
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1216-1226.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0571
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Zhichao1, GUO Xinmiao2, WANG Hui1, XIE Yan1, GAO Yanxia1, LI Jisheng1, GAO Yujun1,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-20
Revised:2024-04-02
Online:2024-12-18
Published:2024-06-21
Contact:
GAO Yujun
SUN Zhichao, GUO Xinmiao, WANG Hui, XIE Yan, GAO Yanxia, LI Jisheng, GAO Yujun. Mechanism of miR408-MnBBP Module Regulating Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Mulberry[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1216-1226.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0571
| 基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| miR408a | ATGCACTGCCTCTTCCCTGGC | |
| AtCHS(At5G13930) | ACATGCCTGGTGCTGACTAC | AAAAGAGCCTGACCGACGAG |
| AtANS(At4G22880) | GAGTCTAGCAAAAAGCGGAA | GATTGTGGGAACTTGAGGAC |
| AtDFR(At5G42800) | CGCCGAAGAGAAAGGATTAG | TATGAGCGTTGCATAAGTCG |
| AtUFGT(At1G07250) | TCGTCCATATTGAATTCGCC | GAATGGAGGAGGATCTTGGA |
| AtFLS(At5G63590) | TGGAATCACACTCCTAGTCG | CCCTATGCTCCACACTCTTA |
| AtARPN(AT2G02850) | GACTCTGGTATCTGGACCTT | CAGTTGTTGTAACTTCCGCT |
| AtCSD1(At1G08830) | TTCAACCCCGATGGTAAAAC | ACAGCCCTACCAACAATAGA |
| AtCSD2(At2G28190) | GGCCTCATGGATTTCATCTC | ATCGGCATTGGCATTTATGT |
| AtSPL7 (At5G18830) | GTATGCTTCCTTGTTCGTGT | AATATCCGCTTCACAATCCG |
| U6(LOC21407692) | GATAAAATTGGAACGATACAG | ATTTGGACCATTTCTCGATTT |
| Ribosomal protein L15 (LOC21390050) | GGCTATGTGATTTACCGTGTT | TTGGTCCAGTATGAGTTGAGAA |
| Actin 2(AT3G18780) | GCCATCCAAGCTGTCTC | GCTCGTAGTCAACAGCAACAA |
Table 1 List of RT-qPCR primer sequences used for genes
| 基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| miR408a | ATGCACTGCCTCTTCCCTGGC | |
| AtCHS(At5G13930) | ACATGCCTGGTGCTGACTAC | AAAAGAGCCTGACCGACGAG |
| AtANS(At4G22880) | GAGTCTAGCAAAAAGCGGAA | GATTGTGGGAACTTGAGGAC |
| AtDFR(At5G42800) | CGCCGAAGAGAAAGGATTAG | TATGAGCGTTGCATAAGTCG |
| AtUFGT(At1G07250) | TCGTCCATATTGAATTCGCC | GAATGGAGGAGGATCTTGGA |
| AtFLS(At5G63590) | TGGAATCACACTCCTAGTCG | CCCTATGCTCCACACTCTTA |
| AtARPN(AT2G02850) | GACTCTGGTATCTGGACCTT | CAGTTGTTGTAACTTCCGCT |
| AtCSD1(At1G08830) | TTCAACCCCGATGGTAAAAC | ACAGCCCTACCAACAATAGA |
| AtCSD2(At2G28190) | GGCCTCATGGATTTCATCTC | ATCGGCATTGGCATTTATGT |
| AtSPL7 (At5G18830) | GTATGCTTCCTTGTTCGTGT | AATATCCGCTTCACAATCCG |
| U6(LOC21407692) | GATAAAATTGGAACGATACAG | ATTTGGACCATTTCTCGATTT |
| Ribosomal protein L15 (LOC21390050) | GGCTATGTGATTTACCGTGTT | TTGGTCCAGTATGAGTTGAGAA |
| Actin 2(AT3G18780) | GCCATCCAAGCTGTCTC | GCTCGTAGTCAACAGCAACAA |

Fig. 2 miR408 targets MnBBP in mulberry A:Mapping of cleavage sites of degraded transcript fragments of MnBBP by degradome sequencing. The red dot indicating read counts consistent with miR408-directed cleavage;B:Mapping of miR408-directed cleavage sites of MnBBP using 5'-RACE. Arrow indicates cleavage site,and the numbers show the frequency of sequenced clones.
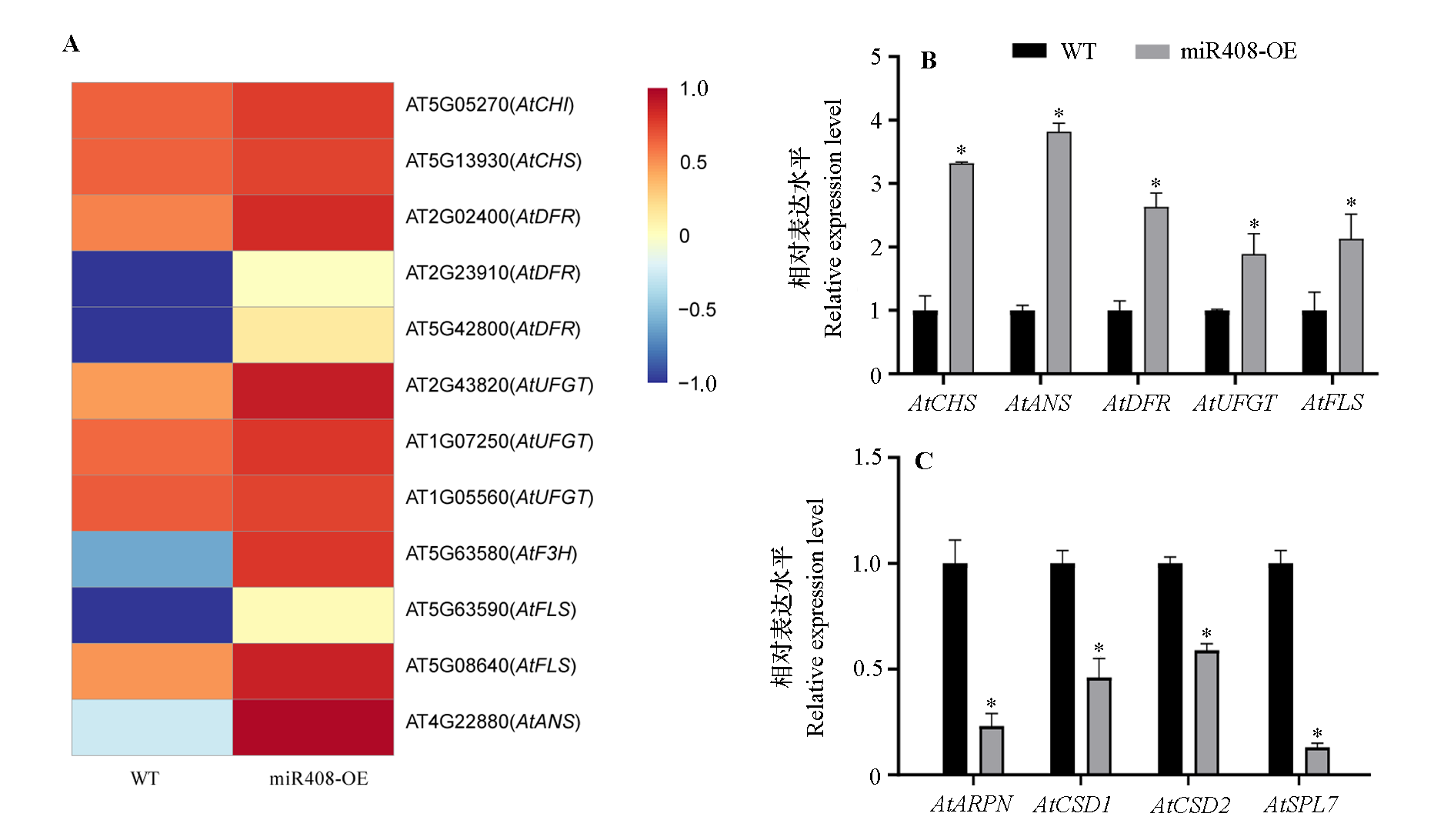
Fig. 6 Heatmap of transcriptome(A)and qRT-PCR(B,C)of differentilly expressed genes related to anthocyanin synthesis between the miR408-OE and wild type(WT)in Arabidopsis * P < 0.05.
| [1] |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801406200 pmid: 18408011 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.17431 pmid: 33908060 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
刘炜婳, 倪珊珊, 林争春, 林玉玲, 赖钟雄. 2017. 植物miR408家族的进化与分子特性. 应用与环境生物学报, 23 (6):1042-1051.
|
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
|
马圣运. 2012. Os-miR408的表达模式及其在水稻种子发育中的功能[硕士论文]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
pmid: 12011346 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.73 pmid: 18546601 |
| [22] |
|
|
孙德权, 郭启高, 胡玉林, 谢江辉. 2009. 改良Trizol法提取香蕉叶片总RNA. 广东农业科学, 19 (5):162-164.
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1047 pmid: 21113019 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
|
王惠聪, 黄旭明, 胡桂兵, 黄辉白. 2004. 荔枝果皮花青苷合成与相关酶的关系研究. 中国农业科学,(12):2028-2032.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
卫春会, 张兰兰, 邓杰, 任志强, 徐升东, 程铁辕. 2020. 桑葚花青素超声波辅助提取工艺优化. 食品工业, 41 (12):96-100.
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
肖竞淇, 陈怡, 谢岩, 韩子琦, 褚升瑞, 董银星, 邢炳楠, 刘善正, 孙志超. 2021. 桑树miR858及MYB转录因子基因在桑椹花青素合成过程中的表达分析. 蚕业科学, 47 (6):501-509.
|
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [1] | XIA Zhilei, YU Bingxin, YANG Meng, LIAN Zilin, GUAN Lilan, HE Yichao, YAN Shuangshuang, CAO Bihao, and QIU Zhengkun, . Fine-Mapping and KASP Marker Development for the Gene Underlying Green Fruit in Eggplant [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2008-2018. |
| [2] | ZHONG Yizhong, WANG Zhou, XIE Jingyao, WANG Zhengpeng, HAO Jingjing, LIU Chaoyang, ZHANG Wei, WU Jing, ZHONG Ziqin, CHEN Chengjie, and HE Yehua, . Flowering and Fruiting Behaviour of Two South China Plum Cultivars with Different Ripening Stages in an Area Near the Northern Boundary of the Tropics [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2105-2119. |
| [3] | LIU Yanfei, HE Xin, TIAN Ailin, and LIU Zhande. A New High-Quality Kiwifruit Cultivar with Better Storability‘Jinfu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2219-2220. |
| [4] | LI Jie, WU Chao, JIA Xiangqian, WANG Juan. Screening of Ziziphus jujuba‘Hupingzao’Fruit Coloring Substances and Their Related Genes [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1728-1742. |
| [5] | LI Xujiao, LÜ Qi, YAO Dongdong, ZHAO Fengyun, WANG Xiaofei, YU Kun. Effect of‘Yanfu 3’Apple Grafted with Different Rootstocks on Absorption and Utilization of 15N-urea [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1868-1880. |
| [6] | ZHANG Lihua, XU Yu, Zheng Litong, Wang Changzhi, ZHU Lingcheng, MA Baiquan, and LI Mingjun, . The Relevance Research Between Acid Transporters and Fruit Acidity [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1474-1488. |
| [7] | WANG Mengyao, WANG Mengjie, LAI Huiping, HE Yaping, YAN Lu, LI Peng, GUO Liting, and AI Ye. Research Progress on the Effect of Temperature on Anthocyanin Accumulation in Plants [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1501-1517. |
| [8] | LI Xin, CHAI Yingfang, TIAN Zhen, WANG Pengwei, and CHENG Yunjiang. Isolation and Purification of Mitochondria and Its Application in Research on Fruit Ripening and Senescence [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1516-1528. |
| [9] | HUANG Yiqi, ZHU Yuqin, DU Zhaoxuan, XU Feng, CHEN Xiaoyi, YANG Guoshun, and XU Yanshuai, . Progress on Bud Sport of Tree Fruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1547-1564. |
| [10] | ZHAO Chongbin, ZHANG Weiyin, LI Shuqing, GUO Yihan, XU Hongxia, CHEN Junwei, YANG Xianghui, PENG Ze. Quantitative Trait Locus Mapping and Analysis of Traits Related to Flower,Fruit,and Leaf in Loquat [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1189-1200. |
| [11] | ZHU Qixuan, LI Xiaoying, WU Junkai, GE Hang, CHEN Junwei, XU Hongxia. Genetic Tendency Analysis and Comprehensive Evaluation of the Fruit Traits in Loquat F1 Generation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1201-1215. |
| [12] | MA Xingyun, FAN Bingli, TANG Guangcai, JIA Zhiqi, LI Ying, XUE Dongqi, ZHANG Shiwen. Preliminary Study on the Mechanism of DXR Regulating Chloroplast Development Flower Color and Fruit Coloring in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [13] | LI Qinqin, DONG Shanrong, LUO Jianrang, ZHANG Yanlong. Cloning and Functional Analysis of PqDFR and PqANS Genes and Its Promoters from Paeonia qiui [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1256-1272. |
| [14] | DONG Xiaoke, CHEN Yuanlei, NIU Youyi, LIU Zhande, WANG Nannan. Leaf Nutrient Diagnosis of‘Xuxiang’Kiwifruit at Different Growth Stages for Achieving High and Stable Yield and High Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1345-1360. |
| [15] | QIAO Chengkui, ZHUANG Ming, TIAN Fajun, WANG Caixia, PANG Tao, CHEN Ruxia, LI Xiaoguang, CHENG Xin, XIE Hanzhong. Degradation Behaviors and Dietary Risk Assessment of Flonicamid and Spirotetramat in Kiwifruit Plantations [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1386-1402. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd