
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1343-1354.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0349
• Cultivation Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Mengyu, HU Yaofang, GU Lin, LI Zhenjian, QIAN Yongqiang, JU Guansheng, LIU Junxiang( ), SUN Zhenyuan(
), SUN Zhenyuan( )
)
Received:2022-04-04
Revised:2023-01-16
Online:2023-06-25
Published:2023-06-27
Contact:
* (E-mail:CLC Number:
MA Mengyu, HU Yaofang, GU Lin, LI Zhenjian, QIAN Yongqiang, JU Guansheng, LIU Junxiang, SUN Zhenyuan. Effect of Branch Light Treatment on Prolonging the Vase Life of Cut Rose[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(6): 1343-1354.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0349
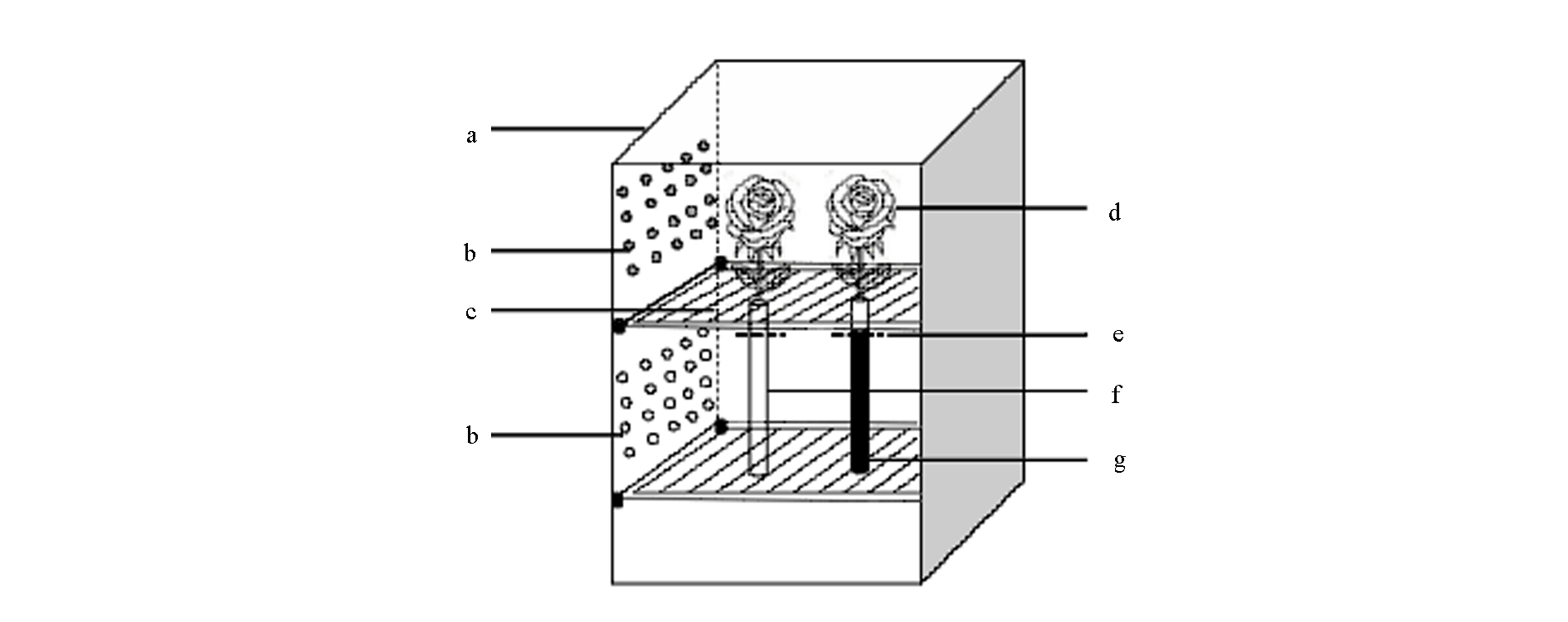
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the vase experimental devices a:Light incubator;b:LED lamp board;c:Partition baffle;d:Cut rose;e:Water level line;f:Transparent glass tube;g:Transparent glass tube wrapped by aluminum foil.
| 样品 Sample | 叶绿素含量/(mg · g-1 FW)Content of chlorophyll | Chl. a/b | 类胡萝卜素含量(mg · g-1 FW) Content of carotenoid | 类胡萝卜素/总叶绿素 Carotenoid/total chlorophyll | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | 总叶绿素 a + b | ||||
| 皮层Cortex | 0.49 ± 0.02* | 0.19 ± 0.01* | 0.68 ± 0.03* | 2.63 ± 0.16* | 0.10 ± 0.01* | 0.15 ± 0.01 |
| 叶片Leaf | 2.10 ± 0.09 | 0.69 ± 0.03 | 2.80 ± 0.11 | 3.05 ± 0.02 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 |
Table 1 The difference in photosynthetic pigment composition between leaf and branch cortex
| 样品 Sample | 叶绿素含量/(mg · g-1 FW)Content of chlorophyll | Chl. a/b | 类胡萝卜素含量(mg · g-1 FW) Content of carotenoid | 类胡萝卜素/总叶绿素 Carotenoid/total chlorophyll | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | 总叶绿素 a + b | ||||
| 皮层Cortex | 0.49 ± 0.02* | 0.19 ± 0.01* | 0.68 ± 0.03* | 2.63 ± 0.16* | 0.10 ± 0.01* | 0.15 ± 0.01 |
| 叶片Leaf | 2.10 ± 0.09 | 0.69 ± 0.03 | 2.80 ± 0.11 | 3.05 ± 0.02 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 |
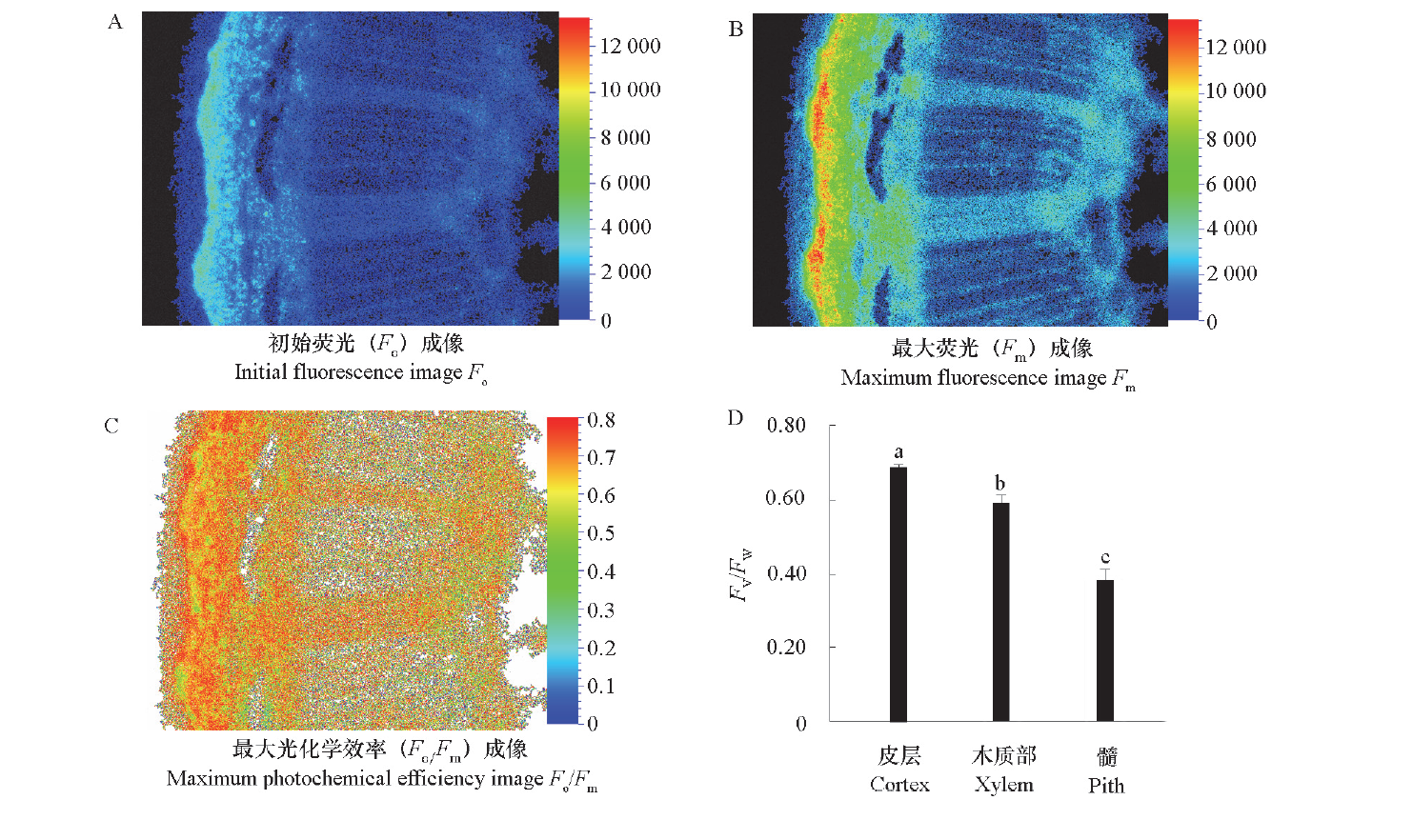
Fig. 2 Chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of the branch cross section of rose Different lowercase letters above the standard error line indicate significant difference at the level of P < 0.05.
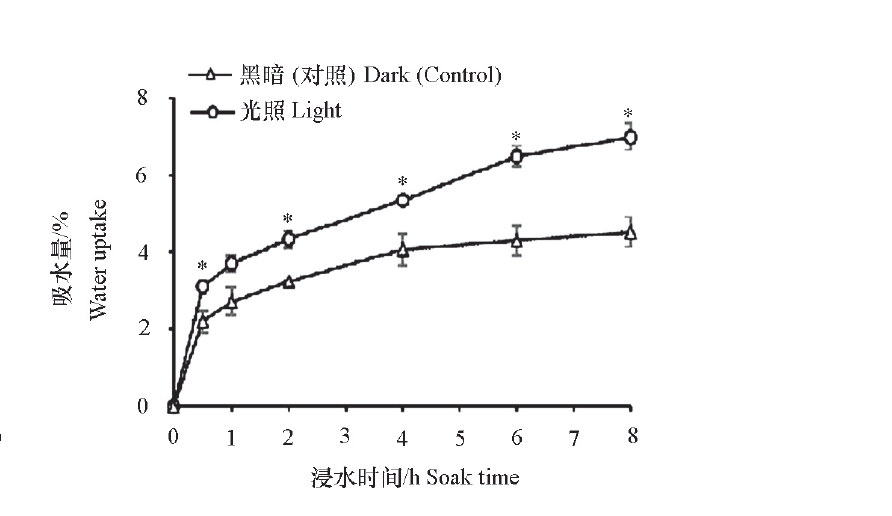
Fig. 4 Effects of light treatment on cortex water uptake of branch * indicates the significant difference between light treatment and dark(control)at a given soaking time at the level of P < 0.05. The same belwow.

Fig. 5 The performance of flower and leaves for the light treatment and dark(control) Different lowercase letters indicate the significant difference between light treatment and dark(control)at the level of P < 0.05.
| 瓶插时间/d Vase period | 处理 Treament | 吸水量/g Water absorption | 失水量/g Water loss | 水分平衡量/g Water balance | 水势/MPa Water potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 光照Light | 5.62 ± 0.21* | 5.37 ± 0.22 | 0.26 ± 0.05* | — |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | 4.82 ± 0.17 | 5.03 ± 0.14 | -0.21 ± 0.14 | — | |
| 2 | 光照Light | 6.06 ± 0.29* | 6.34 ± 0.34* | -0.28 ± 0.08 | -0.51 ± 0.02* |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | 4.89 ± 0.16 | 5.05 ± 0.23 | -0.17 ± 0.11 | -0.85 ± 0.04 | |
| 4 | 光照Light | 5.50 ± 0.26* | 6.87 ± 0.33* | -1.37 ± 0.24 | -0.53 ± 0.06* |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | 3.38 ± 0.34 | 4.70 ± 0.30 | -1.32 ± 0.27 | -1.07 ± 0.07 | |
| 6 | 光照Light | 4.90 ± 0.22* | 5.69 ± 0.25* | -0.79 ± 0.14 | -0.79 ± 0.08* |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | 1.89 ± 0.18 | 3.37 ± 0.25 | -1.48 ± 0.25 | -1.40 ± 0.06 | |
| 8 | 光照Light | 3.89 ± 0.20* | 4.34 ± 0.23* | -0.45 ± 0.05* | -1.03 ± 0.05* |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | 0.87 ± 0.08 | 2.15 ± 0.25 | -1.27 ± 0.18 | -1.63 ± 0.07 | |
| 10 | 光照Light | 3.92 ± 0.29 | 4.60 ± 0.43 | -0.68 ± 0.17 | -1.01 ± 0.09* |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | — | — | — | -4.16 ± 0.19 |
Table 2 Effects of light treatment on water absorption,water loss,water balance and water potential of cut rose
| 瓶插时间/d Vase period | 处理 Treament | 吸水量/g Water absorption | 失水量/g Water loss | 水分平衡量/g Water balance | 水势/MPa Water potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 光照Light | 5.62 ± 0.21* | 5.37 ± 0.22 | 0.26 ± 0.05* | — |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | 4.82 ± 0.17 | 5.03 ± 0.14 | -0.21 ± 0.14 | — | |
| 2 | 光照Light | 6.06 ± 0.29* | 6.34 ± 0.34* | -0.28 ± 0.08 | -0.51 ± 0.02* |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | 4.89 ± 0.16 | 5.05 ± 0.23 | -0.17 ± 0.11 | -0.85 ± 0.04 | |
| 4 | 光照Light | 5.50 ± 0.26* | 6.87 ± 0.33* | -1.37 ± 0.24 | -0.53 ± 0.06* |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | 3.38 ± 0.34 | 4.70 ± 0.30 | -1.32 ± 0.27 | -1.07 ± 0.07 | |
| 6 | 光照Light | 4.90 ± 0.22* | 5.69 ± 0.25* | -0.79 ± 0.14 | -0.79 ± 0.08* |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | 1.89 ± 0.18 | 3.37 ± 0.25 | -1.48 ± 0.25 | -1.40 ± 0.06 | |
| 8 | 光照Light | 3.89 ± 0.20* | 4.34 ± 0.23* | -0.45 ± 0.05* | -1.03 ± 0.05* |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | 0.87 ± 0.08 | 2.15 ± 0.25 | -1.27 ± 0.18 | -1.63 ± 0.07 | |
| 10 | 光照Light | 3.92 ± 0.29 | 4.60 ± 0.43 | -0.68 ± 0.17 | -1.01 ± 0.09* |
| 黑暗(对照)Dark(control) | — | — | — | -4.16 ± 0.19 |
| [1] | Cai Xi-an, Zeng Xiao-ping, Chen Yuan-qi. 2015. Stem corticular photosynthesis:ecophysiological functions and the measurement. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35 (21):6909-6922. (in Chinese) |
| 蔡锡安, 曾小平, 陈远其. 2015. 树干皮层光合作用——生理生态功能和测定方法. 生态学报, 35 (21):6909-6922. | |
| [2] |
Cernusak L A, Cheesman A W. 2015. The benefits of recycling:how photosynthetic bark can increase drought tolerance. New Phytologist, 208 (4):995-997.
doi: 10.1111/nph.13723 pmid: 26536151 |
| [3] |
Chen Hemin, Li Zuo, Ma Nan, Xiao Wenfang, Chen Heming, Lü Fubing, Li Zongyan, Zhu Genfa. 2022. Research advances on fresh-keeping technologies of orchid cut flowers and potted plants. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 49 (12):2743-2760. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0488 URL |
|
陈和敏, 李佐, 马男, 肖文芳, 陈和明, 吕复兵, 李宗艳, 朱根发. 2022. 兰花切花保鲜及盆花品质保持技术研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (12):2743-2760.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0488 URL |
|
| [4] |
Chen X, Zhao P, Zhao X H, Wang Q, Ouyang L, Larjivaara M, Zhu L W, Ni G Y. 2021. Involvement of stem corticular photosynthesis in hydraulic maintenance of Eucalyptus trees and its effect on leaf gas exchange. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 186:104451.
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2021.104451 URL |
| [5] | Earles J M, Sperling O, Silva L C R, McElrone A J, Brodersen C R, North M P, Zwieniecki M A. 2016. Bark water uptake promotes localized hydraulic recovery in coastal redwood crown. Plant,Cell & Environment, 29:320-328. |
| [6] |
Fang H, Wang C L, Wang S Y, Liao W B. 2021. Hydrogen gas increases the vase life of cut rose ‘Movie star’ by regulating bacterial community in the stem ends. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 181:111685.
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2021.111685 URL |
| [7] |
Fang Hua, Wang Chun-lei, Liao Wei-biao, Zhang Jing, Huo Jian-qiang, Huang Deng-jing, Niu Li-Juan, Wang Bo. 2019. NO is involved in ABA-regulated senescence of cut roses by maintaining water content and increasing antioxidant enzyme activities. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (5):901-909. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0659 URL |
|
方华, 王春蕾, 廖伟彪, 张静, 霍建强, 黄登静, 牛丽涓, 王波. 2019. 一氧化氮通过调控水分和抗氧化酶活性参与脱落酸延缓切花月季衰老. 园艺学报, 46 (5):901-909.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0659 URL |
|
| [8] | Gao Jun-feng. 2006. Experimental Guidance for Plant Physiology. 1st ed. Beijng: Higher Education Press: 71-74. (in Chinese) |
| 高俊凤. 2006. 植物生理学实验指导. 1版. 北京: 高等教育出版社:71-74. | |
| [9] | Hamidi E, Roein Z, Karimi M. 2020. Extending the vase life of rose cut flower cv. Bakara using inhibitors of physiological vascular occlusion. Journal of Horticulture and Postharvest Research, 3 (1-March):35-48. |
| [10] | Horibe T, Yamada K. 2017. Petal growth physiology of cut rose flowers: progress and future prospects. Journal of Horticultural Research, 25:5-18. |
| [11] | Huang Jing, Su Jin, Zhou Peng, Zhang Qiang, Zhang Min. 2021. Regulation of chlorophyll metabolism during leaf greening period of Ilex × attenuata ‘Sunny Foster’. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 49 (11):51-54. (in Chinese) |
| 黄婧, 苏金, 周鹏, 张强, 张敏. 2021. 黄金枸骨叶片复绿期叶绿素代谢的调控特征. 东北林业大学学报, 49 (11):51-54. | |
| [12] | Jiang Yu-dong, Wang Zi-hua, Gao Jun-ping. 2010. Effects of GSH on tolerance to water deficit stress in cut rose. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 37 (4):597-606. (in Chinese) |
| 姜玉东, 王子华, 高俊平. 2010. 谷胱甘肽对切花月季‘Samantha’失水胁迫耐性的影响. 园艺学报, 37 (4):597-606. | |
| [13] | Li Bo-wen, Li Ling-min, Xia Meng, Pan Si-yuan, Chen Jia-ying, Lou Yu-xia, Ming Feng. 2021. Effect of IBA on its fresh-keeping of the cut rose Rosa hybrida Hort. Journal of Shanghai Normal University(Natural Sciences), 50 (2):243-252. (in Chinese) |
| 李博文, 李玲敏, 夏萌, 潘思媛, 陈佳灜, 娄玉霞, 明凤. 2021. IBA对月季切花‘黑魔术’保鲜效应的影响. 上海师范大学学报(自然科学版), 50 (2) :243-252. | |
| [14] | Liu J X, Gu L, Yu Y C, Huang P, Wu Z, Zhang Q, Qian Y Q, Wan X C, Sun Z Y. 2019. Corticular photosynthesis drives bark water uptake to refill embolized vessels in dehydrated branches of Salix matsudana. Plant,Cell & Environment, 42:2584-2596. |
| [15] |
Liu J X, Sun C, Zhai F F, Li Z J, Qian Y Q, Gu L, Sun Z Y. 2021. Proteomic insights into the photosynthetic divergence between bark and leaf chloroplasts in Salix matsudana. Tree Physiology, 41:2142-2152.
doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpab055 URL |
| [16] | Liu Jun-xiang, Yu Yong-chang, Lang Peng-peng, Sun Zhen-yuan. 2019. Radical heterogeneity of photochemical characteristics of chloroplasts in current-year twigs of Salix matsudana. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 55 (3):36-42. (in Chinese) |
| 刘俊祥, 于永畅, 郎蓬蓬, 孙振元. 2019. 旱柳枝条叶绿体光化学特征的径向异质性. 林业科学, 55 (3):36-42. | |
| [17] |
Luo J, Chen S J, Cao S H, Zhang T, Li R R, Zhu L C, Wang C Y. 2021. Rose(Rosa hybrida)ethylene responsive factor 3 promotes rose flower senescence via direct activation of the abscisic acid synthesis-related 9-CIS-EPOXYCAROTENOID DIOXYGENASE gene. Plant and Cell Physiology, 62 (6):1030-1043.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcab085 URL |
| [18] |
Mantova M, Herbette S, Cochard H, Torres-Ruiz J. 2022. Hydraulic failure and tree mortality:from correlation to causation. Trends in Plant Science, 27 (4):335-345.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2021.10.003 URL |
| [19] |
Mayr S, Schmid P, Beikircher B, Feng F, Badel E. 2020. Die hard: timberline conifers survive annual winter embolism. New Phytologist, 226:13-20.
doi: 10.1111/nph.16304 pmid: 31677276 |
| [20] |
Pfanz H, Aschan G, Langenfeld-Heyser R, Wittmann C. 2002. Ecology and ecophysiology of tree stems: corticular and wood photosynthesis. Naturwissenschaften, 89 (4):147-162.
doi: 10.1007/s00114-002-0309-z URL |
| [21] |
Pragya A, Anjila A, Rukmangat P, Rameshwor P. 2019. Effects of different concentrations of sucrose and citric acid on vase life of rose. Journal of Agriculture and Natural Resources, 2 (1):127-134.
doi: 10.3126/janr.v2i1.26053 URL |
| [22] | Smolova T, Khorobrykh A, Savchenko T. 2020. Cortical photosynthesis as a physiological marker for grape breeding: methods and approaches. In BIO Web of Conferences,(25):02018. |
| [23] |
van Doorn W G, van Meeteren U. 2003. Flower opening and closure: a review. Journal of Experimental Botany, 54 (389):1801-1812.
pmid: 12869518 |
| [24] | Wang Yi, Wang Kai-xuan, Hu Si-yuan, Zhou Shuang, Shi An-guo. 2021. Effects of ethylene metabolism and energy status on vase quality of cut itoh peony‘Bartzella’flowers. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (6):1135-1149. (in Chinese) |
|
王依, 王凯轩, 胡思源, 周爽, 史国安. 2021. 乙烯代谢和能量状态对‘巴茨拉’牡丹切花瓶插品质的作用研究. 园艺学报, 48 (6):1135-1149.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0094 |
|
| [25] |
Wittmann C, Pfanz H. 2008. Antitranspirant functions of stem periderms and their influence on corticular photosynthesis under drought stress. Trees Structure and Function, 22:187-196.
doi: 10.1007/s00468-007-0194-3 URL |
| [26] |
Wittmann C, Pfanz H. 2016. The optical,absorptive and chlorophyll fluorescence properties of young stems of five woody species. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 121:83-93.
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.05.007 URL |
| [27] |
Wittmann C, Pfanz H. 2018. More than just CO2-recycling: corticular photosynthesis as a mechanism to reduce the risk of an energy crisis induced by low oxygen. New Phytologist, 219 (2):551-564.
doi: 10.1111/nph.2018.219.issue-2 URL |
| [28] | Wu Lin, Liu Ran, Wu Dong-qin, Liu Yi-qing. 2020. Screening and expression analysis of RhRRs responding to rose flower senescence. Journal of Southwest University(Natural Science Edition), 42 (3):35-42. (in Chinese) |
| 吴林, 刘燃, 吴冬琴, 刘奕清. 2020. 响应月季花朵衰老的RhRRs基因筛选及表达特性分析. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 42 (3):35-42. | |
| [29] | Yu Yong-chang. 2020. Effect of drought stress and rewatering on the photosynthetic physiological characteristics of leaves and bark of‘84K’poplar. Journal of Landscape Research, 12 (4):93-102. |
| [30] | Zhang Fu-chun, Pan Ming-qi, MEMETABLA·Memettursun, Zhang Wen, Zhong Hai-xia, Li Tuan-jie, Gao Da-hui, Wu Xin-yu. 2018. Effect of floating dust weather on leaf photosynthesis and water potential of grapes in Karakash River Basin. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 26 (7):990-998. (in Chinese) |
| 张付春, 潘明启, 麦麦提阿卜拉 · 麦麦提图尔荪, 张雯, 钟海霞, 李团结, 高达辉, 伍新宇. 2018. 浮尘天气对墨玉河流域葡萄叶片光合及水势的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 26 (7):990-998. |
| [1] | LIU Jiaqi, GONG Feifei, ZHANG Hao, JING Weikun, QU Suping, MA Nan, GAO Junping, SUN Xiaoming. Jasmonic Acid Carboxy Methyltransferase Gene RhJMT Regulates Petal Senescence in Rosa hybrida [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 1025-1036. |
| [2] | CHANG Xiaoxiao, GUO Xinbo, YE Yutong, PENG Cheng, CHEN Huiqiong, PAN Jianping, QIU Jishui, LU Yusheng. Differential Analysis of Sugar,Acid,Polyphenolics and Antioxidant Activities in Fruits of‘Zaofeng’and‘Jixin’Wampee(Clausena lansium) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 778-790. |
| [3] | YU Jianqiang, GU Kaidi, WANG Chuanzeng, HU Dagang. Functional Characterization of An Apple Pyrophosphate-dependent Phosphofructokinase Gene MdPFPβ in Regulating Soluble Sugar Accumulation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(10): 2223-2235. |
| [4] | WANG Junwen, WU Yue, YU Jihua, ZHANG Jing, XIE Jianming, FENG Zhi, TANG Zhongqi, LIU Xiaoqi, LI Jing, ZHONG Yuan. Soluble Sugar,Organic Acid Quality and Volatile Compounds Contents in Tomato Fruits can be Promoted by Exogenous ALA [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(5): 973-986. |
| [5] | WEN Jiaxin, WANG Chaolin, FENG Hui, LI Shanshan, WANG Liangsheng, WU Ronghua, ZHAO Shiwei. Research Progress on Flower Color of Rose [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(10): 2044-2056. |
| [6] | YE Dan*,LU Zhaowen*,SU Jiangshuo,GUAN Zhiyong,FANG Weimin,CHEN Fadi,and ZHANG Fei**. Association Analysis and QTL Mapping for Vase Life of Cut Chrysanthemum [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(4): 717-724. |
| [7] | LU Jing,MA Qijun,KANG Hui,LI Wenhao,LIU Yajing,HAO Yujin,and YOU Chunxiang*. Ectopic Expressing MdSWEET1 in Tomato Enhanced Salt Tolerance [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(3): 433-443. |
| [8] | ZHANG Lizhi,ZHANG Xin,ZUO Xiya,XING Libo,FAN Sheng,LI Youmei,ZHAO Caiping,HAN Mingyu,and ZHANG Dong*. Effects of Exogenous Glucose Treatment on Soluble Sugar and Expression of Related Genes During Floral Bud Differentiation Stage in Terminal Spur Buds of‘Nagafu 2’Apple [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(1): 11-24. |
| [9] | ZHANG Chengjun,WANG Lei,DUAN Shuyan,SONG Shiren,MA Chao,ZHAO Liping,ZHANG Caixi,WANG Shiping,and XU Wenping*. Effect of Low Light Stress on Photosynthetic Physiology and Gene Expression in‘Khoyo’Grapevine After Blooming [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2017, 44(8): 1450-1462. |
| [10] | DU Lisha,QI Siyan,MA Juanjuan,XING Libo,FAN Sheng,LI Youmei,ZHANG Dong,ZHAO Caiping,and HAN Mingyu*. Effects of De-fruit Treatment on Soluble Sugar Accumulation and Expression of Flowering-related Genes in Terminal Spur Buds and Leaves of‘Fuji’Apple [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2017, 44(4): 622-632. |
| [11] | ZHAO Ai-ling*,XUE Xiao-fang*,WANG Yong-kang,SUI Chuan-ling,REN Hai-yan,and LI Deng-ke**. The Sugars and Organic Acids Composition in Fruits of Different Chinese Jujube Cultivars of Different Development Stages [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(6): 1175-1185. |
| [12] | SHANG Xiao-jiao and WANG Di-hai*. Phenological Change of Soluble Sugar,Protein and C,N,P Content in the#br# Fine Root and Leaf of Chinese Jujube [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(11): 2243-2250. |
| [13] | JIANG Ji-mou*,CHEN Xiu-ping*,HU Wen-shun,JIANG Fan,DENG Chao-jun,and ZHENG Shao-quan**. Characteristics of Components and Contents of Soluble Sugars in Mature Fruits of Loquat Germplasm [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2015, 42(9): 1781-1788. |
| [14] | ZHENG Li-Jing, NIE Ji-Yun, YAN Zhen, XU Guo-Feng, WANG Kun, GAO Yuan, YE Meng-Liang. Studies on the Characteristics of the Composition and Content of Soluble Sugars in Apple Fruit [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2015, 42(5): 950-960. |
| [15] | WANG Xi-cheng,WU Wei-min*,ZHAO Mi-zhen,QIAN Ya-ming,and WANG Zhuang-wei. Effect of NAA Treatment on Sugar Acid Content and Related Gene Expression in Grape Berries [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2015, 42(3): 425-434. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd