
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 2532-2544.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0811
苏秀敏1,*( ), 王佼1, 韩文清1, 李鹏2, 王秋兰1, 李万星1
), 王佼1, 韩文清1, 李鹏2, 王秋兰1, 李万星1
收稿日期:2024-12-02
修回日期:2025-06-05
出版日期:2025-09-25
发布日期:2025-09-24
通讯作者:
基金资助:
SU Xiumin1,*( ), WANG Jiao1, HAN Wenqing1, LI Peng2, WANG Qiulan1, LI Wanxing1
), WANG Jiao1, HAN Wenqing1, LI Peng2, WANG Qiulan1, LI Wanxing1
Received:2024-12-02
Revised:2025-06-05
Published:2025-09-25
Online:2025-09-24
摘要:
以山西省长治市壶关县番茄枯萎病茎秆处样品为试验材料,采用组织分离培养法对该病病原进行分离且培养,泡根接种法测定分离病原菌的致病性。通过常规形态学、ITS序列分析法鉴定该番茄枯萎病病原菌的种类,并对其生物学特性进行研究。同时,从番茄西葫芦轮作两轮后种植西葫芦的土壤中分离到哈茨木霉菌(Trichoderma harzianum)M408,采用平板对峙法测定哈茨木霉M408菌丝及无菌发酵液对该番茄枯萎病原菌的生防能力。经鉴定,山西省长治市壶关县番茄枯萎病的病原菌为层出镰刀菌(Fusarium proliferatum),命名为K11。其最适生长温度28 ℃,最适pH 6.0,24 h全光照下生长速率最快,可利用多种碳源生长,其中碳源为蔗糖时菌丝生长速率最快。用菌丝平板对峙培养法测定,第7天时,菌株哈茨木霉M408对K11菌丝的抑菌率为68.38%,其无菌发酵液对K11菌丝的抑菌率为93.17%。说明M408对K11具有较好的抑制作用,生防机制可能为竞争作用。菌株哈茨木霉M408具有开发成番茄枯萎病抑菌剂的能力。
苏秀敏, 王佼, 韩文清, 李鹏, 王秋兰, 李万星. 山西长治番茄枯萎病病原鉴定及其拮抗菌鉴选[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2532-2544.
SU Xiumin, WANG Jiao, HAN Wenqing, LI Peng, WANG Qiulan, LI Wanxing. Isolation,Biological Characteristics of the Pathogen Causing Fusarium Wilt on Tomato and Antagonistic Fungus Screening[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(9): 2532-2544.

图1 田间症状及K11菌丝形态 A:初步分离的菌落形态;B:纯化后的菌落形态;C:番茄枯萎病茎部剖开图;D:番茄枯萎病后期田间症状
Fig. 1 Symptoms of Fusarium and colony morphology A:Colony morphology of primary isolates;B:Colony morphology after purification;C:Dissection section symptom of stem;D:Symptoms at the later period of infection

图2 孢子形态及PDA培养基上K11菌落形态 A:孢子形态;B,C:PDA培养基上K11菌落形态
Fig. 2 Microconidia and colony morphology on PDA medium A:Macroconidia;B,C:Colony morphology on PDA medium
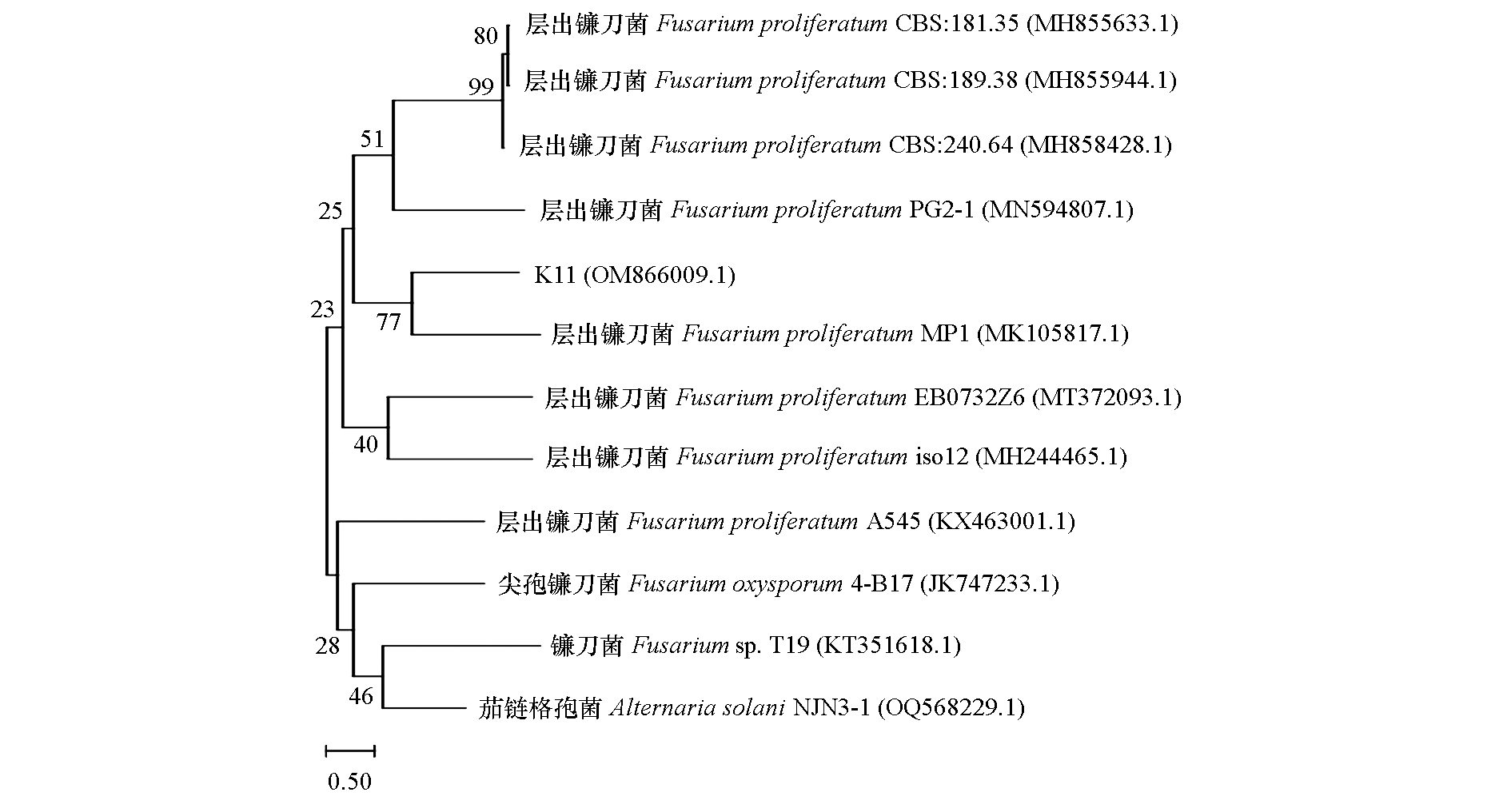
图4 基于 ITS 序列构建的菌株K11系统发育树 系统发育树各分支点上的数字代表bootstrap值;标尺代表进化距离
Fig. 4 The phylogenetic tree of the strain K11 based on ITS sequence The number on each branch point represents the bootstrap;The scale bar represents the evolutionary distance

图5 不同生长条件下 K11菌株的菌落直径(第7天) 不同小写字母表示0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 5 Colony diameters of the K11 strain under different growth conditions(the 7th day) Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at 0.05 level

图6 菌株哈茨木霉M408菌丝与菌株层出镰刀菌K11菌丝对峙培养的菌落形态(1 ~ 7 d)
Fig. 6 The colony morphology confrontation cultured Trichoderma harzianum strain M408 and Fusarium proliferatum strain K11(1-7 d)

图7 菌株哈茨木霉M408无菌发酵液与层出镰刀菌K11菌株对峙培养的菌落形态(第7天)
Fig. 7 The colony morphology confrontation cultured of Trichoderma harzianum strain M408 and Fusarium proliferatum strain K11(the 7th day)
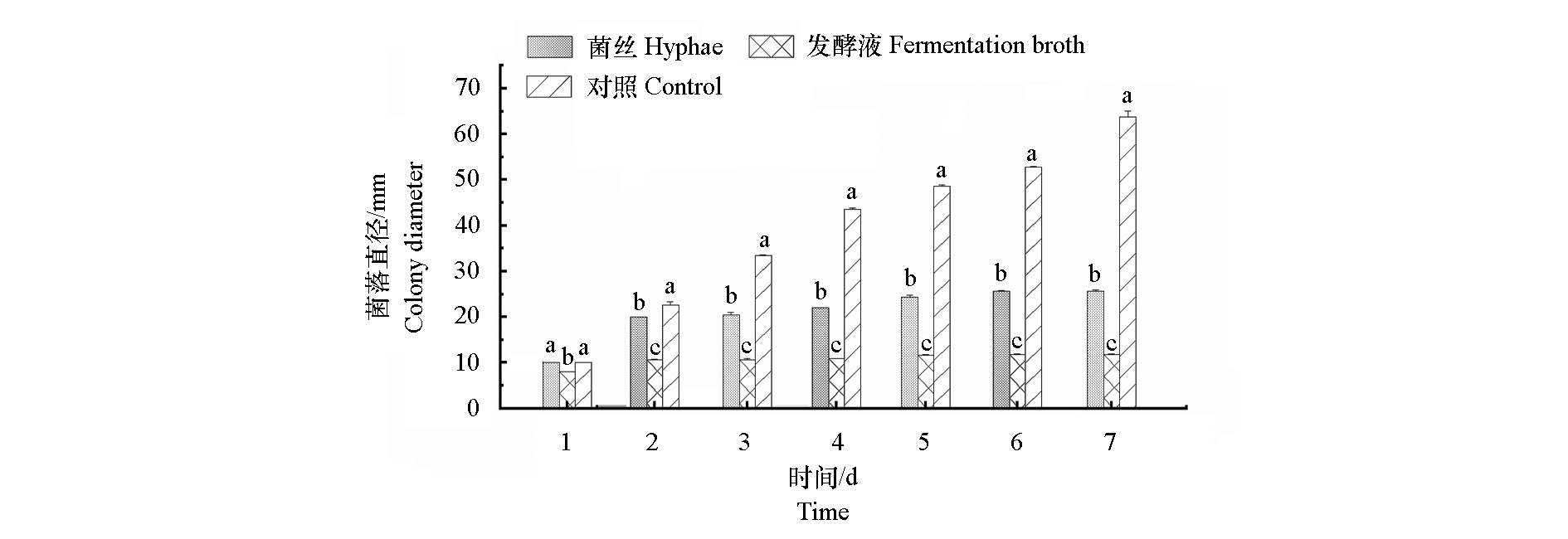
图8 哈茨木霉M408菌丝及无菌发酵液与层出镰刀菌K11菌丝峙培养的k11菌落直径(1 ~ 7 d) 不同小写字母表示0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 8 The colony diameters of K11 confrontation cultured Trichoderma harzianum M408 and Fusarium proliferatum strain K11(1-7 d) Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at 0.05 level
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
陈云云, 李慧霞, 张海英, 徐生军, 刘永刚. 2021. 萎缩芽孢杆菌 MQ19ST15 鉴定及对甘蓝枯萎病的盆栽防效. 植物保护, 47 (5):64-71.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
方中达. 1998. 植病研究方法. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社:63.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
葛晓颖, 孙志刚, 李涛, 欧阳竹. 2016. 设施番茄连作障碍与土壤芽孢杆菌和假单胞菌及微生物群落的关系分析. 农业环境科学学报, 35 (3):514-523.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
郭珺, 武爱莲, 闫敏, 李娓, 池秀蓉, 丁玉川, 焦晓燕. 2016. 芽孢杆菌Pb-4菌株鉴定及其抑菌活性的研究. 华北农学报, 31 (2):224-230.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2016.02.036 |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.11686/cyxb20150321 |
|
李兴龙, 李彦忠. 2015. 土传病害生物防治研究进展. 草业学报, 24 (3):204-212.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb20150321 |
|
| [9] |
|
|
梁雪杰, 张婷婷, 乔俊卿, 杜艳, 刘邮洲. 2014. 番茄土传病害拮抗菌的筛选、评价及鉴定. 西南农业学报, 27 (3):1096-1103.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
孟臻, 张伟萍, 王莹, 李龙, 姬小雪, 董贝, 乔康. 2022. 番茄枯萎病菌 RT-PCR 检测技术的建立与应用,园艺学报, 49 (11):2479-2488.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
沈海斌, 王前程, 陈捷, 吴珏, 杨学东, 朱为民, 张迎迎. 2023. 三株木霉对番茄枯萎病的防治效果和机理研究. 植物生理学报, 59 (5):965-976.
|
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
|
谭娇娇, 王喜刚, 郭成瑾, 张丽荣, 沈瑞清. 2021. 哈茨木霉M-17固体发酵及发酵产物浸提液对镰刀菌的抑制作用. 西北农业学报, 30 (11):1741-1747.
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
田淼, 彭玉飞, 吕红, 秦楠, 任璐, 殷辉, 赵晓军. 2023. 非洲哈茨木霉LMNS-M9 的鉴定、生物学特性及其对藜麦的促生作用. 微生物学通报, 50 (9):3848-3865.
|
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
