
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 3003-3015.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0303
曹凯俊*, 柳欣悦, 单凯歆, 宋春霖, 宋如意, 张超**( ), 付建新**(
), 付建新**( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-22
修回日期:2025-08-25
出版日期:2025-11-26
发布日期:2025-11-26
作者简介:共同第一作者
基金资助:
CAO Kaijun, LIU Xinyue, SHAN Kaixin, SONG Chunlin, SONG Ruyi, ZHANG Chao**( ), and FU Jianxin**(
), and FU Jianxin**( )
)
Received:2025-05-22
Revised:2025-08-25
Published:2025-11-26
Online:2025-11-26
摘要:
花青素和叶绿素在花瓣细胞中含量和分布的不同会影响百日草(Zinnia elegans)舌状花色泽的呈现,而目前关于光照如何影响百日草舌状花花青素和叶绿素代谢尚不清楚。本研究对百日草‘梦境红色’栽培品种的花苞进行黑暗处理,并对其舌状花花瓣色泽、花青素和叶绿素含量以及相关代谢酶基因表达进行测定。结果发现,遮光使百日草花瓣正面的亮度显著上升、色相a*值显著下降;背面的亮度显著上升、色度显著下降。黑暗处理后舌状花中的天竺葵素、矢车菊素及总花青素含量均显著下降,叶绿素a、叶绿素b和总叶绿素含量也显著降低。进一步研究发现,遮光导致百日草舌状花中花青素合成相关酶基因ZeCHS、ZeF3H、ZeF3'H相对表达水平显著上升,而ZeCHI和ZeDFR相对表达水平极显著降低。百日草中存在2个滞绿基因ZeSGR1和ZeSGR2,都含有保守的SGR结构域、N端的叶绿体转运肽、可变的C端区域,经黑暗处理后其相对表达水平均显著提高。
曹凯俊, 柳欣悦, 单凯歆, 宋春霖, 宋如意, 张超, 付建新. 遮光对百日草花瓣花青素和叶绿素积累的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(11): 3003-3015.
CAO Kaijun, LIU Xinyue, SHAN Kaixin, SONG Chunlin, SONG Ruyi, ZHANG Chao, and FU Jianxin. Effects of Shading on Anthocyanin and Chlorophyll Accumulation in Flower Petals of Zinnia elegans[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(11): 3003-3015.
| 基因 Gene | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| ZeACT | ZeACT-qF | TTGTGCTGGATTCTGGGGATGGT |
| ZeACT-qR | GCAGTTTCAAGCTCTTGCTCGTAGTC | |
| ZeCHS | ZeCHS-qR | ACGCAGCGGTTAAAGCCATCAAAG |
| ZeCHS-qR | AACCGTACCACCAGCAAAACATCC | |
| ZeCHI | ZeCHI-qF | TCAAGCGAAGGGAAAGAAG |
| ZeCHI-qR | AAAGTGTTGGCCAAAGATGAA | |
| ZeF3H | ZeF3H-qF | TTCTTAAGCCGCGCCAACTCTA |
| ZeF3H-qR | TTCTTAAGCCGCGCCAACTCTA | |
| ZeF3'H | ZeF3′H-qF | TTGCCCGTGACCCGAAAATGT |
| ZeF3′H-qR | TTCGTCCAGCCCCAAAAGGTATGA | |
| ZeDFR | ZeDFR-qF | AGCCTAATTACCGCACTTTCTT |
| ZeDFR-qR | CCTTTTGCTTCAGGGTTTTCATAC | |
| ZeANS | ZeANS-qF | CAATGGGTGACTGCGAAATGTGT |
| ZeANS-qR | AAACCGCCCAAGAAATCCTAACC | |
| ZeSGR1 | ZeSGR1-qF | GGGTTCTCTAATCATCCCATCC |
| ZeSGR1-qR | CCCAAAAACAGAACCTTCAGC | |
| ZeSGR2 | ZeSGR2-qF | CATTGTCGTTGTCGTCATCAGC |
| ZeSGR2-qR | AGGGATTGAACTCCTTGGTGG |
表1 qRT-PCR引物序列信息
Table 1 Primer sequence information for qRT-PCR
| 基因 Gene | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| ZeACT | ZeACT-qF | TTGTGCTGGATTCTGGGGATGGT |
| ZeACT-qR | GCAGTTTCAAGCTCTTGCTCGTAGTC | |
| ZeCHS | ZeCHS-qR | ACGCAGCGGTTAAAGCCATCAAAG |
| ZeCHS-qR | AACCGTACCACCAGCAAAACATCC | |
| ZeCHI | ZeCHI-qF | TCAAGCGAAGGGAAAGAAG |
| ZeCHI-qR | AAAGTGTTGGCCAAAGATGAA | |
| ZeF3H | ZeF3H-qF | TTCTTAAGCCGCGCCAACTCTA |
| ZeF3H-qR | TTCTTAAGCCGCGCCAACTCTA | |
| ZeF3'H | ZeF3′H-qF | TTGCCCGTGACCCGAAAATGT |
| ZeF3′H-qR | TTCGTCCAGCCCCAAAAGGTATGA | |
| ZeDFR | ZeDFR-qF | AGCCTAATTACCGCACTTTCTT |
| ZeDFR-qR | CCTTTTGCTTCAGGGTTTTCATAC | |
| ZeANS | ZeANS-qF | CAATGGGTGACTGCGAAATGTGT |
| ZeANS-qR | AAACCGCCCAAGAAATCCTAACC | |
| ZeSGR1 | ZeSGR1-qF | GGGTTCTCTAATCATCCCATCC |
| ZeSGR1-qR | CCCAAAAACAGAACCTTCAGC | |
| ZeSGR2 | ZeSGR2-qF | CATTGTCGTTGTCGTCATCAGC |
| ZeSGR2-qR | AGGGATTGAACTCCTTGGTGG |

图2 黑暗和对照处理百日草舌状花花色参数(A)和花瓣组织切片(B)
Fig. 2 The flower color parameters(A)and petal tissue sections(B)of Zinnia elegans from dark treatment and the control treatment t-Test,** P < 0.01,*** P < 0.001,**** P < 0.0001
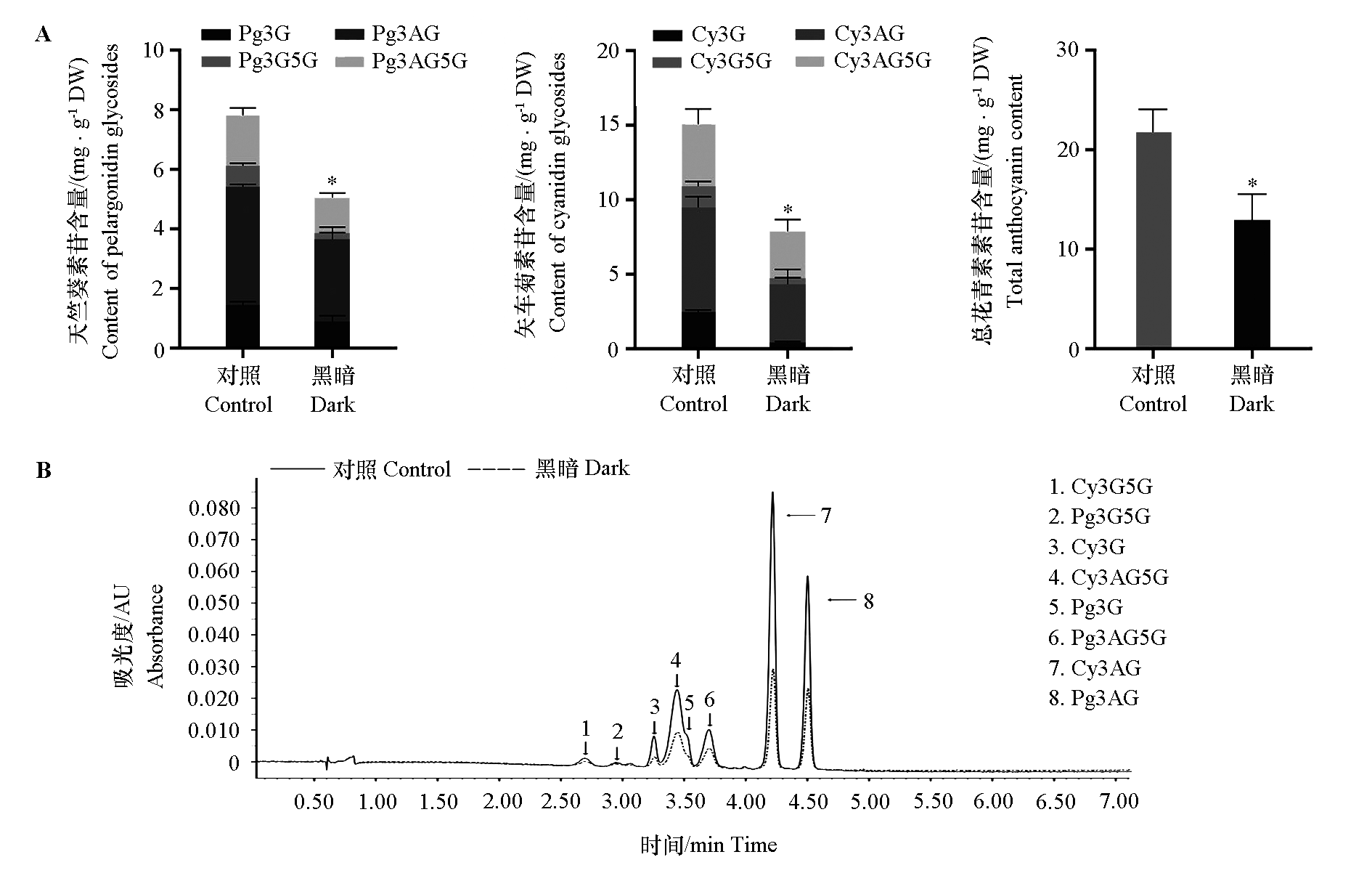
图3 黑暗和对照处理百日草舌状花色素含量(A)和UPLC色谱图(B) Cy3G:矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷;Cy3G5G:矢车菊素-3,5-双葡萄糖苷;Pg3G5G:天竺葵素-3,5-双葡萄糖苷;Cy3AG5G:矢车菊素-3-O-乙酰葡萄糖苷-5-O-葡萄糖苷;Pg3G:天竺葵素-3-O-葡萄糖苷;Pg3AG5G:天竺葵素-3-O-乙酰葡萄糖苷-5-O-葡萄糖苷;Cy3AG:矢车菊素-3-O-乙酰葡萄糖苷;Pg3AG:天竺葵素-3-O-乙酰葡萄糖苷
Fig. 3 Pigment content(A)and UPLC chromatogram(B)of Zinnia elegans from dark treatment and the control treatment Cy3G:Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside;Cy3G5G:Cyanidin-3,5-diglucoside chloride;Pg3G5G:Pelargonidin-3,5-diglucoside chloride;Cy3AG5G:Cyanidin-3-O-(6′′-acetyl)glucoside-5-O-glucoside;Pg3G:Pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside;Pg3AG5G:Pelargonidin-3-O-(6′′-acetyl)glucoside-5-O-glucoside;Cy3AG:Cyanidin-3-O-(6′′-acetyl)glucoside;Pg3AG:Pelargonidin-3-O-(6′′-acetyl)glucoside. t-Test,* P < 0.05
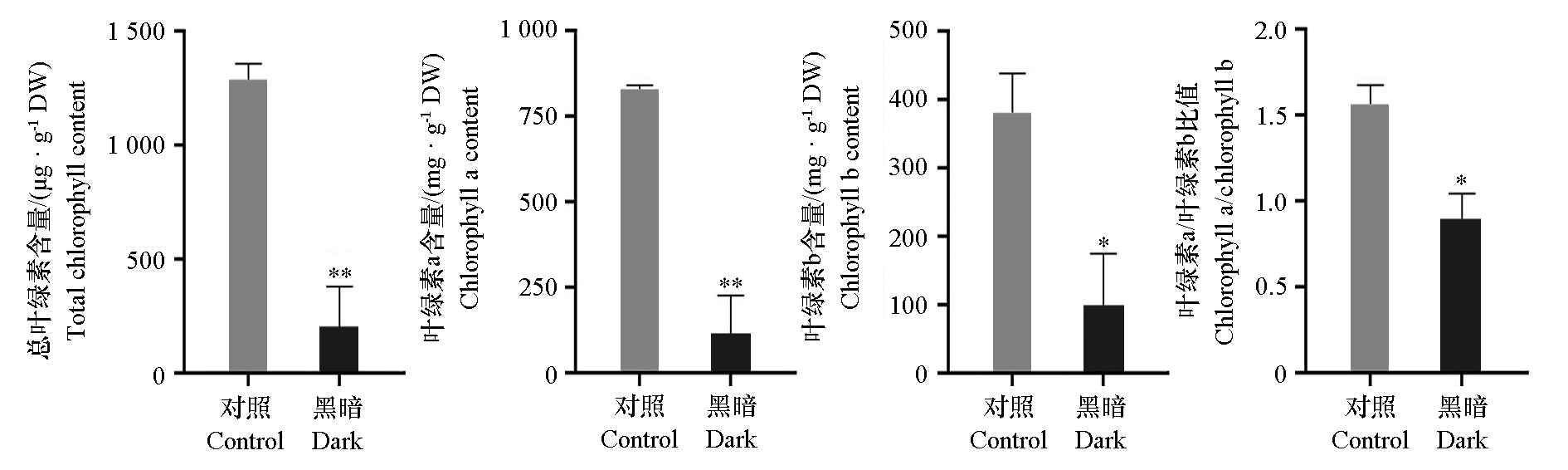
图4 黑暗和对照处理百日草舌状花总叶绿素、叶绿素a和叶绿素b含量及叶绿素a/b比值
Fig. 4 Total chlorophyll content,chlorophyll a content,chlorophyll b content,chlorophyll a/b ratio of Zinnia elegans from dark treatment and the control treatment t-Test,* P < 0.05,** P < 0.01
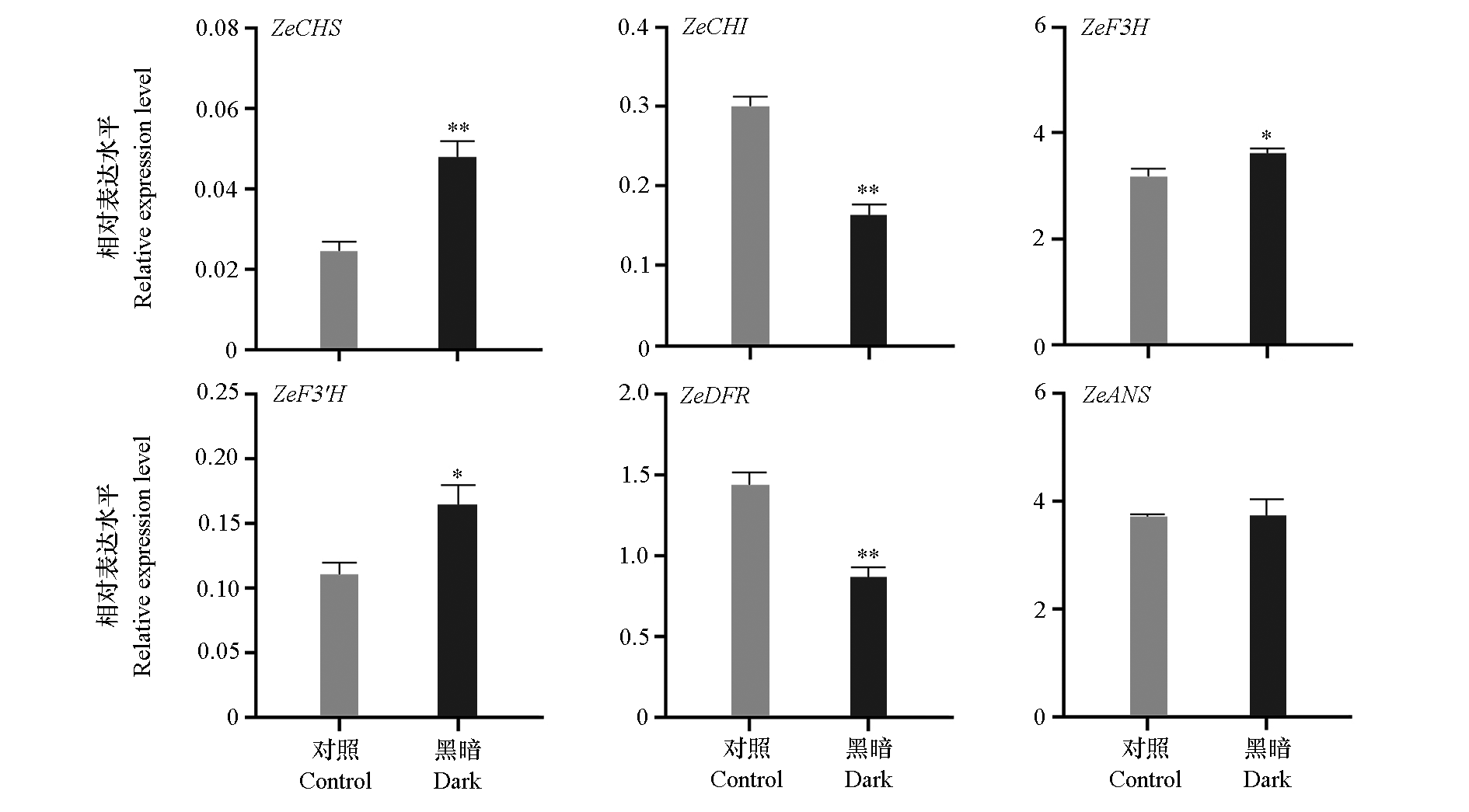
图5 百日草舌状花花青素苷合成相关酶基因的相对表达水平
Fig. 5 Relative expression level of anthocyanin synthesis-related enzyme genes of Zinnia elegans t-Test,* P < 0.05,** P < 0.01

图6 百日草ZeSGR1、ZeSGR2蛋白和其他物种SGR蛋白的系统进化关系(A)及不同物种中SGR氨基酸序列比对(B)
Fig. 6 Phylogenetic relationship among ZeSGR1,ZeSGR2 and SGR proteins from other species(A),amino acid sequence alignment of SGRs from different species(B)
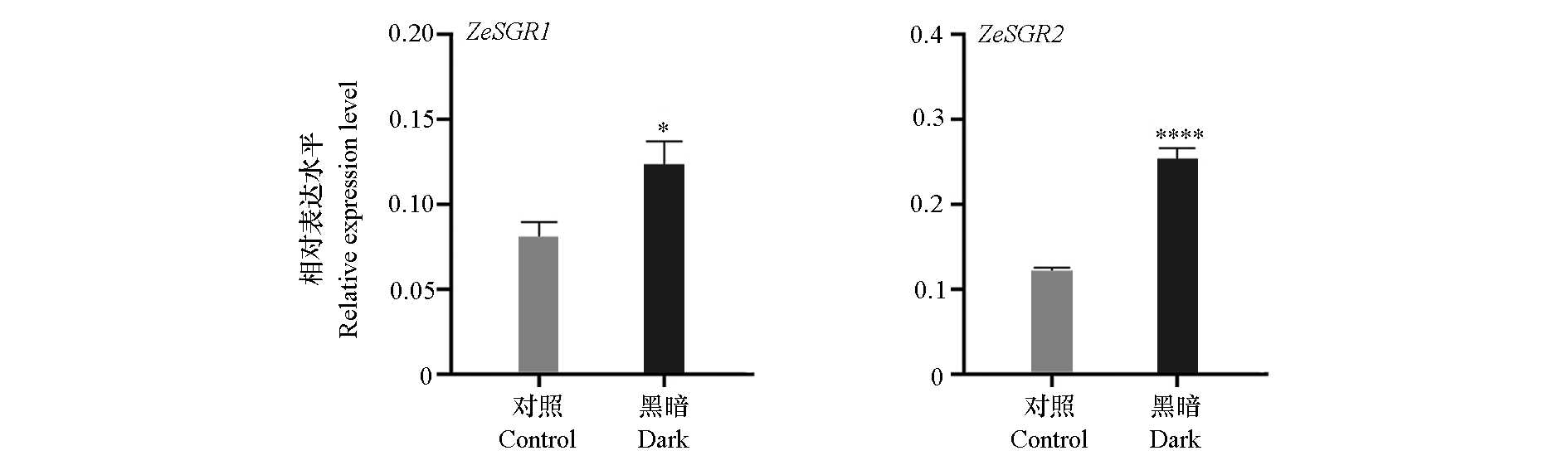
图7 遮光处理百日草滞绿基因ZeSGR1和ZeSGR2表达水平的影响
Fig. 7 Relative expression level of ZeSGR1 and ZeSGR2 of Zinnia elegans in dark treatment t-Test,* P < 0.05,**** P < 0.0001
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
陈耀宇, 王曙光, 孙黛珍. 2019. 作物STAYGREEN功能与调控的研究进展. 生物学杂志, 36 (3):83-87.
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
|
洪艳, 武宇薇, 宋想, 李梦灵, 戴思兰. 2021. 光照调控园艺作物花青素苷生物合成的分子机制. 园艺学报, 48 (10):1983-2000.
|
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
钱婕妤, 蒋玲莉, 郑钢, 陈佳红, 赖吴浩, 许梦晗, 付建新, 张超. 2022. 百日草花青素苷合成相关MYB转录因子筛选及ZeMYB9功能研究. 园艺学报, 49 (7):1505-1518.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
钱婕妤, 赖吴浩, 蒋玲莉, 付建新, 张超. 2020. ‘梦境’百日草花瓣色素分布对花色的影响//中国观赏园艺研究进展2020. 北京:中国林业出版社:148-152.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
钱婕妤, 詹海燕, 翟敏超, 赖吴浩, 庞天虹, 付建新, 张超. 2019. 百日草花瓣中花青素苷组分及其含量分析//中国观赏园艺研究进展2019. 北京:中国林业出版社:479-483.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
滕守连, 李番, 祁丽娟, 郭童童, 张生萍, 妥小云, 罗玉秀. 2021. 不同光照处理甘蓝型油菜幼苗花青素合成的转录组和代谢组分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 49 (11):134-146.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
田密霞, 周福慧, 姜爱丽, 祝朋芳, 陈晨, 刘程惠, 原畅. 2023. 芸薹属植物呈色机理研究进展. 园艺学报, 50 (9):1971-1986.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
希从芳, 郑丽, 字淑慧, 李建宾, 陈疏影, 王有国. 2013. 不同遮阴处理对滇山茶花瓣花青素苷构成的影响. 园艺学报, 40 (10):2006-2014.
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
|
杨君, 孔羽, 刘群录, 叶康, 秦俊. 2023. 遮荫对‘花手鞠’绣球花色和花青素苷组成的影响. 园艺学报, 50 (7):1467-1481.
|
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
|
张计育, 潘德林, 贾展慧, 王刚, 王涛, 翟敏, 郭忠仁. 2018. 中华猕猴桃品种‘Hort16A’果肉颜色形成的分子机制. 植物资源与环境学报, 27 (3):1-10.
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [1] | 冯慧敏, 李海渤, 雷建军, 朱云娜. 高花青素芥菜新品种‘紫敏芥菜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 113-114. |
| [2] | 谢鑫鑫, 黄建都, 林翮飞, 朱海生, 陈继兵, 温庆放. 茄子新品种‘闽茄11号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 117-118. |
| [3] | 田红梅, 王元龙, 王 飞, 潘 弘, 陶 珍, 张 建, 王朋成. 厚皮甜瓜新品种‘金种缘金甜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 153-154. |
| [4] | 储转南, 尹冬梅, 汪炳元, 李卫文, 熊 瑞, 彭星星, 董 玲, 崔广胜, 梁 华, 韩 飘, 吕辛馨. 菊花新品种‘徽菊3号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 175-176. |
| [5] | 唐嘉怡, 缪绸雨, 尹豪杰, 吴明月, 曹向敏, 张惠敏, 金燕, 卢晓鹏, 朱亦赤, 李大志, 盛玲. 外源草酸对采后血橙果实品质和花色苷代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2425-2438. |
| [6] | 任婷婷, 张廷秀, 战良, 张志昌, 任怡然, 季兴龙, 王培培, 刘源霞, 孟庆福, 刘更森, 房经贵, 冷翔鹏. 不同光质补光对设施栽培‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2464-2476. |
| [7] | 马玲玲, SHAMS Shamsullah, 李戎轩, NAEEM Beenish, 张正海, 曹亚从, 于海龙, 冯锡刚, 吴华茂, 王立浩. 辣椒耐低温弱光研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2155-2165. |
| [8] | 苏玉婷, 王慧林, 赵盼, 周心怡, 郑淑雅, 刘冉, 郭惠红. 杨树PagNAC47及其启动子克隆与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(7): 1828-1842. |
| [9] | 郭新淼, 田露瑶, 曹佳琪, 谢岩, 高妍夏, 孙志超. 白色桑椹颜色缺失分子机制初步探讨[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1451-1462. |
| [10] | 李媚晴, 罗思菲, 贾曜豪, 王维贵, 孙锦. 黄瓜脱镁螯合酶基因CsMDC表达分析及其调控叶绿素降解的功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1463-1476. |
| [11] | 李姿燕, 陈炜曦, 李子涵, 黎茵, 梁峰铭, 曾祥利, 荐红举, 吕典秋. 基于RNA-Seq筛选调控马铃薯熟性的候选基因[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1505-1518. |
| [12] | 张美迪, 马明, 李晓楠, 姜明亮. 大白菜耐抽薹性状研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(5): 1136-1158. |
| [13] | 吕桂芳, 臧运平, 陶正国, 刘翠翠, 张华丽, 包满珠, 何燕红. 万寿菊花色表型数量分类与群体花色遗传研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 646-654. |
| [14] | 程小改, 万源, 林琭, 谢鹏, 李志强, 李谧, 王鹏鹏, 牛自勉. 苹果开心树形树干高度对不同冠层部位叶片光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 671-692. |
| [15] | 赵钰磊, 李珊, 李承男, 马金龙, 马红义, 尹晓. 灰霉菌侵染葡萄叶片初期的蛋白质组学研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 279-291. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司