
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1095-1109.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0176
• Cultivation Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUAN Jieli1,2, JIN Xiaoling1,2,*( ), ZHANG Zheng1, XIAO Yujie1, YU Qiuxiu1, HU Xiaoxuan1
), ZHANG Zheng1, XIAO Yujie1, YU Qiuxiu1, HU Xiaoxuan1
Received:2022-11-04
Revised:2023-01-18
Online:2023-05-25
Published:2023-05-31
Contact:
JIN Xiaoling
E-mail:jxl0716@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
YUAN Jieli, JIN Xiaoling, ZHANG Zheng, XIAO Yujie, YU Qiuxiu, HU Xiaoxuan. Volatility Components of Michelia crassipes Tepals at Different Flowering Stages[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 1095-1109.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0176
| 挥发性成分种类 Compound kinds | 含量/(µg · kg-1) Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 花蕾期 Bud | 初花期 First-open | 盛花期 Fully-open | |
| 萜类 Terpenes | 453.736 ± 22.460 b | 547.593 ± 27.079 a | 580.355 ± 28.696 a |
| 酯类 Esters | 35.219 ± 1.786 b | 40.064 ± 2.035 b | 50.718 ± 2.553 a |
| 酮类 Ketones | 2.767 ± 0.184 a | 2.796 ± 0.198 a | 2.891 ± 0.198 a |
| 烷烃类 Alkanes | 2.964 ± 0.180 a | 2.369 ± 0.163 b | 2.062 ± 0.146 b |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 5.258 ± 0.282 b | 8.627 ± 0.456 a | 9.474 ± 0.498 a |
| 芳香族类 Aromatics | 3.359 ± 0.193 c | 5.514 ± 0.292 b | 8.275 ± 0.436 a |
| 烯烃类 Olefins | 4.100 ± 0.227 c | 5.810 ± 0.300 b | 8.126 ± 0.413 a |
| 醛类 Aldehydes | 1.072 ± 0.069 c | 1.651 ± 0.096 a | 1.294 ± 0.096 b |
| 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 1.028 ± 0.057 b | 1.218 ± 0.071 a | 1.188 ± 0.086 a |
| 酸类 Acids | 0.355 ± 0.021 a | 0.329 ± 0.030 ab | 0.308 ± 0.024 b |
| 酚类 Phenols | 0.153 ± 0.011 b | 0.038 ± 0.014 c | 1.161 ± 0.076 a |
| 炔类 Alkynes | 12.550 ± 0.623 a | 12.019 ± 0.601 a | 0.188 ± 0.013 b |
| 醚类 Ethers | 0.029 ± 0.005 b | 0.083 ± 0.005 a | 0.037 ± 0.010 b |
| 生物碱类 Alkaloids | — | — | 2.916 ± 0.004 a |
| 总计 Total | 522.590 ± 26.098 b | 628.111 ± 31.340 a | 668.993 ± 33.388 a |
Table 1 Contents of volatile components of Michelia crassipes tepals at different flowering stages
| 挥发性成分种类 Compound kinds | 含量/(µg · kg-1) Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 花蕾期 Bud | 初花期 First-open | 盛花期 Fully-open | |
| 萜类 Terpenes | 453.736 ± 22.460 b | 547.593 ± 27.079 a | 580.355 ± 28.696 a |
| 酯类 Esters | 35.219 ± 1.786 b | 40.064 ± 2.035 b | 50.718 ± 2.553 a |
| 酮类 Ketones | 2.767 ± 0.184 a | 2.796 ± 0.198 a | 2.891 ± 0.198 a |
| 烷烃类 Alkanes | 2.964 ± 0.180 a | 2.369 ± 0.163 b | 2.062 ± 0.146 b |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 5.258 ± 0.282 b | 8.627 ± 0.456 a | 9.474 ± 0.498 a |
| 芳香族类 Aromatics | 3.359 ± 0.193 c | 5.514 ± 0.292 b | 8.275 ± 0.436 a |
| 烯烃类 Olefins | 4.100 ± 0.227 c | 5.810 ± 0.300 b | 8.126 ± 0.413 a |
| 醛类 Aldehydes | 1.072 ± 0.069 c | 1.651 ± 0.096 a | 1.294 ± 0.096 b |
| 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 1.028 ± 0.057 b | 1.218 ± 0.071 a | 1.188 ± 0.086 a |
| 酸类 Acids | 0.355 ± 0.021 a | 0.329 ± 0.030 ab | 0.308 ± 0.024 b |
| 酚类 Phenols | 0.153 ± 0.011 b | 0.038 ± 0.014 c | 1.161 ± 0.076 a |
| 炔类 Alkynes | 12.550 ± 0.623 a | 12.019 ± 0.601 a | 0.188 ± 0.013 b |
| 醚类 Ethers | 0.029 ± 0.005 b | 0.083 ± 0.005 a | 0.037 ± 0.010 b |
| 生物碱类 Alkaloids | — | — | 2.916 ± 0.004 a |
| 总计 Total | 522.590 ± 26.098 b | 628.111 ± 31.340 a | 668.993 ± 33.388 a |
| 挥发性成分种类 Compound kinds | 共有含量/(µg · kg-1) Shared content | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 花蕾期 Bud | 初花期 First-open | 盛花期 Fully-open | |
| 萜类 Terpenes | 447.324 ± 22.135 b | 504.793 ± 24.952 ab | 526.411 ± 26.024 a |
| 酯类 Esters | 33.564 ± 1.677 a | 28.865 ± 1.450 b | 33.588 ± 1.675 a |
| 酮类 Ketones | 0.637 ± 0.055 b | 0.683 ± 0.070 ab | 0.764 ± 0.070 a |
| 烷烃类 Alkanes | 0.416 ± 0.035 a | 0.422 ± 0.040 a | 0.432 ± 0.046 a |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 4.681 ± 0.243 c | 7.071 ± 0.358 a | 5.912 ± 0.304 b |
| 芳香族类 Aromatics | 0.863 ± 0.070 b | 1.099 ± 0.062 a | 1.186 ± 0.076 a |
| 烯烃类 Olefins | 3.234 ± 0.162 a | 3.482 ± 0.178 a | 2.787 ± 0.141 b |
| 醛类 Aldehydes | 0.277 ± 0.018 b | 0.403 ± 0.023 a | 0.393 ± 0.025 a |
| 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 0.505 ± 0.029 a | 0.475 ± 0.027 ab | 0.456 ± 0.034 b |
| 酸类 Acids | 0.205 ± 0.013 b | 0.300 ± 0.020 a | 0.279 ± 0.020 a |
| 酚类 Phenols | 0.004 ± 0.001 a | 0.008 ± 0.002 a | 0.006 ± 0.003 a |
| 炔类 Alkynes | 0.082 ± 0.005 c | 0.144 ± 0.009 a | 0.130 ± 0.008 b |
| 醚类 Ethers | — | — | — |
| 生物碱类 Alkaloids | — | — | — |
| 总计 Total | 491.795 ± 24.443 b | 547.744 ± 27.191 ab | 572.344 ± 28.426 a |
Table 2 Shared contents of volatile components of Michelia crassipes tepals at different flowering stages
| 挥发性成分种类 Compound kinds | 共有含量/(µg · kg-1) Shared content | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 花蕾期 Bud | 初花期 First-open | 盛花期 Fully-open | |
| 萜类 Terpenes | 447.324 ± 22.135 b | 504.793 ± 24.952 ab | 526.411 ± 26.024 a |
| 酯类 Esters | 33.564 ± 1.677 a | 28.865 ± 1.450 b | 33.588 ± 1.675 a |
| 酮类 Ketones | 0.637 ± 0.055 b | 0.683 ± 0.070 ab | 0.764 ± 0.070 a |
| 烷烃类 Alkanes | 0.416 ± 0.035 a | 0.422 ± 0.040 a | 0.432 ± 0.046 a |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 4.681 ± 0.243 c | 7.071 ± 0.358 a | 5.912 ± 0.304 b |
| 芳香族类 Aromatics | 0.863 ± 0.070 b | 1.099 ± 0.062 a | 1.186 ± 0.076 a |
| 烯烃类 Olefins | 3.234 ± 0.162 a | 3.482 ± 0.178 a | 2.787 ± 0.141 b |
| 醛类 Aldehydes | 0.277 ± 0.018 b | 0.403 ± 0.023 a | 0.393 ± 0.025 a |
| 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 0.505 ± 0.029 a | 0.475 ± 0.027 ab | 0.456 ± 0.034 b |
| 酸类 Acids | 0.205 ± 0.013 b | 0.300 ± 0.020 a | 0.279 ± 0.020 a |
| 酚类 Phenols | 0.004 ± 0.001 a | 0.008 ± 0.002 a | 0.006 ± 0.003 a |
| 炔类 Alkynes | 0.082 ± 0.005 c | 0.144 ± 0.009 a | 0.130 ± 0.008 b |
| 醚类 Ethers | — | — | — |
| 生物碱类 Alkaloids | — | — | — |
| 总计 Total | 491.795 ± 24.443 b | 547.744 ± 27.191 ab | 572.344 ± 28.426 a |
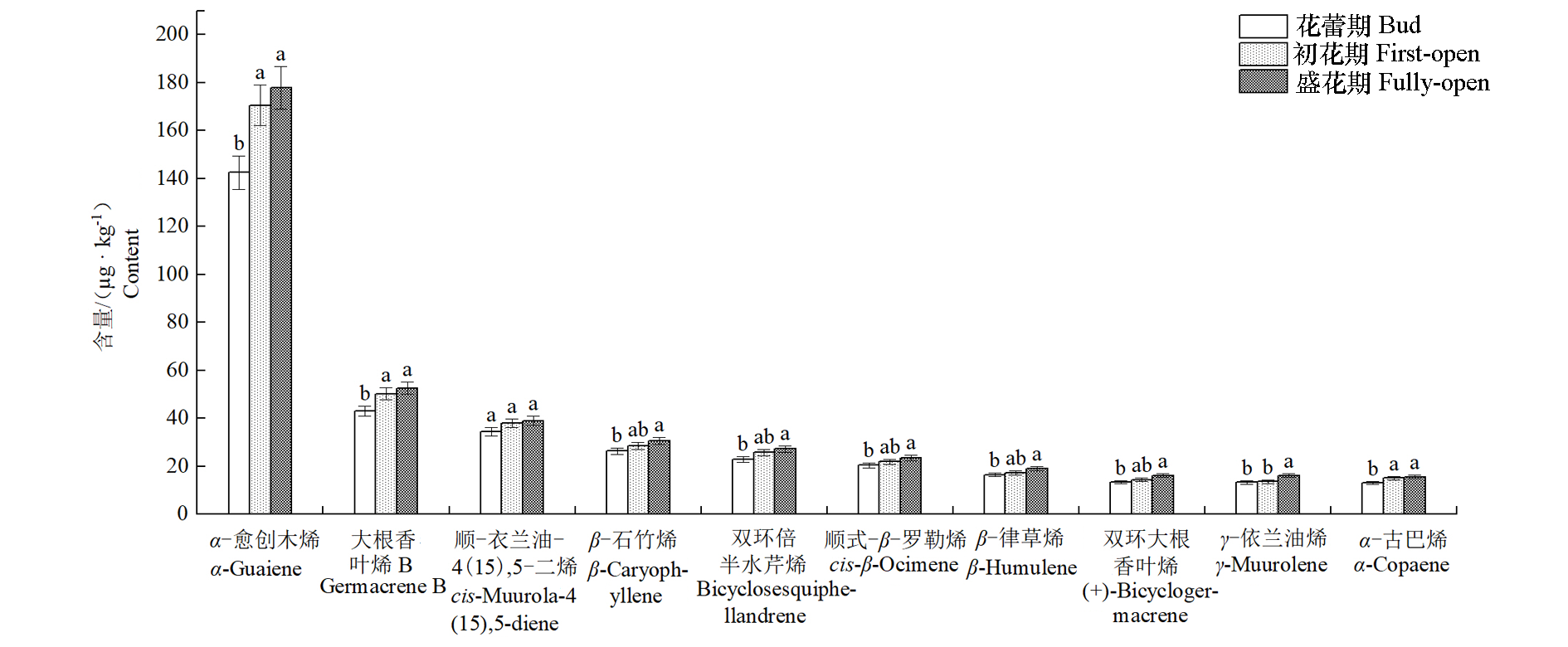
Fig. 4 Variations of 10 major volatile components content of Michelia crassipes tepals at different flowering stages Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference(P < 0.05).
| 化合物 Compound | 香气阈值/ (μg · kg-1) Odor threshold | 香气类型/香味特征 Aroma type/Aroma characteristics | 香气强度值(OAV) Aroma intensity value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花蕾期 Bud | 初花期 First-open | 盛花期 Fully-open | |||
| 苯甲酸甲酯 Methyl benzoate | 0.520 | 香草型/甜香味 Herbal/sweet-like | 2.146 | 1.596 | 1.699 |
| α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | 6.000 | 香草型/松节油味 Herbal/turpentine-like | 1.444 | 1.521 | 1.640 |
| β-紫罗兰酮 β-Ionone | 0.100 | 花香型/鸢尾香味 Floral/orris-like | — | 1.202 | 1.286 |
| 顺式-β-罗勒烯 cis -β-Ocimene | 34.000 | 花香型/旱金莲花香Floral/nasturtium-like | 0.601 | 0.644 | 0.692 |
| 乙酸苄酯 Benzyl acetate | 2.000 | 甜香型/茉莉香 Sweet/jasmin-like | — | — | 0.657 |
| 顺-4,5-环氧-(E)-2-癸烯醛 cis-4,5-Epoxy-(E)-2-decenal | 0.070 | —/— | 0.452 | — | — |
| β-石竹烯 β-Caryophyllene | 64.000 | 木香型/胡椒味 Wood/peppery-like | 0.411 | 0.445 | 0.479 |
| 芳樟醇 Linalool | 6.000 | 花香型/玫瑰香味 Floral/rose-like | 0.398 | 0.422 | 0.346 |
| β-芹子烯 β-Selinene | 1.000 | 香草型/— Herbal/— | — | 0.249 | 0.338 |
| 3-甲基戊酸乙酯 Ethyl 3-methyl valerate | 0.008 | 果香型/菠萝味 Fruity/Pineapple-like | 0.290 | — | 0.157 |
| 橙花叔醇 Nerolidol | 15.000 | 花香型/柑橘味 Floral/citrus-like | 0.188 | 0.208 | 0.186 |
| 丁醛 Butanal | 2.000 | 刺激型/可可味 Pungent/cocoa-like | — | 0.146 | — |
| 乙苯 Ethylbenzene | 2.400 | —/— | — | 0.117 | — |
| 2-甲基丁基乙酸酯 2-Methyl butyl acetate | 5.000 | 果香型/香蕉味 Fruit/banana-like | — | — | 0.096 |
| 苯乙烯 Styrene | 3.600 | 甜香型/香膏味 Sweet/ balsamic-like | 0.075 | 0.085 | 0.034 |
| 异丁醛 Isobutyraldehyde | 1.000 | 清香型/麦芽味 Fresh/malty-like | 0.071 | — | — |
| α-水芹烯 α-Phellandrene | 40.000 | 萜烯型/天兰葵味Terpene/geranium-like | 0.064 | 0.064 | 0.056 |
| α-石竹烯 α-Caryophyllene | 160.000 | 木香型/浓丁香味Wood/spicy-clove-like | 0.055 | 0.059 | 0.064 |
| D-柠檬烯 D-Limonene | 10.000 | 甜香型/橙味 Sweet/orange-like | 0.050 | 0.061 | 0.067 |
| 乙酸冰片酯 Bornyl acetate | 75.000 | 木香型/樟脑味 Wood/camphoreous-like | — | 0.090 | 0.044 |
| 萘 Naphthalene | 6.000 | 刺激型/树脂味 Pungent/resinous-like | 0.043 | — | — |
| 2-戊基呋喃 Furan, 2-pentyl- | 6.000 | 青香型/蔬菜味 Green/vegetable-like | 0.039 | 0.043 | 0.053 |
| 反式-β-罗勒烯 trans-β-Ocimene | 34.000 | 花香型/旱金莲花香Floral/nasturtium-like | 0.034 | 0.034 | 0.028 |
| (Z)-石竹烯 (Z)-Caryophyllene | 64.000 | 甜香型/胡椒味 Sweet/peppery-like | — | — | 0.024 |
| 苯乙醛 Phenyl acetaldehyde | 4.000 | 甜香型/蜂蜜味 Sweet/honey-like | 0.020 | 0.019 | 0.013 |
| 己醛 Hexanal | 20.000 | 青香型/蔬菜味 Green/vegetative-like | 0.007 | — | — |
| 丙酸叔丁酯 Tert-butyl propionate | 43.000 | —/— | 0.006 | — | 0.005 |
| 异戊醇 Isoamylalcohol | 4.000 | 酒香型/威士忌味 Alcoholic/whiskey-like | 0.003 | — | 0.016 |
| (E,E)-2,4-庚二烯醛 2,4-Heptadienal, (E,E)- | 15.400 | 油香型/坚果味 Fatty/nut-like | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.007 |
| 异丁酸丙酯 Propyl isobutyrate | 0.430 | 甜香型/甜瓜味 Sweet/melon-like | — | — | 0.004 |
| 2-正丁基呋喃 2-n-Butyl furan | 5.000 | 辛香型/葡萄酒味 Spicy/wine-like | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.004 |
| 庚醛 Heptanal | 2.800 | 清香型/香菜味 Fresh/cilantro-like | — | 0.003 | — |
| 苯乙醇 Phenylethyl alcohol | 1 000.000 | 花香型/玫瑰香味 Floral/rose-like | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 |
| 乙酸芳樟酯 Linalyl acetate | 1 000.000 | 花香型/薰衣草香味 Floral /lavender-like | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 己酸乙酯 Ethyl hexanoate | 1.000 | 甜香型/菠萝味 Sweet/pineapple-like | — | 0.002 | — |
| α-松油烯 α-Terpinene | 85.000 | 木香型/茶香味 Wood/terpy-like | — | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 丙苯 Phenylpropane | 177.120 | —/— | — | — | 0.002 |
