
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3): 505-517.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0520
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2020-07-08
Online:2021-03-25
Published:2021-04-02
Contact:
CAO Jiashu
E-mail:jshcao@ziu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
LÜ Meiling, CAO Jiashu. Expression Characteristic Analysis of the BcPG17,a Gene Related to Inflorescence Stem Development of Brassica campestris[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(3): 505-517.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0520
| 物种(基因名称) Species(gene name) | GenBank登录号 GenBank No. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana(PGA3) | NP_187439.1 | |||
| 拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana(PGA2) | CAA51692.1 | |||
| 白菜Brassica campestris(BcMF2) | ABW24665.1 | |||
| 白菜Brassica campestris(BcMF6) | ACP74159.1 | |||
| 白菜Brassica campestris(BcMF9) | ABN13878.1 | |||
| 白菜Brassica campestris(BcMF16) | ADJ68232.1 | |||
| 油菜Brassica napus(RDPG) | CAA65072.1 | |||
| 油菜Brassica napus(PGAZ) | CAC05658.1 | |||
| 甜瓜Cucumis melo(MPG2) | AAC26511.1 | |||
| 陆地棉Gossypium hirsutum(G9) | AAA82167.1 | |||
| 荔枝Litchi chinensisv(LcPG1) | AFW04075.1 | |||
| 番茄Solanum lycopersicum(TAPG1) | AAC28903.1 | |||
| 番茄Solanum lycopersicum(TAPG2) | AAC28904.1 | |||
| 烟草Nicotiana tabacum(PG1) | Q05967.1 | |||
| 桃Prunus persica(PRF5) | CAA54150.1 | |||
Table 1 Details of the PG genes used in the multiple alignment analysis
| 物种(基因名称) Species(gene name) | GenBank登录号 GenBank No. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana(PGA3) | NP_187439.1 | |||
| 拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana(PGA2) | CAA51692.1 | |||
| 白菜Brassica campestris(BcMF2) | ABW24665.1 | |||
| 白菜Brassica campestris(BcMF6) | ACP74159.1 | |||
| 白菜Brassica campestris(BcMF9) | ABN13878.1 | |||
| 白菜Brassica campestris(BcMF16) | ADJ68232.1 | |||
| 油菜Brassica napus(RDPG) | CAA65072.1 | |||
| 油菜Brassica napus(PGAZ) | CAC05658.1 | |||
| 甜瓜Cucumis melo(MPG2) | AAC26511.1 | |||
| 陆地棉Gossypium hirsutum(G9) | AAA82167.1 | |||
| 荔枝Litchi chinensisv(LcPG1) | AFW04075.1 | |||
| 番茄Solanum lycopersicum(TAPG1) | AAC28903.1 | |||
| 番茄Solanum lycopersicum(TAPG2) | AAC28904.1 | |||
| 烟草Nicotiana tabacum(PG1) | Q05967.1 | |||
| 桃Prunus persica(PRF5) | CAA54150.1 | |||
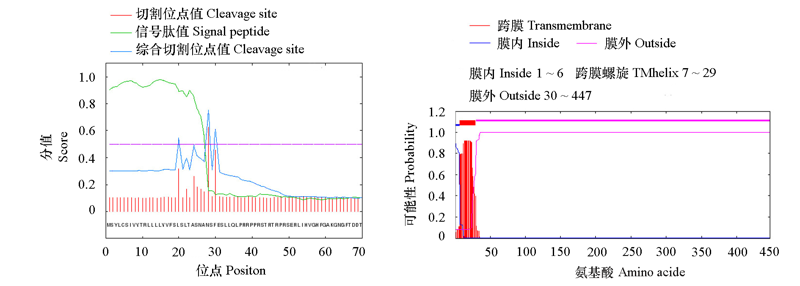
Fig. 2 Signal peptide(A)and transmembrane helices(B)prediction of BcPG17 The most likely cleavage site of signal peptide is between the position of 27 and 28.
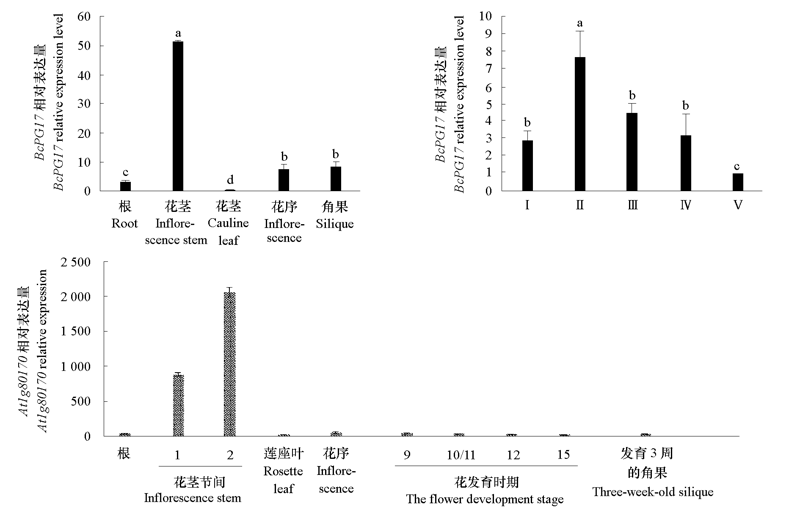
Fig. 5 Analysis of the expression pattern of BcPG17 and the ATH1 GeneChip data of At1g80170 from Arabidopsis database Ⅰ ~ Ⅴ indicate the buds of pollen mother cell stage,tetrad stage,uninucleate microspore stage,binucleate microspore stage and mature pollen respectively.
| 顺式作用元件 cis-acting element | 序列 Sequence | 功能 Function | 数量 Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAAT-box | CAAAT | 启动子和增强子区域常见的顺式作用元件 Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | 8 |
| TATA-box | TATAAAT/TATA | 转录起始位点周围-30左右的核心启动子元件 Core promoter element around-30 of transcription start | 44 |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 水杨酸响应相关的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | 2 |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 脱落酸响应相关的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | 1 |
| TGACG/CGTCA-motif | TGACG/CGTCA | 茉莉酸甲酯响应相关的顺式作用调节元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | 4 |
| GARE-motif | TCTGTTG | 赤霉素响应元件 Gibberellin-responsive element | 1 |
| CAT-box | GCCACT | 与分生组织表达有关的顺式调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element related to meristem expression | 1 |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导的关键顺式作用调节元件 cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction | 2 |
| G-Box | CACGTT | 参与光响应的顺式作用调节元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 光响应相关的保守DNA模块的一部分 Part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness | 4 |
| Gap-box | CAAATGAA(A/G)A | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| AT1-motif | AATTATTTTTTATT | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| AE-box | AGAAACAA | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| GTGA-motif | GTGA | 花药特异基序 Anther specific motif | 4 |
| E-box | CATTG | 绒毡层降解延迟蛋白(TDR)结合位点 Tapetum Degeneration Retardation(TDR)binding site | 2 |
Table 2 The major cis-acting elements of BcPG17 promoter
| 顺式作用元件 cis-acting element | 序列 Sequence | 功能 Function | 数量 Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAAT-box | CAAAT | 启动子和增强子区域常见的顺式作用元件 Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | 8 |
| TATA-box | TATAAAT/TATA | 转录起始位点周围-30左右的核心启动子元件 Core promoter element around-30 of transcription start | 44 |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 水杨酸响应相关的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | 2 |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 脱落酸响应相关的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | 1 |
| TGACG/CGTCA-motif | TGACG/CGTCA | 茉莉酸甲酯响应相关的顺式作用调节元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | 4 |
| GARE-motif | TCTGTTG | 赤霉素响应元件 Gibberellin-responsive element | 1 |
| CAT-box | GCCACT | 与分生组织表达有关的顺式调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element related to meristem expression | 1 |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导的关键顺式作用调节元件 cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction | 2 |
| G-Box | CACGTT | 参与光响应的顺式作用调节元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 光响应相关的保守DNA模块的一部分 Part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness | 4 |
| Gap-box | CAAATGAA(A/G)A | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| AT1-motif | AATTATTTTTTATT | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| AE-box | AGAAACAA | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element | 1 |
| GTGA-motif | GTGA | 花药特异基序 Anther specific motif | 4 |
| E-box | CATTG | 绒毡层降解延迟蛋白(TDR)结合位点 Tapetum Degeneration Retardation(TDR)binding site | 2 |
| [1] |
Allen G C, Flores-Vergara M A, Krasnyanski S, Kumar S, Thompson W F. 2006. A modified protocol for rapid DNA isolation from plant tissues using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nature Protocols, 1:2320-2325.
