
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1048-1062.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0119
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuan Xi, Zhang Man, Ma Kaifeng( ), Wang Jia, Zhang Qixiang
), Wang Jia, Zhang Qixiang
Received:2022-12-05
Revised:2023-02-07
Online:2023-05-25
Published:2023-05-31
Contact:
Ma Kaifeng, Zhang Qixiang
E-mail:makaifeng@bjfu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Yuan Xi, Zhang Man, Ma Kaifeng, Wang Jia, Zhang Qixiang. Function and Expression Regulation Analysis of Prunus mume PmMYB21 During Filament Elongation[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 1048-1062.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0119
| 采样日期/(M-D) Sampling date | 温度/℃ Temperature | 开花阶段 Flowering stage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粉红朱砂 Fenhong Zhusha | 早绿萼 Zaolü’e | ||
| 01-09 | 0 | S2(花芽开始膨大 Bud swelling) | S2(花芽开始膨大 Bud swelling) |
| 02-09 | 0 | S4(萼片全露 Sepals clearly visible) | S2(花芽开始膨大Bud swelling) |
| 03-02 | 15 ~ 18 | S6(花瓣全露 Petal clearly visible) | S4(萼片全露 Sepals clearly visible) |
| 03-13 | 19 | S8(花盛开 Full blooming) | S6(花瓣全露 Petal clearly visible) |
| 03-19 | 23 | S8(花盛开 Full blooming) |
Table 1 Samples information of flower buds of Prunus mume‘Fenhong Zhusha’and‘Zaolü’e’
| 采样日期/(M-D) Sampling date | 温度/℃ Temperature | 开花阶段 Flowering stage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粉红朱砂 Fenhong Zhusha | 早绿萼 Zaolü’e | ||
| 01-09 | 0 | S2(花芽开始膨大 Bud swelling) | S2(花芽开始膨大 Bud swelling) |
| 02-09 | 0 | S4(萼片全露 Sepals clearly visible) | S2(花芽开始膨大Bud swelling) |
| 03-02 | 15 ~ 18 | S6(花瓣全露 Petal clearly visible) | S4(萼片全露 Sepals clearly visible) |
| 03-13 | 19 | S8(花盛开 Full blooming) | S6(花瓣全露 Petal clearly visible) |
| 03-19 | 23 | S8(花盛开 Full blooming) |
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| PmMYB21-1300F | CCAAATCGACTCTAGTCTAGA ATGGATAAAAAGCCATGCAATAGTT |
| PmMYB21-1300R | ATGGTACCGGATCCACTAGT TTACTCTCCATTTAGTAACTGCATAGACC |
| PmMYB21-1300R-TTA | ATGGTACCGGATCCACTAGT CTCTCCATTTAGTAACTGCATAGACC |
| SUPER-C-F | AGCAAGAACGGAATGCGCGTGAC |
| SUPER-C-R | TTGCCGGTGGTGCAGATGAACTTC |
| PmMYB21-qPCR-F | TGAGAAAAGGGCCATGGACC |
| PmMYB21-qPCR-R | CCTAACATCAGGCCGCAGAT |
Table 2 Primers for subcellular localization and qRT-PCR of PmMYB21
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| PmMYB21-1300F | CCAAATCGACTCTAGTCTAGA ATGGATAAAAAGCCATGCAATAGTT |
| PmMYB21-1300R | ATGGTACCGGATCCACTAGT TTACTCTCCATTTAGTAACTGCATAGACC |
| PmMYB21-1300R-TTA | ATGGTACCGGATCCACTAGT CTCTCCATTTAGTAACTGCATAGACC |
| SUPER-C-F | AGCAAGAACGGAATGCGCGTGAC |
| SUPER-C-R | TTGCCGGTGGTGCAGATGAACTTC |
| PmMYB21-qPCR-F | TGAGAAAAGGGCCATGGACC |
| PmMYB21-qPCR-R | CCTAACATCAGGCCGCAGAT |
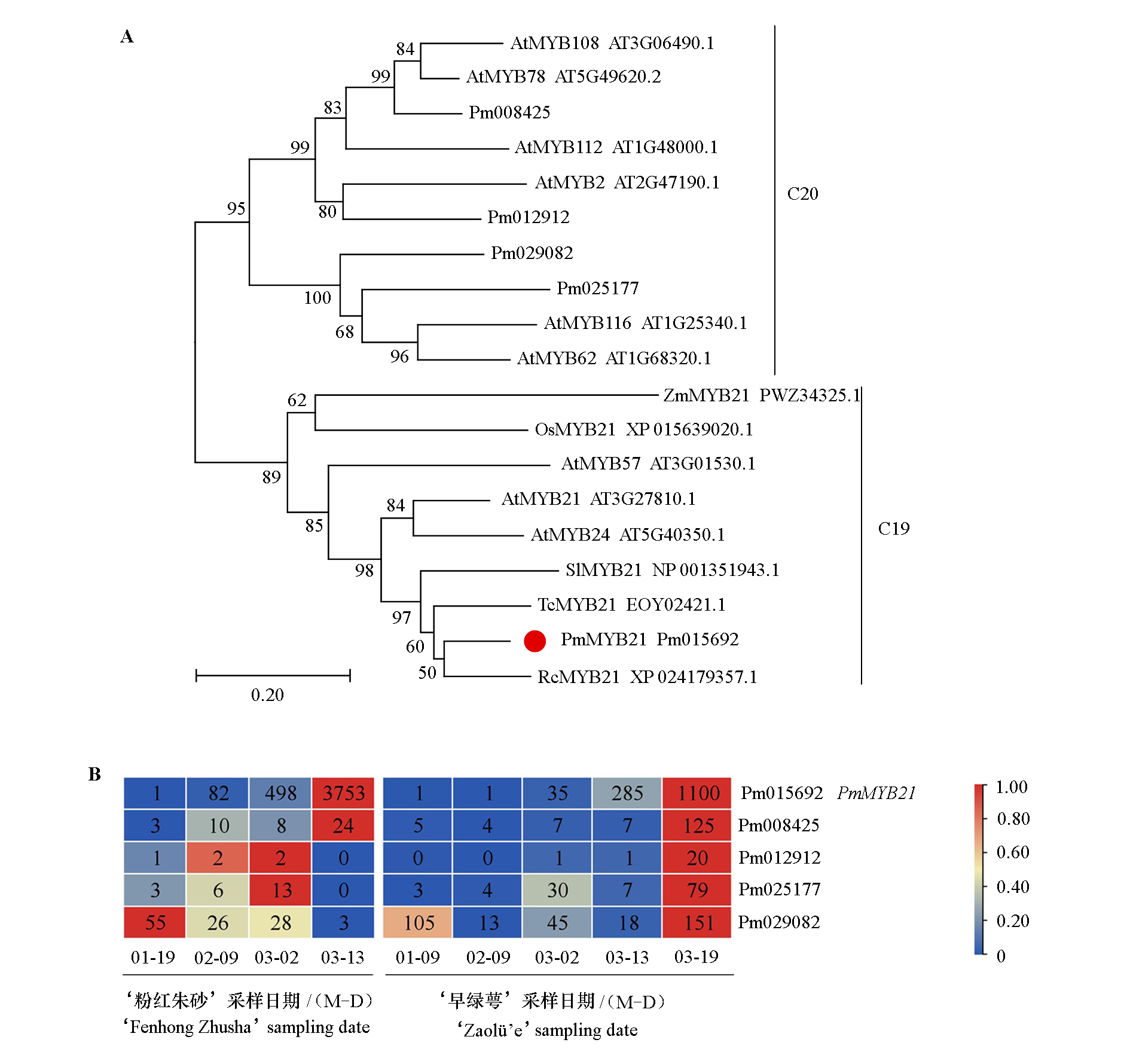
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic tree(A)of MYB21 protein from Prunus mume and other speciesand heat map(B)of the expression of five MYB homologous genes in Prunus mume Pm:Prunus mume;At:Arabidopsis thaliana;Rc:Rosa chinensis;Os:Oryza sativa;Zm:Zea mays;Sl:Solanum lycopersicum;Tc:Theobroma cacao.
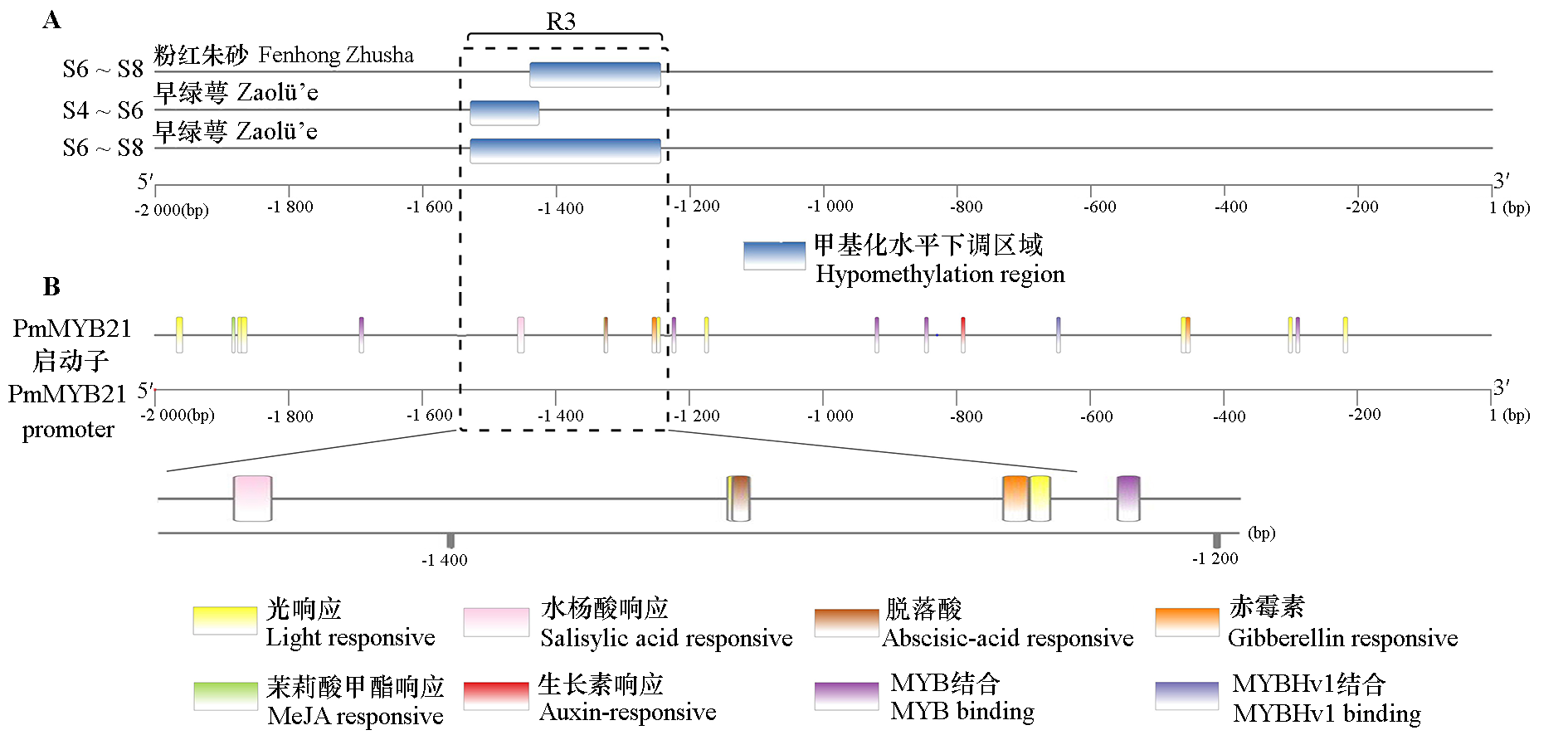
Fig. 4 Different methylation region(A)and predict cis-acting element on the promoter region(B)of PmMYB21 during flowering process of two Prunus mume cultivars S4:Sepals clearly;S6:Petal clearly visible;S8:Full blooming.
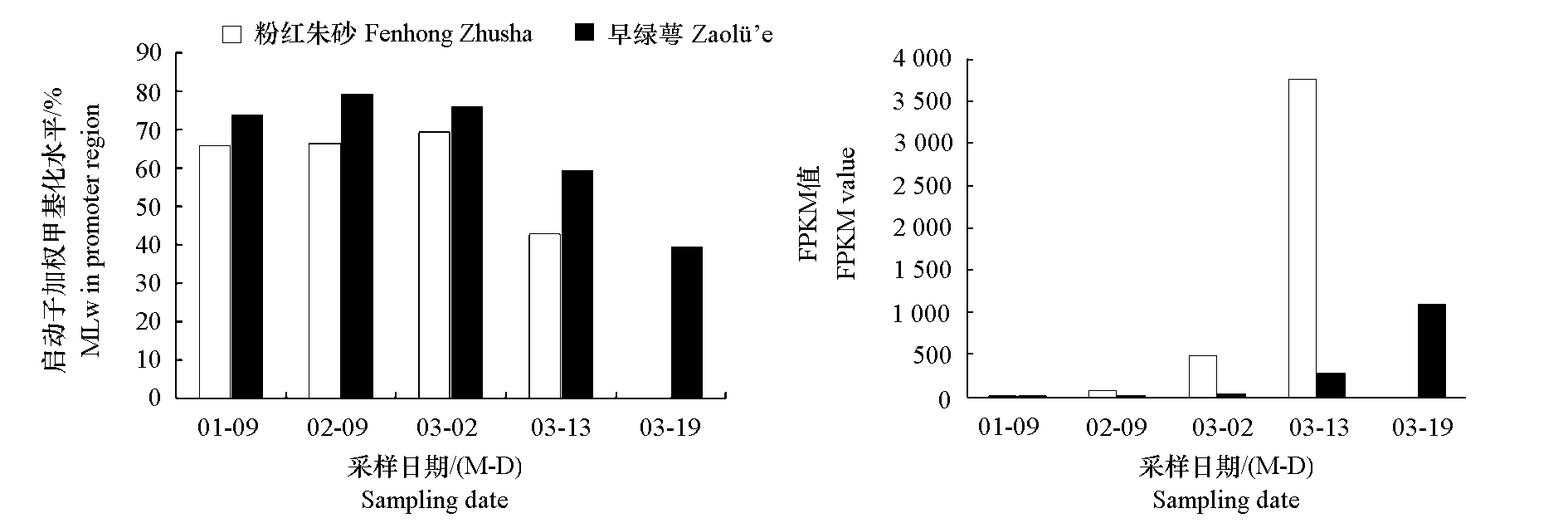
Fig. 5 The fpkm value of PmMYB21 and its weighted methylation level(MLw)in the R3 area of PmMYB21 promoter region during flowering of two Prunus mume cultivars

Fig. 7 KEGG enrichment result(A)nd Network diagram(B)of PmMYB21 co-expression genes in Prunus mume The diamonds represent transcription factors(TF). Blue:MYB;Light red:Auxin-related genes;Light purple:B3 class genes.
| 基因编号 Gene ID | 拟南芥参考基因 Match tair ID | 基因功能注释 Gene function annotions |
|---|---|---|
| Pm010066* | AT1G28300.1 | 推定的转录因子B3域家族 Putative transcription factor B3-Domain family |
| Pm022570* | AT1G76890.2 | 三螺旋转录因子GT-2 like Trihelix transcription factor GT-2-like |
| Pm027133* | AT5G20820.1 | 生长素响应蛋白SAUR 50-like Auxin-responsive protein SAUR 50-like |
| Pm020852* | AT4G38620.1 | MYB相关蛋白308-like MYB-related protein 308-like |
| Pm020227* | AT5G43700.1 | AUX/IAA 转录调节家族蛋白(AtAUX2-11) AUX/IAA transcriptional regulator family protein(AtAUX2-11) |
| Pm018533 | AT4G30080.1 | 生长素响应因子ARF16 Auxin response factor 16 |
| Pm021891 | AT4G38840.1 | SAUR类生长素反应蛋白家族 SAUR-like auxin-responsive protein family |
| Pm003647 | AT1G08550.1 | 非光化学淬灭1(NPQ1) Non-photochemical quenching 1(NPQ1) |
Table 3 Functional annotation of flowering-related genes among high-weight co-expressed genes associated with PmMYB21
| 基因编号 Gene ID | 拟南芥参考基因 Match tair ID | 基因功能注释 Gene function annotions |
|---|---|---|
| Pm010066* | AT1G28300.1 | 推定的转录因子B3域家族 Putative transcription factor B3-Domain family |
| Pm022570* | AT1G76890.2 | 三螺旋转录因子GT-2 like Trihelix transcription factor GT-2-like |
| Pm027133* | AT5G20820.1 | 生长素响应蛋白SAUR 50-like Auxin-responsive protein SAUR 50-like |
| Pm020852* | AT4G38620.1 | MYB相关蛋白308-like MYB-related protein 308-like |
| Pm020227* | AT5G43700.1 | AUX/IAA 转录调节家族蛋白(AtAUX2-11) AUX/IAA transcriptional regulator family protein(AtAUX2-11) |
| Pm018533 | AT4G30080.1 | 生长素响应因子ARF16 Auxin response factor 16 |
| Pm021891 | AT4G38840.1 | SAUR类生长素反应蛋白家族 SAUR-like auxin-responsive protein family |
| Pm003647 | AT1G08550.1 | 非光化学淬灭1(NPQ1) Non-photochemical quenching 1(NPQ1) |
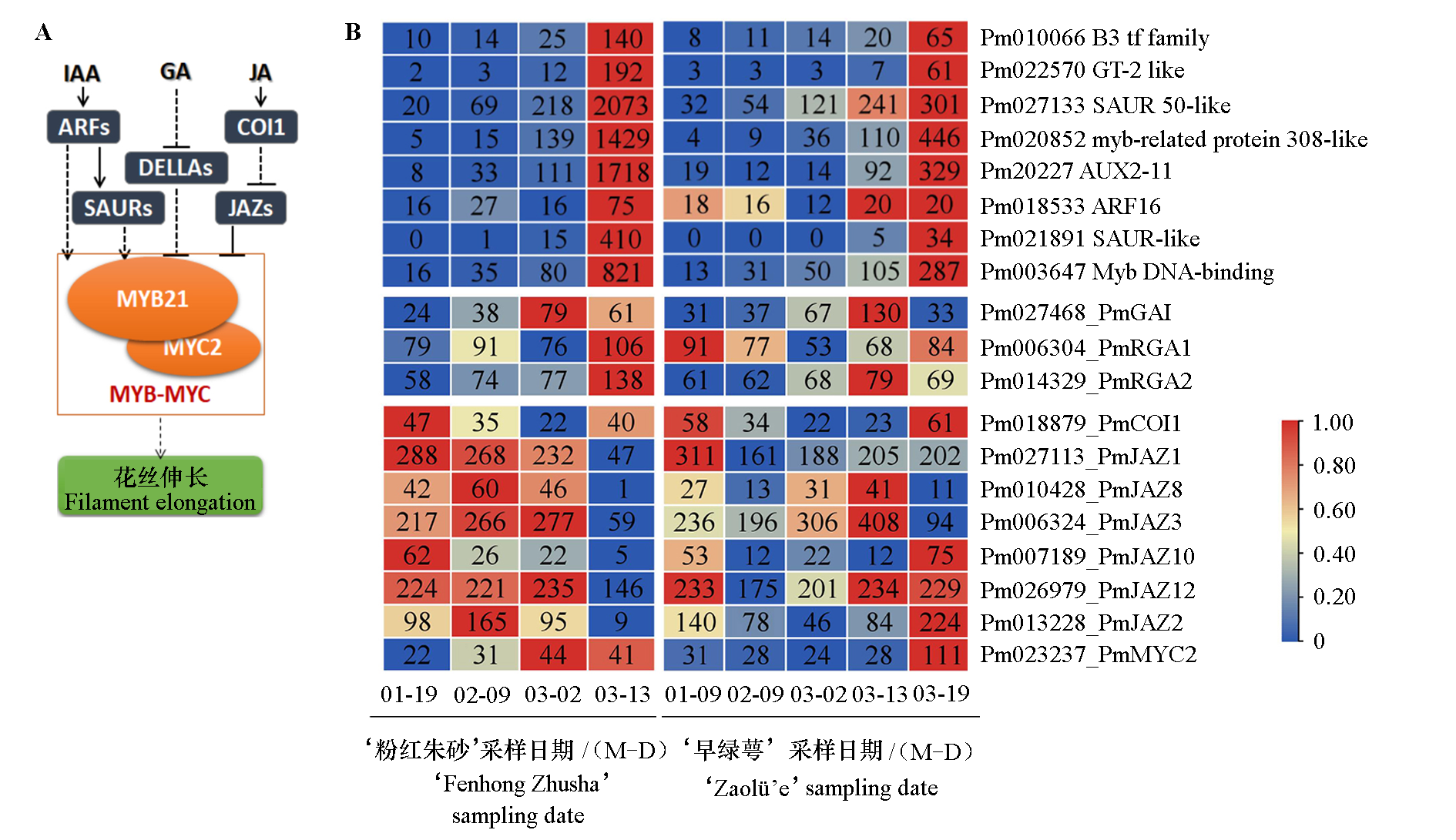