王恩泽. 2020. 番茄枯萎病拮抗菌的筛选及其抑菌效果研究[硕士论文]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学.
|
|
| [22] |
|
|
王飞, 杨瑾, 李雪梦, 赵莹, 刘玉霞, 秦艳红, 高素霞, 文艺, 鲁传涛. 2024. 牛膝枯萎病病原鉴定、生物学特性及防治药剂筛选. 植物病理学报, 54 (1):49-58.
doi: 10.13926/j.cnki.apps.001602 |
|
| [23] |
|
|
王桂清, 曾路, 马迪, 赵鹏. 2018. 我国近10年植物致病真菌生物学特性研究综述. 江苏农业科学, 46 (19):1-5.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
王璐瑶. 2017. 生防解淀粉芽胞杆菌B1619生物学特性、诱导抗病性和田间应用技术研究[硕士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
王前程, 张迎迎, 戴陶宇, 尤佳琪, 郭世荣, 朱为民. 2022. 拟康宁木霉T-51菌株对番茄枯萎病的生物防治及其机理研究. 西北植物学报, 42 (6):974-982.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
王全华, 李景富, 李永镐, 王富. 1996. 黑龙江省番茄枯萎病菌生理小种鉴定. 东北农业大学学报, 27 (4):354-357.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
王永强. 2020. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌SDTB009的分离鉴定及其对番茄枯萎病的防治研究[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
肖辉, 程文娟, 张鹏, 张慧, 焦汝民, 王立艳, 赵杰, 潘洁. 2021. 木醋液与杀菌剂复配对番茄枯萎病和灰霉病的防治效果. 江苏农业科学, 49 (1):82-87.
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
徐艳辉, 李烨, 许向阳. 2008. 番茄枯萎病的研究进展. 东北农业大学学报, 39 (11):128-134.
|
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
|
张斌, 乔俊卿, 梁雪杰, 刘邮洲, 陈志谊. 2015. 番茄枯萎病菌和青枯病菌拮抗细菌的评价. 植物保护学报, 42 (3):353-361.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
张亮, 盛浩, 袁红, 赵兰凤, 李华兴. 2017. 荧光假单胞菌PEF-5#18防控番茄枯萎病的定殖机理. 中国生物防治学报, 33 (5):658-666.
doi: 10.16409/j.cnki.2095-039x.2017.05.012 |
|
| [33] |
|
|
张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 2024. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析. 园艺学报, 51 (6):1413-1425.
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
周东兴, 王恩泽, 刘多, 金聪敏, 李欣, 姜姗, 白皓天. 2020. 番茄枯萎病生防细菌的筛选及对植株防御酶活性的影响. 生态学杂志, 39 (5):1753-1760.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
周晗. 2018. 芽孢杆菌sigX因子防治番茄青枯病和香蕉枯萎病的研究[硕士论文]. 广州: 华南农业大学.
|
| [1] | 范惠冬, 郑士金, 田 松, 郑建超. 番茄新品种‘吉粉7号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 109-110. |
| [2] | 张立微, 戴忠仁, 陈青奇, 雷 娜, 胡海江, 门万杰. 番茄新品种‘哈研中粉果1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 111-112. |
| [3] | 熊自立, 史建磊, 陈勇兵, 张海利, 苏世闻, 宰文珊, 叶曙光. 设施番茄新品种‘瓯秀202’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 113-114. |
| [4] | 王雅慧, 张雨晴, 张榕蓉, 刘佩卓, 梁毅, 周建华, 熊爱生. 胡萝卜番茄红素ε-环化酶基因DcLCYE启动子活性分析及互作因子筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2317-2328. |
| [5] | 陈舒婷, 吴幕绵, 李涛, 黎振兴, 麦培婷, 孙保娟, 郝彦伟, 宫超. 有效微生物群落对番茄产量及根际土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2477-2490. |
| [6] | 张胜男, 逄玉万, 黄建凤, 武美华, 吴昭云, 张木, 李苹, 付弘婷, 吴永沛. 香蕉根系分泌物对枯萎病菌侵染的响应效应[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2519-2531. |
| [7] | 宋琦, 宋晓雅, 焦永鑫, 毛子玥, 吴小刚, 张清霞. 防御假单胞菌FD6对番茄灰霉病菌的抑菌活性及其培养条件优化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2545-2553. |
| [8] | 周明, 韩晨旭, 苑国良, 范小青, 艾鹏飞, 李常保. 番茄雄性不育及育种应用研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2081-2098. |
| [9] | 李丹丹, 葛平飞, 李方曼, 杨旸, 徐浩博, 熊春晖, 张余洋. 番茄风味调控基因及其在品质改良中的应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2099-2113. |
| [10] | 关思慧, 刘晨旭, 周国治, 万红建, 阮美颖, 王荣青, 叶青静, 李志邈, 姚祝平, 程远. 栽培番茄果实挥发性风味物质研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2114-2132. |
| [11] | 陈静, 薛婉钰, 张晓将, 张玲玲, 张婷婷, 陈书霞. 瓜类蔬菜枯萎病抗性遗传及调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2187-2207. |
| [12] | 张瑞益, 封文佳, 李奔奔, 宋怡颖, 韦明月, 柴乖强, 霍彦波. 番茄表皮蜡质合成相关基因SlCER1-7的克隆与功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(7): 1733-1744. |
| [13] | 任潇妍, 贾仡伟, 王潞伟, 李甜爽, 刘海霞, 姚艳平, 王春伟, 王美琴. 番茄灰霉病菌对咪鲜胺的抗性检测及风险评估[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(7): 1915-1925. |
| [14] | 方俊仪, 巫伟峰, 陆乔, 凌宏清, 孔丹宇. 番茄抗青枯病种质TK083的筛选和鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1477-1487. |
| [15] | 萧志浩, 郑涵锴, 张曼楠, 唐怀千, 王嘉颖, 张余洋, 张俊红, 叶志彪, 叶杰. 非生物胁迫下钾对番茄苗期生长发育的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1599-1618. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司