pmid: 17406474 |
| [2] | Bell A D, Bryan A. 2008. Plant form:an illustrated guide to flowering plant morphology. Portland: Timber Press. |
| [3] |
Camejo D, Martí M C, Jiménez A, Cabrera J C, Olmos E, Sevilla F. 2011. Effect of oligogalacturonides on root length,extracellular alkalinization and O-2 (-)-accumulation in alfalfa. Journal of Plant Physiology, 168:566-575.
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2010.09.012 pmid: 21074893 |
| [4] |
Carpita N C, Gibeaut D M. 1993. Structural models of primary-cell walls in flowering plants-consistency of molecular-structure with the physical-properties of the walls during growth. Plant Journal, 3:1-30.
pmid: 8401598 |
| [5] |
Cassab G I. 1998. Plant cell wall proteins. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 49:281-309.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.281 URL |
| [6] |
Chen L, Tu Z M, Hussain J, Cong L, Yan Y J, Jin L, Yang G X, He G Y. 2010. Isolation and heterologous transformation analysis of a pollen-specific promoter from wheat(Triticum aestivum L.). Molecular Biology Reports, 37:737-744.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-009-9582-7 URL |
| [7] |
Dayan J, Voronin N, Gong F, Sun T P, Hedden P, Fromm H, Aloni A. 2012. Leaf-induced gibberellin signaling is essential for internode elongation,cambial activity,and fiber differentiation in tobacco stems. The Plant Cell, 24 (1):66-79.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.093096 URL |
| [8] | Demura T, Tashiro G, Horiguchi G, Kishimoto N, Kubo M, Matsuoka N, Minami A, Nagata-Hiwatashi M, Nakamura K, Okamura Y, Sassa N, Suzuki S, Yazaki J, Kikuchi S, Fukuda H. 2002. Visualization by comprehensive microarray analysis of gene expression programs during transdifferentiation of mesophyll cells into xylem cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99:15794-15799. |
| [9] |
Falasca G, Capitani F, Della Rovere F, Zaghi D, Franchin C, Biondi S, Altamura M M. 2008. Oligogalacturonides enhance cytokinin-induced vegetative shoot formation in tobacco explants,inhibit polyamine biosynthetic gene expression,and promote long-term remobilisation of cell calcium. Planta, 227:835-852.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-007-0660-6 URL |
| [10] | Gifford E M, Foster A S. 1989. Morphology and evolution of vascular plants. New York: Freeman. |
| [11] |
Gomez-Ariza J, Brambilla V, Vicentini G, Landini M, Cerise M, Carrera E, Shrestha R, Chiozzotto R, Galbiati F, Caporali E, López Díaz I, Fornara F. 2019. A transcription factor coordinating internode elongation and photoperiodic signals in rice. Nature Plants, 5:358-362.
doi: 10.1038/s41477-019-0401-4 |
| [12] |
Gómez-Mena C, Sablowski R. 2008. Arabidopsis thaliana HOMEOBOX GENE1 establishes the basal boundaries of shoot organs and controls stem growth. Plant Cell, 20:2059-2072.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.059188 URL |
| [13] |
Hadfield K A, Bennett A B. 1998. Polygalacturonases:many genes in search of a function. Plant Physiology, 117 (2):337-343.
doi: 10.1104/pp.117.2.337 URL |
| [14] | Harrison C J, Morris J L. 2018. The origin and early evolution of vascular plant shoots and leaves. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. SeriesB:Biological Sciences, 373:20160496. |
| [15] |
Hepworth S R, Pautot V A. 2015. Beyond the divide:boundaries for patterning and stem cell regulation in plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6:1052.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01052 pmid: 26697027 |
| [16] |
Huang L, Cao J S, Zhang A H, Ye Y Q, Zhang Y C, Liu T T. 2009a. The polygalacturonase gene BcMF2 from Brassica campestris is associated with intine development. Journal of Experimental Botany, 60:301-313.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern295 URL |
| [17] |
Huang L, Ye Y, Zhang Y, Zhang A, Liu T, Cao J. 2009b. BcMF9,a novel polygalacturonase gene, is required for both Brassica campestris intine and exine formation. Annals of Botany, 104:1339-1351.
doi: 10.1093/aob/mcp244 URL |
| [18] |
Huang L, Zhao X F, Liu T T, Dong H, Cao J S. 2010. Developmental characteristics of floral organs and pollen of Chinese cabbage( Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis). Plant Systematics and Evolution, 286:103-115.
doi: 10.1007/s00606-010-0283-4 URL |
| [19] |
Hwang H J, Kim H, Jeong Y M, Choi M Y, Lee S Y, Kim S G. 2011. Overexpression of EVE1,a novel ubiquitin family protein,arrests inflorescence stem development in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62:4571-458.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/err168 URL |
| [20] |
Imoto K, Yokoyama R, Nishitani K. 2005. Comprehensive approach to genes involved in cell wall modifications in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Molecular Biology, 58 (2):177-192.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-005-5344-7 URL |
| [21] |
Ito T, Nagata N, Yoshiba Y, Ohme-Takagi M, Ma H, Shinozaki K. 2007. Arabidopsis MALE STERILITY1 encodes a PHD-type transcription factor and regulates pollen and tapetum development. The Plant Cell, 19:3549-3562.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.054536 URL |
| [22] |
Kaplan D R, Hagemann W. 1991. The relationship of cell and organism in vascular plants. BioScience, 41:693-703.
doi: 10.2307/1311764 URL |
| [23] |
Kemi U, Leinonen P H, Savolainen O, Kuittinen H. 2019. Inflorescence shoot elongation,but not flower primordia formation,is photoperiodically regulated in Arabidopsis lyrata. Annals of Botany, 124 (1):91-101.
doi: 10.1093/aob/mcz035 URL |
| [24] |
Khan M, Xu M, Murmu J, Tabb P, Liu Y, Storey K, McKim S M, Douglas C J, Hepworth S R. 2012. Antagonistic interaction of BLADE-ON-PETIOLE1 and 2 with BREVIPEDICELLUS and PENNYWISE regulates Arabidopsis inflorescence architecture. Plant Physiology, 158:946-960.
doi: 10.1104/pp.111.188573 URL |
| [25] |
Kim J, Shiu S H, Thoma S, Li W H, Patterson S E. 2006. Patterns of expansion and expression divergence in the plant polygalacturonase gene family. Genome Biology, 7 (9):R87.
doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-9-r87 URL |
| [26] |
Koizumi K, Yokoyama R, Nishitani K. 2009. Mechanical load induces upregulation of transcripts for a set of genes implicated in secondary wall formation in the supporting tissue of Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Plant Research, 122:651-659.
doi: 10.1007/s10265-009-0251-7 pmid: 19582540 |
| [27] |
Liang Y, Yu Y, Shen X, Dong H, Lyu M, Xu L, Ma Z, Liu T, Cao J. 2015. Dissecting the complex molecular evolution and expression of polygalacturonase gene family in Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis. Plant Molecular Biology, 89 (6):629-646.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-015-0390-2 pmid: 26506823 |
| [28] |
Liu N N. 2019. Effects of IAA and ABA on the immature peach fruit development process. Horticultural Plant Journal, 5 (4):145-154.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2019.01.005 URL |
| [29] |
Liu X H, Shangguan Y Y, Zhu J J, Lu Y Q, Han B. 2013. The rice OsLTP6 gene promoter directs anther-specific expression by a combination of positive and negative regulatory elements. Planta, 238:845-857.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-013-1934-9 URL |
| [30] |
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 -∆∆CT method. Methods, 25:402-408.
pmid: 11846609 |
| [31] |
Lyu M, Liang Y, Yu Y, Ma Z, Song L, Yue X, Cao J. 2015. Identification and expression analysis of BoMF25,a novel polygalacturonase gene involved in pollen development of Brassica oleracea. Plant Reproduction, 28:121-132.
doi: 10.1007/s00497-015-0263-5 URL |
| [32] |
McKim S M. 2019. How plants grow up. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 61:257-277.
doi: 10.1111/jipb.v61.3 URL |
| [33] |
McKim S M. 2020. Moving on up-controlling internode growth. New Phytologist, 226 (3):672-678.
doi: 10.1111/nph.v226.3 URL |
| [34] |
Narusaka M, Shiraishi T, Iwabuchi M, Narusaka Y. 2010. The floral inoculating protocol: a simplified Arabidopsis thaliana transformation method modified from floral dipping. Plant biotechnology, 27 (4):349-351.
doi: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.27.349 URL |
| [35] |
Ogawa M, Kay P, Wilson S, Swain S M. 2009. Arabidopsis Dehiscence Zone Polygalacturonase1( ADPG1), ADPG2,and QUARTET2 are polygalacturonases required for cell separation during reproductive development in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 21:216-233.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.063768 URL |
| [36] |
Paniagua C, Pose S, Morris V J, Kirby A R, Quesada M A, Mercado J A. 2014. Fruit softening and pectin disassembly: an overview of nanostructural pectin modifications assessed by atomic force microscopy. Annals of Botany, 114:1375-1383.
doi: 10.1093/aob/mcu149 URL |
| [37] | Patil V, McDermott H I, McAllister T, Cummins M, Silva J C, Mollison E, Meikle R, Morris J, Hedley P E, Waugh R, Dockter C, Hansson M, Hansson M, McKim S M. 2019. APETALA2 control of barley internode elongation. Development, 146:dev170373. |
| [38] |
Piffanelli P, Ross J H E, Murphy D J. 1998. Biogenesis and function of the lipidic structures of pollen grains. Sexual Plant Reproduction, 11:65-80.
doi: 10.1007/s004970050122 URL |
| [39] |
Rhee S Y, Osborne E, Poindexter P D, Somerville C R. 2003. Microspore separation in the quartet 3 mutants of Arabidopsis is impaired by a defect in a developmentally regulated polygalacturonase required for pollen mother cell wall degradation. Plant Physiology, 133:1170-1180.
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.028266 URL |
| [40] |
Rhee S Y, Somerville C R. 1998. Tetrad pollen formation in quartet mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana is associated with persistence of pectic polysaccharides of the pollen mother cell wall. Plant Journal, 15:79-88.
pmid: 9744097 |
| [41] |
Ridley B L, O'Neill M A, Mohnen D A. 2001. Pectins: structure,biosynthesis,and oligogalacturonide-related signaling. Phytochemistry, 57:929-967.
pmid: 11423142 |
| [42] |
Rogers H J, Bate N, Combe J, Sullivan J, Sweetman J, Swan C, Lonsdale D M, Twell D. 2001. Functional analysis of cis-regulatory elements within the promoter of the tobacco late pollen gene g10. Plant Molecular Biology, 45:577-585.
doi: 10.1023/A:1010695226241 URL |
| [43] |
Roongsattham P, Morcillo F, Jantasuriyarat C, Pizot M, Moussu S, Jayaweera D, Collin M, Gonzalez-Carranza Z H, Amblard P, Tregear J W, Tragoonrung S, Verdeil J L, Tranbarger T J. 2012. Temporal and spatial expression of polygalacturonase gene family members reveals divergent regulation during fleshy fruit ripening and abscission in the monocot species oil palm. BMC Plant Biology, 12:150.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-150 pmid: 22920238 |
| [44] |
Sachs R M. 1965. Stem elongation. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 16:73-96.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.pp.16.060165.000445 URL |
| [45] |
Sander L, Child R, Ulvskov P, Albrechtsen M, Borkhardt B. 2001. Analysis of a dehiscence zone endo-polygalacturonase in oilseed rape( Brassica napus)and Arabidopsis thaliana:evidence for roles in cell separation in dehiscence and abscission zones,and in style tissues during pollen tube growth. Plant Molecular Biology, 46:469-479.
doi: 10.1023/A:1010619002833 URL |
| [46] | Siedlecka A, Wiklund S, Peronne M A, Micheli F, Lesniewska J, Sethson I, Edlund U, Richard L, Sundberg B, Mellerowicz E J. 2008. Pectin methyl esterase inhibits intrusive and symplastic cell growth in developing wood cells of Populus. Plant Physiology, 146:554-565. |
| [47] |
Sun L, van Nocker S. 2010. Analysis of promoter activity of members of the PECTATE LYASE-LIKE( PLL)gene family in cell separation in Arabidopsis. Bmc Plant Biology, 10:152.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-152 URL |
| [48] |
Sun T P. 2008. Gibberellin metabolism, percepition and signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. Arabidopsis Book, 6:e0103.
doi: 10.1199/tab.0103 URL |
| [49] |
Tacken E, Ireland H, Gunaseelan K, Karunairetnam S, Wang D, Schultz K, Bowen J, Atkinson R G, Johnston J W, Putterill J, Hellens R P, Schaffer R J. 2010. The role of ethylene and cold temperature in the regulation of the apple POLYGALACTURONASE1 gene and fruit softening. Plant Physiology, 153:294-305.
doi: 10.1104/pp.109.151092 pmid: 20237022 |
| [50] |
Tanaka W, Pautler M, Jackson D, Hirano H Y. 2013. Grass meristems II:inflorescence architecture,flower development and meristem fate. Plant and Cell Physiology, 54:313-324.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct016 URL |
| [51] |
Teo Z W N, Song S, Wang Y Q, Liu J, Yu H. 2014. New insights into the regulation of inflorescence architecture. Trends in Plant Science, 19:158-165.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2013.11.001 URL |
| [52] |
Vincken J P, Schols H A, Oomen R, McCann M C, Ulvskov P, Voragen A G J, Visser R G F. 2003. If homogalacturonan were a side chain of rhamnogalacturonan I. implications for cell wall architecture. Plant Physiology, 132:1781-1789.
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.022350 URL |
| [53] |
Willats W G T, McCartney L, Mackie W, Knox J P. 2001. Pectin: cell biology and prospects for functional analysis. Plant Molecular Biology, 47:9-27.
doi: 10.1023/A:1010662911148 URL |
| [54] |
Wils C R, Kaufmann K. 2017. Gene-regulatory networks controlling inflorescence and flower development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta-Gene Regulatory Mechanisms, 1860:95-105.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.07.014 URL |
| [55] |
Yokoyama R, Nishitani K. 2006. Identification and characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana genes involved in xylem secondary cell walls. Journal of Plant Research, 119 (3):189-194.
doi: 10.1007/s10265-006-0261-7 URL |
| [56] |
Zhang D S, Liang W Q, Yin C S, Zong J, Gu F W, Zhang D B. 2010. OsC6,encoding a lipid transfer protein,is required for postmeiotic anther development in rice. Plant Physiology, 154:149-162.
doi: 10.1104/pp.110.158865 URL |
| [1] | ZHAO Xiuyun, LI Peirong, ZHANG Fenglan, YU Yangjun, ZHANG Deshuang, YU Shuancang, WANG Weihong, SU Tongbing, XIN Xiaoyun. A New Late-bolting Pakchoi Cultivar‘Chunyou 4’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(7): 1429-1430. |
| [2] | ZHAO Yujie, LIU Cuiyu, ZHAO Xueqing, WANG Yuying, YAN Ming, YUAN Zhaohe. Cloning and Spatiotemporal Expression Analysis of PgWUS and PgBEL1 in Punica granatum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(2): 355-366. |
| [3] | ZOU Hui, ZHAO Liang, YUAN Ting, GUO Qigao, WU Di, LIANG Guolu. Cloning and Expression of a Pathogenesis Related Protein Gene EjPR1 from Loquat Induced by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(2): 367-376. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd
