
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 2969-2986.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0257
刘玉洁1, 尹志1, 王媛2, 康敏3, 李瑞珍3, 聂园军3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-21
修回日期:2025-07-06
出版日期:2025-11-26
发布日期:2025-11-26
通讯作者:
基金资助:
LIU Yujie1, YIN Zhi1, WANG Yuan2, KANG Min3, LI Ruizhen3, and NIE Yuanjun3,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-21
Revised:2025-07-06
Published:2025-11-26
Online:2025-11-26
摘要: 以番茄为供试材料,2023—2024年连续2茬(秋茬和冬春茬)在连作番茄8年的设施大棚内设化肥(MF)、有机粪肥替代化肥(OF)、草炭基质(PS)及菌糠牛粪堆腐后的有机基质(OS)4个处理,研究不同栽培基质对番茄根系、植株氮素吸收、产量和品质的影响,以明确采用菌糠和牛粪堆腐后的基质在设施番茄抗连作生产中的效果。结果表明:(1)番茄收获期两茬中OS处理的根系生物量最高,较MF处理分别增加了42.00%和45.04%,较PS分别提高了16.04%和11.51%。PS处理下根系增长较为明显,而OS处理下根系倾向于增粗。与MF相比较,两茬收获期PS处理下总根长分别增加了85.58%和120.46%,OS处理下则分别增加了42.86%和59.74%。OS处理下两茬收获期根平均直径较MF分别提高了20.97%和23.38%。(2)OS处理下番茄根系氮累积量、地上部氮累积量、产量和糖酸比达到最高,与MF相比,秋茬增幅分别为68.71%、63.63%、35.29%和22.49%,冬春茬增幅分别为44.76%、27.46%、31.09%和11.88%。OS处理下秋茬番茄根系氮累积量、地上部氮累积量、产量和糖酸比较PS处理分别增加了41.71%、27.53%、5.26%和12.89%,冬春茬增幅则分别为12.59%、5.88%、4.49%和6.25%。(3)相关性分析表明,两茬中番茄地上部氮累积量与总根长、糖酸比、根系生物量、地上部生物量、根系氮累积量和番茄产量呈显著正相关,与有机酸含量呈显著负相关,且冬春茬中植株地上部氮累积量还与番茄维生素C含量、总糖含量和根表面积呈显著正相关。综上,采用菌糠牛粪堆肥发酵制作而成的有机栽培基质(OS)设施番茄抗连作生产效果优于常规施肥(MF、OF)和草炭基质。主要体现在其能有效改善设施连作番茄根系生长,促进根系增粗,显著提升植株氮素吸收能力,最终实现产量和果实品质的协同提升的同时,大幅降低了生产成本,为设施番茄抗连作生产及农业废弃物资源化利用提供了高效可行的技术方案。
刘玉洁, 尹志, 王媛, 康敏, 李瑞珍, 聂园军. 菌糠堆肥基质对设施连作番茄根系、氮素累积及果实产量和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(11): 2969-2986.
LIU Yujie, YIN Zhi, WANG Yuan, KANG Min, LI Ruizhen, and NIE Yuanjun. Effects of Spent Mushroom Substrates on the Roots,Nitrogen Accumulation,Yield and Fruit Quality of Continuous Tomato in Greenhouse[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(11): 2969-2986.
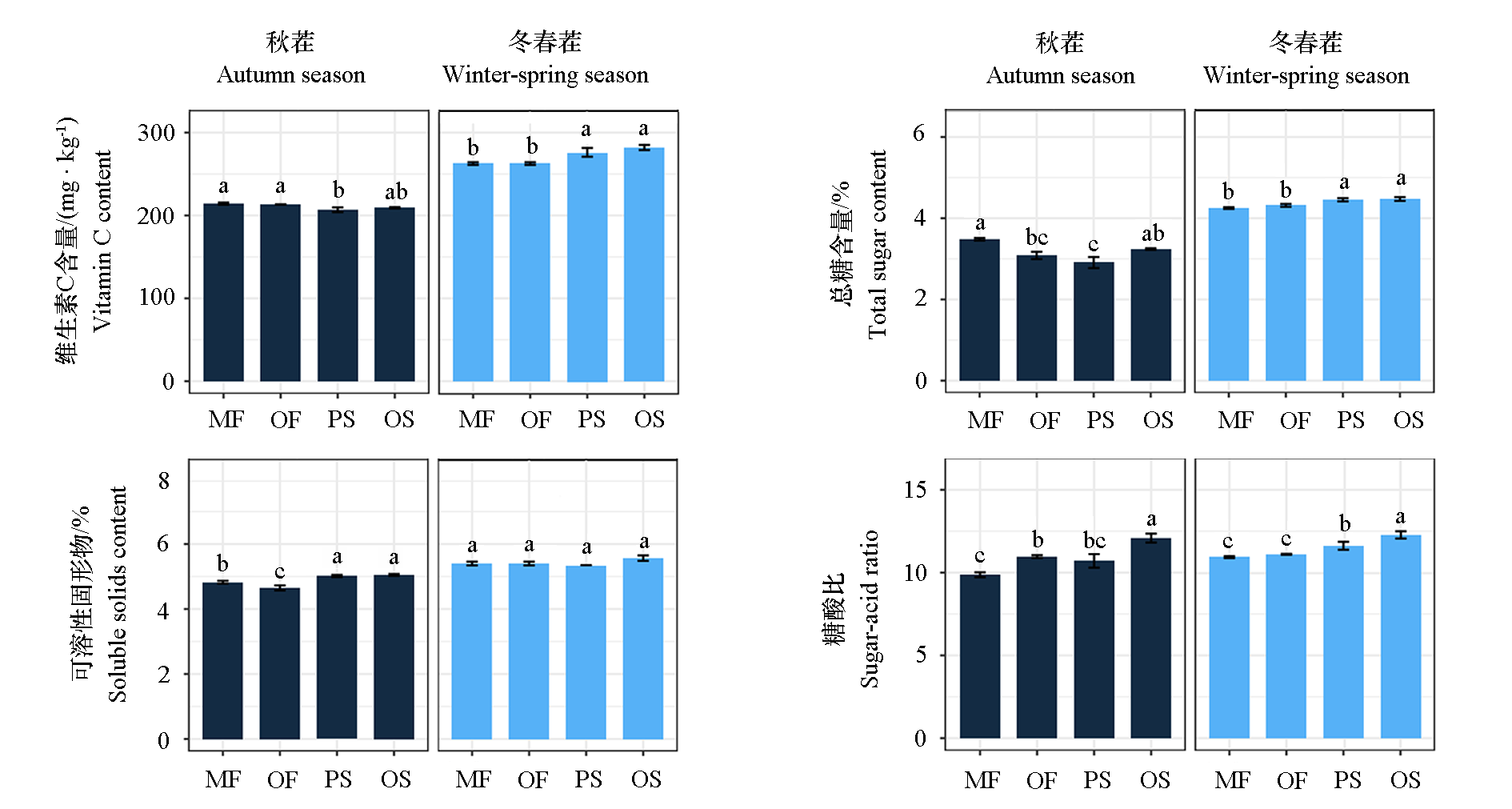
图1 不同栽培处理对番茄果实品质和产量的影响 MF、OF、PS、OS分别代表施用化肥、施用有机肥、采用草炭基质及菌糠堆腐基质的栽培方式。不同小写字母代表不同处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同
Fig. 1 Effects of different cultivation treatments on fruit quality and yield of tomato MF,OF,PS and OS represent the application of chemical fertilizer,organic fertilizer,peat matrix and organic matrix cultivation,respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments(P < 0.05). The same below
| 季节 season | 生育时期 Growth stages | 处理 Treat-ment | 总根长/m Total root length | 根表面积/cm2 Root surface area | 根平均直径/mm Average diameter | 根体积/cm3 Root volume | 比根长/(m · g-1) Specific root length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 秋茬 Autumn season | 苗期 Seedling stage | MF | 14.47 ± 1.03 a | 167.81 ± 1.44 ab | 0.414 ± 0.022 a | 1.61 ± 0.10 a | 149.97 ± 9.23 a |
| OF | 13.57 ± 1.86 a | 158.41 ± 4.58 bc | 0.421 ± 0.004 a | 1.77 ± 0.02 a | 98.14 ± 5.45 c | ||
| PS | 15.23 ± 0.89 a | 175.38 ± 3.62 a | 0.393 ± 0.034 a | 1.62 ± 0.03 a | 122.33 ± 7.38 b | ||
| OS | 11.77 ± 0.23 a | 152.43 ± 5.00 c | 0.429 ± 0.013 a | 1.63 ± 0.04 a | 100.80 ± 2.22 c | ||
| 开花期 Flowering stage | MF | 19.50 ± 0.84 c | 309.52 ± 25.57 b | 0.546 ± 0.003 a | 4.01 ± 0.12 b | 46.78 ± 3.82 c | |
| OF | 20.01 ± 1.10 c | 290.89 ± 4.09 b | 0.503 ± 0.013 b | 3.90 ± 0.25 b | 69.14 ± 3.50 b | ||
| PS | 38.27 ± 0.35 a | 521.33 ± 9.53 a | 0.459 ± 0.006 c | 6.40 ± 0.08 a | 118.32 ± 4.91 a | ||
| OS | 24.39 ± 0.53 b | 314.42 ± 3.96 b | 0.490 ± 0.004 b | 4.21 ± 0.02 b | 60.86 ± 1.05 b | ||
| 收获期 Harvest stage | MF | 23.10 ± 0.58 d | 609.93 ± 12.89 b | 0.619 ± 0.032 b | 10.55 ± 0.40 b | 13.60 ± 0.59 b | |
| OF | 27.01 ± 0.43 c | 617.76 ± 18.99 b | 0.644 ± 0.029 b | 10.16 ± 1.25 b | 12.23 ± 0.38 b | ||
| PS | 42.87 ± 1.57 a | 604.40 ± 27.62 b | 0.534 ± 0.003 c | 12.10 ± 0.28 ab | 19.00 ± 0.61 a | ||
| OS | 33.00 ± 0.36 b | 719.40 ± 7.81 a | 0.749 ± 0.013 a | 13.70 ± 0.23 a | 10.05 ± 0.51 c | ||
| 冬春茬 Winter-spring season | 苗期 Seedling stage | MF | 12.36 ± 0.47 b | 215.97 ± 4.45 b | 0.605 ± 0.004 ab | 3.09 ± 0.01 a | 138.00 ± 3.99 a |
| OF | 10.43 ± 0.14 c | 173.37 ± 5.73 c | 0.610 ± 0.004 a | 2.95 ± 0.03 b | 115.56 ± 5.18 b | ||
| PS | 14.02 ± 0.23 a | 245.97 ± 2.22 a | 0.588 ± 0.009 b | 3.15 ± 0.03 a | 145.80 ± 5.33 a | ||
| OS | 13.54 ± 0.21 a | 223.27 ± 5.01 b | 0.594 ± 0.002 ab | 3.13 ± 0.02 a | 147.26 ± 2.75 a | ||
| 开花期 Flowering stage | MF | 17.51 ± 0.33 c | 342.57 ± 11.81 b | 0.597 ± 0.007 b | 4.86 ± 0.30 b | 29.95 ± 0.93 c | |
| OF | 15.21 ± 0.73 d | 265.66 ± 4.30 c | 0.612 ± 0.005 ab | 4.20 ± 0.17 c | 29.19 ± 0.91 c | ||
| PS | 32.36 ± 0.79 a | 515.49 ± 11.83 a | 0.564 ± 0.012 c | 5.74 ± 0.09 a | 62.85 ± 0.61 a | ||
| OS | 26.07 ± 0.61 b | 488.99 ± 10.91 a | 0.628 ± 0.006 a | 5.15 ± 0.04 b | 41.19 ± 0.10 b | ||
| 收获期 Harvest stage | MF | 19.60 ± 0.24 d | 634.63 ± 32.56 b | 0.770 ± 0.028 b | 15.04 ± 1.20 a | 8.51 ± 0.48 b | |
| OF | 24.53 ± 1.48 c | 812.44 ± 24.11 a | 0.765 ± 0.023 b | 10.04 ± 0.74 b | 8.27 ± 0.50 b | ||
| PS | 43.21 ± 1.15 a | 902.39 ± 31.93 a | 0.690 ± 0.005 c | 13.23 ± 0.53 a | 15.40 ± 0.61 a | ||
| OS | 31.31 ± 1.24 b | 866.65 ± 34.57 a | 0.950 ± 0.009 a | 13.73 ± 0.73 a | 9.77 ± 0.60 b |
表1 不同栽培处理对番茄各生育期根系生长的影响
Table 1 Effects of different cultivation treatments on tomato root growth at different growth stages
| 季节 season | 生育时期 Growth stages | 处理 Treat-ment | 总根长/m Total root length | 根表面积/cm2 Root surface area | 根平均直径/mm Average diameter | 根体积/cm3 Root volume | 比根长/(m · g-1) Specific root length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 秋茬 Autumn season | 苗期 Seedling stage | MF | 14.47 ± 1.03 a | 167.81 ± 1.44 ab | 0.414 ± 0.022 a | 1.61 ± 0.10 a | 149.97 ± 9.23 a |
| OF | 13.57 ± 1.86 a | 158.41 ± 4.58 bc | 0.421 ± 0.004 a | 1.77 ± 0.02 a | 98.14 ± 5.45 c | ||
| PS | 15.23 ± 0.89 a | 175.38 ± 3.62 a | 0.393 ± 0.034 a | 1.62 ± 0.03 a | 122.33 ± 7.38 b | ||
| OS | 11.77 ± 0.23 a | 152.43 ± 5.00 c | 0.429 ± 0.013 a | 1.63 ± 0.04 a | 100.80 ± 2.22 c | ||
| 开花期 Flowering stage | MF | 19.50 ± 0.84 c | 309.52 ± 25.57 b | 0.546 ± 0.003 a | 4.01 ± 0.12 b | 46.78 ± 3.82 c | |
| OF | 20.01 ± 1.10 c | 290.89 ± 4.09 b | 0.503 ± 0.013 b | 3.90 ± 0.25 b | 69.14 ± 3.50 b | ||
| PS | 38.27 ± 0.35 a | 521.33 ± 9.53 a | 0.459 ± 0.006 c | 6.40 ± 0.08 a | 118.32 ± 4.91 a | ||
| OS | 24.39 ± 0.53 b | 314.42 ± 3.96 b | 0.490 ± 0.004 b | 4.21 ± 0.02 b | 60.86 ± 1.05 b | ||
| 收获期 Harvest stage | MF | 23.10 ± 0.58 d | 609.93 ± 12.89 b | 0.619 ± 0.032 b | 10.55 ± 0.40 b | 13.60 ± 0.59 b | |
| OF | 27.01 ± 0.43 c | 617.76 ± 18.99 b | 0.644 ± 0.029 b | 10.16 ± 1.25 b | 12.23 ± 0.38 b | ||
| PS | 42.87 ± 1.57 a | 604.40 ± 27.62 b | 0.534 ± 0.003 c | 12.10 ± 0.28 ab | 19.00 ± 0.61 a | ||
| OS | 33.00 ± 0.36 b | 719.40 ± 7.81 a | 0.749 ± 0.013 a | 13.70 ± 0.23 a | 10.05 ± 0.51 c | ||
| 冬春茬 Winter-spring season | 苗期 Seedling stage | MF | 12.36 ± 0.47 b | 215.97 ± 4.45 b | 0.605 ± 0.004 ab | 3.09 ± 0.01 a | 138.00 ± 3.99 a |
| OF | 10.43 ± 0.14 c | 173.37 ± 5.73 c | 0.610 ± 0.004 a | 2.95 ± 0.03 b | 115.56 ± 5.18 b | ||
| PS | 14.02 ± 0.23 a | 245.97 ± 2.22 a | 0.588 ± 0.009 b | 3.15 ± 0.03 a | 145.80 ± 5.33 a | ||
| OS | 13.54 ± 0.21 a | 223.27 ± 5.01 b | 0.594 ± 0.002 ab | 3.13 ± 0.02 a | 147.26 ± 2.75 a | ||
| 开花期 Flowering stage | MF | 17.51 ± 0.33 c | 342.57 ± 11.81 b | 0.597 ± 0.007 b | 4.86 ± 0.30 b | 29.95 ± 0.93 c | |
| OF | 15.21 ± 0.73 d | 265.66 ± 4.30 c | 0.612 ± 0.005 ab | 4.20 ± 0.17 c | 29.19 ± 0.91 c | ||
| PS | 32.36 ± 0.79 a | 515.49 ± 11.83 a | 0.564 ± 0.012 c | 5.74 ± 0.09 a | 62.85 ± 0.61 a | ||
| OS | 26.07 ± 0.61 b | 488.99 ± 10.91 a | 0.628 ± 0.006 a | 5.15 ± 0.04 b | 41.19 ± 0.10 b | ||
| 收获期 Harvest stage | MF | 19.60 ± 0.24 d | 634.63 ± 32.56 b | 0.770 ± 0.028 b | 15.04 ± 1.20 a | 8.51 ± 0.48 b | |
| OF | 24.53 ± 1.48 c | 812.44 ± 24.11 a | 0.765 ± 0.023 b | 10.04 ± 0.74 b | 8.27 ± 0.50 b | ||
| PS | 43.21 ± 1.15 a | 902.39 ± 31.93 a | 0.690 ± 0.005 c | 13.23 ± 0.53 a | 15.40 ± 0.61 a | ||
| OS | 31.31 ± 1.24 b | 866.65 ± 34.57 a | 0.950 ± 0.009 a | 13.73 ± 0.73 a | 9.77 ± 0.60 b |

图4 番茄氮素吸收与生长及品质指标的相关性分析 A:秋茬;W-S:冬春茬。*、**和***分别表示在0.05、0.01和0.001水平显著相关
Fig. 4 Correlation analysis between nitrogen uptake,growth index and quality of tomato A:Autumn season;W-S:Winter-spring season. *,** and *** indicated significant correlations at 0.05,0.01 and 0.001 levels,respectively
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
|
赵世杰, 史国安, 董新纯. 2002. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社.
|
|
| [85] |
|
|
赵文举, 杨喜爱, 俞海英, 李建承, 马宏. 2024. 腐殖酸对盐碱地基质栽培番茄生长特性的影响. 农业工程学报, 40 (19):105-113.
|
|
| [86] |
|
|
张文昊, 张辉, 刘雨婷, 王艳, 张迎迎, 王馨曼, 王全华, 朱为民, 杨学东. 2024. 番茄含糖量不同的两个材料果实转录组初步分析. 园艺学报, 51 (2):281-294.
|
|
| [87] |
|
|
张泽雄, 丘苑新, 莫观连, 陈彩云, 柳建良, 王琴, 钟乐, 谢宏峰. 2024. 鱼花生大豆废弃物发酵肥的制备及其对桃品质的影响. 园艺学报, 51 (10):2386-2400.
|
|
| [88] |
|
|
周江明, 王利通, 徐庆华, 姜新有. 2015. 适宜猪粪与菌渣配比提高堆肥效率. 农业工程学报, 31 (7):201-207.
|
|
| [89] |
|
|
周杰, 师恺, 夏晓剑, 周艳虹, 喻景权. 2022. 中国蔬菜栽培科技 60 年回顾与展望. 园艺学报, 49 (10):2131-2142.
|
|
| [90] |
|
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
鲍士旦. 2000. 土壤农化分析. 3版. 北京:中国农业出版社:56-188.
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
China Edible Fungi Association. 2025. Analysis of the results of the 2023 national edible fungi statistical survey. Chinese Edible Fungi, 44 (1):120-129. (in Chinese)
|
|
中国食用菌协会. 2025. 2023年度全国食用菌统计调查结果分析. 中国食用菌, 44 (1):120-129.
|
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
DB 14/T 2337-2021. Technical regulation on simplified cultivation of greenhouse tomato using substrates. Shanxi Market Supervision and Administration Bureau. (in Chinese)
|
|
DB 14/T 2337-2021. 设施番茄简易基质栽培技术规程. 山西省市场监督管理局.
|
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
GB 5009.7-2016. National food safety standard-determination of reducing sugars. (in Chinese)
|
|
GB 5009.7-2016. 食品安全国家标准食品中还原糖的测定.
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
|
郭世荣. 2005. 固体栽培基质研究、开发现状及发展趋势. 农业工程学报,(21):1-4.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
韩召强, 陈效民, 曲成闯, 张晓玲, 张俊, 黄春燕, 刘云梅. 2018. 生物质炭对黄瓜连作土壤理化性状、酶活性及土壤质量的持续效应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 24 (5):1227-1236.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
郝丹, 张璐, 孙向阳, 龚小强. 2020. 金盏菊栽培中园林废弃物堆肥与牛粪替代泥炭的效果分析. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26 (8):1556-1564.
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
|
季延海, 赵孟良, 武占会, 梁浩, 刘明池. 2017. 番茄栽培基质中菊芋发酵秸秆的适宜配比研究. 园艺学报, 44 (8):1599-1608.
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
|
李天来, 张亢亢, 余朝阁, 李琳琳. 2012. 外源钙和茉莉酸甲酯诱导番茄植株抗灰霉病研究. 西北植物学报, 32 (3):505-510.
|
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
|
刘小龙, 冯国瑞, 张新疆, 马林, 邢翔, 吕海丽, 危常州. 2022. 干旱区滴灌玉米出苗期施用启动磷肥的增产效应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 28 (10):1937-1946.
|
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
|
沈衡, 王琳, 李骞, 袁守娟, 郑伟, 王涛涛, 叶志彪, 杨长宪. 2024. 番茄风味和功能性成分研究进展. 园艺学报, 51 (2):423-438.
|
|
| [62] |
|
|
时连辉, 张志国, 刘登民, 李文清, 贾文, 鲍仁蕾. 2008. 菇渣和泥炭基质理化特性比较及其调节. 农业工程学报, 24 (4):199-203.
|
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
|
孙光闻, 陈日远, 刘厚诚. 2005. 设施蔬菜连作障碍原因及防治措施. 农业工程学报,(S2):184-188.
|
|
| [65] |
|
|
孙燕, 吴建鑫, 曲植, 韩宁, 陆江岳, 马莹莹, 胡子付. 2023. 生化黄腐酸对不同质地苏打盐碱土水盐运移特征的影响. 农业工程学报, 39 (22):74-84.
|
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
|
王磊, 高方胜, 张志焕, 李炜蔷, 曹逼力, 徐坤. 2024. 嫁接番茄果实糖分变化及其与氮磷含量相关性分析. 园艺学报, 51 (2):361-371.
|
|
| [71] |
|
|
王星林, 刘颖, 胡雨松, 孙周平, 刘义玲. 2024. 蚯蚓粪对日光温室袋培甜瓜生长及营养吸收的影响. 核农学报, 38 (2):345-354.
|
|
| [72] |
|
|
王志强, 吴翠云, 杨哲, 杨凡, 武彦昌. 2018. 盐碱胁迫对酸枣幼苗生长及生理生化特性的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 36 (2):153-160.
|
|
| [73] |
|
|
魏守辉, 肖雪梅, 钟源, 郁继华, 吕剑, 胡琳莉, 唐中祺, 柳帆红, 王舒亚, 坚乃丹. 2020. 日光温室不同时段补光对番茄果实品质及挥发性物质影响. 农业工程学报, 36 (8):188-196.
|
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
|
肖雪梅, 高程斐, 武玥, 唐中祺, 钟源, 张丹, 魏晋梅, 郁继华. 2023. 不同类型叶面肥对日光温室越冬番茄风味品质的影响. 农业工程学报, 39 (10):218-226.
|
|
| [78] |
|
|
熊长明, 王晔, 田晓莉. 2014. 植物矿质养分吸收的长距离反馈调节研究进展. 植物营养与肥料学报, 20 (3):737-746.
|
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [90] |
周杰良, 王建湘, 李树战, 张雄. 2007. 沼液对有机基质栽培青椒果实产量及品质的影响. 农业现代化研究, 28 (2):254-256.
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
|
周录英, 李向东, 王丽丽, 汤笑, 林英杰. 2008. 钙肥不同用量对花生生理特性及产量和品质的影响. 作物学报, 34 (5):879-885.
|
|
| [93] |
|
|
邹春娇, 张勇勇, 张一鸣, 郭小鸥, 李明静, 李天来. 2015. 生物炭对设施连作黄瓜根域基质酶活性和微生物的调节. 应用生态学报, 26 (6):1772-1778.
|
|
| [81] |
|
| [1] | 刘照坤, 王欢, 韩建军, 王莹莹, 周鸿章. 不结球白菜新品种‘苏青1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 101-102. |
| [2] | 宰文珊, 陈先知, 付存念, 苏世闻, 史建磊, 熊自立, 黄少勇. 口感番茄新品种‘瓯秀901’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 121-122. |
| [3] | 王荣青, 姚祝平, 程远, 叶青静, 阮美颖, 万红建, 李志邈, 刘晨旭, 周国治. 高品质耐贮运番茄新品种‘浙粉718’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 123-124. |
| [4] | 郑梦凡, 谢勇, 郑伟, 李光乾, 陈刚, 王煜双, 李聪, 张余洋. 优质番茄新品种‘民丰698’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 125-126. |
| [5] | 朱鹏宇, 谢勇, 郑伟, 李光乾, 陈刚, 王煜双, 李聪, 张余洋. 优质番茄新品种‘希唯美191’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 127-128. |
| [6] | 崔爱花, 朱模勇, 张扬栋, 伍琦, 刘帅, 胡启星, 黄纪刚, 刘家鑫, 刘为胜, 孙巨龙. 大果型番茄新品种‘奥丽亚’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 129-130. |
| [7] | 郑于莉, 刘燕, 潘子旺, 韩兰兰, 李凯, 刘丹, 曹阳, 芦鑫哲, 康永生. 多抗硬粉番茄新品种‘BY002’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 131-132. |
| [8] | 苏世闻, 付存念, 陈先知, 崔丽利, 史建磊, 黄少勇, 熊自立, 宰文珊. 樱桃番茄新品种‘瓯秀红樱5号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 133-134. |
| [9] | 付存念, 苏世闻, 陈先知, 崔丽利, 史建磊, 黄少勇, 熊自立, 宰文珊. 樱桃番茄新品种‘瓯秀橙樱1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 135-136. |
| [10] | 熊自立, 苏世闻, 史建磊, 张海利, 宰文珊, 崔丽利. 番茄砧木新品种‘瓯砧1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 137-138. |
| [11] | 朱德宁, 吴宇军, 余炳伟, 李莲芳. 有棱丝瓜新品种‘夏胜6号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 167-168. |
| [12] | 余小林, 平 凡, 黄 鹂, 曹家树, 宋建伟, 卢 钢. 早中熟不结球白菜新品种‘钱塘青’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 91-92. |
| [13] | 范惠冬, 郑士金, 田 松, 郑建超. 番茄新品种‘吉粉7号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 109-110. |
| [14] | 张立微, 戴忠仁, 陈青奇, 雷 娜, 胡海江, 门万杰. 番茄新品种‘哈研中粉果1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 111-112. |
| [15] | 熊自立, 史建磊, 陈勇兵, 张海利, 苏世闻, 宰文珊, 叶曙光. 设施番茄新品种‘瓯秀202’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 113-114. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司