Fig. 8 The regulation pathway of filament elongation(A)and the expression of PmMYB21 and its upstream regulatory genes during flowering of two Prunus mume cultivars(B)
| [1] |
Bai S, Tuan P A, Saito T, Honda C, Hatsuyama Y, Ito A, Moriguchi T. 2016. Epigenetic regulation of MdMYB1 is associated with paper bagging-induced red pigmentation of apples. Planta, 244 (3):573-586.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2524-4 URL |
| [2] |
Brewer P B, Howles P A, Dorian K, Griffith M E, Ishida T, Kaplan-Levy R N, Kilinc A, Smyth D R. 2004. PETAL LOSS,a trihelix transcription factor gene,regulates perianth architecture in the Arabidopsis flower. Development, 131 (16):4035-4045.
doi: 10.1242/dev.01279 URL |
| [3] |
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas H R, Frank M H, He Y, Xia R. 2020. Tbtools:An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant, 13 (8):1194-1202.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009 URL |
| [4] | Chen Jun-Yu. 1989. China Mei flower(Prunus mume). Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. (in Chinese) |
| 陈俊愉. 1989. 中国梅花品种图志. 北京: 中国林业出版社 | |
| [5] | Chen Jun-yu. 2002. Sixty years in researching Mei flowers. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 24 (5):6. (in Chinese) |
| 陈俊愉. 2002. 梅花研究六十年. 北京林业大学学报, 24 (5):6. | |
| [6] |
Cheng H, Song S, Xiao L, Soo H M, Cheng Z, Xie D, Peng J. 2009. Gibberellin acts through jasmonate to control the expression of MYB21,MYB24,and MYB57 to promote stamen filament growth in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genetics, 5 (3):e1000440.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000440 URL |
| [7] |
Cubas P, Vincent C, Coen E. 1999. An epigenetic mutation responsible for natural variation in floral symmetry. Nature, 401 (6749):157-161.
doi: 10.1038/43657 |
| [8] |
Dai X, Lu Q, Wang J, Wang L, Xiang F, Liu Z. 2021. MiR160 and its target genes ARF10,ARF16 and ARF17 modulate hypocotyl elongation in a light,BRZ,or PAC-dependent manner in Arabidopsis:miR160 promotes hypocotyl elongation. Plant Science, 303:110686.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110686 URL |
| [9] |
Dong J, Sun N, Yang J, Deng Z, Lan J, Qin G, He H, Deng X W, Irish V F, Chen H, Wei N. 2019. The transcription factors TCP4 and PIF 3 antagonistically regulate organ-Specific light induction of SAUR genes to modulate cotyledon opening during de-Etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 31 (5):1155-1170.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00803 |
| [10] |
Dubois A, Remay A, Raymond O, Balzergue S, Chauvet A, Maene M, Pécrix Y, Yang S H, Jeauffre J, Thouroude T, Boltz V, Martin-Magniette M L, Janczarski S, Legeai F, Renou J P, Vergne P, Le Bris M, Foucher F, Bendahmane M. 2011. Genomic approach to study floral development genes in Rosa sp. PLoS ONE, 6 (12):e28455.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028455 URL |
| [11] |
Feng H, Conneely K N, Wu H. 2014. A Bayesian hierarchical model to detect differentially methylated loci from single nucleotide resolution sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Research, 42 (8):e69.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gku154 URL |
| [12] |
Ge X, Chang F, Ma H. 2010. Signaling and transcriptional control of reproductive development in Arabidopsis. Current Biology, 20 (22):R988-997.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.09.040 URL |
| [13] |
Gray W M, Kepinski S, Rouse D, Leyser O, Estelle M. 2001. Auxin regulates SCF(TIR1)-dependent degradation of AUX/IAA proteins. Nature, 414 (6861):271-276.
doi: 10.1038/35104500 URL |
| [14] |
Huang H, Gong Y, Liu B, Wu D, Zhang M, Xie D, Song S. 2020. The DELLA proteins interact with MYB21 and MYB24 to regulate filament elongation in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biology, 20 (1):64.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-2274-0 pmid: 32033528 |
| [15] | Huang H, Liu R, Niu Q, Tang K, Zhang B, Zhang H, Chen K, Zhu J K, Lang Z. 2019. Global increase in DNA methylation during orange fruit development and ripening. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116 (4):1430-1436. |
| [16] |
Jiang L, Zhang M, Ma K. 2020. Whole-Genome DNA methylation associated with differentially expressed genes regulated anthocyanin biosynthesis within flower color chimera of ornamental tree Prunus mume. Forests, 11 (1):90.
doi: 10.3390/f11010090 URL |
| [17] |
Koning R E. 1983. The roles of Auxin,Ethylene,and Acid Growth in filament elongation in Gaillardia grandiflora(Asteraceae). American Journal of Botany, 70 (4):602-610.
doi: 10.1002/ajb2.1983.70.issue-4 URL |
| [18] |
Langfelder P, Horvath S. 2008. WGCNA:an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics, 9:559.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-559 pmid: 19114008 |
| [19] |
Law J A, Jacobsen S E. 2010. Establishing,maintaining and modifying DNA methylation patterns in plants and animals. Nature Reviews Genetics, 11 (3):204-220.
doi: 10.1038/nrg2719 |
| [20] | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S. 2002. PlantCARE,a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 30 (1):325-327. |
| [21] |
Li W F, Ning G X, Mao J, Guo Z G, Zhou Q, Chen B H. 2019. Whole-genome DNA methylation patterns and complex associations with gene expression associated with anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple fruit skin. Planta, 250 (6):1833-1847.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-019-03266-4 |
| [22] |
Liu G, Ren G, Guirgis A, Thornburg R W. 2009. The MYB 305 transcription factor regulates expression of nectarin genes in the ornamental tobacco floral nectary. Plant Cell, 21 (9):2672-2687.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.060079 URL |
| [23] | Murakami Y. 1973. The role of gibberellins in the growth of floral organs of Pharbitis nil. Plant and Cell Physiology, 16 (2):91-102. |
| [24] |
Nagpal P, Ellis C M, Weber H, Ploense S E, Barkawi L S, Guilfoyle T J, Hagen G, Alonso J M, Cohen J D, Farmer E E, Ecker J R, Reed J W. 2005. Auxin response factors ARF6 and ARF 8 promote jasmonic acid production and flower maturation. Development, 132 (18):4107-4118.
doi: 10.1242/dev.01955 URL |
| [25] |
Noh B, Murphy A S, Spalding E P. 2001. Multidrug resistance-like genes of Arabidopsis required for auxin transport and auxin-mediated development. Plant Cell, 13 (11):2441-2454.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.010350 pmid: 11701880 |
| [26] |
Park J H, Halitschke R, Kim H B, Baldwin I T, Feldmann K A, Feyereisen R. 2002. A knock-out mutation in allene oxide synthase results in male sterility and defective wound signal transduction in Arabidopsis due to a block in jasmonic acid biosynthesis. Plant Journal, 31 (1):1-12.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01328.x URL |
| [27] |
Park Y, Wu H. 2016. Differential methylation analysis for BS-seq data under general experimental design. Bioinformatics, 32 (10):1446-1453.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw026 pmid: 26819470 |
| [28] |
Song S, Qi T, Huang H, Ren Q, Wu D, Chang C, Peng W, Liu Y, Peng J, Xie D. 2011. The Jasmonate-ZIM domain proteins interact with the R2R3-MYB transcription factors MYB21 and MYB 24 to affect Jasmonate-regulated stamen development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 23 (3):1000-1013.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.083089 URL |
| [29] | Su G, Morris J H, Demchak B, Bader G D. 2014. Biological network exploration with Cytoscape 3. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics, 47:8.13.1-8.13.24. |
| [30] |
Sun L, Yang W, Zhang Q, Cheng T, Pan H, Xu Z, Zhang J, Chen C. 2013. Genome-wide characterization and linkage mapping of simple sequence repeats in mei(Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc.). PLoS ONE, 8 (3):e59562.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059562 URL |
| [31] |
Suzuki M M, Bird A. 2008. DNA methylation landscapes:provocative insights from epigenomics. Nature Reviews Genetics, 9 (6):465-476.
doi: 10.1038/nrg2341 pmid: 18463664 |
| [32] |
Vaughn M W, Tanurdzić M, Lippman Z, Jiang H, Carrasquillo R, Rabinowicz P D, Dedhia N, McCombie W R, Agier N, Bulski A, Colot V, Doerge R W, Martienssen R A. 2007. Epigenetic natural variation in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Biology, 5 (7):e174.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050174 URL |
| [33] |
Wang J, Sun N, Zhang F, Yu R, Chen H, Deng X W, Wei N. 2020. SAUR17 and SAUR50 differentially regulate PP2C-D 1 during apical hook development and cotyledon opening in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 32 (12):3792-3811.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.20.00283 URL |
| [34] |
Wang T, Hao R, Pan H, Cheng T, Zhang Q. 2014. Selection of suitable reference genes for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in Prunus mume during flowering stages and under different abiotic stress conditions. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 139 (2):113-122.
doi: 10.21273/JASHS.139.2.113 URL |
| [35] | Wang W, Wu P, Liu T, Ren H, Li Y, Hou X. 2017. Genome-wide analysis and expression divergence of the trihelix family in brassica rapa: Insight into the Evolutionary Patterns in Plants. Scientific Report, 7 (1):6463. |
| [36] |
Wang X, Yu R, Wang J, Lin Z, Chen H. 2020. The asymmetric expression of SAUR genes mediated by ARF7/ 19 promotes the gravitropism and phototropism of plant hypocotyls. Cell Reports, 31 (3):107529.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107529 URL |
| [37] |
Wang Z, Meng D, Wang A, Li T, Jiang S, Cong P, Li T. 2013. The methylation of the PcMYB10 promoter is associated with green-skinned sport in Max Red Bartlett pear. Plant Physiology, 162 (2):885-896.
doi: 10.1104/pp.113.214700 URL |
| [38] | Wu H, Xu T, Feng H, Chen L, Li B, Yao B, Qin Z, Jin P, Conneely K N. 2015. Detection of differentially methylated regions from whole-genome bisulfite sequencing data without replicates. Nucleic Acids Research, 43 (21):e141. |
| [39] |
Wyatt R E, Ainley W M, Nagao R T, Conner T W, Key J L. 1993. Expression of the Arabidopsis AtAux2-11 auxin-responsive gene in transgenic plants. Plant Molecular Biology, 22 (5):731-749.
pmid: 8358026 |
| [40] |
Xing L, Li Y, Qi S, Zhang C, Ma W, Zuo X, Liang J, Gao C, Jia P, Shah K, Zhang D, An N, Zhao C, Han M, Zhao J. 2019. Comparative RNA-Sequencing and DNA methylation analyses of apple(Malus × domestica Borkh.) buds with diverse flowering capabilities reveal novel insights into the regulatory mechanisms of flower bud formation. Plant and Cell Physiology, 60 (8):1702-1721.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcz080 URL |
| [41] |
Xu Z, Zhang Q, Sun L, Du D, Cheng T, Pan H, Yang W, Wang J. 2014. Genome-wide identification,characterisation and expression analysis of the MADS-box gene family in Prunus mume. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 289 (5):903-920.
doi: 10.1007/s00438-014-0863-z URL |
| [42] |
Yang Y, Yue R, Sun T, Zhang L, Chen W, Zeng H, Wang H, Shen C. 2015. Genome-wide identification,expression analysis of GH 3 family genes in Medicago truncatula under stress-related hormones and Sinorhizobium meliloti infection. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology, 99 (2):841-854.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6311-5 URL |
| [43] | Yuan X, Ma K F, Zhang M, Zhang Z Y, Wang J, Zhang Q X. 2020. How does an early flowering cultivar of Prunus mume arrange its bud development in late winter? Acta Horticulturae, 1291 (3):15-20. |
| [44] |
Zhang B, Kirov S, Snoddy J. 2005. WebGestalt:an integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological contexts. Nucleic Acids Research, 33 (Web Server issue):W741-748.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gki475 pmid: 15980575 |
| [45] |
Zhang M, Yang Q, Yuan X, Yan X, Wang J, Cheng T, Zhang Q. 2021. Integrating genome-wide association analysis with transcriptome sequencing to identify candidate genes related to blooming time in Prunus mume. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12:690841.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.690841 URL |
| [46] |
Zhang Q, Chen W, Sun L, Zhao F, Huang B, Yang W, Tao Y, Wang J, Yuan Z, Fan G, Xing Z, Han C, Pan H, Zhong X, Shi W, Liang X, Du D, Sun F, Xu Z, Hao R, Lv T, Lv Y, Zheng Z, Sun M, Luo L, Cai M, Gao Y, Wang J, Yin Y, Xu X, Cheng T, Wang J. 2012. The genome of Prunus mume. Nature Communications, 3 (1):1318.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms2290 |
| [47] |
Zhang Q, Zhang H, Sun L, Fan G, Ye M, Jiang L, Liu X, Ma K, Shi C, Bao F, Guan R, Han Y, Fu Y, Pan H, Chen Z, Li L, Wang J, Lv M, Zheng T, Yuan C, Zhou Y, Lee S M, Yan X, Xu X, Wu R, Chen W, Cheng T. 2018. The genetic architecture of floral traits in the woody plant Prunus mume. Nature Communications, 9 (1):1702.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04093-z |
| [48] |
Zhong S, Fei Z, Chen Y R, Zheng Y, Huang M, Vrebalov J, McQuinn R, Gapper N, Liu B, Xiang J, Shao Y, Giovannoni J J. 2013. Single-base resolution methylomes of tomato fruit development reveal epigenome modifications associated with ripening. Nature Biotechnology, 31 (2):154-159.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2462 pmid: 23354102 |
| [49] | Zhou Chan, Chen Chao, Zuo Jing, Yan Xiao-lan, Zhang Jun-wei, Bao Man-zhu. 2015. Identification and expression analysis of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in Prunus mume under cold treatment. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 37:61-65. (in Chinese) |
| 周婵, 陈超, 左静, 晏晓兰, 张俊卫, 包满珠. 2015. 梅R2R3型MYB转录因子的鉴定及低温胁迫下的表达分析. 北京林业大学学报, 37:61-65. | |
| [50] |
Zhu J K. 2009. Active DNA demethylation mediated by DNA glycosylases. Annual Review of Genetics, 43:143-166.
doi: 10.1146/genet.2009.43.issue-1 URL |
| [51] |
Zhuo X, Zheng T, Li S, Zhang Z, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Ahmad S, Sun L, Wang J, Cheng T, Zhang Q. 2021. Identification of the PmWEEP locus controlling weeping traits in Prunus mume through an integrated genome-wide association study and quantitative trait locus mapping. Horticulture Research, 8 (1):131.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00573-4 |
| [1] | WANG Zehan, YU Wentao, WANG Pengjie, LIU Caiguo, FAN Xiaojing, GU Mengya, CAI Chunping, WANG Pan, YE Naixing. WGCNA Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes in Floral Organs of Tea Germplasms with Ovary-glabrous and Ovary-trichome [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 620-634. |
| [2] | LIU Yaoyao, WU Yanyan, Shi Yan, MAO Tianyu, BAO Manzhu, ZHANG Junwei, ZHANG Jie. Preliminary Study on the Relationship Between Promoter Sequence Difference of PmTAC1 and Weeping Trait of Prunus mume [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1327-1338. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd