
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 773-786.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0287
李肯1,*, 张伟1,*, 武云鹏1, 彭冬秀2, 张若纬2,**( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-08
修回日期:2023-12-05
出版日期:2024-04-25
发布日期:2024-04-26
通讯作者:
作者简介:*共同第一作者
基金资助:
LI Ken1, ZHANG Wei1, WU Yunpeng1, PENG Dongxiu2, ZHANG Ruowei2,**( )
)
Received:2023-08-08
Revised:2023-12-05
Published:2024-04-25
Online:2024-04-26
Contact:
摘要:
为提高不同果肉硬度类型甜瓜材料的选择效率,以脆肉甜瓜自交系20S11和软肉甜瓜自交系20S75为亲本,构建F2与BC1F1群体,分析了果肉硬度性状的遗传规律为单基因遗传,脆肉相对于软肉为显性。根据F2分离群体构建果肉硬度极端性状混池,利用全基因组重测序结合图位克隆技术,将果肉硬度基因CmPf1定位在10号染色体上约54.71 kb的区域内。通过重测序分析发现,软肉甜瓜20S75中编码GATL3(galacturonosyltransferase-like 3)的基因MELO3C012216(CmGATL3)存在1处终止密码突变,位于编码区第567位碱基处(C-G),导致蛋白翻译提前终止,造成转移酶蛋白结构域完全缺失。利用qRT-PCR对CmGATL3进行表达模式分析,结果显示其在脆肉甜瓜20S11中的表达量显著高于软肉甜瓜20S75。基于上述变异位点,开发PF-KASP分子标记并对56份甜瓜自交系材料进行基因型检测,其中脆肉材料均表现为C︰C型,软肉材料均表现为G︰G型,标记呈共显性。进一步利用PF-KASP对F2群体进行基因型鉴定,与果肉硬度表型鉴定结果相比较,准确率达到100%。
李肯, 张伟, 武云鹏, 彭冬秀, 张若纬. 甜瓜果肉硬度KASP标记的开发与应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 773-786.
LI Ken, ZHANG Wei, WU Yunpeng, PENG Dongxiu, ZHANG Ruowei. Development and Utilization of KASP Marker for Identification of Pulp Firmness in Melon[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(4): 773-786.
| 引物名称 Primer | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| P1-25 | CATAACCCTAATTCTAATTTCCCC | AACTGAATCTCCTATATGCGTAGC |
| P2-14 | AGATTTAGTTGTCATTCATTCGTATT | TGAGAGACATTGCTTTTCATTTTT |
| P2-19 | TTATCTGTGACTATTTCACCTAAAA | CATTTTTCTCTCTATTATTCACTCTG |
| P6-8 | TTCTTGGGTCTTACTTTCTTATTT | AACCCTATCATCCATCTTATCTCT |
| P7-2 | TAAAAAGGATAAAAAATGGTGG | AACCCTACTTTCCAAATCACTT |
| P9-27 | TTTCTTTCTTTGTCATCCATTTA | TGAAATACGCAATGGAGGA |
| P12-32 | AGTGCTGAAATTACTTTTTGTCG | ATTTTTTATGATTTTTTGTTATTTGA |
| MELO3C012216-1 | TTCGTACCTCAACTACGATCAC | ATCAGCCATTGAATTACGCGA |
| MELO3C012216-2 | CGAGAATGTACTTAGCAGAATC | TGTTGAAGGAGTTGAGCATCGA |
| MELO3C012216-3 | ATGGAACCAACATGGGTTGGAC | TTAGCTAAGTGCCTTACGGATC |
| CmGATL3-q | AATTCGCATGGCAATACTCC | CGCGGTTAATCGAATCATCT |
| CmActin-q | CCGTTCTGTCCCTCTACGCTAGTG | GGAACTGCTCTTTGCACTCTCGAG |
| PF-KASP | 1:GCCATGCGAATTTTACGAACTAC | AGATGCTAAGAAGCCTTGTCCACT |
| 2:TATTGCCATGCGAATTTTACGAACTAG |
表1 本研究中所用的PCR引物序列
Table 1 PCR primer sequences used in this study
| 引物名称 Primer | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| P1-25 | CATAACCCTAATTCTAATTTCCCC | AACTGAATCTCCTATATGCGTAGC |
| P2-14 | AGATTTAGTTGTCATTCATTCGTATT | TGAGAGACATTGCTTTTCATTTTT |
| P2-19 | TTATCTGTGACTATTTCACCTAAAA | CATTTTTCTCTCTATTATTCACTCTG |
| P6-8 | TTCTTGGGTCTTACTTTCTTATTT | AACCCTATCATCCATCTTATCTCT |
| P7-2 | TAAAAAGGATAAAAAATGGTGG | AACCCTACTTTCCAAATCACTT |
| P9-27 | TTTCTTTCTTTGTCATCCATTTA | TGAAATACGCAATGGAGGA |
| P12-32 | AGTGCTGAAATTACTTTTTGTCG | ATTTTTTATGATTTTTTGTTATTTGA |
| MELO3C012216-1 | TTCGTACCTCAACTACGATCAC | ATCAGCCATTGAATTACGCGA |
| MELO3C012216-2 | CGAGAATGTACTTAGCAGAATC | TGTTGAAGGAGTTGAGCATCGA |
| MELO3C012216-3 | ATGGAACCAACATGGGTTGGAC | TTAGCTAAGTGCCTTACGGATC |
| CmGATL3-q | AATTCGCATGGCAATACTCC | CGCGGTTAATCGAATCATCT |
| CmActin-q | CCGTTCTGTCCCTCTACGCTAGTG | GGAACTGCTCTTTGCACTCTCGAG |
| PF-KASP | 1:GCCATGCGAATTTTACGAACTAC | AGATGCTAAGAAGCCTTGTCCACT |
| 2:TATTGCCATGCGAATTTTACGAACTAG |
| 序号 No. | 材料 Accession | 变种 Varieties | 剖面 TPA | 穿刺 Puncture | 类型 Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 硬度/g Hardness | 硬度/N Hardness | 脆性/N · S Brittleness | ||||
| 1 | 20S11 | var. inodorus | 2 532.25 a | 1.75 a | 4.13 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 2 | 20S75 | var. reticulatus | 375.27 b | 0.72 b | 1.31 b | 软 Soft |
| 3 | Sa-1 | var. cantalupensis | 2 486.14 a | 1.69 a | 4.02 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 4 | Sa-2 | var. inodorus | 2 583.11 a | 1.76 a | 3.91 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 5 | Sa-3 | var. inodorus | 2 478.58 a | 1.67 a | 3.87 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 6 | Sa-4 | var. inodorus | 2 528.72 a | 1.72 a | 4.21 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 7 | Sa-5 | var. inodorus | 2 393.23 a | 1.64 a | 3.95 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 8 | Sa-6 | var. inodorus | 2 284.21 a | 1.43 a | 4.08 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 9 | Sa-7 | var. inodorus | 2 308.44 a | 1.45 a | 3.85 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 10 | Sa-8 | var. inodorus | 2 388.28 a | 1.48 a | 3.94 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 11 | Sa-9 | var. inodorus | 2 420.87 a | 1.64 a | 3.61 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 12 | Sa-10 | var. cantalupensis | 2 595.64 a | 1.78 a | 3.24 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 13 | Sa-11 | var. cantalupensis | 2 406.85 a | 1.64 a | 4.11 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 14 | Sa-12 | var. cantalupensis | 2 544.94 a | 1.76 a | 3.34 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 15 | Sa-13 | var. cantalupensis | 2 222.65 a | 1.46 a | 4.40 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 16 | Sa-14 | var. cantalupensis | 2 330.32 a | 1.59 a | 4.90 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 17 | Sa-15 | var. cantalupensis | 2 234.62 a | 1.47 a | 3.31 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 18 | Sa-16 | var. chinensis | 2 503.79 a | 1.73 a | 4.27 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 19 | Sa-17 | var. chinensis | 2 381.80 a | 1.65 a | 4.60 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 20 | Sa-18 | var. chinensis | 2 503.78 a | 1.75 a | 3.52 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 21 | Sa-19 | var. chinensis | 2 553.73 a | 1.74 a | 3.33 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 22 | Sa-20 | var. chinensis | 2 477.75 a | 1.68 a | 4.01 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 23 | Sa-21 | var. conomon | 2 497.37 a | 1.68 a | 3.47 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 24 | Sa-22 | var. conomon | 2 278.44 a | 1.49 a | 4.47 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 25 | Sa-23 | var. conomon | 2 376.49 a | 1.57 a | 4.89 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 26 | Sa-24 | var. inodorus | 1 875.73 ab | 1.59 a | 2.84 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 27 | Sa-25 | var. inodorus | 1 841.34 ab | 1.55 a | 2.48 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 28 | Sa-26 | var. inodorus | 1 889.78 ab | 1.61 a | 2.45 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 29 | Sa-27 | var. inodorus | 1 787.89 ab | 1.47 a | 2.47 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 30 | Sa-28 | var. inodorus | 1 807.25 ab | 1.52 a | 2.50 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 31 | Sa-29 | var. inodorus | 1 721.63 ab | 1.46 a | 2.09 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 32 | Sa-30 | var. inodorus | 1 713.83 ab | 1.45 a | 2.18 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 33 | Sa-31 | var. inodorus | 1 643.27 ab | 1.44 a | 2.77 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 34 | Sa-32 | var. inodorus | 1 818.11 ab | 1.53 a | 2.94 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 35 | Sa-33 | var. inodorus | 1 618.49 ab | 1.46 a | 2.57 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 36 | Sa-34 | var. chinensis | 1 693.06 ab | 1.48 a | 2.33 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 37 | Sa-35 | var. chinensis | 1 795.75 ab | 1.51 a | 2.97 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 38 | Sa-36 | var. chinensis | 1 697.48 ab | 1.47 a | 2.58 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 39 | Sa-37 | var. conomon | 1 753.49 ab | 1.49 a | 2.83 b | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 40 | Sa-38 | var. conomon | 1 767.93 ab | 1.44 a | 2.26 b | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 41 | Sa-39 | var. reticulatus | 328.26 b | 0.66 b | 1.25 b | 软 Soft |
| 42 | Sa-40 | var. reticulatus | 305.93 b | 0.63 b | 1.23 b | 软 Soft |
| 43 | Sa-41 | var. reticulatus | 492.32 b | 0.61 b | 0.92 b | 软 Soft |
| 44 | Sa-42 | var. reticulatus | 346.18 b | 0.68 b | 1.28 b | 软 Soft |
| 45 | Sa-43 | var. reticulatus | 390.25 b | 0.71 b | 1.32 b | 软 Soft |
| 46 | Sa-44 | var. reticulatus | 373.48 b | 0.69 b | 1.30 b | 软 Soft |
| 47 | Sa-45 | var. reticulatus | 383.63 b | 0.37 b | 1.33 b | 软 Soft |
| 48 | Sa-46 | var. reticulatus | 487.27 b | 0.60 b | 1.44 b | 软 Soft |
| 49 | Sa-47 | var. reticulatus | 298.04 b | 0.39 b | 0.84 b | 软 Soft |
| 50 | Sa-48 | var. reticulatus | 314.58 b | 0.43 b | 0.93 b | 软 Soft |
| 51 | Sa-49 | var. chinensis | 346.86 b | 0.48 b | 0.98 b | 软 Soft |
| 52 | Sa-50 | var. chinensis | 522.23 b | 0.65 b | 1.11 b | 软 Soft |
| 53 | Sa-51 | var. chinensis | 366.96 b | 0.67 b | 1.27 b | 软 Soft |
| 54 | Sa-52 | var. conomon | 334.83 b | 0.65 b | 1.25 b | 软 Soft |
| 55 | Sa-53 | var. conomon | 477.69 b | 0.59 b | 0.89 b | 软 Soft |
| 56 | Sa-54 | var. conomon | 415.18 b | 0.63 b | 1.03 b | 软 Soft |
| 57 | Sa-55 | var. conomon | 312.23 b | 0.43 b | 0.92 b | 软 Soft |
| 58 | Sa-56 | var. conomon | 338.12 b | 0.67 b | 1.28 b | 软 Soft |
表2 供试甜瓜材料成熟期果肉硬度的鉴定及分类
Table 2 Identification and classification of pulp firmness during the ripening period of tested melon materials
| 序号 No. | 材料 Accession | 变种 Varieties | 剖面 TPA | 穿刺 Puncture | 类型 Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 硬度/g Hardness | 硬度/N Hardness | 脆性/N · S Brittleness | ||||
| 1 | 20S11 | var. inodorus | 2 532.25 a | 1.75 a | 4.13 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 2 | 20S75 | var. reticulatus | 375.27 b | 0.72 b | 1.31 b | 软 Soft |
| 3 | Sa-1 | var. cantalupensis | 2 486.14 a | 1.69 a | 4.02 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 4 | Sa-2 | var. inodorus | 2 583.11 a | 1.76 a | 3.91 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 5 | Sa-3 | var. inodorus | 2 478.58 a | 1.67 a | 3.87 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 6 | Sa-4 | var. inodorus | 2 528.72 a | 1.72 a | 4.21 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 7 | Sa-5 | var. inodorus | 2 393.23 a | 1.64 a | 3.95 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 8 | Sa-6 | var. inodorus | 2 284.21 a | 1.43 a | 4.08 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 9 | Sa-7 | var. inodorus | 2 308.44 a | 1.45 a | 3.85 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 10 | Sa-8 | var. inodorus | 2 388.28 a | 1.48 a | 3.94 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 11 | Sa-9 | var. inodorus | 2 420.87 a | 1.64 a | 3.61 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 12 | Sa-10 | var. cantalupensis | 2 595.64 a | 1.78 a | 3.24 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 13 | Sa-11 | var. cantalupensis | 2 406.85 a | 1.64 a | 4.11 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 14 | Sa-12 | var. cantalupensis | 2 544.94 a | 1.76 a | 3.34 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 15 | Sa-13 | var. cantalupensis | 2 222.65 a | 1.46 a | 4.40 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 16 | Sa-14 | var. cantalupensis | 2 330.32 a | 1.59 a | 4.90 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 17 | Sa-15 | var. cantalupensis | 2 234.62 a | 1.47 a | 3.31 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 18 | Sa-16 | var. chinensis | 2 503.79 a | 1.73 a | 4.27 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 19 | Sa-17 | var. chinensis | 2 381.80 a | 1.65 a | 4.60 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 20 | Sa-18 | var. chinensis | 2 503.78 a | 1.75 a | 3.52 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 21 | Sa-19 | var. chinensis | 2 553.73 a | 1.74 a | 3.33 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 22 | Sa-20 | var. chinensis | 2 477.75 a | 1.68 a | 4.01 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 23 | Sa-21 | var. conomon | 2 497.37 a | 1.68 a | 3.47 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 24 | Sa-22 | var. conomon | 2 278.44 a | 1.49 a | 4.47 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 25 | Sa-23 | var. conomon | 2 376.49 a | 1.57 a | 4.89 a | 脆 Crisp |
| 26 | Sa-24 | var. inodorus | 1 875.73 ab | 1.59 a | 2.84 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 27 | Sa-25 | var. inodorus | 1 841.34 ab | 1.55 a | 2.48 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 28 | Sa-26 | var. inodorus | 1 889.78 ab | 1.61 a | 2.45 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 29 | Sa-27 | var. inodorus | 1 787.89 ab | 1.47 a | 2.47 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 30 | Sa-28 | var. inodorus | 1 807.25 ab | 1.52 a | 2.50 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 31 | Sa-29 | var. inodorus | 1 721.63 ab | 1.46 a | 2.09 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 32 | Sa-30 | var. inodorus | 1 713.83 ab | 1.45 a | 2.18 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 33 | Sa-31 | var. inodorus | 1 643.27 ab | 1.44 a | 2.77 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 34 | Sa-32 | var. inodorus | 1 818.11 ab | 1.53 a | 2.94 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 35 | Sa-33 | var. inodorus | 1 618.49 ab | 1.46 a | 2.57 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 36 | Sa-34 | var. chinensis | 1 693.06 ab | 1.48 a | 2.33 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 37 | Sa-35 | var. chinensis | 1 795.75 ab | 1.51 a | 2.97 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 38 | Sa-36 | var. chinensis | 1 697.48 ab | 1.47 a | 2.58 ab | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 39 | Sa-37 | var. conomon | 1 753.49 ab | 1.49 a | 2.83 b | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 40 | Sa-38 | var. conomon | 1 767.93 ab | 1.44 a | 2.26 b | 酥脆 Crumbly |
| 41 | Sa-39 | var. reticulatus | 328.26 b | 0.66 b | 1.25 b | 软 Soft |
| 42 | Sa-40 | var. reticulatus | 305.93 b | 0.63 b | 1.23 b | 软 Soft |
| 43 | Sa-41 | var. reticulatus | 492.32 b | 0.61 b | 0.92 b | 软 Soft |
| 44 | Sa-42 | var. reticulatus | 346.18 b | 0.68 b | 1.28 b | 软 Soft |
| 45 | Sa-43 | var. reticulatus | 390.25 b | 0.71 b | 1.32 b | 软 Soft |
| 46 | Sa-44 | var. reticulatus | 373.48 b | 0.69 b | 1.30 b | 软 Soft |
| 47 | Sa-45 | var. reticulatus | 383.63 b | 0.37 b | 1.33 b | 软 Soft |
| 48 | Sa-46 | var. reticulatus | 487.27 b | 0.60 b | 1.44 b | 软 Soft |
| 49 | Sa-47 | var. reticulatus | 298.04 b | 0.39 b | 0.84 b | 软 Soft |
| 50 | Sa-48 | var. reticulatus | 314.58 b | 0.43 b | 0.93 b | 软 Soft |
| 51 | Sa-49 | var. chinensis | 346.86 b | 0.48 b | 0.98 b | 软 Soft |
| 52 | Sa-50 | var. chinensis | 522.23 b | 0.65 b | 1.11 b | 软 Soft |
| 53 | Sa-51 | var. chinensis | 366.96 b | 0.67 b | 1.27 b | 软 Soft |
| 54 | Sa-52 | var. conomon | 334.83 b | 0.65 b | 1.25 b | 软 Soft |
| 55 | Sa-53 | var. conomon | 477.69 b | 0.59 b | 0.89 b | 软 Soft |
| 56 | Sa-54 | var. conomon | 415.18 b | 0.63 b | 1.03 b | 软 Soft |
| 57 | Sa-55 | var. conomon | 312.23 b | 0.43 b | 0.92 b | 软 Soft |
| 58 | Sa-56 | var. conomon | 338.12 b | 0.67 b | 1.28 b | 软 Soft |
| 世代 Generations | 总数 Total | 脆肉 Crisp | 软肉 Soft | 分离比 Segregation ratio | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1(20S11) | 20 | 20 | 0 | ||
| P2(20S75) | 20 | 0 | 20 | ||
| F1(P1 × P2) | 40 | 40 | 0 | ||
| F1(P2 × P1) | 37 | 37 | 0 | ||
| BC1(F1 × 20S11) | 79 | 79 | 0 | ||
| BC1(F1 × 20S75) | 80 | 43 | 37 | 1.16︰1 | 1.21 |
| F2(F1(P1 × P2)⊗) | 1 211 | 917 | 294 | 3.12︰1 | 1.37 |
表3 脆肉甜瓜20S11和软肉甜瓜20S75果肉硬度表型的遗传分析
Table 3 Genetic analysis of pulp firmness in crispy melon 20S11 and soft melon 20S75
| 世代 Generations | 总数 Total | 脆肉 Crisp | 软肉 Soft | 分离比 Segregation ratio | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1(20S11) | 20 | 20 | 0 | ||
| P2(20S75) | 20 | 0 | 20 | ||
| F1(P1 × P2) | 40 | 40 | 0 | ||
| F1(P2 × P1) | 37 | 37 | 0 | ||
| BC1(F1 × 20S11) | 79 | 79 | 0 | ||
| BC1(F1 × 20S75) | 80 | 43 | 37 | 1.16︰1 | 1.21 |
| F2(F1(P1 × P2)⊗) | 1 211 | 917 | 294 | 3.12︰1 | 1.37 |
| 编号 No. | 基因名称 Gene name | 预测基因功能 Putative function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | MELO3C012215 | 编码含NAC结构域的蛋白8 NAC domain-containing protein 8 |
| 2 | MELO3C012216 | 编码多聚半乳糖醛酸转移酶蛋白3 Galacturonosyltransferase-like 3 |
| 3 | MELO3C012217 | 编码含有AP2/ERF和B3结构域的转录抑制因子RAV2 AP2/ERF and B3 domain-containing transcription repressor RAV2 |
| 4 | MELO3C012218 | 编码转录因子HHO2 Transcription factor HHO2 |
| 5 | MELO3C012219 | 编码未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| 6 | MELO3C012220 | 编码未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
表4 甜瓜果肉硬度基因定位区间内的注释基因
Table 4 Annotated gene within the mapping interval of melon pulp firmness gene
| 编号 No. | 基因名称 Gene name | 预测基因功能 Putative function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | MELO3C012215 | 编码含NAC结构域的蛋白8 NAC domain-containing protein 8 |
| 2 | MELO3C012216 | 编码多聚半乳糖醛酸转移酶蛋白3 Galacturonosyltransferase-like 3 |
| 3 | MELO3C012217 | 编码含有AP2/ERF和B3结构域的转录抑制因子RAV2 AP2/ERF and B3 domain-containing transcription repressor RAV2 |
| 4 | MELO3C012218 | 编码转录因子HHO2 Transcription factor HHO2 |
| 5 | MELO3C012219 | 编码未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| 6 | MELO3C012220 | 编码未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |

图3 脆肉甜瓜20S11和软肉甜瓜20S75中注释基因MELO3C012216的重测序(A)、氨基酸变异(B)及编码蛋白结构域(C)
Fig. 3 Resquencing(A),amino acid variation(B),and coding protein domain(C)of annotation gene MELO3C012216 in crispy melon 20S11 and soft melon 20S75
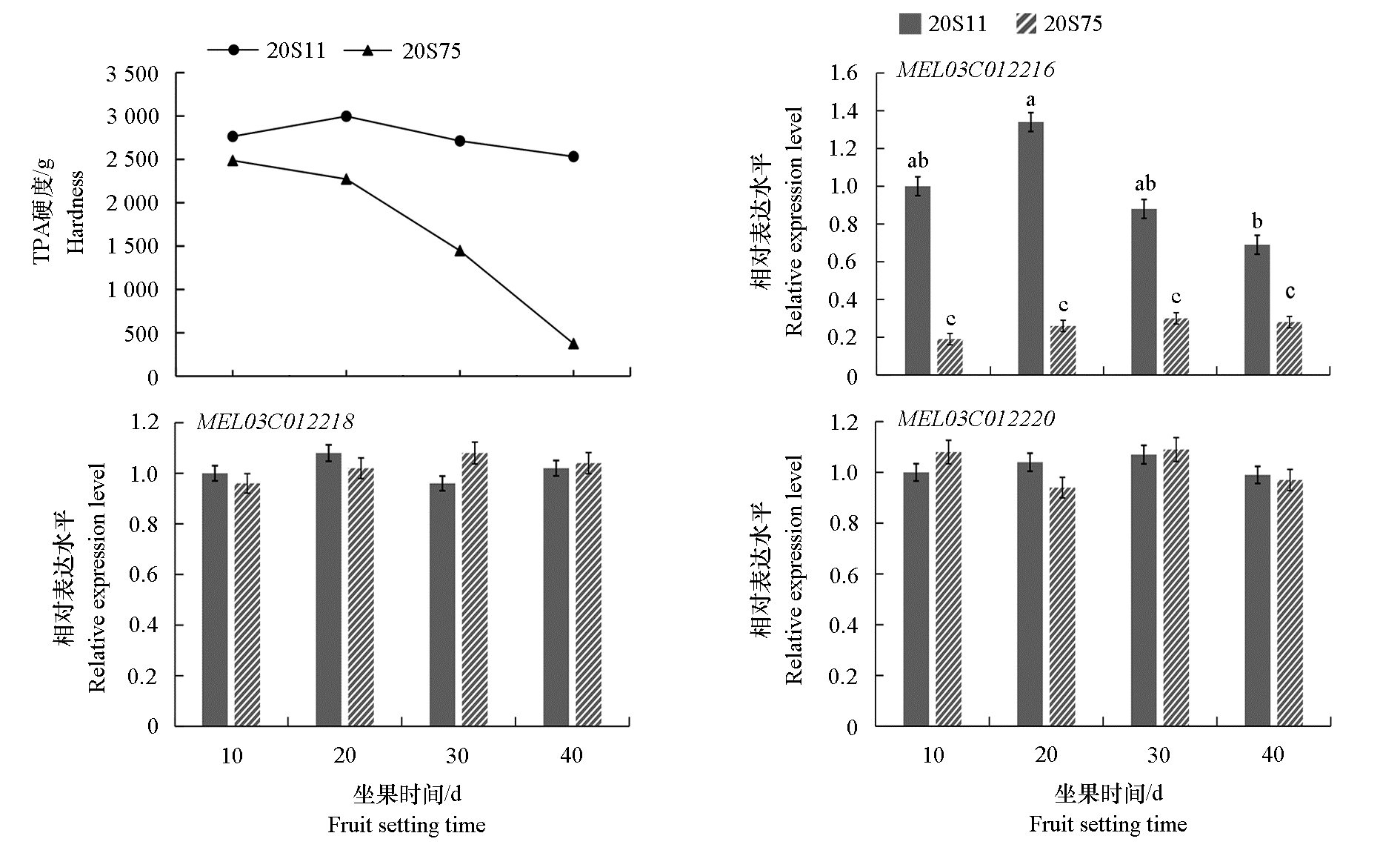
图4 脆肉甜瓜20S11和软肉甜瓜20S75果肉TPA硬度及3个基因在果实中的相对表达量 不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 The relative expression levels of three genes and TPA hardness in crispy melon 20S11 and soft melon 20S75 Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at 0.05 level.
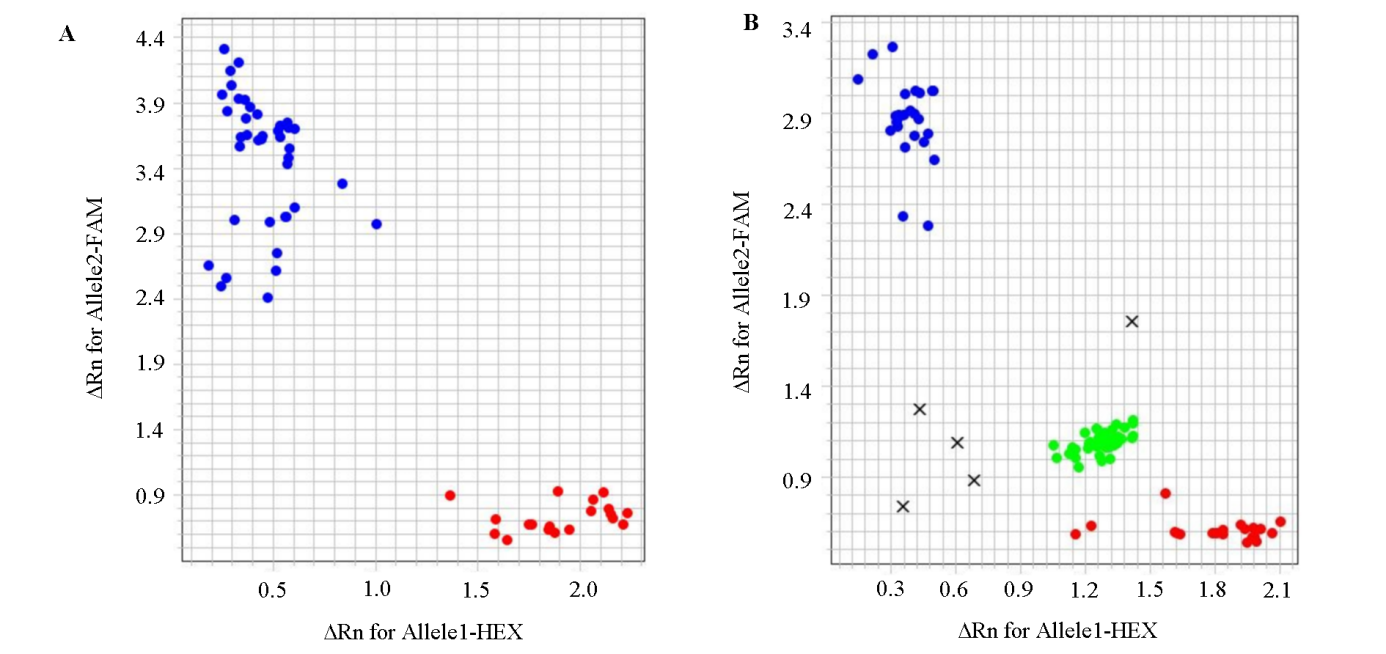
图5 PF-KASP标记在56份甜瓜材料(A)和部分F2代群体(B)中的基因分型结果 蓝色信号:脆肉类型,基因型为C︰C;红色信号:软肉类型,基因型为G︰G;绿色:脆肉类型,基因型为C︰G。
Fig. 5 Genotype of PF-KASP markers in 56 melon materials(A)and some F2 populations(B) Blue signal:Crispy type with genotype C︰C;Red signal:Soft type with genotype G︰G;Green:Crispy type with genotype C︰G.
| 序号 No. | 材料 Accession | 基因型 Genotype | 序号 No. | 材料 Accession | 基因型 Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20S11 | C︰C | 30 | Sa-28 | C︰C |
| 2 | 20S75 | G︰G | 31 | Sa-29 | C︰C |
| 3 | Sa-1 | C︰C | 32 | Sa-30 | C︰C |
| 4 | Sa-2 | C︰C | 33 | Sa-31 | C︰C |
| 5 | Sa-3 | C︰C | 34 | Sa-32 | C︰C |
| 6 | Sa-4 | C︰C | 35 | Sa-33 | C︰C |
| 7 | Sa-5 | C︰C | 36 | Sa-34 | C︰C |
| 8 | Sa-6 | C︰C | 37 | Sa-35 | C︰C |
| 9 | Sa-7 | C︰C | 38 | Sa-36 | C︰C |
| 10 | Sa-8 | C︰C | 39 | Sa-37 | C︰C |
| 11 | Sa-9 | C︰C | 40 | Sa-38 | C︰C |
| 12 | Sa-10 | C︰C | 41 | Sa-39 | G︰G |
| 13 | Sa-11 | C︰C | 42 | Sa-40 | G︰G |
| 14 | Sa-12 | C︰C | 43 | Sa-41 | G︰G |
| 15 | Sa-13 | C︰C | 44 | Sa-42 | G︰G |
| 16 | Sa-14 | C︰C | 45 | Sa-43 | G︰G |
| 17 | Sa-15 | C︰C | 46 | Sa-44 | G︰G |
| 18 | Sa-16 | C︰C | 47 | Sa-45 | G︰G |
| 19 | Sa-17 | C︰C | 48 | Sa-46 | G︰G |
| 20 | Sa-18 | C︰C | 49 | Sa-47 | G︰G |
| 21 | Sa-19 | C︰C | 50 | Sa-48 | G︰G |
| 22 | Sa-20 | C︰C | 51 | Sa-49 | G︰G |
| 23 | Sa-21 | C︰C | 52 | Sa-50 | G︰G |
| 24 | Sa-22 | C︰C | 53 | Sa-51 | G︰G |
| 25 | Sa-23 | C︰C | 54 | Sa-52 | G︰G |
| 26 | Sa-24 | C︰C | 55 | Sa-53 | G︰G |
| 27 | Sa-25 | C︰C | 56 | Sa-54 | G︰G |
| 28 | Sa-26 | C︰C | 57 | Sa-55 | G︰G |
| 29 | Sa-27 | C︰C | 58 | Sa-56 | G︰G |
表5 供试甜瓜材料CmPf1基因型分析
Table 5 CmPf1 genotype of melon materials
| 序号 No. | 材料 Accession | 基因型 Genotype | 序号 No. | 材料 Accession | 基因型 Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20S11 | C︰C | 30 | Sa-28 | C︰C |
| 2 | 20S75 | G︰G | 31 | Sa-29 | C︰C |
| 3 | Sa-1 | C︰C | 32 | Sa-30 | C︰C |
| 4 | Sa-2 | C︰C | 33 | Sa-31 | C︰C |
| 5 | Sa-3 | C︰C | 34 | Sa-32 | C︰C |
| 6 | Sa-4 | C︰C | 35 | Sa-33 | C︰C |
| 7 | Sa-5 | C︰C | 36 | Sa-34 | C︰C |
| 8 | Sa-6 | C︰C | 37 | Sa-35 | C︰C |
| 9 | Sa-7 | C︰C | 38 | Sa-36 | C︰C |
| 10 | Sa-8 | C︰C | 39 | Sa-37 | C︰C |
| 11 | Sa-9 | C︰C | 40 | Sa-38 | C︰C |
| 12 | Sa-10 | C︰C | 41 | Sa-39 | G︰G |
| 13 | Sa-11 | C︰C | 42 | Sa-40 | G︰G |
| 14 | Sa-12 | C︰C | 43 | Sa-41 | G︰G |
| 15 | Sa-13 | C︰C | 44 | Sa-42 | G︰G |
| 16 | Sa-14 | C︰C | 45 | Sa-43 | G︰G |
| 17 | Sa-15 | C︰C | 46 | Sa-44 | G︰G |
| 18 | Sa-16 | C︰C | 47 | Sa-45 | G︰G |
| 19 | Sa-17 | C︰C | 48 | Sa-46 | G︰G |
| 20 | Sa-18 | C︰C | 49 | Sa-47 | G︰G |
| 21 | Sa-19 | C︰C | 50 | Sa-48 | G︰G |
| 22 | Sa-20 | C︰C | 51 | Sa-49 | G︰G |
| 23 | Sa-21 | C︰C | 52 | Sa-50 | G︰G |
| 24 | Sa-22 | C︰C | 53 | Sa-51 | G︰G |
| 25 | Sa-23 | C︰C | 54 | Sa-52 | G︰G |
| 26 | Sa-24 | C︰C | 55 | Sa-53 | G︰G |
| 27 | Sa-25 | C︰C | 56 | Sa-54 | G︰G |
| 28 | Sa-26 | C︰C | 57 | Sa-55 | G︰G |
| 29 | Sa-27 | C︰C | 58 | Sa-56 | G︰G |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042811-105534 pmid: 23451775 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9039-9_6 pmid: 30652284 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
高鹏, 刘识, 崔浩楠, 张泰峰, 王学征, 刘宏宇, 朱子成, 栾非时. 2020. 甜瓜基因组学、功能基因定位及基因工程育种研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (9):1827-1844.
|
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0875 |
|
黄译瑾, 何佳丽, 姜李娜, 曹艳红, 秦嗣军, 吕德国. 2022. 果实脆性变化的生理生化研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (12):2641-2658.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0875 |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9266 pmid: 30009387 |
| [17] |
|
|
李肯, 武云鹏, 彭冬秀, 张若纬. 2022. 利用SSR标记快速检测甜瓜‘天美55’种子纯度与真实性. 分子植物育种, 20 (8):2674-2681.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
刘莉, 高星, 华德平, 刘翔, 李志文, 张平, 李三培, 张少慧. 2016. 不同的质构检测方法对甜瓜果肉质构的评价. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 49 (8):875-881.
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0653 |
|
卢艳清, 林燕金, 卢新坤. 2023. 果皮细胞壁物质代谢及果皮对高温和水分亏缺逆境的响应与‘度尾文旦柚’裂果相关. 园艺学报, 50 (8):1747-1768.
|
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1046 |
|
任海龙, 许东林, 张晶, 邹集文, 李光光, 周贤玉, 肖婉钰, 孙艺嘉. 2023. 菜薹KASP-SNP指纹图谱构建及品种鉴定. 园艺学报, 50 (2):307-318.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1046 |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-018-0217-7 pmid: 30082766 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4669-y pmid: 29685103 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
|
张保才, 周奕华. 2015. 植物细胞壁形成机制的新进展. 中国科学:生命科学, 45:554-556.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [1] | 夏志磊, 俞冰昕, 杨 梦, 连子林, 官利兰, 何艺超, 颜爽爽, 曹必好, 邱正坤, . 茄子绿果基因的精细定位及其KASP标记开发[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2008-2018. |
| [2] | 刘港运, 段世享, 许娜娜, 郭姚淼, 豆峻岭, 杨 森, 牛欢欢, 刘东明, 杨路明, 胡建斌, 朱华玉. 分子标记辅助构建甜瓜矮化基因Cmerecta近等基因系[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2048-2062. |
| [3] | 张 勇, 马建祥, 魏春华, 李 好, 杨建强, 张 显. 厚皮甜瓜新品种‘农大甜10号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2225-2226. |
| [4] | 张正海, 王永富, 吴华茂, 于海龙, 曹亚从, 冯锡刚, 王立浩. 辣椒重要性状遗传定位与候选基因研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 669-696. |
| [5] | 张永平, 刁倩楠, 曹燕燕, 陆世钧, 姚东伟. 网纹甜瓜新品种‘绿华18’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 699-700. |
| [6] | 刘莉铭, 耿艳飞, 郝芳敏, 康保珊, 吴会杰, 古勤生. 新德里番茄曲叶病毒侵染性克隆构建及甜瓜品种抗病性鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2555-2564. |
| [7] | 卢小露 , 樊静华 , 黄 昀 , 蔚玉红 , 陈炳言 , 马英华 , 田甲玺 , 顾海峰 , 周京一 . 甜瓜新品种‘小雪’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 107-108. |
| [8] | 王东, 麦麦提艾则孜·穆合塔尔, 刘艳全, 迪力达尔克孜·吾拉木. 新疆伽师县甜瓜病毒病种类鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1793-1802. |
| [9] | 刁倩楠, 曹燕燕, 陈幼源, 张永平. 甜瓜新品种‘甜蜜20’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1385-1386. |
| [10] | 张慧君, 袁于舒, 张岩, 吴啟菠, 戴祖云. 甜瓜新品种‘淮甜1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 689-690. |
| [11] | 何亚芳, 包慧芳, 王宁, 詹发强, 张学军, 史应武, 杨蓉, 侯新强, 龙宣杞. 甜瓜镰刀菌果腐病菌拮抗菌筛选及其拮抗性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(10): 2257-2270. |
| [12] | 田红梅, 刘 娟, 张长坤, 陶 珍, 张 建, 王朋成, . 甜瓜砧木用南瓜新品种‘皖砧6号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 127-128. |
| [13] | 胡建斌, 袁升凯, 马 强, 张宝金, 孙中伟, 李 琼, 何颖悦, 刘小云, 杨路明, 朱华玉, 马志伟, 孙守如, 马长生, . 耐低温甜瓜新品种‘豫甜蜜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 163-164. |
| [14] | 蔚玉红, 卢小露, 黄 昀, 马英华, 樊静华, 田甲玺. 网纹甜瓜新品种‘华蜜303’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 165-166. |
| [15] | 康利允, 赵卫星, 高宁宁, 李晓慧, 常高正, 梁 慎, 徐小利, 李海伦, 王慧颖. 网纹甜瓜新品种‘兴隆蜜6号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 167-168. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司