
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 623-634.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0382
付琪1,2, 王丹1,2, 景维坤1, 张颢1, 王慧纯1, 蹇洪英1, 邱显钦1, 王其刚1, 唐开学1, 晏慧君1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-02
修回日期:2025-02-20
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
FU Qi1,2, WANG Dan1,2, JING Weikun1, ZHANG Hao1, WANG Huichun1, JIAN Hongying1, QIU Xianqin1, WANG Qigang1, TANG Kaixue1, YAN Huijun1,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-02
Revised:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-25
Online:2025-03-25
摘要:
为揭示类胡萝卜素裂解双加氧酶(carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase,CCDs)在花香合成通路中的作用,以中国古老月季‘月月粉’(Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’)为材料,在花瓣中克隆了RcCCD4并进行功能解析。RT-qPCR结果表明,RcCCD4主要在花瓣中表达,花蕾期表达水平较低,盛开期表达水平最高。RcCCD4蛋白定位于细胞质体中。构建了RcCCD4的原核表达载体,通过酶活性检测发现,RcCCD4可以特异性地切割β-胡萝卜素。进一步分析发现,通过病毒诱导的基因沉默RcCCD4可显著降低花瓣中二氢-β-紫罗兰酮含量,而瞬时过表达RcCCD4可显著提高花瓣中二氢-β-紫罗兰酮含量。以上结果说明RcCCD4可以特异性地裂解β-胡萝卜素,进而合成二氢-β-紫罗兰酮。
付琪, 王丹, 景维坤, 张颢, 王慧纯, 蹇洪英, 邱显钦, 王其刚, 唐开学, 晏慧君. 月季类胡萝卜素裂解双加氧酶基因RcCCD4在花香合成中的功能[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 623-634.
FU Qi, WANG Dan, JING Weikun, ZHANG Hao, WANG Huichun, JIAN Hongying, QIU Xianqin, WANG Qigang, TANG Kaixue, YAN Huijun. Functional Characterization of Carotenoid Cleavage Dioxygenases 4 Gene(RcCCD4)Involved in Biosynthetic Pathway of Floral Scent in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 623-634.
| 用途 Function | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆基因 | RcCCD4-F | ATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCT |
| Gene clone | RcCCD4-R | CAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 病毒诱导的基因沉默 | pTRV1-F | TTACAGGTTATTTGGGCTAG |
| Virus induced gene | pTRV1-R | CCGGGTTCAATTCCTTATC |
| silencing | pTRV2-F | TGGGAGATGATACGCTGTT |
| pTRV2-R | CCTAAAACTTCAGACACG | |
| pTRV2-RcCCD4-F | GAGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCAGCTCGACGTGTCGG | |
| pTRV2-RcCCD4-R | CTCGAGACGCGTGAGCTCGGTACCATACAACAGTCACAACGTTTGTG | |
| 原核表达 | Pet28a(+)-RcCCD4-F | CGCGGCAGCCATATGATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCTT |
| Prokaryotic expression | Pet28a(+)-RcCCD4-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGCAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 过表达 | pSurper-1300-RcCCD4-F | AAGCTTCTGCAGGGGCCCGGGATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCT |
| Overexpression | pSurper-1300-RcCCD4-R | TCCTCGCCCTTGCTCACCATGGTACCCAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR | qRT-RcCCD4-F | AGCTCGACGTGTCGGG |
| qRT-RcCCD4-R | CCTCCGGATTCTCCGGATCC | |
| qRT-RcCCD1-F | GTTGATGTACGACAGTTCTCAGCCT | |
| qRT-RcCCD1-R | ACAAACTCTCCATTCAAGCAATCAGG | |
| qRT-RcCCD7-F | AGTGGAACAAGTCATCAGATTTTCCAGT | |
| qRT-RcCCD7-R | TAGTTGAAGCATTCAGCTTCACCAC | |
| qRT-RcCCD8-F | TGTTTTAATGACATGCCGCCTTGAG | |
| qRT-RcCCD8-R | ATAATTTCTTCTGTGTTGCTAAACCGGT | |
| qRT-RcZAS-F | GAGGGTGAAGCGATTGCAAAAATT | |
| qRT-RcZAS-R | TGACACGGAGAAAATTCATGGTTACAG | |
| qRT-RcZAS-like-F | TGCCAACCTCATCGAACACCTAA | |
| qRT-RcZAS-like-R | ATGGTCAACTACACACTTGTATACGACT | |
| qRT-RcNCED1-F | CAATCTCACTGAACCCACTTGCTT | |
| qRT-RcNCED1-R | CACTACTACTTTAACTCAAAGCCTGCTCC | |
| qRT-RcNCED6-F | AGAAGACGTGGAAGTCGGAGC | |
| qRT-RcNCED6-R | AGCTACTGCTATGCCTGGTTTTTCA |
表1 本研究中所用的引物
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 用途 Function | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆基因 | RcCCD4-F | ATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCT |
| Gene clone | RcCCD4-R | CAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 病毒诱导的基因沉默 | pTRV1-F | TTACAGGTTATTTGGGCTAG |
| Virus induced gene | pTRV1-R | CCGGGTTCAATTCCTTATC |
| silencing | pTRV2-F | TGGGAGATGATACGCTGTT |
| pTRV2-R | CCTAAAACTTCAGACACG | |
| pTRV2-RcCCD4-F | GAGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCAGCTCGACGTGTCGG | |
| pTRV2-RcCCD4-R | CTCGAGACGCGTGAGCTCGGTACCATACAACAGTCACAACGTTTGTG | |
| 原核表达 | Pet28a(+)-RcCCD4-F | CGCGGCAGCCATATGATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCTT |
| Prokaryotic expression | Pet28a(+)-RcCCD4-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGCAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 过表达 | pSurper-1300-RcCCD4-F | AAGCTTCTGCAGGGGCCCGGGATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCT |
| Overexpression | pSurper-1300-RcCCD4-R | TCCTCGCCCTTGCTCACCATGGTACCCAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR | qRT-RcCCD4-F | AGCTCGACGTGTCGGG |
| qRT-RcCCD4-R | CCTCCGGATTCTCCGGATCC | |
| qRT-RcCCD1-F | GTTGATGTACGACAGTTCTCAGCCT | |
| qRT-RcCCD1-R | ACAAACTCTCCATTCAAGCAATCAGG | |
| qRT-RcCCD7-F | AGTGGAACAAGTCATCAGATTTTCCAGT | |
| qRT-RcCCD7-R | TAGTTGAAGCATTCAGCTTCACCAC | |
| qRT-RcCCD8-F | TGTTTTAATGACATGCCGCCTTGAG | |
| qRT-RcCCD8-R | ATAATTTCTTCTGTGTTGCTAAACCGGT | |
| qRT-RcZAS-F | GAGGGTGAAGCGATTGCAAAAATT | |
| qRT-RcZAS-R | TGACACGGAGAAAATTCATGGTTACAG | |
| qRT-RcZAS-like-F | TGCCAACCTCATCGAACACCTAA | |
| qRT-RcZAS-like-R | ATGGTCAACTACACACTTGTATACGACT | |
| qRT-RcNCED1-F | CAATCTCACTGAACCCACTTGCTT | |
| qRT-RcNCED1-R | CACTACTACTTTAACTCAAAGCCTGCTCC | |
| qRT-RcNCED6-F | AGAAGACGTGGAAGTCGGAGC | |
| qRT-RcNCED6-R | AGCTACTGCTATGCCTGGTTTTTCA |
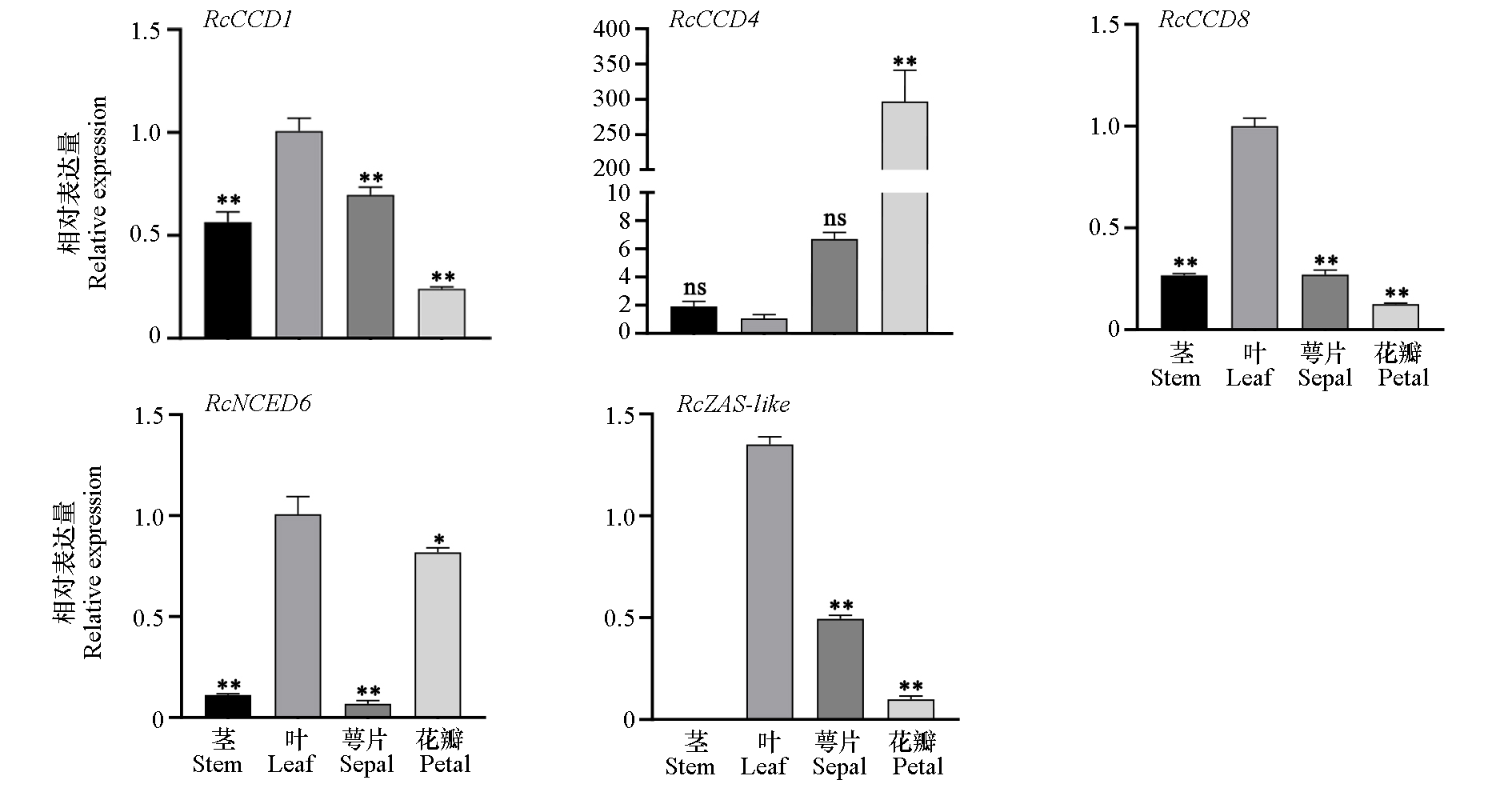
图3 ‘月月粉’月季CCD家族基因在不同组织中的表达 以叶片为对照进行比较,t-test,*代表显著性水平α = 0.05;**代表显著性水平α = 0.01;ns:无显著性
