
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1789-1802.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0791
董炫克1,2, 李映旸1,2, 马豫皖1,2, 蔡艳芳1, 丁启涵1,2, 陈海霞1,2, 李玉帆1,2,*( ), 陈己任1,2,*(
), 陈己任1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-20
修回日期:2025-05-07
出版日期:2025-07-23
发布日期:2025-07-23
通讯作者:
基金资助:
DONG Xuanke1,2, LI Yingyang1,2, MA Yuwan1,2, CAI Yanfang1, DING Qihan1,2, CHEN Haixia1,2, LI Yufan1,2,*( ), and CHEN Jiren1,2,*(
), and CHEN Jiren1,2,*( )
)
Received:2025-05-20
Revised:2025-05-07
Published:2025-07-23
Online:2025-07-23
摘要:
以月季‘月月红’(Rosa chinensis‘Yueyuehong’)扦插苗为材料,分析了RcTCP9基因在盐和干旱胁迫不同时间的表达模式,结果表明,在盐和干旱胁迫条件下RcTCP9的表达量显著上调,说明其对两种胁迫有积极响应。将RcTCP9在烟草中瞬时表达,通过观察绿色荧光信号发现其编码蛋白定位于细胞核上。病毒诱导的基因沉默(VIGS)技术和瞬时过表达试验发现,RcTCP9的沉默会导致植株在盐和干旱胁迫下出现叶片及根系萎蔫等生理损伤表征,植物细胞离子渗透率及丙二醛(MDA)含量增加,过氧化氢酶(CAT)及过氧化物酶(POD)活性水平则降低。过表达的月季花瓣应对两种胁迫细胞膜损伤减少,褪色率和MDA含量降低,表现出更好的抗性。测定过表达植株在盐和干旱胁迫下耐逆相关基因的表达水平,结果显示RcTCP9的表达可能通过调控RcPR4-1和RcNAC091相关通路来增强植物的胁迫耐受性。综上所述,RcTCP9在提高月季对盐和干旱胁迫的耐受性方面具有重要作用。
董炫克, 李映旸, 马豫皖, 蔡艳芳, 丁启涵, 陈海霞, 李玉帆, 陈己任. 月季‘月月红’RcTCP9基因在盐和干旱胁迫中的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(7): 1789-1802.
DONG Xuanke, LI Yingyang, MA Yuwan, CAI Yanfang, DING Qihan, CHEN Haixia, LI Yufan, and CHEN Jiren. The Functional Analysis of RcTCP9 Gene in Response to Salt and Drought Stress in Rosa chinensis‘Yueyuehong’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(7): 1789-1802.
| 用途 Purpose | 名称 Name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆RcTCP9基因CDS全长 Clone the full-length CDS of the RcTCP9 gene | KL-RcTCP9-F | ATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGATCAAG |
| KL-RcTCP9-R | TCACTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTG | |
| 亚细胞定位载体构建 Construction of subcellular localization vector | pBI121-RcTCP9-F | ACGGGGGACTCTAGAGGATCCATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGA |
| pBI121-RcTCP9-R | GGACTGACCACCCGGGGATCCCTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGG | |
| 瞬时过表达载体构建 Construction of transient overexpression vector | 1305-RcTCP9-F | GGAGAGAACACGGGGGACATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGATCA |
| 1305-RcTCP9-R | CATCATGGTCTTTGTAGTCCTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGGCGGG | |
| VIGS基因沉默载体构建 Construction of VIGS gene silencing vector | TRV2-RcTCP9-F | CTGTGAGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCGTTCGTGGGGAACGGCGGAG |
| TRV2-RcTCP9-R | CGCGTGAGCTCGGTACCGGATCCCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGGCGG | |
| 实时荧光定量表达 (qRT-PCR) | RcTCP9-F | TGGTAGTGGTAACAGTAACA |
| RcTCP9-R | CTCCTGCTTATCGTAAATCTC | |
| RcCTP-F | GGGTGATGATGCAGCTTT | |
| RcCTP-R | TTAGCACTTGACCTCCTTCA | |
| RcPR4/1-F | ATGGCCGGAAAACAATGC | |
| RcPR4/1-R | GGGCTTGTCGGCATCC | |
| RcNAC091-F | TGTCTTCCTCGGAGTTACAGTTACC | |
| RcNAC091-R | CCCAGGGGTCGTATTTGTACAG |
表1 试验中所用引物序列
Table 1 The sequences of primers used for experiment
| 用途 Purpose | 名称 Name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆RcTCP9基因CDS全长 Clone the full-length CDS of the RcTCP9 gene | KL-RcTCP9-F | ATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGATCAAG |
| KL-RcTCP9-R | TCACTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTG | |
| 亚细胞定位载体构建 Construction of subcellular localization vector | pBI121-RcTCP9-F | ACGGGGGACTCTAGAGGATCCATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGA |
| pBI121-RcTCP9-R | GGACTGACCACCCGGGGATCCCTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGG | |
| 瞬时过表达载体构建 Construction of transient overexpression vector | 1305-RcTCP9-F | GGAGAGAACACGGGGGACATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGATCA |
| 1305-RcTCP9-R | CATCATGGTCTTTGTAGTCCTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGGCGGG | |
| VIGS基因沉默载体构建 Construction of VIGS gene silencing vector | TRV2-RcTCP9-F | CTGTGAGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCGTTCGTGGGGAACGGCGGAG |
| TRV2-RcTCP9-R | CGCGTGAGCTCGGTACCGGATCCCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGGCGG | |
| 实时荧光定量表达 (qRT-PCR) | RcTCP9-F | TGGTAGTGGTAACAGTAACA |
| RcTCP9-R | CTCCTGCTTATCGTAAATCTC | |
| RcCTP-F | GGGTGATGATGCAGCTTT | |
| RcCTP-R | TTAGCACTTGACCTCCTTCA | |
| RcPR4/1-F | ATGGCCGGAAAACAATGC | |
| RcPR4/1-R | GGGCTTGTCGGCATCC | |
| RcNAC091-F | TGTCTTCCTCGGAGTTACAGTTACC | |
| RcNAC091-R | CCCAGGGGTCGTATTTGTACAG |

图2 TRV2-RcTCP9沉默载体的构建 A:RcTCP9有效片段与TRV2-RcTCP9比对结果;B:菌落PCR凝胶电泳图
Fig. 2 Construction of the TRV2-RcTCP9 silencing vector A:Comparison results between the effective fragment of RcTCP9 and TRV2-RcTCP9;B:Gel electrophoresis image of colony PCR
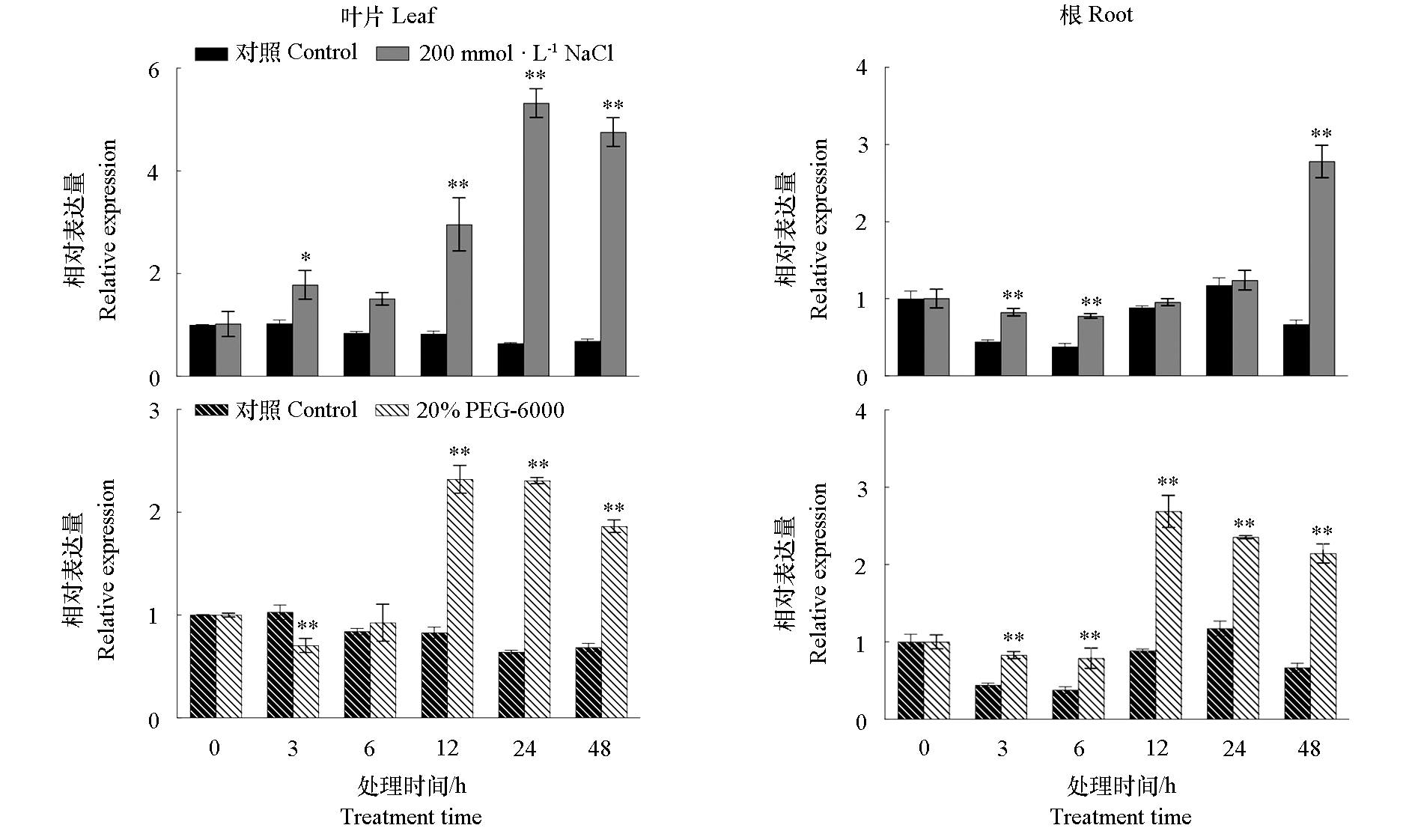
图5 月季‘月月红’扦插苗在盐和干旱胁迫下RcTCP9的组织表达分析 *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01。下同
Fig. 5 Tissue-specific expression analysis of RcTCP9 in cuttings of Rosa chinensis‘Yueyuehong’under salt and drought stress *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01. The same below
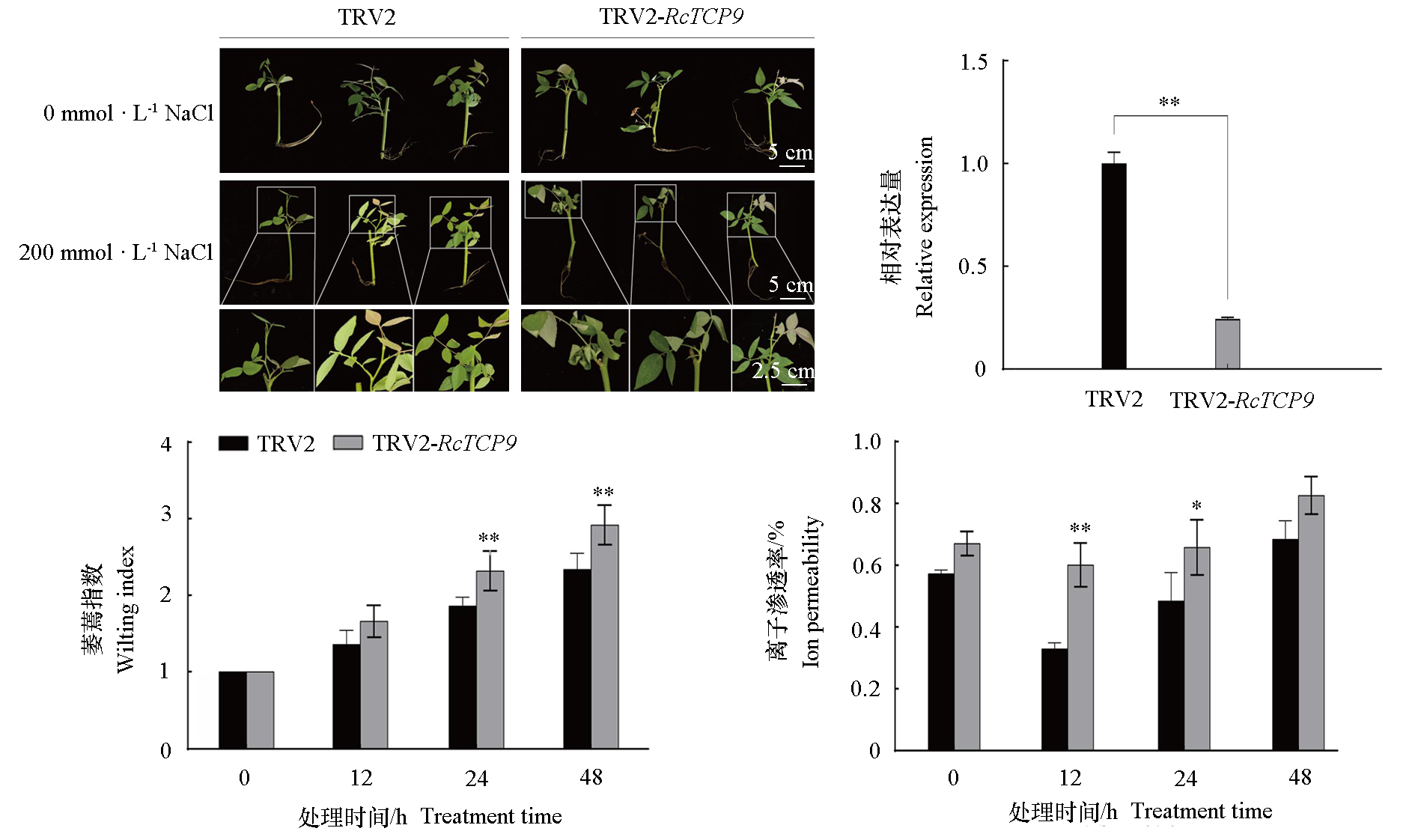
图6 盐胁迫下VIGS沉默RcTCP9组和对照组月季扦插苗表型、RcTCP9表达量及生理指标变化
Fig. 6 The changes of phenotype phenotype,RcTCP9 expression and physiological indexes of roses cutting seedlings in VIGS silencing RcTCP9 group and control group under salt stress
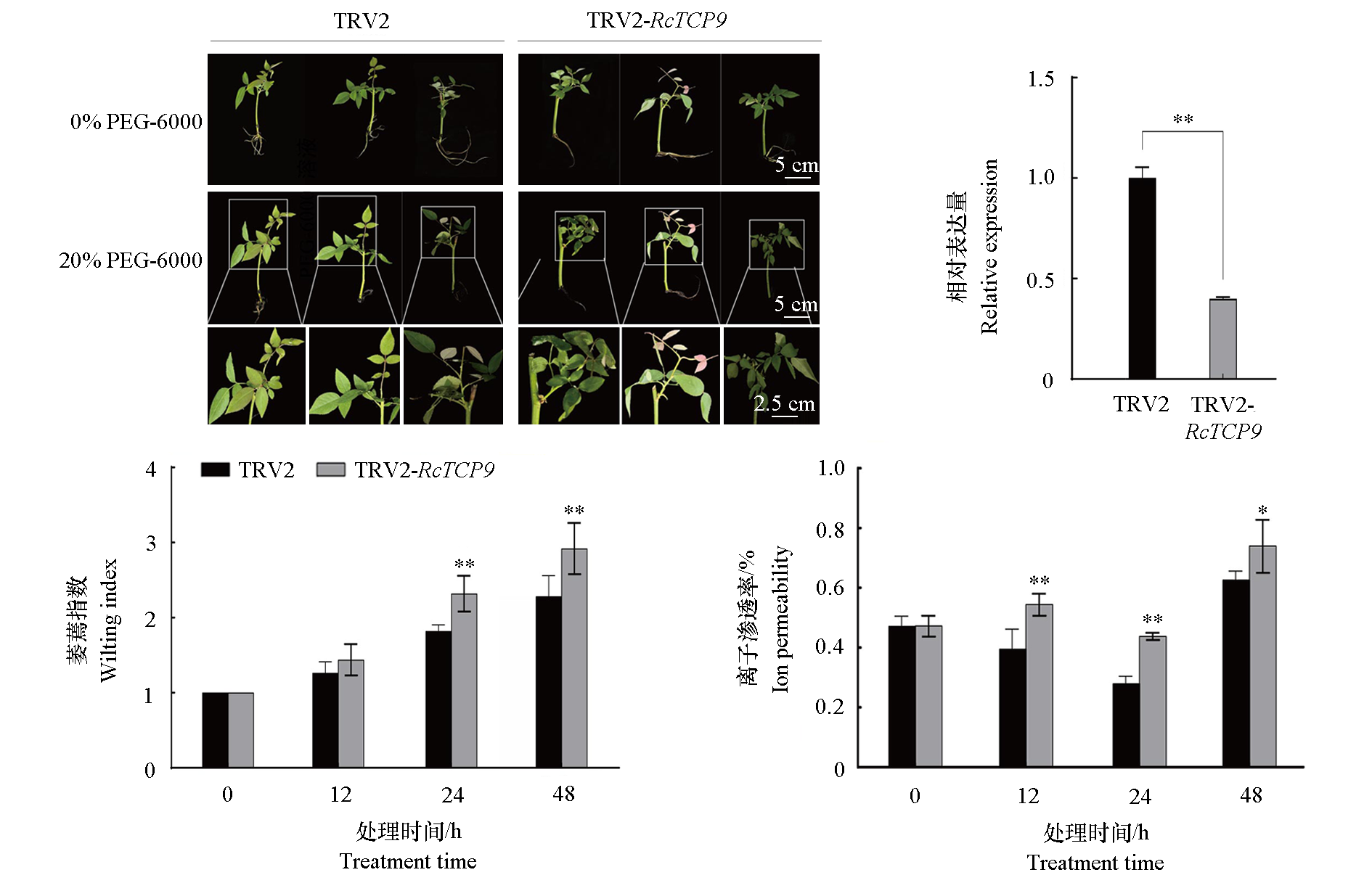
图9 干旱胁迫下VIGS沉默RcTCP9组和对照组月季扦插苗表型、RcTCP9表达量及生理指标变化
Fig. 9 The changes of phenotype,RcTCP9 expression and physiological indexes of roses cuttings in VIGS silencing RcTCP9 group and control group under drought stress
| [1] |
|
|
陈爱葵, 韩瑞宏, 李东洋, 凌连莲, 罗惠霞, 唐上剑. 2010. 植物叶片相对电导率测定方法比较研究. 广东教育学院学报, 30 (5):88-91.
|
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0794 |
|
贾鑫, 曾臻, 陈月, 冯慧, 吕英民, 赵世伟. 2022. 月季‘月月粉’RcDREB2A的克隆与表达分析. 园艺学报, 49 (9):1945-1956.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0794 |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2023-1045 |
|
李慧, 文钰芳, 王悦, 纪超, 石国优, 罗英, 周勇, 李志敏, 吴晓玉, 杨有新, 刘建萍. 2024. 盐胁迫下辣椒CaPIF4的表达特性与功能分析. 生物技术通报, 40 (4):148-158.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2023-1045 |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
刘飞, 杨亲康, 何德钏, 邢宝龙, 李梦蛟. 2024. 豌豆NAC基因家族鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下的响应分析. 农业生物技术学报, 32 (7):504-1517.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
倪芮, 罗悠悠, 黄渺, 蔡骏一, 何奕含, 刘文霖, 姚依妮, 肇瑾. 2024. 火龙果HpTCP9基因克隆及其在干旱胁迫下的表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 32 (7):1533-1542.
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
|
[ 汪桂凤. 2019. PEG模拟耐干旱大豆种质资源的筛选及苗期生理生化特性研究[硕士论文]. 杭州:浙江大学.
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
|
谢磊, 王姗珊, 胡博文, 熊兴耀, 陈己任. 2017. 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术的月季TCP9基因转化拟南芥. 分子植物育种, 15 (3):928-933.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
杨碧楠, 李博文, 杨振宇, 徐奕芃, 阎韵清, 娄玉霞, 奉树成, 明凤. 2024. 月季‘安吉拉’热胁迫反应机制及功能基因的挖掘. 园艺学报, 51 (6):1284-1296.
|
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.14920 pmid: 29205383 |
| [30] |
|
|
姚莹, 王伟, 孙永媛, 曹金锋, 魏建荣, 刘建凤. 2021. 沙棘HrTCP转录因子家族鉴定及其干旱胁迫下的表达分析. 西北植物学报, 41 (4):576-584.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
岳玲, 迟东明, 宋伟, 果鹏忠. 2010. 月季抗性研究进展. 北方园艺,(9):225-227.
|
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
[ 张伟杰. 2023. 野生玫瑰耐盐生理机制研究与耐盐调控因子挖掘[硕士论文]. 扬州:扬州大学
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
[ 张欣. 2020. PdbTCP9基因调控山新杨干旱应答和次生壁合成的功能研究[博士论文]. 哈尔滨:东北林业大学.
|
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
|
周欢欢, 傅卢成, 马玲, 赵亚红, 张汝民, 高岩. 2019. 干旱胁迫及复水对‘波叶金桂’生理特性的影响. 浙江农林大学学报, 36 (4):687-696.
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
周迎雪, 李沛曈, 苏江硕, 王海滨, 房伟民, 陈发棣, 张飞. 2023. 37份菊花近缘种的抗旱性评价. 南京农业大学学报, 46 (6):1060-1068.
|
|
| [38] |
|
|
卓露, 林晓华, 薛山, 梁玉青, 张卓文, 李鸿彬,
|
| [1] | 孔丹睿, 张 玮, 郑萧岳, 王美仙, 赵惠恩. 地被菊新品种‘大漠秋雪’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 169-170. |
| [2] | 孙东宇, 魏冬, 杨胤延, 胡彩珠, 胡志群, 周东辉, 周碧燕. 莲雾开花对喷施氯吡硫磷的生理响应以及转录组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(7): 1718-1732. |
| [3] | 李雯, 李绍朋, 李东海, 吴福川, 田波. 瓷玫瑰切花瓶插期间观赏品质和生理变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1633-1643. |
| [4] | 马豫皖, 刘澳, 刘向东, 张雅婧, 董炫克, 李玉帆, 陈己任. 月季‘月月红’RcRAP2.7的克隆及其在非生物胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 921-932. |
| [5] | 付琪, 王丹, 景维坤, 张颢, 王慧纯, 蹇洪英, 邱显钦, 王其刚, 唐开学, 晏慧君. 月季类胡萝卜素裂解双加氧酶基因RcCCD4在花香合成中的功能[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 623-634. |
| [6] | 阎旭, 李月, 傅小鹏, 宁国贵, 梁梅. 中国古老月季‘月月粉’等位基因不平衡分析与分子标记开发利用[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 365-379. |
| [7] | 李敖, 郑旭, 吴承勖, 聂瑞宁, 姬新颖, 唐佳莉, 张俊佩. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下核桃幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 423-438. |
| [8] | 杨碧楠, 李博文, 杨振宇, 徐奕芃, 阎韵清, 娄玉霞, 奉树成, 明凤. 月季‘安吉拉’热胁迫反应机制及功能基因的挖掘[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1284-1296. |
| [9] | 王雯雨, 王家荫, 杜婷婷, 张晶晶, 张超, 辛翠花, 郭江波, 裴海霞. 月季RhRNF185-like的克隆及其对花瓣衰老影响分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1047-1055. |
| [10] | 兰伟, 孟艳琼, 宣云, 朱糠宁, 丁晓浩, 樊德新, 康丽云. 月季新品种‘颍荷’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 925-926. |
| [11] | 王雅楠, 刘绪涛, 景桐彤, 柴亚婷, 张晓伟, 艾希珍, 毕焕改. 褪黑素对番茄衰老叶片抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2594-2606. |
| [12] | 王宇航, 李斗, 王春恒, 金鑫, 陈亚娟, 戴子博, 冯丽丹, 杨江山. 褪黑素对葡萄叶片发育衰老过程中亚细胞活性氧代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 103-120. |
| [13] | 周 燕 , 高述民 , 崔荣峰 , 孙丽萍 , 付子豪 , . 月季新品种‘燕京黄’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 149-150. |
| [14] | 周洁, 李甜竹, 刘汝懿, 李陈浩, 袁泽南, 李建明. 空气湿度与土壤含水量耦合对番茄灰霉病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1779-1792. |
| [15] | 马梦宇, 胡耀芳, 古琳, 李振坚, 钱永强, 巨关升, 刘俊祥, 孙振元. 瓶插月季枝条光照处理对切花寿命的延长效应[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1343-1354. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司