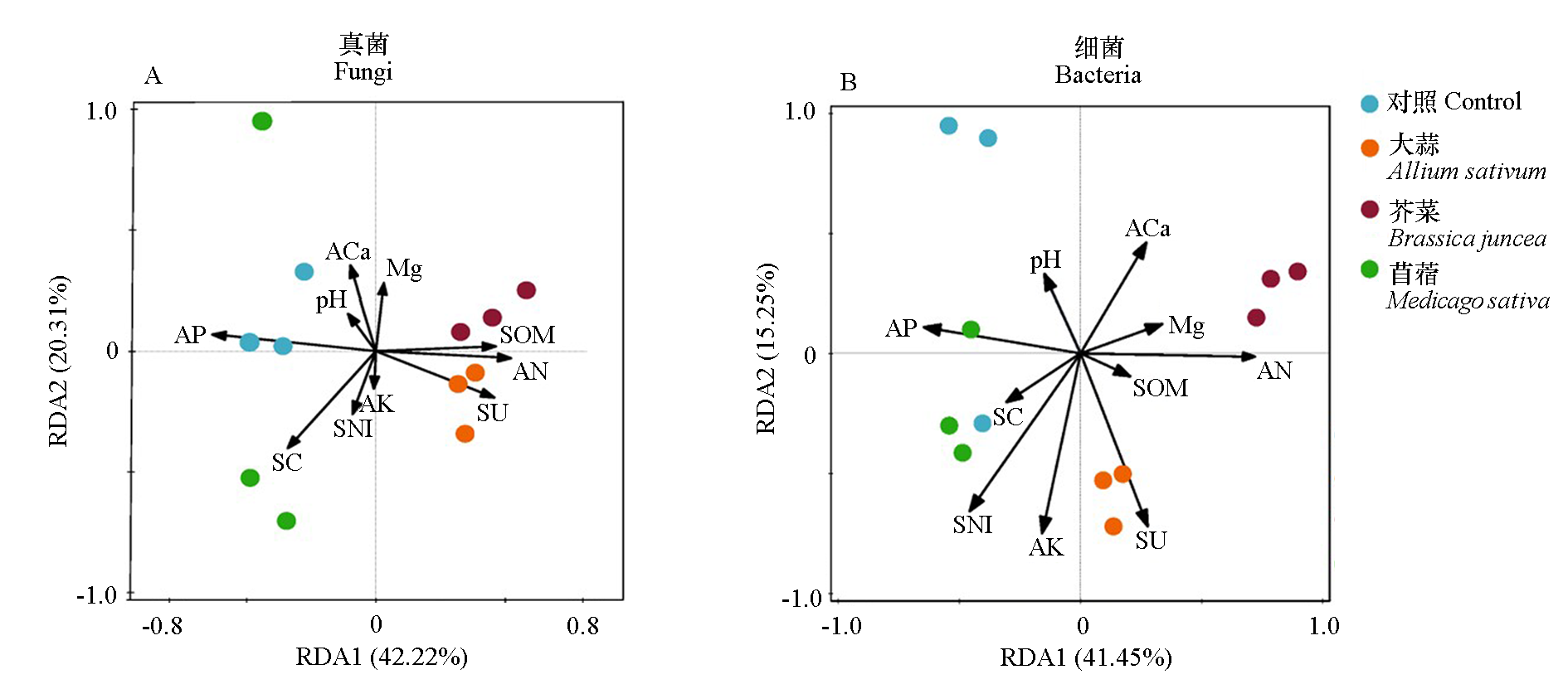
Fig. 7 Redundancy analysis of soil physiochemical properties and microbial community under different mixed copping treatments AN:Available nitrogen,AP:Available phosphate,AK:Available potassium;Aca:Available calcium;SOM:Soil organic matter; SC:Soil catalase,SU:Soil urease;SNI:Soil neutral invertase. The dots of different colors represent different sample points. The quadrant of each environmental factor represents the positive and negative correlation between the environmental factor and the sorting axis. The length of the arrow represents the degree of correlation(the longer the arrow,the greater the correlation,and vice versa)
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
黄煜峰. 2022. 连作土壤灭菌和不同孔径浸提液对桃苗生长的影响[硕士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0680-9 pmid: 32483328 |
| [12] |
|
|
李梦洁, 何昊, 朱炜, 李玺来, 刘军伟, 李国怀. 2019. 桃树根皮腐解物成分鉴定及其高效降解菌的鉴定和应用研究. 园艺学报, 46 (S1):2504.
|
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12342 pmid: 26892826 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
|
刘涛, 沃林峰, 赵丽, 杨丽娜, 房明华, 毛文龙, 胡渊渊. 2019. 不同连作土壤处理对再植水蜜桃苗生长状况及光合特性的影响. 经济林研究, 37 (1):173-180.
|
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0187 URL |
|
刘英浩, 李允, 吕伟静, 陈冉, 姜伟涛, 尹承苗, 毛志泉, 王艳芳. 2024. 不同温度烧制的生物炭对苹果连作土壤真菌群落结构的影响. 园艺学报, 51 (8):1853-1867.
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
潘凤兵, 陈冉, 姜伟涛, 王海燕, 吕毅, 沈向, 陈学森, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 2022. 不同蛋白发酵物对连作土壤微生物环境和平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (2):395-406.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0066 URL |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
|
宋士清, 王久兴. 2016. 蔬菜栽培制度. 设施蔬菜栽培. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
王芳, 王晓立, 张颖, 张楠. 2022. 设施蔬菜复种连作对土壤理化性质和生物学特性的影响. 江苏农业科学, 50 (7):214-220.
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
|
王功帅. 2018. 环渤海连作土壤真菌群落结构分析及混作葱减轻苹果连作障碍的研究[博士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
王海燕, 盛月凡, 李前进, 王玫, 潘凤兵, 陈学森, 沈向, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 2022. 葱、芥菜和小麦轮作对老龄苹果园土壤环境的影响. 园艺学报, 46 (11):2224-2238.
|
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0941 URL |
|
王晓琪, 姜伟涛, 姚媛媛, 尹承苗, 陈学森, 毛志泉. 2020. 苹果连作障碍土壤微生物的研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (11):2223-2237.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
王志强, 牛良, 鲁振华, 崔国朝, 曾文芳, 潘磊, 宗学普. 2016. 抗重茬桃砧木新品种‘中桃砧1号’的选育. 果树学报, 33 (4):504-508.
|
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.21775/cimb.030.089 pmid: 30070653 |
| [33] |
|
|
吴凤芝, 赵凤艳, 刘元英. 2000. 设施蔬菜连作障碍原因综合分析与防治措施. 东北农业大学学报, 31:241-247.
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
杨洪强. 2014. 有机生态园的生态防护. 有机农业生产原理与技术. 北京: 中国农业出版社.
|
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0524 URL |
|
尹承苗, 王玫, 王嘉艳, 陈学森, 沈向, 张民, 毛志泉. 2017. 苹果连作障碍研究进展. 园艺学报, 44 (11):2215-2230.
|
|
| [38] |
|
|
曾维爱, 杨昭玥, 黄洋, 谷亚冰, 陶界锰, 刘勇军, 谢鹏飞, 蔡海林, 尹华群. 2022. 长期连作农田土壤细菌群落结构和共现网络拓扑性质对土壤理化性质的响应. 微生物学报, 62 (6):2403-2416.
|
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0604 URL |
|
张帆, 杨阳, 王鸿, 张雪冰. 2024. 生物肥和有机肥对桃重茬土理化性状和细菌群落的改善作用. 园艺学报, 51 (9):2089-2104.
|
|
| [40] |
|
|
赵雅姣, 刘晓静, 童长春, 吴勇. 2020. 紫花苜蓿/玉米间作对紫花苜蓿结瘤固氮特性的影响. 草业学报, 29 (1):95-105.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2019383 |
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0858 URL |
|
周杰, 师恺, 夏晓剑, 周艳虹, 喻景权. 2022. 中国蔬菜栽培科技60年回顾与展望. 园艺学报, 49 (10):2131-2142.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0858 URL |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [1] | ZHOU Ping, YAN Shaobin, GUO Rui, JIN Guang. Identification and Expressional Analysis of MGT Gene Family in Prunus persica [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 463-478. |
| [2] | PAN Jiajia, ZHANG Dongmei, MENG Jian, GAO Sunan, ZHU Kaijie, LIU Junwei, LI Guohuai. Optimization and Validation of PpPDS Gene Silencing Induced by Prunus Necrotic Ring Spot Virus in Prunus persica [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1587-1600. |
| [3] | LI Chunhong, WANG Kaituo, LEI Changyi, XU Feng, JI Nana, JIANG Yongbo. Identification of TGA Gene Family in Peach and Analysis of Expression Mode Involved in a BABA-Induced Disease Resistance [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 265-280. |
| [4] | LIU Liying1,*,XU Chao1,*,LIU Kexin1,CHI Xiaoli1,ZHU Hao1,ZHANG Xiao1,JIN Xiao1,LIU Weiwei1,SUN Zhongtao1,**,and MAO Zhiquan2,**. Effects of Two Endophytic Antagonistic Bacteria on Growth of Pot Experiment Malus hupehensis Seedlings and the Soil Enzymes Activity Under Continuous Cropping Conditions [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(7): 1238-1248. |
| [5] | LIU Liying1,*,LIU Kexin1,*,CHI Xiaoli1,ZHANG Xiao1,XU Chao1,ZHU Hao1,JIN Xiao1,LIU Weiwei1,SUN Zhongtao1,**,and MAO Zhiquan2,**. Effects of Bioorganic Fertilizer SNB-86 Special for Continuous Cropping Apple on Malus hupehensis Seedlings and Soil Environment Under Replant Disease Condition [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2018, 45(10): 2008-2018. |
| [6] | XU Shaozhuo1,LIU Yusong1,XIA Mingxing2,WANG Yingping2,CHEN Xuesen1,SHEN Xiang1,YIN Chengmiao1,*,and MAO Zhiquan1,*. Dazomet Fumigation and Short-time Allium fistulosum Rotation Can Significantly Reduce the Apple Replant Disease [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2018, 45(1): 11-20. |
| [7] | YIN Cheng-miao1,XIANG Li1,SUN Chuan-xiang1,SHEN Xiang1,CHEN Xue-sen1,ZHOU Hui2,and MAO Zhi-quan1,*. Effects of Different Apple Rootstocks on the Soil Microbial Quantity and Enzyme Activity of Apple Replanted Orchard Soil [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(12): 2423-2431. |
| [8] | FU Xue-Qin, LIU Ju-Er, HUANG Wen-Xin. Effects of Natural Grass on Soil Microbiology,Nutrient and Fruit Quality of Nanfeng Tangerine Yard [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2015, 42(8): 1551-1558. |
| [9] | SUN Bu-lei,WANG Yan-fang,ZHANG Xian-fu,SHEN Xiang,CHEN Xue-sen,and MAO Zhi-quan. Effect of Residual Roots on the Biomass of Malus hupehensis Seedlings,Phenolic Acids and Microbiology in the Soil of Continuous Cropping [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2015, 42(1): 131-139. |
| [10] | LIU Tong-Jin, CHENG Zhi-Hui, ZHAO Hui-Ling, CHANG Li, YU Ting, Imran Ahmad . [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2013, 40(3): 555-561. |
| [11] | XU Qiang;XIE Bao-ying;LU Tao;and CHENG Zhi-hui;. Studies on Uptake and Utilization of Nitrogen,Phosphorus and Potassium and Yield Advantage in Capsicum/Maize Relay Intercropping System [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2010, 37(8): 1247-1256. |
| [12] | ZHANG Liang;CHENG Zhi-hui;ZHOU Yan-li;DONG Xiao-yan;and WEI Ling. Variation of Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities in the Rhizosphere Soil of Lily at Different Developmental Periods [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2008, 35(7): 1031-1038. |
| [13] | Sun Yan;Zhou Tianfu;Wang Yunyue;Chen Jianbin;He Xiahong;Li Chengyun;Zhu Youyong. Effect of Intercropping on Disease Management and Yield of Chilli Pepper and Maize [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2006, 33(5): 995-1000. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd