
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 596-606.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1250
薛玉前1,2,*, 柳志勇2,*, 孙凯荣2, 张秀新2, 吕英民1,**( ), 薛璟祺2,**(
), 薛璟祺2,**( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-25
修回日期:2023-01-13
出版日期:2023-03-25
发布日期:2023-04-03
通讯作者:
**(E-mail:xuejingqi@caas.cn,luyingmin@bjfu.edu.cn)
作者简介:*共同第一作者
基金资助:
XUE Yuqian1,2,*, LIU Zhiyong2,*, SUN Kairong2, ZHANG Xiuxin2, LÜ Yingmin1,**( ), XUE Jingqi2,**(
), XUE Jingqi2,**( )
)
Received:2022-11-25
Revised:2023-01-13
Online:2023-03-25
Published:2023-04-03
Contact:
**(E-mail:xuejingqi@caas.cn,luyingmin@bjfu.edu.cn)
摘要:
以牡丹栽培品种‘洛阳红’为试材,在促成栽培条件下对花芽进行剥叶和涂抹赤霉素处理,探究其对花芽发育、叶片气孔特征、葡萄糖、果糖、蔗糖和海藻糖-6-磷酸(T6P)水平以及糖信号相关基因表达模式等的影响。结果表明,剥叶和赤霉素处理均有效促进牡丹花蕾发育且能够显著促进叶片气孔的发育,提高气孔的开度;剥叶和赤霉素处理能够促进蔗糖和葡萄糖的代谢,并通过促进T6P的积累触发糖信号,最终通过上调PsTPS1及抑制PsSnRK1和PsHXK1在叶片中的表达,诱导花蕾发育。
中图分类号:
薛玉前, 柳志勇, 孙凯荣, 张秀新, 吕英民, 薛璟祺. 牡丹促成栽培中糖信号调控成花的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 596-606.
XUE Yuqian, LIU Zhiyong, SUN Kairong, ZHANG Xiuxin, LÜ Yingmin, XUE Jingqi. The Mechanism of Sugar Signal Involved in Regulating Re-flowering of Tree Peony Under Forcing Culture[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 596-606.
| 基因名称 Gene name | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 产物长度/bp Length of product |
|---|---|---|---|
| PsTPS1 | qRTTPS1 | F:CTCTCGACTTCCATGCCTTA;R:CTGTGATGTTCCAAGGGTTC | 207 |
| PsSnRK1 | qRTSnRK1 | F:CACGAAGGAATGGCGAATA;R:CAAGGAAGGCAGCACAAAG | 211 |
| PsHXK1 | qRTHXK1 | F:ATAAGAAAAGCCGTGGTAGAGC;R:AGTGTTCATACAAGCCACCATC | 166 |
| Actin | qRTActin | F:GAGAGATTCCGTTGCCCAG;R:TCCTTGCTCATTCTGTCTGC | 191 |
表1 糖信号相关基因表达引物序列
Table 1 Primers sequences of sugar signaling-related genes for expression analysis
| 基因名称 Gene name | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 产物长度/bp Length of product |
|---|---|---|---|
| PsTPS1 | qRTTPS1 | F:CTCTCGACTTCCATGCCTTA;R:CTGTGATGTTCCAAGGGTTC | 207 |
| PsSnRK1 | qRTSnRK1 | F:CACGAAGGAATGGCGAATA;R:CAAGGAAGGCAGCACAAAG | 211 |
| PsHXK1 | qRTHXK1 | F:ATAAGAAAAGCCGTGGTAGAGC;R:AGTGTTCATACAAGCCACCATC | 166 |
| Actin | qRTActin | F:GAGAGATTCCGTTGCCCAG;R:TCCTTGCTCATTCTGTCTGC | 191 |
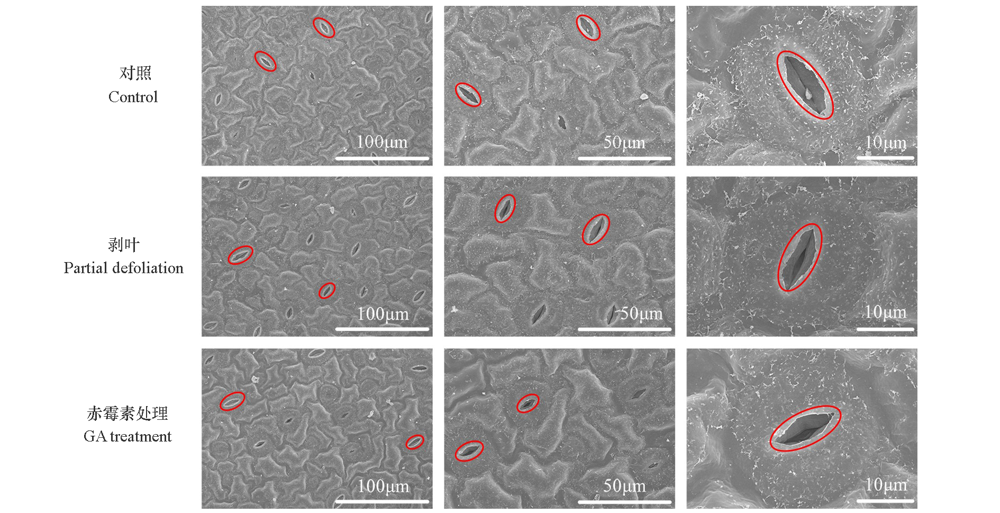
图2 ‘洛阳红’牡丹剥叶和赤霉素处理15 d 时叶片气孔的扫描电镜观察
Fig. 2 SEM micrograph cross-sections of tree peony‘Luoyang Hong’leaf stomata under partial defoliation and GA treatment on the 15th day
| 处理 Treatment | 气孔开度/μm Stomatal aperture | 气孔密度/(No · mm-2) Stomatal density | 气孔长度/μm Stomatal length | 气孔宽度/μm Stomatal width | 气孔面积/μm2 Stomatal area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Control | 0.27 ± 0.21 c | 251.85 ± 26.91 a | 28.68 ± 2.81 a | 23.58 ± 1.96 b | 501.44 ± 31.66 c |
| 剥叶Partial defoliation | 0.55 ± 0.20 b | 237.04 ± 36.29 a | 28.96 ± 1.95 a | 24.92 ± 1.31 a | 559.46 ± 23.42 b |
| 赤霉素GA | 0.98 ± 0.47 a | 181.49 ± 21.85 b | 28.80 ± 2.20 a | 25.69 ± 2.11 a | 593.61 ± 26.55 a |
表2 ‘洛阳红’牡丹剥叶和赤霉素处理15 d时叶片气孔的特征
Table 2 Characteristics of leaf stomata of tree peony‘Luoyang Hong’under partial defoliation and GA treatment on the 15th day
| 处理 Treatment | 气孔开度/μm Stomatal aperture | 气孔密度/(No · mm-2) Stomatal density | 气孔长度/μm Stomatal length | 气孔宽度/μm Stomatal width | 气孔面积/μm2 Stomatal area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Control | 0.27 ± 0.21 c | 251.85 ± 26.91 a | 28.68 ± 2.81 a | 23.58 ± 1.96 b | 501.44 ± 31.66 c |
| 剥叶Partial defoliation | 0.55 ± 0.20 b | 237.04 ± 36.29 a | 28.96 ± 1.95 a | 24.92 ± 1.31 a | 559.46 ± 23.42 b |
| 赤霉素GA | 0.98 ± 0.47 a | 181.49 ± 21.85 b | 28.80 ± 2.20 a | 25.69 ± 2.11 a | 593.61 ± 26.55 a |
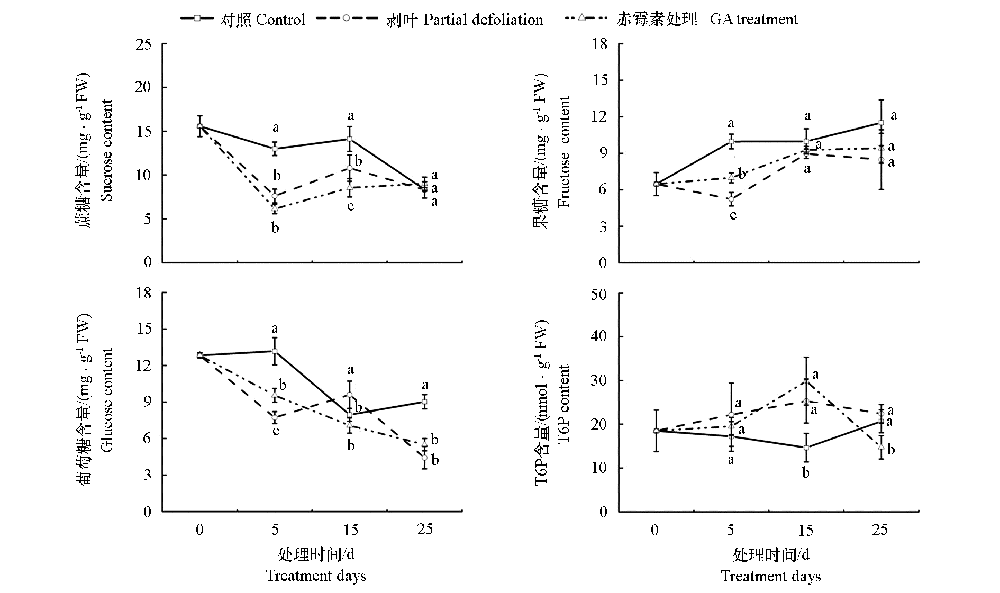
图3 ‘洛阳红’牡丹促成栽培条件下叶片中蔗糖、葡萄糖、果糖和T6P含量的变化 不同小字母表示在P < 0.05水平上显著差异,n = 3。
Fig. 3 The change of sucrose,glucose,fructose and T6P content at‘Luoyang Hong’tree peony under forcing culture Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 level,n = 3.

图4 不同植物中TPS1(A)、SnRK1(B)和HXK1(C)氨基酸序列进化树 标尺表示不同植物TPS1、SnRK1或HXK1氨基酸序列之间的差异。
Fig. 4 Phylogenetic analysis of TPS1(A),SnRK1(B)and HXK1(C)amino acid in various plants The scale in represent the difference of every TPS1,SnRK1 and HXK1 amino acid from different plants.
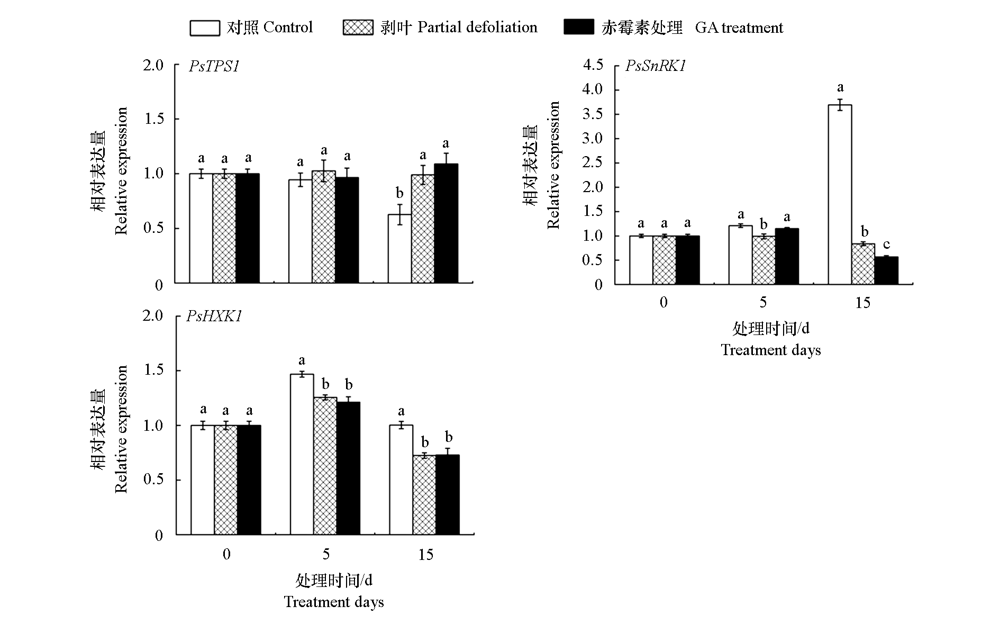
图5 ‘洛阳红’牡丹剥叶和赤霉素处理对糖信号相关基因PsTPS1、PsSnRK1和PsHXK1在叶片中的表达水平的影响 不同的小写字母表示同一时期不同处理间在0.05水平上差异显著(数据为平均数 ± 标准差,n = 3)。
Fig. 5 Effect of defoliation and GA treatment on the expression of PsTPS1,PsSnRK1,and PsHXK1 in leaves of tree peony‘Luoyang Hong’ The different lowercase letters indicated a significant difference among different treatment in expression of gene(Duncan’s test at P < 0.05 after analysis of variance;data are shown as mean ± SD,n = 3).
| [1] |
Baena-Gonzalez E, Lunn J E. 2020. SnRK1 and trehalose 6-phosphate - two ancient pathways converge to regulate plant metabolism and growth. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 55:52-59.
doi: S1369-5266(20)30021-2 pmid: 32259743 |
| [2] |
Baena-Gonzalez E, Rolland F, Thevelein J M, Sheen J. 2007. A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signalling. Nature, 448 (7156):938-942.
doi: 10.1038/nature06069 |
| [3] |
Barbier F F, Cao D, Fichtner F, Weiste C, Perez-Garcia M D, Caradeuc M, Gourrierec J L, Sakr S, Beveridge C A. 2021. HEXOKINASE 1 signalling promotes shoot branching and interacts with cytokinin and strigolactone pathway. New Phytologist, 231:1088-1104.
doi: 10.1111/nph.v231.3 URL |
| [4] |
Chary S N, Hicks G R, Choi Y G, Carter D, Raikhel N V. 2008. Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase regulates cell shape and plant architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 146 (1):97-107.
doi: 10.1104/pp.107.107441 URL |
| [5] |
Chen Q S, Zhang J, Li G. 2021. Dynamic epigenetic modifications in plant sugar signal transduction. Trends in Plant Sciences, 27 (4):379-390.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2021.10.009 URL |
| [6] |
Dai N, Schaffer A, Petreikov M, Shahak Y, Giller Y, Ratner K, Levine A, Granot D. 1999. Overexpression of Arabidopsis hexokinase in tomato plants inhibits growth,reduces photosynthesis,and induces rapid senescence. The Plant Cell, 11 (7):1253-1266.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.11.7.1253 URL |
| [7] |
Du L, Qi S, Ma J, Xing L, Fan S, Zhang S, Li Y, Shen Y, Zhang D, Han M. 2017. Identification of TPS family members in apple(Malus × domestica Borkh.)and the effect of sucrose sprays on TPS expression and floral induction. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 120:10-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.09.015 URL |
| [8] |
Eastmond P J, van Dijken A J, Spielman M, Kerr A, Tissier A F, Dickinson H G, Jones J D, Smeekens S C, Graham I A. 2002. Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1,which catalyses the first step in trehalose synthesis,is essential for Arabidopsis embryo maturation. The Plant Journal, 29 (2):225-235.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01220.x URL |
| [9] |
Fichtner F, Olas J J, Feil R, Watanabe M, Krause U, Hoefgen R, Stitt M, Lunn J E. 2020. Functional features of TREHALOSE-6-PHOSPHATE SYNTHASE1,an essential enzyme in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 32:1949-1972.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00837 URL |
| [10] |
Gai S P, Zhang Y X, Liu C Y, Zhang Y, Zheng G S. 2013. Transcript profiling of Paoenia ostii during artificial chilling induced dormancy release identifies activation of GA pathway and carbohydrate metabolism. PLoS ONE, 8 (2):e55297.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055297 URL |
| [11] |
Granot D, David-Schwartz R, Kelly G. 2013. Hexose kinases and their role in sugar-sensing and plant development. Frontiers in Plant Science, 4:44.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00044 pmid: 23487525 |
| [12] | Guan Yan-ran, Wang Shun-li, Xue Jing-qi, Sun Zhen-yuan, Xue Yu-qian, Zhang Xiu-xin. 2017. Research advance on the forcing culture of tree peony. Journal of Anhui Agri Sci, 45 (34):40-43,49. (in Chinese) |
| 管艳忍, 王顺利, 薛璟祺, 孙振元, 薛玉前, 张秀新. 2017. 牡丹促成栽培研究进展. 安徽农业科学, 45 (34):40-43,49. | |
| [13] |
Lastdrager J, Hanson J, Smeekens S. 2014. Sugar signals and the control of plant growth and development. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65 (3):799-807.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert474 pmid: 24453229 |
| [14] |
Li N N, Qian W J, Wang L, Cao H L, Hao X Y, Yang Y J, Wang X C. 2017. Isolation and expression features of hexose kinase genes under various abiotic stresses in the tea plant(Camellia sinensis). Journal of Plant Physiology, 209:95-104.
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2016.11.007 URL |
| [15] | Li Ting-ting, Xue Jing-qi, Wang Shun-li, Xue Yu-qian, Hu Feng-rong, Zhang Xiu-xin. 2018. Research advances in the metabolism and transport of non-structural carbohydrates in plants. Plant Physiology Journal, 54 (1):25-35. (in Chinese) |
| 李婷婷, 薛璟祺, 王顺利, 薛玉前, 胡凤荣, 张秀新. 2018. 植物非结构性碳水化合物代谢及体内转运研究进展. 植物生理学报, 54 (1):25-35. | |
| [16] | Liu Bo, Zheng Guo-sheng, Zhao Hai-jun. 2004. The effect of different low temperature hours on the release of dormancy in tree peony flower buds. Shandong Agricultural Sciences,(3):41-42. (in Chinese) |
| 刘波, 郑国生, 赵海军. 2004. 不同低温时数对牡丹花芽解除休眠的影响. 山东农业科学,(3):41-42. | |
| [17] |
Liu Z Y, Shi Y T, Xue Y Q, Wang X P, Huang Z, Xue J Q, Zhang X X. 2021. Non-structural carbohydrates coordinate tree peony flowering both as energy substrates and as sugar signaling tiggers,with the bracts playing an essential role. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 159:80-88.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.12.012 URL |
| [18] |
Lu Y, Sasaki Y, Li X, Mori I C, Matsuura T, Hirayama T, Sato T, Yamaguchi J. 2015. ABI 1 regulates carbon/nitrogen-nutrient signal transduction independent of ABA biosynthesis and canonical ABA signalling pathways in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 66 (15):4851.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv264 |
| [19] |
Margalha L, Confraria A, Baena-Gonzalez E. 2019. SnRK1 and TOR:modulating growth-defense trade-offs in plant stress responses. Journal of Experimental Botany, 70:2261-2274.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz066 pmid: 30793201 |
| [20] | Moghaddam B M R, Ende V D W. 2013. Sugars,the clock and transition to flowering. Frontiers in Plant Science, 4 (22):1-6. |
| [21] |
Moore B, Zhou L, Rolland F, Hall Q, Cheng W H, Liu Y X, Hwang I, Jones T, Sheen J. 2003. Role of the Arabidopsis glucose sensor HXK 1 in nutrient,light,and hormonal signaling. Science, 300 (5617):332-366.
doi: 10.1126/science.1080585 URL |
| [22] |
Nuccio M L, Wu J, Mowers R, Zhou H P, Meghji M, Primavesi L F, Paul M J, Chen X, Gao Y, Haque E, Basu S S, Lagrimini L M. 2015. Expression of trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase in maize ears improves yield in well-watered and drought conditions. Nature Biotechnology, 33 (8):862-869.
pmid: 26473199 |
| [23] |
Oszvald M, Primavesi L F, Griffiths C A, Cohn J, Basu S S, Nuccio M L, Paul M J. 2018. Trehalose 6-phosphate regulates photosynthesis and assimilate partitioning in reproductive tissue. Plant Physiology, 176 (4):2623-2638.
doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01673 pmid: 29437777 |
| [24] |
Paul M J, Primavesi L F, Jhurreea D, Zhang Y. 2008. Trehalose metabolism and signaling. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 59:417-441.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092945 pmid: 18257709 |
| [25] |
Redondo-Gómez S, Mateos-Naranjo E, Moreno F J. 2010. Physiological characterization of photosynthesis,chloroplast ultrastructure,and nutrient content in bracts and rosette leaves from Glaucium flavum. Photosynthetica, 48 (4):488-493.
doi: 10.1007/s11099-010-0065-9 URL |
| [26] |
Rolland F, Moore B, Sheen J. 2002. Sugar sensing and signaling in plants. The Plant Cell, 14:S185-S205.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.010455 URL |
| [27] |
Tsai A Y L, Gazzarrini S. 2012. AKIN10 and FUSCA 3 interact to control lateral organ development and phase transitions in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 69 (5):809-821.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2012.69.issue-5 URL |
| [28] | Tsai A Y L, Gazzarrini S. 2014. Trehalose-6-phosphate and SnRK 1 kinases in plant development and signaling:the emerging picture. Frontiers in Plant Science, 5 (119):1-9. |
| [29] |
Vandesteene L, Ramon M le Roy K, van Dijck P, Rolland F. 2010. A single active trehalose-6-P synthase(TPS)and a family of putative regulatory TPS-like proteins in Arabidopsis. Molecular Plant, 3 (2):406-419.
doi: 10.1093/mp/ssp114 pmid: 20100798 |
| [30] |
Wahl V, Ponnu J, Schlereth A, Arrivault S, Langenecker T, Franke A, Feil R, Lunn J E, Stitt M, Schmid M. 2013. Regulation of flowering by trehalose-6-phosphate signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science, 339 (6120):704-707.
doi: 10.1126/science.1230406 URL |
| [31] |
Wang S L, Xue J Q, Ahmadi N, Holloway P, Zhu F Y, Ren X X, Zhang X X. 2014. Molecular characterization and expression patterns of PsSVP genes reveal distinct roles in flower bud abortion and flowering in tree peony(Paeonia suffruticosa). Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 94 (7):1181-1193.
doi: 10.4141/cjps2013-360 URL |
| [32] |
Wingler A, Delatte T L, O'Hara L E, Primavesi L F, Jhurreea D, Paul M J, Schluepmann H. 2012. Trehalose 6-phosphate is required for the onset of leaf senescence associated with high carbon availability. Plant Physiology, 158 (3):1241-1251. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1104/pp.111.191908 pmid: 22247267 |
| [33] | Xu Gui-ying, Xu Bi-yu, Xing Wen-ting, Jia Cai-hong, Wang Zhuo, Chang Sheng-he, Wang An-bang, Shu Hai-yan, Jin Zhi-qiang. 2015. Characterization and expression analysis of MaTPS1 from banana. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 35 (10):1934-1940. (in Chinese) |
| 许桂莺, 徐碧玉, 邢文婷, 贾彩虹, 王卓, 常胜和, 王安邦, 舒海燕, 金志强. 2015. 香蕉MaTPS1基因序列及其表达特性分析. 西北植物学报, 35 (10):1934-1940. | |
| [34] |
Xue J Q, Li T T, Wang S L, Xue Y Q, Liu X W, Zhang X X. 2019. Defoliation and gibberellin synergistically induce tree peony flowering with non-structural carbohydrates as intermedia. Journal of Plant Physiology, 233:31-41.
doi: S0176-1617(18)30621-7 pmid: 30580057 |
| [35] |
Xue J Q, Tang Y, Wang S L, Yang R W, Xue Y Q, Wu C H, Zhang X X. 2018. Assessment of vase quality and transcriptional regulation of sucrose transporter and invertase genes in cut peony(Paeonia lactiflora‘Yang Fei Chu Yu’)treated by exogenous sucrose. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 143:92-101.
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.04.014 URL |
| [36] |
Yang Weihai, Zeng Lizhen, Xiao Qiusheng, Shi Shengyou. 2021. Changes of fruit abscission and carbohydrate,ABA and related genes expression in the pericarp and fruit abscission zone of longan under starvation stress. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (8):1457-1469. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0538 URL |
|
杨为海, 曾利珍, 肖秋生, 石胜友. 2021. 饥饿胁迫条件下龙眼落果与果皮和离区糖、ABA及相关基因表达的变化. 园艺学报, 48 (8):1457-1469.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0538 |
|
| [37] | Yonekura M, Aoki N, Hirose T, Onai K, Ishiura M, Okamura M, Ohsugi R, Ohto C. 2013. The promoter activities of sucrose phosphate synthase genes in rice,OsSP1 and OsSPS11,are controlled by light and circadian clock,but not by sucrose. Frontiers in Plant Science, 4 (31):1-8. |
| [38] | Zhang Lizhi, Zhang Xin, Zuo Xiya, Xing Libo, Fan Sheng, Li Youmei, Zhang Dong, Zhao Caiping, Han Mingyu, Zhang Dong. 2019. Effects of exogenous glucose treatment on soluble sugar and expression of related genes during floral bud differentiation stage in terminal spur buds of‘Nagafu 2’apple. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (1):11-24. (in Chinese) |
|
张丽之, 张昕, 左希亚, 邢利博, 樊胜, 李有梅, 张东, 赵彩平, 韩明玉, 张东. 2019. 外源葡萄糖对‘长富2号’苹果花芽生理分化期可溶性糖和相关基因表达的影响. 园艺学报, 46 (1):11-24.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0173 |
|
| [39] | Zhang Yu-xi, Gai Shu-peng, Liu Chun-ying, Mu Ping, Zhen Guo-sheng. 2011. Selection of control genes in real-time qPCR analysis during bud dormancy release in tree peony(Paeonia suffruticosa). Molecular Plant Breeding, 9:1052-1056. (in Chinese) |
| 张玉喜, 盖树鹏, 刘春英, 穆平, 郑国生. 2011. 牡丹花芽休眠解除过程中实时定量PCR内参基因的选择. 分子植物育种, 9:1052-1056. | |
| [40] | Zhen Guo-sheng. 2003. Study on the physiological characteristics of flowering and the mechanism of flower formation of tree peony(Paeonia suffruticosa)in winter[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 郑国生. 2003. 牡丹(Paeonia suffruticosa)开花生理特性与冬季成花机理的研究[博士论文]. 太原: 山西农业大学. | |
| [41] |
Zúñiga-Sánchez E, Rodríguez-Sotres R, Coello P, Martínez-Barajas E. 2019. Effect of catalytic subunit phosphorylation on the properties of SnRK 1 from Phaseolus vulgaris embryos. Physiologia Plantarum, 165 (3):632-643.
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2019.165.issue-3 URL |
| [1] | 李瑞雅, 宋程威, 牛童非, 魏祯祯, 郭丽丽, 侯小改. ‘海黄’牡丹花挥发性物质释放规律及PsGDS的克隆与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 331-344. |
| [2] | 何智宏, 何丽霞, 张延东, 杨国州, 李 睿, 徐晶晶, 瞿 丹, 李京璟. 牡丹新品种‘余霞散绮’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 219-220. |
| [3] | 赵海军, 盖树鹏, 晁 振, 闫闪闪, 房义福, 张 佩. 牡丹新品种‘福照粉蓝’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 221-222. |
| [4] | 张婉青, 张红晓, 廉小芳, 李昱莹, 郭丽丽, 侯小改. ‘凤丹’牡丹愈伤组织分化和生根诱导中的DNA甲基化分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1735-1746. |
| [5] | 程世平, 姚鹏强, 耿喜宁, 刘春洋, 谢丽华. 高温诱导牡丹产生未减数花粉[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 581-589. |
| [6] | 郭鑫, 成仿云, 钟原, 成信云, 陶熙文. 紫斑牡丹花色表型数量分类研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 86-99. |
| [7] | 刘蓉, 慈惠婷, 任秀霞, 高洁, 王顺利, 张秀新. ‘凤丹’牡丹幼胚愈伤组织诱导的优化和再生体系的建立[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 166-174. |
| [8] | 叶 康, 胡永红, 张 颖. 牡丹新品种‘金琉鹤舞’[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(S2): 2959-2960. |
| [9] | 叶 康, 胡永红, 张 颖. 牡丹新品种‘银粟紫染’[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(S2): 2961-2962. |
| [10] | 王依, 王凯轩, 胡思源, 周爽, 史国安. 乙烯代谢和能量状态对‘巴茨拉’牡丹切花瓶插品质的作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(6): 1135-1149. |
| [11] | 虞钦岚, 刘守赞, 徐韧析谋, 潘晨航, 颜忆铭, 王义英, 夏国华. 珍稀濒危植物江南牡丹草种群结构和繁育系统研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(3): 539-552. |
| [12] | 邹红竹, 周琳, 韩璐璐, 吕纪杭, 王雁. 滇牡丹花瓣着色过程中类胡萝卜素成分变化和相关基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(10): 1934-1944. |
| [13] | 袁涛, 陈庭巧, 唐英. 大花黄牡丹枝条二次发育特点的观察[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(1): 117-126. |
| [14] | 罗 浩, 成仿云, 郭 鑫, 陶熙文, 王 旭. 基于灰色关联度分析法评价筛选紫斑牡丹切花品种[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(11): 2169-2180. |
| [15] | 王凯轩, 王 依, 史 田, 丁熙柠, 袁军辉, 史国安, 胡永红, . 雷帕霉素预处理延缓牡丹‘洛阳红’切花衰老的生理效应[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(10): 1956-1968. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司