| 丁香酚 Eugenol | 6.000 | 甜香型/丁香味 Sweet/clove-like | — | — | 0.002 |
| 异丁醇 Isobutyl alcohol | 550.000 | 酒香型/葡萄酒味 Alcoholic/winey-like | — | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| 十一酮 2-Undecanone | 41.000 | 果香型/奶酪味 Fruit/cheese-like | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 1-甲基萘 Naphthalene, 1-methyl- | 8.000 | 萘基型/樟脑味 Naphthyl camphor-like | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 水杨酸戊酯 Amyl salicylate | 2.900 | 香草型/三叶草香味 Herbal/clover-like | 0.001 | — | 0.001 |
| 戊酸乙酯 Ethyl Valerate | 5.000 | 甜香型/草莓味 Sweet/strawberry-like | 0.000 | — | 0.001 |
| 异丁酸戊酯 Amyl isobutyrate | 43.000 | 果香型/苹果味 Fruity/apple-like | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
Table 3 The aroma intensity of main volatile components of Michelia crassipes tepals
| 化合物 Compound | 香气阈值/ (μg · kg-1) Odor threshold | 香气类型/香味特征 Aroma type/Aroma characteristics | 香气强度值(OAV) Aroma intensity value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花蕾期 Bud | 初花期 First-open | 盛花期 Fully-open | |||
| 苯甲酸甲酯 Methyl benzoate | 0.520 | 香草型/甜香味 Herbal/sweet-like | 2.146 | 1.596 | 1.699 |
| α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | 6.000 | 香草型/松节油味 Herbal/turpentine-like | 1.444 | 1.521 | 1.640 |
| β-紫罗兰酮 β-Ionone | 0.100 | 花香型/鸢尾香味 Floral/orris-like | — | 1.202 | 1.286 |
| 顺式-β-罗勒烯 cis -β-Ocimene | 34.000 | 花香型/旱金莲花香Floral/nasturtium-like | 0.601 | 0.644 | 0.692 |
| 乙酸苄酯 Benzyl acetate | 2.000 | 甜香型/茉莉香 Sweet/jasmin-like | — | — | 0.657 |
| 顺-4,5-环氧-(E)-2-癸烯醛 cis-4,5-Epoxy-(E)-2-decenal | 0.070 | —/— | 0.452 | — | — |
| β-石竹烯 β-Caryophyllene | 64.000 | 木香型/胡椒味 Wood/peppery-like | 0.411 | 0.445 | 0.479 |
| 芳樟醇 Linalool | 6.000 | 花香型/玫瑰香味 Floral/rose-like | 0.398 | 0.422 | 0.346 |
| β-芹子烯 β-Selinene | 1.000 | 香草型/— Herbal/— | — | 0.249 | 0.338 |
| 3-甲基戊酸乙酯 Ethyl 3-methyl valerate | 0.008 | 果香型/菠萝味 Fruity/Pineapple-like | 0.290 | — | 0.157 |
| 橙花叔醇 Nerolidol | 15.000 | 花香型/柑橘味 Floral/citrus-like | 0.188 | 0.208 | 0.186 |
| 丁醛 Butanal | 2.000 | 刺激型/可可味 Pungent/cocoa-like | — | 0.146 | — |
| 乙苯 Ethylbenzene | 2.400 | —/— | — | 0.117 | — |
| 2-甲基丁基乙酸酯 2-Methyl butyl acetate | 5.000 | 果香型/香蕉味 Fruit/banana-like | — | — | 0.096 |
| 苯乙烯 Styrene | 3.600 | 甜香型/香膏味 Sweet/ balsamic-like | 0.075 | 0.085 | 0.034 |
| 异丁醛 Isobutyraldehyde | 1.000 | 清香型/麦芽味 Fresh/malty-like | 0.071 | — | — |
| α-水芹烯 α-Phellandrene | 40.000 | 萜烯型/天兰葵味Terpene/geranium-like | 0.064 | 0.064 | 0.056 |
| α-石竹烯 α-Caryophyllene | 160.000 | 木香型/浓丁香味Wood/spicy-clove-like | 0.055 | 0.059 | 0.064 |
| D-柠檬烯 D-Limonene | 10.000 | 甜香型/橙味 Sweet/orange-like | 0.050 | 0.061 | 0.067 |
| 乙酸冰片酯 Bornyl acetate | 75.000 | 木香型/樟脑味 Wood/camphoreous-like | — | 0.090 | 0.044 |
| 萘 Naphthalene | 6.000 | 刺激型/树脂味 Pungent/resinous-like | 0.043 | — | — |
| 2-戊基呋喃 Furan, 2-pentyl- | 6.000 | 青香型/蔬菜味 Green/vegetable-like | 0.039 | 0.043 | 0.053 |
| 反式-β-罗勒烯 trans-β-Ocimene | 34.000 | 花香型/旱金莲花香Floral/nasturtium-like | 0.034 | 0.034 | 0.028 |
| (Z)-石竹烯 (Z)-Caryophyllene | 64.000 | 甜香型/胡椒味 Sweet/peppery-like | — | — | 0.024 |
| 苯乙醛 Phenyl acetaldehyde | 4.000 | 甜香型/蜂蜜味 Sweet/honey-like | 0.020 | 0.019 | 0.013 |
| 己醛 Hexanal | 20.000 | 青香型/蔬菜味 Green/vegetative-like | 0.007 | — | — |
| 丙酸叔丁酯 Tert-butyl propionate | 43.000 | —/— | 0.006 | — | 0.005 |
| 异戊醇 Isoamylalcohol | 4.000 | 酒香型/威士忌味 Alcoholic/whiskey-like | 0.003 | — | 0.016 |
| (E,E)-2,4-庚二烯醛 2,4-Heptadienal, (E,E)- | 15.400 | 油香型/坚果味 Fatty/nut-like | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.007 |
| 异丁酸丙酯 Propyl isobutyrate | 0.430 | 甜香型/甜瓜味 Sweet/melon-like | — | — | 0.004 |
| 2-正丁基呋喃 2-n-Butyl furan | 5.000 | 辛香型/葡萄酒味 Spicy/wine-like | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.004 |
| 庚醛 Heptanal | 2.800 | 清香型/香菜味 Fresh/cilantro-like | — | 0.003 | — |
| 苯乙醇 Phenylethyl alcohol | 1 000.000 | 花香型/玫瑰香味 Floral/rose-like | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 |
| 乙酸芳樟酯 Linalyl acetate | 1 000.000 | 花香型/薰衣草香味 Floral /lavender-like | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 己酸乙酯 Ethyl hexanoate | 1.000 | 甜香型/菠萝味 Sweet/pineapple-like | — | 0.002 | — |
| α-松油烯 α-Terpinene | 85.000 | 木香型/茶香味 Wood/terpy-like | — | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 丙苯 Phenylpropane | 177.120 | —/— | — | — | 0.002 |
| 丁香酚 Eugenol | 6.000 | 甜香型/丁香味 Sweet/clove-like | — | — | 0.002 |
| 异丁醇 Isobutyl alcohol | 550.000 | 酒香型/葡萄酒味 Alcoholic/winey-like | — | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| 十一酮 2-Undecanone | 41.000 | 果香型/奶酪味 Fruit/cheese-like | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 1-甲基萘 Naphthalene, 1-methyl- | 8.000 | 萘基型/樟脑味 Naphthyl camphor-like | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 水杨酸戊酯 Amyl salicylate | 2.900 | 香草型/三叶草香味 Herbal/clover-like | 0.001 | — | 0.001 |
| 戊酸乙酯 Ethyl Valerate | 5.000 | 甜香型/草莓味 Sweet/strawberry-like | 0.000 | — | 0.001 |
| 异丁酸戊酯 Amyl isobutyrate | 43.000 | 果香型/苹果味 Fruity/apple-like | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| 化合物 Compound | PC1 | PC2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 载荷量 Load capacity | 特征向量 Feature vector | 载荷量 Load capacity | 特征向量 Feature vector | |
| α-愈创木烯 α-Guaiene | 0.948 | 0.125 | 0.318 | 0.063 |
| 大根香叶烯B Germacrene B | 0.962 | 0.127 | 0.272 | 0.054 |
| 顺-衣兰油-4(15), 5-二烯 cis-Muurola-4(15),5-diene | 0.957 | 0.126 | 0.291 | 0.058 |
| β-石竹烯 β-Caryophyllene | 1.000 | 0.132 | -0.007 | -0.001 |
| 双环倍半水芹烯 Bicyclosesquiphellandrene | 0.984 | 0.130 | 0.179 | 0.035 |
| 顺式-β-罗勒烯 cis-β-Ocimene | 1.000 | 0.132 | -0.030 | -0.006 |
| β-律草烯 β-Humulene | 0.973 | 0.128 | -0.232 | -0.046 |
| 双环大根香叶烯 Bicyclogermacrene | 0.987 | 0.130 | -0.158 | -0.031 |
| γ-依兰油烯 γ-Muurolene | 0.909 | 0.120 | -0.418 | -0.083 |
| α-古巴烯 α-Copaene | 0.943 | 0.124 | 0.334 | 0.066 |
| α-布藜烯 α-Bulnesene | 0.897 | 0.118 | 0.441 | 0.087 |
| 间苯二甲酸二烯丙酯 Diallyl isophthalate | -0.864 | -0.114 | 0.503 | 0.100 |
| β-古巴烯 β-Copaene | 0.980 | 0.129 | 0.198 | 0.039 |
| α-石竹烯 α-Caryophyllene | 0.999 | 0.132 | -0.034 | -0.007 |
| α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | 0.992 | 0.131 | -0.125 | -0.025 |
| 大根香叶烯 D (-)-Germacrene D | 0.902 | 0.119 | 0.431 | 0.085 |
| 丙酮酸乙酯 Ethyl pyruvate | -0.416 | -0.055 | -0.909 | -0.180 |
| 乙酸乙烯酯 Acetic acid ethenyl ester | 0.952 | 0.126 | 0.305 | 0.060 |
| 巴伦西亚橘烯 Valencene(+)-Val | 0.894 | 0.118 | 0.448 | 0.089 |
| 氧化石竹烯 Caryophyllene oxide | 0.998 | 0.132 | 0.063 | 0.013 |
| α-橄榄烯 α-Maaliene | 0.730 | 0.096 | 0.684 | 0.135 |
| δ-杜松烯 δ-Cadinene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| α-古芸烯 α-Gurjunene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 姜烯 Zingiberene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 荜澄茄油烯 Cubenene | 0.813 | 0.107 | 0.582 | 0.115 |
| 香树烯 Alloaromadendrene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| γ-松油醇 γ-Terpineol | 0.999 | 0.132 | 0.032 | 0.006 |
| 桉叶-3,7(11)-二烯 Eudesma-3,7(11)-diene | -0.977 | -0.129 | 0.211 | 0.042 |
| 乙酸冰片酯 Bornyl acetate | 0.490 | 0.065 | 0.872 | 0.173 |
| β-人参烯 β-Panasinsene | -0.984 | -0.130 | -0.179 | -0.035 |
| 巴豆酸异丁酯 2-Butenoic acid, 2-methylpropyl ester | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 4-蒈烯 4-Carene | 0.824 | 0.109 | 0.566 | 0.112 |
| 油醇 Oleyl alcohol | 0.906 | 0.120 | 0.422 | 0.084 |
| 四氢东非马钱碱 Tetrahydro-akagerine | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 橙花叔醇 Nerolidol | -0.053 | -0.007 | 0.999 | 0.198 |
| 去氢白菖烯 Calamenene | 0.960 | 0.127 | 0.282 | 0.056 |
| β-杜松烯 β-Cadinene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 1-(1-乙基丙基)-2-丙基苯Benzene, 1-(1-ethylpropyl)-2-propyl- | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 乙酸芳樟酯 Linalyl acetate | 0.999 | 0.132 | 0.032 | 0.006 |
| 香榧醇 Torreyol | -0.575 | -0.076 | -0.818 | -0.162 |
| α-柏木萜烯 α-Funebrene | 0.822 | 0.108 | 0.569 | 0.113 |
| 邻苯二甲酸二环己酯 Dicyclohexyl phthalate | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 Dibutyl phthalate | 0.127 | 0.017 | -0.992 | -0.197 |
| α-水芹烯 α-Phellandrene | -0.827 | -0.109 | 0.562 | 0.111 |
| (1-乙基辛基)苯 Benzene, (1-ethyloctyl)- | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 芳樟醇 Linalool | -0.670 | -0.088 | 0.742 | 0.147 |
| 己酸,3,5-二甲基环己酯Hexanoic acid,3,5-dimethylcyclohexyl ester | -0.972 | -0.128 | 0.236 | 0.047 |
| 6,9-愈创木二烯 Guaia-6,9-diene | -0.931 | -0.123 | 0.364 | 0.072 |
| 桉油烯醇 Spathulenol | 0.993 | 0.131 | -0.118 | -0.023 |
| 苯乙醇 Phenylethyl Alcohol | -0.395 | -0.052 | 0.919 | 0.182 |
| 异喇叭烯 (-)-Isoledene | 0.817 | 0.108 | 0.577 | 0.114 |
| α-榄香烯 α-Elemene | -0.937 | -0.124 | 0.349 | 0.069 |
| γ-榄香烯 γ-Elemene | -0.995 | -0.131 | 0.100 | 0.020 |
| 表双环倍半水芹烯 (+)-epi-Bicyclosesquiphellandrene | -0.942 | -0.124 | 0.337 | 0.067 |
| 异丁烯 Isobutylene | 0.725 | 0.096 | -0.689 | -0.137 |
| β-荜澄茄烯 (-)-β-Cadinen | 0.761 | 0.100 | 0.649 | 0.129 |
| 异丁醇 Isobutyl alcohol | 0.993 | 0.131 | -0.116 | -0.023 |
| 异戊烯 Isoamylene | 0.714 | 0.094 | 0.700 | 0.139 |
| α-芹子烯 α-Selinene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 邻苯二酚 Catechol | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 4-苯基戊-1-烯 4-phenylpent-1-ene | 0.863 | 0.114 | 0.506 | 0.100 |
| 6,6-二甲基辛-1-烯-7-炔 1-Octen-7-yne, 6,6-dimethyl- | -0.883 | -0.116 | 0.468 | 0.093 |
| α-荜澄茄油烯 (-)-α-Cubebene | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| 丙酮酸丙酯 Propyl pyruvate | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| 1-(1-乙基丙基)-4-甲基-苯Benzene,1-(1-ethylpropyl)-4-methyl- | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| γ-杜松烯 γ-Cadinene | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| 蓝桉醇 Globulol | -0.666 | -0.088 | 0.746 | 0.148 |
| α-雪松烯 α-Cedrene | 0.507 | 0.067 | 0.862 | 0.171 |
| (Z)-石竹烯 (Z)-Caryophyllene | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| 乙酸苄酯 Benzyl acetate | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| 反式-β-罗勒烯 trans-β-ocimene | -0.884 | -0.117 | 0.468 | 0.093 |
| 2-蒈烯 2-Carene | -0.772 | -0.102 | 0.635 | 0.126 |
| γ-桉叶醇 γ-eudesmol | -0.868 | -0.114 | -0.497 | -0.098 |
| 十一烷 Undecane | -0.868 | -0.114 | -0.497 | -0.098 |
| 4-庚烯-2-酮 4-Hepten-2-one | -0.868 | -0.114 | -0.497 | -0.098 |
| 苯甲酸甲酯 Methyl benzoate | -0.766 | -0.101 | -0.643 | -0.127 |
| 顺-4,5-环氧-(E)-2-癸烯醛 cis-4,5-Epoxy-(E)-2-decenal | -0.868 | -0.114 | -0.497 | -0.098 |
| 3-甲基戊酸乙酯 Ethyl 3-methyl valerate | -0.868 | -0.114 | -0.497 | -0.098 |
| β-紫罗兰酮 β-Ionone | 0.897 | 0.118 | 0.441 | 0.087 |
| 丁醛 Butanal | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 乙苯 Ethylbenzene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| β-芹子烯 β-Selinene | 0.966 | 0.127 | 0.260 | 0.051 |
Table 4 Eigenvectors and load capacities of the first two principal components
| 化合物 Compound | PC1 | PC2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 载荷量 Load capacity | 特征向量 Feature vector | 载荷量 Load capacity | 特征向量 Feature vector | |
| α-愈创木烯 α-Guaiene | 0.948 | 0.125 | 0.318 | 0.063 |
| 大根香叶烯B Germacrene B | 0.962 | 0.127 | 0.272 | 0.054 |
| 顺-衣兰油-4(15), 5-二烯 cis-Muurola-4(15),5-diene | 0.957 | 0.126 | 0.291 | 0.058 |
| β-石竹烯 β-Caryophyllene | 1.000 | 0.132 | -0.007 | -0.001 |
| 双环倍半水芹烯 Bicyclosesquiphellandrene | 0.984 | 0.130 | 0.179 | 0.035 |
| 顺式-β-罗勒烯 cis-β-Ocimene | 1.000 | 0.132 | -0.030 | -0.006 |
| β-律草烯 β-Humulene | 0.973 | 0.128 | -0.232 | -0.046 |
| 双环大根香叶烯 Bicyclogermacrene | 0.987 | 0.130 | -0.158 | -0.031 |
| γ-依兰油烯 γ-Muurolene | 0.909 | 0.120 | -0.418 | -0.083 |
| α-古巴烯 α-Copaene | 0.943 | 0.124 | 0.334 | 0.066 |
| α-布藜烯 α-Bulnesene | 0.897 | 0.118 | 0.441 | 0.087 |
| 间苯二甲酸二烯丙酯 Diallyl isophthalate | -0.864 | -0.114 | 0.503 | 0.100 |
| β-古巴烯 β-Copaene | 0.980 | 0.129 | 0.198 | 0.039 |
| α-石竹烯 α-Caryophyllene | 0.999 | 0.132 | -0.034 | -0.007 |
| α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | 0.992 | 0.131 | -0.125 | -0.025 |
| 大根香叶烯 D (-)-Germacrene D | 0.902 | 0.119 | 0.431 | 0.085 |
| 丙酮酸乙酯 Ethyl pyruvate | -0.416 | -0.055 | -0.909 | -0.180 |
| 乙酸乙烯酯 Acetic acid ethenyl ester | 0.952 | 0.126 | 0.305 | 0.060 |
| 巴伦西亚橘烯 Valencene(+)-Val | 0.894 | 0.118 | 0.448 | 0.089 |
| 氧化石竹烯 Caryophyllene oxide | 0.998 | 0.132 | 0.063 | 0.013 |
| α-橄榄烯 α-Maaliene | 0.730 | 0.096 | 0.684 | 0.135 |
| δ-杜松烯 δ-Cadinene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| α-古芸烯 α-Gurjunene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 姜烯 Zingiberene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 荜澄茄油烯 Cubenene | 0.813 | 0.107 | 0.582 | 0.115 |
| 香树烯 Alloaromadendrene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| γ-松油醇 γ-Terpineol | 0.999 | 0.132 | 0.032 | 0.006 |
| 桉叶-3,7(11)-二烯 Eudesma-3,7(11)-diene | -0.977 | -0.129 | 0.211 | 0.042 |
| 乙酸冰片酯 Bornyl acetate | 0.490 | 0.065 | 0.872 | 0.173 |
| β-人参烯 β-Panasinsene | -0.984 | -0.130 | -0.179 | -0.035 |
| 巴豆酸异丁酯 2-Butenoic acid, 2-methylpropyl ester | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 4-蒈烯 4-Carene | 0.824 | 0.109 | 0.566 | 0.112 |
| 油醇 Oleyl alcohol | 0.906 | 0.120 | 0.422 | 0.084 |
| 四氢东非马钱碱 Tetrahydro-akagerine | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 橙花叔醇 Nerolidol | -0.053 | -0.007 | 0.999 | 0.198 |
| 去氢白菖烯 Calamenene | 0.960 | 0.127 | 0.282 | 0.056 |
| β-杜松烯 β-Cadinene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 1-(1-乙基丙基)-2-丙基苯Benzene, 1-(1-ethylpropyl)-2-propyl- | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 乙酸芳樟酯 Linalyl acetate | 0.999 | 0.132 | 0.032 | 0.006 |
| 香榧醇 Torreyol | -0.575 | -0.076 | -0.818 | -0.162 |
| α-柏木萜烯 α-Funebrene | 0.822 | 0.108 | 0.569 | 0.113 |
| 邻苯二甲酸二环己酯 Dicyclohexyl phthalate | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 Dibutyl phthalate | 0.127 | 0.017 | -0.992 | -0.197 |
| α-水芹烯 α-Phellandrene | -0.827 | -0.109 | 0.562 | 0.111 |
| (1-乙基辛基)苯 Benzene, (1-ethyloctyl)- | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 芳樟醇 Linalool | -0.670 | -0.088 | 0.742 | 0.147 |
| 己酸,3,5-二甲基环己酯Hexanoic acid,3,5-dimethylcyclohexyl ester | -0.972 | -0.128 | 0.236 | 0.047 |
| 6,9-愈创木二烯 Guaia-6,9-diene | -0.931 | -0.123 | 0.364 | 0.072 |
| 桉油烯醇 Spathulenol | 0.993 | 0.131 | -0.118 | -0.023 |
| 苯乙醇 Phenylethyl Alcohol | -0.395 | -0.052 | 0.919 | 0.182 |
| 异喇叭烯 (-)-Isoledene | 0.817 | 0.108 | 0.577 | 0.114 |
| α-榄香烯 α-Elemene | -0.937 | -0.124 | 0.349 | 0.069 |
| γ-榄香烯 γ-Elemene | -0.995 | -0.131 | 0.100 | 0.020 |
| 表双环倍半水芹烯 (+)-epi-Bicyclosesquiphellandrene | -0.942 | -0.124 | 0.337 | 0.067 |
| 异丁烯 Isobutylene | 0.725 | 0.096 | -0.689 | -0.137 |
| β-荜澄茄烯 (-)-β-Cadinen | 0.761 | 0.100 | 0.649 | 0.129 |
| 异丁醇 Isobutyl alcohol | 0.993 | 0.131 | -0.116 | -0.023 |
| 异戊烯 Isoamylene | 0.714 | 0.094 | 0.700 | 0.139 |