Fig. 3 Expression of CCD family genes in different organs of Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ Compared with leaf as a control,t-test,* represents a significance level of α = 0.05;** represents a significance level of α = 0.01;ns:No significant
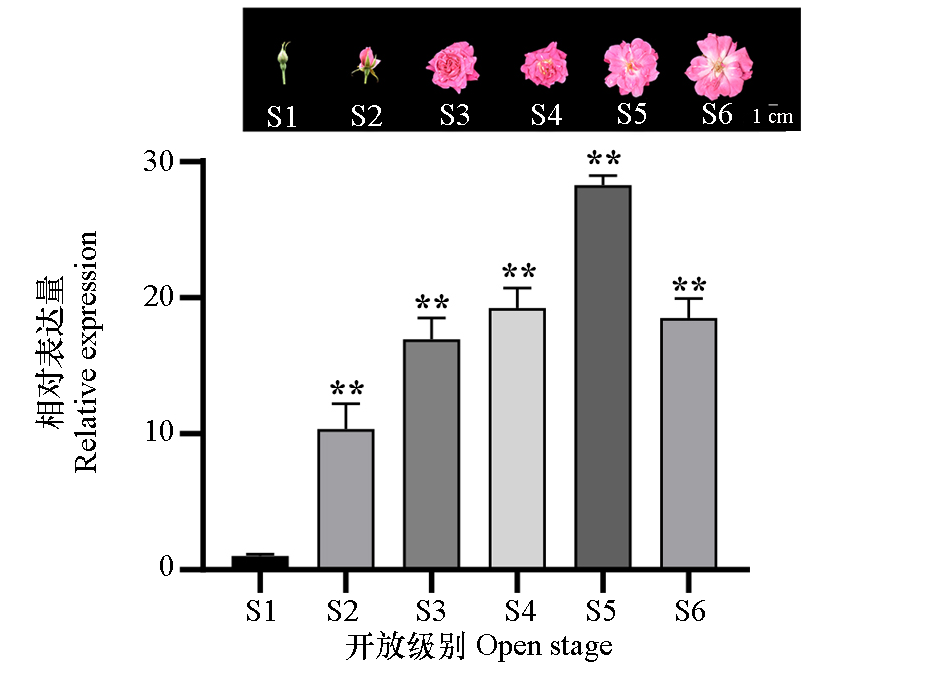
图4 ‘月月粉’月季RcCCD4在不同开放时期花瓣中的表达 以花蕾期S1级为对照进行比较,t-test,*代表显著性水平α = 0.05;**代表显著性水平α = 0.01;ns:无显著性
Fig. 4 Expression of RcCCD4 in the petals during different developmental stages of Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ Compared with S1 stage in the bud stage as a control,t-test,* represents a significance level of α = 0.05;** represents a significance level of α = 0.01;ns:No significant
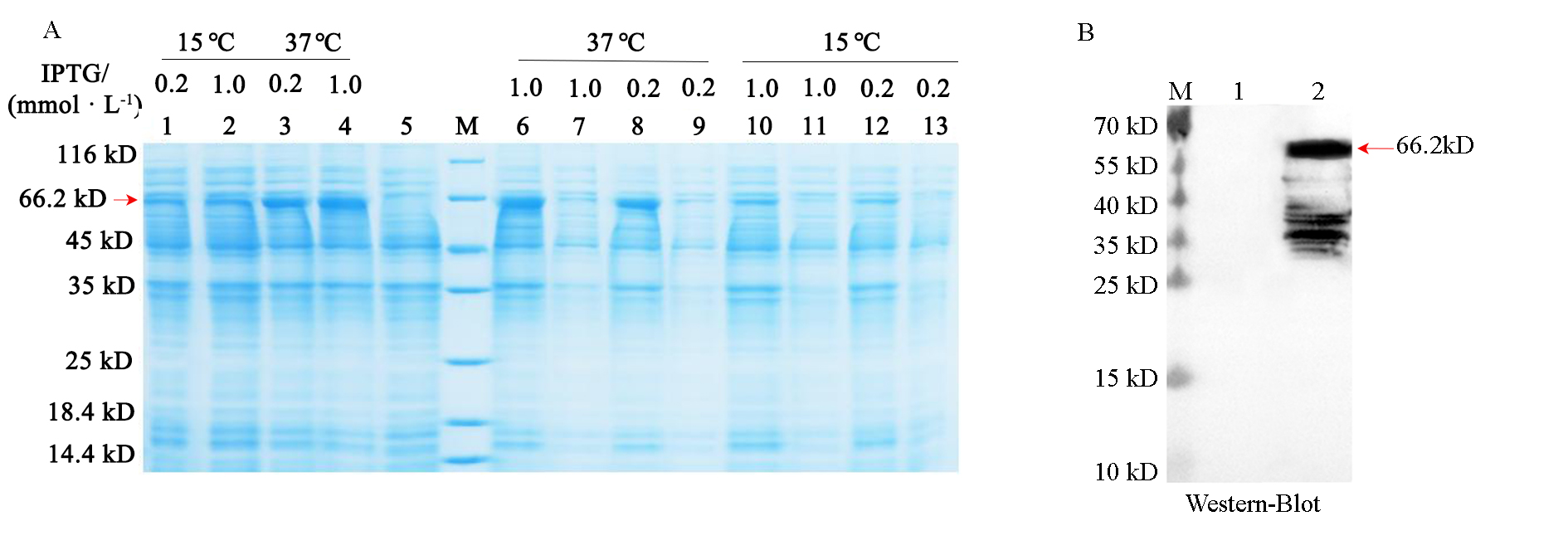
图5 RcCCD4融合蛋白诱导条件优化(A)和Western-Blot印迹(B) M:Marker。箭头指示目的蛋白;1 ~ 4:不同温度及不同浓度IPTG诱导样品;5:未诱导样品;6、8、10、12:沉淀样品;7、9、11、13:上清液样品
Fig. 5 Conditions optimization(A)and Western-Blot analysis(B)of RcCCD4 recombination protein M:Marker. The arrows indicate the protein of interest;1-4:IPTG-induced samples at different temperatures and concentrations;5:Uninduced sample;6,8,10,12:Precipitated sample;7,9,11,13:Supernatant samples

图7 ‘洛神’月季RcCCD4沉默株系花瓣中基因相对表达量和二氢-β-紫罗兰酮含量 t-test,*代表显著性水平α = 0.05;**代表显著性水平α = 0.01;ns:无显著性;NT:未处理样本,Mock:TRV空载样本。下同
Fig. 7 Expression of RcCCD4 in infected plants by qRT-PCR and relative contents of dihydro-β-ionone in Rosa hybrida‘Luoshen’ t-test,* represents a significance level of α = 0.05;** represents a significance level of α = 0.01;ns:No significant;NT:No-treatment sample;Mock:TRV empty sample. The same below
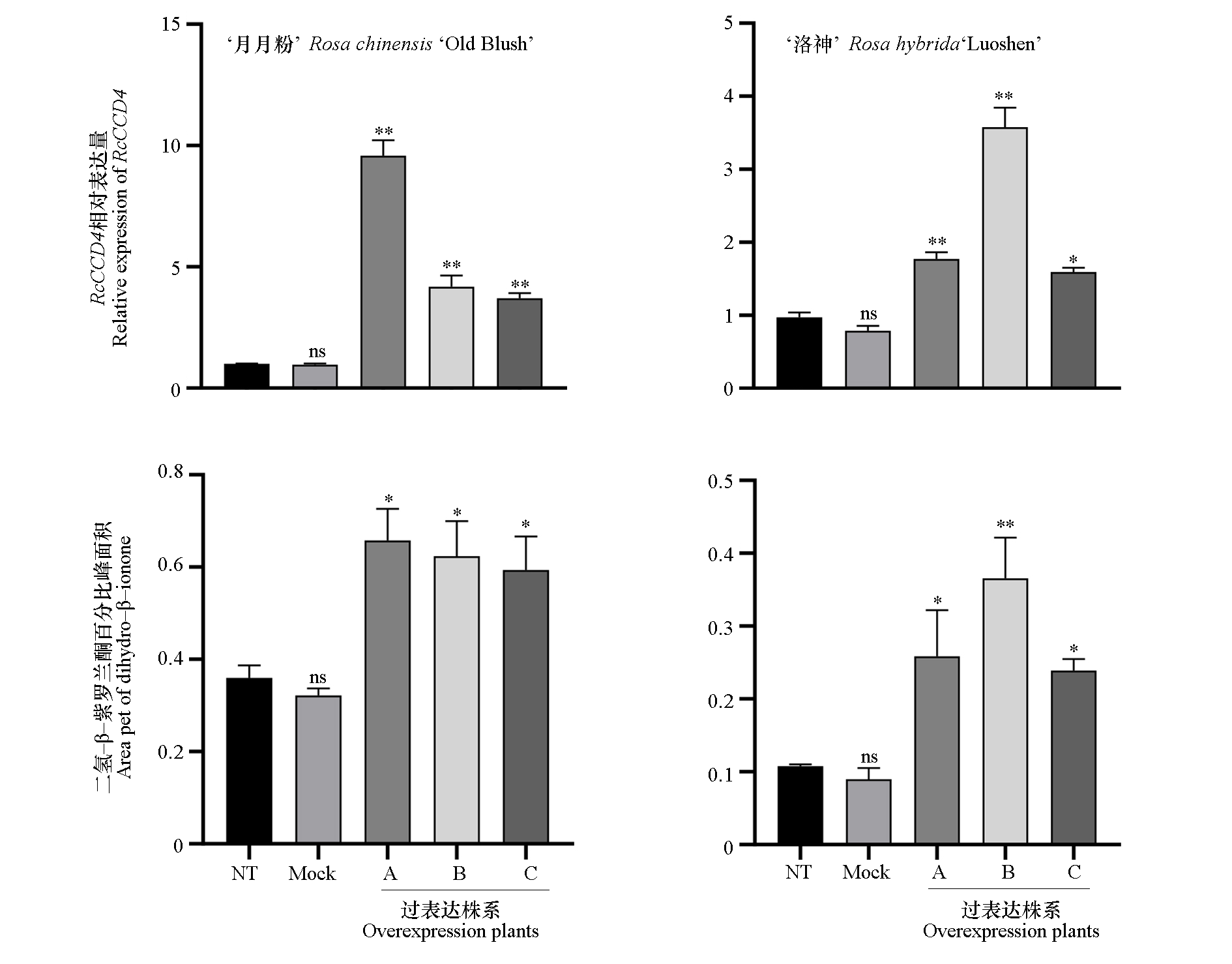
图8 ‘月月粉’和‘洛神’月季RcCCD4过表达株系花瓣中基因表达量和二氢-β-紫罗兰酮含量
Fig. 8 Expression of RcCCD4 in overexpression plants by qRT-PCR and relative contents of dihydro-β-ionone in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’and Rosa hybrida‘Luoshen’
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2006.03.005 pmid: 16616608 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq123 pmid: 20478967 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: S0003-9861(15)00073-9 pmid: 25703194 |
| [5] |
|
|
房强. 2020. 香雪兰类胡萝卜素裂解双加氧酶(FhCCDs)基因克隆与功能鉴定[博士论文]. 长春: 东北师范大学.
|
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1007/s11130-015-0482-9 pmid: 25861766 |
| [7] |
pmid: 12368489 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1221 URL |
|
侯异璇, 张玲, 吕梦雯, 武耀星, 王亮生, 张秀卿, 李珊珊. 2023. 芍药属组间杂种花香成分分析. 园艺学报, 50 (4):842-852.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1221 URL |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
刘家仁, 杨艳梅, 董宏伟, 孙向荣, 于佳, 赵淑媛, 陈炳卿. 2005. β-紫罗兰酮对人乳腺癌细胞(Er-)MAPK途径的影响. 卫生研究, 34 (6):4.
|
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0962-8 pmid: 23100158 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
pmid: 16980560 |
| [20] |
Pino, Jorge, Antonio, Quijano, Clara, Elizabeth. 2012. Study of the volatile compounds from plum(Prunus domestica L. cv. Horvin)and estimation of their contribution to the fruit aroma. Ciência E Tecnologia De Alimentos, 32 (1):76-83
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2023-0208 |
|
叶云芳, 田清尹, 施婷婷, 王亮, 岳远征, 杨秀莲, 王良桂. 2023. 植物中β-紫罗兰酮生物合成及调控研究进展. 生物技术通报, 39 (8):91-105.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2023-0208 |
|
| [34] |
|
|
易星. 2014. ‘月月红’月季胚性愈伤组织诱导及遗传转化基础研究[硕士论文]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学.
|
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.13335 pmid: 25690717 |
| [36] |
|
|
赵静, 胡增辉, 冷平生, 杨晓红. 2013. 两个金鱼草品种香气成分分析. 北京农学院学报, 28 (3):5.
|
| [1] | 阎旭, 李月, 傅小鹏, 宁国贵, 梁梅. 中国古老月季‘月月粉’等位基因不平衡分析与分子标记开发利用[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 365-379. |
| [2] | 王飞龙, 梁前艳, 尚均忠, 陈龙清, 向林. 蜡梅CpBEAT的克隆、表达分析及功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 160-170. |
| [3] | 任恒泽, 李丹莹, 余亚婷, 吕务云, 郝心愿, 王新超, 王玉春. 植物VIGS载体构建策略研究与应用进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1455-1473. |
| [4] | 杨碧楠, 李博文, 杨振宇, 徐奕芃, 阎韵清, 娄玉霞, 奉树成, 明凤. 月季‘安吉拉’热胁迫反应机制及功能基因的挖掘[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1284-1296. |
| [5] | 王雯雨, 王家荫, 杜婷婷, 张晶晶, 张超, 辛翠花, 郭江波, 裴海霞. 月季RhRNF185-like的克隆及其对花瓣衰老影响分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1047-1055. |
| [6] | 兰伟, 孟艳琼, 宣云, 朱糠宁, 丁晓浩, 樊德新, 康丽云. 月季新品种‘颍荷’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 925-926. |
| [7] | 胡锦瑜, 刘桂芝, 陈兰, 黄梦迪, 苏芹, 谭月萍, 刘硕谦, 田娜. 烟草脆裂病毒介导的茶树VIGS体系的构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2710-2724. |
| [8] | 吕梦雯 , 杨 勇 , 王亮生 , 李珊珊 , . 牡丹新品种‘华玉脂凝’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 145-146. |
| [9] | 周 燕 , 高述民 , 崔荣峰 , 孙丽萍 , 付子豪 , . 月季新品种‘燕京黄’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 149-150. |
| [10] | 潘佳佳, 张东梅, 孟建, 高苏南, 朱凯杰, 刘军伟, 李国怀. 李坏死环斑病毒诱导的桃PpPDS沉默体系的优化及验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1587-1600. |
| [11] | 马梦宇, 胡耀芳, 古琳, 李振坚, 钱永强, 巨关升, 刘俊祥, 孙振元. 瓶插月季枝条光照处理对切花寿命的延长效应[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1343-1354. |
| [12] | 刘嘉琦, 公菲菲, 张颢, 景维坤, 瞿素萍, 马男, 高俊平, 孙小明. 月季茉莉酸羧基甲基转移酶基因RhJMT对花瓣衰老的调控[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1025-1036. |
| [13] | 高俊平, 马男, 周厚高, 王嘉曦, 张常青, 李永红, 周晓锋, 孙小明. 切花月季新品种‘菲韵’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 915-916. |
| [14] | 任菲, 卢苗苗, 刘吉祥, 陈信立, 刘道凤, 眭顺照, 马婧. 蜡梅胚胎晚期丰富蛋白基因CpLEA的表达及抗性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 359-370. |
| [15] | 申玉晓, 邹金玉, 罗平, 尚文倩, 李永华, 何松林, 王政, 石力匀. ‘月月粉’月季PP2C家族基因鉴定及非生物胁迫响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(10): 2139-2156. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司