| α-芹子烯 α-Selinene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 邻苯二酚 Catechol | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 4-苯基戊-1-烯 4-phenylpent-1-ene | 0.863 | 0.114 | 0.506 | 0.100 |
| 6,6-二甲基辛-1-烯-7-炔 1-Octen-7-yne, 6,6-dimethyl- | -0.883 | -0.116 | 0.468 | 0.093 |
| α-荜澄茄油烯 (-)-α-Cubebene | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| 丙酮酸丙酯 Propyl pyruvate | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| 1-(1-乙基丙基)-4-甲基-苯Benzene,1-(1-ethylpropyl)-4-methyl- | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| γ-杜松烯 γ-Cadinene | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| 蓝桉醇 Globulol | -0.666 | -0.088 | 0.746 | 0.148 |
| α-雪松烯 α-Cedrene | 0.507 | 0.067 | 0.862 | 0.171 |
| (Z)-石竹烯 (Z)-Caryophyllene | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| 乙酸苄酯 Benzyl acetate | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.198 |
| 反式-β-罗勒烯 trans-β-ocimene | -0.884 | -0.117 | 0.468 | 0.093 |
| 2-蒈烯 2-Carene | -0.772 | -0.102 | 0.635 | 0.126 |
| γ-桉叶醇 γ-eudesmol | -0.868 | -0.114 | -0.497 | -0.098 |
| 十一烷 Undecane | -0.868 | -0.114 | -0.497 | -0.098 |
| 4-庚烯-2-酮 4-Hepten-2-one | -0.868 | -0.114 | -0.497 | -0.098 |
| 苯甲酸甲酯 Methyl benzoate | -0.766 | -0.101 | -0.643 | -0.127 |
| 顺-4,5-环氧-(E)-2-癸烯醛 cis-4,5-Epoxy-(E)-2-decenal | -0.868 | -0.114 | -0.497 | -0.098 |
| 3-甲基戊酸乙酯 Ethyl 3-methyl valerate | -0.868 | -0.114 | -0.497 | -0.098 |
| β-紫罗兰酮 β-Ionone | 0.897 | 0.118 | 0.441 | 0.087 |
| 丁醛 Butanal | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| 乙苯 Ethylbenzene | 0.864 | 0.114 | -0.503 | -0.100 |
| β-芹子烯 β-Selinene | 0.966 | 0.127 | 0.260 | 0.051 |
| [1] | Báez D, Morales D, Pino J A. 2012. Volatiles from Michelia champaca flower:comparative analysis by simultaneous distillation-extraction and solid phase microextraction. Natural Product Communications, 7 (5):659-660. |
| [2] | Chai Yi-xia, Cai Meng-ying, Jin Xiao-ling, Zhang Dong-lin. 2017. Pollination biology of Michelia crassipes. Guihaia, 37 (10):1322-1329. (in Chinese) |
| 柴弋霞, 蔡梦颖, 金晓玲, 张冬林. 2017. 紫花含笑传粉生物学初探. 广西植物, 37 (10):1322-1329. | |
| [3] | Chen Yu. 2021. Study on the clinical effect and vision recovery of pilocarpine eye drops assisted phacoemulsification combined with angle separation in thetreatment ofpatients with angle-closure glaucoma. Contemporary Medicine, 27 (34):66-68. (in Chinese) |
| 陈钰. 2021. 毛果芸香碱滴眼液辅助超声乳化联合房角分离术治疗闭角型青光眼患者的临床效果及视力恢复情况探究. 当代医学, 27 (34):66-68. | |
| [4] | Ding Qian-qian, Wu Xing-bo, Liu Fang, Xu Gai-ping, Zheng Jie, Gao Yan. 2013. Volatile organic compounds in flowers of four Magnoliaceae species. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 30 (4):477-483. (in Chinese) |
| 丁倩倩, 吴兴波, 刘芳, 许改平, 郑洁, 高岩. 2013. 木兰科 4 种植物鲜花挥发物成分分析. 浙江农林大学学报, 30 (4):477-483. | |
| [5] | Efferth T, Oesch F. 2021. Repurposing of plant alkaloids for cancer therapy:Pharmacology and toxicology//Seminars in cancer biology. Academic Press: 68:143-163. |
| [6] | Fang Xiao-ping, Hu Guang-ping. 2010. Effect of different extract methodson volatile components of Michelia maudiae. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 38 (5):81-84. (in Chinese) |
| 方小平, 胡光平. 2010. 不同提取方法对深山含笑花挥发性成分的影响. 贵州农业科学, 38 (5):81-84. | |
| [7] | Gao Hua-juan. 2009. The forming and releasing and chemical components of fragrance of three species in Mickelia Linn[M. D. Dissertation]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University. (in Chinese) |
| 高华娟. 2009. 含笑属 3 个种花香形成和释放及化学成分的研究[硕士论文]. 福州: 福建农林大学. | |
| [8] | Gemert L J. 2018. Compilations of odour threshold values in air,water and other media. Beijing: Science Press. |
| [9] | Ghosh D, Chaudhary N, Uma K K, Singh J, Tripathi P, Meena A, Luqman S, Yadav A, Chanotiya C S, Pandey G, Kumar N. 2021. Diversity of essential oil-secretory cells and oil composition in flowers and buds of Magnolia sirindhorniae and its biological activities. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 18 (1):1-26. |
| [10] | Gong Wei, Xiao Ju-hong, Gan Qing, Huang Feng-long, Ouyang Shao-lin, He Long. 2018. The effects of the substrate and rooting reagent on the rooting of Michelia crassipes by cutting propagation. Fujan Forestry,(4):37-40. (in Chinese) |
| 龚伟, 肖菊红, 甘青, 黄逢龙, 欧阳少林, 贺珑. 2018. 扦插基质和生根剂处理对紫花含笑扦插生根的影响. 福建林业,(4):37-40. | |
| [11] | He Xue-yan. 2019. Analysis of volatile components of four aromatic plants and their effect on human health[M. D. Dissertation]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A & F University. (in Chinese) |
| 何雪雁. 2019. 四种芳香植物挥发物成分分析及其对人体健康干预效应研究[硕士论文]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学. | |
| [12] | Holopainen J K, Blande J D. 2013. Where do herbivore-induced plant volatiles go? Frontiers in Plant Science, 4 (11):185. |
| [13] |
Hossain S J, Aoshima H, Koda H, Kiso Y. 2004. Fragrances in oolong tea that enhance the response of GABAA receptors. Bioscience,Biotechnology,and Biochemistry, 68 (9):1842-1848.
doi: 10.1271/bbb.68.1842 URL |
| [14] | Hu Guang-ping, Fang Xiao-ping, Yang Zhan-nan, Chen Ben-liu. 2010. Study on the volatile components in different part of Michelia yunnanensis flower. Journal of Anhui Agri Sci, 38 (14):7321-7323. (in Chinese) |
| 胡光平, 方小平, 杨占南, 陈奔流. 2010. 云南含笑花不同部位挥发性成分研究. 安徽农业科学, 38 (14):7321-7323. | |
| [15] |
Hu M, Bai M, Ye W, Wang Y, Wu H. 2018. Variations in volatile oil yield and composition of“Xin-yi”(Magnolia biondii pamp. flower buds)at different growth stages. Journal of Oleo Science, 67 (6):779-787.
doi: 10.5650/jos.ess17229 URL |
| [16] |
Huang G C, Kao C L, Yeh H C, Li H T, Chen C Y. 2019. Secondary metabolites from the flowers of Michelia crassipes. Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 55 (5):982-983.
doi: 10.1007/s10600-019-02869-3 |
| [17] | Kim H K, Seo J W, Kim G H. 2020. Various effects of volatile constituents from Magnolia kobus flowers against Aedes albopictus(Diptera:Culicidae). Industrial Crops and Products, 145:112-119. |
| [18] | Lee Y J, Lee Y M, Lee C K, Jung J K, Han S B, Hong J T. 2011. Therapeutic applications of compounds in the Magnolia family. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 130 (2):157-176. |
| [19] | Lei Ling-hua, Zhu Qiang-gen, Xia Geng-shou, Xiao You, Yu Xiao-ying. 2019. Volatile components analysis from different fresh tissues of Michelia martini. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 36 (1):193-199. (in Chinese) |
| 雷凌华, 朱强根, 夏更寿, 肖悠, 于晓英. 2019. 黄心夜合不同组织挥发油成分分析. 浙江农林大学学报, 36 (1):193-199. | |
| [20] |
Lesueur D, Serra D D R, Bighelli A, Hoi T M, Ban N K, Thai T H, Casanova J. 2007. Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of the essential oil of Michelia foveolata Merryll ex Dandy from Vietnam. Flavour and Fragrance Journal, 22 (4):317-321.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1026 URL |
| [21] | Li Xiaoying, Wu Junkai, Wang Haijing, Zhang Hongxia, Guo Xuemin. 2019. Analysis of volatile components in whorl tepals of Magnolia denudate‘Feihuang’during its development. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (10):2009-2020. (in Chinese) |
| 李晓颍, 武军凯, 王海静, 张红霞, 郭学民. 2019. ‘飞黄’玉兰花发育期各轮花被片挥发性成分分析. 园艺学报, 46 (10):2009-2020. | |
| [22] | Lin Jia-zheng, Tu zheng, Chen Lin, Ye Yang, Liu Fei, Wang Yu-wan, Yang Yun-fei, Wu Xun, Lü Hao-wei. 2021. The effect of red light withering on the volatile components of tea leaves and the quality of black tea product. Journal of Tea Science, 41 (3):393-405. (in Chinese) |
| 林家正, 涂政, 陈琳, 叶阳, 刘飞, 王玉婉, 杨云飞, 伍洵, 吕昊威. 2021. 红光萎凋对茶叶挥发性成分及其成品红茶品质的影响. 茶叶科学, 41 (3):393-405. | |
| [23] |
Liu C X, Yu Q X, Li Z, Jin X L, Xing W. 2020. Metabolic and transcriptomic analysis related to flavonoid biosynthesis during the color formation of Michelia crassipes tepal. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 155:938-951.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.06.050 URL |
| [24] | Liu Hui-ming, Gao Ji-xi, Song Chuang-ye, Yu Sheng-xiang. 2019. Conservation status and human disturbance of the habitats of Michelia crassipes Law in China. China Environmental Science, 39 (9):3976-3981. (in Chinese) |
| 刘慧明, 高吉喜, 宋创业, 于胜祥. 2019. 紫花含笑适宜生境的保护空缺与人类干扰分析. 中国环境科学, 39 (9):3976-3981. | |
| [25] | Liu Lu, Fang Xiao-ping, Liu Ying-liang, Chi Hai-hong. 2017. Analysis of volatile oils ingredient from the different parts of Michelia fulgens Dandy by GC-MS. Molecular Plant Breeding, 15 (1):339-345. (in Chinese) |
| 刘璐, 方小平, 刘映良, 迟海红. 2017. 亮叶含笑不同器官精油成分GC-MS分析. 分子植物育种, 15 (1):339-345. | |
| [26] | Ma Hui-fen, Sima Yong-kang, Hao Jia-bo, Chen Shao-yu, Han Ming-yue, Li Dan, Xu Liang, Zhou Bin, Chai Yong. 2011. Study on chemical components in the volatile oils from Michelia polyneura C.Y. Wu ex Law et Y. F. Wu. and Michelia macclurei Dandy. Guangdong Agricultural Science, 38 (23):110-113. (in Chinese) |
| 马惠芬, 司马永康, 郝佳波, 陈少瑜, 韩明跃, 李丹, 徐亮, 周彬, 柴勇. 2011. 多脉含笑和醉香含笑挥发油的化学成分研究. 广东农业科学, 38 (23):110-113. | |
| [27] |
Maiti S, Mitra A. 2017. Morphological,physiological and ultrastructural changes in flowers explain the spatio-temporal emission of scent volatiles in Polianthes tuberosa L. Plant and Cell Physiology, 58 (12):2095-2111.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcx143 URL |
| [28] | Phrutivorapongkul A, Ichino C, Ruangrungsi N, Ishiyama A, Sekiguchi H, Namatame M, Kiyohara H, Otoguro K, Yamada H, Omura S. 2006. Anti-plasmodial activity of bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids from Michelia figo leaves. Thai J Health Res, 20 (2):121-129. |
| [29] |
Pichersky E, Gang D R. 2000. Genetics and biochemistry of secondary metabolites in plants:an evolutionary perspective. Trends in Plant Science, 5 (10):439-445.
doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(00)01741-6 pmid: 11044721 |
| [30] |
Piechowska K, Mizerska-Kowalska M, Zdzisińska B, Cytarska J, Baranowska-Łączkowska A, Jaroch K, Łączkowski K Z. 2020. Tropinone-derived alkaloids as potent anticancer agents:synthesis,tyrosinase inhibition,mechanism of action,DFT calculation and molecular docking studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21 (23):9050.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21239050 URL |
| [31] |
Qi H T, Ding S H, Pan Z P, Li X, Fu F. 2020. Characteristic volatile fingerprints and odor activity values in different citrus-tea by HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Molecules, 25 (24):6027.
doi: 10.3390/molecules25246027 URL |
| [32] |
Qiao Zhenglin, Hu Huizhen, Yan Bo, Chen Longqing. 2021. Advances of researches on biosynthesis and regulation of floral volatile benzenoids/phenylpropanoids. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (9):1815-1826. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0549 |
|
谯正林, 胡慧贞, 鄢波, 陈龙清. 2021. 花香挥发性苯/苯丙素类化合物的生物合成及基因调控研究进展. 园艺学报, 48 (9):1815-1826.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0549 |
|
| [33] | Qin Jun. 2017. Identification of aromatic components and mechanism of aroma formation of Narcissus spp. [M. D. Dissertation]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University. (in Chinese) |
| 秦军. 2017. 洋水仙香气成分的鉴定与香气形成机制研究[硕士论文]. 福州: 福建农林大学. | |
| [34] |
Rasouli H, Yarani R, Pociot J, Popović Djordjević F. 2020. Anti-diabetic potential of plant alkaloids:revisiting current findings and future perspectives. Pharmacological research, 155:104723.
doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104723 URL |
| [35] |
Rivera Pérez A, Romero González R, Garrido F A. 2021. Feasibility of applying untargeted metabolomics with GC-Orbitrap-HRMS and chemometrics for authentication of black pepper(Piper nigrum L.) and identification of geographical and processing markers. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 69 (19):5547-5558.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01515 pmid: 33957048 |
| [36] |
Shang C, Hu Y, Deng C, Hu K. 2002. Rapid determination of volatile constituents of Michelia alba flowers by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry with solid-phase microextraction. Journal of Chromatography A, 942 (1-2):283-288.
doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(01)01382-6 URL |
| [37] | Shi Ting-ting, Yang Xiu-lian, Wang Liang-gui. 2020. Dynamic characteristics of floral components and anatomical observation of petalsin three cultivars of Osmanthus fragrans. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Sciences Edition), 44 (4):12-20. (in Chinese) |
| 施婷婷, 杨秀莲, 王良桂. 2020. 3 个桂花品种花香组分动态特征及花被片结构解剖学观测. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 44 (4):12-20. | |
| [38] |
Shi Liting, Zhou Xinyang, Ye Jianfeng, Zhou Jiahao, Wang Gang, Xia Guohua. 2021. Advances in remote hybridization breeding of woody ornamental plants. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (9):1827-1838. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0565 |
|
施丽婷, 周鑫洋, 叶建丰, 周家豪, 王刚, 夏国华. 2021. 木本观赏植物远缘杂交育种研究进展. 园艺学报, 48 (9):1827-1838.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0565 |
|
| [39] |
Shimada K, Fukuda S, Maeda K, Kawasaki T, Kono Y, Jissho S, Yoshikawa J. 2011. Aromatherapy alleviates endothelial dysfunction of medical staff after night-shift work:preliminary observations. Hypertension Research, 34 (2):264-267.
doi: 10.1038/hr.2010.228 pmid: 21107332 |
| [40] | Si Min-zhen, Li Jia-wang, Yang Yong’an, Li Lun, Zhang Chuan-yun, Zhang De-qing. 2021. In situ research on three Michelia figo volatile organic compounds with Raman. The Journal Of Light Scattering, 33 (1):52-58. (in Chinese) |
|
司民真, 李家旺, 杨永安, 李伦, 张川云, 张德清. 2021. 三种含笑属植物花挥发物的原位显微拉曼光谱检测. 光散射学报, 33 (1):52-58.
doi: 10.13883/j.issn1004-5929.202101007 |
|
| [41] | Song Xiao-chen, Tian Jing, Xiao Fu-ming, Jiang Xiang-mei, Zeng Xian-rong, Zeng Xiu. 2015. Propagation for grafting of Michelia crassipes. South China Forestry Science, 43 (4):13-15,45. (in Chinese) |
| 宋晓琛, 田径, 肖复明, 江香梅, 曾宪荣, 曾秀. 2015. 紫花含笑嫁接繁殖技术研究. 南方林业科学, 43 (4):13-15,45. | |
| [42] | Su Y C, Hsu K P, Wang E I C, Ho C L. 2015. Chemical composition and anti-mildew activities of essential oils from different parts of Michelia compressa var. formosana. Natural Product Communications, 10 (4):665-668. |
| [43] | Sun L, Zhu B, Wang X, Sun X, Yan A, Zhang G, Wang H, Xu H. 2016. GC-MS with spectral similarity analysis and retention index. J Inst Anal, 3:525-528. |
| [44] | Sun Ling-feng, Xi Chun-lin, Liang Guo-zhong. 1993. Study on morphological characteristics and fragrance components of Michelia fallaca Dandy. Journal of Jiangxi Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 17 (1):54-61. (in Chinese) |
| 孙凌峰, 漆春林, 梁国忠. 1993. 大叶含笑树的形态特性及其含香成分研究. 江西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 17 (1):54-61. | |
| [45] | Tan Yin-yin, Jin Xiao-ling, Yu Qiu-xiu, Sun Ling-xiao. 2021. Screening of leaf cold-resistant structural indexes and cold-resistance evaluation of five Michelia species. Guihaia, 41 (8):1296-1305. (in Chinese) |
| 谭殷殷, 金晓玲, 余秋岫, 孙凌霄. 2021. 5 种含笑属植物叶片抗寒结构指标的筛选与抗寒性评价. 广西植物, 41 (8):1296-1305. | |
| [46] | Wang Qing-yi. 2021. Analysis of volatile components of four aromatic plants and their effects on human physical and mental health[M. D. Dissertation]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A & F University. (in Chinese) |
| 王晴艺. 2021. 四种芳香植物挥发物成分分析及其对人体身心健康的影响研究[硕士论文]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学. | |
| [47] | Wang Xin, Sun Shao-hua, Jia Rui-bao, Song Yan, Wang Ming-quan, Zhao Qing-hua, Ji Guang-xue. 2019. Application of high-resolution mass spectrometry technologies in identification of degradation products of organic pollutants. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 26 (2):84-90. (in Chinese) |
| 王鑫, 孙韶华, 贾瑞宝, 宋艳, 王明泉, 赵清华, 姬广雪. 2019. 高分辨质谱技术在有机污染物降解产物鉴定中的应用进展. 安全与环境工程, 26 (2):84-90. | |
| [48] | Wu Lin, Zhang Qiang, Zang Hui-ming, Xu Zhen-biao, Xu Dei-bing. 2020. Evaluation of volatile aroma components in blueberry peel,pulp and juice by odor activity value. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 41 (1):195-200. (in Chinese) |
| 吴林, 张强, 臧慧明, 徐振彪, 徐德冰. 2020. 气味活度值法评价蓝莓果皮、果肉、果汁挥发性香气成分. 食品工业科技, 41 (1):195-200. | |
| [49] | Xia Qi-han. 2019. Study on healthy mechanism of plant VOCs beneficial molecules[M. D. Dissertation]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A & F University. (in Chinese) |
| 夏琪涵. 2019. 植物 VOCs 有益成分的分子康养作用机理研究[硕士论文]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学. | |
| [50] |
Xu F X, Chen D Q, Specht C. 2013. Comparative microsporogenesis and anther development of selected species from Magnoliaceae. Nordic Journal of Botany, 31 (3):291-300.
doi: 10.1111/more.2013.31.issue-3 URL |
| [51] |
Yu M, Li T, S H. 2022. Characterization of key aroma-active compounds in four commercial oyster sauce by SGC/GC × GC-O-MS,AEDA,and OAV. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 107:104368.
doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2021.104368 URL |
| [52] | Yu Ya-xin, Hu Xi-jun, Jin Xiao-ling. 2013. Carbon fixation and oxygen release,cooling and humidification of 12 Magnoliaceae species. Guangdong Agricultural Science, 40 (6):47-50,60. (in Chinese) |
| 于雅鑫, 胡希军, 金晓玲. 2013. 12种木兰科乔木固碳释氧和降温增湿能力研究. 广东农业科学, 40 (6):47-50,60. | |
| [53] | Zhang Wei. 2020. Study on extraction of volatile oil from white orchid and its aroma components[M. D. Dissertation]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology. (in Chinese) |
| 张伟. 2020. 白兰花挥发油的提取及其香气组分的研究[硕士论文]. 广州: 华南理工大学. | |
| [54] | Zhou L J, Yu C, Cheng B X, Han Y, Luo L, Pan H T, Zhang Q X. 2020. Studies on the volatile compounds in flower extracts of Rosa odorata and R. chinensis. Industrial Crops & Products, 146:112143. |
| [1] | ZHANG Zheng, YANG Yun, WEI Jian-He, MENG Hui, WANG Meng-Xi, HAN Xiao-Min, SUI Chun. Response of Endogenous Jasmonates and Sesquiterpenes to Mechanical Wound in Aquilaria sinensis Stem [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2013, 40(1): 163-168. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd